Crossing Barriers: PEGylated Gold Nanoparticles as Promising Delivery Vehicles for siRNA Delivery in Alzheimer’s Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. AuNPs and siRNA
2.2. Cell Lines
2.3. Cytotoxicity
2.4. Genotoxicity
2.5. Cellular Uptake
2.6. Reactive Oxygen Species Formation
2.7. Mitochondrial Membrane Potential
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
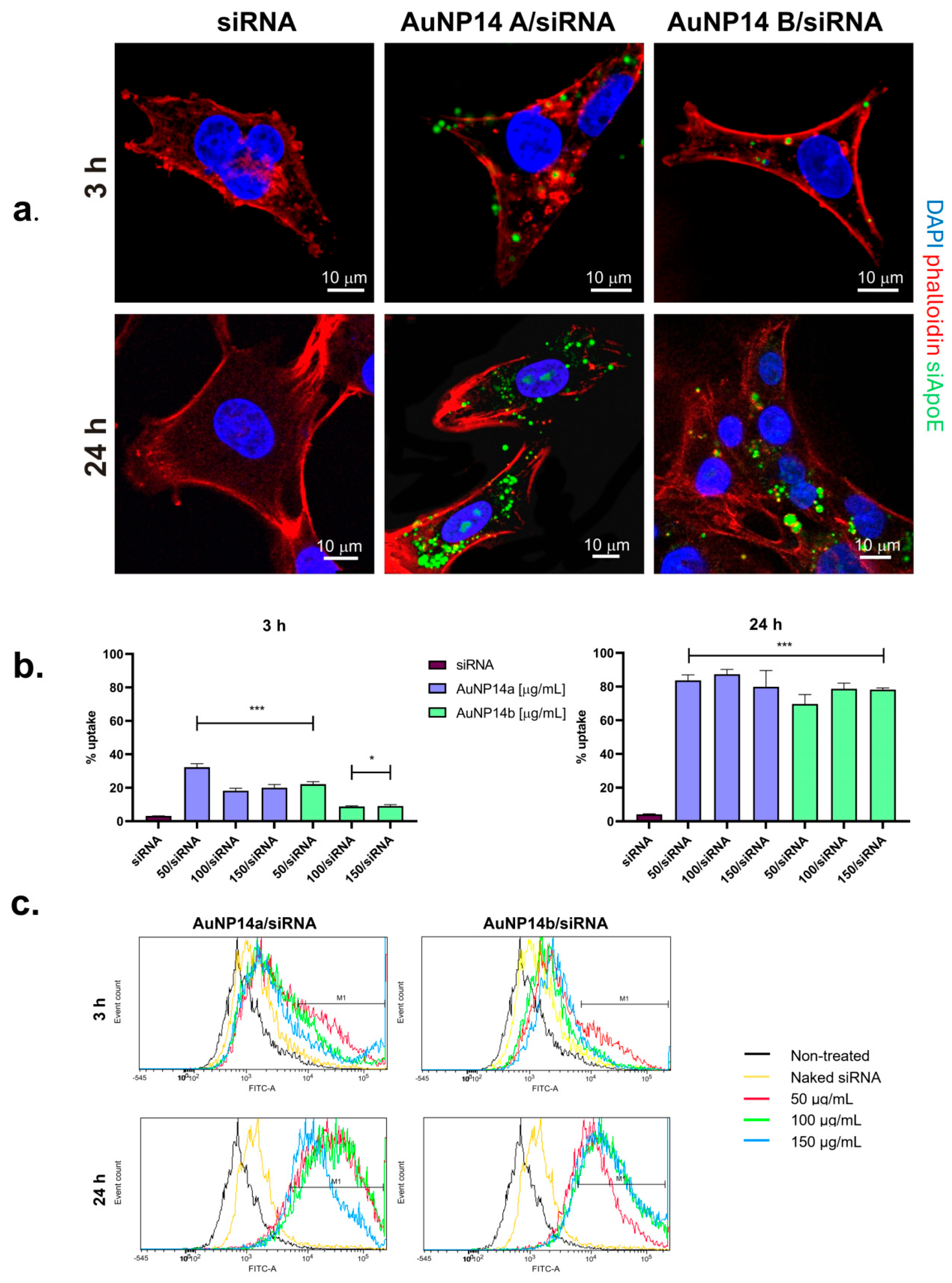
3.1. Complex Cellular Uptake
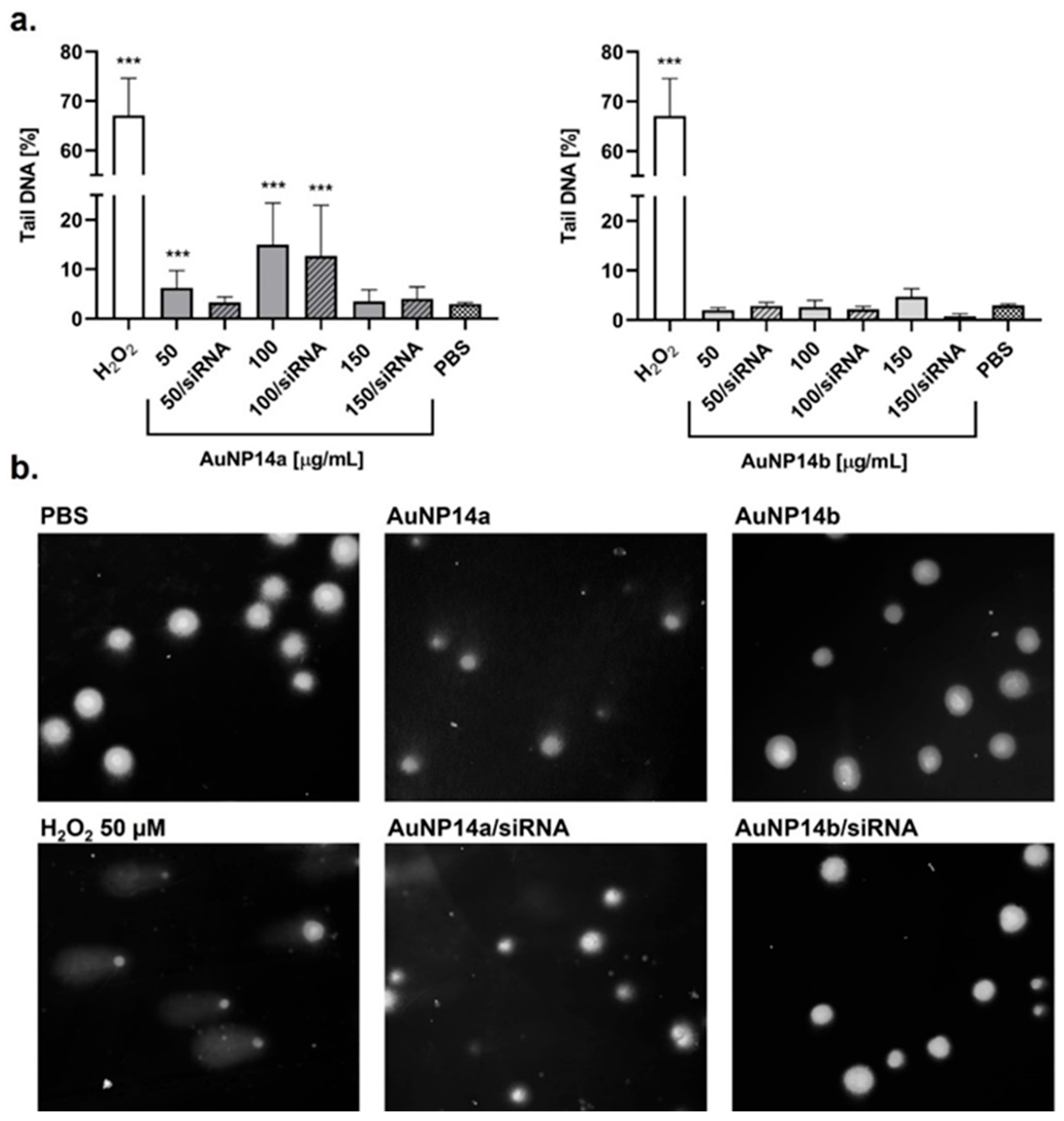
3.2. Genotoxicity
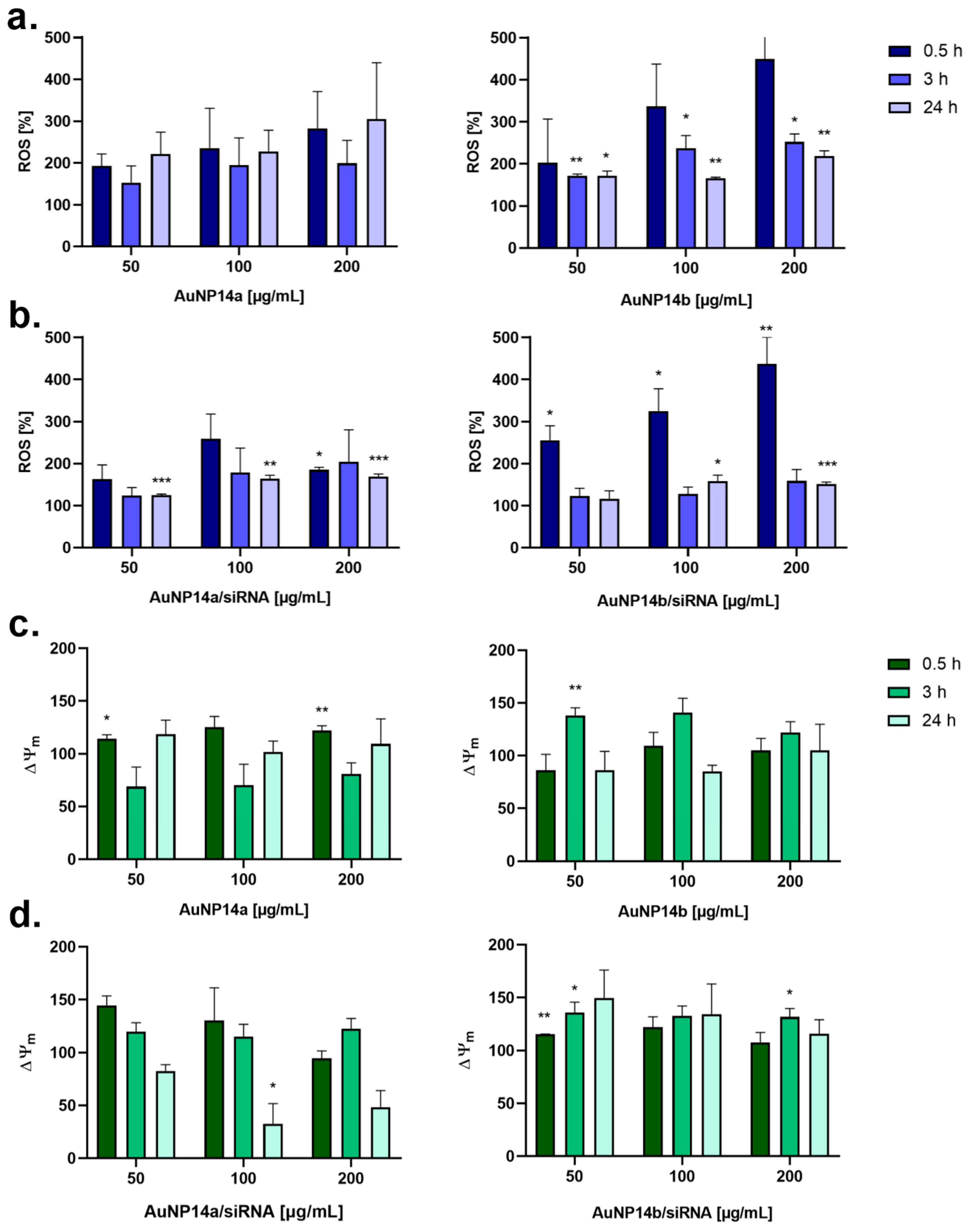
3.3. Reactive Oxygen Species and Mitochondrial Membranes Potential Changes
3.4. AuNPs Cytotoxicity Towards Human Brain Vascular Pericytes and Astrocytes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AuNPs | Gold nanoparticles |
| BACE1 | Beta-secretase 1 |
| BBB | Blood–brain barrier |
| BCB | Blood–cerebrospinal fluid barrier |
| DAPI | 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| GalNAc | N-acetylgalactosamine |
| HA | Human astrocytes |
| HBVP | Human brain vascular pericytes |
| JC-1 | 5,5′,6,6′-tetrachloro-1,1′,3,3′-tetraethylbenzimidazolylcarbocyanine iodide |
| NMDA | N-methyl-D-aspartate |
| PEG | Polyethylene glycol |
| ROCK2 | Rho associated coiled-coil containing protein kinase 2 |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
References
- Steinmetz, J.D.; Seeher, K.M.; Schiess, N.; Nichols, E.; Cao, B.; Servili, C.; Cavallera, V.; Cousin, E.; Hagins, H.; E Moberg, M.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of disorders affecting the nervous system, 1990–2021: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Neurol. 2024, 23, 344–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillama Barroso, G.; Narayan, M.; Alvarado, M.; Armendariz, I.; Bernal, J.; Carabaza, X.; Chavez, S.; Cruz, P.; Escalante, V.; Viel, S.; et al. Nanocarriers as Potential Drug Delivery Candidates for Overcoming the Blood-Brain Barrier: Challenges and Possibilities. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 12583–12595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattahi, F.; Asadi, M.R.; Abed, S.; Kouchakali, G.; Kazemi, M.; Mansoori Derakhshan, S.; Shekari Khaniani, M. Blood-based microRNAs as the potential biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease: Evidence from a systematic review. Metab. Brain Dis. 2024, 40, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacabelos, R.; Naidoo, V.; Martínez-Iglesias, O.; Corzo, L.; Cacabelos, N.; Pego, R.; Carril, J.C. Personalized Management and Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Life 2022, 12, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheltens, P.; De Strooper, B.; Kivipelto, M.; Holstege, H.; Chételat, G.; Teunissen, C.E.; Cummings, J.; van der Flier, W.M. Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 2021, 397, 1577–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, Y.; Zhao, N.; Caulfield, T.R.; Liu, C.C.; Bu, G. Apolipoprotein E and Alzheimer disease: Pathobiology and targeting strategies. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 501–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Zhang, H.; Lu, Q.; Tian, L.; Yao, S.; Lai, F.; Liang, Y.; Liu, C.; Lu, Y.; Ren, W.; et al. Nanocarrier-mediated siRNA delivery: A new approach for the treatment of traumatic brain injury–related Alzheimer’s disease. Neural Regen. Res. 2025, 20, 2538–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, A.; Barreto, G.; Sathyapalan, T.; Sahebkar, A. Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.net siRNA Therapeutics: Future Promise for Neurodegenerative Diseases. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2021, 19, 1896–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez-Jugo, C.; Masoumi, S.; Chan, P.P.Y.; Friend, J.; Yeo, L. Nebulization of siRNA for inhalation therapy based on a microfluidic surface acoustic wave platform. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2022, 88, 106088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali Zaidi, S.S.; Fatima, F.; Ali Zaidi, S.A.; Zhou, D.; Deng, W.; Liu, S. Engineering siRNA therapeutics: Challenges and strategies. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Carrión, M.D.; Posadas, I.; Ceña, V. Nanoparticles and siRNA: A new era in therapeutics? Pharmacol. Res. 2024, 201, 107102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, K. RNA-based therapeutics for neurological diseases. RNA Biol. 2022, 19, 176–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graczyk, A.; Pawlowska, R.; Chworos, A. Gold Nanoparticles as Carriers for Functional RNA Nanostructures. Bioconjug. Chem. 2021, 32, 1667–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moazzam, M.; Zhang, M.; Hussain, A.; Yu, X.; Huang, J.; Huang, Y. The landscape of nanoparticle-based siRNA delivery and therapeutic development. Mol. Ther. 2024, 32, 284–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrios-Gumiel, A.; Sánchez-Nieves, J.; Pedziwiatr-Werbicka, E.; Abashkin, V.; Shcharbina, N.; Shcharbin, D.; Glińska, S.; Ciepluch, K.; Kuc-Ciepluch, D.; de la Mata, F.J.; et al. Effect of PEGylation on the biological properties of cationic carbosilane dendronized gold nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 573, 118867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okła, E.; Białecki, P.; Kędzierska, M.; Pędziwiatr-Werbicka, E.; Miłowska, K.; Takvor, S.; Gómez, R.; de la Mata, F.J.; Bryszewska, M.; Ionov, M. Pegylated Gold Nanoparticles Conjugated with siRNA: Complexes Formation and Cytotoxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okła, E.; Michlewska, S.; Buczkowski, A.; Zawadzki, S.; Miłowska, K.; Sánchez-Nieves, J.; Gómez, R.; de la Mata, F.J.; Bryszewska, M.; Blasiak, J.; et al. Pegylated gold nanoparticles interact with lipid bilayer and human serum albumin and transferrin. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 24408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almutary, A.G.; Chauhan, P.; Baldaniya, L.; Menon, S.V.; Kumar, M.R.; Chaturvedi, B.; Sharma, N.; Chauhan, A.S.; Abomughaid, M.M.; Kumar Jha, N.; et al. Overcoming challenges in the design of drug delivery systems targeting the central nervous system. Nanomedicine 2024, 20, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowicz-Piasecka, M.; Darłak, P.; Markiewicz, A.; Sikora, J.; Adla, S.K.; Bagina, S.; Huttunen, K.M. Current approaches to facilitate improved drug delivery to the central nervous system. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2022, 181, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taschauer, A.; Polzer, W.; Pöschl, S.; Metz, S.; Tepe, N.; Decker, S.; Cyran, N.; Scholda, J.; Maier, J.; Bloß, H.; et al. Combined Chemisorption and Complexation Generate siRNA Nanocarriers with Biophysics Optimized for Efficient Gene Knockdown and Air–Blood Barrier Crossing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 30095–30111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumthekar, P.; Ko, C.H.; Paunesku, T.; Dixit, K.; Sonabend, A.M.; Bloch, O.; Tate, M.; Schwartz, M.; Zuckerman, L.; Lezon, R.; et al. A first-in-human phase 0 clinical study of RNA interference-based Spherical Nucleic Acids in patients with recurrent Glioblastoma. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabb3945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artiga, Á.; Serrano-Sevilla, I.; De Matteis, L.; Mitchell, S.G.; De La Fuente, J.M. Current status and future perspectives of gold nanoparticle vectors for siRNA delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 876–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-León, E.; Rodríguez-Vázquez, B.E.; Martínez-Higuera, A.; Rodríguez-Beas, C.; Larios-Rodríguez, E.; Navarro, R.E.; López-Esparza, R.; Iñiguez-Palomares, R.A. Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles Using Mimosa tenuiflora Extract, Assessments of Cytotoxicity, Cellular Uptake, and Catalysis. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Yamani, N.; Rundén-Pran, E.; Collins, A.R.; Longhin, E.M.; Elje, E.; Hoet, P.; Vrček, I.V.; Doak, S.H.; Fessard, V.; Dusinska, M. The miniaturized enzyme-modified comet assay for genotoxicity testing of nanomaterials. Front. Toxicol. 2022, 4, 986318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, S.; Faria, H.; Soares, M.E.; Duarte, J.A.; Soares, L.; Pereira, E.; Costa-Pereira, C.; Teixeira, J.P.; de Lourdes Bastos, M.; Carmo, H. Influence of the surface coating on the cytotoxicity, genotoxicity and uptake of gold nanoparticles in human HepG2 cells. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2013, 33, 1111–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávalos, A.; Haza, A.I.; Mateo, D.; Morales, P. In vitro and in vivo genotoxicity assessment of gold nanoparticles of different sizes by comet and SMART assays. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 120, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Feng, Q.; Xiao, K. The effect of particle size on the genotoxicity of gold nanoparticles. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2017, 105, 710–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebedová, J.; Hedberg, Y.S.; Odnevall Wallinder, I.; Karlsson, H.L. Size-dependent genotoxicity of silver, gold and platinum nanoparticles studied using the mini-gel comet assay and micronucleus scoring with flow cytometry. Mutagenesis 2018, 33, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, R.K.; Badiye, A.; Vajpayee, K.; Kapoor, N. Genotoxic Potential of Nanoparticles: Structural and Functional Modifications in DNA. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 728250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, C.-Y.; Tsai, S.-W.; Niu, H.; Chen, F.-H.; Hwang, H.-C.; Chao, T.-C.; Hsiao, I.-T.; Liaw, J.-W. Gold-Nanoparticles-Enhanced Production of Reactive Oxygen Species in Cells at Spread-Out Bragg Peak under Proton Beam Radiation. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 17922–17931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcicek, I.; Aysit, N.; Cakici, C.; Aydeger, A. The effects of surface functionality and size of gold nanoparticles on neuronal toxicity, apoptosis, ROS production and cellular/suborgan biodistribution. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 128, 112308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juan, C.A.; de la Lastra, J.M.P.; Plou, F.J.; Pérez-Lebeña, E. The Chemistry of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Revisited: Outlining Their Role in Biological Macromolecules (DNA, Lipids and Proteins) and Induced Pathologies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shcherbakov, V.; Denisov, S.A.; Mostafavi, M. A mechanistic study of gold nanoparticles catalysis of O2 reduction by ascorbate and hydroethidine, investigating reactive oxygen species reactivity. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 8557–8563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Wang, D.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, B.; Tong, Z.; Tian, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y. Nanozyme-based inulin@nanogold for adhesive and antibacterial agent with enhanced biosafety. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 262, 129207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, S.; Hirsch, C.; Rippl, A.; Bohmer, N.; Kaiser, J.-P.; Diener, L.; Wichser, A.; Bürkle, A.; Wick, P. Transient DNA damage following exposure to gold nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 15723–15735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meesaragandla, B.; Komaragiri, Y.; Schlüter, R.; Otto, O.; Delcea, M. The impact of cell culture media on the interaction of biopolymer-functionalized gold nanoparticles with cells: Mechanical and toxicological properties. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knipp, G.T.; E Lubin, K. Design of experiment based optimization of an in vitro direct contact triculture blood brain barrier model for permeability screening. Pharm. Pharmacol. Int. J. 2021, 9, 143–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, N.L.; England, T.J.; O’sUllivan, S.E. A Novel Transwell Blood Brain Barrier Model Using Primary Human Cells. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kus-Liśkiewicz, M.; Fickers, P.; Ben Tahar, I. Biocompatibility and cytotoxicity of gold nanoparticles: Recent advances in methodologies and regulations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gran, E.R.; Bertorelle, F.; Fakhouri, H.; Antoine, R.; Bakulić, M.P.; Maršić, Ž.S.; Bonačić-Koutecký, V.; Blain, M.; Antel, J.; Maysinger, D. Size and ligand effects of gold nanoclusters in alteration of organellar state and translocation of transcription factors in human primary astrocytes. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 3173–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Huang, J.; Feng, Q.; Chen, X.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, T.; Xiao, S.; Li, H.; Zhong, Z.; et al. Size- and cell type-dependent cellular uptake, cytotoxicity and in vivo distribution of gold nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 6957–6970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rekatsina, M.; Paladini, A.; Piroli, A.; Zis, P.; Pergolizzi, J.V.; Varrassi, G. Pathophysiology and Therapeutic Perspectives of Oxidative Stress and Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Narrative Review. Adv. Ther. 2020, 37, 113–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.-M.; Cheng, T.-L.; Roffler, S.R. Polyethylene Glycol Immunogenicity: Theoretical, Clinical, and Practical Aspects of Anti-Polyethylene Glycol Antibodies. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 14022–14048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Kiessling, F.; Lammers, T.; Pallares, R.M. Clinical translation of gold nanoparticles. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2023, 13, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| AuNP | Solubility | Dendron/PEG Molar Ratio | 1 ZP [mV] | 2 dz [nm] | 3 PDI | 4 dn [nm] | 5 %L |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AuNP14a | water | 3/1 | +44.9 | 34.00 | 0.54 | 3.7 | 67.6 |
| AuNP14b | water | 1/1 | +41.1 | 23.3 | 0.298 | 2.8 | 66.6 |
| Complex | 1 siRNA [µM] | 2 AuNP [µg/mL] | 3 ZP [mV] | 4 dz [nm] | 5 PDI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AuNP14a/siRNA | 1 | 40 | +21.97 | 227.23 | 0.57 |
| AuNP14b/siRNA | 1 | 50 | +7.97 | 161.53 | 0.219 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Okła, E.; Hołota, M.; Michlewska, S.; Zawadzki, S.; Miłowska, K.; Sánchez-Nieves, J.; Gómez, R.; De la Mata, F.J.; Bryszewska, M.; Ionov, M. Crossing Barriers: PEGylated Gold Nanoparticles as Promising Delivery Vehicles for siRNA Delivery in Alzheimer’s Disease. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2108. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092108
Okła E, Hołota M, Michlewska S, Zawadzki S, Miłowska K, Sánchez-Nieves J, Gómez R, De la Mata FJ, Bryszewska M, Ionov M. Crossing Barriers: PEGylated Gold Nanoparticles as Promising Delivery Vehicles for siRNA Delivery in Alzheimer’s Disease. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(9):2108. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092108
Chicago/Turabian StyleOkła, Elżbieta, Marcin Hołota, Sylwia Michlewska, Serafin Zawadzki, Katarzyna Miłowska, Javier Sánchez-Nieves, Rafael Gómez, Francisco Javier De la Mata, Maria Bryszewska, and Maksim Ionov. 2025. "Crossing Barriers: PEGylated Gold Nanoparticles as Promising Delivery Vehicles for siRNA Delivery in Alzheimer’s Disease" Biomedicines 13, no. 9: 2108. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092108
APA StyleOkła, E., Hołota, M., Michlewska, S., Zawadzki, S., Miłowska, K., Sánchez-Nieves, J., Gómez, R., De la Mata, F. J., Bryszewska, M., & Ionov, M. (2025). Crossing Barriers: PEGylated Gold Nanoparticles as Promising Delivery Vehicles for siRNA Delivery in Alzheimer’s Disease. Biomedicines, 13(9), 2108. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092108










