Enhanced M2 Polarization of Retinal Microglia in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mice upon Autoimmune Stimulation †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Creation of STZ-Induced Diabetic Mice
2.3. EAU Induction
2.4. EAU Scoring
2.5. Flow Cytometry
2.6. Histological and Immunohistochemical Analyses
2.7. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing (scRNA-Seq)
2.7.1. Retinal Single-Cell Preparation
2.7.2. Rod Cell Depletion
2.7.3. scRNA-Seq Data Acquisition
2.7.4. scRNA-Seq Data Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
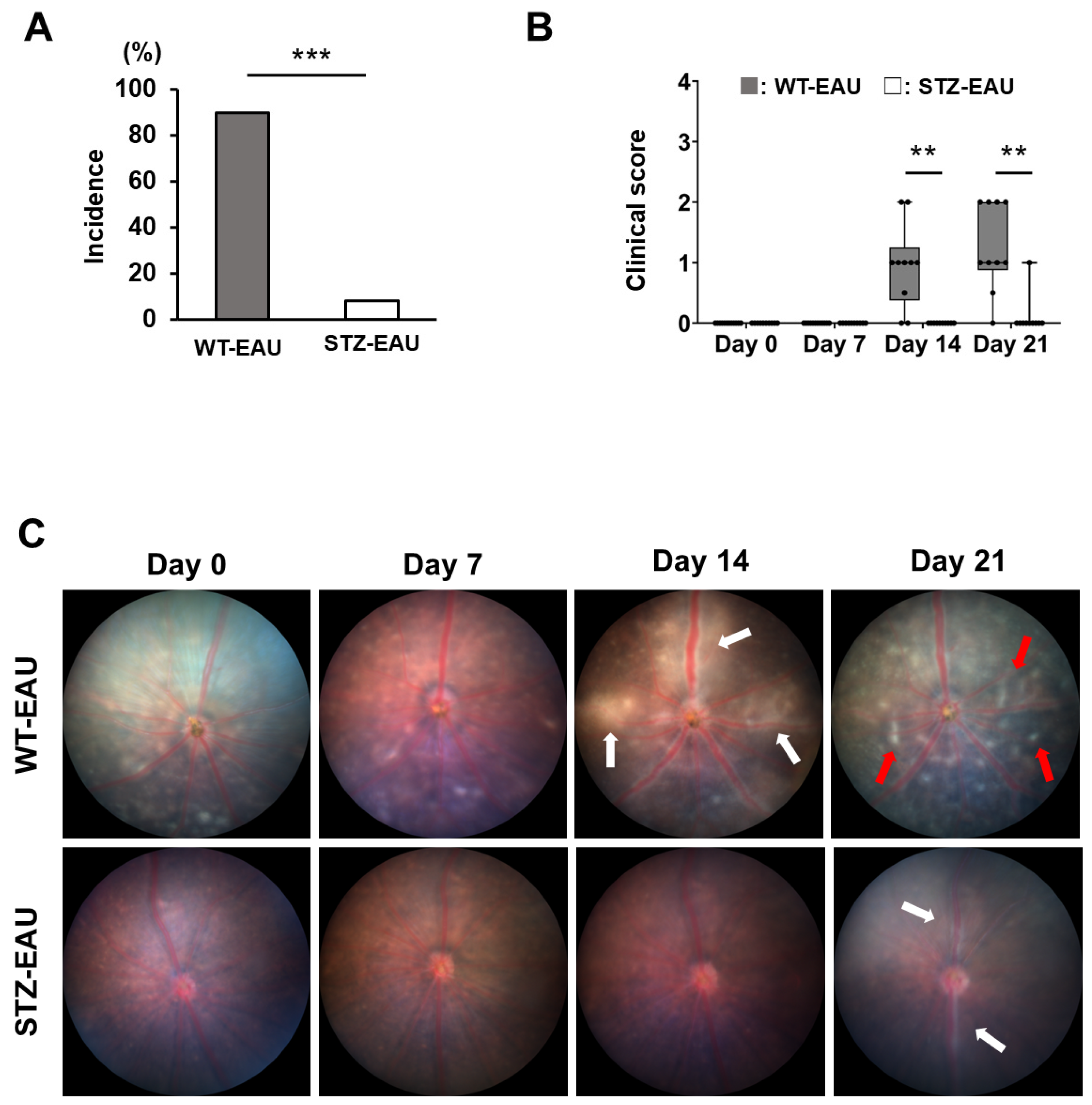
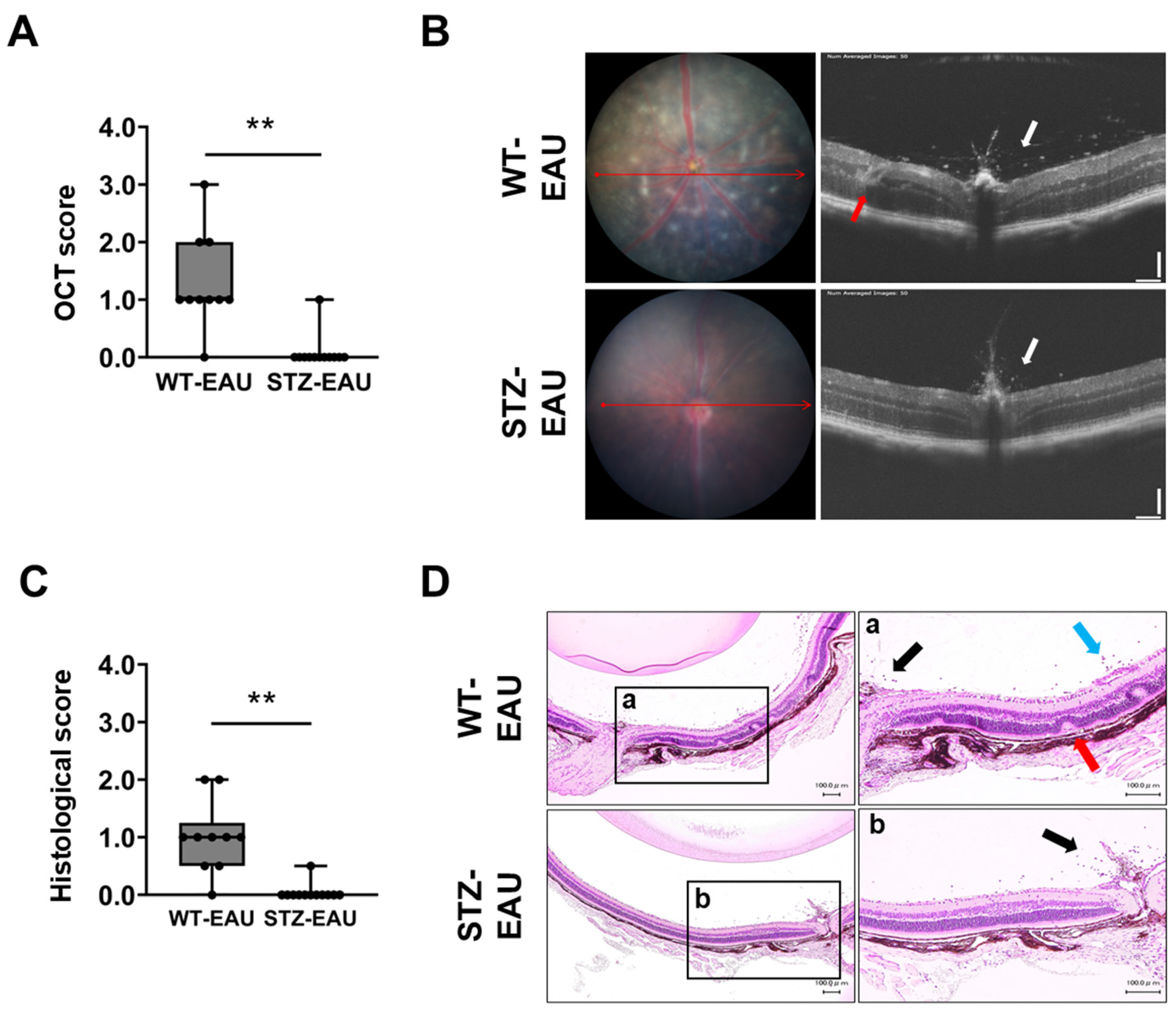
3.1. EAU Development Is Suppressed Under STZ-Induced Diabetic Conditions
3.2. Decreased Th1 Cell Proportion in Diabetic Mice
3.3. Reduction in the Number of Microglia in Retina of the STZ-Induced Diabetic Mice with Autoimmune Uveitis
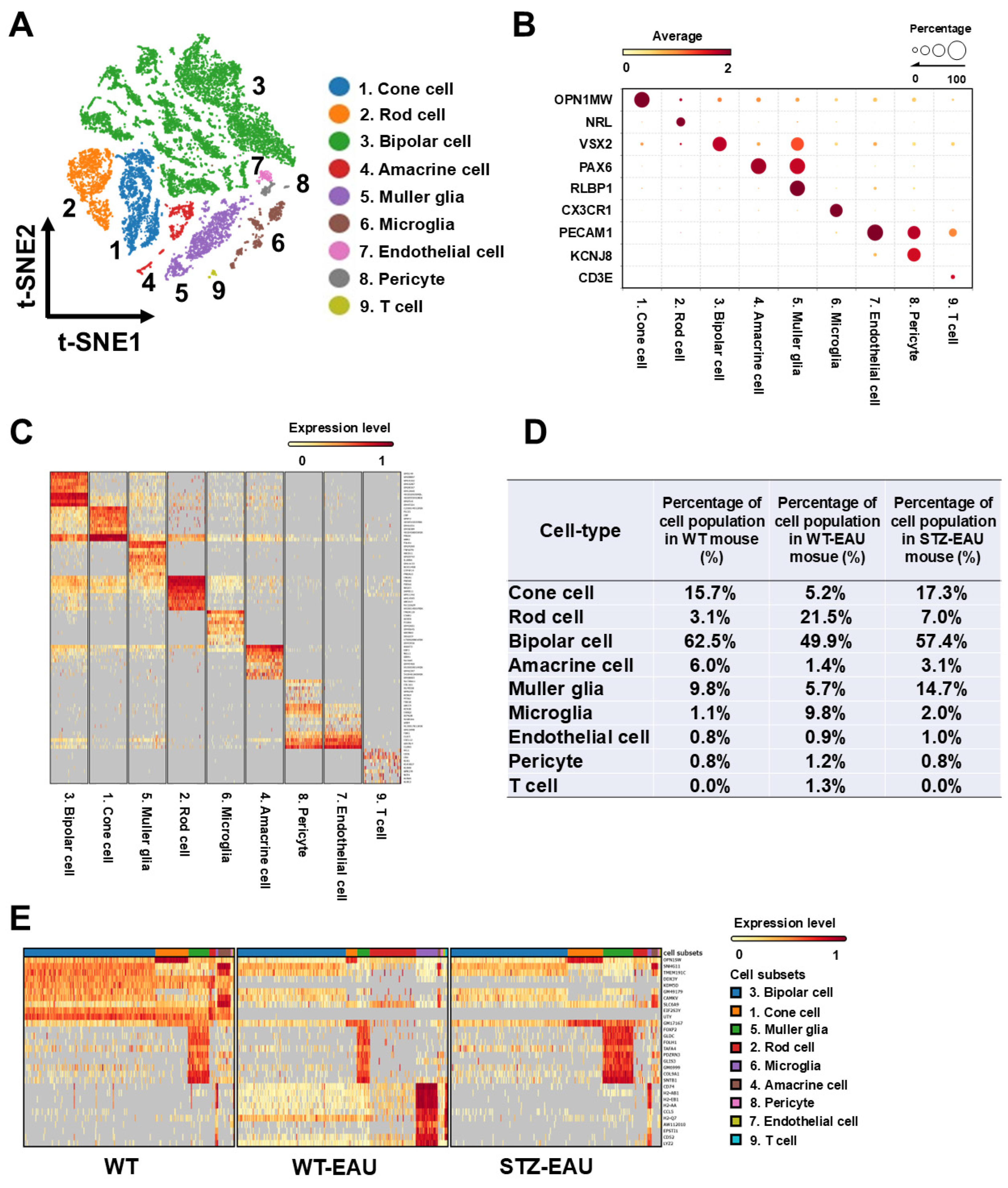
3.4. Transcriptome Atlas of Diabetic Retinal Cells in Autoimmune Uveitis
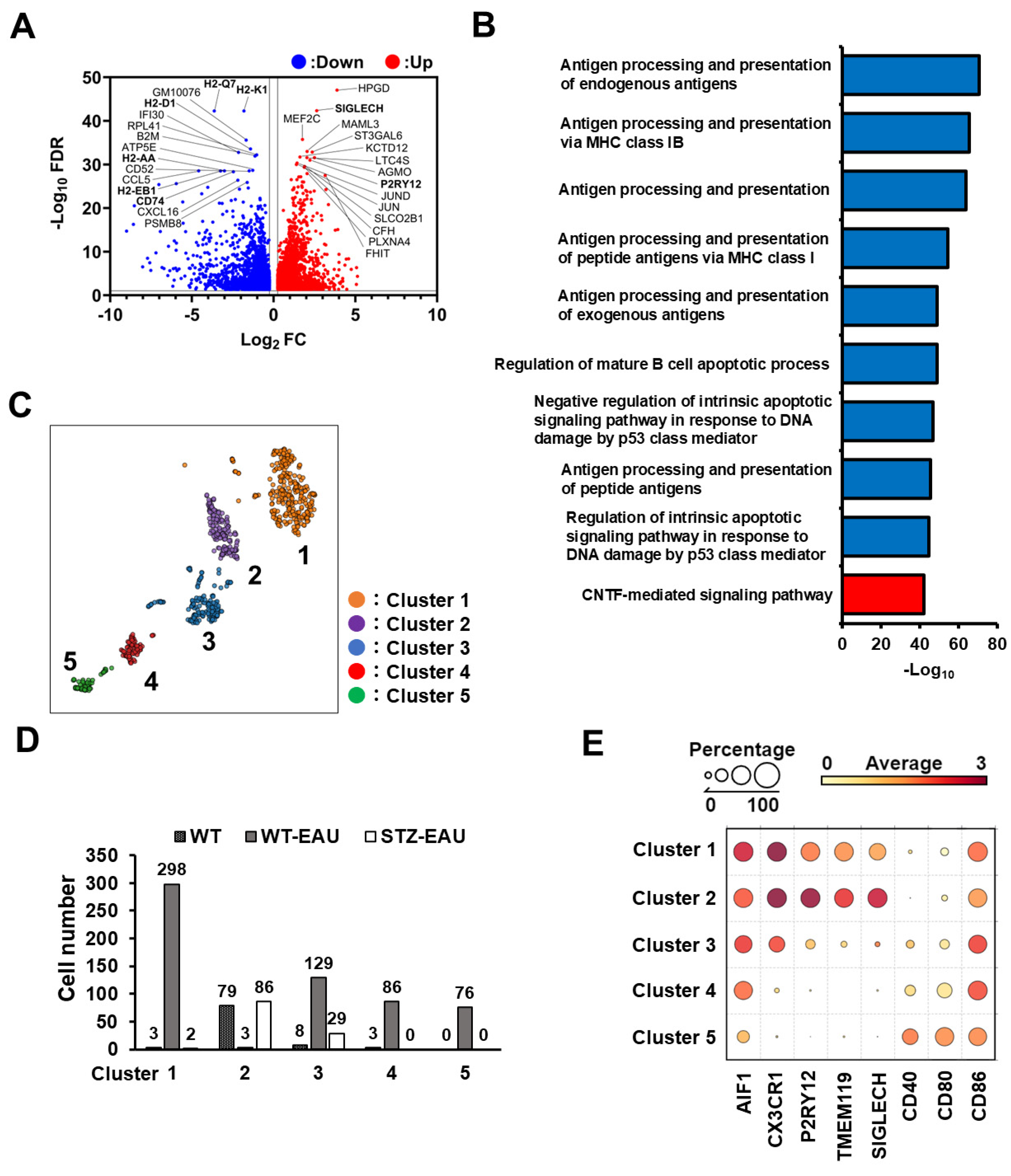
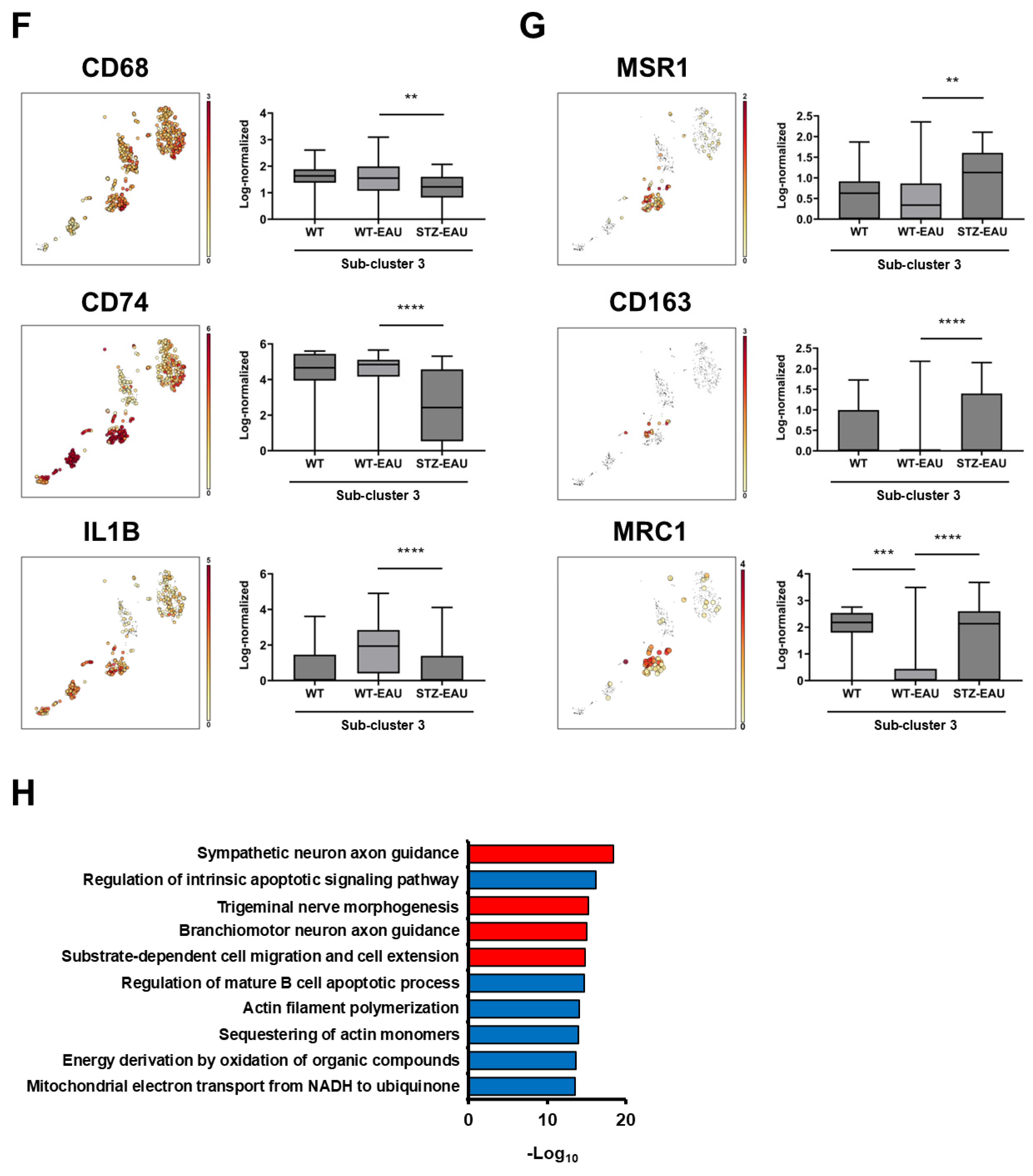
3.5. M2 Polarization of Retinal Microglia in Diabetic Mice with Autoimmune Uveitis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Kropp, M.; Golubnitschaja, O.; Mazurakova, A.; Koklesova, L.; Sargheini, N.; Vo, T.K.S.; de Clerck, E.; Polivka, J., Jr.; Potuznik, P.; Polivka, J.; et al. Diabetic retinopathy as the leading cause of blindness and early predictor of cascading complications-risks and mitigation. EPMA J. 2023, 14, 21–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altmann, C.; Schmidt, M.H.H. The Role of Microglia in Diabetic Retinopathy: Inflammation, Microvasculature Defects and Neurodegeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boss, J.D.; Singh, P.K.; Pandya, H.K.; Tosi, J.; Kim, C.; Tewari, A.; Juzych, M.S.; Abrams, G.W.; Kumar, A. Assessment of Neurotrophins and Inflammatory Mediators in Vitreous of Patients with Diabetic Retinopathy. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2017, 58, 5594–5603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semeraro, F.; Cancarini, A.; dell’Omo, R.; Rezzola, S.; Romano, M.R.; Costagliola, C. Diabetic Retinopathy: Vascular and Inflammatory Disease. J. Diabetes Res. 2015, 2015, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, M.; Sato, T.; Tanaka, A.; Muraoka, T.; Taguchi, M.; Sakurai, Y.; Karasawa, Y.; Ito, M. Elevated Levels of Cytokines Associated with Th2 and Th17 Cells in Vitreous Fluid of Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy Patients. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, M.; Sato, T.; Sakurai, Y.; Taguchi, M.; Harimoto, K.; Karasawa, Y.; Ito, M. Association between aqueous humor and vitreous fluid levels of Th17 cell-related cytokines in patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, A.; Schmidt, M.H.H.; Heinig, N. Microglia in retinal angiogenesis and diabetic retinopathy. Angiogenesis 2024, 27, 311–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinuthia, U.M.; Wolf, A.; Langmann, T. Microglia and Inflammatory Responses in Diabetic Retinopathy. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 564077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Xu, H. Parainflammation, chronic inflammation, and age-related macular degeneration. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2015, 98, 713–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlstetter, M.; Scholz, R.; Rutar, M.; Wong, W.T.; Provis, J.M.; Langmann, T. Retinal microglia: Just bystander or target for therapy? Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2015, 45, 30–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barati, M.; Ghahremani, A.; Namdar Ahmadabad, H. Intermittent fasting: A promising dietary intervention for autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2023, 22, 103408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, R.K.; Silver, P.B.; Caspi, R.R. Rodent models of experimental autoimmune uveitis. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 900, 443–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caspi, R.R. Understanding autoimmune uveitis through animal models. The Friedenwald Lecture. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 1872–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harimoto, K.; Nishio, Y.; Someya, H.; Sato, T.; Ito, M.; Takeuchi, M. Anti-inflammatory actions of ripasudil ameliorate experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis in the acute phase. BMJ Open Ophthalmol. 2025, 10, e001981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasper, M.; Karlstetter, M.; Wildschutz, L.; Scholz, R.; Busch, M.; Bauer, D.; Meyer Zu Horste, G.; Thanos, S.; Langmann, T.; Heiligenhaus, A. Kinetic changes in microglia-related retinal transcripts in experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis (EAU) of B10.RIII mice. J. Neuroinflamm. 2025, 22, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.M.; Yun, K.; Jeon, J.; Yang, H.Y.; Kim, B.; Jeong, S.; Lee, J.; Oh, W.Y.; Uemura, A.; Song, J.S.; et al. Multimodal evaluation of an interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein-induced mouse model of experimental autoimmune uveitis. Exp. Mol. Med. 2022, 54, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okunuki, Y.; Mukai, R.; Nakao, T.; Tabor, S.J.; Butovsky, O.; Dana, R.; Ksander, B.R.; Connor, K.M. Retinal microglia initiate neuroinflammation in ocular autoimmunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 9989–9998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Yang, J.; Oh, Y.; Hartsock, M.J.; Xia, S.; Kim, Y.C.; Ding, Z.; Meng, T.; Eberhart, C.G.; Ensign, L.M.; et al. Controlled release of corticosteroid with biodegradable nanoparticles for treating experimental autoimmune uveitis. J. Control. Release 2019, 296, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, X.; Li, L.; Hua, X.; Guo, S.; Yuan, X. Long-acting acid-sensitive ketal-linked dexamethasone microcrystals for treating experimental autoimmune uveitis. APL Bioeng. 2022, 6, 046101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Meng, J.; Li, N.; Xu, Z.; Liu, X.; Hou, S. Galectin-3 regulates microglial activation and promotes inflammation through TLR4/MyD88/NF-kB in experimental autoimmune uveitis. Clin. Immunol. 2022, 236, 108939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, N.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, R.; Li, W.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Tao, L.; Zhang, L.; et al. Apigenin Alleviates Autoimmune Uveitis by Inhibiting Microglia M1 Pro-Inflammatory Polarization. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2023, 64, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, K.; Ying, H.; Hu, G.; Hu, J.; Jian, Q.; Zhang, F. Integrated multi-omics reveals the activated retinal microglia with intracellular metabolic reprogramming contributes to inflammation in STZ-induced early diabetic retinopathy. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 942768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, M.; Nishio, Y.; Someya, H.; Sato, T.; Yoshimura, A.; Ito, M.; Harimoto, K. Autoimmune uveitis attenuated in diabetic mice through imbalance of Th1/Th17 differentiation via suppression of AP-1 signaling pathway in Th cells. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1347018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Someya, H.; Ito, M.; Nishio, Y.; Sato, T.; Harimoto, K.; Takeuchi, M. Osteopontin-induced vascular hyperpermeability through tight junction disruption in diabetic retina. Exp. Eye Res. 2022, 220, 109094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harimoto, K.; Ito, M.; Karasawa, Y.; Sakurai, Y.; Takeuchi, M. Evaluation of mouse experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis by spectral domain optical coherence tomography. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2014, 98, 808–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wang, R.; Hu, G.; Liu, H.; Lv, K.; Duan, Y.; Shen, N.; Wu, J.; Hu, J.; Liu, Y.; et al. Single cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-Seq) deciphering pathological alterations in streptozotocin-induced diabetic retinas. Exp. Eye Res. 2021, 210, 108718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karademir, D.; Todorova, V.; Ebner, L.J.A.; Samardzija, M.; Grimm, C. Single-cell RNA sequencing of the retina in a model of retinitis pigmentosa reveals early responses to degeneration in rods and cones. BMC Biol. 2022, 20, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Dong, Y.; Yan, J.; Wang, L.; Yu, S.; Jiao, K.; Paquet-Durand, F. Single-Cell Transcriptomic Profiling in Inherited Retinal Degeneration Reveals Distinct Metabolic Pathways in Rod and Cone Photoreceptors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, H.; Truong, T.; Phan, T.; Pham, S. Venice: A New Algorithm for Finding Marker Genes in Single-Cell Transcriptomic Data. bioRxiv 2020, 2020, 2020-11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, B. The multifaceted roles of the invariant chain CD74–More than just a chaperone. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1863, 1269–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, S.E.; Hollopeter, G.; Yang, G.; Kurpius, D.; Dailey, M.E.; Gan, W.B.; Julius, D. The P2Y12 receptor regulates microglial activation by extracellular nucleotides. Nat. Neurosci. 2006, 9, 1512–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Wageningen, T.A.; Vlaar, E.; Kooij, G.; Jongenelen, C.A.M.; Geurts, J.J.G.; van Dam, A.M. Regulation of microglial TMEM119 and P2RY12 immunoreactivity in multiple sclerosis white and grey matter lesions is dependent on their inflammatory environment. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2019, 7, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, A.; Ayala-Ramirez, R.; Zenteno, J.C.; Huffman, K.; Sasik, R.; Ayyagari, R.; Borooah, S. Single cell RNA sequencing confirms retinal microglia activation associated with early onset retinal degeneration. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wachholz, S.; Eßlinger, M.; Plümper, J.; Manitz, M.P.; Juckel, G.; Friebe, A. Microglia activation is associated with IFN-α induced depressive-like behavior. Brain Behav. Immun. 2016, 55, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipski, D.A.; Dewispelaere, R.; Foucart, V.; Caspers, L.E.; Defrance, M.; Bruyns, C.; Willermain, F. MHC class II expression and potential antigen-presenting cells in the retina during experimental autoimmune uveitis. J. Neuroinflammation 2017, 14, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Huang, W.; Chen, J.; Li, N.; Mao, L.; Hou, S. Retinal microglia: Functions and diseases. Immunology 2022, 166, 268–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Xu, G.T.; Zhang, J.F. Inflammation in diabetic retinopathy: Possible roles in pathogenesis and potential implications for therapy. Neural Regen. Res. 2023, 18, 976–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrester, J.V.; Kuffova, L.; Delibegovic, M. The Role of Inflammation in Diabetic Retinopathy. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 583687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeifer, C.W.; Walsh, J.T.; Santeford, A.; Lin, J.B.; Beatty, W.L.; Terao, R.; Liu, Y.A.; Hase, K.; Ruzycki, P.A.; Apte, R.S. Dysregulated CD200-CD200R signaling in early diabetes modulates microglia-mediated retinopathy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2308214120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, Q.; Li, K. Macrophage/microglia polarization for the treatment of diabetic retinopathy. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1276225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, W.C.; Yen, C.L.; Wu, Y.H.; Chen, S.Y.; Hsieh, C.Y.; Chang, T.C.; Ou, H.Y.; Shieh, C.C. Increased resistin may suppress reactive oxygen species production and inflammasome activation in type 2 diabetic patients with pulmonary tuberculosis infection. Microbes Infect. 2015, 17, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegenga, M.E.; van der Crabben, S.N.; Blümer, R.M.; Levi, M.; Meijers, J.C.; Serlie, M.J.; Tanck, M.W.; Sauerwein, H.P.; van der Poll, T. Hyperglycemia enhances coagulation and reduces neutrophil degranulation, whereas hyperinsulinemia inhibits fibrinolysis during human endotoxemia. Blood 2008, 112, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, M.B.; Lad, A.; Bharath Prasad, A.S.; Balakrishnan, A.; Ramachandra, L.; Satyamoorthy, K. High glucose modulates IL-6 mediated immune homeostasis through impeding neutrophil extracellular trap formation. FEBS Lett. 2013, 587, 2241–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berrou, J.; Fougeray, S.; Venot, M.; Chardiny, V.; Gautier, J.F.; Dulphy, N.; Toubert, A.; Peraldi, M.N. Natural killer cell function, an important target for infection and tumor protection, is impaired in type 2 diabetes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecube, A.; Pachón, G.; Petriz, J.; Hernández, C.; Simó, R. Phagocytic activity is impaired in type 2 diabetes mellitus and increases after metabolic improvement. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restrepo, B.I.; Twahirwa, M.; Rahbar, M.H.; Schlesinger, L.S. Phagocytosis via complement or Fc-gamma receptors is compromised in monocytes from type 2 diabetes patients with chronic hyperglycemia. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala, T.S.; Tessaro, F.H.G.; Jannuzzi, G.P.; Bella, L.M.; Ferreira, K.S.; Martins, J.O. High Glucose Environments Interfere with Bone Marrow-Derived Macrophage Inflammatory Mediator Release, the TLR4 Pathway and Glucose Metabolism. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlou, S.; Lindsay, J.; Ingram, R.; Xu, H.; Chen, M. Sustained high glucose exposure sensitizes macrophage responses to cytokine stimuli but reduces their phagocytic activity. BMC Immunol. 2018, 19, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobs, S.P.; Kolodziejczyk, A.A.; Adler, L.; Horesh, N.; Botscharnikow, C.; Herzog, E.; Mohapatra, G.; Hejndorf, S.; Hodgetts, R.J.; Spivak, I.; et al. Lung dendritic-cell metabolism underlies susceptibility to viral infection in diabetes. Nature 2023, 624, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadini, G.P.; de Kreutzenberg, S.V.; Boscaro, E.; Albiero, M.; Cappellari, R.; Kränkel, N.; Landmesser, U.; Toniolo, A.; Bolego, C.; Cignarella, A.; et al. An unbalanced monocyte polarisation in peripheral blood and bone marrow of patients with type 2 diabetes has an impact on microangiopathy. Diabetologia 2013, 56, 1856–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Zhu, W.; Wang, C.; Dong, X.; Yu, F.; Su, Y.; Huang, J.; Huo, L.; Wan, P. ALKBH5-Mediated m(6)A Modification of A20 Regulates Microglia Polarization in Diabetic Retinopathy. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 813979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Wu, S.; Hong, Z.; Chen, X.; Shan, X.; Fischbach, S.; Xiao, X. Chronic hyperglycemia regulates microglia polarization through ERK5. Aging 2019, 11, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Li, B.; Zheng, Y. Role of microglia/macrophage polarisation in intraocular diseases (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2024, 53, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Jiang, P.; Tang, H.; Wen, J.; Zhou, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Yang, Q. Shh regulates M2 microglial polarization and fibrotic scar formation after ischemic stroke. Neurochem. Int. 2024, 180, 105862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liao, X.; Li, N.; Xu, Z.; Yang, W.; Zhou, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, G.; Hou, S. Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals inflammatory retinal microglia in experimental autoimmune uveitis. MedComm 2024, 5, e534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, R.E.; Guabiraba, R.; Russo, R.C.; Teixeira, M.M. Targeting CCL5 in inflammation. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2013, 17, 1439–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Sun, X.; Zhao, J.; Xia, L.; Li, J.; Xu, M.; Wang, B.; Guo, H.; Yu, C.; Gao, Y.; et al. CCL5 deficiency promotes liver repair by improving inflammation resolution and liver regeneration through M2 macrophage polarization. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 17, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nishio, Y.; Someya, H.; Harimoto, K.; Sato, T.; Ito, M.; Takeuchi, M. Enhanced M2 Polarization of Retinal Microglia in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mice upon Autoimmune Stimulation. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2049. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092049
Nishio Y, Someya H, Harimoto K, Sato T, Ito M, Takeuchi M. Enhanced M2 Polarization of Retinal Microglia in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mice upon Autoimmune Stimulation. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(9):2049. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092049
Chicago/Turabian StyleNishio, Yoshiaki, Hideaki Someya, Kozo Harimoto, Tomohito Sato, Masataka Ito, and Masaru Takeuchi. 2025. "Enhanced M2 Polarization of Retinal Microglia in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mice upon Autoimmune Stimulation" Biomedicines 13, no. 9: 2049. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092049
APA StyleNishio, Y., Someya, H., Harimoto, K., Sato, T., Ito, M., & Takeuchi, M. (2025). Enhanced M2 Polarization of Retinal Microglia in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mice upon Autoimmune Stimulation. Biomedicines, 13(9), 2049. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092049





