Lyme-Borreliosis Disease: IgM Epitope Mapping and Evaluation of a Serological Assay Based on Immunodominant Bi-Specific Peptides
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Human Serum Samples
2.2. Preparation of the Cellulose Membrane-Bound Peptide Array
2.3. Evaluation of SPOT Membranes
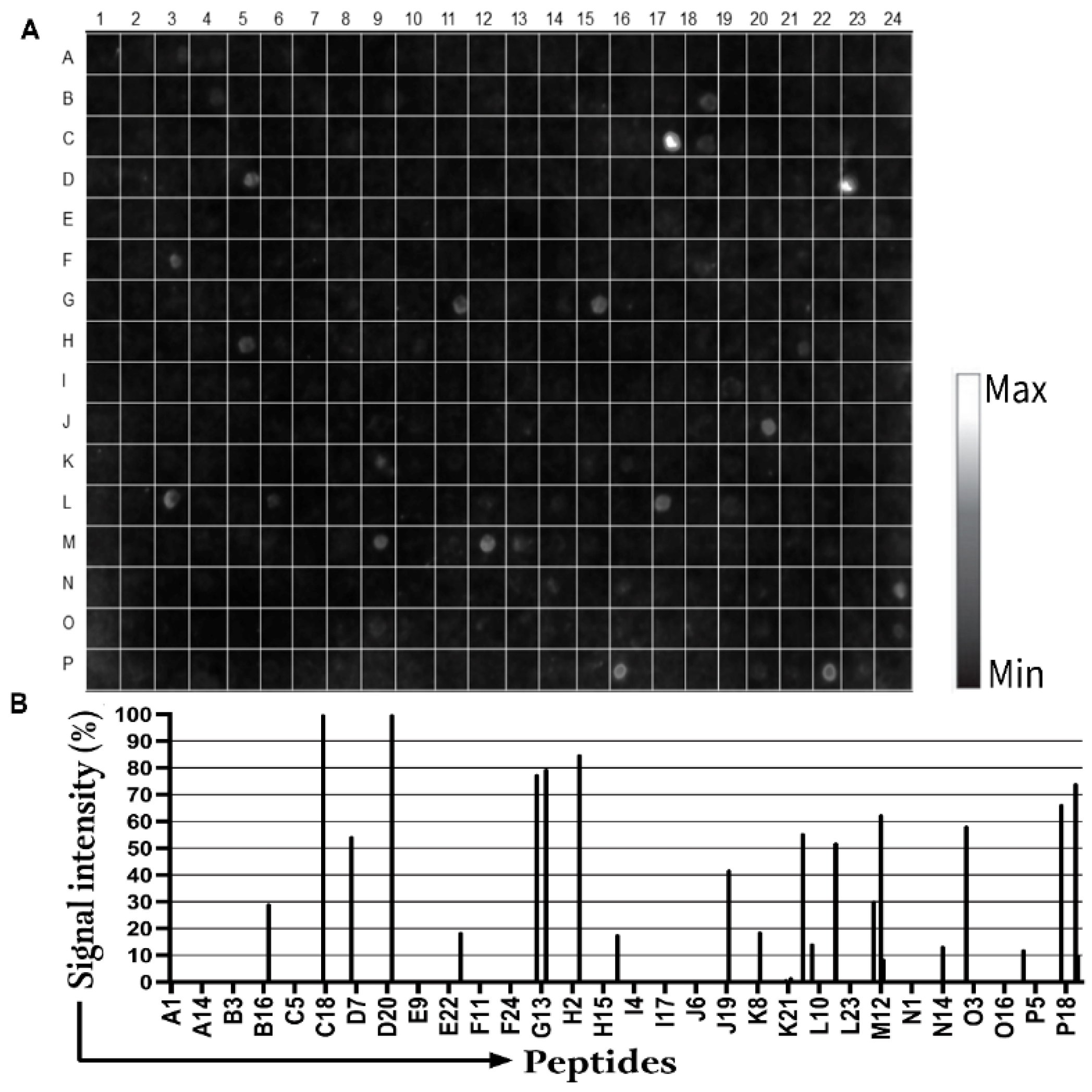
2.4. Scanning and Quantification of Spot Signal Intensities
2.5. Peptide Preparation
2.6. Synthesis of Bi-Specific Antigen Peptides
2.7. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.8. Computational Tools
2.9. Data Analysis
3. Result
3.1. Detection of IgM Epitopes in Surface Proteins of B. burgdorferi
3.2. Secondary Structure and Structural Mapping of the IgM Epitopes
3.3. ELISA Screening
3.4. Potential Cross-Reactivity of the Epitopes In Silico
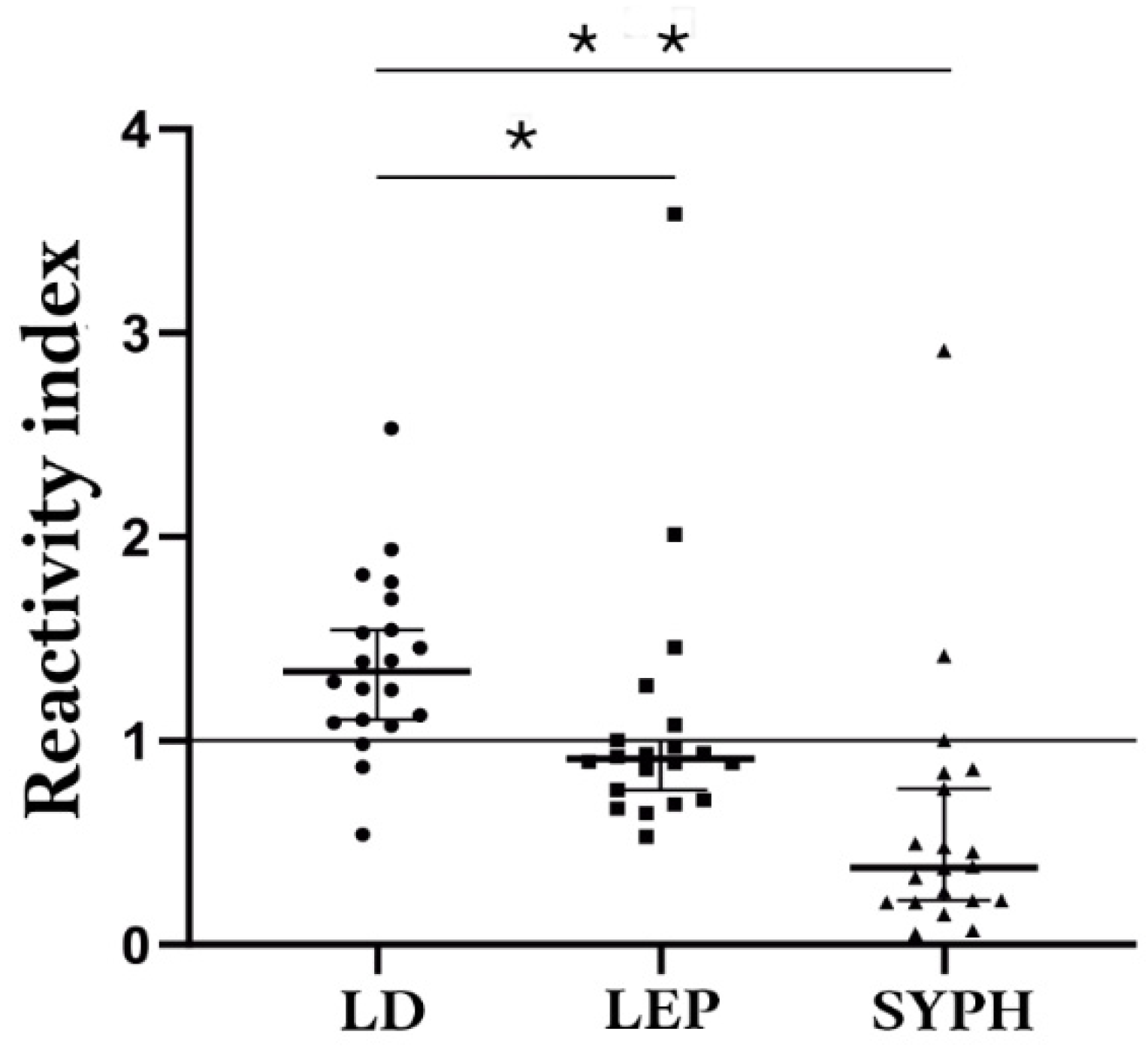
3.5. Potential Cross-Reactivity and Validation of Bi-Specific Peptides as Antigens
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mead, P.; Hinckley, A.; Kugeler, K. Lyme disease surveillance and epidemiology in the United States: A historical perspective. J. Infect. Dis. 2024, 230, S11–S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burn, L.; Vyse, A.; Pilz, A.; Tran, T.M.P.; Fletcher, M.A.; Angulo, F.J.; Gessner, B.D.; Moïsi, J.C.; Stark, J.H. Incidence of Lyme Borreliosis in Europe: A systematic review (2005–2020). Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2023, 23, 172–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykes, R.A.; Makiello, P. An estimate of Lyme borreliosis incidence in Western Europe. J. Public Health 2016, 39, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshinari, N.H.; Bonoldi, V.L.N.; Bonin, S.; Falkingham, E.; Trevisan, G. The current state of knowledge on Baggio-Yoshinari syndrome (Brazilian Lyme Disease-like Illness): Chronological presentation of historical and scientific events observed over the last 30 Years. Pathogens 2022, 11, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonoldi, V.L.N.; Yoshinari, N.H.; Trevisan, G.; Bonin, S. Baggio-Yoshinari syndrome: A report of five cases. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorge, F.R.; Muñoz-Leal, S.; de Oliveira, G.M.B.; Serpa, M.C.A.; Magalhães, M.M.L.; de Oliveira, L.M.B.; Moura, F.B.P.; Teixeira, B.M.; Labruna, M.B. Novel Borrelia genotypes from Brazil indicate a new group of Borrelia spp. associated with South American Bats. J. Med. Entomol. 2023, 60, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnishi, J.; Piesman, J.; de Silva, A.M. Antigenic and genetic heterogeneity of Borrelia burgdorferi populations transmitted by ticks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miziara, C.S.M.G.; Gelmeti Serrano, V.A.; Yoshinari, N. Passage of Borrelia burgdorferi through diverse Ixodid hard ticks causes distinct diseases: Lyme borreliosis and Baggio-Yoshinari syndrome. Clinics 2018, 73, e394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wodecka, B.; Kolomiiets, V. Genetic diversity of Borreliaceae species detected in natural populations of Ixodes ricinus ticks in northern Poland. Life 2023, 13, 972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karageorgou, I.; Koutantou, M.; Papadogiannaki, I.; Voulgari-Kokota, A.; Makka, S.; Angelakis, E. Serological evidence of possible Borrelia afzelii Lyme disease in Greece. New Microbes New Infect. 2022, 46, 100978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancilla-Agrono, L.Y.; Banguero-Micolta, L.F.; Ossa-Lopez, P.A.; Ramirez-Chaves, H.E.; Castano-Villa, G.J.; Rivera-Paez, F.A. Is Borrelia burgdorferi sensu stricto in South America? First molecular evidence of its presence in Colombia. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2022, 7, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudenko, N.; Golovchenko, M.; Horak, A.; Grubhoffer, L.; Mongodin, E.F.; Fraser, C.M.; Qiu, W.; Luft, B.J.; Morgan, R.G.; Casjens, S.R.; et al. Genomic confirmation of Borrelia garinii. U. S. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2023, 29, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansmann, Y.; Leyer, C.; Lefebvre, N.; Revest, M.; Rabaud, C.; Alfandari, S.; Christmann, D.; Tattevin, P. Feedback on difficulties raised by interpreting serological tests for Lyme disease diagnosis. Med. Mal. Infect. 2014, 44, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodym, P.; Kurzová, Z.; Berenová, D.; Pícha, D.; Smíšková, D.; Moravcová, L.; Malý, M. Serological diagnostics of Lyme Borreliosis: Comparison of universal and Borrelia species-specific tests based on whole-cell and recombinant antigens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e00601-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ružić-Sabljić, E.; Cerar, T. Progress in the molecular diagnosis of Lyme disease. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2017, 17, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldin, C.; Parola, P.; Raoult, D. Limitations of diagnostic tests for bacterial infections. Med. Mal. Infect. 2019, 49, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toumanios, C.; Prisco, L.; Dattwyler, R.J.; Arnaboldi, P.M. Linear B cell epitopes derived from the multifunctional surface lipoprotein BBK32 as targets for the serodiagnosis of Lyme disease. mSphere 2019, 4, e00111-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokarz, R.; Guo, C.; Sanchez-Vicente, S.; Horn, E.; Eschman, A.; Turk, S.P.; Lipkin, W.I.; Marques, A. Identification of reactive Borrelia burgdorferi peptides associated with Lyme disease. mBio 2024, 15, e0236024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durans, A.M.; Napoleão-Pêgo, P.; Reis, F.C.G.; Dias, E.R.; Machado, L.E.S.F.; Lechuga, G.C.; Junqueira, A.C.V.; De-Simone, S.G.; Provance, D.W., Jr. Chagas disease diagnosis with Trypanosoma cruzi exclusive epitopes in GFP. Vaccines 2024, 12, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guérin, M.; Shawky, M.; Zedan, A.; Octave, S.; Avalle, B.; Maffucci, I.; Padiolleau-Lefèvre, S. Lyme borreliosis diagnosis: State of the art of improvements and innovations. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilly, K.; Krum, J.G.; Bestor, A.; Jewett, M.W.; Grimm, D.; Bueschel, D.; Byram, R.; Dorward, D.; Vanraden, M.J.; Stewart, P.; et al. Borrelia burgdorferi OspC protein is required exclusively in a crucial early stage of mammalian infection. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 3554–3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battisti, J.M.; Bono, J.L.; Rosa, P.A.; Schrumpf, M.E.; Schwan, T.G.; Policastro, P.F. Outer surface protein A protects Lyme disease spirochetes from acquired host immunity in the tick vector. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 5228–5237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bykowski, T.; Woodman, M.E.; Cooley, A.E.; Brissette, C.A.; Wallich, R.; Brade, V.; Kraiczy, P.; Stevenson, B. Borrelia burgdorferi complement regulator-acquiring surface proteins (BbCRASPs): Expression patterns during the mammal-tick infection cycle. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 298, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brissette, C.A.; Haupt, K.; Barthel, D.; Cooley, A.E.; Bowman, A.; Skerka, C.; Wallich, R.; Zipfel, P.F.; Kraiczy, P.; Stevenson, B. Borrelia burgdorferi infection-associated surface proteins ErpP, ErpA, and ErpC bind human plasminogen. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Sultan, S.; Yerke, A.; Moon, K.H.; Wooten, R.M.; Motaleb, M.A. Borrelia burgdorferi CheY2 is dispensable for chemotaxis or motility but crucial for the infectious life cycle of the spirochete. Infect. Immun. 2017, 85, 10-1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, K.H.; Hobbs, G.; Motaleb, M.A. Borrelia burgdorferi CheD promotes various functions in chemotaxis and the pathogenic life cycle of the spirochete. Infect. Immun. 2016, 84, 1743–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulzova, L.; Bhide, M. Outer surface proteins of Borrelia: Peerless immune evasion tools. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2014, 15, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Carroll, B.L.; Liu, J. Structural basis of bacterial flagellar motor rotation and switching. Trends Microbiol. 2021, 29, 1024–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Qin, Z.; Chang, Y.; Liu, J.; Malkowski, M.G.; Shipa, S.; Li, L.; Qiu, W.; Zhang, J.R.; Li, C. Analysis of a flagellar filament cap mutant reveals that HtrA serine protease degrades unfolded flagellin protein in the periplasm of Borrelia burgdorferi. Mol. Microbiol. 2019, 111, 1652–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutemark, C.; Alicot, E.; Bergman, A.; Ma, M.; Getahun, A.; Ellmerich, S.; Carroll, M.C.; Heyman, B. Requirement for complement in antibody responses is not explained by the classic pathway activator IgM. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, E934–E942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowicz, M.; Reiter, M.; Gamper, J.; Stanek, G.; Stockinger, H. Persistent anti-Borrelia IgM antibodies without Lyme Borreliosis in the clinical and immunological context. Microbiol. Spectr. 2021, 9, e0102021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavnezer, J.; Amemiya, C.T. Evolution of isotype switching. Semin. Immunol. 2004, 16, 257–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chino, M.E.T.A.; Bonoldi, V.L.N.; Pereira, R.M.R.; Gazeta, G.S.; Carvalho, J.P.R.S.; Napoleão-Pêgo, P.; Durans, A.M.; Souza, A.L.A.; De-Simone, S.G. New epitopes for the serodiagnosis of human Borreliosis. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connolly, S.E.; Thanassi, D.G.; Benach, J.L. Generation of a complement-independent bactericidal IgM against a relapsing fever Borrelia. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 1191–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stelma, F.F.; Berende, A.; Ter Hofstede, H.; Vrijmoeth, H.D.; Vos, F.; Kullberg, B.J. Classical Borrelia Serology does not aid in the diagnosis of persistent symptoms attributed to Lyme Borreliosis: A retrospective cohort study. Life 2023, 13, 1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalish, R.A.; McHugh, G.; Granquist, J.; Shea, B.; Ruthazer, R.; Steere, A.C. Persistence of immunoglobulin M or immunoglobulin G antibody responses to Borrelia burgdorferi 10–20 years after active Lyme disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 33, 780–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bockenstedt, L.K.; Wooten, R.M.; Baumgarth, N. Immune response to Borrelia: Lessons from Lyme disease spirochetes. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2021, 42, 145–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, A.; Nelson, C.; Molins, C.; Mead, P.; Schriefer, M. Current guidelines, common clinical pitfalls, and future directions for laboratory diagnosis of Lyme disease, United States. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 1169–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshinari, N.H.; Mantovani, E.; Bonoldi, V.L.; Marangoni, R.G.; Gauditano, G. Brazilian lyme-like disease or Baggio-Yoshinari syndrome: Exotic and emerging Brazilian tick-borne zoonosis. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2010, 56, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haselbeck, A.H.; Im, J.; Prifti, K.; Marks, F.; Holm, M.; Zellweger, R.M. Serology as a tool to assess infectious disease landscapes and guide public health policy. Pathogens 2022, 11, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Signorino, G.; Arnaboldi, P.M.; Petzke, M.M.; Dattwyler, R.J. Identification of OppA2 linear epitopes as serodiagnostic markers for Lyme disease. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2014, 21, 704–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, S.; Nayak, S.; Williams, T.; di Santa Maria, F.S.; Guedes, M.S.; Chaves, R.C.; Linder, V.; Marques, A.R.; Horn, E.J.; Wong, S.J.; et al. A multiplexed serologic test for diagnosis of Lyme disease for point-of-care use. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2019, 57, e01142-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Morrissey, J.J.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Naik, R.R.; Singamaneni, S. Plasmonically enhanced ultrasensitive epitope-specific serologic assay for COVID-19. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, H.S. Measuring molecular biomarkers in epidemiologic studies: Laboratory techniques and biospecimen considerations. Stat. Med. 2012, 31, 2400–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De-Simone, S.G.; Napoleão-Pego, P.; Teixeira-Pinto, L.A.; Santos, J.D.; De-Simone, T.S.; Melgarejo, A.R.; Aguiar, A.S.; Marchi-Salvador, D.P. Linear B-cell epitopes in BthTX-1, BthTX-II and BthA-1, phospholipase A₂’s from Bothrops jararacussu snake venom, recognized by therapeutically neutralizing commercial horse antivenom. Toxicon 2013, 72, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, F.R.; Napoleão-Pego, P.; De-Simone, S.G. Identification of linear B epitope of pertactin of Bordetela pertussis induced by immunization with whole and acellular vaccine. Vaccine 2014, 32, 6251–6258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De-Simone, S.G.; Gomes, L.R.; Napoleão-Pêgo, P.; Lechuga, G.C.; de Pina, J.S.; da Silva, F.R. Epitope Mapping of the diphtheria toxin and development of an ELISA-specific diagnostic assay. Vaccines 2021, 9, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, M.E.; Lechuga, G.C.; Napoleão-Pego, P.; Carvalho, J.P.R.S.; Gomes, L.R.; Morel, C.M.; Provance-Jr, D.W.; De-Simone, S.G. Humoral imune response to SARS-CoV-2 spike protein receptor-binding motif linear epitopes. Vaccines 2024, 12, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, R.; Joung, H.A.; Goncharov, A.; Palanisamy, B.; Ngo, K.; Pejcinovic, K.; Krockenberger, N.; Horn, E.J.; Garner, O.B.; Ghazal, E.; et al. Rapid single-tier serodiagnosis of Lyme disease. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 7124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenedy, M.R.; Lenhart, T.R.; Akins, D.R. The role of Borrelia burgdorferi outer surface proteins. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 66, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilske, B.; Luft, B.; Schubach, W.H.; Zumstein, G.; Jauris, S.; Preac-Mursic, V.; Kramer, M.D. Molecular analysis of the outer surface protein A (OspA) of Borrelia burgdorferi for conserved and variable antibody binding domains. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 1992, 181, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, A.; Schüler, W.; Seidel, S.; Gomez, I.; Meinke, A.; Comstedt, P.; Lundberg, U. Broadly Protective Multivalent OspA vaccine against Lyme Borreliosis, developed based on surface shaping of the c-terminal fragment. Infect Immun 2020, 88, e00917-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Luft, B.J.; Schubach, W.; Dattwyler, R.J.; Gorevic, P.D. Mapping the major antigenic domains of the native flagellar antigen of Borrelia burgdorferi. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1992, 30, 1535–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, W.; Ma, X.; Nyman, D.; Povlsen, K.; Akguen, N.; Schneider, E.M. Antigen biochips verify and extend the scope of antibody detection in Lyme borreliosis. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2007, 59, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, M.J.; Miller, M.; James, M.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, K.; Li, C.; Charon, N.W.; Crane, B.R. Structure and chemistry of lysinoalanine cross-linking in the spirochaete flagella hook. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2019, 15, 959–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridmanis, J.; Bobrovs, R.; Brangulis, K.; Tārs, K.; Jaudzems, K. Structural and Functional Analysis of BBA03, Borrelia burgdorferi competitive advantage promoting outer surface lipoprotein. Pathogens 2020, 9, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondino, S.; San Martin, F.; Buschiazzo, A. 3D cryo-EM imaging of bacterial flagella: Novel structural and mechanistic insights into cell motility. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 102105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izac, J.R.; Oliver, L.D., Jr.; Earnhart, C.G.; Marconi, R.T. Identification of a defined linear epitope in the OspA protein of the Lyme disease spirochetes that elicits bactericidal antibody responses: Implications for vaccine development. Vaccine 2017, 35, 3178–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedeljković, M.; Sastre, D.E.; Sundberg, E.J. Bacterial Flagellar Filament: A supramolecular multifunctional nanostructure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steere, A.; Sikand, V.K.; Meurice, F.; Parenti, D.L.; Fikrig, E.; Schoen, R.T.; Nowakowski, J.; Schmid, C.H.; Laukamp, S.; Buscarino, C.; et al. Vaccination against Lyme disease with recombinant Borrelia burgdorferi outer-surface lipoprotein A with adjuvant. Lyme disease vaccine study group. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigal, L.H.; Zahradnik, J.M.; Lavin, P.; Patella, S.J.; Bryant, G.; Haselby, R.; Hilton, E.; Kunkel, M.; Adler-Klein, D.; Doherty, T.; et al. A vaccine consisting of recombinant Borrelia burgdorferi outer-surface protein A to prevent Lyme disease. Recombinant outer-surface protein A Lyme Disease Vaccine Study Consortium. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 216–222, Erratum in: N. Eng. J. Med. 1998, 339, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gingerich, M.C.; Nair, N.; Azevedo, J.F.; Samanta, K.; Kundu, S.; He, B.; Gomes-Solecki, M. Intranasal vaccine for Lyme disease provides protection against tick transmitted Borrelia burgdorferi beyond one year. NPJ Vaccines 2024, 9, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharjee, A.; Oeemig, J.S.; Kolodziejczyk, R.; Meri, T.; Kajander, T.; Lehtinen, M.J.; Iwaï, H.; Jokiranta, T.S.; Goldman, A. Structural basis for complement evasion by Lyme disease pathogen Borrelia burgdorferi. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 18685–18695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makabe, K.; Tereshko, V.; Gawlak, G.; Yan, S.; Koide, S. Atomic-resolution crystal structure of Borrelia burgdorferi outer surface protein A via surface engineering. Protein Sci. 2006, 15, 1907–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreutzberger, M.A.B.; Sobe, R.C.; Sauder, A.B.; Chatterjee, S.; Peña, A.; Wang, F.; Giron, J.A.; Kiessling, V.; Costa, T.R.D.; Conticello, V.P.; et al. Flagellin outer domain dimerization modulates pathogenic and soil bacteria motility from viscous environments. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, N.; Zhang, W.; Cheng, X.; Yan, Z.; Shao, G.; Wang, X.; Wang, R.; Fu, C. Therapeutic peptides: Current applications and future directions. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De-Simone, S.G.; Napoleão-Pêgo, P.; Lechuga, G.C.; Carvalho, J.P.R.S.; Gomes, L.R.; Cardozo, S.V.; Morel, C.M.; Provance, D.W.; Silva, F.R.d. High-throughput IgG epitope mapping of tetanus neurotoxin: Implications for immunotherapy and vaccine design. Toxins 2023, 15, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waddell, L.A.; Greig, J.; Mascarenhas, M.; Harding, S.; Lindsay, R.; Ogden, N. The accuracy of diagnostic tests for Lyme disease in humans, A systematic review and meta-analysis of North American research. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, A.R. Laboratory diagnosis of Lyme disease: Advances and challenges. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 29, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagatie, O.; Verheyen, A.; Nijs, E.; Batsa Debrah, L.; Debrah, Y.A.; Stuyver, L.J. Performance evaluation of 3 serodiagnostic peptide epitopes and the derived multiepitope peptide OvNMP-48 for detection of Onchocerca volvulus infection. Parasitol. Res. 2019, 118, 2263–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandrowski, E.L.; Turbett, S.E.; Nigrovic, L.E.; Klontz, E.H.; Branda, J.A. Comparative evaluation of commercial test kits cleared for use in modified two-tiered testing algorithms for serodiagnosis of Lyme disease. J. Infect. Dis. 2024, 14, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Bier, N.S.; Camire, A.C.; Patel, D.T.; Billingsley, J.S.; Hodges, K.R.; Marconi, R.T. Development of novel multi-protein chimeric immunogens that protect against infection with the Lyme disease agent, Borrelia burgdorferi. mBio 2024, 7, e0215924. [Google Scholar]
- Magnarelli, L.A.; Anderson, J.F.; Johnson, R.C. Cross-reactivity in serological tests for Lyme disease and other spirochetal infections. J. Infect. Dis. 1987, 156, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojciechowska-Koszko, I.; Kwiatkowski, P.; Sienkiewicz, M.; Kowalczyk, M.; Kowalczyk, E.; Dołęgowska, B. Cross-reactive results in serological tests for Borreliosis in patients with active viral infections. Pathogens 2022, 11, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doskaliuk, B.; Zimba, O. Borrelia burgdorferi and autoimmune mechanisms: Implications for mimicry, misdiagnosis, and mismanagement in Lyme disease and autoimmune disorders. Rheumatol. Int. 2024, 44, 2265–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grąźlewska, W.; Chmielewski, T.; Fiecek, B.; Holec-Gąsior, L. New BB0108, BB0126, BB0298, BB0323, and BB0689 chromosomally encoded recombinant proteins of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato for serodiagnosis of Lyme Disease. Pathogens 2024, 13, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Seropositive Cases | Suspected Cases | |
|---|---|---|
| Clinical signs | Erythema migrans, arthritis, neurological abnormalities, cardiac involvement, relapsing symptoms. Chronic fatigue or cognitive disturbances. | Erythema migrans, arthritis, neurological abnormalities, cardiac involvement, relapsing symptoms. Chronic fatigue or cognitive disturbances. |
| Serological status | Positive | Negative |
| Epidemiological exposure | History of tick bite and/or environmental exposure in endemic areas. | History of tick bite and/or environmental exposure in endemic areas. |
| Protein | Epitope | 2nd Structure * | a Number | Peptide Match ** |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FlgE | Bburg/01/huM | C | 209 SLYDSFGN 216 | Various Borrelia sp. |
| Bburg/02/huM | C | 321 GYGMGYME 328 | Various Borrelia sp. | |
| Bburg/03/huM | C+S | 381 VRIGETGLAGLGDIR 395 | Another organism | |
| Flg41 kDa | Bburg/04/huM | H+C | 121 ANLSKTQEKLSSGYR 135 | Another organism |
| Bburg/05/huM | H+C | 322 AQANQVPQYVLSLLR 336 | Another organism. | |
| Flg hook2 | Bburg/06/huM | C | 08 PGLESKYN 15 | Various Borrelia sp. |
| Bburg/07/huM | C+S | 76 SGNSSNSEVLTLSTR 90 | Another organism | |
| Bburg/08/huM | C+S | 391 AENAKIKFDGVDVER 405 | Another organism | |
| Bburg/09/huM | H+C+S | 546 RYLRLDEKKFDESIR 560 | Another organism | |
| Bburg/10/huM | H | 616 QKNKVEDYKKKYEDR 630 | Another organism | |
| BBA03 | Bburg/11/huM | C | 31 DEKSQAKSNLVD 42 | Another organism |
| Bburg/12/huM | H+C | 46 IEFSKATPLEKLVSR 60 | Another organism | |
| OSP A | Bburg/13/huM | C | 56 ATVDKLELKGTSDKN 70 | Various Borrelia sp. |
| Bburg/14/huM | C | 266 EGSAVEITKL 275 | Another organism |
| Suspected Case | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Infected | >3 Months | <3 Months | ||||||||
| Peptide | Se (%) | Sp (%) | AUC | Ac (%) | Se (%) | Sp (%) | AUC | Se (%) | Sp (%) | AUC |
| Bburg/01/huM | 82.4 | 56.2 | 0.721 | 66.6 | 72.7 | 56.2 | 0.557 | 76.9 | 59.4 | 0.671 |
| Bburg/02/huM | 100.0 | 97.44 | 0.999 | 96.2 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 1 | 92.3 | 100.0 | 0.925 |
| Bburg/06/huM | 94.74 | 100.0 | 0.996 | 98.2 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 1 | 92.3 | 100.0 | 0.925 |
| Bburg/13/huM | 47.37 | 87.18 | 0.652 | 74.1 | 72.7 | 59.0 | 0.622 | 76.9 | 59.4 | 0.694 |
| Comparison Group | Median | 75% Percentile | 25% Percentile |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lyme-Borreliosis | 0.2613 | 0.3235 | 0.2131 |
| Leptospirosis | 0.0755 | 0.08788 | 0.060 |
| Syphilis | 0.02175 | 0.04738 | 0.01213 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chino, M.E.T.A.; Napoleão-Pêgo, P.; Bonoldi, V.L.N.; Gazeta, G.S.; Carvalho, J.P.R.S.; Morel, C.M.; Provance-Jr, D.W.; De-Simone, S.G. Lyme-Borreliosis Disease: IgM Epitope Mapping and Evaluation of a Serological Assay Based on Immunodominant Bi-Specific Peptides. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1930. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081930
Chino META, Napoleão-Pêgo P, Bonoldi VLN, Gazeta GS, Carvalho JPRS, Morel CM, Provance-Jr DW, De-Simone SG. Lyme-Borreliosis Disease: IgM Epitope Mapping and Evaluation of a Serological Assay Based on Immunodominant Bi-Specific Peptides. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(8):1930. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081930
Chicago/Turabian StyleChino, Mônica E. T. A., Paloma Napoleão-Pêgo, Virgínia L. N. Bonoldi, Gilberto S. Gazeta, João P. R. S. Carvalho, Carlos M. Morel, David W. Provance-Jr, and Salvatore G. De-Simone. 2025. "Lyme-Borreliosis Disease: IgM Epitope Mapping and Evaluation of a Serological Assay Based on Immunodominant Bi-Specific Peptides" Biomedicines 13, no. 8: 1930. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081930
APA StyleChino, M. E. T. A., Napoleão-Pêgo, P., Bonoldi, V. L. N., Gazeta, G. S., Carvalho, J. P. R. S., Morel, C. M., Provance-Jr, D. W., & De-Simone, S. G. (2025). Lyme-Borreliosis Disease: IgM Epitope Mapping and Evaluation of a Serological Assay Based on Immunodominant Bi-Specific Peptides. Biomedicines, 13(8), 1930. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081930










