Therapeutic Potential of Rho Kinase Inhibitors in Corneal Disease: A Systematic Review of Preclinical and Clinical Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Study Selection
2.4. Data Extraction and Synthesis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Trials of ROCK Inhibitors in Corneal Endothelial Disease
3.1.1. Study Designs, Interventions, and Disease Targets
3.1.2. Outcomes and Efficacy
3.2. Preclinical Investigations of ROCK Inhibitors
3.2.1. Experimental Models and Approaches
| Study, Year | Country | Sample Size and Model | Study Design | Experimental Approach | Intervention |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Okumura et al., 2015 [45] | Japan | 9 rabbits; 3 humans | In vivo/clinical | Rabbit wound model; human case series | 10 mM Y-27632 drops |
| Chan et al., 2016 [53] | UK | 12 porcine corneas | In vitro | Mucoadhesive film deposition | HPMC-PEG 400 films with Y-27632 |
| Meekins et al., 2016 [9] | USA | 6 human post-mortem eyes; 6 rabbits | In vivo/ex vivo | IHC; scratch/migration; in vivo scrape + H-1152 drops | Y-27632 (in vitro/ex vivo); H-1152 (in vivo) |
| Wu et al., 2017 [50] | China | 6 human donor corneas | In vitro | Culture of primary and passaged HCECs | Thiazovivin at various concentrations (2, 4, 6 µM); comparison with Y-27632 as positive control |
| Schlötzer-Schrehardt et al., 2020 [46] | Germany | FECD explants (n = 450); wounds (n = 30); intact (n = 20); cell lines (n = 3) | In vitro/ex vivo | Organ-culture wound model | Ripasudil |
| Shin et al., 2020 [48] | South Korea | 10 human corneal tissues | In vitro | HCEP culture and differentiation | 10 µM Y-27632 |
| Song et al., 2021 [54] | China | PCECs (from 4 pigs)/7 rabbits | In vitro/in vivo | PCEC primary culture; ICC (NSE); MTT assay; EdU assay; rabbit CED model; | Y-27632 at 0–200 µM |
| Kim et al., 2022 [52] | South Korea | hCEnCs/porcine corneas | In vitro/ex vivo | hCEnC culture; BrdU, Ki67, scratch assay, ICC, WB, Mito assays | Y-27632 (control), sovesudil, PHP-0961 |
| Parekh et al., 2022 [47] | USA | Biological triplicates. | Ex vivo | Live-cell migration on DM | Ripasudil 1 µM |
| Peh et al., 2023 [49] | Singapore | 32 cadaver corneas | In vitro/ex vivo | EDM explant + primary CEC assays | Y-27632, Netarsudil, AR-13503, verosudil, ripasudil, Y-39983 |
| So et al., 2023 [55] | South Korea | 20 rabbits | In vivo/in vitro | iPSC; NCC; CEC differentiation; rabbit CED model | Fasudil 10 µM |
| Parekh et al., 2024 [18] | USA | Biological triplicates | Ex vivo | TrackMate; scratch; Rac1 assays | Ripasudil 1 µM |
| Vercammen et al., 2024 [51] | Belgium | Biological triplicates | In vitro | MTS, scratch assay, proliferation (OrBITS), ICC, WB | ROCKi library (15 compounds including Y-27632, Ripasudil, Thiazovivin, Fasudil; 50 μM–5 nM) |
| Zhang et al., 2024 [56] | China | Rats/B4G12 human CEC line | In vivo/in vitro | hCEC culture; TGF-β1-induced EndMT; EDU assay; scratch assay; ICC; WB; qPCR | Y-27632 0.2 μM |
3.2.2. Summary of Preclinical Findings
3.3. Risk of Bias
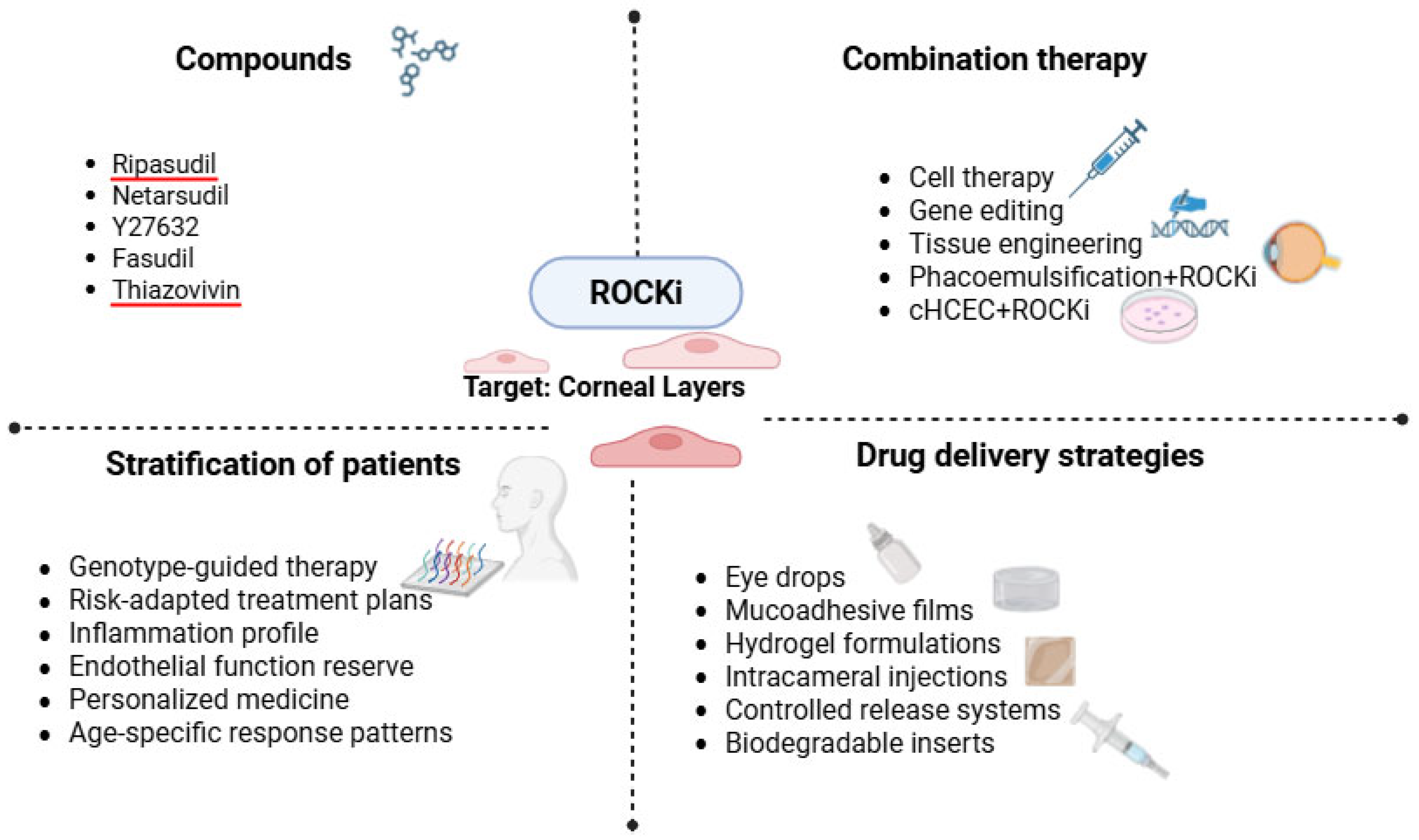
4. Perspectives
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Julian, L.; Olson, M.F. Rho-Associated Coiled-Coil Containing Kinases (ROCK): Structure, Regulation, and Functions. Small GTPases 2014, 5, e29846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, G.; Cannon, R.D.; Coates, D.E.; Mei, L. Effect of the Rho-Kinase/ROCK Signaling Pathway on Cytoskeleton Components. Genes 2023, 14, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassianidou, E.; Hughes, J.H.; Kumar, S. Activation of ROCK and MLCK Tunes Regional Stress Fiber Formation and Mechanics via Preferential Myosin Light Chain Phosphorylation. Mol. Biol. Cell 2017, 28, 3832–3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirth, A. Rho Kinase and Hypertension. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Mol. Basis Dis. 2010, 1802, 1276–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Lee, C.; Read, A.T.; Wang, K.; Ha, J.; Kuhn, M.; Navarro, I.; Cui, J.; Young, K.; Gorijavolu, R.; et al. Anti-Fibrotic Activity of a Rho-Kinase Inhibitor Restores Outflow Function and Intraocular Pressure Homeostasis. eLife 2021, 10, e60831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Lu, J.; Yu, F.-S.X. Role of Small GTPase Rho in Regulating Corneal Epithelial Wound Healing. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2008, 49, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Dang, Y. Rho-Kinase Inhibitors as Emerging Targets for Glaucoma Therapy. Ophthalmol. Ther. 2023, 12, 2943–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanihara, H.; Kakuda, T.; Sano, T.; Kanno, T.; Imada, R.; Shingaki, W.; Gunji, R. Safety and Efficacy of Ripasudil in Japanese Patients with Glaucoma or Ocular Hypertension: 3-Month Interim Analysis of ROCK-J, a Post-Marketing Surveillance Study. Adv. Ther. 2019, 36, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meekins, L.C.; Rosado-Adames, N.; Maddala, R.; Zhao, J.J.; Rao, P.V.; Afshari, N.A. Corneal Endothelial Cell Migration and Proliferation Enhanced by Rho Kinase (ROCK) Inhibitors in In Vitro and In Vivo Models. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, 6731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.K.; Sahu, S.K. Rho-Kinase Inhibitors: Role in Corneal Endothelial Disorders. Semin. Ophthalmol. 2023, 38, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.-F.; Meng, J.; Li, Y.-H.; Yu, J.-Z.; Liu, C.-Y.; Feng, L.; Yang, W.-F.; Li, J.-L.; Feng, Q.-J.; Xiao, B.-G.; et al. The Inhibition of Rho Kinase Blocks Cell Migration and Accumulation Possibly by Challenging Inflammatory Cytokines and Chemokines on Astrocytes. J. Neurol. Sci. 2014, 343, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, B.; Lee, H.; Kim, S.; Tchah, H.; Hwang, C. Effect of Rho-Associated Kinase Inhibitor and Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Conditioned Medium on Corneal Endothelial Cell Senescence and Proliferation. Cells 2021, 10, 1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macsai, M.S.; Shiloach, M. Use of Topical Rho Kinase Inhibitors in the Treatment of Fuchs Dystrophy After Descemet Stripping Only. Cornea 2019, 38, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnyliukh, N.; Boukherroub, R.; Szunerits, S. Corneal endothelial dysfunction treatments: Recent advances in non-invasive treatment strategies. Nano Today 2025, 63, 102740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armitage, W.J.; Goodchild, C.; Griffin, M.D.; Gunn, D.J.; Hjortdal, J.; Lohan, P.; Murphy, C.C.; Pleyer, U.; Ritter, T.; Tole, D.M.; et al. High-risk Corneal Transplantation: Recent Developments and Future Possibilities. Transplantation 2019, 103, 2468–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rolev, K.; Coussons, P.; King, L.; Rajan, M. Experimental Models of Corneal Endothelial Cell Therapy and Translational Challenges to Clinical Practice. Exp. Eye Res. 2019, 188, 107794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurnani, B.; Somani, A.N.; Moshirfar, M.; Patel, B.C. Fuchs Endothelial Dystrophy. In StatPearls; National Library of Medicine: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Parekh, M.; Miall, A.; Chou, A.; Buhl, L.; Deshpande, N.; Price, M.O.; Price, F.W.; Jurkunas, U.V. Enhanced Migration of Fuchs Corneal Endothelial Cells by Rho Kinase Inhibition: A Novel Ex Vivo Descemet’s Stripping Only Model. Cells 2024, 13, 1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, W.; Chang, J.; Chen, T.; Wang, J.; Chang, S.; Yang, M.; Jou, T.; Wang, I. Inhibition of Rho-associated Protein Kinase Activity Enhances Oxidative Phosphorylation to Support Corneal Endothelial Cell Migration. FASEB J. 2022, 36, e22397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.B.; Harris, J.M.; Baldwin, G.; Goss, D.; Margeta, M.A. Ocular Effects of Rho Kinase (ROCK) Inhibition: A Systematic Review. Eye 2024, 38, 3418–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, N.; Sakamoto, Y.; Fujii, K.; Kitano, J.; Nakano, S.; Tsujimoto, Y.; Nakamura, S.; Ueno, M.; Hagiya, M.; Hamuro, J.; et al. Rho Kinase Inhibitor Enables Cell-Based Therapy for Corneal Endothelial Dysfunction. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, N.; Koizumi, N.; Ueno, M.; Sakamoto, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Tsuchiya, H.; Hamuro, J.; Kinoshita, S. ROCK Inhibitor Converts Corneal Endothelial Cells into a Phenotype Capable of Regenerating In Vivo Endothelial Tissue. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 181, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramachandran, C.; Patil, R.V.; Combrink, K.; Sharif, N.A.; Srinivas, S.P. Rho-Rho kinase pathway in the actomyosin contraction and cell-matrix adhesion in immortalized human trabecular meshwork cells. Mol Vis. 2011, 17, 1877–1890. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kümper, S.; Mardakheh, F.K.; McCarthy, A.; Yeo, M.; Stamp, G.W.; Paul, A.; Worboys, J.; Sadok, A.; Jørgensen, C.; Guichard, S.; et al. Rho-associated kinase (ROCK) function is essential for cell cycle progression, senescence and tumorigenesis. eLife 2016, 5, e12994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Croft, D.R.; Olson, M.F. The Rho GTPase effector ROCK regulates cyclin A, cyclin D1, and p27Kip1 levels by distinct mechanisms. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 26, 4612–4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, S.; Liu, Z.; Deng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Jie, Y. The ROCK inhibitor netarsudil in the treatment of corneal endothelial decompensation caused by corneal endotheliitis: A case report and literature review. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 30, 112195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Futterknecht, S.; Chatzimichail, E.; Gugleta, K.; Panos, G.D.; Gatzioufas, Z. The Role of Rho Kinase Inhibitors in Corneal Diseases. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2024, 19, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Van Amerongen, G.P.N.; Beckers, C.; Achekar, I.; Zeeman, S.; Musters, R.; van Hinsbergh, V. Involvement of Rho kinase in endothelial barrier maintenance. Arter. Thromb Vasc Biol. 2007, 27, 2332–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinoshita, S.; Koizumi, N.; Ueno, M.; Okumura, N.; Imai, K.; Tanaka, H.; Yamamoto, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Inatomi, T.; Bush, J.; et al. Injection of Cultured Cells with a ROCK Inhibitor for Bullous Keratopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numa, K.; Imai, K.; Ueno, M.; Kitazawa, K.; Tanaka, H.; Bush, J.D.; Teramukai, S.; Okumura, N.; Koizumi, N.; Hamuro, J.; et al. Five-Year Follow-up of First 11 Patients Undergoing Injection of Cultured Corneal Endothelial Cells for Corneal Endothelial Failure. Ophthalmology 2021, 128, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, E. Case Series: Novel Utilization of Rho-Kinase Inhibitor for the Treatment of Corneal Edema. Cornea 2021, 40, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, M.O.; Price, F.W. Randomized, Double-Masked, Pilot Study of Netarsudil 0.02% Ophthalmic Solution for Treatment of Corneal Edema in Fuchs Dystrophy. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 227, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimoto, H.; Setoguchi, Y.; Kiryu, J. The ROCK Inhibitor Ripasudil Shows an Endothelial Protective Effect in Patients With Low Corneal Endothelial Cell Density After Cataract Surgery. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2021, 10, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimoto, H.; Kiryu, J. Efficacy of the Rho-Kinase Inhibitor Ripasudil for Fuchs’ Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy. J. Ophthalmol. Res. 2021, 4, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzel-Severing, J.; Schrader, S.; Schlötzer-Schrehardt, U.; Geerling, G. Transcorneal Freezing and Topical Rho-Kinase Inhibitor Treatment in Fuchs Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy. Eye 2022, 36, 891–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonini, M.; Coassin, M.; Gaudenzi, D.; Di Zazzo, A. Rho-Associated Kinase Inhibitor Eye Drops in Challenging Cataract Surgery. Am. J. Ophthalmol. Case Rep. 2022, 25, 101245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, E.J.; Yeu, E.; Giegengack, M.; Berdahl, J.; Jordan, E.; Quesada, R.; Quesada, G.; Kinoshita, S.; Sotozono, C.; Toda, M.; et al. Escalón: A Prospective Randomized Trial of Corneal Endothelial Cell Therapy in Subjects with Corneal Edema. Cornea 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomioka, Y.; Kitazawa, K.; Fukuoka, H.; Ueno, M.; Koizumi, N.; Sotozono, C.; Kinoshita, S. Twelve-Year Outcome of Rho-Associated Protein Kinase Inhibitor Eye Drop Treatment for Fuchs Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy: A Case Study. Am. J. Ophthalmol. Case Rep. 2023, 30, 101839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahuam-López, N.; Yeung, S.N.; Iovieno, A. Resolution of Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency with the Use of a Topical Rho Kinase Inhibitor. Can. J. Ophthalmol. 2024, 59, e271–e272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavy, I.; Erdinest, N.; Corredores, J.; Wajnsztajn, D.; Smadja, D. Evaluating the Efficacy of Rho Kinase Inhibitor Eye Drops in the Management of Corneal Edema: A Single-Center Retrospective Cohort Study. Taiwan J. Ophthalmol. 2024, 14, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, M.; Imai, K.; Tomioka, Y.; Horiguchi, G.; Kameda, T.; Teramukai, S.; Tsujikawa, A.; Inatomi, T.; Sotozono, C.; Kinoshita, S. Comprehensive Combined Analysis of Physician-Initiated Phase II and III Clinical Trials on a Cultured Human Corneal Endothelial Cell Product for Treating Bullous Keratopathy. Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 2024, 68, 660–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkharashi, M.; Abusayf, M.M.; Otaif, W.; Alkharashi, A. The Protective Effect of Rho-Associated Kinase Inhibitor Eye Drops (Ripasudil) on Corneal Endothelial Cells After Cataract Surgery: A Prospective Comparative Study. Ophthalmol. Ther. 2024, 13, 1773–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdinest, N.; Shemesh, N.; Weill, Y.; Morad, S.; Nitzan, I.; Smadja, D.; Landau, D.; Lavy, I. Managing Pseudophakic Bullous Keratopathy with a Topical Rho Kinase Inhibitor: A Case Series. J. Med. Case Rep. 2025, 19, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keeratidamkerngsakul, B.; Puangsricharern, V.; Chokesuwattanaskul, S.; Pongpirul, K.; Kittipibul, T. Efficacy of the Rho-Kinase Inhibitor for Corneal Endothelial Protection in Fuchs Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy After Phacoemulsification. Cornea 2025, 44, 896–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okumura, N.; Inoue, R.; Okazaki, Y.; Nakano, S.; Nakagawa, H.; Kinoshita, S.; Koizumi, N. Effect of the Rho Kinase Inhibitor Y-27632 on Corneal Endothelial Wound Healing. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2015, 56, 6067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlötzer-Schrehardt, U.; Zenkel, M.; Strunz, M.; Gießl, A.; Schondorf, H.; Da Silva, H.; Schmidt, G.A.; Greiner, M.A.; Okumura, N.; Koizumi, N.; et al. Potential Functional Restoration of Corneal Endothelial Cells in Fuchs Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy by ROCK Inhibitor (Ripasudil). Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 224, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parekh, M.; Miall, A.; Deshpande, N.; Jurkunas, U.V. Effect of ROCK Inhibitor on Cell Migration in Fuchs Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2022, 63, 3634. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, H.; Min, J.K.; Kim, N.R.; Seo, K.Y.; Chin, H.S.; Lee, S.; Jung, J.W. Effects of Y-27632, a Rho-Associated Kinase Inhibitor, on Human Corneal Endothelial Cells Cultured by Isolating Human Corneal Endothelial Progenitor Cells. Korean J. Ophthalmol. 2023, 37, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peh, G.S.L.; Bandeira, F.; Neo, D.; Adnan, K.; Hartono, Y.; Ong, H.S.; Naso, S.; Venkatraman, A.; Gomes, J.A.P.; Kocaba, V.; et al. Effects of Rho-Associated Kinase (Rock) Inhibitors (Alternative to Y-27632) on Primary Human Corneal Endothelial Cells. Cells 2023, 12, 1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Ouyang, C.; Xie, L.; Ling, Y.; Huang, T. The ROCK inhibitor, thiazovivin, inhibits human corneal endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition/epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and increases ionic transporter expression. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 40, 1009–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Vercammen, H.; Ondra, M.; Kotulova, J.; De La Hoz, E.C.; Witters, C.; Jecmenova, K.; Le Compte, M.; Deben, C.; Ní Dhubhghaill, S.; Koppen, C.; et al. ”Keep on ROCKIn”: Repurposed ROCK inhibitors to boost corneal endothelial regeneration. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024, 174, 116435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.W.; Shin, Y.J.; Lee, S.C.S. Novel ROCK Inhibitors, Sovesudil and PHP-0961, Enhance Proliferation, Adhesion and Migration of Corneal Endothelial Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chan, W.; Akhbanbetova, A.; Quantock, A.J.; Heard, C.M. Topical Delivery of a Rho-Kinase Inhibitor to the Cornea via Mucoadhesive Film. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 91, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Song, Y.W.; Chen, J.Y.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Pan, Z.Q. Therapeutic potential of Rho-associated kinase inhibitor Y27632 in corneal endothelial dysfunction: An in vitro and in vivo study. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 14, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- So, S.; Park, Y.; Kang, S.S.; Han, J.; Sunwoo, J.H.; Lee, W.; Kim, J.; Ye, E.A.; Kim, J.Y.; Tchah, H.; et al. Therapeutic Potency of Induced Pluripotent Stem-Cell-Derived Corneal Endothelial-like Cells for Corneal Endothelial Dysfunction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Wan, C.; Li, Y.; Ren, C.; Lu, J.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y. Verteporfin combined with ROCK inhibitor promotes the restoration of corneal endothelial cell dysfunction in rats. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2025, 231, 116641, Erratum in Biochem Pharmacol. 2025, 232, 116737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateos-Olivares, M.; García-Onrubia, L.; Valentín-Bravo, F.C.O.J.; González-Sarmiento, R.; Lopez-Galvez, M.; Pastor, J.C.; Usategui-Martín, R.; Pastor-Idoate, S. Rho-Kinase Inhibitors for the Treatment of Refractory Diabetic Macular Oedema. Cells 2021, 10, 1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Lin, Q.; Li, J.; Han, Y.; Chang, P.; Lu, F.; Zhao, Y. ROCK Inhibitor Modified Intraocular Lens as an Approach for Inhibiting the Proliferation and Migration of Lens Epithelial Cells and Posterior Capsule Opacification. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 4208–4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.-C.; Chen, Y.-H.; Lu, D.-W. The Application of Rho Kinase Inhibitors in the Management of Glaucoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osi, B.; Al-Kinani, A.A.; Al-Qaysi, Z.K.; Khoder, M.; Alany, R.G. Exploring the Ocular Absorption Pathway of Fasudil Hydrochloride towards Developing a Nanoparticulate Formulation with Improved Performance. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mietzner, R.; Kade, C.; Froemel, F.; Pauly, D.; Stamer, W.D.; Ohlmann, A.; Wegener, J.; Fuchshofer, R.; Breunig, M. Fasudil Loaded PLGA Microspheres as Potential Intravitreal Depot Formulation for Glaucoma Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

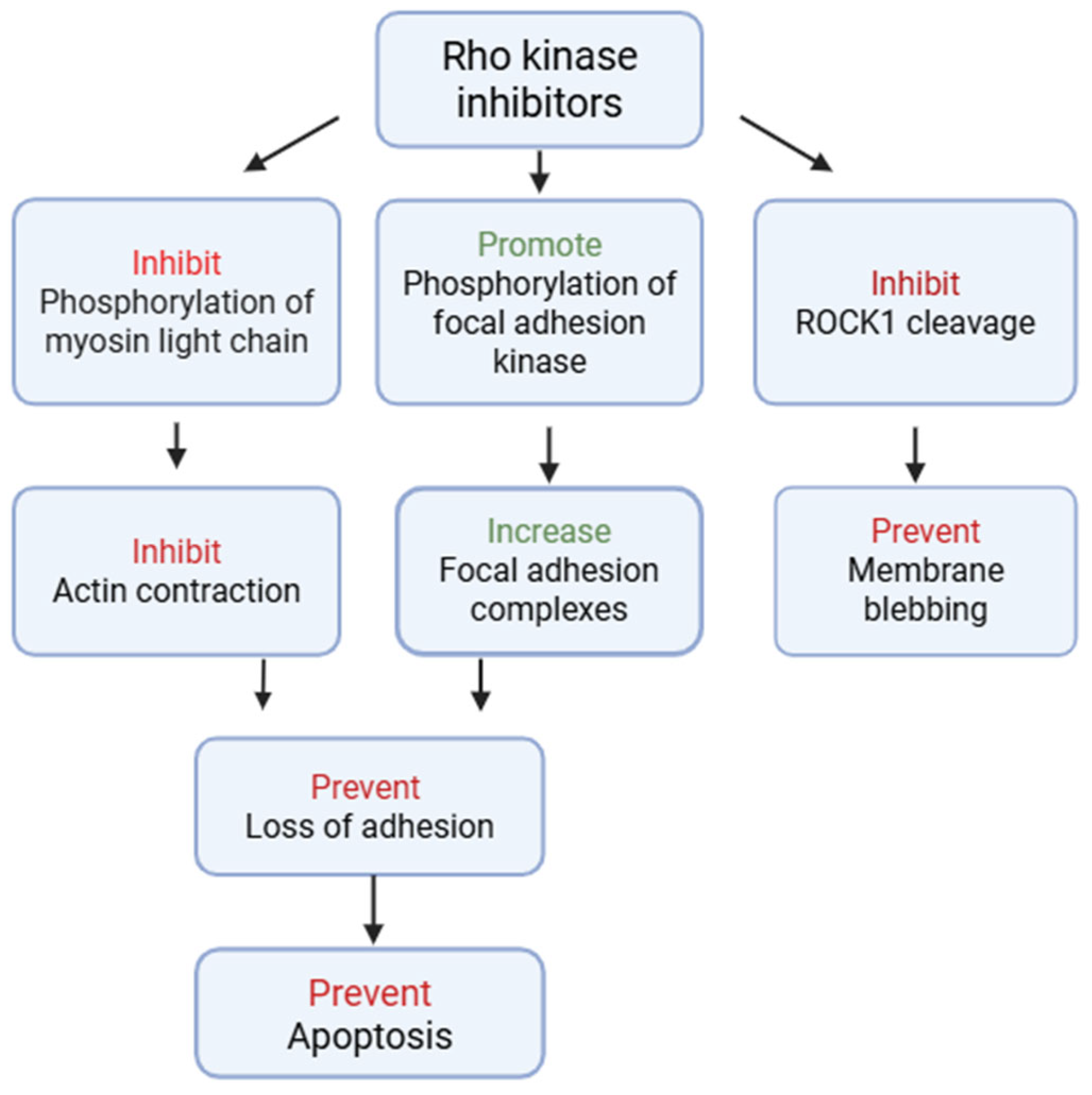
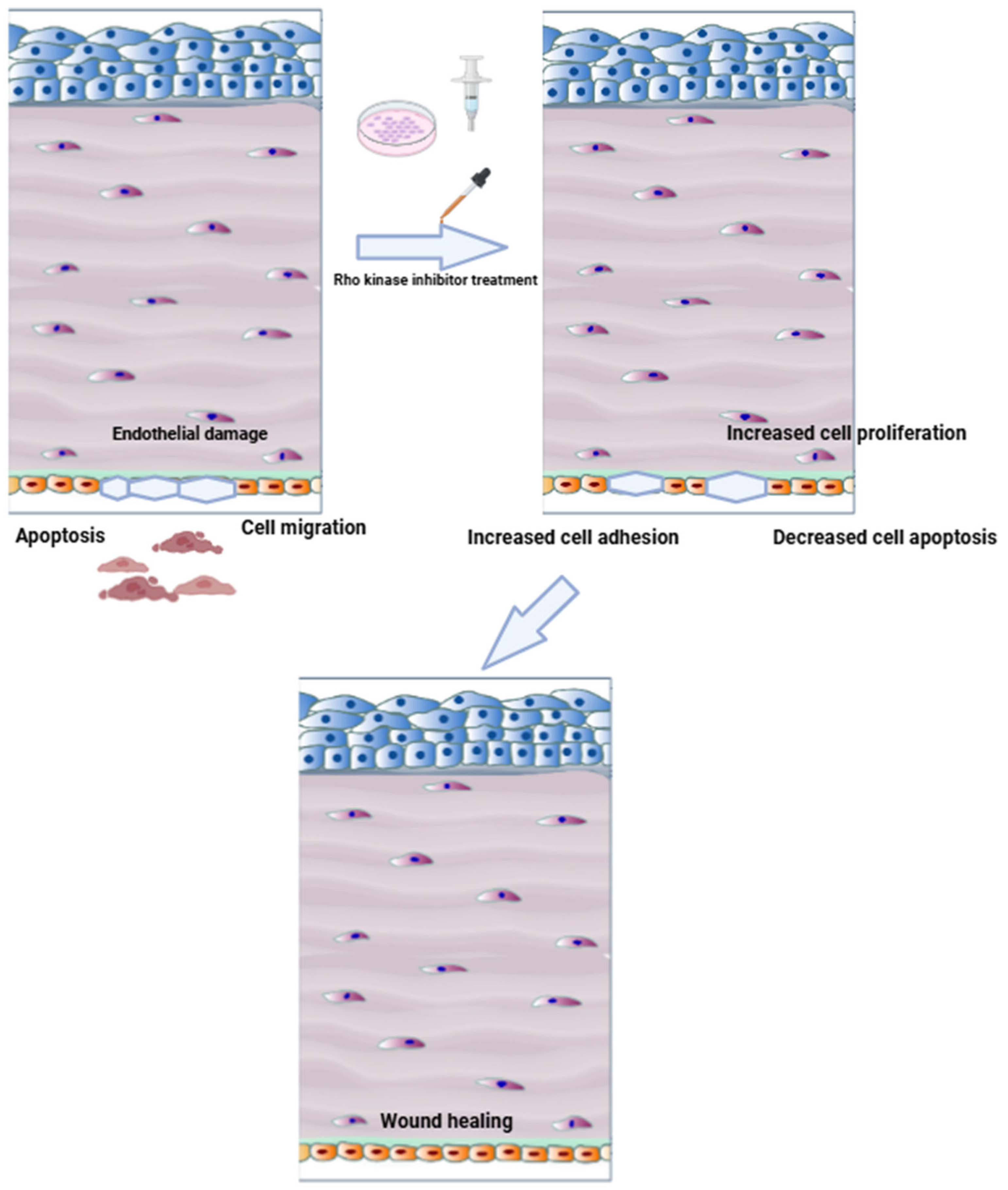

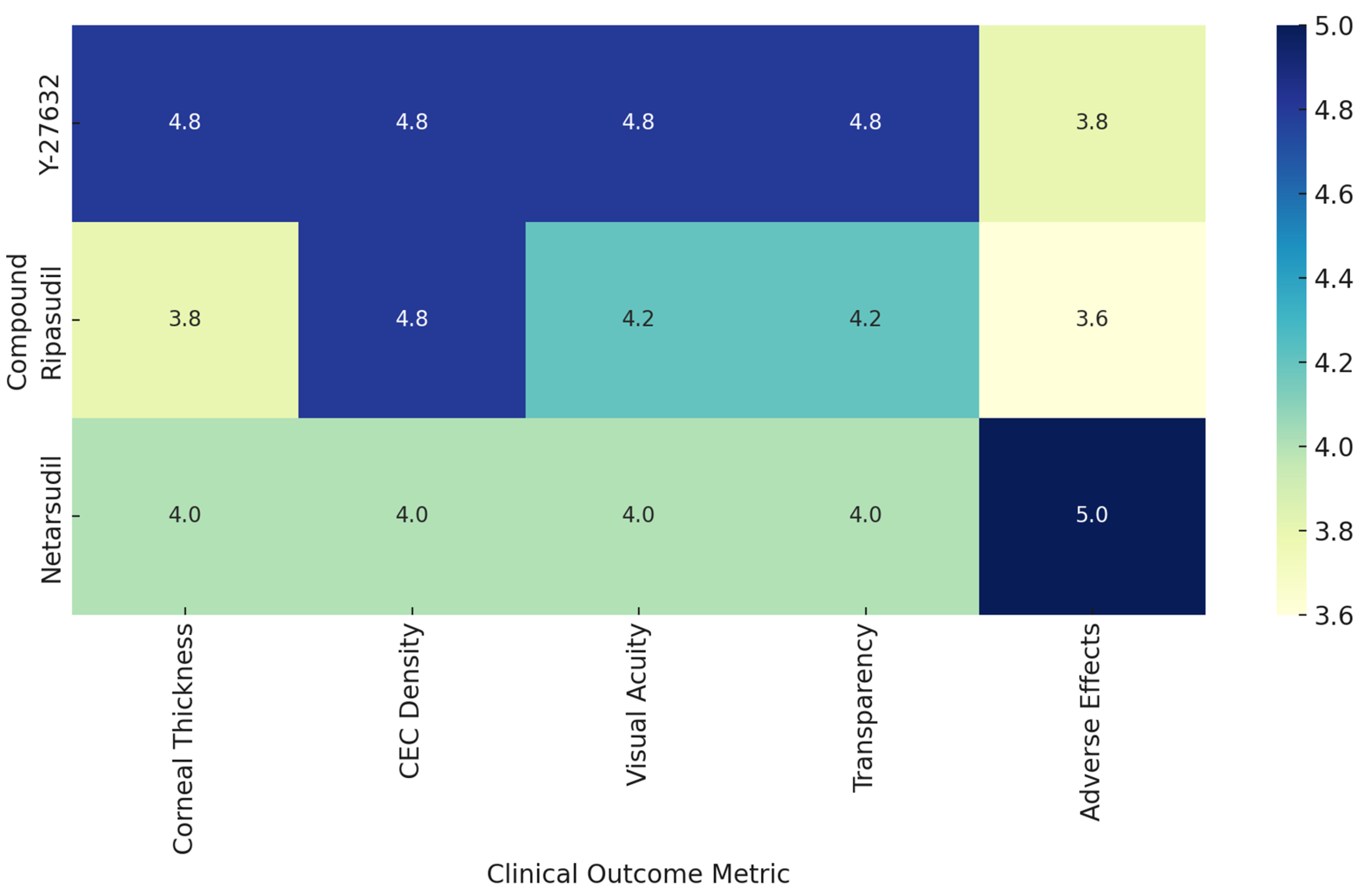
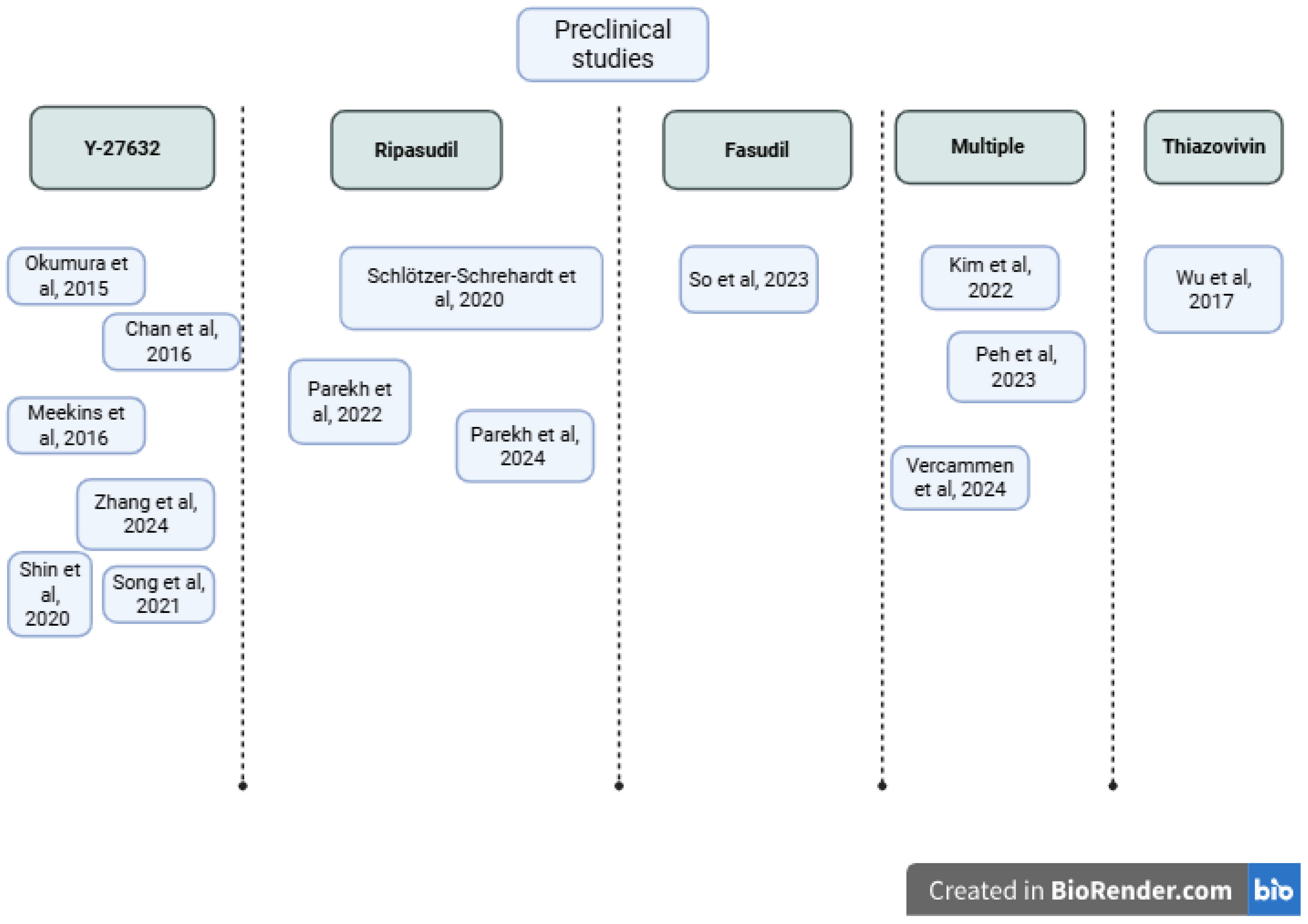
| Study, Year | Country | Design | Patients | Indication | Intervention |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kinoshita et al., 2018 [29] | Japan | Uncontrolled, single group study | 11 patients | Bullous keratopathy | Surgical transfer of cHCECs with a Rho-associated kinase inhibitor (Y-27632) into the anterior chamber |
| Macsai et al., 2019 [13] | USA | Prospective, non–placebo-controlled clinical trial | 18 patients | FECD | Ripasudil after Descemet stripping only |
| Numa et al., 2020 [30] | Japan | Prospective observational study | 11 patients | Pseudophakic endothelial failure | cHCECs supplemented with Rho-associated protein kinase inhibitor (Y-27632) |
| Davies et al., 2020 [31] | USA | Case series | 4 patients | Multiple | Netarsudil |
| Price et al., 2021 [32] | USA | Prospective, double masked RCT | 29 patients | FECD | Netarsudil |
| Fujimoto et al., 2021 [33] | Japan | Retrospective observational study | 26 patients (33 eyes) | Pseudophakic endothelial failure | Ripasudil |
| Fujimoto et al., 2021 [34] | Japan | Retrospective observational study | 24 patients | FECD | Ripasudil |
| Menzel-Severing et al., 2022 [35] | Germany | Case series | 3 patients | FECD | Transcorneal freezing and Ripasudil |
| Antonini et al., 2022 [36] | Italy | Case series | 3 patients | FECD | Ripasudil |
| Holland et al., 2023 [37] | USA | Prospective, randomized, double-masked study | 22 patients | Multiple | Intracameral injection of CECs + Y-27632 |
| Tomioka et al., 2023 [38] | Japan | Case report | 1 patient | FECD | Transcorneal freezing and topical Rho kinase inhibitor |
| Kahuam-López et al., 2024 [39] | Mexico | Case report | 1 patient | LSCD | Ripasudil |
| Lavy et al., 2024 [40] | Japan | Single-center retrospective cohort study | 16 patients | Multiple | Ripasudil |
| Ueno et al., 2024 [41] | Japan | Multicenter, double-blind physician-initiated phase II clinical trial | 29 eyes | Bullous keratopathy | Surgical transfer of cHCECs with a Rho-associated kinase inhibitor (Y-27632) into the anterior chamber |
| Alkharashi et al., 2024 [42] | Saudi Arabia | Prospective, non-randomized, non-blinded comparative study | 43 patients | Pseudophakic endothelial failure | Ripasudil |
| Erdinest et al., 2025 [43] | Israel | Case series | 3 patients | Multiple | Ripasudil |
| Keeratidamkerngsakul et al., 2025 [44] | Thailand | Randomized controlled trial | 31 patients | FECD | Ripasudil |
| Indication | Study | Primary Outcomes | Secondary Outcomes | Key Efficacy Results | Additional Outcomes | Safety |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bullous keratopathy | [29] | Corneal transparency, CEC density >500 cells/mm2 | Corneal thickness <630 µm, BCVA +2 lines | Corneal transparency 100%; CEC mean 1924 cells/mm2 (range 947–2833) | CT <630 μm in 91% (mean 549 μm); BCVA ↑ ≥2 lines in 82% | No adverse effects |
| [41] | CEC density ≥1000 cells/mm2 at 24 weeks | Corneal thickness, edema, BCVA | 94.1% achieved target CEC; BCVA 100%; CCT improved; edema resolved | CT <630 μm in 82.4%; ΔCT −187.4 μm; BCVA ↑ in 100% | Eye pain (33.3%), IOP ↑ (14.8%) | |
| Fuchs distrophy | [32] | Change in central corneal thickness | CDVA, FECD disability score | CCT reduced by 26 µm at 3 months; CDVA +1.6 lines | Scotopic CDVA ↑ by +1.6 lines; no change in disability score | One withdrawal due to epithelial bullae |
| [13] | Pachymetry, ECD, VA to 20/40 | ECD >1000, BCVA ≥20/50, haze-free | All achieved 20/40 VA by 2 months; CCT and ECD improved | - | No adverse effects | |
| [34] | LogMAR VA, CCT, TCT | Mean VA: 0.024; CCT: 0.972; TCT: 0.970 at 1 month | - | Not assessed | ||
| [37] | Safety | Change in CCT and BCVA | CCT ↓ 133.4 µm (–17.74%); BCVA ↑ 0.662 logMAR; 89% had ≥3-line improvement | BAT ↑ 0.97 logMAR; ECD ↑ ~823 cells/mm2; no dose–response | Mild/moderate TEAEs; transient IOP ↑ (5/22); 1 unrelated SAE | |
| [44] | Central ECD loss at 3 months | Paracentral ECD loss, CCT change ratio | ECD ↑ by 145 cells/mm2; paracentral loss ↓ to 0.4%; CCT stable | Central ECD ↑ by +145 cells/mm2; paracentral loss ↓ to 0.4%; stable densitometry | Transient conjunctival erythema | |
| Pseudophakic endothelial failure | [42] | CCT and ECD | BCVA | CCT change: 0.9%; ECD loss: 4.5%; BCVA improved from 0.70 to 0.15 logMAR | BCVA ↓ from 0.70 → 0.15 LogMAR at 12 months | No adverse effects |
| [30] | ECD, CCT, BCVA | IOP, CV, % hexagonality | ECD 91%; BCVA improved to 0.046 logMAR; CV and % hexagonality improved | No IOP change; CV ↓ from 0.46 → 0.37; Hexagonality ↑ from 47% → 54% | Not assessed | |
| [33] | TCT, CCT, and ECD | - | TCT and CCT ratios improved; ECD loss reduced from 14.1% to –4.5% | - | Not assessed |
| Study | Confounding | Selection of Participants | Classification of Intervention | Deviations from Intended Interventions | Missing Data | Measurement of Outcomes | Selection of Reported Results | Overall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ueno et al. [41] | Serious | Moderate | Low | Low | Moderate | Low | Low | Moderate |
| Macsai et al. [13] | Serious | Moderate | Low | Moderate | Low/moderate | Low | Low | Moderate |
| Alkharashi et al. [42] | Serious | Moderate | Low | Moderate | Low | Low | Low | Moderate |
| Fujimoto et al. [33] | Low/moderate | Low | Low | Low | Moderate | Low | Low | Low |
| Lavy et al. [40] | Low/moderate | Low | Low | Low | Moderate | Low | Low | Low |
| Fujimoto et al. [34] | Moderate/serious | Serious | Low | Moderate | Moderate | Low | Low | Moderate |
| Study | Randomization Process | Deviations from Intended Interventions | Missing Outcome Data | Measurement of the Outcome | Reported Results | Overall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Price et al. [32] | Low | Low | Moderate | Low | Low | Low |
| Holland et al. [37] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| Keeratidamkerngsaku et al. [44] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| Study | D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 | D5 | D6 | D7 | D8 | D9 | D10 | Overall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Okumura et al. [45] | Unclear | Low | Unclear | Unclear | Low | Unclear | Unclear | Low | Low | Low | Low/Moderate |
| Meekins et al. [9] | Unclear | Low | Unclear | Unclear | Low | Unclear | Unclear | Low | Low | Low | Moderate |
| Song et al. [54] | Unclear | Low | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Low | Low | High | Moderate/High |
| So et al. [55] | Unclear | Low | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Low | Unclear | High | Moderate/High |
| Zhang et al. [56] | Unclear | Low | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Low | Low | Low | Moderate |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghenciu, L.A.; Andrei, D.; Borza, C.; Iacob, R.; Stoicescu, E.R.; Bolintineanu, S.L.; Iacob, D.; Haţegan, O.A. Therapeutic Potential of Rho Kinase Inhibitors in Corneal Disease: A Systematic Review of Preclinical and Clinical Studies. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1602. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071602
Ghenciu LA, Andrei D, Borza C, Iacob R, Stoicescu ER, Bolintineanu SL, Iacob D, Haţegan OA. Therapeutic Potential of Rho Kinase Inhibitors in Corneal Disease: A Systematic Review of Preclinical and Clinical Studies. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(7):1602. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071602
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhenciu, Laura Andreea, Diana Andrei, Claudia Borza, Roxana Iacob, Emil Robert Stoicescu, Sorin Lucian Bolintineanu, Daniela Iacob, and Ovidiu Alin Haţegan. 2025. "Therapeutic Potential of Rho Kinase Inhibitors in Corneal Disease: A Systematic Review of Preclinical and Clinical Studies" Biomedicines 13, no. 7: 1602. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071602
APA StyleGhenciu, L. A., Andrei, D., Borza, C., Iacob, R., Stoicescu, E. R., Bolintineanu, S. L., Iacob, D., & Haţegan, O. A. (2025). Therapeutic Potential of Rho Kinase Inhibitors in Corneal Disease: A Systematic Review of Preclinical and Clinical Studies. Biomedicines, 13(7), 1602. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071602







