IDH1 Mutation Impacts DNA Repair Through ALKBH2 Rendering Glioblastoma Cells Sensitive to Artesunate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Drug Treatment
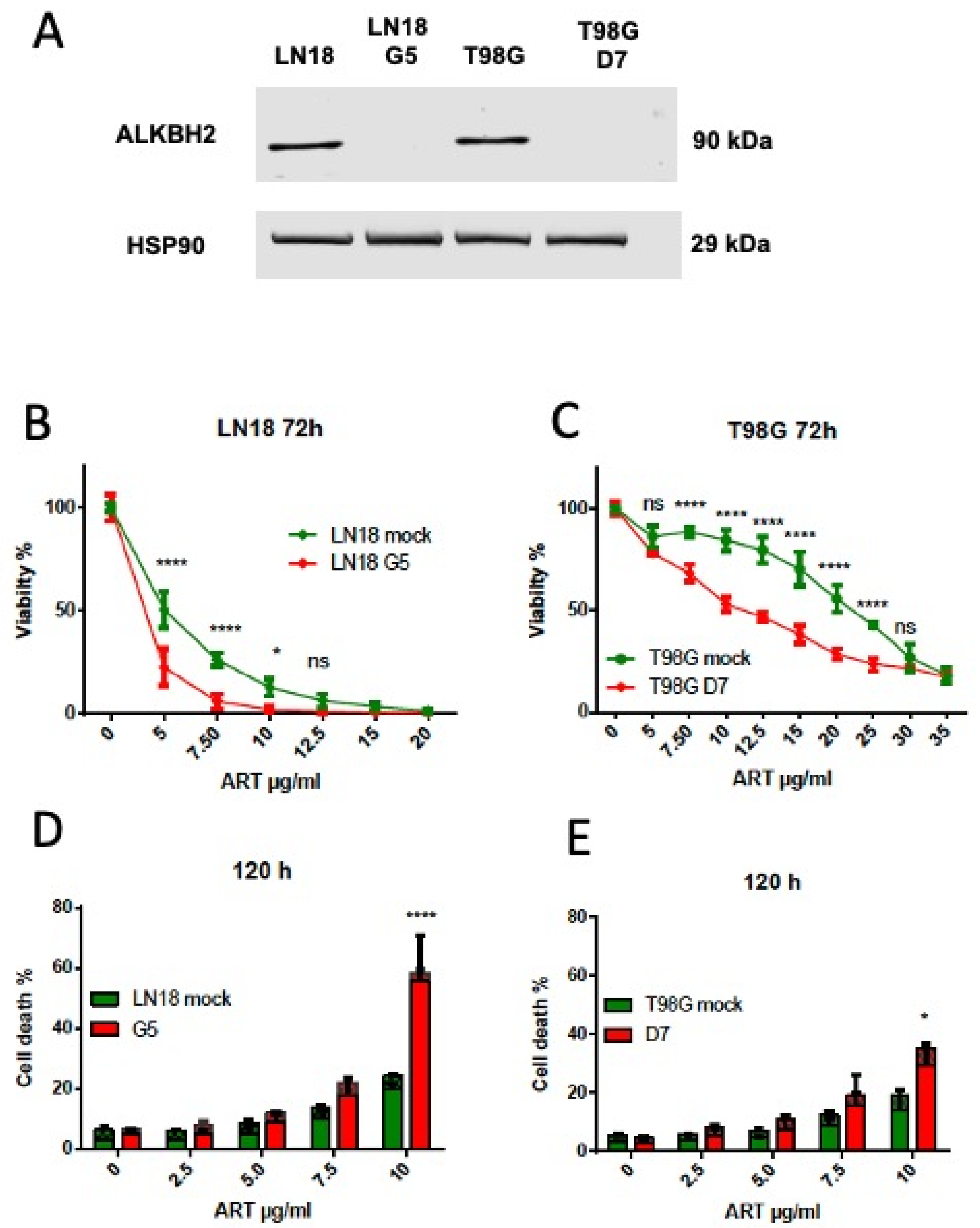
2.2. Generation of Knockout and Western Blots
2.3. Cytotoxicity Assays
2.4. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. IDH1 Mutation Renders Cells More Sensitive to Artesunate
3.2. 2-Hydroxyglutarate Increases the Toxicity of Artesunate
3.3. ALKBH2 Knockout Causes an Increase in Artesunate Toxicity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Wesseling, P.; Brat, D.J.; Cree, I.A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Hawkins, C.; Ng, H.K.; Pfister, S.M.; Reifenberger, G.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Neuro Oncol. 2021, 23, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, L.; Xiong, P.; Luo, Y.; Bu, X.; Qian, S.; Zhong, W.; Lv, S. Association between IDH1/2 mutations and brain glioma grade. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 5405–5409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.J.; Castro, L.N.G.; McBrayer, S.; Weller, M.; Cloughesy, T.; Portnow, J.; Andronesi, O.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S.; Baumert, B.G.; Berger, M.S.; et al. Isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) mutant gliomas: A Society for Neuro-Oncology (SNO) consensus review on diagnosis, management, and future directions. Neuro Oncol. 2023, 25, 4–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuss, D.E.; Kratz, A.; Sahm, F.; Capper, D.; Schrimpf, D.; Koelsche, C.; Hovestadt, V.; Bewerunge-Hudler, M.; Jones, D.T.; Schittenhelm, J.; et al. Adult IDH wild type astrocytomas biologically and clinically resolve into other tumor entities. Acta Neuropathol. 2015, 130, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mardis, E.R.; Ding, L.; Dooling, D.J.; Larson, D.E.; McLellan, M.D.; Chen, K.; Koboldt, D.C.; Fulton, R.S.; Delehaunty, K.D.; McGrath, S.D.; et al. Recurring mutations found by sequencing an acute myeloid leukemia genome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1058–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, K.E.; Bittinger, M.A.; Su, S.M.; Fantin, V.R. Cancer-associated IDH mutations: Biomarker and therapeutic opportunities. Oncogene 2010, 29, 6409–6417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Guan, K.L. IDH1 mutant structures reveal a mechanism of dominant inhibition. Cell Res. 2010, 20, 1279–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.L.; Holmen, S.L.; Colman, H. IDH1 and IDH2 mutations in gliomas. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2013, 13, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.K.; Parachoniak, C.A.; Bardeesy, N. IDH mutations in liver cell plasticity and biliary cancer. Cell Cycle 2014, 13, 3176–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, H.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.; Li, M.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, T. Methylation associated genes contribute to the favorable prognosis of gliomas with isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 mutation. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 2745–2755. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, R.; Yeoh, K.K.; Tian, Y.M.; Hillringhaus, L.; Bagg, E.A.; Rose, N.R.; Leung, I.K.; Li, X.S.; Woon, E.C.; Yang, M.; et al. The oncometabolite 2-hydroxyglutarate inhibits histone lysine demethylases. EMBO Rep. 2011, 12, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, L.; White, D.W.; Gross, S.; Bennett, B.D.; Bittinger, M.A.; Driggers, E.M.; Fantin, V.R.; Jang, H.G.; Jin, S.; Keenan, M.C.; et al. Cancer-associated IDH1 mutations produce 2-hydroxyglutarate. Nature 2009, 462, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andronesi, O.C.; Kim, G.S.; Gerstner, E.; Batchelor, T.; Tzika, A.A.; Fantin, V.R.; Heiden, M.G.V.; Sorensen, A.G. Detection of 2-hydroxyglutarate in IDH-mutated glioma patients by in vivo spectral-editing and 2D correlation magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 116ra4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, C.; Hentschel, B.; Wick, W.; Capper, D.; Felsberg, J.; Simon, M.; Westphal, M.; Schackert, G.; Meyermann, R.; Pietsch, T.; et al. Patients with IDH1 wild type anaplastic astrocytomas exhibit worse prognosis than IDH1-mutated glioblastomas, and IDH1 mutation status accounts for the unfavorable prognostic effect of higher age: Implications for classification of gliomas. Acta Neuropathol. 2010, 120, 707–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Bent, M.J.; Dubbink, H.J.; Marie, Y.; Brandes, A.A.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Wesseling, P.; Frenay, M.; Tijssen, C.C.; Lacombe, D.; Idbaih, A.; et al. IDH1 and IDH2 mutations are prognostic but not predictive for outcome in anaplastic oligodendroglial tumors: A report of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Brain Tumor Group. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 1597–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.B.; Dong, D.F.; Wang, M.D.; Gao, K. IDH1 overexpression induced chemotherapy resistance and IDH1 mutation enhanced chemotherapy sensitivity in Glioma cells in vitro and in vivo. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houillier, C.; Wang, X.; Kaloshi, G.; Mokhtari, K.; Guillevin, R.; Laffaire, J.; Paris, S.; Boisselier, B.; Idbaih, A.; Laigle-Donadey, F.; et al. IDH1 or IDH2 mutations predict longer survival and response to temozolomide in low-grade gliomas. Neurology 2010, 75, 1560–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, A.N.; Lai, A.; Li, S.; Pope, W.B.; Teixeira, S.; Harris, R.J.; Woodworth, D.C.; Nghiemphu, P.L.; Cloughesy, T.F.; Ellingson, B.M. Increased sensitivity to radiochemotherapy in IDH1 mutant glioblastoma as demonstrated by serial quantitative MR volumetry. Neuro-Oncology 2014, 16, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Chou, A.P.; Chen, W.; Chen, R.; Deng, Y.; Phillips, H.S.; Selfridge, J.; Zurayk, M.; Lou, J.J.; Everson, R.G.; et al. Overexpression of isocitrate dehydrogenase mutant proteins renders glioma cells more sensitive to radiation. Neuro-Oncology 2013, 15, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohba, S.; Mukherjee, J.; See, W.L.; Pieper, R.O. Mutant IDH1-driven cellular transformation increases RAD51-mediated homologous recombination and temozolomide resistance. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 4836–4844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulkowski, P.L.; Corso, C.D.; Robinson, N.D.; Scanlon, S.E.; Purshouse, K.R.; Bai, H.; Liu, Y.; Sundaram, R.K.; Hegan, D.C.; Fons, N.R.; et al. 2-Hydroxyglutarate produced by neomorphic IDH mutations suppresses homologous recombination and induces PARP inhibitor sensitivity. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaal2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubbink, H.J.; Taal, W.; van Marion, R.; Kros, J.M.; van Heuvel, I.; Bromberg, J.E.; Zonnenberg, B.A.; Zonnenberg, C.B.; Postma, T.J.; Gijtenbeek, J.M.; et al. IDH1 mutations in low-grade astrocytomas predict survival but not response to temozolomide. Neurology 2009, 73, 1792–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Sun, B.; Shi, W.; Zuo, H.; Cui, D.; Ni, L.; Chen, J. Decreasing GSH and increasing ROS in chemosensitivity gliomas with IDH1 mutation. Tumour Biol. J. Int. Soc. Oncodev. Biol. Med. 2015, 36, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, A.; Cruz, M.M.A.; Jyotsana, N.; Sharma, A.; Yun, H.; Gorlich, K.; Wichmann, M.; Schwarzer, A.; Preller, M.; Thol, F.; et al. Mutant IDH1 promotes leukemogenesis in vivo and can be specifically targeted in human AML. Blood 2013, 122, 2877–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohrenz, I.V.; Antonietti, P.; Pusch, S.; Capper, D.; Balss, J.; Voigt, S.; Weissert, S.; Mukrowsky, A.; Frank, J.; Senft, C.; et al. Isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 mutant R132H sensitizes glioma cells to BCNU-induced oxidative stress and cell death. Apoptosis Int. J. Program. Cell Death 2013, 18, 1416–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, M.R.; Liu, Y.; Neltner, J.; Pu, H.; Morris, A.; Sunkara, M.; Pittman, T.; Kyprianou, N.; Horbinski, C. Autophagy and oxidative stress in gliomas with IDH1 mutations. Acta Neuropathol. 2014, 127, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wu, J.; Ma, S.; Zhang, L.; Yao, J.; Hoadley, K.A.; Wilkerson, M.D.; Perou, C.M.; Guan, K.L.; Ye, D.; et al. Oncometabolite D-2-Hydroxyglutarate Inhibits ALKBH DNA Repair Enzymes and Sensitizes IDH Mutant Cells to Alkylating Agents. Cell Rep. 2015, 13, 2353–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klayman, D.L. Qinghaosu (artemisinin): An antimalarial drug from China. Science 1985, 228, 1049–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efferth, T.; Kahl, S.; Paulus, K.; Adams, M.; Rauh, R.; Boechzelt, H.; Hao, X.; Kaina, B.; Bauer, R. Phytochemistry and pharmacogenomics of natural products derived from traditional Chinese medicine and Chinese materia medica with activity against tumor cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strik, H.; Efferth, T.; Kaina, B. Artesunate in glioblastoma therapy: Case reports and review of clinical studies. Phytomed. Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2024, 123, 155274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, S.A.; Efferth, T.; Asangani, I.A.; Allgayer, H. First evidence that the antimalarial drug artesunate inhibits invasion and in vivo metastasis in lung cancer by targeting essential extracellular proteases. Int. J. Cancer J. Int. Du Cancer 2010, 127, 1475–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konkimalla, V.B.; McCubrey, J.A.; Efferth, T. The role of downstream signaling pathways of the epidermal growth factor receptor for Artesunate’s activity in cancer cells. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2009, 9, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sertel, S.; Eichhorn, T.; Sieber, S.; Sauer, A.; Weiss, J.; Plinkert, P.K.; Efferth, T. Factors determining sensitivity or resistance of tumor cell lines towards artesunate. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2010, 185, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sertel, S.; Eichhorn, T.; Simon, C.H.; Plinkert, P.K.; Johnson, S.W.; Efferth, T. Pharmacogenomic identification of c-Myc/Max-regulated genes associated with cytotoxicity of artesunate towards human colon, ovarian and lung cancer cell lines. Molecules 2010, 15, 2886–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell, R.; Pfeffer, U.; Vene, R.; Anfosso, L.; Forlani, A.; Albini, A.; Efferth, T. Inhibition of angiogenesis in vivo and growth of Kaposi’s sarcoma xenograft tumors by the anti-malarial artesunate. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2004, 68, 2359–2366. [Google Scholar]
- Soomro, S.; Langenberg, T.; Mahringer, A.; Konkimalla, V.B.; Horwedel, C.; Holenya, P.; Brand, A.; Cetin, C.; Fricker, G.; Dewerchin, M.; et al. Design of novel artemisinin-like derivatives with cytotoxic and anti-angiogenic properties. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2011, 15, 1122–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdelle, N.; Nikolova, T.; Quiros, S.; Efferth, T.; Kaina, B. Artesunate induces oxidative DNA damage, sustained DNA double-strand breaks, and the ATM/ATR damage response in cancer cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, 2224–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaney, J.C.; Smeester, L.; Wong, C.; Frick, L.E.; Taghizadeh, K.; Wishnok, J.S.; Drennan, C.L.; Samson, L.D.; Essigmann, J.M. AlkB reverses etheno DNA lesions caused by lipid oxidation in vitro and in vivo. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2005, 12, 855–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringvoll, J.; Moen, M.N.; Nordstrand, L.M.; Meira, L.B.; Pang, B.; Bekkelund, A.; Dedon, P.C.; Bjelland, S.; Samson, L.D.; Falnes, P.O.; et al. AlkB homologue 2-mediated repair of ethenoadenine lesions in mammalian DNA. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 4142–4149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berte, N.; Lokan, S.; Eich, M.; Kim, E.; Kaina, B. Artesunate enhances the therapeutic response of glioma cells to temozolomide by inhibition of homologous recombination and senescence. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 67235–67250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermisson, M.; Klumpp, A.; Wick, W.; Wischhusen, J.; Nagel, G.; Roos, W.; Kaina, B.; Weller, M. O6-methylguanine DNA methyltransferase and p53 status predict temozolomide sensitivity in human malignant glioma cells. J. Neurochem. 2006, 96, 766–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birner, P.; Pusch, S.; Christov, C.; Mihaylova, S.; Toumangelova-Uzeir, K.; Natchev, S.; Schoppmann, S.F.; Tchorbanov, A.; Streubel, B.; Tuettenberg, J.; et al. Mutant IDH1 inhibits PI3K/Akt signaling in human glioma. Cancer 2014, 120, 2440–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltzig, L.; Schwarzenbach, C.; Leukel, P.; Frauenknecht, K.B.M.; Sommer, C.; Tancredi, A.; Hegi, M.E.; Christmann, M.; Kaina, B. Senescence Is the Main Trait Induced by Temozolomide in Glioblastoma Cells. Cancers 2022, 14, 2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turcan, S.; Rohle, D.; Goenka, A.; Walsh, L.A.; Fang, F.; Yilmaz, E.; Campos, C.; Fabius, A.W.; Lu, C.; Ward, P.S.; et al. IDH1 mutation is sufficient to establish the glioma hypermethylator phenotype. Nature 2012, 483, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Xu, Z.; Peng, J.; Zhang, M. The AlkB Family: Potential Prognostic Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets in Glioblastoma. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 847821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunse, L.; Pusch, S.; Bunse, T.; Sahm, F.; Sanghvi, K.; Friedrich, M.; Alansary, D.; Sonner, J.K.; Green, E.; Deumelandt, K.; et al. Suppression of antitumor T cell immunity by the oncometabolite (R)-2-hydroxyglutarate. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1192–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupp, R.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Weller, M.; Fisher, B.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Belanger, K.; Brandes, A.A.; Marosi, C.; Bogdahn, U.; et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pentsova, E.I.; Reiner, A.S.; Panageas, K.S.; DeAngelis, L.M. Anaplastic astrocytoma and non-1p/19q co-deleted anaplastic oligoastrocytoma: Long-term survival, employment, and performance status of survivors. Neuro-Oncol. Pract. 2016, 3, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, T.; Trewick, S.C.; Koivisto, P.; Bates, P.A.; Lindahl, T.; Sedgwick, B. Reversal of DNA alkylation damage by two human dioxygenases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 16660–16665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aas, P.A.; Otterlei, M.; Falnes, P.O.; Vagbo, C.B.; Skorpen, F.; Akbari, M.; Sundheim, O.; Bjoras, M.; Slupphaug, G.; Seeberg, E.; et al. Human and bacterial oxidative demethylases repair alkylation damage in both RNA and DNA. Nature 2003, 421, 859–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaina, B. Temozolomide, Procarbazine and Nitrosoureas in the Therapy of Malignant Gliomas: Update of Mechanisms, Drug Resistance and Therapeutic Implications. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 7442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannessen, T.C.; Prestegarden, L.; Grudic, A.; Hegi, M.E.; Tysnes, B.B.; Bjerkvig, R. The DNA repair protein ALKBH2 mediates temozolomide resistance in human glioblastoma cells. Neuro-Oncology 2013, 15, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, S.A.P.; Li, D.; Wetmore, S.D. Insights into the Direct Oxidative Repair of Etheno Lesions: MD and QM/MM Study on the Substrate Scope of ALKBH2 and AlkB. DNA Repair 2020, 96, 102944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- el Ghissassi, F.; Barbin, A.; Nair, J.; Bartsch, H. Formation of 1,N6-ethenoadenine and 3,N4-ethenocytosine by lipid peroxidation products and nucleic acid bases. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 1995, 8, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winczura, A.; Czubaty, A.; Winczura, K.; Maslowska, K.; Nalecz, M.; Dudzinska, D.A.; Saparbaev, M.; Staron, K.; Tudek, B. Lipid peroxidation product 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal modulates base excision repair in human cells. DNA Repair 2014, 22, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swenberg, J.A.; Lu, K.; Moeller, B.C.; Gao, L.; Upton, P.B.; Nakamura, J.; Starr, T.B. Endogenous versus exogenous DNA adducts: Their role in carcinogenesis, epidemiology, and risk assessment. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 120 (Suppl. 1), S130–S145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.C.; Lam, E.; Roos, W.P.; Zdzienicka, M.Z.; Kaina, B.; Efferth, T. Artesunate derived from traditional Chinese medicine induces DNA damage and repair. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 4347–4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eling, N.; Reuter, L.; Hazin, J.; Hamacher-Brady, A.; Brady, N.R. Identification of artesunate as a specific activator of ferroptosis in pancreatic cancer cells. Oncoscience 2015, 2, 517–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Shou, L.M.; Lin, F.; Duan, W.M.; Wu, M.Y.; Xie, X.; Xie, Y.F.; Li, W.; Tao, M. Artesunate induces G2/M cell cycle arrest through autophagy induction in breast cancer cells. Anticancer Drugs 2014, 25, 652–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpel-Massler, G.; Westhoff, M.A.; Kast, R.E.; Dwucet, A.; Nonnenmacher, L.; Wirtz, C.R.; Debatin, K.M.; Halatsch, M.E. Artesunate enhances the antiproliferative effect of temozolomide on U87MG and A172 glioblastoma cell lines. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2014, 14, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltzig, L.; Christmann, M.; Kaina, B. Abrogation of Cellular Senescence Induced by Temozolomide in Glioblastoma Cells: Search for Senolytics. Cells 2022, 11, 2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demaria, M.; O’Leary, M.N.; Chang, J.; Shao, L.; Liu, S.; Alimirah, F.; Koenig, K.; Le, C.; Mitin, N.; Deal, A.M.; et al. Cellular Senescence Promotes Adverse Effects of Chemotherapy and Cancer Relapse. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chojak, R.; Fares, J.; Petrosyan, E.; Lesniak, M.S. Cellular senescence in glioma. J. Neurooncol. 2023, 164, 11–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, F.; Wu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Cai, Y.; Huang, S.; He, N.; Hu, Z.; et al. Artesunate induces autophagy dependent apoptosis through upregulating ROS and activating AMPK-mTOR-ULK1 axis in human bladder cancer cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2020, 331, 109273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Liao, L.; Liu, J.; Zhao, J.; Tang, Q.; Liao, Y. Lower dose of metformin combined with artesunate induced autophagy-dependent apoptosis of glioblastoma by activating ROS-AMPK-mTOR axis. Exp. Cell Res. 2023, 430, 113691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Xie, L.H.; Haeberle, A.; Zhang, J.; Weina, P. The evaluation of radiolabeled artesunate on tissue distribution in rats and protein binding in humans. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2006, 75, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemmer, L.; Martins, Y.C.; Zanini, G.M.; Frangos, J.A.; Carvalho, L.J. Artemether and artesunate show the highest efficacies in rescuing mice with late-stage cerebral malaria and rapidly decrease leukocyte accumulation in the brain. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 1383–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aasland, D.; Gotzinger, L.; Hauck, L.; Berte, N.; Meyer, J.; Effenberger, M.; Schneider, S.; Reuber, E.E.; Roos, W.P.; Tomicic, M.T.; et al. Temozolomide Induces Senescence and Repression of DNA Repair Pathways in Glioblastoma Cells via Activation of ATR-CHK1, p21, and NF-kappaB. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kast, R.E.; Karpel-Massler, G.; Halatsch, M.E. CUSP9* treatment protocol for recurrent glioblastoma: Aprepitant, artesunate, auranofin, captopril, celecoxib, disulfiram, itraconazole, ritonavir, sertraline augmenting continuous low dose temozolomide. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 8052–8082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Switzeny, O.; Pusch, S.; Christmann, M.; Kaina, B. IDH1 Mutation Impacts DNA Repair Through ALKBH2 Rendering Glioblastoma Cells Sensitive to Artesunate. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1479. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061479
Switzeny O, Pusch S, Christmann M, Kaina B. IDH1 Mutation Impacts DNA Repair Through ALKBH2 Rendering Glioblastoma Cells Sensitive to Artesunate. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(6):1479. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061479
Chicago/Turabian StyleSwitzeny, Olivier, Stefan Pusch, Markus Christmann, and Bernd Kaina. 2025. "IDH1 Mutation Impacts DNA Repair Through ALKBH2 Rendering Glioblastoma Cells Sensitive to Artesunate" Biomedicines 13, no. 6: 1479. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061479
APA StyleSwitzeny, O., Pusch, S., Christmann, M., & Kaina, B. (2025). IDH1 Mutation Impacts DNA Repair Through ALKBH2 Rendering Glioblastoma Cells Sensitive to Artesunate. Biomedicines, 13(6), 1479. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061479








