Improved Translational Relevance of In Vitro Fibrosis Models by Integrating IOX2-Mediated Hypoxia-Mimicking Pathways
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
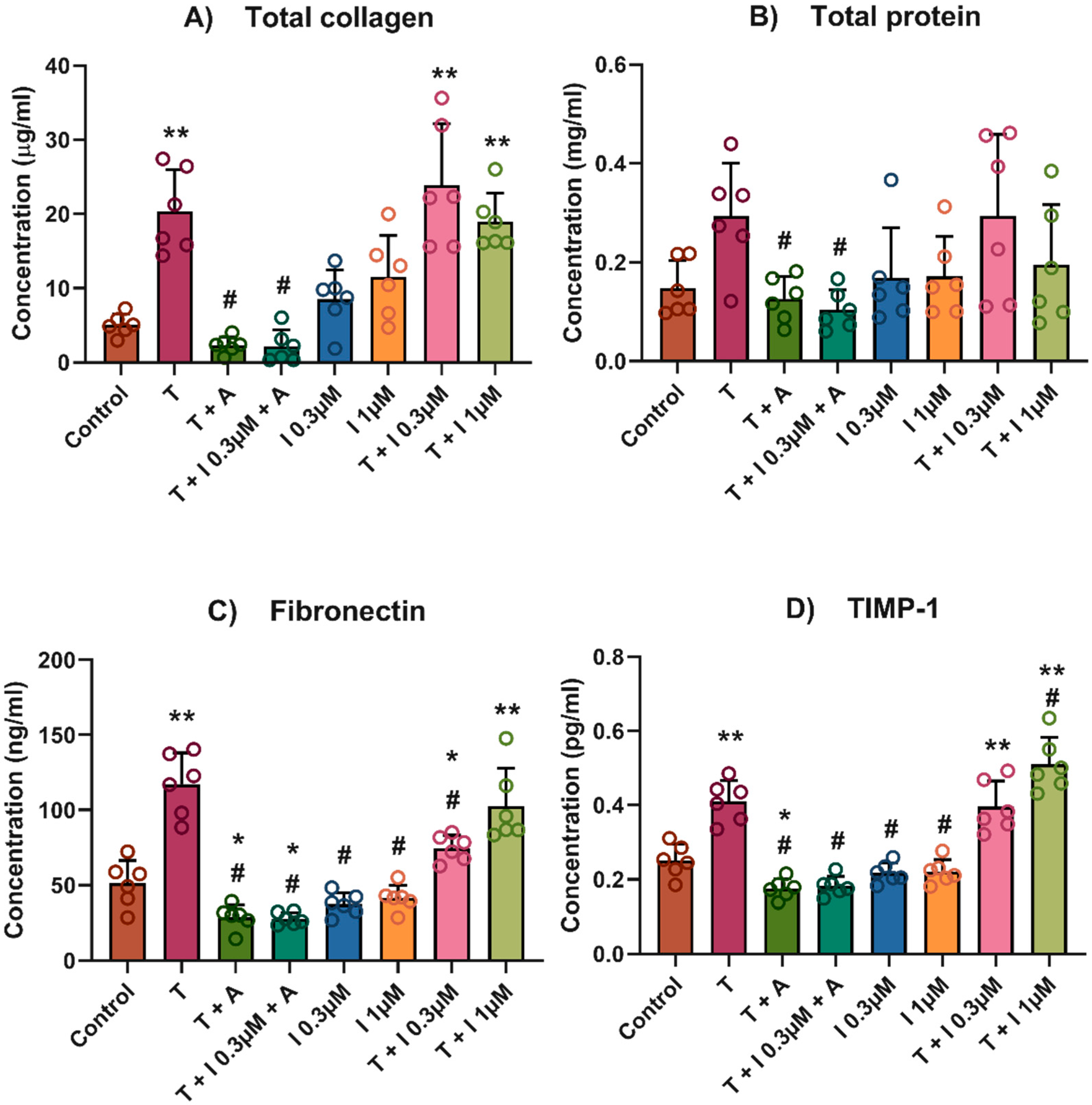
2.2. Total Collagen, Total Protein and Conditioned Media
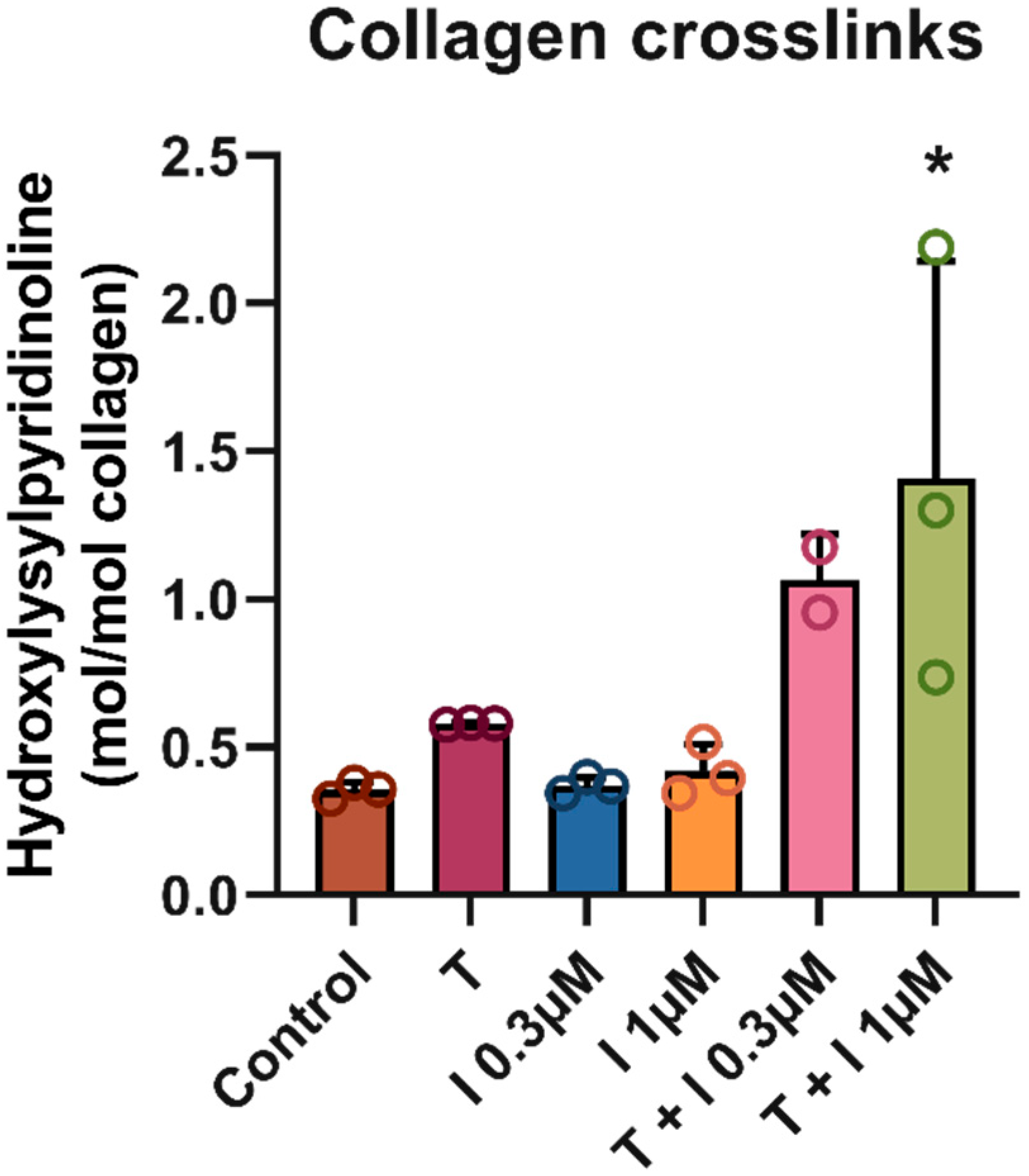
2.3. Crosslinks
2.4. Statistics
2.5. Cell Viability and Toxicity
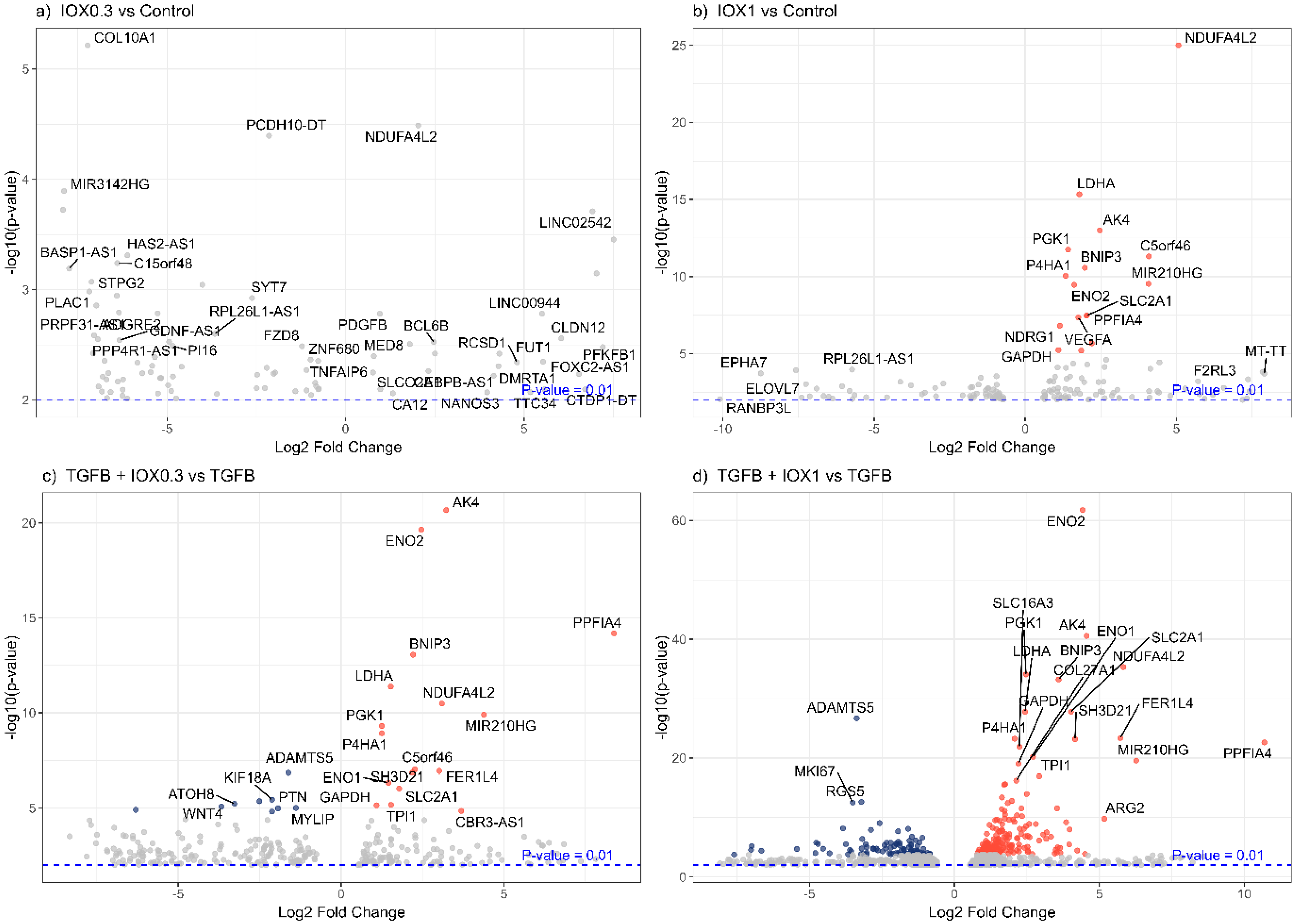
2.6. Transcriptomics
2.6.1. Data Processing
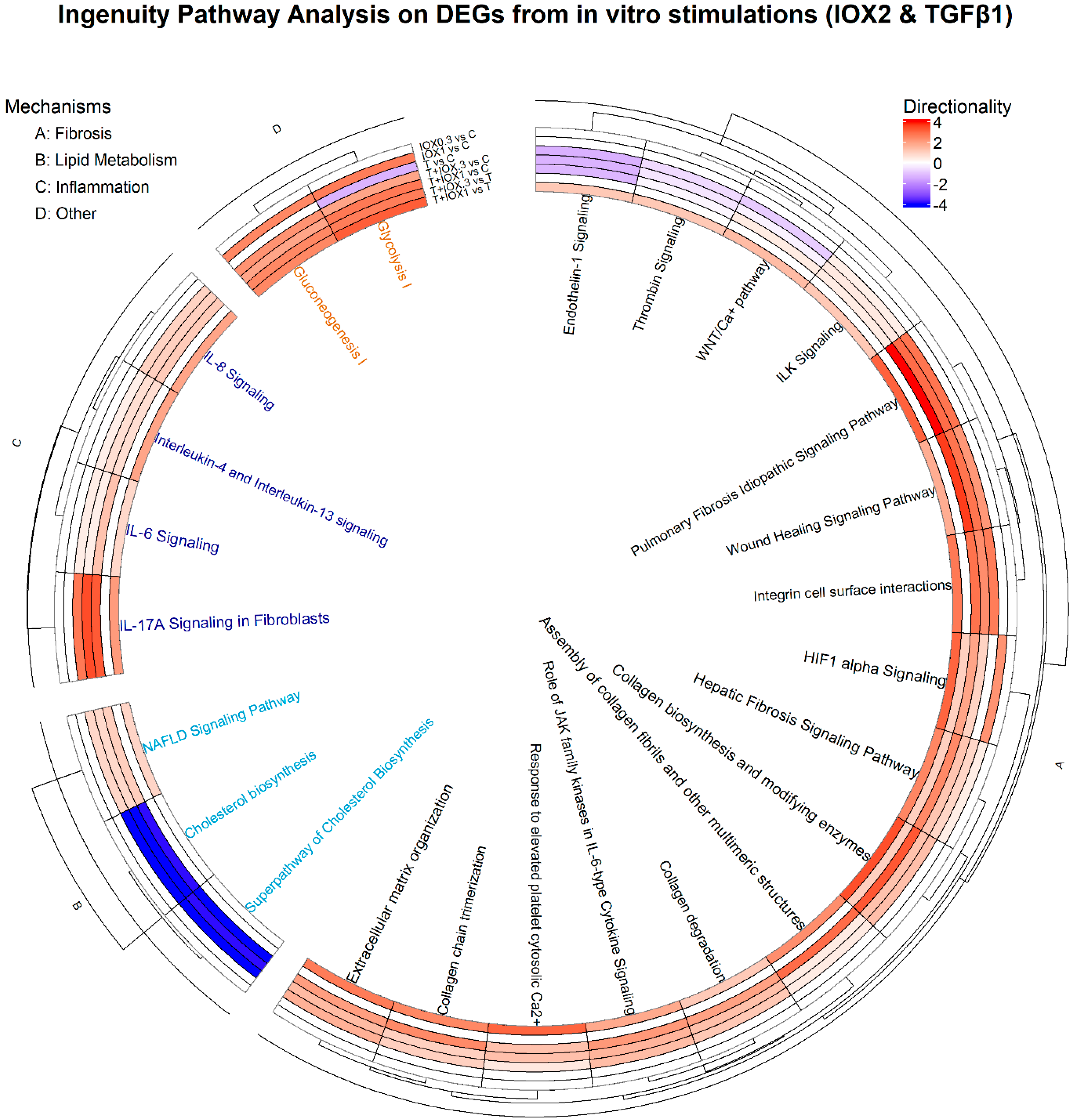
2.6.2. Bioinformatics
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BMP-1 | Bone Morphogenetic Protein 1 |
| DEGs | Differentially Expressed Genes |
| DMOG | Dimethyloxallyl Glycine |
| ECM | Extracellular Matrix |
| EMT | Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition |
| HCC | Hepatocellular Carcinoma |
| HIF-1α | Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1 Alpha |
| HSC | Hepatic Stellate Cell |
| IH | Intermittent Hypoxia |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| IL-17 | Interleukin-17 |
| IPA | Ingenuity Pathway Analysis |
| IOX2 | 1-benzyl-4-hydroxy-2-oxo-1,2-dihydroquinoline-3-carbonyl)glycine |
| LOX | Lysyl Oxidase |
| LOXL2 | Lysyl Oxidase-Like 2 |
| LOXL3 | Lysyl Oxidase-Like 3 |
| MASH | Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis |
| MASLD | Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease |
| NGS | Next Generation Sequencing |
| PLOD2 | Procollagen-Lysine, 2-Oxoglutarate 5-Dioxygenase 2 |
| RNA-seq | RNA Sequencing |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| TGFβ1 | Transforming Growth Factor Beta 1 |
| VEGF | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor |
References
- Kisseleva, T.; Brenner, D. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of liver fibrosis and its regression. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, L.A.; Xu, Y.; Sanchez-Azofra, A.; Moya, E.A.; Zhang, M.P.; Crotty Alexander, L.E.; Malhotra, A.; Mesarwi, O. Duration of intermittent hypoxia impacts metabolic outcomes and severity of murine NAFLD. Front. Sleep 2023, 2, 1215944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaucher, J.; Montellier, E.; Vial, G.; Chuffart, F.; Guellerin, M.; Bouyon, S.; Lemarie, E.; Botté, Y.Y.; Dirani, A.; Ben Messaoud, R.; et al. Long-term intermittent hypoxia in mice induces inflammatory pathways implicated in sleep apnea and steatohepatitis in humans. iScience 2024, 27, 108837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paternostro, C.; David, E.; Novo, E.; Parola, M. Hypoxia, angiogenesis and liver fibrogenesis in the progression of chronic liver diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foglia, B.; Novo, E.; Protopapa, F.; Maggiora, M.; Bocca, C.; Cannito, S.; Parola, M. Hypoxia, Hypoxia-Inducible Factors and Liver Fibrosis. Cells 2021, 10, 1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Liang, S.; Lin, W.; Li, S.; Yuan, J.; Jin, M.; Nie, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhai, X.; Zhou, L.; et al. Hypoxia-induced exosomes facilitate lung pre-metastatic niche formation in hepatocellular carcinoma through the miR-4508-RFX1-IL17A-p38 MAPK-NF-κB pathway. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 19, 4744–4762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strowitzki, M.J.; Kirchberg, J.; Tuffs, C.; Schiedeck, M.; Ritter, A.S.; Biller, M.; Harnoss, J.M.; Lasitschka, F.; Schmidt, T.; Radhakrishnan, P.; et al. Loss of Prolyl-Hydroxylase 1 Protects against Biliary Fibrosis via Attenuated Activation of Hepatic Stellate Cells. Am. J. Pathol. 2018, 188, 2826–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirscherl, K.; Schläpfer, M.; Roth Z’graggen, B.; Wenger, R.H.; Booy, C.; Flury-Frei, R.; Fatzer, R.; Aloman, C.; Bartosch, B.; Parent, R.; et al. Hypoxia sensing by hepatic stellate cells leads to VEGF-dependent angiogenesis and may contribute to accelerated liver regeneration. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minville Dr, C.; Hilleret Dr, M.N.; Tamisier, R.; Aron-Wisnewsky, J.; Clement, K.; Trocme, C.; Borel, J.C.; Lévy, P.; Zarski Dr, J.P.; Pépin, J.L. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, nocturnal hypoxia, and endothelial function in patients with sleep apnea. Chest 2014, 145, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, K.; Li, S.; Qiu, W.; Fan, Z.; Li, M.; Lv, G. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1α/IL-6 axis in activated hepatic stellate cells aggravates liver fibrosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2023, 653, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd, S.M.; He, Y. Exploring Extracellular Matrix Crosslinking as a Therapeutic Approach to Fibrosis. Cells 2024, 13, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, K.J.; Copple, B.L. Role of Hypoxia-Inducible Factors in the Development of Liver Fibrosis. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol.—CMGH 2015, 1, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewidar, B.; Meyer, C.; Dooley, S.; Meindl-Beinker, N. Tgf-β in hepatic stellate cell activation and liver fibrogenesis—Updated 2019. Cells 2019, 8, 8111419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brereton, C.J.; Yao, L.; Davies, E.R.; Zhou, Y.; Vukmirovic, M.; Bell, J.A.; Wang, S.; Ridley, R.A.; Dean, L.S.N.; Andriotis, O.G.; et al. Pseudohypoxic HIF pathway activation dysregulates collagen structure-function in human lung fibrosis. Elife 2022, 11, e69348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chan, M.C.; Atasoylu, O.; Hodson, E.; Tumber, A.; Leung, I.K.; Chowdhury, R.; Gómez-Pérez, V.; Demetriades, M.; Rydzik, A.M.; Holt-Martyn, J.; et al. Potent and Selective Triazole-Based Inhibitors of the Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Prolyl-Hydroxylases with Activity in the Murine Brain. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gart, E.; van Duyvenvoorde, W.; Toet, K.; Caspers, M.P.M.; Verschuren, L.; Nielsen, M.J.; Leeming, D.J.; Souto Lima, E.; Menke, A.; Hanemaaijer, R.; et al. Butyrate Protects against Diet-Induced NASH and Liver Fibrosis and Suppresses Specific Non-Canonical TGF-β Signaling Pathways in Human Hepatic Stellate Cells. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Smith-Cortinez, N.; Fagundes, R.R.; Gomez, V.; Kong, D.; de Waart, D.R.; Heegsma, J.; Sydor, S.; Olinga, P.; de Meijer, V.E.; Taylor, C.T.; et al. Collagen release by human hepatic stellate cells requires vitamin C and is efficiently blocked by hydroxylase inhibition. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Slot-Verhoeven, A.J.; van Dura, E.A.; Attema, J.; Blauw, B.; Degroot, J.; Huizinga, T.W.; Zuurmond, A.M.; Bank, R.A. The type of collagen cross-link determines the reversibility of experimental skin fibrosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2005, 1740, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govaere, O.; Cockell, S.; Tiniakos, D.; Queen, R.; Younes, R.; Vacca, M.; Alexander, L.; Ravaioli, F.; Palmer, J.; Petta, S.; et al. Transcriptomic profiling across the nonalcoholic fatty liver disease spectrum reveals gene signatures for steatohepatitis and fibrosis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eaba4448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Gene set Enrichment Analysis: A Knowledge-Based Approach for Interpreting Genome-Wide Expression Profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kisseleva, T.; Ganguly, S.; Murad, R.; Wang, A.; Brenner, D.A. Regulation of Hepatic Stellate Cell Phenotypes in MASH. Gastroenterology 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Hu, M.; Chen, Z.; Ling, Z. The roles and mechanisms of hypoxia in liver fibrosis. J. Transl. Med. 2021, 19, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- French, S.W. The role of hypoxia in the pathogenesis of alcoholic liver disease. Hepatol. Res. 2004, 29, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Chen, L.; Kong, D.; Zhang, X.; Xia, S.; Liang, B.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Shao, J.; et al. Canonical Wnt signaling promotes HSC glycolysis and liver fibrosis through an LDH-A/HIF-1α transcriptional complex. Hepatology 2024, 79, 606–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallikarjuna, P.; Zhou, Y.; Landström, M. The Synergistic Cooperation between TGF-β and Hypoxia in Cancer and Fibrosis. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulou, D.; Mavrikaki, V.; Charalampous, F.; Tzaferis, C.; Samiotaki, M.; Papavasileiou, K.D.; Afantitis, A.; Karagianni, N.; Denis, M.C.; Sanchez, J.; et al. Discovery of the First-in-Class Inhibitors of Hypoxia Up-Regulated Protein 1 (HYOU1) Suppressing Pathogenic Fibroblast Activation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2024, 63, 202319157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Modulation | Human Dataset #DEGs | In Vitro Experimental Conditions #DEGs | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F4 vs. F0 | T vs. C | T + I 0.3 vs. C | T + I 1 vs. C | T + A vs. C | |
| Upregulated | 2053 | 178 (8.6%) | 211 (10.27%) | 289 (14%) | 24 (1%) |
| Downregulated | 1217 | 125 (10.2%) | 135 (11%) | 164 (13.4%) | 22 (1.8%) |
| Total DEGs | 3270 | 303 (9.2%) | 346 (10.6%) | 453 (14%) | 46 (1.4%) |
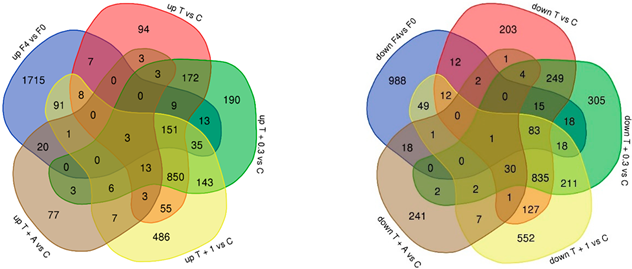 | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
González Hernández, M.A.; Venhorst, J.; Verschuren, L.; Toet, K.; Caspers, M.P.M.; Morrison, M.C.; Coornaert, B.; van Westen, G.J.P.; Hanemaaijer, R. Improved Translational Relevance of In Vitro Fibrosis Models by Integrating IOX2-Mediated Hypoxia-Mimicking Pathways. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1448. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061448
González Hernández MA, Venhorst J, Verschuren L, Toet K, Caspers MPM, Morrison MC, Coornaert B, van Westen GJP, Hanemaaijer R. Improved Translational Relevance of In Vitro Fibrosis Models by Integrating IOX2-Mediated Hypoxia-Mimicking Pathways. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(6):1448. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061448
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonzález Hernández, Manuel A., Jennifer Venhorst, Lars Verschuren, Karin Toet, Martien P. M. Caspers, Martine C. Morrison, Beatrice Coornaert, Gerard J. P. van Westen, and Roeland Hanemaaijer. 2025. "Improved Translational Relevance of In Vitro Fibrosis Models by Integrating IOX2-Mediated Hypoxia-Mimicking Pathways" Biomedicines 13, no. 6: 1448. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061448
APA StyleGonzález Hernández, M. A., Venhorst, J., Verschuren, L., Toet, K., Caspers, M. P. M., Morrison, M. C., Coornaert, B., van Westen, G. J. P., & Hanemaaijer, R. (2025). Improved Translational Relevance of In Vitro Fibrosis Models by Integrating IOX2-Mediated Hypoxia-Mimicking Pathways. Biomedicines, 13(6), 1448. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061448






