Pulmonary and Renal Predictors of Mortality in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis: A Regional Experience from Türkiye
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Patient Demographics, Laboratory Findings, and Treatment Approaches
3.2. Systemic Manifestations Across Vasculitis Subtypes
3.3. Predictors of Relapse and Mortality
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAV | Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis |
| ACR | American College of Rheumatology |
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| ANA | Antinuclear antibody |
| ANCA | Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody |
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| BVAS | Birmingham Vasculitis Activity Score |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| DAH | Diffuse alveolar haemorrhage |
| EGPA | Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| ENT | Ear, nose, and throat |
| ESR | Erythrocyte sedimentation rate |
| ESRD | End-stage renal disease |
| GFR | Glomerular filtration rate |
| GPA | Granulomatosis with polyangiitis |
| ICU | Intensive care unit |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
| MPA | Microscopic polyangiitis |
| MPO | Myeloperoxidase |
| NETs | Neutrophil extracellular traps |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| p-ANCA | Perinuclear anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody |
| PI | Pulmonary involvement |
| pr3 | Proteinase 3 |
| pr3-ANCA | Proteinase 3 anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody |
| RI | Renal involvement |
| RF | Rheumatoid factor |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| SPSS | Statistical Package for the Social Sciences |
References
- Troum, O.M.; Pimienta, O.L.; Wells, A. Imaging in vasculitis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2025, 37, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horai, Y.; Kurushima, S.; Kawakami, A. Current Diagnosis and Treatment of Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis: A Review Including a Comparison of Characteristics in Europe and Japan. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Liu, Y.; Wei, W.; Liu, M.-L. Extracellular vesicles in autoimmune vasculitis—Little dirts light the fire in blood vessels. Autoimmun. Rev. 2019, 18, 593–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granel, J.; Korkmaz, B.; Nouar, D.; Weiss, S.A.I.; Jenne, D.E.; Lemoine, R.; Hoarau, C. Pathogenicity of Proteinase 3-Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody in Granulomatosis With Polyangiitis: Implications as Biomarker and Future Therapies. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 571933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walulik, A.; Łysak, K.; Błaszkiewicz, M.; Górecki, I.; Gomułka, K. The Role of Neutrophils in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis: The Pathogenic Role and Diagnostic Utility of Autoantibodies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukavina, K.; Zlopasa, O.; Vukovic Brinar, I.; Dzubur, F.; Anic, B.; Vujaklija Brajkovic, A. Critically Ill Patients with Newly Diagnosed Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis: Case Series and Literature Review. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, S.E.; Watts, R.A.; Shepstone, L.; Scott, D.G. Primary systemic vasculitis: Clinical features and mortality. QJM 2005, 98, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foulon, G.; Delaval, P.; Valeyre, D.; Wallaert, B.; Debray, M.-P.; Brauner, M.; Nicaise, P.; Cadranel, J.; Cottin, V.; Tazi, A.; et al. ANCA-associated lung fibrosis: Analysis of 17 patients. Respir. Med. 2008, 102, 1392–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, C.W.; Bartholmai, B.J.; Baqir, M.; Geske, J.R.; Specks, U. Pulmonary Low Attenuation Areas on CT in ANCA-associated Vasculitis: A quantitative and semi-quantitative analysis correlated with pulmonary function testing for obstructive airway disease. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffus. Lung Dis. 2020, 37, e2020016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millet, A.; Pederzoli-Ribeil, M.; Guillevin, L.; Witko-Sarsat, V.; Mouthon, L. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitides: Is it time to split up the group? Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 1273–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Kallenberg, C.G.M. The environment, geoepidemiology and ANCA-associated vasculitides. Autoimmun. Rev. 2010, 9, A293–A298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molnár, A.; Studinger, P.; Ledó, N. Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approach in ANCA-Associated Glomerulonephritis: A Review on Management Strategies. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 884188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, X.-N.; Wei, Z.-N.; Yao, X.-Y.; Xu, J.; Qian, W.-T.; Pan, X.-X.; Shen, P.-Y.; Shi, H.; Zhang, W.; Chen, X.-N.; et al. Evaluating renal outcome of ANCA-associated renal vasculitis: Comparative study of two histopathological scoring systems. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2021, 39 (Suppl. S129), 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Alamo, B.; Moi, L.; Bajema, I.; Berden, A.; Flossmann, O.; Hruskova, Z.; Jayne, D.; Wester-Trejo, M.; Wallquist, C.; Westman, K. Long-term outcome of kidney function in patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2024, 39, 1483–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terrier, B.; Guillevin, L. Treatment of Pulmonary Vasculitis. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 39, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comarmond, C.; Pagnoux, C.; Khellaf, M.; Cordier, J.; Hamidou, M.; Viallard, J.; Maurier, F.; Jouneau, S.; Bienvenu, B.; Puéchal, X.; et al. Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Churg-Strauss): Clinical characteristics and long-term follow up of the 383 patients enrolled in the French Vasculitis Study Group cohort. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennette, J.C.; Falk, R.J.; Bacon, P.A.; Basu, N.; Cid, M.C.; Ferrario, F.; Flores-Suarez, L.F.; Gross, W.L.; Guillevin, L.; Hagen, E.C.; et al. 2012 revised International Chapel Hill Consensus Conference Nomenclature of Vasculitides. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grayson, P.C.; Ponte, C.; Suppiah, R.; Robson, J.C.; Craven, A.; Judge, A.; Khalid, S.; Hutchings, A.; A Luqmani, R.; A Watts, R.; et al. 2022 American College of Rheumatology/European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology Classification Criteria for Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suppiah, R.; Robson, J.C.; Grayson, P.C.; Ponte, C.; Craven, A.; Khalid, S.; Judge, A.; Hutchings, A.; A Merkel, P.; A Luqmani, R.; et al. 2022 American College of Rheumatology/European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology classification criteria for microscopic polyangiitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robson, J.C.; Grayson, P.C.; Ponte, C.; Suppiah, R.; Craven, A.; Judge, A.; Khalid, S.; Hutchings, A.; Watts, R.A.; Merkel, P.A.; et al. 2022 American College of Rheumatology/European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology classification criteria for granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhtyar, C.; Lee, R.; Brown, D.; Carruthers, D.; Dasgupta, B.; Dubey, S.; Flossmann, O.; Hall, C.; Hollywood, J.; Jayne, D.; et al. Modification and validation of the Birmingham Vasculitis Activity Score (version 3). Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 68, 1827–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Beers, J.; Vanderlocht, J.; Roozendaal, C.; Damoiseaux, J. Detection of Anti-neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibodies (ANCA) by Indirect Immunofluorescence. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1901, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossuyt, X.; Tervaert, J.-W.C.; Arimura, Y.; Blockmans, D.; Flores-Suárez, L.F.; Guillevin, L.; Hellmich, B.; Jayne, D.; Jennette, J.C.; Kallenberg, C.G.M.; et al. Position paper: Revised 2017 international consensus on testing of ANCAs in granulomatosis with polyangiitis and microscopic polyangiitis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2017, 13, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, A.D. Relapse in Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasm Antibody (ANCA)-Associated Vasculitis. Kidney Int. Rep. 2020, 5, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhtyar, C.; Hellmich, B.; Jayne, D.; Flossmann, O.; Luqmani, R. Remission in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated systemic vasculitis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2006, 24, S-93-8. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Suppiah, R. Outcome measures in primary systemic vasculitis. Indian J. Rheumatol. 2013, 8, S61–S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redondo-Rodriguez, R.; Mena-Vázquez, N.; Cabezas-Lucena, A.M.; Manrique-Arija, S.; Mucientes, A.; Fernández-Nebro, A. Systematic Review and Metaanalysis of Worldwide Incidence and Prevalence of Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody (ANCA) Associated Vasculitis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, C. Clinical Features and Prognosis in ANCA Associated Vasculitis Patients with Acute Kidney Injury. Arch. Iran. Med. 2022, 25, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiik, A. What you should know about PR3-ANCA. An introduction. Arthritis Res. 2000, 2, 252–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Monti, S.; Felicetti, M.; Delvino, P.; Padoan, R.; Berti, A.; Paolazzi, G.; Brunori, G.; Schiavon, F.; Caporali, R.; Montecucco, C. Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody specificity determines a different clinical subset in granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2021, 39 (Suppl. S129), 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koç, E.; Aşık, M.A.; Erdoğan, E.K.; Arslan, D.; Özbek, S.; Özer, H.T.E. ANCA ASSOCIATED VASCULITIS: CLINICAL COURSE AND OUTCOME OF 44 PATIENTS FROM A SINGLE CENTER IN TURKEY. Rheumatol. Q. 2023, 1, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Ávila, D.G.; Rondón-Carvajal, J.; Villota-Eraso, C.; Gutiérrez-Dávila, J.M.; Contreras-Villamizar, K.M. Demographic and clinical characteristics of patients with ANCA-positive vasculitis in a Colombian University Hospital over a 12-year period: 2005–2017. Rheumatol. Int. 2020, 40, 1283–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geetha, D.; Jefferson, J.A. ANCA-Associated Vasculitis: Core Curriculum 2020. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 75, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, D.; Sukumaran, S. Childhood-Onset ANCA-Associated Vasculitis: Single center experience from Central California. Pediatr. Rheumatol. 2023, 21, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binda, V.; Moroni, G.; Messa, P. ANCA-associated vasculitis with renal involvement. J. Nephrol. 2018, 31, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álamo, B.S.; Moi, L.; Bajema, I.; Faurshou, M.; Flossmann, O.; Hauser, T.; Hruskova, Z.; Jayne, D.; Luqmani, R.; Mahr, A.; et al. Long-term outcomes and prognostic factors for survival of patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2023, 38, 1655–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacoto, G.; Boukhlal, S.; Specks, U.; Flores-Suárez, L.F.; Cornec, D. Lung involvement in ANCA-associated vasculitis. Presse Méd. 2020, 49, 104039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim Dogan, H.G.; Yildirim, F.; Icacan, O.C.; Yalcin Mutlu, M.; Celik, S.; Bes, C. Pulmonary involvement in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitides: A single center experience from Turkey. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 26, 1495–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Li, Z.; Gao, L.; Que, C.; Li, H.; Ma, J.; Wang, G.; Chen, M. Pulmonary involvement of ANCA-associated vasculitis in adult Chinese patients. BMC Pulm. Med. 2022, 22, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables | Total n = 78 | GPA n = 44 | MPA n = 30 | EGPA n = 4 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographics | |||||
| Median age at diagnosis (years, IQR) | 53.0 (26.0) | 44.5 (19.5) | 61.0 (9.5) | 48.5 (16.5) | 0.006 |
| Sex (male), n (%) | 38 (48.7) | 28 (63.6) | 8 (26.6) | 2 (50) | 0.044 |
| Median duration of symptoms (years, IQR) | 0.5 (0.7) | 0.5 (0.7) | 0.5 (0.8) | 0.8 (0.2) | 0.762 |
| Smoking history, n (%) | 26 (33.3) | 18 (40.9) | 8 (26.6) | 0 (0) | 1.00 |
| Number of cases with comorbidity, n (%) | 40 (51.2) | 16 (36.3) | 22 (73.3) | 2 (50) | 0.011 |
| Comorbidities | |||||
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 16 (20.5) | 4 (9.1) | 12 (40) | 0 (0) | 0.100 |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 30 (38.4) | 6 (13.6) | 22 (73.3) | 2 (50) | <0.001 |
| Coronary artery disease, n (%) | 6 (7.69) | 2 (4.5) | 4 (13.3) | 0 (0) | 0.719 |
| Hyperlipidaemia, n (%) | 8 (10.2) | 2 (4.5) | 6 (20) | 0 (0) | 0.445 |
| Outcome | |||||
| ICU admission, n (%) | 22 (28.2) | 16 (36.3) | 4 (13.3) | 2 (50) | 0.243 |
| Dialysis, n (%) | 40 (51.2) | 20 (45.4) | 18 (60) | 2 (50) | 0.685 |
| Mortality, n (%) | 16 (20.5) | 12 (27.3) | 2 (6.7) | 2 (50) | 0.178 |
| Remission, n (%) | 62 (79.5) | 34 (77.3) | 26 (86.7) | 2 (50) | 0.448 |
| Relapse, n (%) | 10 (12.8) | 8 (18.2) | 2 (6.7) | 0 (0) | 0.505 |
| Laboratory values, mean ± SD, n (%) | |||||
| BVAS at presentation (mean ± SD) | 19.67 ± 8.77 | 22.55 ± 10.02 | 16.13 ± 4.85 | 14.5 ± 7.78 | 0.063 |
| ANA positivity, n (%) | 18 (23.1) | 8 (18.2) | 8 (26.7) | 2 (50) | 0.543 |
| RF positivity, n (%) | 8 (10.3) | 6 (13.6) | 2 (6.7) | 0 (0) | 0.701 |
| pr3 ANCA positivity, n (%) | 40 (51.2) | 40 (90.9) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1.000 |
| MPO ANCA positivity, n (%) | 33 (42.3) | 0 (0) | 30 (100) | 3 (75) | 1.000 |
| Creatinine at presentation, mg/dL | 3.14 ±2.63 | 2.79 ± 2.69 | 3.91 ± 2.56 | 1.17 ± 0.57 | 0.164 |
| eGFR at presentation | 48.49 ± 40.12 | 57.85 ± 44.92 | 32.29 ± 26.81 | 67.0 ± 46.67 | 0.291 |
| AST (IU/mL) | 20.53 ± 9.70 | 23.62 ± 10.43 | 16.87 ± 7.48 | 14.00 ± 2.83 | 0.035 |
| ALT (IU/mL) | 22.85 ± 12.45 | 26.41 ± 13.37 | 18.60 ± 10.28 | 15.50 ± 0.71 | 0.041 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.65 ± 0.71 | 3.68 ± 0.70 | 3.68 ± 0.66 | 3.16 ± 1.48 | 0.799 |
| Immune-suppressive treatment | |||||
| Corticosteroid, n (%) | 78 (100.0) | 88 (100.0) | 60 (100.0) | 4 (100.0) | 1.000 |
| Cyclophosphamide, n (%) | 52 (66.7) | 22 (50.0) | 28 (93.3) | 2 (50.0) | 0.010 |
| Azathioprine, n (%) | 24 (30.8) | 10 (22.7) | 12 (40.0) | 2 (50.0) | 0.295 |
| Methotrexate, n (%) | 10 (12.8) | 10 (22.7) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0) | 0.067 |
| Mycophenolate mofetil, n (%) | 27 (23.1) | 10 (22.7) | 8 (26.7) | 0 (0) | 1.000 |
| Rituximab, n (%) | 24 (30.8) | 18 (40.9) | 6 (20) | 0 (0) | 0.286 |
| Plasma exchange, n (%) | 14 (17.9) | 12 (27.3) | 2 (6.7) | 0 (0) | 0.204 |
| Total n = 78 | GPA n = 44 | MPA n = 30 | EGPA n = 4 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constitutional symptoms, n (%) | 54 (69.2) | 32 (72.7) | 20 (66.7) | 2 (50) | 0.772 |
| Neurologic involvement, n (%) | 4 (5.1) | 2 (4.5) | 2 (6.7) | 0 (0) | 0.913 |
| Arthralgia, n (%) | 54 (69.2) | 28 (63.6) | 24 (80.0) | 2 (50.0) | 0.471 |
| Arthritis, n (%) | 10 (12.8) | 16 (18.2) | 4 (6.7) | 0 (0) | 0.630 |
| Eye involvement, n (%) | 10 (12.8) | 10 (22.7) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0.114 |
| Cutaneous, n (%) | 6 (7.7) | 4 (9.1) | 2 (6.7) | 0 (0) | 0.881 |
| ENT involvement, n (%) | 40 (51.3) | 36 (81.8) | 0 (0) | 4 (100.0) | <0.000001 |
| Epistaxis, n (%) | 8 (10.3) | 8 (18.2) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0.132 |
| Sinusitis, n (%) | 32 (41) | 28 (63.6) | 0 (0) | 4 (100) | <0.0001 |
| Chronic nasal discharge, n (%) | 30 (38.5) | 28 (63.6) | 0 (0) | 2 (50) | <0.0001 |
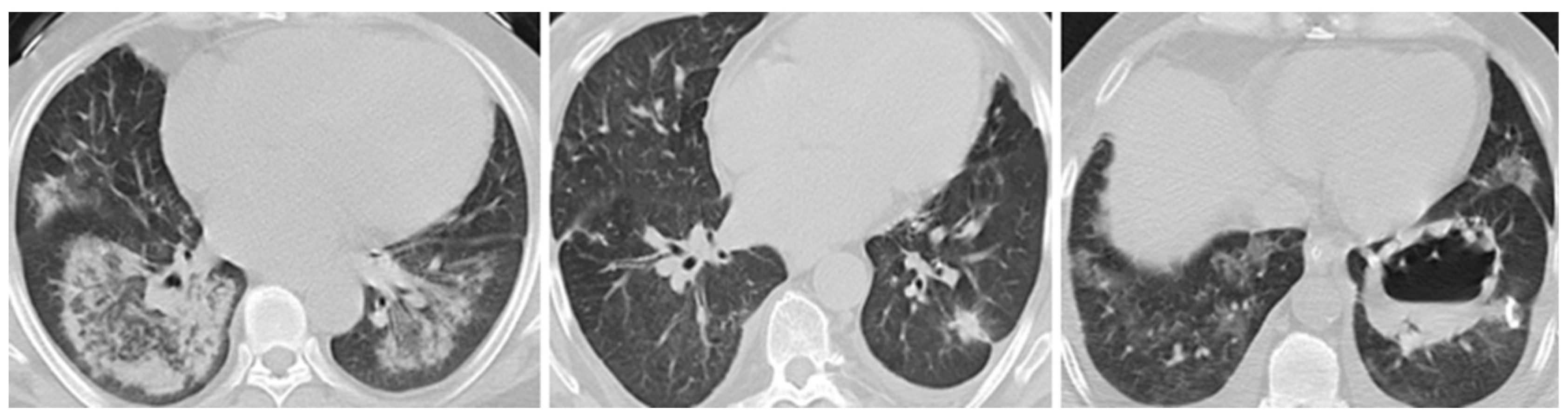
| Pulmonary involvement, n (%) | 56 (71.8) | 40 (90.9) | 12 (40) | 4 (100) | 0.002 |
| Alveolar haemorrhage/haemoptysis, n (%) | 28 (35.9) | 20 (45.5) | 8 (26.7) | 0 (0) | 0.312 |
| Respiratory failure, n (%) | 14 (17.9) | 12 (27.3) | 2 (6.7) | 0 (0) | 0.202 |
| Pleural effusion, n (%) | 10 (12.8) | 6 (13.6) | 4 (13.3) | 0 (0) | 1.000 |
| Pulmonary nodules, n (%) | 40 (51.3) | 26 (59.1) | 12 (40) | 2 (50) | 0.321 |
| Pulmonary infiltrates, n (%) | 32 (41) | 18 (40.9) | 10 (33.3) | 4 (100) | 0.744 |
| Cavitary lesions, n (%) | 20 (25.6) | 20 (45.5) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0.002 |
| Renal impairment, n (%) | 58 (74.4) | 28 (63.6) | 28 (93.3) | 2 (50) | 0.046 |
| Haematuria, n (%) | 54 (69.2) | 26 (59.1) | 26 (86.7) | 2 (50) | 0.143 |
| Proteinuria, n (%) | 58 (74.4) | 26 (59.1) | 30 (100) | 2 (50) | 0.050 |
| Cardiovascular, n (%) | 20 (25.6) | 16 (36.4) | 4 (13.3) | 0 (0) | 0.159 |
| Pericardial effusion, n (%) | 12 (15.4) | 8 (18.2) | 4 (13.3) | 0 (0) | 1.000 |
| Variables | Total n = 78 | PI n = 56 | Non-PI n = 22 | p-Value | RI n = 58 | Non-RI n = 20 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median age at diagnosis (years, IQR) | 53.0 (26.0) | 52.5 (27.5) | 56.0 (18.0) | 0.574 | 56.0 (18.0) | 38.0 (22.8) | 0.023 |
| Sex (male), n (%) | 38 (48.7) | 34 (60.7) | 4 (22.2) | 0.031 | 24 (41.4) | 14 (70) | 0.155 |
| Median duration of symptoms (years, IQR) | 0.5 (0.7) | 0.5 (0.7) | 0.5 (0.5) | 0.987 | 0.5 (0.75) | 0.45 (0.2) | 0.342 |
| BVAS at presentation (mean ± SD) | 19.7 ± 8.8 | 22.2 ± 9.0 | 13.1 ± 2.7 | 0.001 | 20.7 ± 9.1 | 16.6 ± 7.3 | 0.166 |
| pr3 ANCA positivity | 40 (51.2) | 36 (64.28) | 4 (18.18) | 0.004 | 24 (44.4) | 16 (88.9) | 0.026 |
| MPO ANCA positivity | 32 (41.02) | 14 (25) | 18 (81.8) | 0.004 | 30 (55.6) | 2 (11.1) | 0.026 |
| GPA cases, n (%) | 44 (56.4) | 40 (71.4) | 4 (18.1) | 0.004 | 28 (48.3) | 16 (80) | 0.140 |
| EGPA cases, n (%) | 4 (5.1) | 4 (7.1) | 0 (0) | 1.00 | 2 (3.4) | 2 (10) | 1.000 |
| MPA cases, n (%) | 30 (38.4) | 12 (21.4) | 18 (81.8) | 1.00 | 28 (48.3) | 2 (10) | 1.000 |
| ENT involvement, n (%) | 40 (51.3) | 36 (64.3) | 4 (18.2) | 0.014 | 22 (37.9) | 18 (90) | 0.008 |
| Mortality, n (%) | 16 (20.5) | 16 (28.6) | 0 (0) | 0.048 | 30 (51.7) | 2 (5) | 0.065 |
| ICU, n (%) | 22(28.2) | 20(35.7) | 2(9.1) | 0.130 | 18(31) | 4(20) | 0.693 |
| Remission, n (%) | 62 (79.5) | 42 (75.0) | 20 (90.9) | 0.400 | 44 (75.9) | 18 (90) | 0.653 |
| Relapse, n (%) | 10(12.8) | 10(17.9) | 1 (4.5) | 0.048 | 9(15.5) | 1 (5) | 0.056 |
| AST (IU/mL), (mean ± SD) | 20.5 ± 9.7 | 21.0 ± 10.4 | 19.4 ± 7.8 | 0.601 | 20.1 ± 10.1 | 21.9 ± 8.8 | 0.590 |
| ESR (mm/h), (mean ± SD) | 68.3 ± 31.1 | 68.9 ± 32.8 | 66.8 ± 27.9 | 0.844 | 74.0 ± 28.5 | 51.9 ± 33.9 | 0.087 |
| CRP (mg/dL), (mean ± SD) | 86.6 ± 72.9 | 90.4 ± 73.6 | 77.0 ± 73.7 | 0.616 | 88.2 ± 71.5 | 81.8 ± 80.8 | 0.827 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dl), (mean ± SD) | 11.1 ± 2.2 | 11.1 ± 2.3 | 10.9 ± 2.1 | 0.789 | 10.6 ± 2.0 | 12.4 ± 2.2 | 0.033 |
| Factors Related to Relapse | B | SE | Wald | p | Odds Ratio 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ESR | −0.226 | 0.192 | −1.175 | 0.239 | 0.79 (0.547–1.163) |
| CRP | 0.072 | 0.053 | −1.351 | 0.176 | 0.93 (0.837–1.033) |
| Creatinine | 2.166 | 1.964 | 1.102 | 0.270 | 8.73 (0.186–410.78) |
| Albumin | −5.236 | 3.753 | −1.395 | 0.162 | 0.005 (0–8.33) |
| Cyclophosphamide | 0.263 | 1.196 | 0.220 | 0.825 | 1.30 (0.124–13.57) |
| Rituximab | 2.378 | 1.208 | 1.968 | 0.049 | 10.79 (1.010–115.31) |
| Renal | 1.553 | 0.624 | 2.49 | 0.013 | 4.73 (1.40–15.94) |
| Pulmonary | 1.918 | 0.625 | 3.07 | 0.002 | 3.82 (2.06–22.61) |
| ANCA titre | −0.008 | 0.012 | −0.686 | 0.492 | 0.991 (0.967–1.01) |
| Age | 0.061 | 0.091 | −0.669 | 0.502 | 0.940 (0.78–1.12) |
| Sex | 2.636 | 2.664 | 0.989 | 0.322 | 13.96 (0.07–2588.3) |
| Factors Related to Death | B | SE | Wald | p | Odds Ratio 95% CI |
| ESR | 0.010 | 0.013 | 0.775 | 0.438 | 0.010 (0.98–1.03) |
| CRP | 0.009 | 0.007 | 1.40 | 0.003 | 1.01 (1.00–1.023) |
| Creatinine | 0.33 | 0.19 | 1.75 | 0.028 | 1.418 (1.03–1.93) |
| Albumin | −0.64 | 0.81 | −0.79 | 0.046 | 0.237 (0.05–0.97) |
| Cyclophosphamide | 0.500 | 0.898 | 0.557 | 0.577 | 1.650 (0.28–9.60) |
| Rituximab | −1.348 | 1.133 | −1.189 | 0.234 | 0.259 (0.02–2.39) |
| Renal | 1.052 | 0.487 | 2.16 | 0.031 | 2.863 (1.10–7.40) |
| Pulmonary | 2.220 | 0.743 | 2.99 | 0.003 | 3.21 (2.23–38.10) |
| Age | 0.061 | 0.091 | −0.669 | 0.402 | 0.540 (0.60–2.42) |
| Sex | −0.704 | 0.814 | −0.865 | 0.386 | 0.494 (0.10–2.43) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bulut Gökten, D.; Karabağ, S.; Mercan, R. Pulmonary and Renal Predictors of Mortality in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis: A Regional Experience from Türkiye. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1401. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061401
Bulut Gökten D, Karabağ S, Mercan R. Pulmonary and Renal Predictors of Mortality in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis: A Regional Experience from Türkiye. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(6):1401. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061401
Chicago/Turabian StyleBulut Gökten, Dilara, Sevil Karabağ, and Rıdvan Mercan. 2025. "Pulmonary and Renal Predictors of Mortality in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis: A Regional Experience from Türkiye" Biomedicines 13, no. 6: 1401. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061401
APA StyleBulut Gökten, D., Karabağ, S., & Mercan, R. (2025). Pulmonary and Renal Predictors of Mortality in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis: A Regional Experience from Türkiye. Biomedicines, 13(6), 1401. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061401







