Longitudinal Changes in Neuroaxonal and Inflammatory CSF Biomarkers in Multiple Sclerosis Patients Undergoing Interferon Beta Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Methods
2.1.1. Study Population
2.1.2. CSF Analysis
2.1.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients’ Characteristics
3.2. The Impact of the Immunomodulatory Treatment with IFN Beta on Biomarkers in CSF
3.3. CSF Biomarkers and Demographic Data
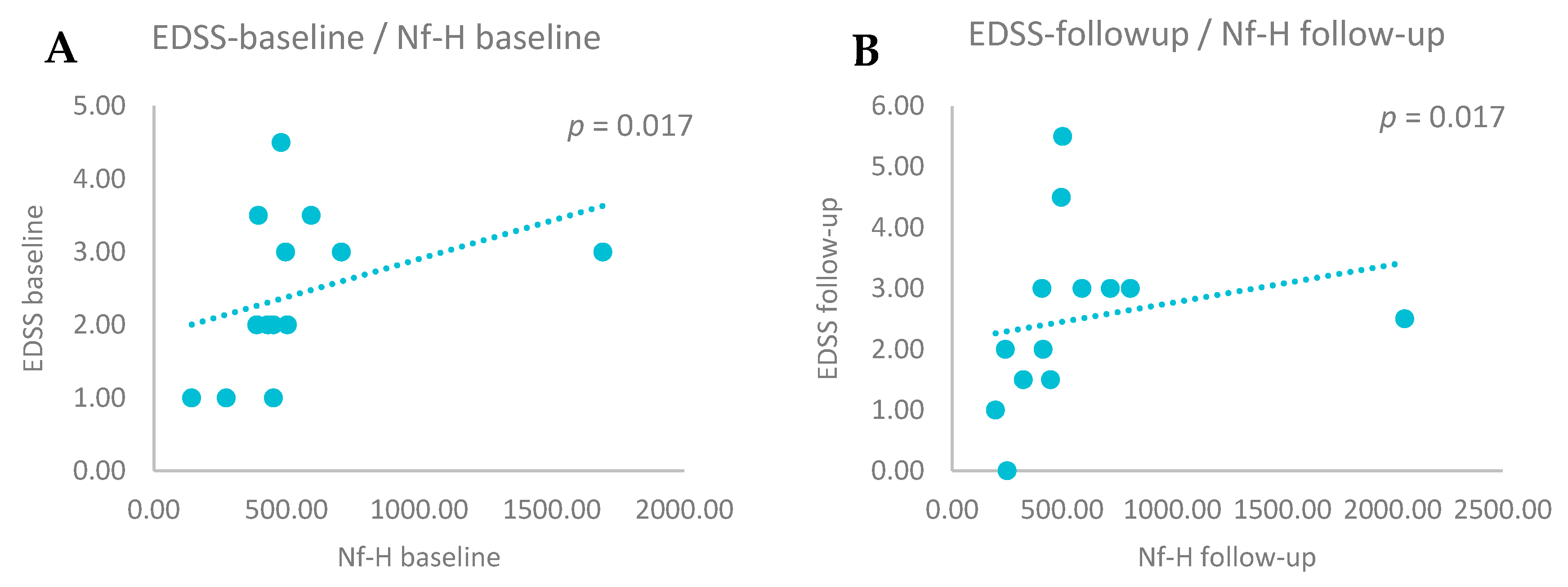
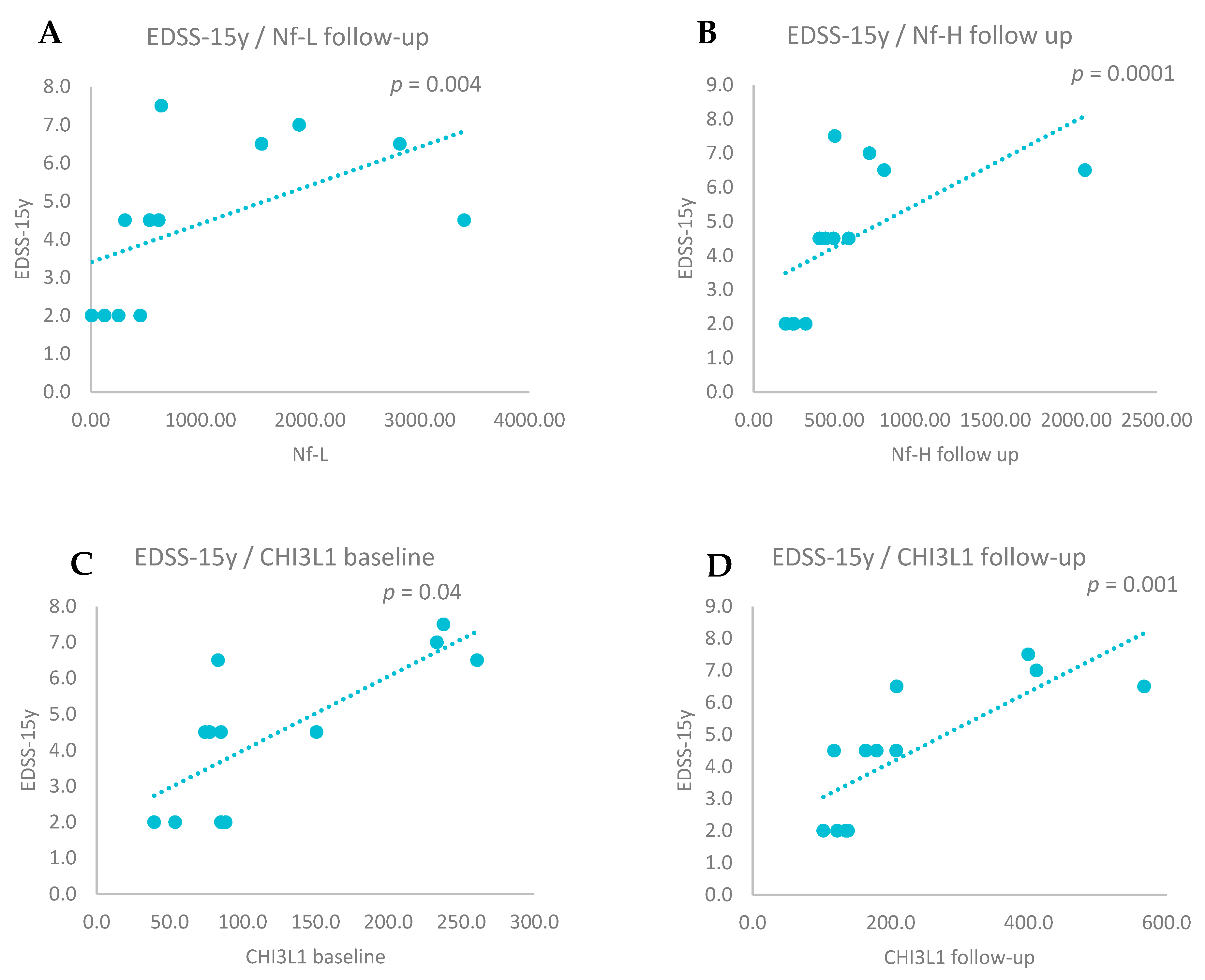
3.4. CSF Biomarkers and EDSS
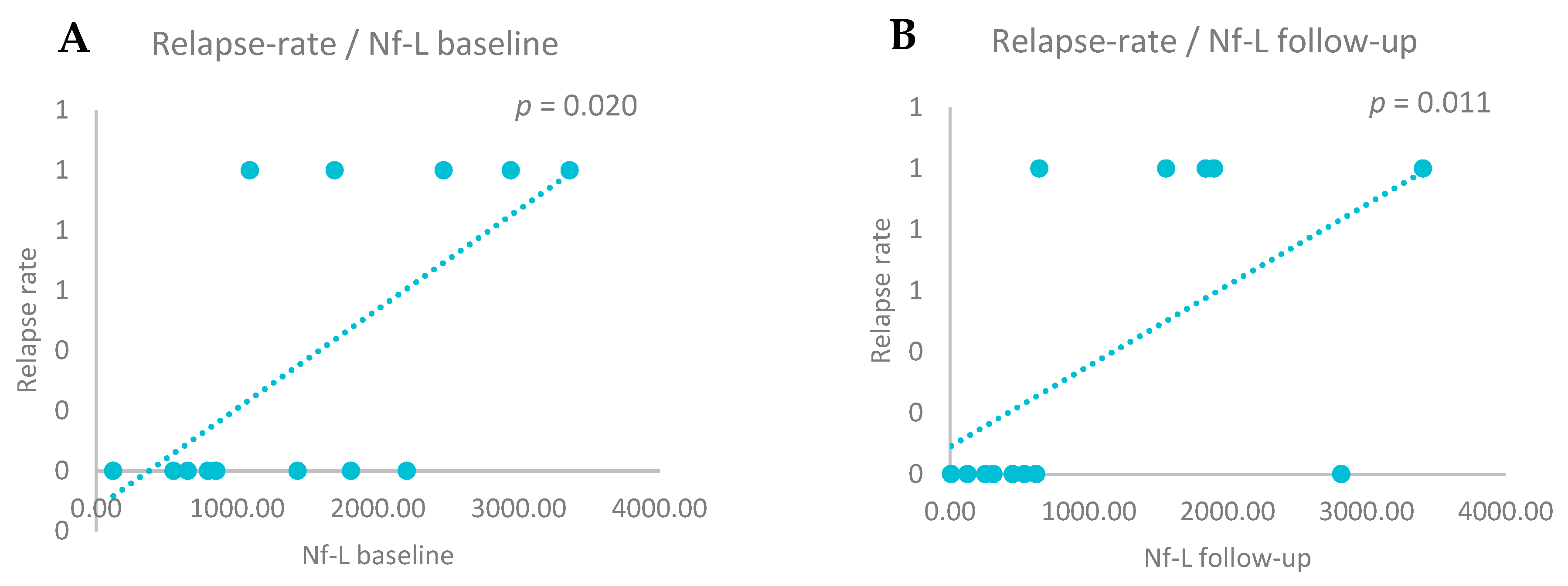
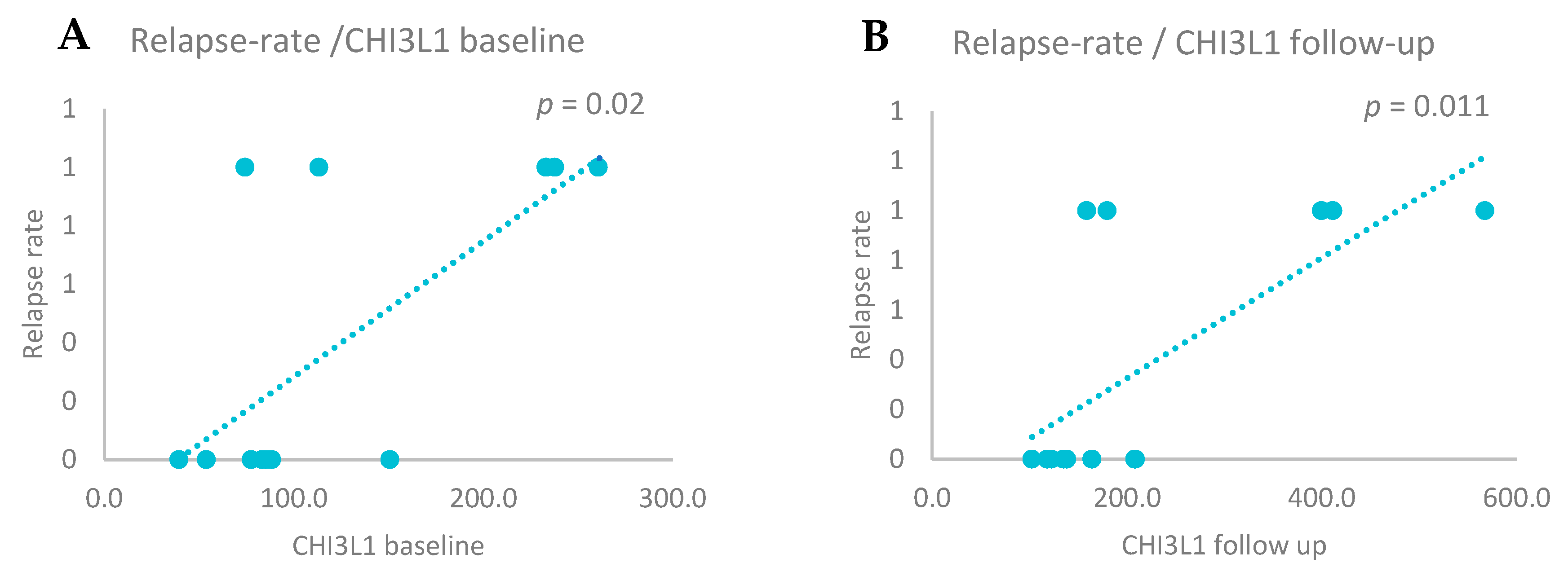
3.5. CSF Biomarkers and Relapse Rate
3.6. CSF Biomarkers’ Variation and Radiological Signs of Disease Activity on Brain MRI
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lassmann, H. Multiple sclerosis pathology. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2018, 8, a028936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franciotta, D. Biological markers in multiple sclerosis. Int. MS J. 2004, 11, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kouchaki, E.; Dashti, F.; Mirazimi, S.M.A.; Alirezaei, Z.; Jafari, S.H.; Hamblin, M.R.; Mirzaei, H. Neurofilament light chain as a biomarker for diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. EXCLI J. 2021, 20, 1308. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhlmann, T.; Moccia, M.; Coetzee, T.; Cohen, J.A.; Correale, J.; Graves, J.; Marrie, R.A.; Montalban, X.; Yong, V.W.; Thompson, A.J.; et al. Time for a new mechanism-driven framework to define multiple sclerosis progression. Lancet Neurol. 2022, 22, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Hamade, M.; Wu, Q.; Wang, Q.; Axtell, R.; Giri, S.; Mao-Draayer, Y. Current and Future Biomarkers in Multiple Sclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, J.; Macaron, G.; Khaled, K.J.A. Biomarkers in multiple sclerosis: An update. Biomark. Neuropsychiatry 2023, 9, 100075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, T.; Reindl, M. Biomarkers in Multiple Sclerosis: Role of Antibodies. Dis. Markers 2006, 22, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teunissen, C.E.; Khalil, M. Neurofilaments as biomarkers in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. J. 2012, 18, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, C.; Menge, T.; Altintas, A.; Álvarez-Cermeño, J.C.; Bertolotto, A.; Berven, F.S.; Brundin, L.; Comabella, M.; Degn, M.; Deisenhammer, F.; et al. Consensus definitions and application guidelines for control groups in cerebrospinal fluid biomarker studies in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. J. 2013, 19, 1802–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, M.; Teunissen, C.E.; Otto, M.; Piehl, F.; Sormani, M.P.; Gattringer, T.; Barro, C.; Kappos, L.; Comabella, M.; Fazekas, F.; et al. Neurofilaments as biomarkers in neurological disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uphaus, T.; Bittner, S.; Gröschel, S.; Steffen, F.; Muthuraman, M.; Wasser, K.; Weber-Krüger, M.; Zipp, F.; Wachter, R.; Gröschel, K. NfL (Neurofilament Light Chain) Levels as a Predictive Marker for Long-Term Outcome After Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2019, 50, 3077–3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moseby-Knappe, M.; Mattsson, N.; Nielsen, N.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; Dankiewicz, J.; Dragancea, I.; Friberg, H.; Lilja, G.; Insel, P.S.; et al. Serum Neurofilament Light Chain for Prognosis of Outcome after Cardiac Arrest. JAMA Neurol. 2019, 76, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gresle, M.M.; Shaw, G.; Jarrott, B.; Alexandrou, E.N.; Friedhuber, A.; Kilpatrick, T.J.; Butzkueven, H. Validation of a novel biomarker for acute axonal injury in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Neurosci. Res. 2008, 86, 3548–3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, A.; Rao, M.V.; Veeranna, N.R.; Nixon, R.A. Neurofilaments and Neurofilament Proteins in Health and Disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2017, 9, a018309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittner, S.; Oh, J.; Havrdová, E.K.; Tintoré, M.; Zipp, F. The potential of serum neurofilament as biomarker for multiple sclerosis. Brain 2021, 144, 2954–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Lee, B.H.; Yip, W.; Chou, P.; Yip, B.-S. Neurofilament Proteins as Prognostic Biomarkers in Neurological Disorders. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2020, 25, 4560–4569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghezzi, A.; Neuteboom, R.F. Neurofilament Light Chain in Adult and Pediatric Multiple Sclerosis: A Promising Biomarker to Better Characterize Disease Activity and Personalize MS Treatment. Neurol. Ther. 2023, 12, 1867–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaetani, L.; Blennow, K.; Calabresi, P.; Di Filippo, M.; Parnetti, L.; Zetterberg, H. Neurofilament light chain as a biomarker in neurological disorders. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2019, 90, 870–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhle, J.; Kropshofer, H.; Haering, D.A.; Kundu, U.; Meinert, R.; Barro, C.; Dahlke, F.; Tomic, D.; Leppert, D.; Kappos, L. Blood neurofilament light chain as a biomarker of MS disease activity and treatment response. Neurology 2019, 92, e1007–e1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridel, C.; Van Wieringen, W.N.; Zetterberg, H.; Tijms, B.M.; Teunissen, C.E.; the NFL Group. Diagnostic Value of Cerebrospinal Fluid Neurofilament Light Protein in Neurology: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Neurol. 2019, 76, 1035–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaby, C.; Bousiges, O.; Bouvier, D.; Fillée, C.; Fourier, A.; Mondésert, E.; Nezry, N.; Omar, S.; Quadrio, I.; Rucheton, B.; et al. Neurofilaments contribution in clinic: State of the art. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 1034684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petzold, A.; Altintas, A.; Andreoni, L.; Bartos, A.; Berthele, A.; Blankenstein, M.A.; Buee, L.; Castellazzi, M.; Cepok, S.; Comabella, M.; et al. Neurofilament ELISA validation. J. Immunol. Methods 2010, 352, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, D.H.; Rissin, D.M.; Kan, C.W.; Fournier, D.R.; Piech, T.; Campbell, T.G.; Meyer, R.E.; Fishburn, M.W.; Cabrera, C.; Patel, P.P.; et al. The Simoa HD-1 Analyzer: A Novel Fully Automated Digital Immunoassay Analyzer with Single-Molecule Sensitivity and Multiplexing. J. Lab. Autom. 2016, 21, 533–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhle, J.; Barro, C.; Andreasson, U.; Derfuss, T.; Lindberg, R.; Sandelius, Å.; Liman, V.; Norgren, N.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H. Comparison of three analytical platforms for quantification of the neurofilament light chain in blood samples: ELISA, electrochemiluminescence immunoassay and Simoa. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2016, 54, 1655–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floro, S.; Carandini, T.; Pietroboni, A.M.; De Riz, M.A.; Scarpini, E.; Galimberti, D. Role of Chitinase 3-like 1 as a Biomarker in Multiple Sclerosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 9, e1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jatczak-Pawlik, I.; Jurewicz, A.; Domowicz, M.; Ewiak-Paszyńska, A.; Stasiołek, M. CHI3L1 in Multiple Sclerosis—From Bench to Clinic. Cells 2024, 13, 2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucchini, M.; De Arcangelis, V.; Piro, G.; Nociti, V.; Bianco, A.; De Fino, C.; Di Sante, G.; Ria, F.; Calabresi, P.; Mirabella, M. CSF CXCL13 and Chitinase 3-like-1 Levels Predict Disease Course in Relapsing Multiple Sclerosis. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 60, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrabar, D.; Bakula, D.; Vrkljan, N.; Ratkajec, V.; Glavcic, G.; Miler, M.; Pelajic, S.; Rogic, D.; Blazevic, N.; Pavic, T. YKL-40 as a biomarker in various inflammatory diseases: A review. Biochem. Medica 2023, 34, 010502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talaat, F.; Abdelatty, S.; Ragaie, C.; Dahshan, A. Chitinase-3-like 1-protein in CSF: A novel biomarker for progression in patients with multiple sclerosis. Neurol. Sci. 2023, 44, 3243–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, M.S.; Al-Rubae’I, S.H.; Rheima, A.M.; Al-Kazazz, F.F. A novel sandwich ELISA method for quantifying CHI3L1 in blood serum and cerebrospinal fluid multiple sclerosis patients using sustainable photo-irradiated zero-valence gold nanoparticles. Results Chem. 2024, 11, 101856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubas-Núñez, L.; Gil-Perotín, S.; Castillo-Villalba, J.; López, V.; Tarazona, L.S.; Gasqué-Rubio, R.; Carratalá-Boscá, S.; Alcalá-Vicente, C.; Pérez-Miralles, F.; Lassmann, H.; et al. Potential Role of CHI3L1+ Astrocytes in Progression in MS. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 8, e972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polman, C.H.; Reingold, S.C.; Edan, G.; Filippi, M.; Hartung, H.-P.; Kappos, L.; Lublin, F.D.; Metz, L.M.; McFarland, H.F.; O’Connor, P.W.; et al. Diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: 2005 Revisions to the ‘McDonald Criteria’. Ann. Neurol. 2005, 58, 840–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtzke, J.F. Rating neurologic impairment in multiple sclerosis: An expanded disability status scale (EDSS). Neurology 1983, 33, 1444–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, A.J.; Banwell, B.L.; Barkhof, F.; Carroll, W.M.; Coetzee, T.; Comi, G.; Correale, J.; Fazekas, F.; Filippi, M.; Freedman, M.S.; et al. Diagnosis of multiple sclerosis: 2017 revisions of the McDonald criteria. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yik, J.T.; Becquart, P.; Gill, J.; Petkau, J.; Traboulsee, A.; Carruthers, R.; Kolind, S.H.; Devonshire, V.; Sayao, A.-L.; Schabas, A.; et al. Serum neurofilament light chain correlates with myelin and axonal magnetic resonance imaging markers in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2022, 57, 103366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, A.v.D.; Fransen, N.; Mason, M.; Rozemuller, A.J.; Teunissen, C.; Smolders, J.; Huitinga, I. Neurofilament Light Chain Levels in Multiple Sclerosis Correlate With Lesions Containing Foamy Macrophages and With Acute Axonal Damage. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 9, e1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenstein, I.; Axelsson, M.; Novakova, L.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Lycke, J. Exploring CSF neurofilament light as a biomarker for MS in clinical practice; a retrospective registry-based study. Mult. Scler. J. 2021, 28, 872–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delcoigne, B.; Manouchehrinia, A.; Barro, C.; Benkert, P.; Michalak, Z.; Kappos, L.; Leppert, D.; Tsai, J.A.; Plavina, T.; Kieseier, B.C.; et al. Blood neurofilament light levels segregate treatment effects in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 2020, 94, e1201–e1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkert, P.; Meier, S.; Schaedelin, S.; Manouchehrinia, A.; Yaldizli, Ö.; Maceski, A.; Oechtering, J.; Achtnichts, L.; Conen, D.; Derfuss, T.; et al. Serum neurofilament light chain for individual prognostication of disease activity in people with multiple sclerosis: A retrospective modelling and validation study. Lancet Neurol. 2022, 21, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petzold, A.; Eikelenboom, M.J.; Keir, G.; Grant, D.; Lazeron, R.H.C.; Polman, C.H.; Uitdehaag, B.M.J.; Thompson, E.J.; Giovannoni, G. Axonal damage accumulates in the progressive phase of multiple sclerosis: Three year follow up study. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2005, 76, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şanlı, E.Ş.; Tüzün, E.; Akbayır, E.; Türkoğlu, R. Phosphorylated neurofilament heavy chain (pNFH) in clinically isolated syndrome and multiple sclerosis. Noro Psikiyatr. Arsivi 2021, 58, 255–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Angelis, F.; Ammoscato, F.; Parker, R.A.; Plantone, D.; Doshi, A.; John, N.A.; Williams, T.; Stutters, J.; MacManus, D.; Schmierer, K.; et al. Neurofilament heavy chain in secondary progressive multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. J. 2025, 31, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil-Perotin, S.; Castillo-Villalba, J.; Cubas-Nuñez, L.; Gasque, R.; Hervas, D.; Gomez-Mateu, J.; Alcala, C.; Perez-Miralles, F.; Gascon, F.; Dominguez, J.A.; et al. Combined Cerebrospinal Fluid Neurofilament Light Chain Protein and Chitinase-3 Like-1 Levels in Defining Disease Course and Prognosis in Multiple Sclerosis. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, I.; Wergeland, S.; Oveland, E.; Bø, L. An Association of Chitinase-3 Like-Protein-1 With Neuronal Deterioration in Multiple Sclerosis. ASN Neuro 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellebjerg, F.; Royen, L.; Sørensen, P.S.; Oturai, A.B.; Jensen, P.E.H. Prognostic value of cerebrospinal fluid neurofilament light chain and chitinase-3-like-1 in newly diagnosed patients with multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. J. 2018, 25, 1444–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Filippo, M.; Gaetani, L.; Centonze, D.; Hegen, H.; Kuhle, J.; Teunissen, C.E.; Tintoré, M.; Villar, L.M.; Willemse, E.A.; Zetterberg, H.; et al. Fluid biomarkers in multiple sclerosis: From current to future applications. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2024, 44, 101009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magliozzi, R.; Cross, A.H. Can CSF biomarkers predict future MS disease activity and severity? Mult. Scler. J. 2020, 26, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| N | Min | Max | Mean | Std. Deviation | Median (lq, hq) | Std. Error of Mean | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex: no (%) | 13 | ||||||
| Female | 9 (69.2%) | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| Male | 4 (30.8%) | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| Age | 13 | 23 | 47 | 32.54 | 8.800 | 30 (24.5, 41.5) | 2.44 |
| EDSS baseline | 13 | 1.0 | 4.5 | 2.43 | 1.0963 | 2.0 (1.5, 3.25) | 0.3041 |
| EDSS follow-up | 13 | 0.0 | 5.5 | 2.5 | 1.4434 | 2.5 (1.5, 3.0) | 0.4003 |
| EDSS 15y | 12 | 2.0 | 7.0 | 4.45 | 2.0939 | 4.5 (2.0, 6.5) | 0.6045 |
| N | |
|---|---|
| Brain MRI baseline: no (%) | |
| Gd (−) lesions | 8 (61.5%) |
| Gd (+) lesions | 5 (38.5%) |
| Brain MRI follow-up: no (%) | |
| Gd (−) lesions | 8 (61.5%) |
| Gd (+) lesions | 5 (38.5%) |
| N | Min | Max | Mean | Std. Deviation | Median (lq, hq) | Std. Error of Mean | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nf-L (pg/mL): | |||||||
| Baseline | 13 | 122 | 3362 | 1536.6 | 987.9 | 1430 (723, 2337) | 274 |
| Follow-up | 13 | 9 | 3408 | 1114.8 | 1092.8 | 621 (284, 1873) | 303.1 |
| Nf-H (pg/mL): | |||||||
| Baseline | 13 | 147.7 | 1693.9 | 539.1 | 373 | 451.6 (391.6, 548.8) | 103.4 |
| Follow-up | 13 | 197.8 | 2056.8 | 573.8 | 480.8 | 447.2 (287.2, 654.6) | 133.3 |
| CHI3L1 (ng/mL): | |||||||
| Baseline | 13 | 39.4 | 260.8 | 121.7 | 74.1 | 85.3 (75.9, 191.9) | 20.7 |
| Follow-up | 13 | 102.4 | 567.4 | 224.1 | 143 | 163.9 (128.7, 304.1) | 39.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Petrescu, S.; Dumitru-Martoiu, M.-M.; Panea, C.A.; Teunissen, C.E. Longitudinal Changes in Neuroaxonal and Inflammatory CSF Biomarkers in Multiple Sclerosis Patients Undergoing Interferon Beta Therapy. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1394. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061394
Petrescu S, Dumitru-Martoiu M-M, Panea CA, Teunissen CE. Longitudinal Changes in Neuroaxonal and Inflammatory CSF Biomarkers in Multiple Sclerosis Patients Undergoing Interferon Beta Therapy. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(6):1394. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061394
Chicago/Turabian StylePetrescu, Simona, Maria-Melania Dumitru-Martoiu, Cristina Aura Panea, and Charlotte E. Teunissen. 2025. "Longitudinal Changes in Neuroaxonal and Inflammatory CSF Biomarkers in Multiple Sclerosis Patients Undergoing Interferon Beta Therapy" Biomedicines 13, no. 6: 1394. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061394
APA StylePetrescu, S., Dumitru-Martoiu, M.-M., Panea, C. A., & Teunissen, C. E. (2025). Longitudinal Changes in Neuroaxonal and Inflammatory CSF Biomarkers in Multiple Sclerosis Patients Undergoing Interferon Beta Therapy. Biomedicines, 13(6), 1394. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061394








