Comparative Pharmacovigilance Analysis of Approved and Repurposed Antivirals for COVID-19: Insights from EudraVigilance Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Data Collection
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
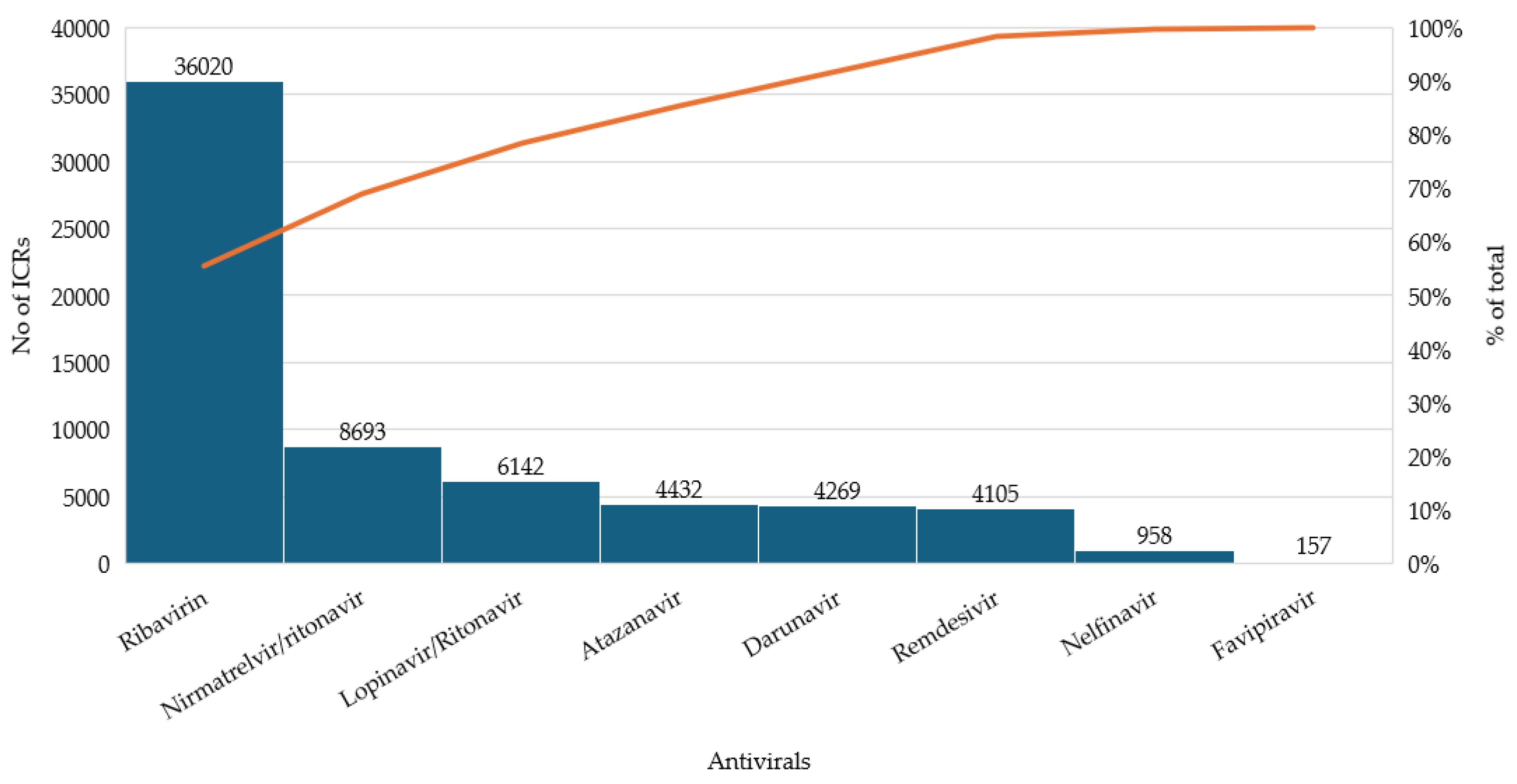
3.1. Distribution of Reported Cases Across Antivirals
3.2. Demographic and Reporting Characteristics of Adverse Event Cases
3.3. Severity and System Organ Class (SOC) Distribution of Adverse Events
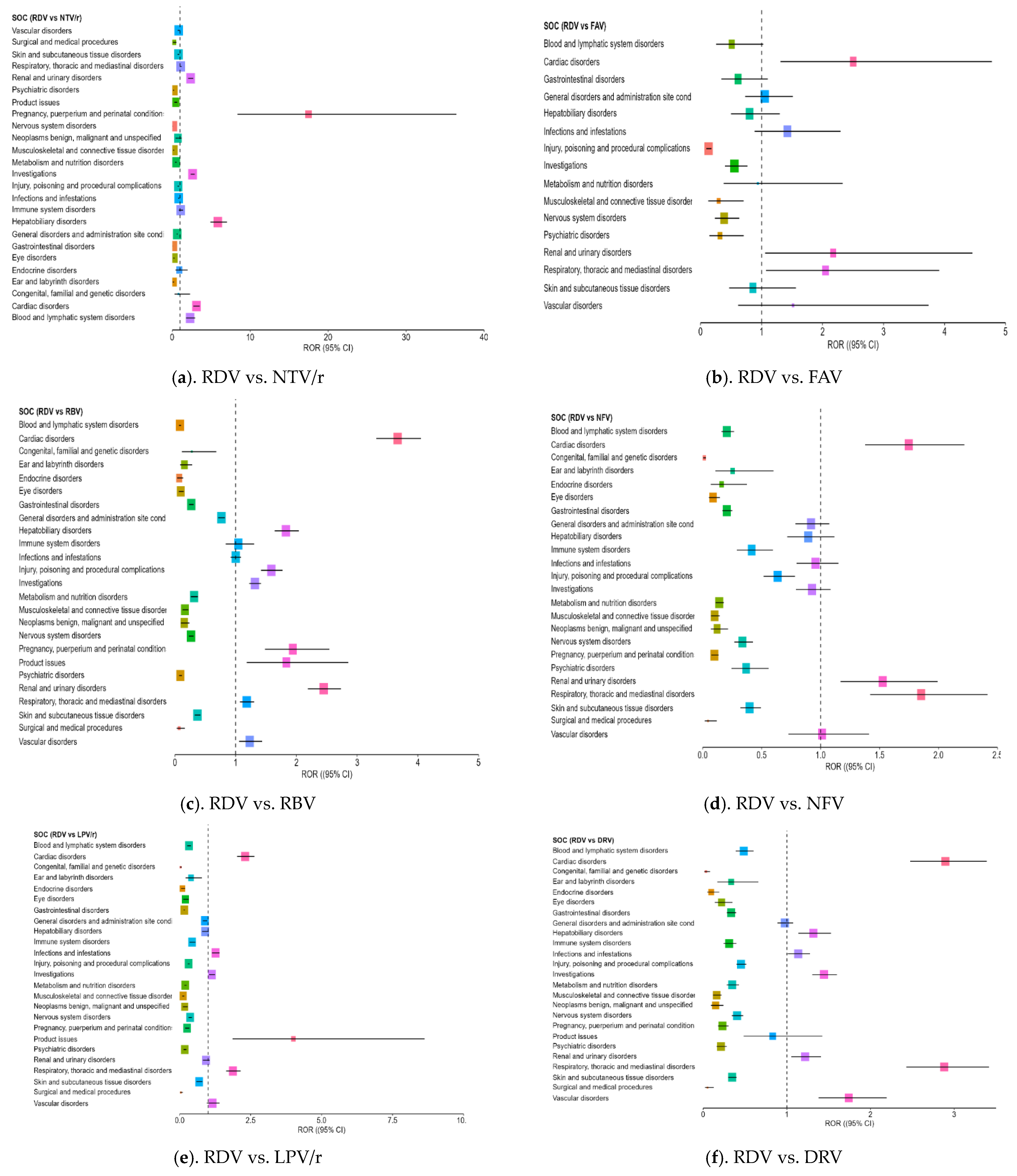
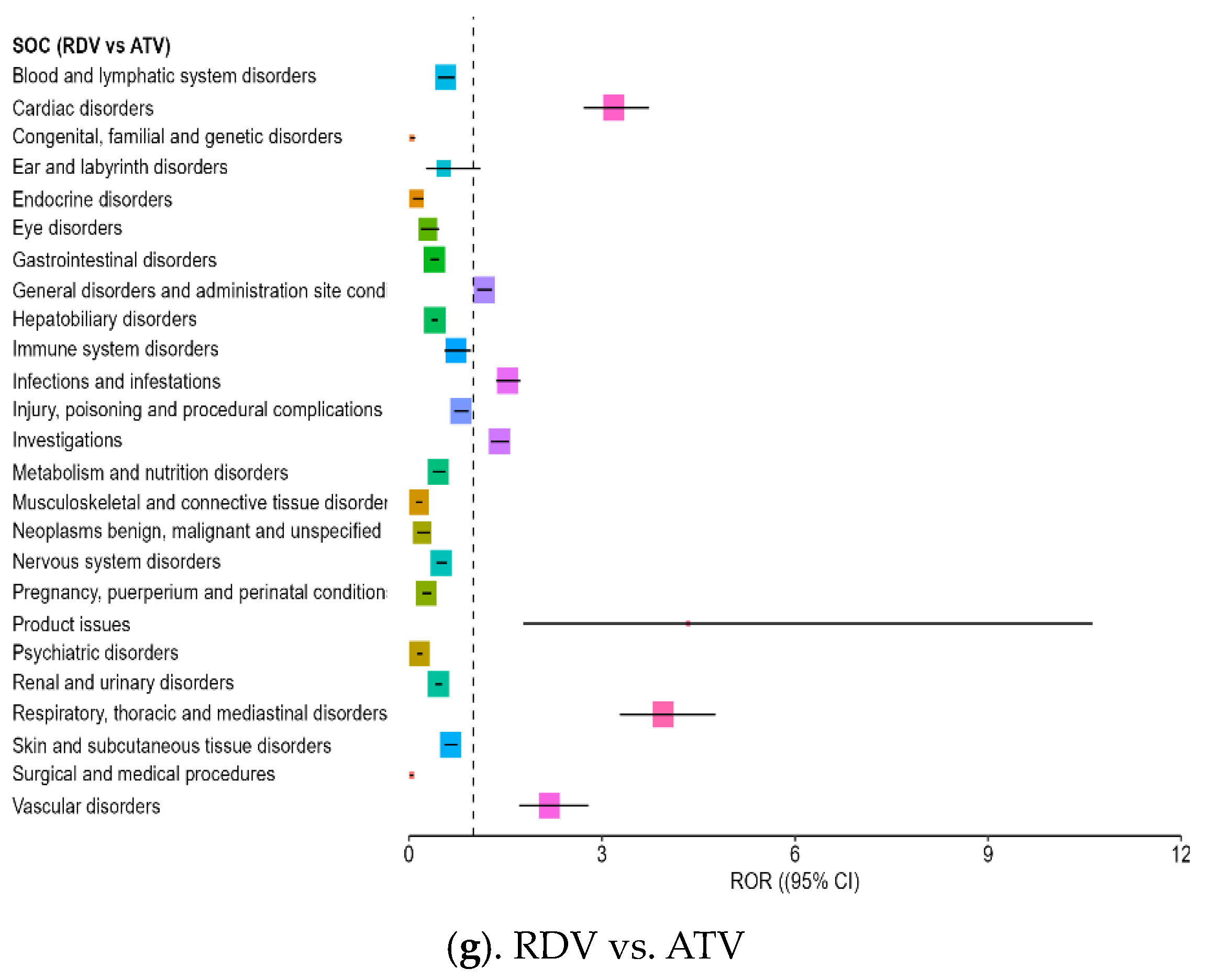
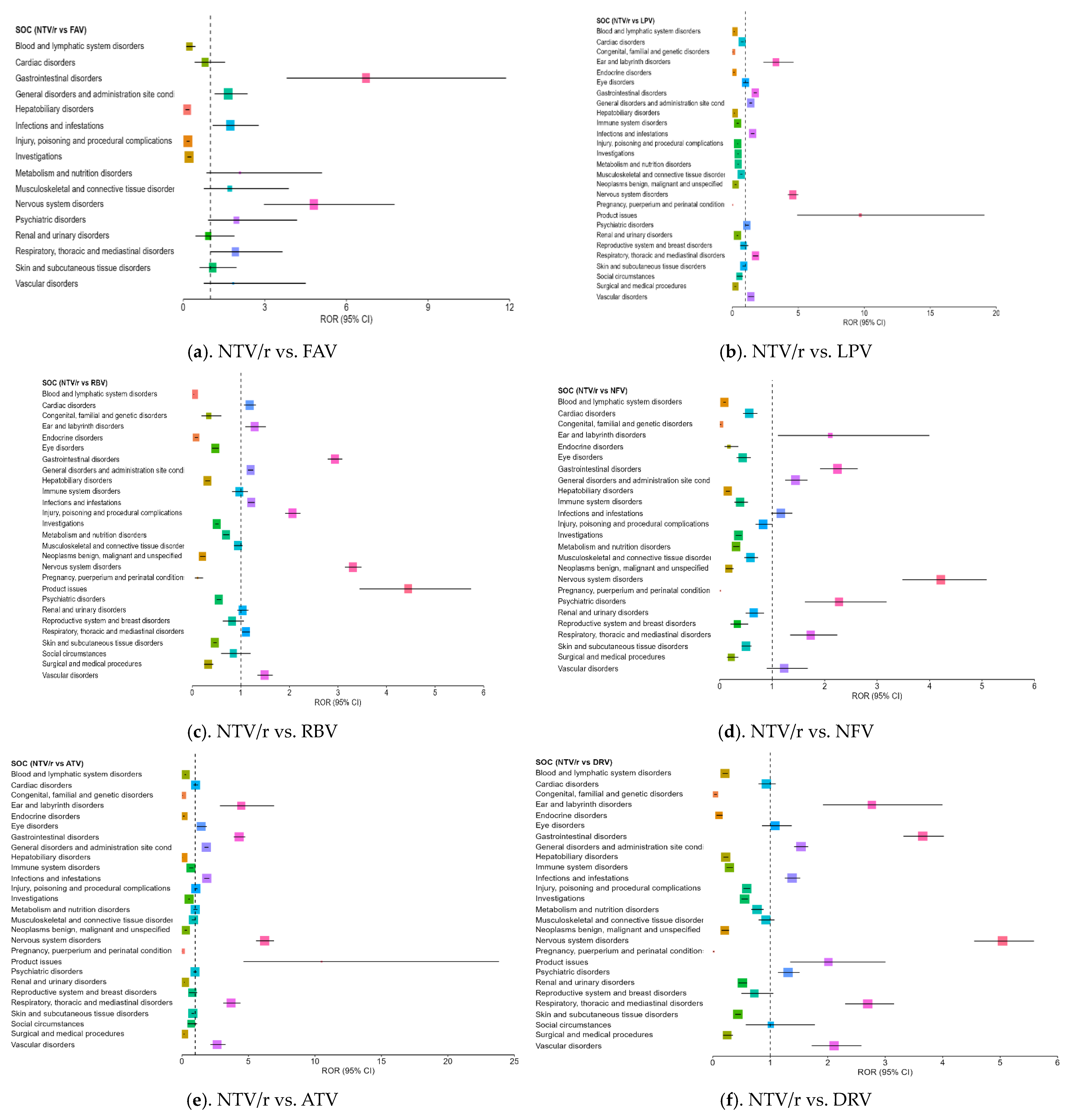
3.4. Disproportionality Analysis of Reporting Odds Ratios Highlighting Comparative Safety Signals
- –
- Cardiac disorders: Strong ROR signals were found across comparisons, including ROR = 3.18 vs. ATV (CI: 2.71–3.73) and ROR = 3.10 vs. NTV/r (CI: 2.732–3.531), suggesting possible cardiotoxicity in some patients.
- –
- Hepatobiliary disorders: RDV was associated with a significantly higher reporting rate compared to NTV/r (ROR = 5.85, CI: 4.88–7.01) and ROR > 1 against RBV and DRV, supporting its known hepatic impact.
- –
- Renal and urinary disorders: Elevated RORs (>2) were observed across several comparisons, indicating frequent reports of renal impairment or dysfunction, aligning with the need for renal monitoring in clinical use.
- –
- Investigations (abnormal lab findings): Disproportionate reporting may reflect increased clinical monitoring in hospitalized patients receiving RDV, rather than direct systemic effects of the drug,
- –
- General disorders and administration site conditions: RDV also showed an excess of reporting in this broad category, which includes symptoms such as fatigue, fever, or injection site reactions (ROR = 1.73 vs. NTV/r).
- –
- Psychiatric disorders: Reports were notably higher than for some comparators, including ROR = 2.17 vs. NFV (CI: 1.62–3.18), indicating the need for further clinical observation in this area.
- –
- Product issues: NTV/r was significantly associated with technical or quality-related complaints (ROR = 1.80 vs. RDV; CI: 1.18–2.76), possibly due to its widespread use in outpatient settings.
- –
- Vascular disorders: Mildly elevated RORs (1.40–2.64) were observed in some comparisons, warranting further exploration in vulnerable populations.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADRs | Adverse drug reactions |
| ATV | Atazanavir |
| COVID-19 | Coronavirus disease 2019 |
| DRV | Darunavir |
| EEA | European Economic Area |
| EMA | European Medicines Agency |
| EV | EudraVigilance |
| FVP | Favipiravir |
| HIV | Human immunodeficiency virus |
| LPV/r | Lopinavir/ritonavir |
| NFV | Nelfinavir |
| NTV/r | Nirmatrelvir/ritonavir |
| RDV | Remdesivir |
| RBV | Ribavirin |
| RTV | Ritonavir |
| SARS-CoV-2 | Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 |
| SOC | System organ class |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| SmPCs | Official product characteristics |
| ICSr | Individual case safety reports |
References
- Cascella, M.; Rajnik, M.; Cuomo, A.; Dulebohn, S.C.; Di Napoli, R. Features, Evaluation, and Treatment of Coronavirus (COVID-19). Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554776/ (accessed on 14 April 2025).
- COVID-19 Cases, World. World Health Organization COVID-19 Dashboard. Available online: https://data.who.int/dashboards/covid19/cases?n=c (accessed on 17 April 2025).
- Watson, O.J.; Barnsley, G.; Toor, J.; Hogan, A.B.; Winskill, P.; Ghani, A.C. Global Impact of the First Year of COVID-19 Vaccination: A Mathematical Modelling Study. Lancet. Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gudima, G.; Kofiadi, I.; Shilovskiy, I.; Kudlay, D.; Khaitov, M. Antiviral Therapy of COVID-19. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulick, R.M.; Pau, A.K.; Daar, E.; Evans, L.; Gandhi, R.T.; Tebas, P.; Ridzon, R.; Masur, H.; Lane, H.C.; Adimora, A.A.; et al. National Institutes of Health COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines Panel: Perspectives and Lessons Learned. Ann. Intern. Med. 2024, 177, 1547–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Treatment Guidelines. National Institutes of Health. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK570371/pdf/Bookshelf_NBK570371.pdf (accessed on 15 April 2025).
- Negru, P.A.; Radu, A.-F.; Vesa, C.M.; Behl, T.; Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Nechifor, A.C.; Endres, L.; Stoicescu, M.; Pasca, B.; Tit, D.M.; et al. Therapeutic Dilemmas in Addressing SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Favipiravir versus Remdesivir. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 147, 112700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Xie, Y.; Zhu, M.; Yi, D.; Zhao, J.; Guo, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; et al. Identification of Darunavir Derivatives for Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 3CL(Pro). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 16011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, K.-T.; Wong, A.Y.-L.; Kaewpreedee, P.; Sia, S.F.; Chen, D.; Hui, K.P.Y.; Chu, D.K.W.; Chan, M.C.W.; Cheung, P.P.-H.; Huang, X.; et al. Remdesivir, Lopinavir, Emetine, and Homoharringtonine Inhibit SARS-CoV-2 Replication in Vitro. Antivir. Res. 2020, 178, 104786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, M.T.; Uddin, M.S.; Hossain, M.F.; Abdulhakim, J.A.; Alam, M.A.; Ashraf, G.M.; Bungau, S.G.; Bin-Jumah, M.N.; Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Aleya, L. NCOVID-19 Pandemic: From Molecular Pathogenesis to Potential Investigational Therapeutics. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruijssers, A.J.; George, A.S.; Schäfer, A.; Leist, S.R.; Gralinksi, L.E.; Dinnon, K.H., 3rd; Yount, B.L.; Agostini, M.L.; Stevens, L.J.; Chappell, J.D.; et al. Remdesivir Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 in Human Lung Cells and Chimeric SARS-CoV Expressing the SARS-CoV-2 RNA Polymerase in Mice. Cell Rep. 2020, 32, 107940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, H.A. Remdesivir: A Review in COVID-19. Drugs 2023, 83, 1215–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godwin, P.O.; Polsonetti, B.; Caron, M.F.; Oppelt, T.F. Remdesivir for the Treatment of COVID-19: A Narrative Review. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2024, 13, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabati, M.; Parsaee, H. Potential Cardiotoxic Effects of Remdesivir on Cardiovascular System: A Literature Review. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2022, 22, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.M.; Jung, S.Y.; Kim, M.S.; Lee, S.W.; Yon, D.K.; Shin, J.I.; Lee, J.Y. Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Adverse Events Associated with Intravitreal Anti-VEGF Monoclonal Antibodies: A World Health Organization Pharmacovigilance Study. Ophthalmology 2025, 132, 62–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrara, F.; Zovi, A.; Trama, U.; Vitiello, A. Nirmatrelvir-Remdesivir Association for Non-Hospitalized Adults with COVID-19, Point of View. Inflammopharmacology 2022, 30, 1927–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Du, Z.; Wang, L.; Lau, E.H.Y.; Fung, I.C.-H.; Holme, P.; Cowling, B.J.; Galvani, A.P.; Krug, R.M.; Meyers, L.A. Public Health Impact of Paxlovid as Treatment for COVID-19, United States. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2024, 30, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleem, A.; Kothadia, J.P. Remdesivir. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK563261/ (accessed on 25 May 2025).
- Bellino, S. COVID-19 Treatments Approved in the European Union and Clinical Recommendations for the Management of Non-Hospitalized and Hospitalized Patients. Ann. Med. 2022, 54, 2856–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veklury. European Medicines Agency. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/veklury (accessed on 25 May 2025).
- Introduction to Therapeutics and COVID-19. World Health Organization. Available online: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/module-1-introduction-to-therapeutics-for-covid-19.pdf (accessed on 25 May 2025).
- Lamb, Y.N. Nirmatrelvir Plus Ritonavir: First Approval. Drugs 2022, 82, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxlovid. European Medicines Agency. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/paxlovid (accessed on 25 May 2025).
- Coronavirus (COVID-19) Update: FDA Authorizes First Oral Antiviral for Treatment of COVID-19. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19-update-fda-authorizes-first-oral-antiviral-treatment-covid-19 (accessed on 26 May 2025).
- Agrawal, U.; Raju, R.; Udwadia, Z.F. Favipiravir: A New and Emerging Antiviral Option in COVID-19. Med. J. Armed Forces India 2020, 76, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Report on the Deliberation Results. Review Report. Favipiravir. Available online: https://www.pmda.go.jp/files/000210319.pdf (accessed on 25 May 2025).
- Lopinavir/Ritonavir. Summary of Product Characteristics. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/lopinavir-ritonavir-viatris-epar-product-information_en.pdf (accessed on 25 May 2025).
- Lopinavir/Ritonavir. Rezumatul Caracteristicilor Produsului. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/health/documents/community-register/2016/20160114133755/anx_133755_ro.pdf (accessed on 25 May 2025).
- Lopinavir and Ritonavir. Highlights of Prescribing Information. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2016/021251s052_021906s046lbl.pdf (accessed on 25 May 2025).
- Ray, S.C.; Thomas, D.L. 156–Hepatitis C. In Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett’s Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases, 8th ed.; Bennett, J.E., Dolin, R., Blaser, M.J., Eds.; W.B. Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2015; pp. 1904–1927.e9. ISBN 978-1-4557-4801-3. [Google Scholar]
- Ribavirin. Highlights of Prescribing Information. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2013/020903s052,021546s008lbl.pdf (accessed on 25 May 2025).
- Ribavirin. European Medicines Agency. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/ribavirin-teva (accessed on 25 May 2025).
- Nelfinavir. Summary of Product Characteristics. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/health/documents/community-register/2010/2010012073128/anx_73128_en.pdf (accessed on 25 May 2025).
- Gidari, A.; Sabbatini, S.; Pallotto, C.; Bastianelli, S.; Pierucci, S.; Busti, C.; Schiaroli, E.; Francisci, D. Nelfinavir: An Old Ally in the COVID-19 Fight? Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, C.S.; Abdelnabi, R.; Kaptein, S.J.F.; Zhang, X.; Ter Horst, S.; Mols, R.; Delang, L.; Rocha-Pereira, J.; Coelmont, L.; Leyssen, P.; et al. HIV Protease Inhibitors Nelfinavir and Lopinavir/Ritonavir Markedly Improve Lung Pathology in SARS-CoV-2-Infected Syrian Hamsters despite Lack of an Antiviral Effect. Antivir. Res. 2022, 202, 105311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atazanavir. Summary of Product Characteristics. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/atazanavir-krka-epar-product-information_en.pdf (accessed on 25 May 2025).
- Atazanavir. Available online: https://clinicalinfo.hiv.gov/en/drugs/atazanavir/patient (accessed on 25 May 2025).
- Fintelman-Rodrigues, N.; Sacramento, C.Q.; Ribeiro Lima, C.; Souza da Silva, F.; Ferreira, A.C.; Mattos, M.; de Freitas, C.S.; Soares, V.C.; Dias, S.d.S.G.; Temerozo, J.R.; et al. Atazanavir, Alone or in Combination with Ritonavir, Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Replication and Proinflammatory Cytokine Production. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darunavir. European Medicines Agency. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/darunavir-krka (accessed on 25 May 2025).
- De Meyer, S.; Bojkova, D.; Cinatl, J.; Van Damme, E.; Buyck, C.; Van Loock, M.; Woodfall, B.; Ciesek, S. Lack of Antiviral Activity of Darunavir against SARS-CoV-2. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 97, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.J.; Choi, S.H.; Park, J.S.; Kwon, Y.S.; Lee, J.; Kim, Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Choi, E.Y. Use of Darunavir-Cobicistat as a Treatment Option for Critically Ill Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Yonsei Med. J. 2020, 61, 826–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EudraVigilance. European Medicines Agency. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/human-regulatory-overview/research-development/pharmacovigilance-research-development/eudravigilance (accessed on 24 May 2025).
- European Medicines Agency. Online Access to Suspected Side-Effect Reports: EudraVigilance—European Database of Suspected Adverse Drug Reaction Reports. Available online: https://www.adrreports.eu (accessed on 12 February 2025).
- Introductory Guide for Standardised MedDRA Queries (SMQs) Version 27.0. The International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use. Available online: https://admin.meddra.org/sites/default/files/guidance/file/SMQ_intguide_27_0_English.pdf (accessed on 26 February 2025).
- International Council for Harmonisation (ICH). Clinical Safety Data Management: Definitions and Standards for Expedited Reporting (E2A). Available online: https://database.ich.org/sites/default/files/E2A_Guideline.pdf (accessed on 26 February 2025).
- Open Source Epidemiologic Statistics for Public Health. Available online: https://www.openepi.com/Menu/OE_Menu.htm (accessed on 12 April 2025).
- Vonica, R.C.; Butuca, A.; Morgovan, C.; Pumnea, M.; Cipaian, R.C.; Frum, A.; Dobrea, C.M.; Vonica-Tincu, A.L.; Pacnejer, A.-M.; Ghibu, S.; et al. Bevacizumab—Insights from EudraVigilance Database on the Assessments of the Safety Profile of Monoclonal Antibodies Used as Targeted Cancer Treatment. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pop, G.; Farcaș, A.; Butucă, A.; Morgovan, C.; Arseniu, A.M.; Pumnea, M.; Teodoru, M.; Gligor, F.G. Post-Marketing Surveillance of Statins-A Descriptive Analysis of Psychiatric Adverse Reactions in EudraVigilance. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, K. Two by Two Tables Containing Counts (TwobyTwo). OpenEpi: Open Source Epidemiologic Statistics for Public Health. Available online: https://www.openepi.com/PDFDocs/TwobyTwoDoc.pdf (accessed on 26 February 2025).
- Screening for Adverse Drug Reactions in EudraVigilance. European Medicines Agency. Available online: https://policycommons.net/artifacts/3181767/screening-for-adverse-reactions-in-eudravigilance/3980283/ (accessed on 12 April 2025).
- Fusaroli, M.; Emanuel, R.; Elisabetta, P.; Hauben, M. The Evolving Role of Disproportionality Analysis in Pharmacovigilance. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2024, 23, 981–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; de Wit, E. Antiviral Agents for the Treatment of COVID-19: Progress and Challenges. Cell Rep. Med. 2022, 3, 100549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Kang, C.K.; Im, J.H.; Cho, Y.; Kang, D.Y.; Lee, J.-Y. Adverse Drug Events Associated with Remdesivir in Real-World Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19, Including Vulnerable Populations: A Retrospective Multicenter Study. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2023, 38, e346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.J.; Kim, H.; Kim, Y.K.; Lee, S.S.; Jung, E.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, J. Effectiveness and Adverse Events of Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir Versus Molnupiravir for COVID-19 in Outpatient Setting: Multicenter Prospective Observational Study. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2023, 38, e347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remdesivir. Summary of Product Characteristics. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/veklury-epar-product-information_en.pdf (accessed on 26 May 2025).
- Rafaniello, C.; Ferrajolo, C.; Sullo, M.G.; Gaio, M.; Zinzi, A.; Scavone, C.; Gargano, F.; Coscioni, E.; Rossi, F.; Capuano, A. Cardiac Events Potentially Associated to Remdesivir: An Analysis from the European Spontaneous Adverse Event Reporting System. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, A.; Huynh, N.; Heger, M.; Bakir, M. Adverse Effects of Remdesivir for the Treatment of Acute COVID-19 in the Pediatric Population: A Retrospective Observational Study. Mol. Cell. Pediatr. 2024, 11, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsowaida, Y.S.; Shehadeh, F.; Kalligeros, M.; Mylonakis, E. Incidence and Potential Risk Factors for Remdesivir-Associated Bradycardia in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1106044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abedipour, F.; Mirzaei, H.H.; Ansari, H.; Ehsanzadeh, N.; Rashki, A.; Vahedi, M.M.; Rashki, A. Remdesivir-Related Cardiac Adverse Effects in COVID-19 Patients: A Case-Control Study. Drug Res. 2024, 74, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montastruc, F.; Thuriot, S.; Durrieu, G. Hepatic Disorders With the Use of Remdesivir for Coronavirus 2019. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 2835–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FakhriRavari, A.; Malakouti, M. Remdesivir and the Liver: A Concise Narrative Review of Remdesivir-Associated Hepatotoxicity in Patients Hospitalized Due to COVID-19. Pharmacoepidemiology 2024, 3, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grein, J.; Ohmagari, N.; Shin, D.; Diaz, G.; Asperges, E.; Castagna, A.; Feldt, T.; Green, G.; Green, M.L.; Lescure, F.-X.; et al. Compassionate Use of Remdesivir for Patients with Severe COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2327–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.; Chaudhary, J.K.; Jain, N.; Chaudhary, P.K.; Khanra, S.; Dhamija, P.; Sharma, A.; Kumar, A.; Handu, S. Role of Structural and Non-Structural Proteins and Therapeutic Targets of SARS-CoV-2 for COVID-19. Cells 2021, 10, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romão, B.M.S.; Duval, F.V.; Lima, E.C.; da Silva, F.A.B.; de Matos, G.C. Detection of Potential Safety Signals Related to the Use of Remdesivir and Tocilizumab in the COVID Era during Pregnancy, Resorting to Open Data from the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS). Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1349543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Zhang, B.; Ma, J.; Zhang, S. Safety Profile of the Antiviral Drug Remdesivir: An Update. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 130, 110532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandham, R.; Eerike, M.; Raj, G.M.; Bisoi, D.; Priyadarshini, R.; Agarwal, N. Adverse Events Following Remdesivir Administration in Moderately Ill COVID-19 Patients—A Retrospective Analysis. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2022, 11, 3693–3698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira-da-Silva, R.; Ribeiro-Vaz, I.; Morato, M.; Junqueira Polónia, J. A Comprehensive Review of Adverse Events to Drugs Used in COVID-19 Patients: Recent Clinical Evidence. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 52, e13763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-J.; Wei, Y.-J.; Chang, H.-L.; Chang, P.-Y.; Tsai, C.-C.; Chen, Y.-H.; Hsueh, P.-R. Remdesivir Use in the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic: A Mini-Review. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2021, 54, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, N.A.d.O.; Zara, A.L.d.S.A.; Figueras, A.; de Melo, D.O. Potential Kidney Damage Associated with the Use of Remdesivir for COVID-19: Analysis of a Pharmacovigilance Database. Cad. Saude Publica 2021, 37, e00077721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chouchana, L.; Preta, L.-H.; Tisseyre, M.; Terrier, B.; Treluyer, J.-M.; Montastruc, F. Kidney Disorders as Serious Adverse Drug Reactions of Remdesivir in Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Retrospective Case-Noncase Study. Kidney Int. 2021, 99, 1235–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izcovich, A.; Siemieniuk, R.A.; Bartoszko, J.J.; Ge, L.; Zeraatkar, D.; Kum, E.; Qasim, A.; Khamis, A.M.; Rochwerg, B.; Agoritsas, T.; et al. Adverse Effects of Remdesivir, Hydroxychloroquine and Lopinavir/Ritonavir When Used for COVID-19: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Trials. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e048502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charan, J.; Kaur, R.J.; Bhardwaj, P.; Haque, M.; Sharma, P.; Misra, S.; Godman, B. Rapid Review of Suspected Adverse Drug Events Due to Remdesivir in the WHO Database; Findings and Implications. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 14, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beigel, J.H.; Tomashek, K.M.; Dodd, L.E.; Mehta, A.K.; Zingman, B.S.; Kalil, A.C.; Hohmann, E.; Chu, H.Y.; Luetkemeyer, A.; Kline, S.; et al. Remdesivir for the Treatment of COVID-19—Final Report. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1813–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir. Summary of Product Characteristics. Summary of Product Characteristics. European Medicines Agency. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/paxlovid-epar-product-information_en.pdf (accessed on 25 May 2025).
- Gu, J.; Han, Z.-H.; Wang, C.-Q.; Zhang, J.-F. The Impacts of Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir on Myocardial Injury and Long-Term Cardiovascular Outcomes in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19 amid the Omicron Wave of the Pandemic. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2025, 39, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lenarda, A.; Ferri, N.; Lanzafame, M.; Montuori, E.A.; Pacelli, L. Cardiovascular Drug Interactions with Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir for COVID-19: Considerations for Daily Practice. Eur. Cardiol. 2024, 19, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wee, L.E.; Lim, J.T.; Tay, A.T.; Chiew, C.J.; Young, B.E.; Wong, B.; Lim, R.; Lee, C.L.; Tan, J.; Vasoo, S.; et al. Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir Treatment and Risk for Postacute Sequelae of COVID-19 in Older Singaporeans. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2025, 31, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganipisetti, V.M.; Bollimunta, P.; Maringanti, S. Paxlovid-Induced Symptomatic Bradycardia and Syncope. Cureus 2023, 15, e33831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzupoli, G.M.; Savastano, M.C.; Falsini, B.; Savastano, A.; Rizzo, S. Possible Retinal Impairment Secondary to Ritonavir Use in SARS-CoV-2 Patients: A Narrative Systematic Review. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 2020, 5350494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Zhang, Q.-S.; Liu, X.-L.; Wang, H.-L.; Liu, W. Adverse Events Associated with Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir: A Pharmacovigilance Analysis Based on FAERS. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, B.; Rousseau, M.; Gauthier, R.; Calmy, A.; Schneider, M.P. Patient Experiences With Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir for COVID-19 in a Collaborative Care Model: A Cross-Sectional Study on Self-Management, Information, and Medication Impact. J. Patient Exp. 2025, 12, 23743735251342126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Deng, X.; Huang, J.; He, G.; Huang, S. Data Mining of Adverse Drug Event Signals with Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir from FAERS. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0316573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Liu, Z.; Zou, Z.; Mao, L.; Zhang, J. Effects of Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir (Paxlovid) on the Nervous System: Analysis on Adverse Events Released by FDA. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2025, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacnejer, A.-M.; Negru, M.C.; Arseniu, A.M.; Trandafirescu, C.; Oancea, C.; Gligor, F.G.; Morgovan, C.; Butuca, A.; Dehelean, C.A. Comparative Analysis of Neuropsychiatric Adverse Reactions Associated with Remdesivir and Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir in COVID-19 Treatment: Insights from EudraVigilance Data. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, C.; Patel, P. Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK585126/ (accessed on 26 May 2025).
- Ribavirin. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK548115/ (accessed on 14 April 2025).
- Zorych, I.; Madigan, D.; Ryan, P.; Bate, A. Disproportionality Methods for Pharmacovigilance in Longitudinal Observational Databases. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 2013, 22, 39–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bate, A.; Evans, S.J.W. Quantitative Signal Detection Using Spontaneous ADR Reporting. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2009, 18, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coste, A.; Wong, A.; Bokern, M.; Bate, A.; Douglas, I.J. Methods for Drug Safety Signal Detection Using Routinely Collected Observational Electronic Health Care Data: A Systematic Review. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2023, 32, 28–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, I.R.; Aronson, J.K. Adverse Drug Reactions: Definitions, Diagnosis, and Management. Lancet 2000, 356, 1255–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.Y.; Lee, J.M.; Jung, S.Y.; Kim, M.S.; Lee, S.W.; Kronbichler, A.; Tizaoui, K.; Koyanagi, A.; Kim, E.Y.; Song, K.; et al. Comparison of Agranulocytosis and Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis Caused by Two Antithyroid Drugs: A Pharmacovigilance Study Using the WHO International Database. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2024, 38, 780–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, J.-E.; Manouchehri, A.; Moey, M.; Lebrun-Vignes, B.; Bastarache, L.; Pariente, A.; Gobert, A.; Spano, J.-P.; Balko, J.M.; Bonaca, M.P.; et al. Cardiovascular Toxicities Associated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: An Observational, Retrospective, Pharmacovigilance Study. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 1579–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Drugs Name/ COVID-19 Approval Status | Original Indication | Indication (COVID-19 Use) | Timeframe and Deployment | Known Adverse Effects | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Remdesivir/ Approved | Developed to treat hepatitis C, investigated for Ebola virus disease and Marburg virus infection [18,19] | Hospitalized patients with moderate-to-severe COVID-19 | EMA Conditional Approval—July 2020; widely used globally | Elevated liver enzymes, renal impairment, nausea | [20,21] |
| Nirmatrelvir and ritonavir/ Approved | Treatment and post-exposure prophylaxis of COVID-19 [22] | Early treatment in non-hospitalized high-risk patients | EMA Conditional Approval—January 2022; moderate use in EU | Dysgeusia, diarrhea, drug interactions, taste disturbances | [23,24] |
| Favipiravir/ Off-label | Treatment of Influenzas virus infection in Japan [25] | Investigational/off-label use for mild to moderate cases | Used in Japan, India, Russia; not approved by EMA | Hyperuricemia, liver enzyme elevation, teratogenicity | [25,26] |
| Lopinavir and Ritonavir/ Off-label | Treatment of HIV-1 infection [27] | Off-label use during early pandemic phase | Deployed globally in early 2020; later disfavored due to inefficacy | Diarrhea, QT prolongation, hepatotoxicity | [28,29] |
| Ribavirin/ Off-label | Treatment of chronic hepatitis C with viral hemorrhagic fever [30] | Investigational use based on past SARS-CoV/MERS data | Limited use, mainly in Asia and MENA during early pandemic | Hemolytic anemia, fatigue, teratogenicity | [31,32] |
| Nelfinavir/ Off-label | Treatment of HIV-1 infection [33] | Investigational use based on in vitro activity against SARS-CoV-2 | Limited use; evaluated in clinical trials during early pandemic | Gastrointestinal intolerance, diarrhea, flatulence | [34,35] |
| Atazanavir/ Off-label | Treatment of HIV-1 infection [36] | Investigational use; evaluated for SARS-CoV-2 protease inhibition | Limited use; studied in vitro and in clinical settings | Hyperbilirubinemia, jaundice, gastrointestinal disturbances, potential cardiac arrhythmias | [37,38] |
| Darunavir/ Off-label | Treatment of HIV-1 infection [39] | Investigational use; assessed for potential anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity | Limited use: clinical trials did not demonstrate efficacy | Rash, diarrhea, headache, abdominal pain, potential liver enzyme elevations | [40,41] |
| Antiviral | Total ADRs | ICSRs | ADRs per ICSR |
|---|---|---|---|
| RDV | 6748 | 4105 | 1.64 |
| NTV/r | 19,977 | 8693 | 2.30 |
| FVP | 329 | 157 | 2.10 |
| LPVr | 15,194 | 6142 | 2.47 |
| RBV | 84,326 | 36,020 | 2.34 |
| NFV | 2580 | 958 | 2.69 |
| ATV | 9073 | 4432 | 2.05 |
| DRV | 9043 | 4269 | 2.11 |
| Category | RDV | NTV/r | FAV | LPV/r | RBV | NFV | ATV | DRV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age group | ||||||||
| Not specified | 594 (14.5) | 1401 (16.1) | 24 (14.74) | 1399 (22.8) | 8049 (22.3) | 205 (21.4) | 1115 (25.2) | 1221 (28.6) |
| 0–1 month | 5 (0.1) | 5 (0.1) | 0 (0.0) | 142 (2.3) | 36 (0.1) | 49 (5.1) | 38 (0.9) | 72 (1.7) |
| 2 months–2 years | 24 (0.6) | 1 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 82 (1.3) | 48 (0.1) | 14 (1.5) | 15 (0.3) | 13 (0.3) |
| 3–11 years | 28 (0.7) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 70 (1.1) | 60 (0.2) | 21 (2.2) | 8 (0.2) | 14 (0.3) |
| 12–17 years | 28 (0.7) | 19 (0.2) | 0 (0.0) | 87 (1.4) | 78 (0.2) | 18 (1.9) | 36 (0.8) | 47 (1.1) |
| 18–64 years | 1523 (37.1) | 3269 (37.6) | 92 (58.97) | 3754 (61.1) | 22,916 (63.6) | 628 (65.6) | 2998 (67.6) | 2670 (62.5) |
| 65–85 years | 1477 (36.0) | 3330 (38.3) | 39 (25.0) | 566 (9.2) | 4777 (13.3) | 23 (2.4) | 214 (4.8) | 223 (5.2) |
| >85 years | 426 (10.4) | 668 (7.7) | 2 (1.28) | 42 (0.7) | 56 (0.2) | 0 (0.0) | 8 (0.2) | 9 (0.2) |
| Sex | ||||||||
| Female | 1522 (37.1) | 5364 (61.7) | 60 (37.82) | 2210 (36.0) | 14,538 (40.4) | 324 (33.8) | 1393 (31.4) | 1384 (32.4) |
| Male | 2406 (58.6) | 2956 (34.0) | 93 (59.62) | 3309 (53.9) | 19,064 (52.9) | 571 (59.6) | 2639 (59.5) | 2482 (58.1) |
| Not specified | 177 (4.3) | 373 (4.3) | 4 (2.56) | 630 (10.1) | 2418 (6.7) | 63 (6.6) | 400 (9.0) | 404 (9.5) |
| Category | RDV | NTV/r | FAV | LPV/r | RBV | NFV | ATV | DRV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geographic origin | ||||||||
| EEA | 1472 (35.9) | 4206 (48.4) | 75 (48.08) | 2965 (48.3) | 12,582 (34.9) | 454 (47.4) | 2486 (56.1) | 2530 (59.3%) |
| Non-EEA | 2633 (64.1) | 4487 (51.6) | 82 (51.92) | 3177 (51.7) | 23,438 (65.1) | 504 (52.6) | 1946 (43.9) | 1739 (40.7%) |
| Reported group | ||||||||
| Healthcare professional | 3829 (93.3) | 4753 (54.7) | 143 (91.03) | 5269 (85.8) | 31,712 (88.0) | 859 (89.7) | 4143 (93.5) | 3890 (91.1%) |
| Non-healthcare professional | 276 (6.7) | 3940 (45.3) | 14 (8.97) | 441 (7.2) | 4209 (11.7) | 51 (5.3) | 251 (5.7) | 379 (8.9%) |
| Not specified | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 432 (7.0) | 99 (0.3) | 48 (5.0) | 38 (0.9) | 0 (0.0%) |
| Total | 4105 | 8693 | 157 | 6142 | 36,020 | 958 | 4432 | 4269 |
| Antiviral | S Cases | NS-Cases | S/NS Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| Remdesivir | 3448 (84) | 657 (16) | 5.24 |
| Nirmatrelvir/ritonavir | 5202 (59.8) | 3491 (40.2) | 1.49 |
| Favipiravir | 127 (81) | 30 (19) | 4.23 |
| Lopinavir/ritonavir | 5353 (87.2) | 789 (12.8) | 6.78 |
| Ribavirin | 33,442 (92.9) | 2578 (7.1) | 12.97 |
| Nelfinavir | 917 (95.7) | 41 (4.3) | 22.36 |
| Atazanavir | 4066 (91.7) | 366 (8.3) | 11.11 |
| Darunavir | 3565 (83.5) | 704 (16.5) | 5.06 |
| Total | 56,120 (86.6) | 8656 (13.4) | 6.48 |
| SOC Category (Specific Adverse Conditions Most Frequently Reported) | RDV | NTV/r | FVP | LPVr | RBV | NFV | ATV | DRV | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| General disorders and administration site conditions/ (fatigue, pyrexia, injection site reaction) | 1113 (5.4) | 3207 (15.6) | 41 (0.2) | 1812 (8.8) | 11,796 (57.6) | 276 (1.3) | 1070 (5.2) | 1178 (5.7) | 20,493 (31.6) |
| Investigations (elevated liver enzymes, abnormal blood glucose, prolonged prothrombin time) | 1070 (8.1) | 1036 (7.8) | 61 (0.5) | 1455 (11.0) | 7606 (57.5) | 264 (2.0) | 889 (6.7) | 838 (6.3) | 13,219 (20.4) |
| Gastrointestinal disorders (diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain) | 216 (1.7) | 3282 (26.0) | 13 (0.1) | 1590 (12.6) | 6165 (48.8) | 204 (1.6) | 547 (4.3) | 608 (4.8) | 12,625 (19.5) |
| Nervous system disorders (headache, dizziness, dysgeusia, neuropathy) | 207 (1.8) | 3460 (30.1) | 19 (0.2) | 774 (6.7) | 6000 (52.1) | 130 (1.1) | 426 (3.7) | 495 (4.3) | 11,511 (17.8) |
| Blood and lymphatic system disorders (anemia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia) | 124 (1.1) | 117 (1.0) | 9 (0.1) | 534 (4.7) | 9910 (87.6) | 126 (1.1) | 231 (2.0) | 258 (2.3) | 11,309 (17.5) |
| Infections and infestations (COVID-19, pneumonia, sepsis, oral candidiasis) | 707 (6.5) | 1755 (16.1) | 20 (0.2) | 868 (7.9) | 6207 (56.8) | 171 (1.6) | 530 (4.9) | 661 (6.1) | 10,919 (16.9) |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders (rash, pruritus, urticaria) | 272 (3.1) | 715 (8.2) | 12 (0.1) | 576 (6.6) | 5788 (66.7) | 145 (1.7) | 439 (5.1) | 727 (8.4) | 8674 (13.4) |
| Psychiatric disorders (insomnia, anxiety, confusional state, depression) | 60 (0.8) | 727 (10.3) | 7 (0.1) | 468 (6.6) | 5133 (72.4) | 37 (0.5) | 377 (5.3) | 278 (3.9) | 7087 (10.9) |
| Injury, poisoning and procedural complications (infusion site extravasation, overdose, administration error) | 400 (5.8) | 1072 (15.5) | 71 (1.0) | 1573 (22.8) | 2295 (33.3) | 139 (2.0) | 524 (7.6) | 822 (11.9) | 6896 (10.6) |
| Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders (dyspnea, respiratory failure, cough) | 502 (8.2) | 1003 (16.3) | 10 (0.2) | 425 (6.9) | 3801 (61.7) | 67 (1.1) | 151 (2.5) | 197 (3.2) | 6156 (9.5) |
| Metabolism and nutrition disorders (hyperglycemia, electrolyte imbalance, decreased appetite) | 123 (2.2) | 558 (10.1) | 5 (0.1) | 828 (14.9) | 3228 (58.2) | 173 (3.1) | 282 (5.1) | 349 (6.3) | 5546 (8.6) |
| Hepatobiliary disorders (hepatic enzyme increased, hepatitis, liver injury) | 431 (8.7) | 171 (3.4) | 20 (0.4) | 710 (14.3) | 2172 (43.7) | 111 (2.2) | 1006 (20.2) | 349 (7.0) | 4970 (7.7) |
| Renal and urinary disorders (acute kidney injury, increased creatinine, renal failure) | 429 (9.5) | 409 (9.1) | 8 (0.2) | 687 (15.2) | 1640 (36.3) | 68 (1.5) | 902 (20.0) | 373 (8.3) | 4516 (7.0) |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders (myalgia, arthralgia, back pain) | 48 (1.1) | 553 (12.8) | 6 (0.1) | 563 (13.1) | 2420 (56.2) | 100 (2.3) | 323 (7.5) | 292 (6.8) | 4305 (6.6) |
| Cardiac disorders (bradycardia, tachycardia, cardiac arrest, palpitations) | 597 (16.5) | 452 (12.5) | 10 (0.3) | 422 (11.6) | 1598 (44.1) | 85 (2.3) | 225 (6.2) | 237 (6.5) | 3626 (5.6) |
| Vascular disorders (hypertension, hypotension, deep vein thrombosis) | 195 (7.5) | 496 (19.0) | 5 (0.2) | 253 (9.7) | 1403 (53.7) | 45 (1.7) | 99 (3.8) | 119 (4.6) | 2615 (4.0) |
| Eye disorders (visual impairment, blurred vision, retinal changes) | 22 (0.9) | 225 (8.8) | 2 (0.1) | 158 (6.2) | 1916 (74.8) | 55 (2.1) | 80 (3.1) | 102 (4.0) | 2560 (4.0) |
| Immune system disorders (hypersensitivity, anaphylactic reaction, cytokine release syndrome) | 88 (5.0) | 174 (9.9) | 1 (0.1) | 293 (16.7) | 741 (42.2) | 48 (2.7) | 129 (7.4) | 281 (16.0) | 1755 (2.7) |
| Neoplasms benign, malignant and unspecified-including cysts and polyps (lymphoma, leukemia, benign neoplasm) | 19 (1.2) | 56 (3.6) | 1 (0.1) | 161 (10.2) | 1071 (68.1) | 35 (2.2) | 101 (6.4) | 129 (8.2) | 1573 (2.4) |
| Endocrine disorders (thyroid dysfunction, diabetes mellitus, adrenal insufficiency) | 9 (0.6) | 21 (1.4) | 2 (0.1) | 134 (9.2) | 1096 (75.4) | 13 (0.9) | 84 (5.8) | 95 (6.5) | 1454 (2.2) |
| Pregnancy, puerperium and perinatal conditions (spontaneous abortion, preterm labor, low birth weight) | 65 (4.7) | 8 (0.6) | 3 (0.2) | 358 (25.7) | 296 (21.2) | 133 (9.5) | 253 (18.1) | 278 (19.9) | 1394 (2.2) |
| Surgical and medical procedures (catheter placement, device removal, surgical intervention) | 5 (0.4) | 51 (4.4) | 0 (0.0) | 166 (14.4) | 637 (55.2) | 25 (2.2) | 172 (14.9) | 98 (8.5) | 1154 (1.8) |
| Ear and labyrinth disorders (tinnitus, hearing loss, vertigo) | 11 (1.2) | 189 (20.6) | 1 (0.1) | 41 (4.5) | 611 (66.5) | 10 (1.1) | 22 (2.4) | 34 (3.7) | 919 (1.4) |
| Congenital, familial and genetic disorders (congenital anomaly, genetic mutation, familial disorder) | 5 (0.6) | 13 (1.7) | 0 (0.0) | 231 (29.4) | 157 (20.0) | 95 (12.1) | 134 (17.0) | 151 (19.2) | 786 (1.2) |
| Reproductive system and breast disorders (menstrual disorder, gynecomastia, erectile dysfunction) | 2 (0.3) | 68 (11.7) | 2 (0.3) | 56 (9.6) | 343 (58.8) | 22 (3.8) | 44 (7.5) | 46 (7.9) | 583 (0.9) |
| Social circumstances (social isolation, caregiver burden, living conditions affected) | 4 (1.3) | 37 (11.6) | 0 (0.0) | 49 (15.4) | 181 (56.7) | 3 (0.9) | 27 (8.5) | 18 (5.6) | 319 (0.5) |
| Product issues (packaging error, product contamination, device malfunction) | 24 (7.8) | 122 (39.9) | 0 (0.0) | 9 (2.9) | 115 (37.6) | 0 (0.0) | 6 (2.0) | 30 (9.8) | 306 (0.5) |
| SOC | Comp | ROR RDV | CI Low RDV | CI High RDV | ROR NTV/r | CI Low NTV/r | CI High NTV/r |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cardiac disorders | ATV | 3.182 | 2.712 | 3.733 | - | - | - |
| DRV | 2.895 | 2.474 | 3.388 | - | - | - | |
| FVP | 2.502 | 1.311 | 4.775 | - | - | - | |
| LPV/r | 2.307 | 2.022 | 2.631 | - | - | - | |
| NFV | 1.748 | 1.376 | 2.22 | - | - | - | |
| RBV | 3.666 | 3.316 | 4.052 | 1.181 | 1.061 | 1.315 | |
| Ear and labyrinth disorders | ATV | - | - | - | 4.455 | 2.861 | 6.938 |
| DRV | - | - | - | 2.768 | 1.918 | 3.996 | |
| LPV/r | - | - | - | 3.307 | 2.356 | 4.643 | |
| NFV | - | - | - | 2.107 | 1.111 | 3.994 | |
| RBV | - | - | - | 1.288 | 1.092 | 1.519 | |
| Eye disorders | ATV | - | - | - | 1.445 | 1.117 | 1.87 |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ATV | - | - | - | 4.308 | 3.9 | 4.758 |
| DRV | - | - | - | 3.652 | 3.317 | 4.021 | |
| FVP | - | - | - | 6.719 | 3.802 | 11.872 | |
| LPV/r | - | - | - | 1.736 | 1.616 | 1.866 | |
| NFV | - | - | - | 2.242 | 1.909 | 2.633 | |
| RBV | - | - | - | 2.937 | 2.79 | 3.092 | |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | ATV | 1.169 | 1.06 | 1.288 | 1.837 | 1.693 | 1.993 |
| DRV | - | - | - | 1.534 | 1.416 | 1.662 | |
| FVP | - | - | - | 1.654 | 1.155 | 2.368 | |
| LPV/r | - | - | - | 1.397 | 1.302 | 1.498 | |
| NFV | - | - | - | 1.445 | 1.248 | 1.672 | |
| RBV | - | - | - | 1.2 | 1.143 | 1.261 | |
| Hepatobiliary disorders | DRV | 1.318 | 1.136 | 1.528 | - | - | - |
| RBV | 1.828 | 1.64 | 2.038 | - | - | - | |
| Infections and infestations | ATV | 1.532 | 1.356 | 1.73 | 1.862 | 1.677 | 2.068 |
| DRV | 1.136 | 1.011 | 1.275 | 1.381 | 1.252 | 1.523 | |
| FVP | - | - | - | 1.733 | 1.081 | 2.778 | |
| LPV/r | 1.264 | 1.134 | 1.409 | 1.537 | 1.406 | 1.68 | |
| RBV | - | - | - | 1.215 | 1.145 | 1.289 | |
| Injury, poisoning and procedural complications | RBV | 1.587 | 1.419 | 1.774 | 2.067 | 1.915 | 2.232 |
| Investigations | ATV | 1.405 | 1.27 | 1.555 | - | - | - |
| DRV | 1.443 | 1.302 | 1.6 | - | - | - | |
| LPV/r | 1.136 | 1.037 | 1.244 | - | - | - | |
| RBV | 1.317 | 1.223 | 1.418 | - | - | - | |
| Nervous system disorders | ATV | - | - | - | 6.218 | 5.577 | 6.932 |
| DRV | - | - | - | 5.041 | 4.547 | 5.588 | |
| FVP | - | - | - | 4.802 | 2.967 | 7.773 | |
| LPV/r | - | - | - | 4.586 | 4.205 | 5.001 | |
| NFV | - | - | - | 4.211 | 3.483 | 5.092 | |
| RBV | - | - | - | 3.308 | 3.143 | 3.482 | |
| Pregnancy, puerperium and perinatal conditions | RBV | 1.942 | 1.482 | 2.545 | - | - | - |
| Product issues | ATV | 4.338 | 1.771 | 10.624 | 10.5 | 4.623 | 23.85 |
| DRV | 2.011 | 1.347 | 3.004 | ||||
| LPV/r | 4.008 | 1.861 | 8.63 | 9.7 | 4.925 | 19.104 | |
| RBV | 1.836 | 1.181 | 2.854 | 4.444 | 3.441 | 5.74 | |
| Psychiatric disorders | DRV | - | - | - | 1.31 | 1.135 | 1.512 |
| NFV | - | - | - | 2.272 | 1.621 | 3.183 | |
| Renal and urinary disorders | DRV | 1.219 | 1.053 | 1.41 | - | - | - |
| FVP | 2.174 | 1.06 | 4.458 | - | - | - | |
| NFV | 1.527 | 1.171 | 1.993 | - | - | - | |
| RBV | 2.446 | 2.188 | 2.735 | - | - | - | |
| Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | ATV | 3.95 | 3.276 | 4.763 | 3.698 | 3.104 | 4.406 |
| DRV | 2.88 | 2.428 | 3.416 | 2.696 | 2.303 | 3.156 | |
| FVP | 2.048 | 1.072 | 3.913 | 1.917 | 1.007 | 3.65 | |
| LPV/r | 1.874 | 1.636 | 2.147 | 1.755 | 1.558 | 1.975 | |
| NFV | 1.853 | 1.421 | 2.416 | 1.735 | 1.342 | 2.242 | |
| RBV | 1.181 | 1.069 | 1.304 | 1.106 | 1.027 | 1.19 | |
| Vascular disorders | ATV | 2.183 | 1.707 | 2.791 | 2.648 | 2.128 | 3.296 |
| DRV | 1.739 | 1.379 | 2.194 | 2.11 | 1.722 | 2.587 | |
| LPV/r | - | - | - | 1.408 | 1.206 | 1.645 | |
| RBV | 1.231 | 1.056 | 1.435 | 1.493 | 1.344 | 1.659 |
| SOC Categories ROR > 1 (EudraVigilance) | Listed in SmPC | Findings in Other Studies | Observations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Remdesivir [55] | |||
| Cardiac disorders RORs (1.75–3.67) vs. all | No (sinus bradycardia * post-marketing) | Bradycardia [14,56,57,58], induced cardiotoxicity [14,59] | Noted in the literature, not consistently reflected in labeling |
| General disorders and administration site conditions ROR = 1.17 vs. ATV | Yes (infusion-related reaction r) | No data found | Listed in SmPC |
| Hepatobiliary disorders RORs (1.32–5.85) vs. DRV, RBV, and NTV/r | Yes (↑alanine aminotransferase/aspartate aminotransferase vc) | Elevated hepatic enzymes [60,61]; liver injury [62,63] | Listed in SmPC, consistent with known hepatic effects |
| Infections and Infestations RORs (1.14–1.53) vs. ATV, DRV, and LPV/r | No | No data found | Not listed in SmPC, disproportionate reporting can be caused by its antiviral mechanism that may have an influence on the immune system, increasing the risk of opportunistic infections |
| Injury, poisoning and procedural Complications ROR = 1.59 vs. RBV | Yes (infusion-related reaction r) | Injection site reaction [64,65] | Listed in SmPC |
| Investigations (abnormal lab findings) RORs (1.14–2.61) vs. ATV, DRV, LPV/r, RBV, and NTV/r | Yes (prothrombin time prolonged vc) | Rise in blood sugars [66,67]; low albumin, low potassium, low red blood cell count, low platelet count [68] | Listed in SmPC |
| Pregnancy and reproductive system disorders RORs (1.94, 17.47) vs. RBV and NTV/r | Precautionary guidance only; no adverse events listed | Limited published evidence; no confirmed safety signal to date [64] | Not listed in SmPC; low case numbers but disproportionate reporting suggests need for targeted monitoring in pregnancy-related contexts |
| Product issues RORs (1.84–4.34) vs. ATV, LPV/r, and RBV | No | Limited post-marketing reports on formulation and packaging; no peer-reviewed studies available | Not listed in SmPC—may indicate formulation or distribution-related concerns |
| Renal and urinary disorders RORs (1.22–2.45) vs. DRV, FVP, NFV, RBV and NTV/r | No | Kidney injury [62,69]; kidney disorders [70] acute kidney injury [71]; decreased glomerular filtration rate [67] | Noted in the literature, not currently listed in SmPC- may reflect underrecognized risk. |
| Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders RORs (1.07–3.95) vs. all | No | Respiratory failure [67,72,73] | Noted in the literature, not currently listed in SmPC may reflect disease severity rather than a direct effect of the drug |
| Vascular disorders RORs (1.23–2.18) vs. ATV, DRV, and RBV | No | No data found | Not listed in SmPC, may be related to disease progression, patient comorbidities, or the related cardiac adverse events presented in the literature |
| Nirmatrelvir/ritonavir [74] | |||
| Cardiac disorders ROR= 1.18 vs. ATV | No | Troponin I level changes [75]; DDIs in patients with cardiac diseases [76]; Cardiovascular sequelae [77]; Bradycardia [78] | Not listed in SmPC; may reflect cardiac risk, drug interactions or may be due to patients’ comorbidities, without confirmed causality |
| Ear and labyrinth disorders RORs (1.28–4.45) vs. all except FAV | No | No data found | Not listed in SmPC; may be caused by the infection itself which alter cochlear function |
| Eye disorders ROR= 1.44 vs. ATV | No | Retinal impairment [79] | Not listed in SmPC; may be caused just by ritonavir; ongoing pharmacovigilance and further studies are essential |
| Gastrointestinal disorders RORs (1.74–6.72) vs. all | Diarrhea c, vomiting c, nausea c Abdominal pain | Dysgeusia and diarrhea [80]; diarrhea, stomach pain [81]; nausea [54] | Listed in SmPC |
| General disorders and administration site conditions RORs (1.20–1.81) vs. all | Malaise r | Pale-colored stools, chromaturia, yellow skin, tongue coating [82] | Listed in SmPC |
| Infections and infestations RORs (1.21–1.84) vs. ATV, DRV, FVP, LPV/r, and RBV | No | No data found | Not listed in SmPC; may reflect opportunistic or secondary infections during COVID-19 |
| Injury, poisoning and procedural complications ROR= 1.27 vs. RBV | No | No data found | Not listed in SmPC; may result from administration errors or unrelated incidents during treatment; no confirmed causal link to the drug itself |
| Nervous system disorders | Dysgeusia c, headache c | Neurological sequelae [77]; neurological adverse reactions [83]; Headache [84]; dizziness [54] | Listed in SmPC |
| Product issues RORs (2.01–10.5) vs. ATV, DRV, LPV/r, and RBV | No | Limited post-marketing reports on formulation and packaging; no peer-reviewed studies found. | Not currently listed in SmPC—may indicate formulation or distribution-related concerns. |
| Psychiatric disorders RORs (1.31, 2.27) vs. DRV and NFV | Yes (Dysgeusia, headache c) | Neuropsychiatric effects [80,82,84] | Listed in SmPC |
| Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders RORs (1.11–3.70) vs. all | No | Dyspnea [85] | Not listed in SmPC; may reflect COVID-19 progression rather than a direct effect of the drug; it is a cause for worry, particularly in people who have pre-existing respiratory disorders. |
| Vascular disorders RORs (1.41–2.65) vs. ATV, DRV, LPV/r, and RBV | No | No data found | Not listed in SmPC; may reflect COVID-19–related vascular risk or drug interactions, or can be linked with the cardiac disorders |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Negru, P.A.; Tit, D.M.; Radu, A.F.; Bungau, G.; Corb Aron, R.A.; Marin, R.C. Comparative Pharmacovigilance Analysis of Approved and Repurposed Antivirals for COVID-19: Insights from EudraVigilance Data. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1387. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061387
Negru PA, Tit DM, Radu AF, Bungau G, Corb Aron RA, Marin RC. Comparative Pharmacovigilance Analysis of Approved and Repurposed Antivirals for COVID-19: Insights from EudraVigilance Data. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(6):1387. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061387
Chicago/Turabian StyleNegru, Paul Andrei, Delia Mirela Tit, Andrei Flavius Radu, Gabriela Bungau, Raluca Anca Corb Aron, and Ruxandra Cristina Marin. 2025. "Comparative Pharmacovigilance Analysis of Approved and Repurposed Antivirals for COVID-19: Insights from EudraVigilance Data" Biomedicines 13, no. 6: 1387. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061387
APA StyleNegru, P. A., Tit, D. M., Radu, A. F., Bungau, G., Corb Aron, R. A., & Marin, R. C. (2025). Comparative Pharmacovigilance Analysis of Approved and Repurposed Antivirals for COVID-19: Insights from EudraVigilance Data. Biomedicines, 13(6), 1387. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061387








