Abstract
Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes characterized by an extremely low rate of progression. It takes several years to move from the onset of diabetes, both type 1 and type 2, to the development of retinal microaneurysms, then leading to proliferative diabetic retinopathy and vision loss. The recent demonstration that retinal microaneurysms are preceded and, possibly, caused by a subclinical neurodegeneration mainly affecting the neurovascular unit has suggested, on one hand, the possible existence of a previously unknown early neurodegenerative stage of diabetic retinopathy and, on the other, that an early “neuroprotective” treatment could end up preventing the development of the microvascular stages. This review summarizes the present situation in the field and focuses on the prevention of diabetic retinopathy, which seems, for the first time, to be within reach.
1. Introduction
There is presently still no cure for diabetes. Both type 1 and type 2 diabetes are successfully treated with insulin [1] or with oral hypoglycemic agents [2], but the slight difference between cure and treatment, when protracted for years or decades, may still result in the development of diabetic complications [3,4].
Diabetic retinopathy (DR), neuropathy and nephropathy are defined as the microvascular complications of diabetes [3,5]. Just like neuropathy and nephropathy, DR is specific to patients affected by diabetes, but it is not mandatory; there are, in fact, individuals, so-called medalists, with 50 or more years of diabetes who are free of complications [6,7].
Microangiopathy represents the key feature of DR [8], characterized by abnormal growth and increased vascular permeability of retinal micro-vessels. The parallel death of pericytes worsens the situation and increases the permeability, thus leading to retinal edema. Dysfunctional vascular regeneration coupled to inflammation, oxidative stress and hyperosmolar stress [9] cooperate to accelerate the progression rate of the complication.
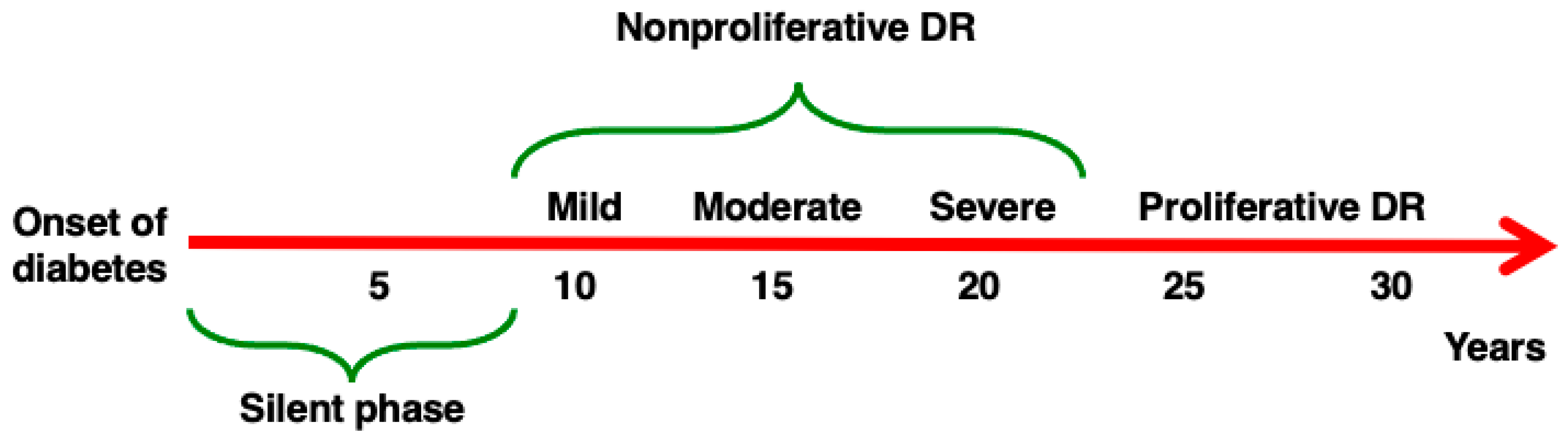
DR is characterized by an extremely slow rate of progression [10], as described in Figure 1, but all attempts thus far to stop or prevent its evolution have been substantially unsuccessful, and the only effective treatments for advanced DR currently are laser photocoagulation and intravitreal anti-VEGF injections [11,12].
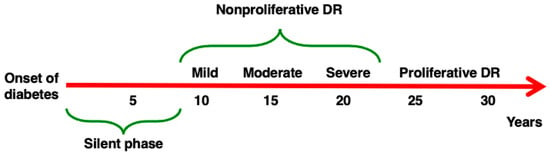
Figure 1.
Progression of DR. DR may develop in patients affected by both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes. After an initial silent phase, the four stages of DR develop in sequence. (1) Mild non-proliferative (NP) DR (characterized by the development of microaneurysms), (2) moderate NPDR (abnormal structure and caliber of blood vessels), (3) severe NPDR (reduced perfusion, diffuse ischemia), (4) proliferative DR (proliferation of new fragile blood vessels). The rate of progression of DR described here is approximative, as the natural history of the complication differs in different individuals.
The recent demonstration that microaneurysms might be preceded by a subclinical retinal neurodegeneration [13,14] could, on one hand, help clarify the pathogenesis of DR [15] and, on the other, allow us to set up, for the first time, a successful preventive strategy for DR.
2. Diabetic Retinopathy
DR is a well-established complication of diabetes that affects both type 1 and type 2 diabetic patients [16,17]. After the onset of diabetes, it takes a few years to develop retinal microaneurysms, the first clinical sign of DR. This stage, also known as non-proliferative retinopathy, may be followed by the development of intra-retinal hemorrhages, macular edema, hard exudates and capillary dropout resulting in microinfarcts resulting in diffuse ischemia. In a subset of patients, retinal ischemia leads to an angiogenic switch characterized by the increased synthesis of local vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), causing rapid growth of new, incompetent and leaky capillaries that can easily break and cause major bleeding and consequent hemovitreous. All the clinical signs described above are referable to a diffuse disease affecting small vessels and capillaries of the retina, thus justifying the inclusion of DR among the microvascular complications of diabetes [16,17].
From an epidemiological point of view, and despite the recent significant improvements in the therapeutic approaches for both types of diabetes, proliferative DR presently remains a prominent cause of blindness in working-age individuals in developed countries [18,19] and a cause of major psychological burden in the entire diabetic population [20].
3. Neurovascular Unit
Distribution and structure of the vasculature in the different tissues of an organism have always been supposed to be homogeneous. In 1885, however, Paul Ehrlich discovered that, after injecting a water-soluble dye into the circulatory system of different animals, the tracer stained all the organs with the exception of the brain, retina and spinal cord. A few years later a student of Paul Ehrlich, Edwin Goldman, showed that the phenomenon was reversible because, when the dye was injected inside the cerebrospinal fluid, it was able to stain the brain, but the rest of the organism remained unaffected by the procedure [21]. The brain and retina are therefore separated from the rest of the organism, and this was the first demonstration of the existence of a Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB) and of a Blood–Retina Barrier (BRB) [21,22].
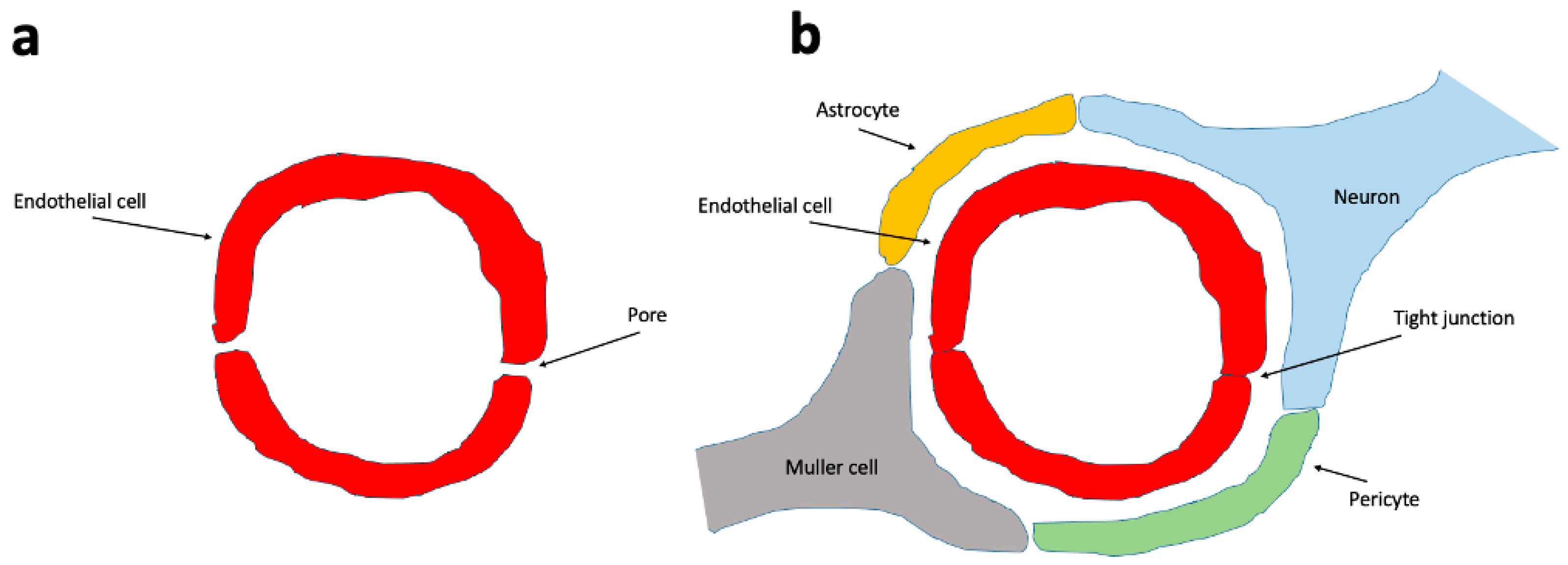
The BRB consists of the inner and outer BRB. The inner BRB (iBRB) consists of retinal capillary endothelial cells that form tight junctions and give rise to the microvascular component. This component, in addition to pericytes, neural cells such as ganglion cells, amacrine cells, bipolar and horizontal cells, immune cells (including microglia and macrophages), and macroglia (Muller cells), constitutes the retinal neurovascular unit (NVU, Figure 2), which also exists in the brain with the presence of BBB [22,23].
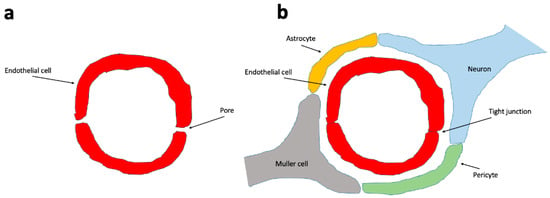
Figure 2.
The blood vessels that do not form a neurovascular unit have a more permeable endothelium. (a) The endothelial cells of all vessels have tight junctions. The non-neurovascular unit blood vessels’ endothelial cells do have numerous inter-endothelial cell gaps (permeable pores), making them more permeable to certain molecules. In the neurovascular unit (b), the endothelial cells are connected to each other by tight junctions and lack permeable pores. Endothelial cells are surrounded by pericytes, neurons and astrocytes that reinforce and stabilize the neurovascular unit.
The other retinal barrier, the oBRB, stands between the choriocapillaris and the retina and is formed by the choroid, Bruch’s membrane and the retinal pigmented epithelium.
Breakdown of the BRB that may follow the disruption of tight junctions and scattered neovascularization, but also neurodegeneration and pericyte dropout, results in cellular stress, retinal ischemia, leakage, and, finally, the development of diffuse edema. A scenario that is common to different retinal diseases [22,23].
4. Diseases Characterized by Retinal Neurodegeneration
The retina consists of a combination of vascular and neuronal components. When the light signal reaches the retina, it crosses all the neuronal layers and goes straight to the outer (deeper) side of the retina, where photoreceptors are situated.
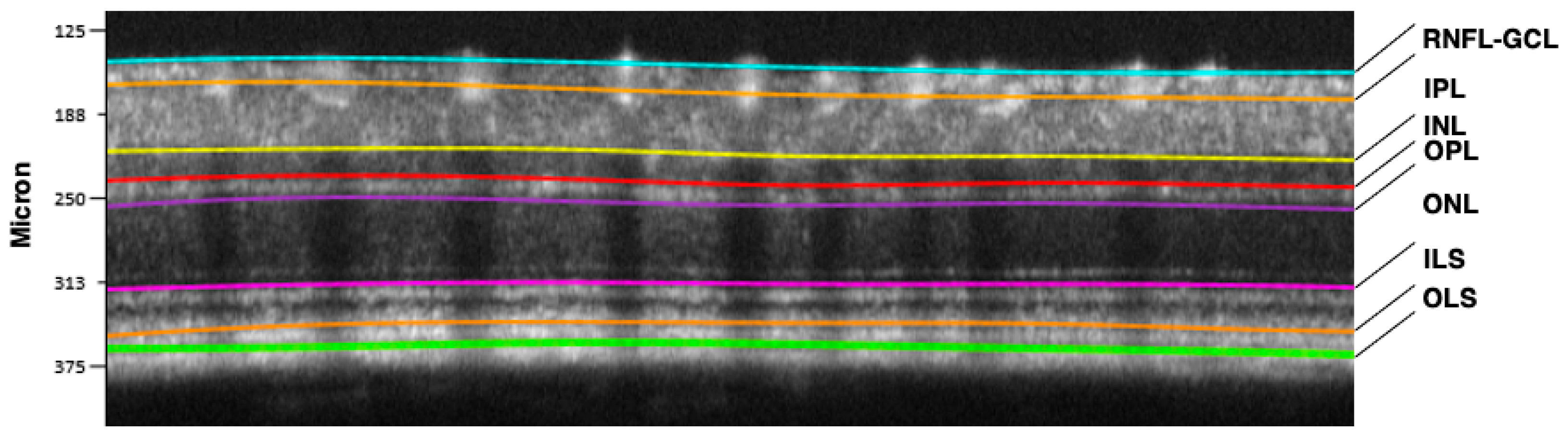
Starting from there, the signal is progressively sent back through the vertical pathway formed by photoreceptors, bipolar and retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) with their regulation by amacrine and horizontal neurons (horizontal pathway). RGC axons form the optic nerve, the “bridge” between the retina and the brain cortex [24,25]. A representative optical coherence tomography (OCT) scan of a normal murine retina describing in detail the different neuronal layers is shown in Figure 3.
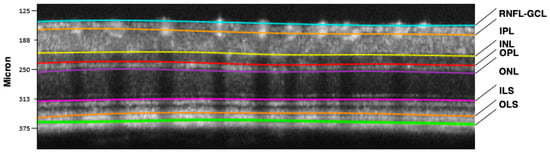
Figure 3.
Retinal segmentation performed by the Micron IV OCT System and InSight software, Version 1. (Phoenix Technology Group, Pleasanton, CA, USA) in a C57BL6J mouse. RNFL-GCL: retinal nerve fiber layer—ganglion cell layer complex (containing axons and bodies of retinal ganglion cells); IPL: inner plexiform layer (synaptic connections between amacrine, bipolar, and retinal ganglion cells); INL: inner nuclear layer (cell bodies of amacrine, bipolar, and horizontal cells); OPL: outer plexiform layer (synaptic connections between photoreceptors, bipolar and horizontal cells); ONL: outer nuclear layer (cell bodies of photoreceptors, rods and cones); ILS: photoreceptor inner segments; OLS: photoreceptor outer segments.
This system is extremely complex and is actually the target of a number of neurodegenerative diseases [26].
Glaucoma: Behind the term glaucoma lies a number of different optic neuropathies sharing the same clinical feature: the progressive degeneration of RGC and the lesion of the optic nerve. The disease is often associated with an increased intraocular pressure, but this is not always the case, as approximately half of the patients have a normal intraocular pressure. The strongest risk factors for glaucoma are age, followed by intraocular pressure and family history of the disease. Genetic factors are also involved in the predisposition to develop glaucoma [27,28].
Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD): In contrast with the wet form of AMD, which is the consequence of neovascularization, the dry form (the most common, 80% of the cases) is characterized by the suffering and dysfunction of retinal pigmented epithelium, by the progressive loss of photoreceptors, and by the degeneration of the retina. In both forms of AMD, the presence of drusen (fragments of cellular waste material) becomes detectable inside the retina. Risk factors for AMD are age, smoking habits, family history of the disease, dyslipidemia and hypertension [29,30].
Retinitis Pigmentosa: An inherited disease with a slow progression, characterized by the progressive death of photoreceptors and atrophy of retinal pigmented epithelium, eventually leading to blindness. The pathogenesis of the disease is the consequence of mutations in a number of specific genes of photoreceptors (in particular rods), causing degeneration of cones and dysfunction of retinal pigment epithelium and RGC [31,32].
The above-described diseases have the retina as the major target, but retinal neurodegeneration may be a “side” manifestation of brain diseases, as described below.
Alzheimer’s disease: Plaques of amyloid beta and neurofibrils of tau protein (the classic markers of Alzheimer’s disease in the brain) have been demonstrated in the retina of patients affected by Alzheimer’s disease, suggesting that these dysfunctions could explain the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s-associated retinal degeneration, a phenomenon characterized, in particular, by thinning of the retinal nerve fiber layer and loss of RGC [33,34].
Parkinson’s disease: Thinning of the retinal nerve fiber layer, of the ganglion cell-inner plexiform layer and of the retina in total characterizes the eye of the patients affected by Parkinson’s disease, confirming that retinal neurodegeneration is a central feature of the disease [35,36,37].
5. Diabetes-Driven Retinal Neurodegeneration
The concept that diabetes can directly induce the degeneration and death of neurons is a relatively new one. Endothelial cells have always been considered as the specific target of diabetes and, in particular, of glucotoxicity [38,39].
Peripheral nerves have also been identified as a target of diabetes, and in fact, once affected, they are directly involved in the pathogenesis of diabetic neuropathy [40]. Neurons, also known to express the insulin receptor, have been considered resistant to the dysmetabolism induced by diabetes [41,42].
We now know that diabetes may cause retinal neurodegeneration in different ways. Hyperglycemia by itself may damage retinal vessels and neural cells through multiple mechanisms, such as overproduction of advanced glycation end-products (AGEs) and activation of the polyol, hexosamine and diacylglycerol-protein kinase C pathways. In particular, increased production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the Krebs cycle may act as a “unifying mechanism” of the above pathways, as suggested by Brownlee et al. [43,44].
Recent evidence suggests that, in the case of diabetes, inflammation plays a major role in the early loss of RGC, the phenomenon that is now considered by many authors as the “primum movens” in the pathogenesis of DR [45,46]. Among the different transcription factors involved in the development of inflammation, the nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-kB) seems to have a specific role in the case of diabetes [47]. NF-kB is a widely expressed inducible transcription factor, a key regulator of the activity of many genes involved in inflammation and immune responses, and a major player in the modulation of cellular proliferation and apoptosis.
NF-kB, once activated, induces the transcription of pro-inflammatory proteins (such as inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM), and cytokines). Diabetes was shown to activate NF-kB in murine retinas [48,49] and to cause the nuclear relocation of its p65 subunit inside retinal endothelial cells, pericytes, RGCs, and cells of the inner nuclear layer [50,51]. DNA-binding activity of NF-kB is increased in retinal endothelial cells and pericytes exposed to elevated glucose concentrations. Finally, an increased NF-kB expression was demonstrated in epiretinal membranes of patients with proliferative DR [52]. Altogether these findings confirm the central role of NF-kB in the pathogenesis of early stages of DR.
From a functional/histologic point of view, features of diabetes-induced neurodegeneration, primarily attributable to metabolic alterations [53], include the activation of glial cells [54], the reduction in retinal neuronal function and the apoptosis of neuronal cells (in particular amacrine cells, RGC and photoreceptors) [15,55]. The search for biomarkers of retinal neurodegeneration of clinical use is presently under way; circulating biomarkers of increasing interest are glial-fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and neurofilament light chain (NFL) [56]. Recently, CXC-motif chemokine ligand 13 (CXCL13) has also been added to the list of candidate biomarkers [57].
As described above, the retina, just like the brain, is characterized by the presence of the neurovascular unit (NVU), a structure that is based on the physical and biochemical interaction between neurons, glial cells and retinal vessels [58]. The reciprocal interactions between the various components of the NVU may be significantly modified in the case of diabetes that causes the unbalancing of the mediators contained in the NVU itself, such as ATP, lactate, nitric oxide, arachidonic acid and other lipids [59]. Several studies have clearly demonstrated that diabetes-driven metabolic alterations cause neuronal degeneration, as evidenced by the impairment of glutamatergic and dopaminergic neurotransmitter signaling [60], by the modification of the dendritic fields [61] and by the reduced expression of synaptic proteins [58] induced by chronic hyperglycemia.
Another consequence of prolonged hyperglycemia is the activation of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta, an event that induces hyperphosphorylation of the tau protein and down-regulation of beta-catenin. These dysfunctions end up leading to mitochondrial abnormalities of RGC and to an acceleration of apoptosis [62].
In parallel, neuronal damage may also follow the development of insulin resistance and the reduction in sensitivity to neurotrophic factors, such as brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) [16].
Neurons by themselves may undergo apoptosis due to the persistent and uncontrolled hyperglycemia [63]. Glial cells may also endure significant modifications in case of diabetes, as demonstrated by the dysfunctional interconversion of glutamate and glutamine [64], the altered regulation of potassium channels [65], and the activation of glutamate-aspartate transporter and intermediate filament proteins, such as the glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP). Astrocytes, which are in tight contact with retinal blood vessels and with synapses [59], may also be dysfunctional, for still poorly understood reasons, in the case of diabetes [66]. Microglia probably play an adaptive role, at least in the short period, but may contribute to retinal damage when chronically stimulated [67].
In humans, the hypothesis of early neuronal damage induced by diabetes is supported by electrophysiology, imaging and clinical evidence, which demonstrate alterations already in the early stages of DR [68,69,70,71,72]. Electrophysiological alterations are assessed by the technique of multifocal electroretinography (mfERG), which allows us to highlight that, in the case of diabetes, the timing of mfERG is delayed in retinal areas affected by vascular lesions and that the delay increases with the increase in the dimensions of the lesions. The amplitude of mfERG is instead normal or slightly reduced both inside and outside the retinal lesions [71,73,74].
Anatomical distribution of neuro-retinal alterations can be precisely investigated by optical coherence tomography (OCT), which, in the early stages of the disease, is able to demonstrate a significant thinning of the retinal nerve fiber layer and photoreceptor layers in patients with type 1 diabetes, while in type 2 diabetic patients, there is a diffuse thinning of the retinal nerve fiber layer, ganglion cell layer, inner plexiform layer, inner nuclear layer, outer plexiform layer and photoreceptor layers [75]. In the early phase of DR, during which no alterations are noted on fundus examination, a reduced contrast sensitivity and an alteration in color vision have been demonstrated [76,77,78].
6. Diabetes-Driven Retinal Neurodegeneration as the First Stage of Diabetic Retinopathy
DR is a complication of both type 1 and type 2 diabetes characterized by an extremely slow rate of progression. It takes years, in most cases decades, to move from the onset of diabetes to the development of retinal microaneurysms, the “classic” first signs of the complication [16,17]. Even though it has always been reasonable to assume that diabetes should actually start acting on the retina since its first manifestation, we have been, until recently, unable to document morphological changes in a diabetic retina during the silent phase that precedes the appearance of microaneurysms.
Even though neurodegeneration was for the first time suggested to be involved in the pathogenesis of DR in 1962 by JM Bloodworth [79], it took 40 more years before it was shown that retinal neurodegeneration may precede the vascular stage of DR and therefore that, at least potentially, it could also contribute to its development [80,81,82]. Neuronal dysfunction involves different cells inside the NVU, and typical signs of neurodegeneration, such as glial activation and RGC death, have been identified in animal models of diabetes and ex vivo in retinas of diabetic patients before any detectable signs of vascular stages of DR [63,83,84,85,86,87,88].
During the last few years, the technology applied to the field of ophthalmology has significantly improved, and new techniques have been developed and subsequently applied to clarify the role of early retinal neurodegeneration in the pathogenesis of DR [89,90,91,92]. OCT [13,93], OCT angiography (OCTA) [68,94], flicker-evoked retinal vasodilation [95,96] and mfERG [97,98], have rapidly become of common use, first as research tools (both in humans and in different animal models) and then rapidly translated into clinical practice.
The results of these studies substantially confirmed that, in the case of diabetes, retinal neurodegeneration precedes or parallels the development of the vascular signs of DR. As a consequence of these findings, in 2017 the American Diabetes Association turned the definition of DR from “vascular complication of diabetes” to “neurovascular complication of diabetes” [10].
The issue that still remains to be clarified is whether retinal neurodegeneration is a necessary or an optional step in the pathogenesis of DR. The evidence that patients with long-lasting type 1 diabetes and absence of DR are also free of retinal neurodegeneration [99] is in line with the hypothesis that the absence of neurodegeneration may protect from the subsequent development of DR. Conversely, the results of the large EUROCONDOR study [98] performed in type 2 diabetic patients suggest that, in a subset of patients, DR develops without a preceding retinal neurodegeneration.
A possible alternative way to clarify the role of retinal neurodegeneration in the pathogenesis of DR consists of verifying whether it is possible to avoid the development of the vascular stages of DR through an early preventive treatment based on agents known to have a neuroprotective effect.
7. Diabetes-Driven Retinal Neurodegeneration as a Pharmacological Target to Prevent the Vascular Stages of Diabetic Retinopathy
As described above, retinal neurodegeneration plays a significant role in the pathogenesis of DR, and it has been observed to precede microvascular alterations [100,101]. Early retinal neurodegeneration therefore represents the ideal target when planning to set up a pharmacologic strategy aimed to stop the progression of the complication and to avoid the development of its sight-threatening vascular stages. A number of different approaches have been implemented in the last few years to reach this aim.
Fenofibrate is an oral medication of the fibrate class and a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARalfa) agonist [102]. Two major clinical trials (Fenofibrate Intervention and Event Lowering in Diabetes (FIELD) Study and Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes (ACCORD) Eye Study) have demonstrated that fenofibrate is able to interrupt the progression of DR in patients affected by type 2 diabetes [103,104,105]. Studies on a murine model of type 2 diabetes (db/db mice) have revealed that fenofibrate influences circulating lipids, modulates gliosis and improves electroretinogram (ERG) abnormalities [106], thus confirming its neuroprotective (by reducing reactive gliosis, apoptosis and glutamate excitotoxicity [103]) and vasculotropic effect [107].
Calcium dobesilate (CaD) is a drug that has been approved for the treatment of DR in different countries, but only recently has its neuroprotective effect been deeply studied, thus confirming its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties and its vascular effects [108]. Bogdanov et al. demonstrated that CaD is able to determine a decrease in oxidative stress and a downregulation of several pro-inflammatory cytokines, like IL-6, KC analog IL-8, TNF-alpha and MCP-1, determining a reduction in both neurodegeneration and vascular leakage in a murine model of diabetes (db/db mice) [109]. Additionally, it has been shown that CaD reduces the levels of endothelin-1 (ET-1), a vasoconstrictor peptide, thereby decreasing the activity of endothelin B receptor (ETB-R) expressed by retinal neurons and endothelin A receptor (ETA-R) expressed by blood vessels [110].
Bosentan is a dual ETA-R and ETB-R antagonist [111]. Upregulation of ET-1 and ETB-R was demonstrated in the retinas of diabetic patients [112]. Bosentan, given via topical administration (eye drops), was able to reduce the levels of retinal ET-1, ETB-R and ETA-R (after quantification of immunofluorescence) in db/db mice, thus resulting in a reduction in both reactive gliosis and apoptosis rates [112], in an improvement of the integrity of the vasculature, and in a reduction in the number of acellular capillaries, a characteristic of DR common to diabetic patients and animal models of diabetes [113].
TNF-alpha blockers, such as Etanercept and CNT05048, are drugs targeting TNF-alpha, a well-established inflammatory cytokine [54]. TNF-alpha activates the NF-kB pathway, thus inducing iNOS expression, ROS formation and upregulation of adhesion molecules such as VCAM, ICAM-1 and E-selectin, all of which contribute to leukostasis and DR progression [114]. The blockade of TNF-alpha inflammatory pathway results in apoptosis reduction, anti-VEGF effect and decrease in leukostasis, confirming the central role of inflammation in the pathogenesis of DR and underlying its potential as a pharmacological target [115]. Clinical translation of these results is expected when clinical trials are completed [116].
Suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCS) are a family of intracellular proteins whose role is to inhibit cytokine signaling through the downregulation of the JAK/signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) signaling pathway in different cell types. In particular, SOCS1 and SOCS3 modulate the innate and adaptive immune response [117]. Treatment based on cell-penetrating peptides derived from the kinase inhibitory region of SOCS1 and SOCS3 (R9-SOCS1-KIR and R9-SOCS3-KIR) was shown to reduce inflammation, oxidative stress and neo-angiogenesis, pathways involved in retinal neurodegeneration and vascular alterations, thus confirming their possible role in managing DR [118]. R9-SOCS3-KIR was shown to reduce inflammation and oxidative stress in a human retinal pigment epithelium cell line [119].
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are a widely prescribed pharmacological class, known for its anti-inflammatory, antipyretic and analgesic effects [54]. Yukiko et al. demonstrated that administration of Sulindac has the capability to halt DR progression through the inhibition of cyclooxygenase (COX)-1 and COX-2 and through the blockade of the NF-kB pathway [120]. Other NSAIDs, such as indomethacin, bromfenac and nepafenac, were shown to be effective in reducing inflammation, ameliorating alterations in retinal thickness and in arteriole diameter [121]. In a recent study, a polypill, including metformin, aspirin, simvastatin, and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, was administered in a mixed murine model of Alzheimer’s disease and type 2 diabetes, showing promising results in ameliorating metabolic parameters, cognitive impairment, brain atrophy, neuronal and synaptic loss, amyloid burden, tau phosphorylation, central inflammation and central spontaneous bleeding [122]. Common pathways relating dementia and DR have been identified, suggesting new therapeutic opportunities to prevent the diabetic complications [55]. However, more studies on the application of NSAIDs in diabetes-driven retinal neurodegeneration are needed to verify its neuroprotective effects.
Antioxidant active compounds have been demonstrated to be effective in reducing inflammation and oxidative stress, both playing a pivotal role in DR pathogenesis, as confirmed in vitro and in animal studies [123]. Oxidative stress determines an increase in ROS production, thereby determining vascular damage via capillary cell apoptosis and inflammation and neurodegeneration in the early phases of DR [124]. For all these reasons, antioxidant molecules could represent a valid tool to counteract retinal neurodegeneration, in particular when administered in the early phase of the disease [125].
Peptides with neurotrophic and anti-angiogenic activities, such as pigment epithelial growth factor (PEDF), somatostatin, glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) or molecules that prevent the degradation of these peptides, such as DPP-IV inhibitors, were studied in experimental models and were shown to be effective strategies in slowing down DR progression [126,127,128,129]. Sitagliptin (DPP-IV inhibitor) administered as eye drops improved the dysfunction of the neurovascular unit in the Trpv2+/− rat (a non-diabetic animal model that develops DR-like lesions), determining a significant reduction in retinal thinning, glial activation, inflammation, oxidative stress, abnormal vasodilatation and vasodegeneration, thus confirming its protective effect against the development of retinal neurodegeneration [130]. Moreover, sitagliptin and liraglutide (a GLP-1 receptor agonist) were shown to be effective in reducing the phosphorylation of tau, a toxic mediator of retinal ganglion cell synaptic neurodegeneration, underlying the important role of correct synaptic connectivity in order to prevent retinal degeneration in DR [131]. Other molecules, like taurine [132] and lutein [133], may also have a conservative role, protecting in particular the retinal synaptic connections.
Complement modulators have also been taken into consideration as a possible pharmacological strategy to prevent retinal neurodegeneration [131]. Innate immunity is upregulated in DM, determining chronic inflammation and, ultimately, neuronal and vascular damage [134]. However, the role of the activation of the complement system in the pathogenesis of diabetes-driven retinal neurodegeneration remains unclear [135].
Neurotrophins, including nerve growth factor (NGF) and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), were studied to assess the possibility of preventing retinal neurodegeneration in DR and, consequently, to avert retinal vascular damage [136,137]. Studies on a murine model of diabetes (Ins2akita mouse) have demonstrated that topical administration of NGF has the capability of preventing early retinal neurodegeneration and subsequent loss of retinal pericytes and development of acellular capillaries, two retinal dysfunctions of DR common to humans and animal models of diabetes [138]. A key point in this field is to identify a way to perform a long-lasting administration of neurotrophins directly in the eye to avoid multiple eye drop deliveries and to prevent the systemic side effects of these powerful growth factors [137]. As a possible solution, Pelusi et al. demonstrated the effectiveness of bioengineered human corneal lenticule as a promising delivery system for recombinant human NGF (rhNGF) [139].
Mesenchymal stromal/stem cells (MSCs) have also been explored as a potential therapy in DR. MSCs are known to release factors such as fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), VEGF, insulin-like growth factor (IGF), NGF and BDNF, factors that are known to protect from neurodegeneration [140]. In particular, a study based on human retinal progenitor cells (RPCs) derived from fetal retinas, embryonic stem cells (ESCs) and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) demonstrated the capacity of these cells to integrate into the retina of a murine model of diabetes when injected under the retina [141]. In this way it is possible to prevent neuronal loss and diabetes-driven retinal neurodegeneration [141]. In addition, amniotic stem cells, placental stem cells, neural stem cells and human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (HUCMSCs) were all found effective in regenerating neuronal cells in murine models of diabetes [142]. A list of neuroprotective drugs is described in Table 1.

Table 1.
List of drugs used in the prevention and/or treatment of diabetes-driven retinal neurodegeneration.
8. Conclusions and Perspectives
There is a substantial agreement in the recent literature that diabetes, besides retinal microangiopathy, is also the cause of the early development of retinal neurodegeneration.
Retinal neurodegeneration is a well-known common feature of diseases such as glaucoma, AMD, Retinitis pigmentosa, Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. In all these cases, however, behind the development of retinal dysfunction, there is familial and/or genetic predisposition. Conversely, in the case of DR, retinal neurodegeneration seems to be the direct consequence of the dysmetabolism induced by diabetes and, in particular, of high ambient glucose.
Whether retinal neurodegeneration may also represent the initial cause of DR is presently still unclear, even though a large number of basic and clinical studies are aimed at clarifying this issue. The possibility that early retinal neurodegeneration may represent a necessary step toward the development of the vascular stages in some, but not in all, diabetic patients has also been suggested [13].
Whatever the case, the discovery that diabetes, by itself, may cause retinal neurodegeneration and that this dysfunction could, at least potentially, contribute to the development of the subsequent stages of DR paves the way toward the search for specific treatments that can prevent or treat the dysfunction. As described above, a large number of basic and clinical studies are presently ongoing with the aim to identify the best possible neuroprotective agent able to prevent the retinal neurodegeneration induced by diabetes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.Z., A.A., R.L. and I.V.; methodology, D.G. and S.G.; data curation, G.B., V.P. and S.G.; writing—original draft preparation, G.Z., V.P., I.V., D.G., G.B. and E.A.; writing—review and editing, R.L., A.A. and E.A.; supervision, G.Z., F.B. and I.V.; funding acquisition, F.B., D.G. and G.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the European Union—Next Generation EU—NRRP M6C2—Investment 2.1 Enhancement and strengthening of biomedical research in the NHS. PNRR-MAD-2022-12376008, Cup Master C43C22001100007.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Carr, A.L.J.; Evans-Molina, C.; Oram, R.A. Precision medicine in type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 2022, 65, 1854–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, E.; Lim, S.; Lamptey, R.; Webb, D.R.; Davies, M.J. Type 2 diabetes. Lancet 2022, 400, 1803–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, J.M.; Cooper, M.E. Mechanisms of diabetic complications. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 137–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiborn, C.; Schulze, M.B. Precision prognostics for the development of complications in diabetes. Diabetologia 2022, 65, 1867–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishriky, B.M.; Cummings, D.M.; Powell, J.R. Diabetes-Related Microvascular Complications—A Practical Approach. Prim. Care 2022, 49, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.K.; Keenan, H.A.; Cavallerano, J.D.; Asztalos, B.F.; Schaefer, E.J.; Sell, D.R.; Strauch, C.M.; Monnier, V.M.; Doria, A.; Aiello, L.P.; et al. Protection from retinopathy and other complications in patients with type 1 diabetes of extreme duration: The joslin 50-year medalist study. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 968–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keenan, H.A.; Costacou, T.; Sun, J.K.; Doria, A.; Cavellerano, J.; Coney, J.; Orchard, T.J.; Aiello, L.P.; King, G.L. Clinical factors associated with resistance to microvascular complications in diabetic patients of extreme disease duration: The 50-year medalist study. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 1995–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madonna, R.; Balistreri, C.R.; Geng, Y.J.; De Caterina, R. Diabetic microangiopathy: Pathogenetic insights and novel therapeutic approaches. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2017, 90, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madonna, R.; Giovannelli, G.; Confalone, P.; Renna, F.V.; Geng, Y.J.; De Caterina, R. High glucose-induced hyperosmolarity contributes to COX-2 expression and angiogenesis: Implications for diabetic retinopathy. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2016, 15, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, S.D.; Chew, E.; Duh, E.J.; Sobrin, L.; Sun, J.K.; VanderBeek, B.L.; Wykoff, C.C.; Gardner, T.W. Diabetic Retinopathy: A Position Statement by the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandello, F.; Lattanzio, R.; Zucchiatti, I.; Del Turco, C. Pathophysiology and treatment of diabetic retinopathy. Acta Diabetol. 2013, 50, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrigo, A.; Aragona, E.; Bandello, F. VEGF-targeting drugs for the treatment of retinal neovascularization in diabetic retinopathy. Ann. Med. 2022, 54, 1089–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, E.H.; van Dijk, H.W.; Jiao, C.; Kok, P.H.; Jeong, W.; Demirkaya, N.; Garmager, A.; Wit, F.; Kucukevcilioglu, M.; van Velthoven, M.E.; et al. Retinal neurodegeneration may precede microvascular changes characteristic of diabetic retinopathy in diabetes mellitus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E2655–E2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, W.W.; Bearse, M.A., Jr.; Ng, J.S.; Jewell, N.P.; Barez, S.; Burger, D.; Schneck, M.E.; Adams, A.J. Multifocal electroretinograms predict onset of diabetic retinopathy in adult patients with diabetes. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 772–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simó, R.; Stitt, A.W.; Gardner, T.W. Neurodegeneration in diabetic retinopathy: Does it really matter? Diabetologia 2018, 61, 1902–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonetti, D.A.; Klein, R.; Gardner, T.W. Diabetic retinopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1227–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, N.; Mitchell, P.; Wong, T.Y. Diabetic retinopathy. Lancet 2010, 376, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, J.W.; Rogers, S.L.; Kawasaki, R.; Lamoureux, E.L.; Kowalski, J.W.; Bek, T.; Chen, S.J.; Dekker, J.M.; Fletcher, A.; Grauslund, J.; et al. Global prevalence and major risk factors of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leasher, J.L.; Bourne, R.R.; Flaxman, S.R.; Jonas, J.B.; Keeffe, J.; Naidoo, K.; Pesudovs, K.; Price, H.; White, R.A.; Wong, T.Y.; et al. Global estimates on the number of people blind or visually impaired by diabetic retinopathy: A meta-analysis from 1990 to 2010. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 1643–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenwick, E.; Rees, G.; Pesudovs, K.; Dirani, M.; Kawasaki, R.; Franzco, T.Y.W.; Lamoureux, E. Social and emotional impact of diabetic retinopathy: A review. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2012, 40, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, B.T.; Davis, T.P. The blood-brain barrier/neurovascular unit in health and disease. Pharmacol. Rev. 2005, 57, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha-Vaz, J.; Bernardes, R.; Lobo, C. Blood-retinal barrier. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2011, 21, S3–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, F.; Campbell, M. The blood-retina barrier in health and disease. FEBS J. 2023, 290, 878–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoon, M.; Okawa, H.; Della Santina, L.; Wong, R.O. Functional architecture of the retina: Development and disease. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2014, 42, 44–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masland, R.H. The fundamental plan of the retina. Nat. Neurosci. 2001, 4, 877–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, A.; Guimarães, P.; Martins, J.; Moreira, P.I.; Ambrósio, A.F.; Castelo-Branco, M.; Serranho, P.; Bernardes, R. Normative mice retinal thickness: 16-month longitudinal characterization of wild-type mice and changes in a model of Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1161847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinreb, R.N.; Aung, T.; Medeiros, F.A. The pathophysiology and treatment of glaucoma: A review. JAMA 2014, 311, 1901–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaram, H.; Kolko, M.; Friedman, D.S.; Gazzard, G. Glaucoma: Now and beyond. Lancet 2023, 402, 1788–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambati, J.; Fowler, B.J. Mechanisms of age-related macular degeneration. Neuron 2012, 75, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, N.M.; Bhardwaj, S.; Barclay, C.; Gaspar, L.; Schwartz, J. Global Burden of Dry Age-Related Macular Degeneration: A Targeted Literature Review. Clin. Ther. 2021, 43, 1792–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, S.; Li, P.; Yao, K. Retinitis Pigmentosa: Progress in Molecular Pathology and Biotherapeutical Strategies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamde, S.P.; Anjankar, A. Retinitis Pigmentosa: Pathogenesis, Diagnostic Findings, and Treatment. Cureus 2023, 15, e48006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koronyo-Hamaoui, M.; Koronyo, Y.; Ljubimov, A.V.; Miller, C.A.; Ko, M.K.; Black, K.L.; Schwartz, M.; Farkas, D.L. Identification of amyloid plaques in retinas from Alzheimer’s patients and noninvasive in vivo optical imaging of retinal plaques in a mouse model. Neuroimage 2011, 54 (Suppl. S1), S204–S217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, M.R.; Robinson, E.; Koronyo, Y.; Salobrar-Garcia, E.; Rentsendorj, A.; Gaire, B.P.; Mirzaei, N.; Kayed, R.; Sadun, A.A.; Ljubimov, A.V.; et al. Retinal ganglion cell vulnerability to pathogenic tau in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2025, 13, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poveda, S.; Arellano, X.; Bernal-Pacheco, O.; Valencia López, A. Structural changes in the retina as a potential biomarker in Parkinson’s disease: An approach from optical coherence tomography. Front. Neuroimaging 2024, 3, 1340754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murueta-Goyena, A.; Romero-Bascones, D.; Teijeira-Portas, S.; Urcola, J.A.; Ruiz-Martínez, J.; Del Pino, R.; Acera, M.; Petzold, A.; Wagner, S.K.; Keane, P.A.; et al. Association of retinal neurodegeneration with the progression of cognitive decline in Parkinson’s disease. npj Park. Dis. 2024, 10, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murueta-Goyena, A.; Teijeira-Portas, S.; Blanco Martín, E.; Vázquez-Picón, R.; Ruiz Bajo, B.; Bocos, J.; Sánchez-Molina, J.; Alves Dias, P.; Croitoru, I.; Rodríguez Agirretxe, I.; et al. Dynamics of retinal changes in early-stage Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2025, 13, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzi, M.; Cagliero, E.; Toledo, S. Glucose toxicity for human endothelial cells in culture. Delayed replication, disturbed cell cycle, and accelerated death. Diabetes 1985, 34, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzi, M.; Montisano, D.F.; Toledo, S.; Barrieux, A. High glucose induces DNA damage in cultured human endothelial cells. J. Clin. Investig. 1986, 77, 322–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, E.L.; Callaghan, B.C.; Pop-Busui, R.; Zochodne, D.W.; Wright, D.E.; Bennett, D.L.; Bril, V.; Russell, J.W.; Viswanathan, V. Diabetic neuropathy. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milstein, J.L.; Ferris, H.A. The brain as an insulin-sensitive metabolic organ. Mol. Metab. 2021, 52, 101234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gralle, M. The neuronal insulin receptor in its environment. J. Neurochem. 2017, 140, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, T.; Edelstein, D.; Brownlee, M. The missing link: A single unifying mechanism for diabetic complications. Kidney Int. 2000, 58, S26–S30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brownlee, M. The pathobiology of diabetic complications: A unifying mechanism. Diabetes 2005, 54, 1615–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Kern, T.S. Inflammation in diabetic retinopathy. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2011, 30, 343–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kern, T.S.; Barber, A.J. Retinal ganglion cells in diabetes. J. Physiol. 2008, 15, 4401–4408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, R.G.; Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. NF-κB, inflammation, and metabolic disease. Cell Metab. 2011, 13, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Szab, C.; Kern, T.S. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase is involved in the development of diabetic retinopathy via regulation of nuclear factor-kappaB. Diabetes 2004, 53, 2960–2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowluru, R.A.; Kowluru, V.; Xiong, Y.; Ho, Y.S. Overexpression of mitochondrial superoxide dismutase in mice protects the retina from diabetes-induced oxidative stress. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2006, 41, 1191–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, G.; Liu, W.H.; Asnaghi, V.; Kern, T.S.; Lorenzi, M. Activation of nuclear factor-kappaB induced by diabetes and high glucose regulates a proapoptotic program in retinal pericytes. Diabetes 2002, 51, 2241–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Howell, S.J.; Hatala, D.A.; Huang, K.; Kern, T.S. Salicylate-based anti-inflammatory drugs inhibit the early lesion of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes 2007, 56, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitamura, Y.; Harada, T.; Harada, C.; Ohtsuka, K.; Kotake, S.; Ohno, S.; Tanaka, K.; Takeuchi, S.; Wada, K. NF-kappaB in epiretinal membranes after human diabetic retinopathy. Diabetologia 2003, 46, 699–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Li, B.; Huang, T.; Wang, B.; Li, S.; Yu, K.; Cai, L.; Ye, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhu, H.; et al. Update in the molecular mechanism and biomarkers of diabetic retinopathy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2025, 1871, 167758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, H.; Hernández, C.; Simó, R.; Simó-Servat, O. Inflammation: The Link between Neural and Vascular Impairment in the Diabetic Retina and Therapeutic Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, K.; Llorián-Salvador, M.; Scullion, S.; Hernández, C.; Simó-Servat, O.; Del Marco, A.; Bosma, E.; Vargas-Soria, M.; Carranza-Naval, M.J.; Van Bergen, T.; et al. Common pathways in dementia and diabetic retinopathy: Understanding the mechanisms of diabetes-related cognitive decline. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 33, 50–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández, C.; Simó-Servat, O.; Porta, M.; Grauslund, J.; Harding, S.P.; Frydkjaer-Olsen, U.; García-Arumí, J.; Ribeiro, L.; Scanlon, P.; Cunha-Vaz, J.; et al. Serum glial fibrillary acidic protein and neurofilament light chain as biomarkers of retinal neurodysfunction in early diabetic retinopathy: Results of the EUROCONDOR study. Acta Diabetol. 2023, 60, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajari, J.N.; Ilginis, T.; Pedersen, T.T.; Lønkvist, C.S.; Saunte, J.P.; Hofsli, M.; Schmidt, D.C.; Al-Abaiji, H.A.; Ahmed, Y.; Bach-Holm, D.; et al. Novel Blood-Biomarkers to Detect Retinal Neurodegeneration and Inflammation in Diabetic Retinopathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, T.W.; Davila, J.R. The neurovascular unit and the pathophysiologic basis of diabetic retinopathy. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2017, 255, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, E.A. Glial cell regulation of neuronal activity and blood flow in the retina by release of gliotransmitters. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 370, 20140195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aung, M.H.; Park, H.N.; Han, M.K.; Obertone, T.S.; Abey, J.; Aseem, F.; Thule, P.M.; Iuvone, P.M.; Pardue, M.T. Dopamine deficiency contributes to early visual dysfunction in a rodent model of type 1 diabetes. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 726–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastinger, M.J.; Kunselman, A.R.; Conboy, E.E.; Bronson, S.K.; Barber, A.J. Dendrite remodeling and other abnormalities in the retinal ganglion cells of Ins2 Akita diabetic mice. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2008, 49, 2635–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragiotta, S.; Pinazo-Durán, M.D.; Scuderi, G. Understanding Neurodegeneration from a Clinical and Therapeutic Perspective in Early Diabetic Retinopathy. Nutrients 2022, 14, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, A.J.; Gardner, T.W.; Abcouwer, S.F. The significance of vascular and neural apoptosis to the pathology of diabetic retinopathy. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 1156–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieth, E.; LaNoue, K.F.; Antonetti, D.A.; Ratz, M. Diabetes reduces glutamate oxidation and glutamine synthesis in the retina. Exp. Eye Res. 2000, 70, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pannicke, T.; Iandiev, I.; Wurm, A.; Uckermann, O.; vom Hagen, F.; Reichenbach, A.; Wiedemann, P.; Hammes, H.P.; Bringmann, A. Diabetes alters osmotic swelling characteristics and membrane conductance of glial cells in rat retina. Diabetes 2006, 55, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, A.J.; Antonetti, D.A.; Gardner, T.W. Altered expression of retinal occludin and glial fibrillary acidic protein in experimental diabetes. The Penn State Retina Research Group. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2000, 41, 3561–3568. [Google Scholar]
- Karlstetter, M.; Scholz, R.; Rutar, M.; Wong, W.T.; Provis, J.M.; Langmann, T. Retinal microglia: Just bystander or target for therapy? Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2015, 45, 30–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Kim, E.S.; Kim, D.G.; Yu, S.Y. Progressive retinal neurodegeneration and microvascular change in diabetic retinopathy: Longitudinal study using OCT angiography. Acta Diabetol. 2019, 56, 1275–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.C.; Chau, F.Y.; Lim, J.I.; McAnany, J.J. Electrophysiological and pupillometric measures of inner retina function in nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy. Doc. Ophthalmol. 2019, 139, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Zhong, Z.; Bao, T.; Wang, S.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhu, X. Evaluation of Early Retinal Nerve Injury in Type 2 Diabetes Patients Without Diabetic Retinopathy. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 475672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAnany, J.J.; Persidina, O.S.; Park, J.C. Clinical electroretinography in diabetic retinopathy: A review. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2022, 67, 712–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Li, W.; Guo, C.; Guo, C.; Chen, M. Early diagnosis of retinal neurovascular injury in diabetic patients without retinopathy by quantitative analysis of OCT and OCTA. Acta Diabetol. 2023, 60, 1063–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyrberg, M.; Lindblad, U.; Melander, A.; Lövestam-Adrian, M.; Ponjavic, V.; Andréasson, S. Electrophysiological studies in newly onset type 2 diabetes without visible vascular retinopathy. Doc. Ophthalmol. 2011, 123, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, T.; Cortese, F.; Nilsson, J.; Westall, C. Analysis of multifocal electroretinograms from a population with type 1 diabetes using partial least squares reveals spatial and temporal distribution of changes to retinal function. Doc. Ophthalmol. 2012, 125, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Clerck, E.E.; Schouten, J.S.; Berendschot, T.T.; Kessels, A.G.; Nuijts, R.M.; Beckers, H.J.; Schram, M.T.; Stehouwer, C.D.; Webers, C.A. New ophthalmologic imaging techniques for detection and monitoring of neurodegenerative changes in diabetes: A systematic review. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015, 3, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, T.; Sakurai, Y.; Sato, H.; Chihara, E.; Takeuchi, M. Do type 2 diabetes patients without diabetic retinopathy or subjects with impaired fasting glucose have impaired colour vision? The Okubo Color Study Report. Diabet. Med. 2011, 28, 865–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, N.C.; Yip, W.F.; Kallakuri, S.; Sankari, U.; Koh, Y.L.E. Factors associated with impaired color vision without retinopathy amongst people with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A cross-sectional study. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2017, 17, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safi, H.; Safi, S.; Hafezi-Moghadam, A.; Ahmadieh, H. Early detection of diabetic retinopathy. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2018, 63, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloodworth, J.M. Diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes 1962, 11, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Barber, A.J.; Lieth, E.; Khin, S.A.; Antonetti, D.A.; Buchanan, A.G.; Gardner, T.W. Neural apoptosis in the retina during experimental and human diabetes. Early onset and effect of insulin. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 102, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, M.; Sango, K.; Horie, H.; Sato, M.; Iijima, Y.; Ohno, S.; Inoue, S.; Ishikawa, Y. Diabetes alters neurite regeneration from mouse retinal explants in culture. Neurosci. Lett. 1999, 275, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieth, E.; Gardner, T.W.; Barber, A.J.; Antonetti, D.A.; Penn State Retina Research Group. Retinal neurodegeneration: Early pathology in diabetes. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2000, 28, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonetti, D.A.; Barber, A.J.; Bronson, S.K.; Freeman, W.M.; Gardner, T.W.; Jefferson, L.S.; Kester, M.; Kimball, S.R.; Krady, J.K.; LaNoue, K.F.; et al. Diabetic retinopathy: Seeing beyond glucose-induced microvascular disease. Diabetes 2006, 55, 2401–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzi, M.; Gerhardinger, C. Early cellular and molecular changes induced by diabetes in the retina. Diabetologia 2001, 44, 791–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, E.L.; Phipps, J.A.; Wilkinson-Berka, J.L. Dysfunction of retinal neurons and glia during diabetes. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2005, 88, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asnaghi, V.; Gerhardinger, C.; Hoehn, T.; Adeboje, A.; Lorenzi, M. A role for the polyol pathway in the early neuroretinal apoptosis and glial changes induced by diabetes in the rat. Diabetes 2003, 52, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, P.M.; Roon, P.; Van Ells, T.K.; Ganapathy, V.; Smith, S.B. Death of retinal neurons in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2004, 45, 3330–3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshitari, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Hata, N.; Roy, S. Mitochondria- and caspase-dependent cell death pathway involved in neuronal degeneration in diabetic retinopathy. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2008, 92, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajree, S.; Borooah, S.; Dhillon, B. Imaging in Diabetic Retinopathy: A Review of Current and Future Techniques. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2017, 13, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crincoli, E.; Sacconi, R.; Querques, L.; Querques, G. OCT angiography 2023 update: Focus on diabetic retinopathy. Acta Diabetol. 2024, 61, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metea, M.R.; Newman, E.A. Signalling within the neurovascular unit in the mammalian retina. Exp. Physiol. 2007, 92, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simão, S.; Costa, M.Â.; Sun, J.K.; Cunha-Vaz, J.; Simó, R.; European Consortium for the Early Treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy (EUROCONDOR). Development of a Normative Database for Multifocal Electroretinography in the Context of a Multicenter Clinical Trial. Ophthalmic Res. 2017, 57, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, A.J.; Baccouche, B. Neurodegeneration in diabetic retinopathy: Potential for novel therapies. Vision. Res. 2017, 139, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reste-Ferreira, D.; Marques, I.P.; Santos, T.; Ribeiro, M.L.; Mendes, L.; Santos, A.R.; Lobo, C.; Cunha-Vaz, J. Retinal neurodegeneration in eyes with NPDR risk phenotypes: A two-year longitudinal study. Acta Ophthalmol. 2024, 102, e539–e547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lott, M.E.; Slocomb, J.E.; Shivkumar, V.; Smith, B.; Gabbay, R.A.; Quillen, D.; Gardner, T.W.; Bettermann, K. Comparison of retinal vasodilator and constrictor responses in type 2 diabetes. Acta Ophthalmol. 2012, 90, e434–e441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tecilazich, F.; Feke, G.T.; Mazzantini, S.; Sobrin, L.; Lorenzi, M. Defective Myogenic Response of Retinal Vessels Is Associated with Accelerated Onset of Retinopathy in Type 1 Diabetic Individuals. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, 1523–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonsson, K.B.; Frydkjaer-Olsen, U.; Grauslund, J. Vascular Changes and Neurodegeneration in the Early Stages of Diabetic Retinopathy: Which Comes First? Ophthalmic Res. 2016, 56, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.R.; Ribeiro, L.; Bandello, F.; Lattanzio, R.; Egan, C.; Frydkjaer-Olsen, U.; García-Arumí, J.; Gibson, J.; Grauslund, J.; Harding, S.P.; et al. Functional and Structural Findings of Neurodegeneration in Early Stages of Diabetic Retinopathy: Cross-sectional Analyses of Baseline Data of the EUROCONDOR Project. Diabetes 2017, 66, 2503–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacconi, R.; Lamanna, F.; Borrelli, E.; Mulinacci, G.; Casaluci, M.; Gelormini, F.; Carnevali, A.; Querques, L.; Zerbini, G.; Bandello, F.; et al. Morphofunctional analysis of the retina in patients with type 1 diabetes without complications after 30 years of disease. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simó, R.; Hernández, C. New Insights into Treating Early and Advanced Stage Diabetic Retinopathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdeva, M.M. Retinal Neurodegeneration in Diabetes: An Emerging Concept in Diabetic Retinopathy. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2021, 21, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klahan, B.; O’Reilly, N.J.; Sigurdsson, H.H.; Chauhan, A.; Mering, S.; Fitzhenry, L. Delivery of Fenofibrate to Ocular Tissues using 2-Hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin-Based Micelles. Int. J. Pharm. 2025, 673, 125417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogdanov, P.; Hernández, C.; Corraliza, L.; Carvalho, A.R.; Simó, R. Effect of fenofibrate on retinal neurodegeneration in an experimental model of type 2 diabetes. Acta Diabetol. 2015, 52, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preiss, D.; Logue, J.; Sammons, E.; Zayed, M.; Emberson, J.; Wade, R.; Wallendszus, K.; Stevens, W.; Cretney, R.; Harding, S.; et al. Effect of Fenofibrate on Progression of Diabetic Retinopathy. NEJM Evid. 2024, 3, EVIDoa2400179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simó, R.; Hernández, C. Fenofibrate for Treating Diabetic Eye Disease. Diabetes 2023, 72, 838–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enright, J.M.; Zhang, S.; Thebeau, C.; Siebert, E.; Jin, A.; Gadiraju, V.; Zhang, X.; Chen, S.; Semenkovich, C.F.; Rajagopal, R. Fenofibrate Reduces the Severity of Neuroretinopathy in a Type 2 Model of Diabetes without Inducing Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Alpha-Dependent Retinal Gene Expression. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 10, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanaguri, J.; Nagai, N.; Yokota, H.; Kushiyama, A.; Watanabe, M.; Yamagami, S.; Nagaoka, T. Fenofibrate Nano-Eyedrops Ameliorate Retinal Blood Flow Dysregulation and Neurovascular Coupling in Type 2 Diabetic Mice. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simó-Servat, O.; Solà-Adell, C.; Bogdanov, P.; Hernández, C.; Simó, R. Mechanisms of retinal neuroprotection of calcium dobesilate: Therapeutic implications. Neural Regen. Res. 2017, 12, 1620–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanov, P.; Solà-Adell, C.; Hernández, C.; García-Ramírez, M.; Sampedro, J.; Simó-Servat, O.; Valeri, M.; Pasquali, C.; Simó, R. Calcium dobesilate prevents the oxidative stress and inflammation induced by diabetes in the retina of db/db mice. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2017, 31, 1481–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solà-Adell, C.; Bogdanov, P.; Hernández, C.; Sampedro, J.; Valeri, M.; Garcia-Ramirez, M.; Pasquali, C.; Simó, R. Calcium Dobesilate Prevents Neurodegeneration and Vascular Leakage in Experimental Diabetes. Curr. Eye Res. 2017, 42, 1273–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, R.; Luan, H.; Berkowitz, B.A. Blocking ET-1 receptors does not correct subnormal retinal oxygenation response in experimental diabetic retinopathy. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2006, 47, 3550–3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogdanov, P.; Simó-Servat, O.; Sampedro, J.; Solà-Adell, C.; Garcia-Ramírez, M.; Ramos, H.; Guerrero, M.; Suñé-Negre, J.M.; Ticó, J.R.; Montoro, B.; et al. Topical Administration of Bosentan Prevents Retinal Neurodegeneration in Experimental Diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, J.C.; Rollins, S.D.; Ye, M.; Batlle, D.; Fawzi, A.A. Endothelin receptor-A antagonist attenuates retinal vascular and neuroretinal pathology in diabetic mice. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 2516–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, H.; Rojas, M.; Caldwell, R.W.; Caldwell, R.B. Anti-inflammatory therapy for diabetic retinopathy. Immunotherapy 2011, 3, 609–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Lin, Y.N.; Xie, M.S.; Yao, Y.H.; Tang, S.M.; Huang, Y.; Wang, X.H.; Zhu, Y.H. Effects of etanercept on the apoptosis of ganglion cells and expression of Fas, TNF-alpha, caspase-8 in the retina of diabetic rats. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 12, 1083–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Sharma, I.; Das, G.K.; Sahu, P.K.; Rohatgi, J. Commentary: Recent concepts of pathophysiology and advancements in treatment strategies of diabetic retinopathy. Indian. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 69, 3050–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, B.J.; Akhtar, L.N.; Benveniste, E.N. SOCS1 and SOCS3 in the control of CNS immunity. Trends Immunol. 2009, 30, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, C.M.; Johnson, H.M.; Lewin, A.S. Corneal application of SOCS1/3 peptides for the treatment of eye diseases mediated by inflammation and oxidative stress. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1416181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, C.M.; Patel, A.P.; Johnson, H.M.; Ildefonso, C.J.; Lewin, A.S. Suppressor of cytokine signaling 3-derived peptide as a therapeutic for inflammatory and oxidative stress-induced damage to the retina. Mol. Vis. 2023, 29, 338–356. [Google Scholar]
- Hattori, Y.; Hashizume, K.; Nakajima, K.; Nishimura, Y.; Naka, M.; Miyanaga, K. The effect of long-term treatment with sulindac on the progression of diabetic retinopathy. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2007, 23, 1913–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles-Rivera, R.R.; Castellanos-González, J.A.; Olvera-Montaño, C.; Flores-Martin, R.A.; López-Contreras, A.K.; Arevalo-Simental, D.E.; Cardona-Muñoz, E.G.; Roman-Pintos, L.M.; Rodríguez-Carrizalez, A.D. Adjuvant Therapies in Diabetic Retinopathy as an Early Approach to Delay Its Progression: The Importance of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 3096470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Infante-Garcia, C.; Ramos-Rodriguez, J.J.; Hierro-Bujalance, C.; Ortegon, E.; Pickett, E.; Jackson, R.; Hernandez-Pacho, F.; Spires-Jones, T.; Garcia-Alloza, M. Antidiabetic Polypill Improves Central Pathology and Cognitive Impairment in a Mixed Model of Alzheimer’s Disease and Type 2 Diabetes. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 6130–6144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Medina, J.J.; Rubio-Velazquez, E.; Foulquie-Moreno, E.; Casaroli-Marano, R.P.; Pinazo-Duran, M.D.; Zanon-Moreno, V.; Del-Rio-Vellosillo, M. Update on the Effects of Antioxidants on Diabetic Retinopathy: In Vitro Experiments, Animal Studies and Clinical Trials. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Q.; Yang, C. Oxidative stress and diabetic retinopathy: Molecular mechanisms, pathogenetic role and therapeutic implications. Redox Biol. 2020, 37, 101799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haydinger, C.D.; Oliver, G.F.; Ashander, L.M.; Smith, J.R. Oxidative Stress and Its Regulation in Diabetic Retinopathy. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, S.; Gao, S.; Li, N.; Huang, H.; Liu, X.; Yao, H.; Shen, X. Pigment epithelium-derived factor exerts neuroprotection in oxygen-induced retinopathy by targeting endoplasmic reticulum stress and oxidative stress. Exp. Eye Res. 2024, 249, 110147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Zeng, L.; Liu, J.; Ou, K. On implications of somatostatin in diabetic retinopathy. Neural Regen. Res. 2024, 19, 1984–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Młynarska, E.; Czarnik, W.; Dzieża, N.; Jędraszak, W.; Majchrowicz, G.; Prusinowski, F.; Stabrawa, M.; Rysz, J.; Franczyk, B. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: New Pathogenetic Mechanisms, Treatment and the Most Important Complications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanov, P.; Ramos, H.; Valeri, M.; Deàs-Just, A.; Huerta, J.; Simó, R.; Hernández, C. Minimum Effective Dose of DPP-4 Inhibitors for Treating Early Stages of Diabetic Retinopathy in an Experimental Model. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, H.; Augustine, J.; Karan, B.M.; Hernández, C.; Stitt, A.W.; Curtis, T.M.; Simó, R. Sitagliptin eye drops prevent the impairment of retinal neurovascular unit in the new Trpv2+/− rat model. J. Neuroinflammation 2024, 21, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simó, R.; Simó-Servat, O.; Bogdanov, P.; Hernández, C. Neurovascular Unit: A New Target for Treating Early Stages of Diabetic Retinopathy. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, M.S.; Ayman, F.; Attia, M.S.; Yahya, G.; Zahra, M.H.; Khalil, M.M.I.; Diab, A.A.A. Mitigating diabetes-related complications: Empowering metformin with cholecalciferol and taurine supplementation in type 2 diabetic rats. World J. Diabetes 2024, 15, 1778–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozawa, Y.; Sasaki, M.; Takahashi, N.; Kamoshita, M.; Miyake, S.; Tsubota, K. Neuroprotective effects of lutein in the retina. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2012, 18, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Chen, M. Diabetic retinopathy and dysregulated innate immunity. Vision. Res. 2017, 139, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Chen, M. Targeting the complement system for the management of retinal inflammatory and degenerative diseases. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 787, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerbini, G.; Maestroni, S.; Leocani, L.; Mosca, A.; Godi, M.; Paleari, R.; Belvedere, A.; Gabellini, D.; Tirassa, P.; Castoldi, V.; et al. Topical nerve growth factor prevents neurodegenerative and vascular stages of diabetic retinopathy. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1015522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanase, D.M.; Valasciuc, E.; Gosav, E.M.; Floria, M.; Buliga-Finis, O.N.; Ouatu, A.; Cucu, A.I.; Botoc, T.; Costea, C.F. Enhancing Retinal Resilience: The Neuroprotective Promise of BDNF in Diabetic Retinopathy. Life 2025, 15, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castoldi, V.; Zerbini, G.; Maestroni, S.; Viganò, I.; Rama, P.; Leocani, L. Topical Nerve Growth Factor (NGF) restores electrophysiological alterations in the Ins2Akita mouse model of diabetic retinopathy. Exp. Eye Res. 2023, 237, 109693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelusi, L.; Hurst, J.; Detta, N.; Pipino, C.; Lamolinara, A.; Conte, G.; Mastropasqua, R.; Allegretti, M.; Di Pietrantonio, N.; Romeo, T.; et al. Effects of mesenchymal stromal cells and human recombinant Nerve Growth Factor delivered by bioengineered human corneal lenticule on an innovative model of diabetic retinopathy. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1462043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiori, A.; Terlizzi, V.; Kremer, H.; Gebauer, J.; Hammes, H.P.; Harmsen, M.C.; Bieback, K. Mesenchymal stromal/stem cells as potential therapy in diabetic retinopathy. Immunobiology 2018, 223, 729–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechner, J.; Medina, R.J.; Lois, N.; Stitt, A.W. Advances in cell therapies using stem cells/progenitors as a novel approach for neurovascular repair of the diabetic retina. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022, 13, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kąpa, M.; Koryciarz, I.; Kustosik, N.; Jurowski, P.; Pniakowska, Z. Future Directions in Diabetic Retinopathy Treatment: Stem Cell Therapy, Nanotechnology, and PPARα Modulation. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).