Identification of Hub Genes Correlated with the Initiation and Progression of CKD in the Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Affymetrix Microarray Data Information
2.2. Identification of DEGs
2.3. Analysis of DEGs’ Functional Enrichment
2.4. Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) Network, Module Analyses, and Hub Genes Identification
2.5. Animal Model
2.6. Morphometric Analysis
2.7. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.8. Real-Time qPCR
2.9. Western Blot
2.10. GeneMANIA
2.11. Metascape
2.12. Statistics Analysis
3. Results
3.1. DESs Identification
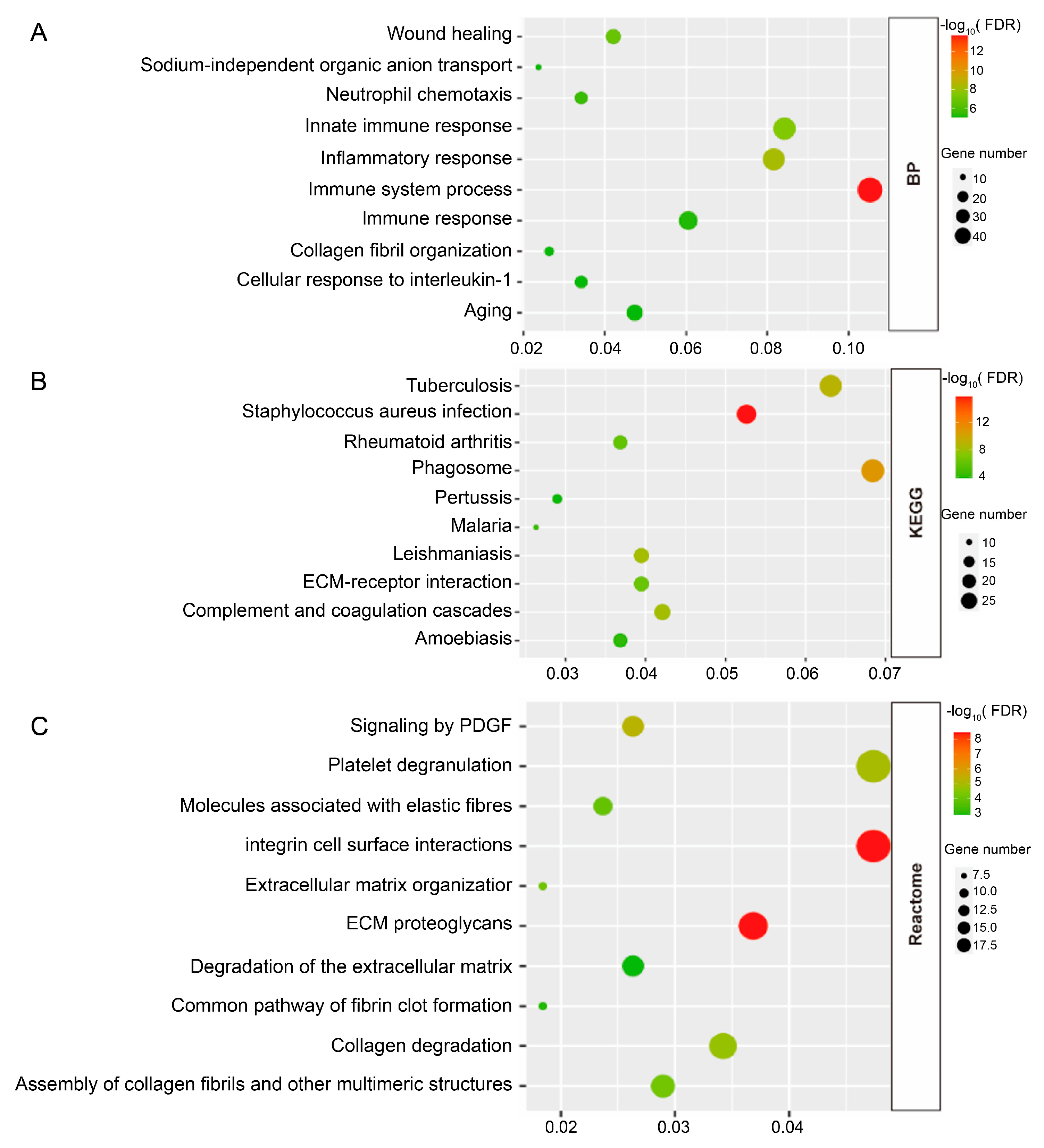
3.2. Enrichment Analyses
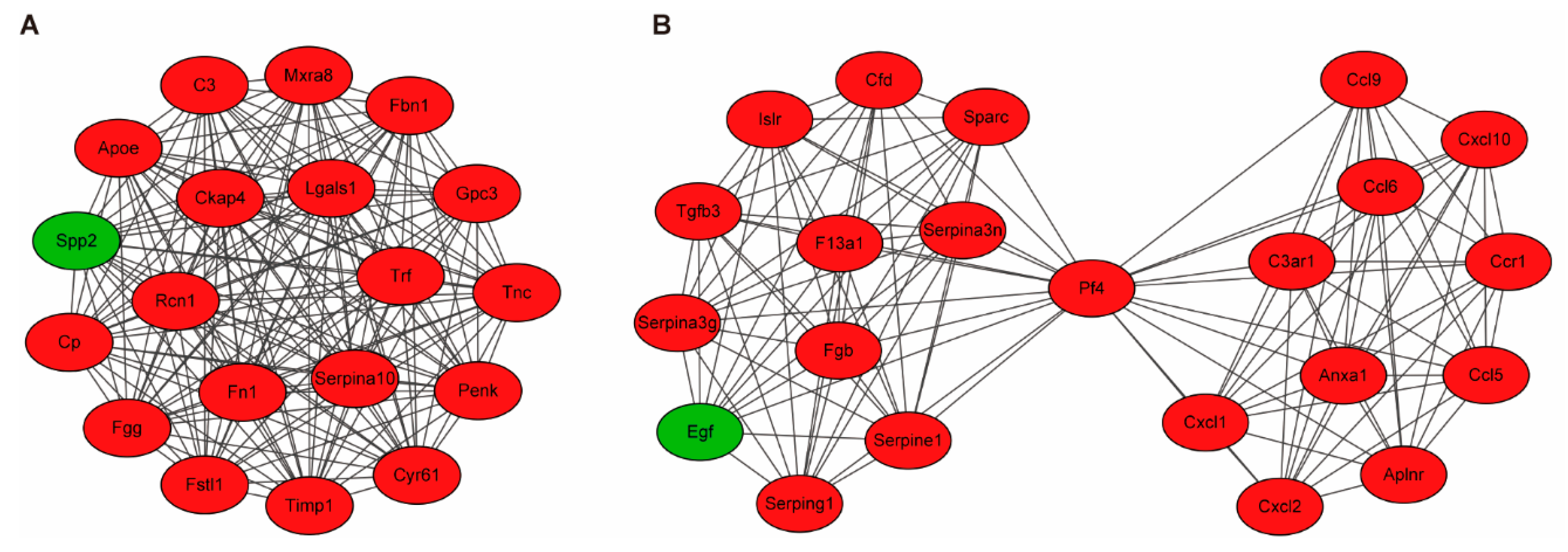
3.3. Building PPI Networks and Module Analysis
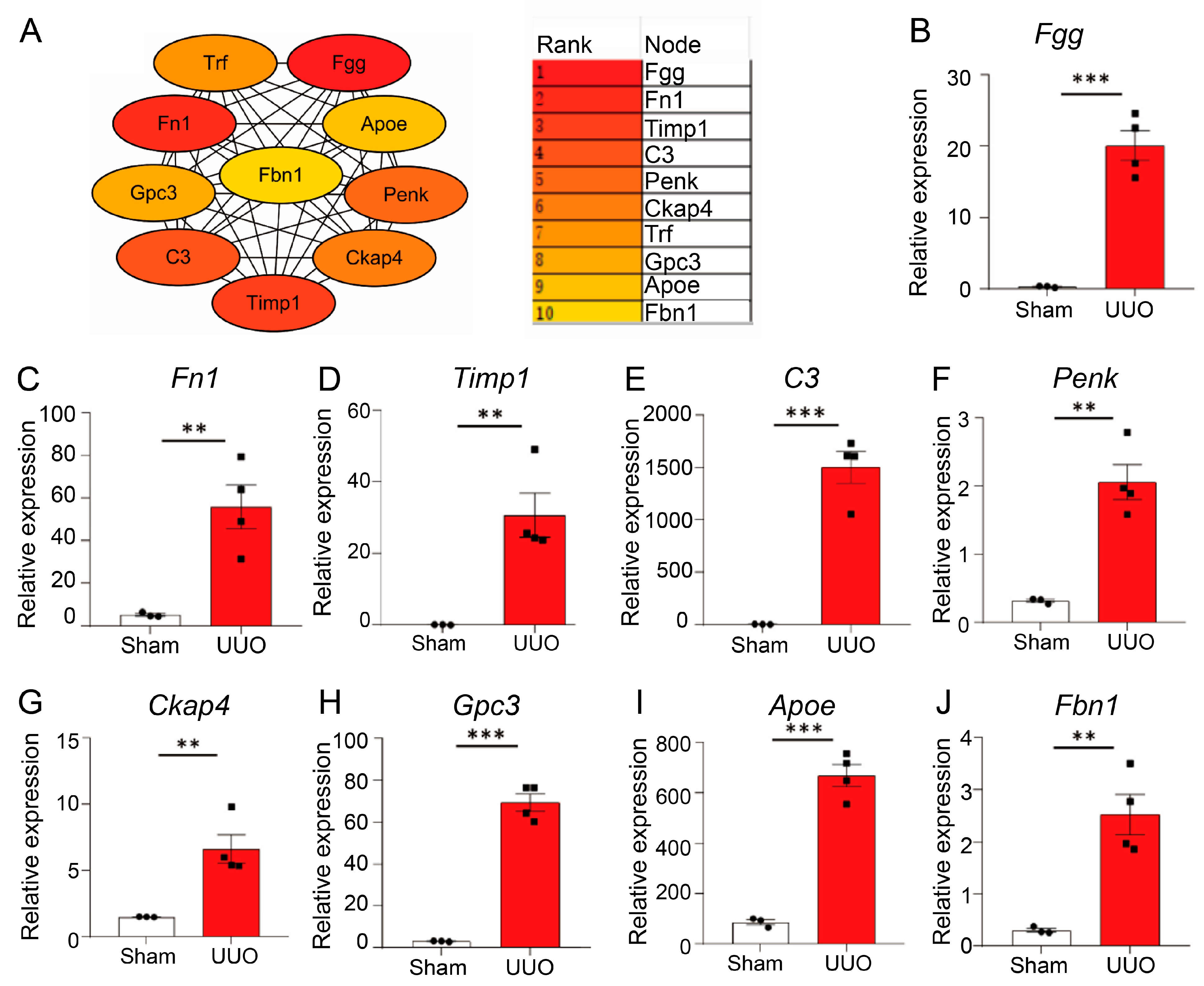
3.4. Identification of Hub Genes
3.5. Validation of Hub Genes In Vivo
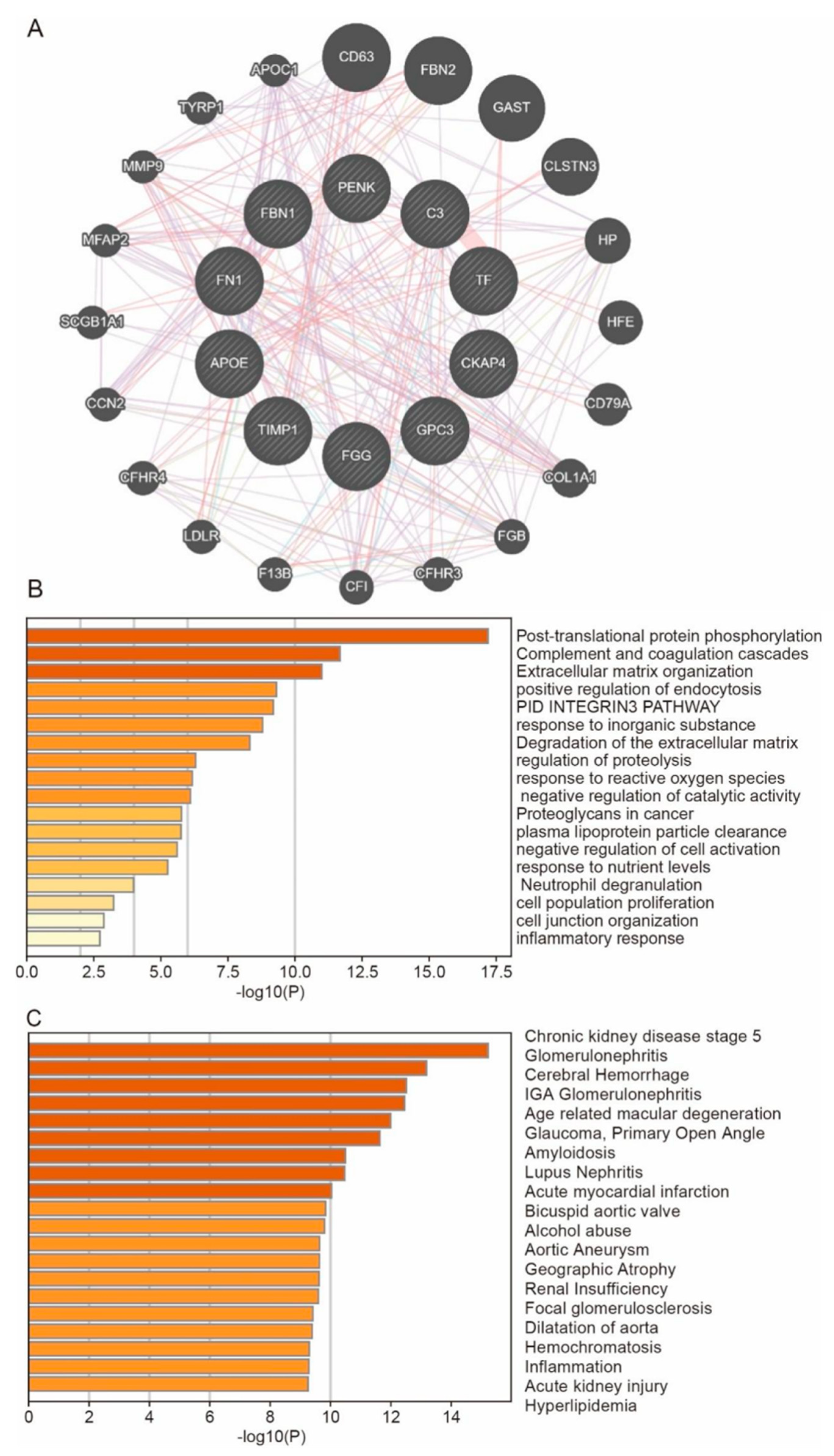
3.6. Predict the Co-Expressed Genes of Hub Genes and Their Enrichment Functions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Jafar, T.H.; Nitsch, D.; Neuen, B.L.; Perkovic, V. Chronic kidney disease. Lancet 2021, 398, 786–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garimella, P.S.; Lee, A.K.; Ambrosius, W.T.; Bhatt, U.; Cheung, A.K.; Chonchol, M.; Craven, T.; Hawfield, A.T.; Jotwani, V.; Killeen, A.; et al. Markers of kidney tubule function and risk of cardiovascular disease events and mortality in the SPRINT trial. Eur. Heart J. 2019, 40, 3486–3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badal, S.S.; Al Tuhaifi, T.; Yu, Y.F.; Lopez, D.; Plato, C.T.; Joly, K.; Breckenridge, D.G.; Yang, H.C.; Liles, J.T.; Fogo, A.B. Selonsertib Enhances Kidney Protection Beyond Standard of Care in a Hypertensive, Secondary Glomerulosclerosis CKD Model. Kidney360 2022, 3, 1169–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, P.M.; Nikolic-Paterson, D.J.; Lan, H.Y. Macrophages: Versatile players in renal inflammation and fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2019, 15, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Portilla, D.; Okusa, M.D. Role of perivascular cells in kidney homeostasis, inflammation, repair and fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2023, 19, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.D.; You, Y.K.; Shao, B.Y.; Wu, W.F.; Wang, Y.F.; Guo, J.B.; Meng, X.M.; Chen, H. Roles and crosstalks of macrophages in diabetic nephropathy. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1015142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, N.; Zhuang, S. Macrophages in Renal Injury, Repair, Fibrosis Following Acute Kidney Injury and Targeted Therapy. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 934299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huen, S.C.; Cantley, L.G. Macrophages in Renal Injury and Repair. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2017, 79, 449–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Sharkey, D.; Cantley, L.G. Tubular GM-CSF Promotes Late MCP-1/CCR2-Mediated Fibrosis and Inflammation after Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 30, 1825–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warde-Farley, D.; Donaldson, S.L.; Comes, O.; Zuberi, K.; Badrawi, R.; Chao, P.; Franz, M.; Grouios, C.; Kazi, F.; Lopes, C.T.; et al. The GeneMANIA prediction server: Biological network integration for gene prioritization and predicting gene function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, W214–W220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhou, B.; Pache, L.; Chang, M.; Khodabakhshi, A.H.; Tanaseichuk, O.; Benner, C.; Chanda, S.K. Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems-level datasets. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badr, M.; El Koumi, M.A.; Ali, Y.F.; El-Morshedy, S.; Almonem, N.A.; Hassan, T.; El Rahman, R.A.; Afify, M. Renal tubular dysfunction in children with sickle cell haemoglobinopathy. Nephrology 2013, 18, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Liu, X.Q.; Zhang, S.Q.; Qi, X.M.; Zhang, Q.; Yard, B.; Wu, Y.G. Correlation between serum carnosinase concentration and renal damage in diabetic nephropathy patients. Amino Acids 2021, 53, 687–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, X.L.; Zhou, Z.L.; Wang, P.; Zhou, X.M.; Xie, M.Y.; Mei, J.; Weng, J.; Xi, H.T.; Chen, C.; Wang, Z.Y.; et al. Small molecule proteomics quantifies differences between normal and fibrotic pulmonary extracellular matrices. Chin. Med. J. 2020, 133, 1192–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puzanov, G.A. Identification of key genes of the ccRCC subtype with poor prognosis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigdel, T.K.; Salomonis, N.; Nicora, C.D.; Ryu, S.; He, J.; Dinh, V.; Orton, D.J.; Moore, R.J.; Hsieh, S.C.; Dai, H.; et al. The identification of novel potential injury mechanisms and candidate biomarkers in renal allograft rejection by quantitative proteomics. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2014, 13, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craciun, F.L.; Ajay, A.K.; Hoffmann, D.; Saikumar, J.; Fabian, S.L.; Bijol, V.; Humphreys, B.D.; Vaidya, V.S. Pharmacological and genetic depletion of fibrinogen protects from kidney fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2014, 307, F471–F484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorensen, I.; Susnik, N.; Inhester, T.; Degen, J.L.; Melk, A.; Haller, H.; Schmitt, R. Fibrinogen, acting as a mitogen for tubulointerstitial fibroblasts, promotes renal fibrosis. Kidney Int. 2011, 80, 1035–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zheng, C.; Lu, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Yin, R.; Zhu, P.; Zhou, M.; Liu, Z. Urinary Fibrinogen as a Predictor of Progression of CKD. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 12, 1922–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicu-Andreescu, I.; Garneata, L.; Ciurea, O.A.; Dicu-Andreescu, I.G.; Ungureanu, E.A.; Vlad, D.V.; Visan, A.C.; Ungureanu, V.G.; Vlad, V.V.; Vasioiu, P.C.; et al. Are the Hematological Parameters Useful in Differentiating Acute Pyelonephritis from Cystitis in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease? Maedica 2024, 19, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.; Wang, M.; Zhao, M.; Ni, W.; Zhang, M. Discovery of Fibrinogen gamma-chain as a potential urinary biomarker for renal interstitial fibrosis in IgA nephropathy. BMC Nephrol. 2023, 24, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Liu, X.; He, Z.; Zhang, J.; Tan, X.; Yang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, T.; Liao, S.; Dai, L.; et al. Proenkephalin-A secreted by renal proximal tubules functions as a brake in kidney regeneration. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, K.; Jiang, W.; Song, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, L.; Feng, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, T.; Wang, H.; et al. Persistent acute kidney injury biomarkers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Chim. Acta. 2025, 564, 119907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grycuk, W.; Jakubowska, Z.; Malyszko, J. Proenkephalin (PENK): A functional biomarker in chronic kidney diseases—Hope or just a new bystander? J. Nephrol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullen, A.L.; Katz, R.; Poursadrolah, S.; Short, S.A.P.; Long, D.L.; Cheung, K.L.; Sharma, S.; Al-Rousan, T.; Fregoso, A.; Schulte, J.; et al. Plasma proenkephalin A and incident chronic kidney disease and albuminuria in the REasons for Geographic And Racial Differences in Stroke (REGARDS) cohort. BMC Nephrol. 2024, 25, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Jin, X.; Yang, M.; Jia, J.; Yao, H.; Yuan, W.; Wang, K.; Rong, S. CKAP4 contributes to the progression of vascular calcification (VC) in chronic kidney disease (CKD) by modulating YAP phosphorylation and MMP2 expression. Cell. Signal. 2022, 93, 110270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Chen, Z.; Chen, F.; Xu, W.; Liu, X. CKAP4 participates in tryptase-induced phenotypic conversion in atrial fibroblasts through PAR2/p38/JNK pathway. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2021, 13, 2270–2282. [Google Scholar]
- McCallion, S.; McLarnon, T.; Cooper, E.; English, A.R.; Watterson, S.; Chemaly, M.E.; McGeough, C.; Eakin, A.; Ahmed, T.; Gardiner, P.; et al. Senescence Biomarkers CKAP4 and PTX3 Stratify Severe Kidney Disease Patients. Cells 2024, 13, 1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capurro, M.I.; Xu, P.; Shi, W.; Li, F.; Jia, A.; Filmus, J. Glypican-3 inhibits Hedgehog signaling during development by competing with patched for Hedgehog binding. Dev. Cell. 2008, 14, 700–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Han, N.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, L.; Filmus, J.; Li, F. Assembling custom side chains on proteoglycans to interrogate their function in living cells. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisaru, S.; Cano-Gauci, D.; Tee, J.; Filmus, J.; Rosenblum, N.D. Glypican-3 modulates BMP- and FGF-mediated effects during renal branching morphogenesis. Dev. Biol. 2001, 231, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udomsinprasert, W.; Angkathunyakul, N.; Klaikeaw, N.; Vejchapipat, P.; Poovorawan, Y.; Honsawek, S. Hepatic glypican-3 and alpha-smooth muscle actin overexpressions reflect severity of liver fibrosis and predict outcome after successful portoenterostomy in biliary atresia. Surgery 2020, 167, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Gene | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| Fn1 | GGCCACCATIACTGGTCTGG | GGAAGGGTAACCAGTTGGGG |
| α-SMA | AGCCATCTTTCATIGGGATGG | CCCCTGACAGGACGTTGTTA |
| Fgg | GCACCACAGAGTTTTGGCTG | ATAGTCCGCAGTGCTGGTTC |
| Timp1 | GCAACTCGGACCTGGTCATAA | CGCTGGTATAAGGTGGTCTCG |
| C3 | TCCTTCACTATGGGACCAGC | TGGGAGTAATGATGGAATACATGG |
| Penk | AGGCGCGTTCTTCTCTCCTA | AGTGTGCACGCCAGGAAAT |
| Ckap4 | GGCTGGTATGTCCATCACGTC | CTTGCAGGGATTGGACCTTCTG |
| GPC3 | ATCCAGCCGAAGAAGGGAAC | TTCTTGTCCGTTCCAGCACA |
| Apoe | ATCCGATCCCCTGCTCAGAC | TGATIGGCCAGTCTCCCCTT |
| Fbn1 | ACGATACTTGAAGAGGACAGGC | TGTCCTGATGCAGAGAGGTC |
| IL-6 | CTCATICTGCTCTGGAGCCC | CAACTGGATGGAAGTCTCTTGC |
| Trf | GTGTGACGAGTGGAGCATCA | TCCGCTTCTCCGTTCACAAT |
| MCP-1 | CACTCACCTGCTGCTACTCA | GCTTGGTGACAAAAACTACAGC |
| GAPDH | GGTTGTCTCCTGCGACTTCA | TGGTCCAGGGTTTCTTACTCC |
| Gene | Function # |
|---|---|
| Fgg | Fibrinogen gamma chain: Together with fibrinogen alpha (FGA) and fibrinogen beta (FGB), it polymerizes to form an insoluble fibrin matrix. It has a major function in hemostasis as one of the primary components of blood clots. In addition, it functions during the early stages of wound repair to stabilize the lesion and guide cell migration during re-epithelialization. |
| Fn1 | Fibronectin 1: Fibronectin type III domain containing endogenous ligands. |
| Timp1 | Metalloproteinase inhibitor 1: Metalloproteinase inhibitor that functions by forming one-to-one complexes with target metalloproteinases, such as collagenases, and irreversibly inactivates them by binding to their catalytic zinc cofactor. It acts on MMP1, MMP2, MMP3, MMP7, MMP8, MMP9, MMP10, MMP11, MMP12, MMP13, and MMP16. It does not act on MMP14. It also functions as a growth factor that regulates cell differentiation, migration, and cell death and activates cellular signaling cascades via CD63 and ITGB1. It plays a role in integrin signaling. |
| C3 | Complement C3: C3 plays a central role in the activation of the complement system. Its processing by C3 convertase is the central reaction in both classical and alternative complement pathways. After activation C3b can bind covalently, via its reactive thioester, to cell surface carbohydrates or immune aggregates; C3 and PZP-like alpha-2-macroglobulin domain containing. |
| Penk | Proenkephalin-A: Met- and Leu-enkephalins compete with and mimic the effects of opiate drugs. They play a role in a number of physiologic functions, including pain perception and responses to stress. |
| Ckap4 | Cytoskeleton-associated protein 4: High-affinity epithelial cell surface receptor for APF. |
| Trf | It is predicted to enable iron chaperone activity; iron ion binding activity; and transferrin receptor binding activity. It is involved in several processes, including ERK1 and ERK2 cascade; osteoclast differentiation; and positive regulation of bone resorption. It acts upstream of or within SMAD protein signal transduction. |
| Gpc3 | Glypican-3: Cell surface proteoglycan that bears heparan sulfate. It inhibits the dipeptidyl peptidase activity of DPP4. It may be involved in the suppression/modulation of growth in the predominantly mesodermal tissues and organs. It may play a role in the modulation of IGF2 interactions with its receptor and thereby modulate its function. It may regulate growth and tumor predisposition. |
| Apoe | Apolipoprotein E: It mediates the binding, internalization, and catabolism of lipoprotein particles. It can serve as a ligand for the LDL (apo B/E) receptor and for the specific apo-E receptor (chylomicron remnant) of hepatic tissues. |
| Fbn1 | Fibrillin-1: Structural component of the 10–12 nm diameter microfibrils of the extracellular matrix, which conveys both structural and regulatory properties to load-bearing connective tissues. Fibrillin-1 containing microfibrils provide long-term force bearing structural support. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Li, J.; Yao, X.; Yang, J. Identification of Hub Genes Correlated with the Initiation and Progression of CKD in the Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction Model. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1316. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061316
Li X, Li J, Yao X, Yang J. Identification of Hub Genes Correlated with the Initiation and Progression of CKD in the Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction Model. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(6):1316. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061316
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xinxin, Junjie Li, Xiaobing Yao, and Jun Yang. 2025. "Identification of Hub Genes Correlated with the Initiation and Progression of CKD in the Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction Model" Biomedicines 13, no. 6: 1316. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061316
APA StyleLi, X., Li, J., Yao, X., & Yang, J. (2025). Identification of Hub Genes Correlated with the Initiation and Progression of CKD in the Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction Model. Biomedicines, 13(6), 1316. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061316





