Combination Therapy of Half-Dose Resmetirom and Metformin Attenuates Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis Through Improving Cholesterol Metabolism and Inflammation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Cell Culture and Treatment
2.3. Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR)
2.4. Blood Biochemical Parameters
2.5. Histopathology
2.6. Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
2.7. Protein Extraction and Western Blot
2.8. Transcriptomic Sequencing Analysis
2.9. Lipidomics Sequencing Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
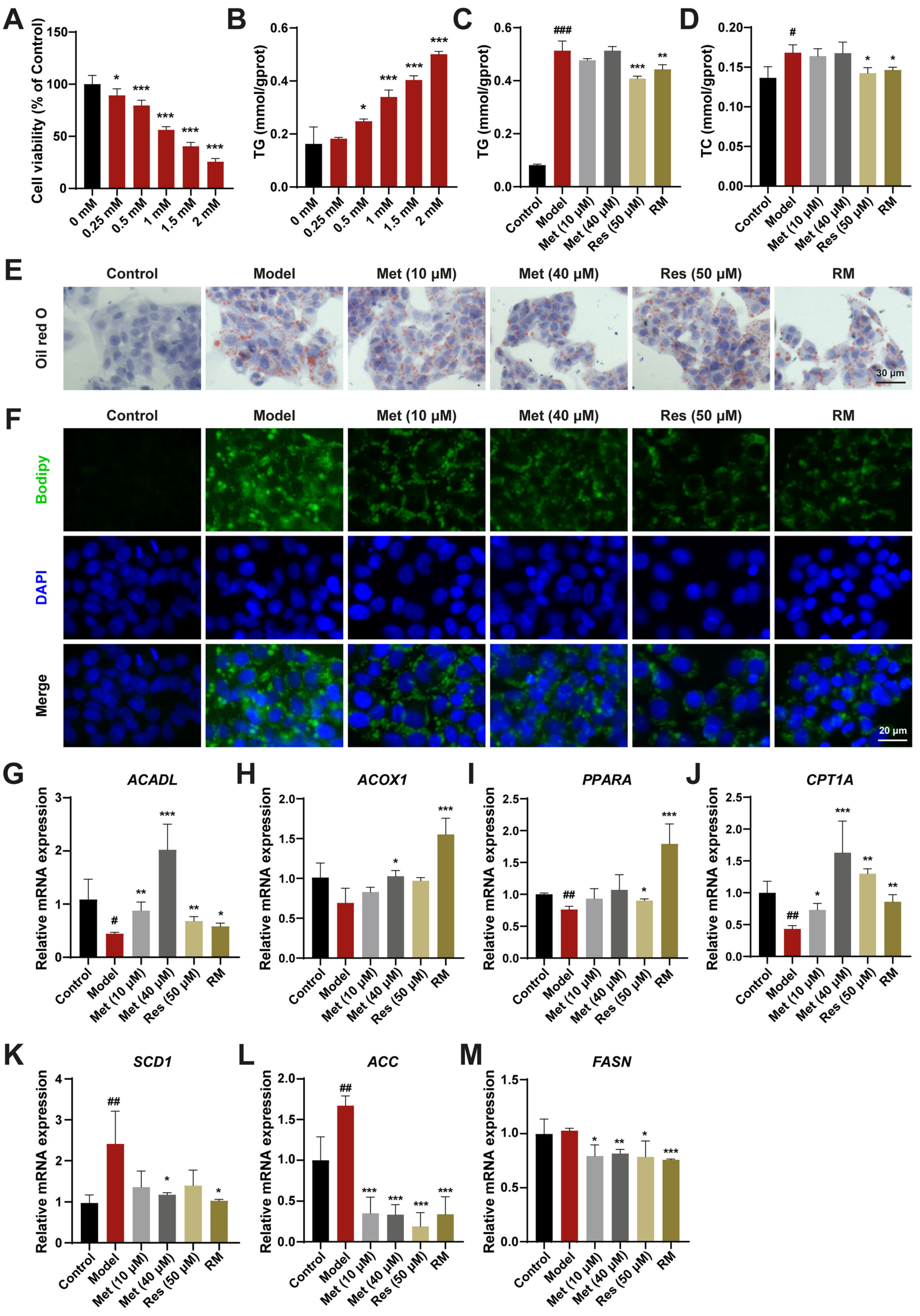
3.1. A Combination of Half-Dose Res and Met Alleviated Lipid Metabolism Disorders in HepG2 Cells Treated with FFA
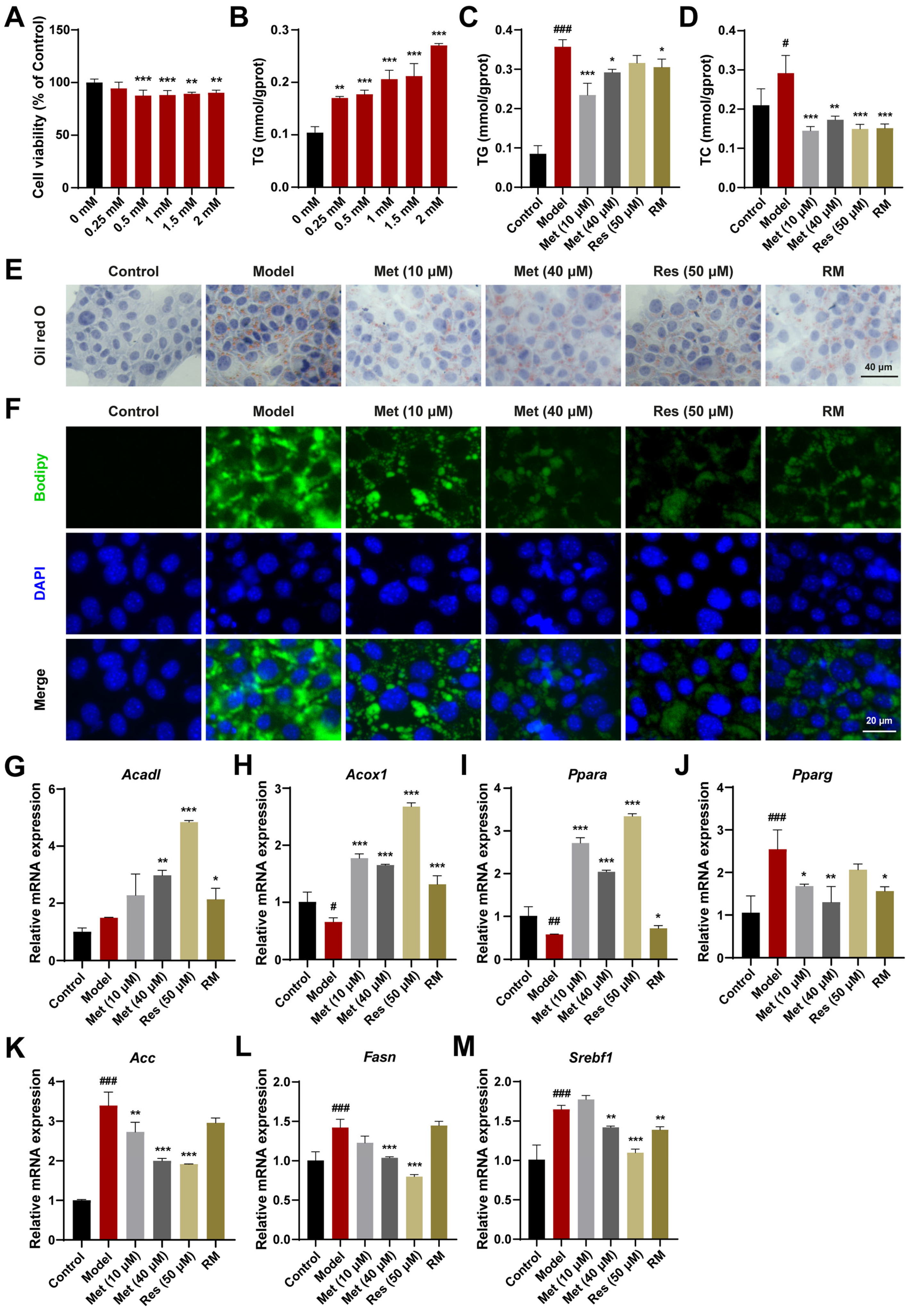
3.2. A Combination of Half-Dose Res and Met Decreased Lipid Accumulation in AML12 Cells Treated with FFA
3.3. Concomitant Half-Dose Res and Met Ameliorated Hepatic Lipid Accumulation and Metabolism Disorders in db/db Mice
3.4. Combination Therapies Improved Inflammation and Liver Fibrosis in db/db Mice
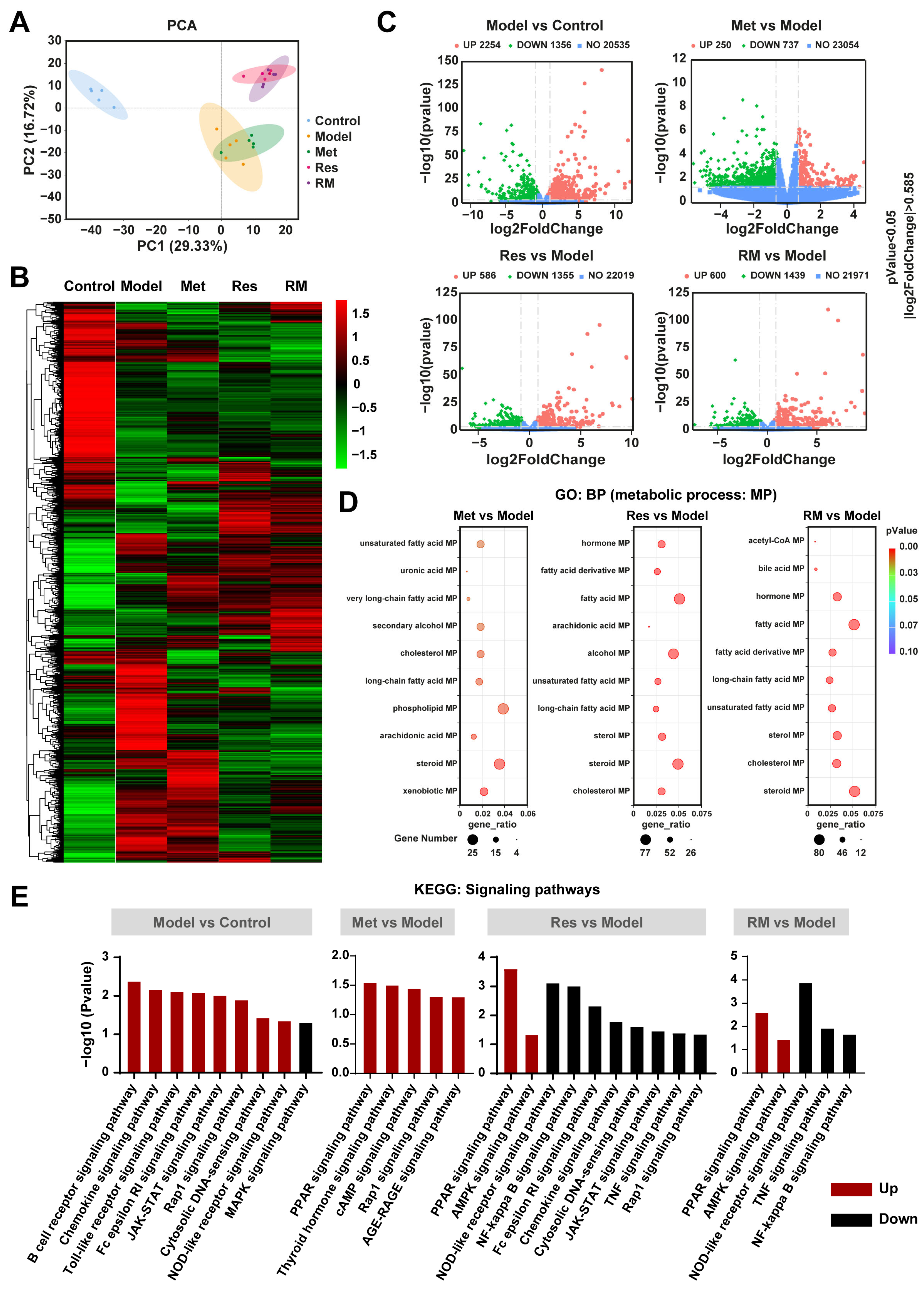
3.5. Resmetirom and Metformin Extensively Regulated the Expression of Genes and Multiple Metabolism Processes in the Liver
3.6. Met, Res, and RM Extensively Changed the Lipid Profile in the Liver
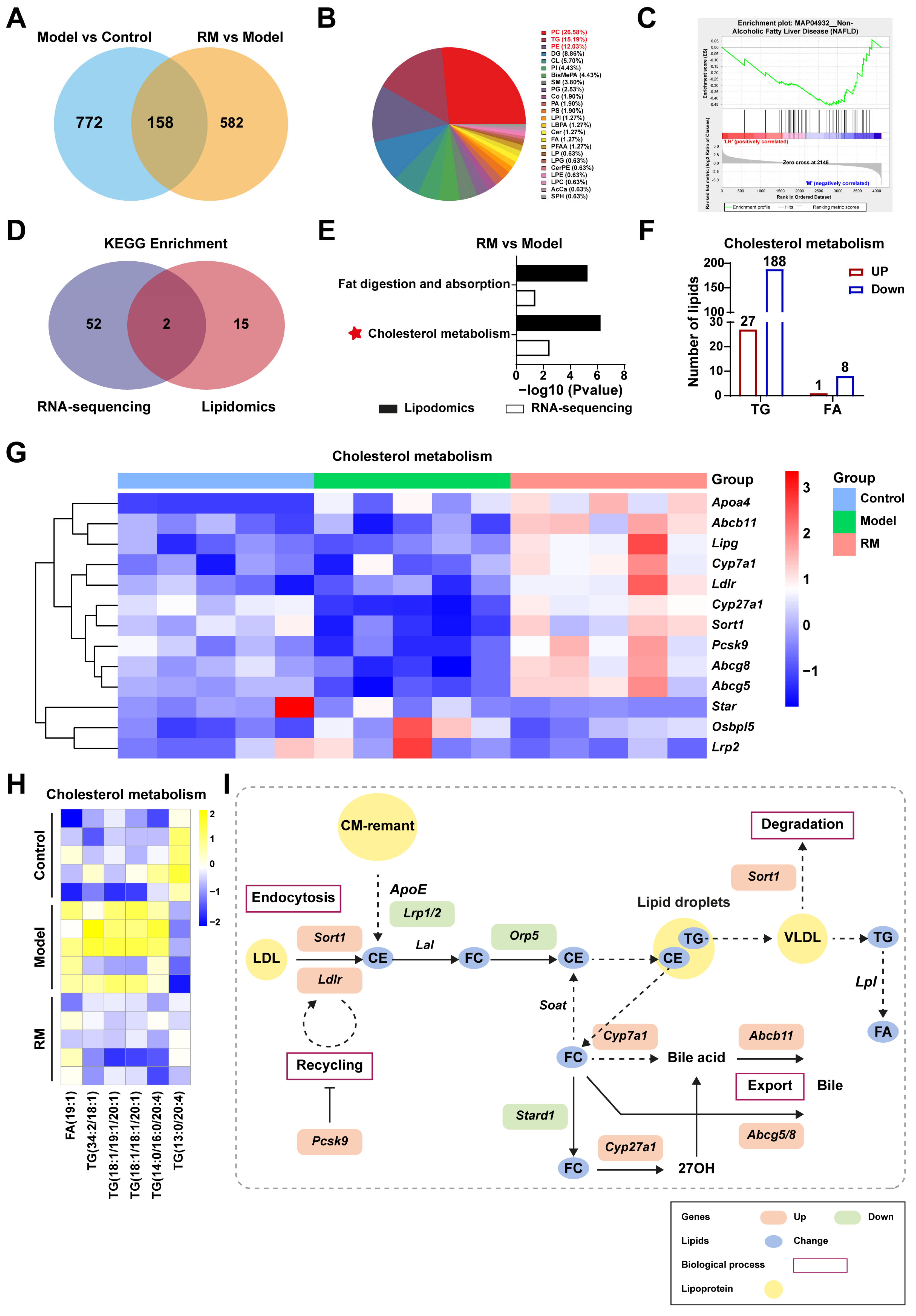
3.7. Comprehensive Analysis of Transcriptomics and Lipidomics in db/db Mice Treated with RM
3.8. RM Ameliorated MASH by Promoting Cholesterol Metabolism in the Fatty Liver of db/db Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MASH | metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis |
| Res | resmetirom |
| Met | metformin |
| RM | half-dose Res and Met |
| MASLD | metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease |
| T2DM | type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| FFA | free fatty acids |
| HCC | hepatocellular carcinoma |
| THR-β | thyroid hormone receptor-beta |
| HMGCR | 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase |
| LDLR | low-density lipoprotein receptor |
| CYP7A1 | cytochrome P450 family 7 subfamily A member 1 |
| CYP27A1 | cytochrome P450 family 27 subfamily A member 1 |
| ABCG5/G8 | ATP-binding cassette subfamily G member 5 or G member 8 |
| TG | triglyceride |
| ACADL | long-chain acyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase |
| ACOX1 | acyl-coenzyme A oxidase 1 |
| PPARA | proliferator-activated receptor α |
| CPT1A | carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1α |
| SCD1 | stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 |
| ACC | acetyl-CoA carboxylase |
| FASN | fatty acid synthase |
| CCK8 | cell counting kit-8 |
| PPARG | proliferator-activated receptor γ |
| SREBF1 | sterol regulatory element binding transcription factor 1 |
| H&E | hematoxylin and eosin |
| TEM | transmission electron microscope |
| ALT | alanine aminotransferase |
| AST | aspartate aminotransferase |
| ELISA | enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor-alpha |
| IL | interleukin |
| COL1A1 | collagen type I alpha 1 |
| COL1A2 | collagen type I alpha 2 |
| TIMP1 | tissue inhibitor of metal protease 1 |
| ACTA2 | alpha actin 2 |
| PCA | principal components analysis |
| DEGs | differentially expressed genes |
| GO | gene ontology |
| BP | biological processes |
| MP | metabolic processes |
| KEGG | Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes |
| PLS-DA | partial least squares discrimination analysis |
| DALs | differentially altered lipids |
| DG | diradylglycerols |
| SPH | sphingoid bases |
| PC | glycerophosphocholines |
| PG | glycerophosphoglycerols |
| CL | glycerophosphoglycerophosphoglycerols |
| PE | glycerophosphoethanolamines |
| GSEA | gene set enrichment analysis |
| QALYs | quality-adjusted life-years |
| SDS-PAGE | sodium dodecyl-sulfate polyacrylamide gel |
References
- Feng, G.; Valenti, L.; Wong, V.W.; Fouad, Y.M.; Yilmaz, Y.; Kim, W.; Sebastiani, G.; Younossi, Z.M.; Hernandez-Gea, V.; Zheng, M.H. Recompensation in cirrhosis: Unravelling the evolving natural history of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 21, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, E.E.; Wong, V.W.; Rinella, M. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Lancet 2021, 397, 2212–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwal, F.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Loomba, R.; Rinella, M.E. Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: Update and impact of new nomenclature on the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases practice guidance on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2024, 79, 1212–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Westerhoff, M.; Pai, R.K.; Choi, W.T.; Gao, Z.H.; Hart, J. Centrilobular ductular reaction correlates with fibrosis stage and fibrosis progression in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Mod. Pathol. 2018, 31, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ge, J.; Li, Y.; Cai, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Huang, N.; Gu, Y.; Han, Q.; Li, Y.; Sun, R.; et al. Integrative lipidomic and transcriptomic study unravels the therapeutic effects of saikosaponins A and D on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 3527–3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M. Predicting Liver-Related Outcomes in Steatotic Liver Disease. JAMA 2024, 331, 1274–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarus, J.V.; Ivancovsky Wajcman, D.; Mark, H.E.; Younossi, Z.M.; Kopka, C.J.; Cohen, N.; Bansal, M.B.; Betel, M.; Brennan, P.N. Opportunities and challenges following approval of resmetirom for MASH liver disease. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 3402–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keam, S.J. Resmetirom: First Approval. Drugs 2024, 84, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal-Cevallos, P.; Chávez-Tapia, N. Resmetirom, the long-awaited first treatment for metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis and liver fibrosis? Med 2024, 5, 375–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, J.; Kim, Y.; Parisé, H.; Bercaw, E.; Smith, Z. Budget impact of resmetirom for the treatment of adults with non-cirrhotic non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) with moderate to advanced liver fibrosis (consistent with stages F2 to F3 fibrosis). J. Med. Econ. 2024, 27, 1108–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.A.; Bedossa, P.; Guy, C.D.; Schattenberg, J.M.; Loomba, R.; Taub, R.; Labriola, D.; Moussa, S.E.; Neff, G.W.; Rinella, M.E.; et al. A Phase 3, Randomized, Controlled Trial of Resmetirom in NASH with Liver Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Q. Adverse events of hepatic anti-fibrotic agents in phase 3 and above clinical trials: A descriptive analysis of the WHO-VigiAccess database. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1534628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, J.R.; Natarajan, Y.; Dai, J.; Yu, X.; Li, L.; El-Serag, H.B.; Kanwal, F. Effect of diabetes medications and glycemic control on risk of hepatocellular cancer in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2022, 75, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazina, I.; Selph, S. Diabetes drugs for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review. Syst. Rev. 2019, 8, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Targher, G.; Corey, K.E.; Byrne, C.D.; Roden, M. The complex link between NAFLD and type 2 diabetes mellitus—Mechanisms and treatments. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 599–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Golabi, P.; de Avila, L.; Paik, J.M.; Srishord, M.; Fukui, N.; Qiu, Y.; Burns, L.; Afendy, A.; Nader, F. The global epidemiology of NAFLD and NASH in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; Targher, G.; Byrne, C.D.; Cao, Y.Y.; Zheng, M.H. Current status and future trends of the global burden of MASLD. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 35, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.Q.; Noureddin, N.; Ajmera, V.; Amangurbanova, M.; Bettencourt, R.; Truong, E.; Gidener, T.; Siddiqi, H.; Majzoub, A.M.; Nayfeh, T.; et al. Type 2 diabetes, hepatic decompensation, and hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: An individual participant-level data meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 8, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, M.; Rahimlou, M.; Mahmoodi, M.; Moosavian, S.P.; Symonds, M.E.; Jalali, R.; Zare, M.; Imanieh, M.H.; Stasi, C. The effects of metformin administration on liver enzymes and body composition in non-diabetic patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and/or non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: An up-to date systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 159, 104799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCreight, L.J.; Bailey, C.J.; Pearson, E.R. Metformin and the gastrointestinal tract. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, H.K.; Kapoor, A.; Fuchs, M.; Mirshahi, F.; Zhou, H.; Maher, J.; Kellum, J.; Warnick, R.; Contos, M.J.; Sanyal, A.J. Increased hepatic synthesis and dysregulation of cholesterol metabolism is associated with the severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Cell Metab. 2012, 15, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Yu, X.H.; Ou, X.; Ouyang, X.P.; Tang, C.K. Hepatic cholesterol transport and its role in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and atherosclerosis. Prog. Lipid Res. 2021, 83, 101109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzolo, D.; Kong, B.; Taylor, R.E.; Brinker, A.; Goedken, M.; Buckley, B.; Guo, G.L. Bile acid homeostasis in female mice deficient in Cyp7a1 and Cyp27a1. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 3847–3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Zhang, X.; Heiyan-Perhat, S.U.; Yang, P.; Han, H.; Li, Y.; Gao, J.; He, E.; Li, Y. Therapeutic Role of Polyphenol Extract from Prunus cerasifera Ehrhart on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver. Plants 2024, 13, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Xu, S.; Zhang, B.; Sun, X. Ramulus Mori (Sangzhi) Alkaloids Alleviate Diabetic Nephropathy through Improving Gut Microbiota Disorder. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Wei, M.; Rajani, C.; Zheng, X. Targeting the alternative bile acid synthetic pathway for metabolic diseases. Protein Cell 2021, 12, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sookoian, S.; Pirola, C.J. Resmetirom for treatment of MASH. Cell 2024, 187, 2897–2897.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.A.; Taub, R. A Phase 3 Trial of Resmetirom in NASH with Liver Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 1632–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wabitsch, S.; McCallen, J.D.; Kamenyeva, O.; Ruf, B.; McVey, J.C.; Kabat, J.; Walz, J.S.; Rotman, Y.; Bauer, K.C.; Craig, A.J.; et al. Metformin treatment rescues CD8(+) T-cell response to immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy in mice with NAFLD. J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, 748–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Rah, S.Y.; An, H.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Roh, G.S.; Ryter, S.W.; Park, J.W.; Yang, C.H.; Surh, Y.J.; Kim, U.H.; et al. Metformin-induced TTP mediates communication between Kupffer cells and hepatocytes to alleviate hepatic steatosis by regulating lipophagy and necroptosis. Metabolism 2023, 141, 155516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wang, H.; Lin, S.; Chen, T.; Chang, D.; Sun, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Song, J.; et al. Advanced effect of curcumin and resveratrol on mitigating hepatic steatosis in metabolic associated fatty liver disease via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR and HIF-1/VEGF cascade. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 165, 115279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javanbakht, M.; Fishman, J.; Moloney, E.; Rydqvist, P.; Ansaripour, A. Early Cost-Effectiveness and Price Threshold Analyses of Resmetirom: An Investigational Treatment for Management of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. PharmacoEconomics-Open 2023, 7, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.S.; Zhang, S.F.; Luo, G.; Cheng, B.C.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.W.; Qiu, X.Y.; Zhou, X.H.; Wang, Q.G.; Song, X.L.; et al. Schisandrin B mitigates hepatic steatosis and promotes fatty acid oxidation by inducing autophagy through AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway. Metabolism 2022, 131, 155200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.C.; Yan, Q.; Yue, S.Q.; Pan, L.X.; Yang, D.S.; Tao, L.S.; Wei, Z.Y.; Rong, F.; Qian, C.; Han, M.Q.; et al. NUP85 alleviates lipid metabolism and inflammation by regulating PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2024, 20, 2219–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, C.; Chen, J.; Sang, T.; Peng, H.; Lin, X.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, S.; Eling, T.; Wang, X. Overexpression of NAG-1/GDF15 prevents hepatic steatosis through inhibiting oxidative stress-mediated dsDNA release and AIM2 inflammasome activation. Redox Biol. 2022, 52, 102322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, S.; Xia, M.; Vale, G.; Wang, S.; Kim, C.W.; Li, S.; McDonald, J.G.; Radhakrishnan, A.; Horton, J.D. DGAT2 inhibition blocks SREBP-1 cleavage and improves hepatic steatosis by increasing phosphatidylethanolamine in the ER. Cell Metab. 2024, 36, 617–629.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Pan, Z.; Xie, W.; Zhao, J.; Miao, D.; Zhao, L.; Liu, M.; Zhong, Y.; Zhong, C.; Gonzalez, F.J.; et al. Hepatocyte-specific SLC27A4 deletion ameliorates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mice via suppression of phosphatidylcholine-mediated PXR activation. Metabolism 2024, 162, 156054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luukkonen, P.K.; Juuti, A.; Sammalkorpi, H.; Penttilä, A.K.; Orešič, M.; Hyötyläinen, T.; Arola, J.; Orho-Melander, M.; Yki-Järvinen, H. MARC1 variant rs2642438 increases hepatic phosphatidylcholines and decreases severity of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in humans. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 725–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cai, B.; Yang, X.; Sonubi, O.O.; Zheng, Z.; Ramakrishnan, R.; Shi, H.; Valenti, L.; Pajvani, U.B.; Sandhu, J.; et al. Cholesterol Stabilizes TAZ in Hepatocytes to Promote Experimental Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis. Cell Metab. 2020, 31, 969–986.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szántó, M.; Gupte, R.; Kraus, W.L.; Pacher, P.; Bai, P. PARPs in lipid metabolism and related diseases. Prog. Lipid Res. 2021, 84, 101117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handelman, S.K.; Puentes, Y.M.; Kuppa, A.; Chen, Y.; Du, X.; Feitosa, M.F.; Palmer, N.D.; Speliotes, E.K. Population-based meta-analysis and gene-set enrichment identifies FXR/RXR pathway as common to fatty liver disease and serum lipids. Hepatol. Commun. 2022, 6, 3120–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, B.; Tong, J.; Hao, H.; Yang, Z.; Chen, K.; Xu, H.; Wang, A. Bile acid coordinates microbiota homeostasis and systemic immunometabolism in cardiometabolic diseases. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 2129–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graf, G.A.; Yu, L.; Li, W.P.; Gerard, R.; Tuma, P.L.; Cohen, J.C.; Hobbs, H.H. ABCG5 and ABCG8 are obligate heterodimers for protein trafficking and biliary cholesterol excretion. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 48275–48282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, D.; Finck, B.N. Emerging therapeutic approaches for the treatment of NAFLD and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2021, 17, 484–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazankov, K.; Jørgensen, S.M.D.; Thomsen, K.L.; Møller, H.J.; Vilstrup, H.; George, J.; Schuppan, D.; Grønbæk, H. The role of macrophages in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C. The emerging roles of NOD-like receptors in antiviral innate immune signaling pathways. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 169, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calcagno, D.M.; Chu, A.; Gaul, S.; Taghdiri, N.; Toomu, A.; Leszczynska, A.; Kaufmann, B.; Papouchado, B.; Wree, A.; Geisler, L.; et al. NOD-like receptor protein 3 activation causes spontaneous inflammation and fibrosis that mimics human NASH. Hepatology 2022, 76, 727–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.M.; Koh, D.H.; Jun, D.W.; Roh, Y.J.; Kang, H.T.; Oh, J.H.; Kim, H.S. Auranofin attenuates hepatic steatosis and fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease via NRF2 and NF- κB signaling pathways. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2022, 28, 827–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.; Zhou, G.; Zhu, A.; Jin, C.; Li, M.; Ding, K. RG-I pectin-like polysaccharide from Rosa chinensis inhibits inflammation and fibrosis associated to HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway to improve non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 337, 122139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Gene | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| H-18S | GTAACCCGTTGAACCCCATT | CCATCCAATCGGTAGTAGCG |
| H-ACADL | AGGGGATCTGTACTCCGCAG | CTCTGTCATTGCTATTGCACCA |
| H-ACOX1 | ACTCGCAGCCAGCGTTATG | AGGGTCAGCGATGCCAAAC |
| H-PPARA | TTCGCAATCCATCGGCGAG | CCACAGGATAAGTCACCGAGG |
| H-CPT1A | TCCAGTTGGCTTATCGTGGTG | TCCAGAGTCCGATTGATTTTTGC |
| H-SCD1 | GGGGGTGTGCTGACAACTTA | AGGCCCCTTTTTCTACCAGC |
| H-ACC | ACAGTGGACAGAATTGAGGG | AGTGGAGCTAGAATTGGACTTG |
| H-FASN | AAGGACCTGTCTAGGTTTGATGC | TGGCTTCATAGGTGACTTCCA |
| M-18S | GCCGTTCTTAGTTGGTGGAG | AACGCCACTTGTCCCTCTAA |
| M-Acadl | TTTCCTCGGAGCATGACATTTT | GCCAGCTTTTTCCCAGACCT |
| M-Acox1 | GGAAGACTTCCAATCATGCGATAG | GACAACAAAGGCATGTAACCCG |
| M-Ppara | AACATCGAGTGTCGAATATGTGG | CCGAATAGTTCGCCGAAAGAA |
| M-Pparg | GGAAGACCACTCGCATTCCTT | GTAATCAGCAACCATTGGGTCA |
| M-Acc | ACAGTGGACAGAATTGAGGG | AGTGGAGCTAGAATTGGACTTG |
| M-Fasn | CAGAGCAGCCATGGAGGAG | TCCGTGACCATCTCCACAC |
| M-Srebf1 | GGCACTAAGTGCCCTCAACCT | GCCACATAGATCTCTGCCAGTGT |
| M-Cpt1a | TGGCATCATCACTGGTGTGTT | GTCTAGGGTCCGATTGATCTTTG |
| M-Tnfa | GACGTGGAACTGGCAGAAGAG | TTGGTGGTTTGTGAGTGTGAG |
| M-Il10 | GCTCTTACTGACTGGCATGAG | CGCAGCTCTAGGAGCATGTG |
| M-Col1a1 | CATAAAGGGTCATCGTGGCT | TTGAGTCCGTCTTTGCCAG |
| M-Col1a2 | AAGGATACAGTGGATTGCAGG | TCTACCATCTTTGCCAACGG |
| M-Timp1 | CGAGACCACCTTATACCAGCG | ATGACTGGGGTGTAGGCGTA |
| M-Acta2 | GTGAAGAGGAAGACAGCACAG | GCCCATTCCAACCATTACTCC |
| M-Apoa4 | CCAATGTGGTGTGGGATTACTT | AGTGACATCCGTCTTCTGAAAC |
| M-Abcb11 | TCTGACTCAGTGATTCTTCGCA | CCCATAAACATCAGCCAGTTGT |
| M-Lipg | ATGCGAAACACGGTTTTCCTG | GTAGCTGGTACTCCAGTGGG |
| M-Cyp7a1 | GGGATTGCTGTGGTAGTGAGC | GGTATGGAATCAACCCGTTGTC |
| M-Ldlr | TGACTCAGACGAACAAGGCTG | ATCTAGGCAATCTCGGTCTCC |
| M-Cyp27a1 | CCAGGCACAGGAGAGTACG | GGGCAAGTGCAGCACATAG |
| M-Sort1 | CCCGGACTTCATCGCCAAG | AGGACGAGAATAACCCCAGTG |
| M-Lrp2 | AAAATGGAAACGGGGTGACTT | GGCTGCATACATTGGGTTTTCA |
| M-Abcg8 | CTGTGGAATGGGACTGTACTTC | GTTGGACTGACCACTGTAGGT |
| M-Abcg5 | AGGGCCTCACATCAACAGAG | GCTGACGCTGTAGGACACAT |
| M-Star | ATGTTCCTCGCTACGTTCAAG | CCCAGTGCTCTCCAGTTGAG |
| M-Osbpl5 | TTCTGGGCTGCGAAAATGAG | GTCAGATCCATGCATAGCCTG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, W.; Yao, F.; Wang, J.; Shao, N.; Cao, X.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, B.; Sun, X. Combination Therapy of Half-Dose Resmetirom and Metformin Attenuates Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis Through Improving Cholesterol Metabolism and Inflammation. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061315
Liu W, Yao F, Wang J, Shao N, Cao X, Dong Z, Zhang B, Sun X. Combination Therapy of Half-Dose Resmetirom and Metformin Attenuates Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis Through Improving Cholesterol Metabolism and Inflammation. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(6):1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061315
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Wenxiu, Fan Yao, Jinghan Wang, Nan Shao, Xinxin Cao, Zhengqi Dong, Bin Zhang, and Xiaobo Sun. 2025. "Combination Therapy of Half-Dose Resmetirom and Metformin Attenuates Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis Through Improving Cholesterol Metabolism and Inflammation" Biomedicines 13, no. 6: 1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061315
APA StyleLiu, W., Yao, F., Wang, J., Shao, N., Cao, X., Dong, Z., Zhang, B., & Sun, X. (2025). Combination Therapy of Half-Dose Resmetirom and Metformin Attenuates Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis Through Improving Cholesterol Metabolism and Inflammation. Biomedicines, 13(6), 1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061315





