Adjunct Therapy with Ipragliflozin Exerts Limited Effects on Kidney Protection in Type 1 Diabetes: A Retrospective Study Conducted at 25 Centers in Japan (IPRA-CKD)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Data Collection and Handling During the COVID-19 Pandemic
2.4. Primary/Secondary Outcomes and Safety Endpoints
2.5. Statistical Analyses
2.6. Ethical Considerations
3. Results
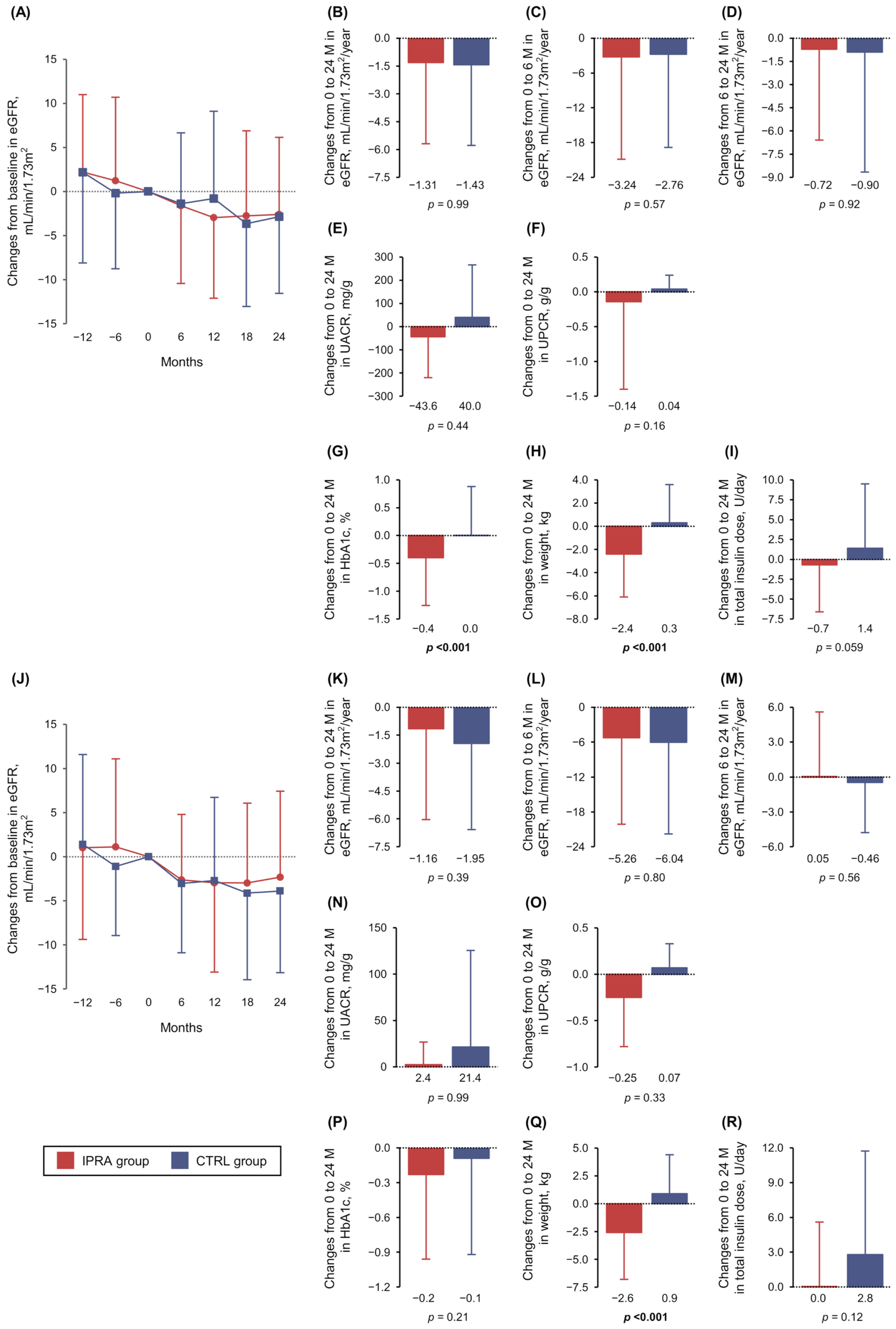
3.1. Primary Outcome
3.2. Secondary Outcomes
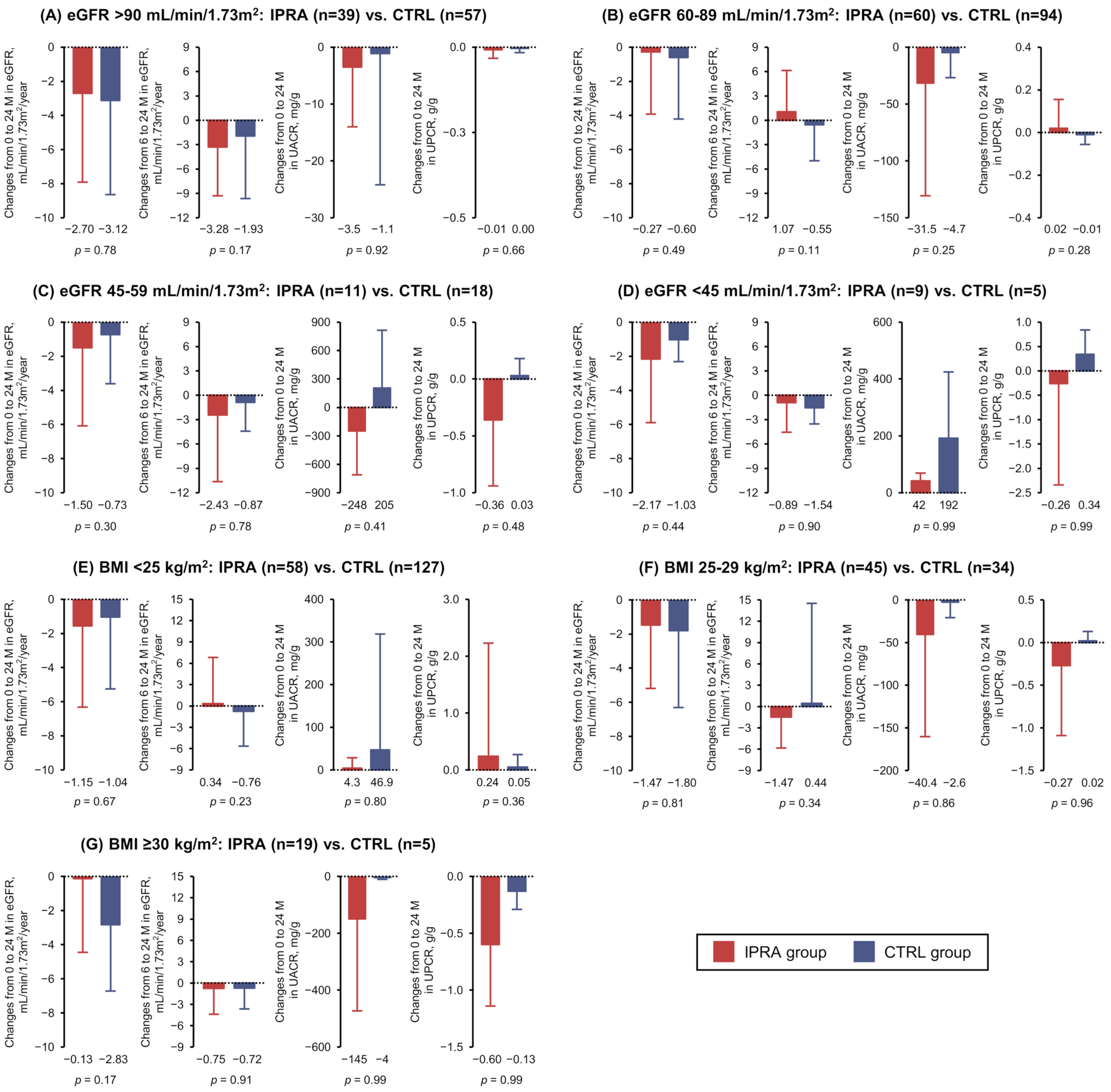
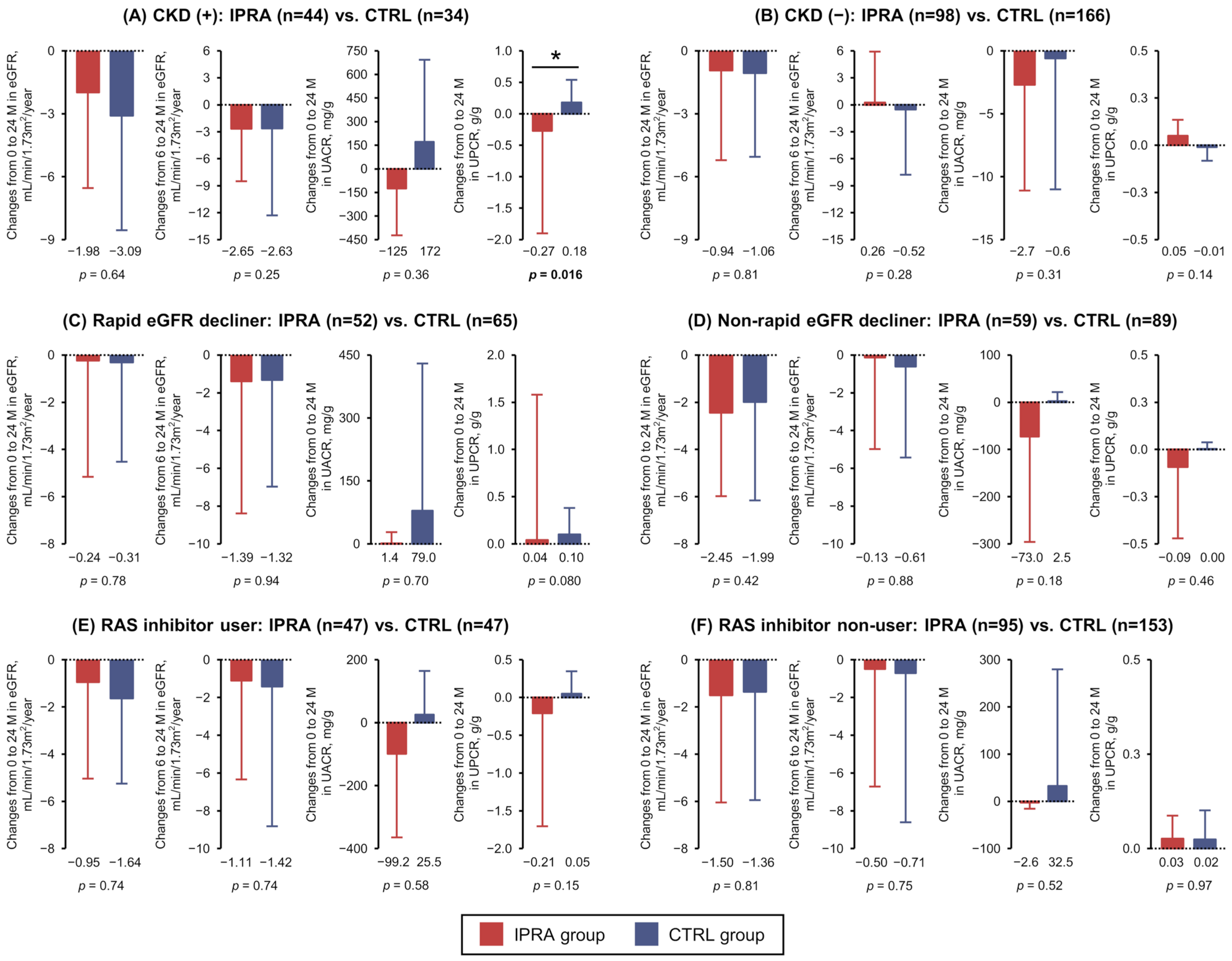
3.3. Post Hoc Analyses
3.4. Safety Endpoints
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACE | Angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitor |
| ARB | Angiotensin II receptor blocker |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| CKD | Chronic kidney disease |
| COVID-19 | Coronavirus disease 2019 |
| CVD | Cardiovascular disease |
| DKA | Diabetic ketoacidosis |
| eGFR | Estimated glomerular filtration rate |
| ESKD | End-stage kidney disease |
| HbA1c | Glycated hemoglobin |
| SGLT | Sodium–glucose cotransporter |
| T1D | Type 1 diabetes |
| T2D | Type 2 diabetes |
| UACR | Urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio |
| UPCR | Urinary protein-to-creatine ratio |
References
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 9. Pharmacologic Approaches to Glycemic Treatment: Standards of Care in Diabetes-2024. Diabetes Care 2024, 47, S158–S178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waijer, S.W.; Vart, P.; Cherney, D.Z.I.; Chertow, G.M.; Jongs, N.; Langkilde, A.M.; Mann, J.F.E.; Mosenzon, O.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Rossing, P.; et al. Effect of dapagliflozin on kidney and cardiovascular outcomes by baseline KDIGO risk categories: A post hoc analysis of the DAPA-CKD trial. Diabetologia 2022, 65, 1085–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhund, P.S.; Kondo, T.; Butt, J.H.; Docherty, K.F.; Claggett, B.L.; Desai, A.S.; Vaduganathan, M.; Gasparyan, S.B.; Bengtsson, O.; Lindholm, D.; et al. Dapagliflozin across the range of ejection fraction in patients with heart failure: A patient-level, pooled meta-analysis of DAPA-HF and DELIVER. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1956–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anker, S.D.; Butler, J.; Filippatos, G.; Ferreira, J.P.; Bocchi, E.; Bohm, M.; Brunner-La Rocca, H.P.; Choi, D.J.; Chopra, V.; Chuquiure-Valenzuela, E.; et al. Empagliflozin in Heart Failure with a Preserved Ejection Fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1451–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, R.R.; Thakkar, P.; Tong, C.; Polidori, D.; Alba, M. Efficacy and Safety of Canagliflozin, a Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor, as Add-on to Insulin in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 2258–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandona, P.; Mathieu, C.; Phillip, M.; Hansen, L.; Griffen, S.C.; Tschope, D.; Thoren, F.; Xu, J.; Langkilde, A.M.; DEPICT-1 Investigators. Efficacy and safety of dapagliflozin in patients with inadequately controlled type 1 diabetes (DEPICT-1): 24 week results from a multicentre, double-blind, phase 3, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017, 5, 864–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandona, P.; Mathieu, C.; Phillip, M.; Hansen, L.; Tschope, D.; Thoren, F.; Xu, J.; Langkilde, A.M.; DEPICT-1 Investigators. Efficacy and Safety of Dapagliflozin in Patients with Inadequately Controlled Type 1 Diabetes: The DEPICT-1 52-Week Study. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 2552–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, C.; Dandona, P.; Gillard, P.; Senior, P.; Hasslacher, C.; Araki, E.; Lind, M.; Bain, S.C.; Jabbour, S.; Arya, N.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Dapagliflozin in Patients with Inadequately Controlled Type 1 Diabetes (the DEPICT-2 Study): 24-Week Results From a Randomized Controlled Trial. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 1938–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenstock, J.; Marquard, J.; Laffel, L.M.; Neubacher, D.; Kaspers, S.; Cherney, D.Z.; Zinman, B.; Skyler, J.S.; George, J.; Soleymanlou, N.; et al. Empagliflozin as Adjunctive to Insulin Therapy in Type 1 Diabetes: The EASE Trials. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 2560–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buse, J.B.; Garg, S.K.; Rosenstock, J.; Bailey, T.S.; Banks, P.; Bode, B.W.; Danne, T.; Kushner, J.A.; Lane, W.S.; Lapuerta, P.; et al. Sotagliflozin in Combination with Optimized Insulin Therapy in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes: The North American inTandem1 Study. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 1970–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danne, T.; Cariou, B.; Banks, P.; Brandle, M.; Brath, H.; Franek, E.; Kushner, J.A.; Lapuerta, P.; McGuire, D.K.; Peters, A.L.; et al. HbA(1c) and Hypoglycemia Reductions at 24 and 52 Weeks with Sotagliflozin in Combination with Insulin in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes: The European inTandem2 Study. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 1981–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, S.K.; Henry, R.R.; Banks, P.; Buse, J.B.; Davies, M.J.; Fulcher, G.R.; Pozzilli, P.; Gesty-Palmer, D.; Lapuerta, P.; Simo, R.; et al. Effects of Sotagliflozin Added to Insulin in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2337–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaku, K.; Isaka, H.; Sakatani, T.; Toyoshima, J. Efficacy and safety of ipragliflozin add-on therapy to insulin in Japanese patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus: A randomized, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2019, 21, 2284–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araki, E.; Watada, H.; Uchigata, Y.; Tomonaga, O.; Fujii, H.; Ohashi, H.; Okabe, T.; Asano, M.; Thoren, F.; Kim, H.; et al. Efficacy and safety of dapagliflozin in Japanese patients with inadequately controlled type 1 diabetes (DEPICT-5): 52-week results from a randomized, open-label, phase III clinical trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2020, 22, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathieu, C.; Dandona, P.; Phillip, M.; Oron, T.; Lind, M.; Hansen, L.; Thoren, F.; Xu, J.; Langkilde, A.M.; DEPICT-1 and DEPICT-2 Investigators. Glucose Variables in Type 1 Diabetes Studies with Dapagliflozin: Pooled Analysis of Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data From DEPICT-1 and -2. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 1081–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danne, T.; Cariou, B.; Buse, J.B.; Garg, S.K.; Rosenstock, J.; Banks, P.; Kushner, J.A.; McGuire, D.K.; Peters, A.L.; Sawhney, S.; et al. Improved Time in Range and Glycemic Variability with Sotagliflozin in Combination with Insulin in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes: A Pooled Analysis of 24-Week Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data From the inTandem Program. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 919–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, A.; Hanafusa, T.; Yasui, A.; Lee, G.; Taneda, Y.; Sarashina, A.; Shiki, K.; George, J.; Soleymanlou, N.; Marquard, J. Empagliflozin as adjunct to insulin in Japanese participants with type 1 diabetes: Results of a 4-week, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 2190–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.I.; Blau, J.E.; Rother, K.I.; Beitelshees, A.L. SGLT2 inhibitors as adjunctive therapy for type 1 diabetes: Balancing benefits and risks. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Shojima, N.; Noma, H.; Yamauchi, T.; Kadowaki, T. Sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors as add-on therapy to insulin for type 1 diabetes mellitus: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 1755–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, J.; Wang, D.; Zhong, R.; Liu, F.; Luo, J.; Tang, P.; Song, X.; Zhang, L. Sodium glucose cotransporter2 inhibitors for type 1 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Prim. Care Diabetes 2024, 18, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maffei, P.; Bettini, S.; Busetto, L.; Dassie, F. SGLT2 Inhibitors in the Management of Type 1 Diabetes (T1D): An Update on Current Evidence and Recommendations. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2023, 16, 3579–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 10. Cardiovascular Disease and Risk Management: Standards of Care in Diabetes-2024. Diabetes Care 2024, 47, S179–S218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 11. Chronic Kidney Disease and Risk Management: Standards of Care in Diabetes-2024. Diabetes Care 2024, 47, S219–S230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, M.J.; Aroda, V.R.; Collins, B.S.; Gabbay, R.A.; Green, J.; Maruthur, N.M.; Rosas, S.E.; Del Prato, S.; Mathieu, C.; Mingrone, G.; et al. Management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes, 2022. A consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetologia 2022, 65, 1925–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakasis, P.; Popovic, D.S.; Patoulias, D.; Koufakis, T.; Papanas, N.; Fragakis, N.; Rizzo, M. The Effect of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter Inhibitors on Renal Function as Adjunctive to Insulin in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes: An Updated Multilevel Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Diabetes Ther. 2024, 15, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Raalte, D.H.; Bjornstad, P.; Persson, F.; Powell, D.R.; de Cassia Castro, R.; Wang, P.S.; Liu, M.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Cherney, D. The Impact of Sotagliflozin on Renal Function, Albuminuria, Blood Pressure, and Hematocrit in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 1921–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherney, D.Z.I.; Bjornstad, P.; Perkins, B.A.; Rosenstock, J.; Neubacher, D.; Marquard, J.; Soleymanlou, N. Kidney Effects of Empagliflozin in People with Type 1 Diabetes. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 16, 1715–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groop, P.H.; Dandona, P.; Phillip, M.; Gillard, P.; Edelman, S.; Jendle, J.; Xu, J.; Scheerer, M.F.; Thoren, F.; Iqbal, N.; et al. Effect of dapagliflozin as an adjunct to insulin over 52 weeks in individuals with type 1 diabetes: Post-hoc renal analysis of the DEPICT randomised controlled trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherney, D.Z.; Perkins, B.A.; Soleymanlou, N.; Maione, M.; Lai, V.; Lee, A.; Fagan, N.M.; Woerle, H.J.; Johansen, O.E.; Broedl, U.C.; et al. Renal hemodynamic effect of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Circulation 2014, 129, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stougaard, E.B.; Rossing, P.; Cherney, D.; Vistisen, D.; Persson, F. Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors as adjunct therapy for type 1 diabetes and the benefit on cardiovascular and renal disease evaluated by Steno risk engines. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2022, 36, 108257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.S.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Coresh, J.; Inker, L.A.; Heerspink, H.L.; Grams, M.E.; Greene, T.; Tighiouart, H.; Matsushita, K.; Ballew, S.H.; et al. Change in Albuminuria and GFR as End Points for Clinical Trials in Early Stages of CKD: A Scientific Workshop Sponsored by the National Kidney Foundation in Collaboration with the US Food and Drug Administration and European Medicines Agency. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 75, 84–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, K.; Li, X.; Lingvay, I. Clinical and Safety Outcomes with GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and SGLT2 Inhibitors in Type 1 Diabetes: A Real-World Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 108, 920–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palanca, A.; van Nes, F.; Pardo, F.; Ampudia Blasco, F.J.; Mathieu, C. Real-world Evidence of Efficacy and Safety of SGLT2 Inhibitors as Adjunctive Therapy in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes: A European Two-Center Experience. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 650–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hironaka, J.; Okada, H.; Hamaguchi, M.; Sakai, K.; Minamida, M.; Kondo, Y.; Hashimoto, Y.; Kitagawa, N.; Yano, M.; Yamazaki, M.; et al. Effects of dapagliflozin on renal function in type 1 diabetes patients in the real world: A retrospective multicenter study of the KAMOGAWA-A cohort. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2023, 202, 110794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrannini, E.; Mark, M.; Mayoux, E. CV Protection in the EMPA-REG OUTCOME Trial: A “Thrifty Substrate” Hypothesis. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 1108–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrannini, E.; Baldi, S.; Frascerra, S.; Astiarraga, B.; Heise, T.; Bizzotto, R.; Mari, A.; Pieber, T.R.; Muscelli, E. Shift to Fatty Substrate Utilization in Response to Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibition in Subjects Without Diabetes and Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes 2016, 65, 1190–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, I.; Kume, S.; Sugahara, S.; Osawa, N.; Yamahara, K.; Yasuda-Yamahara, M.; Takeda, N.; Chin-Kanasaki, M.; Kaneko, T.; Mayoux, E.; et al. SGLT2 Inhibition Mediates Protection from Diabetic Kidney Disease by Promoting Ketone Body-Induced mTORC1 Inhibition. Cell Metab. 2020, 32, 404–419.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Horie, I.; Kitamura, T.; Kusunoki, Y.; Nishida, K.; Yamamoto, A.; Hirota, Y.; Fukui, T.; Maeda, Y.; Minami, M.; et al. Glucagon secretion and its association with glycaemic control and ketogenesis during sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition by ipragliflozin in people with type 1 diabetes: Results from the multicentre, open-label, prospective study. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2024, 26, 1605–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| IPRA Group | CTRL Group | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| N | 159 | 200 | |
| Age, years | 46.2 ± 12.7 | 48.1 ± 14.3 | 0.10 |
| Male/female, n | 58/101 | 73/127 | 0.99 |
| Duration of diabetes, yrs | 16.7 ± 10.0 | 16.1 ± 10.3 | 0.37 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 25.6 ± 3.6 | 23.0 ± 3.6 | <0.001 |
| SBP, mmHg | 127 ± 16 | 124 ± 18 | 0.30 |
| DBP, mmHg | 74 ± 12 | 71 ± 12 | 0.027 |
| Total insulin, unit/day | 47.3 ± 23.8 | 38.5 ± 17.1 | <0.001 |
| HbA1c, % | 8.3 ± 1.1 | 7.7 ± 1.1 | <0.001 |
| eGFR, mL/min 1.73 m2 | 81.3 ± 21.9 | 81.4 ± 20.9 | 0.98 |
| UACR, mg/gCr | 11.0 (5.0, 84.1) | 11.7 (5.4, 23.0) | 0.33 |
| UPCR, g/gCr | 0.54 (0.06, 1.13) | 0.07 (0.04, 0.13) | 0.027 |
| Neuropathy—yes, n (%) | 45 (28.3) | 54 (27.0) | 0.81 |
| Retinopathy—yes, n (%) | 54 (34.0) | 52 (26.0) | 0.11 |
| CKD—yes, n (%) | 46 (28.9) | 34 (17.0) | 0.008 |
| CVD—yes, n (%) | 9 (5.7) | 8 (4.0) | 0.47 |
| Hypertension—yes, n (%) | 63 (39.6) | 73 (36.5) | 0.59 |
| Dyslipidemia—yes, n (%) | 78 (49.1) | 67 (33.5) | 0.003 |
| Smoking—yes, n (%) | 53 (33.3) | 61 (30.5) | 0.57 |
| Severe hypoglycemia—yes, n (%) | 21 (13.2) | 44 (22.0) | 0.038 |
| History of ketoacidosis—yes, n (%) | 33 (20.8) | 52 (26.0) | 0.26 |
| RAS inhibitor—yes, n (%) | 51 (32.1) | 47 (23.5) | 0.075 |
| Statin—yes, n (%) | 59 (37.1) | 43 (21.5) | 0.001 |
| After propensity score matching | |||
| N | 65 | 65 | |
| Age, years | 49.0 ± 12.7 | 48.4 ± 14.9 | 0.89 |
| Male/female, n | 23/42 | 23/42 | 0.99 |
| Duration of diabetes, yrs | 15.0 ± 9.4 | 16.9 ± 11.3 | 0.45 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 24.8 ± 3.2 | 24.8 ± 4.0 | 0.55 |
| SBP, mmHg | 129 ± 18 | 130 ± 16 | 0.41 |
| DBP, mmHg | 74 ± 11 | 73 ± 13 | 0.57 |
| Total insulin, U/day | 43.2 ± 21.3 | 42.2 ± 19.5 | 0.87 |
| HbA1c, % | 7.9 ± 1.0 | 8.0 ± 1.2 | 0.85 |
| eGFR, mL/min 1.73 m2 | 81.2 ± 21.8 | 79.4 ± 22.9 | 0.58 |
| UACR, mg/gCr | 14.1 (5.1, 84.9) | 12.8 (6.4, 21.1) | 0.72 |
| UPCR, g/gCr | 0.13 (0.06, 0.97) | 0.08 (0.05, 0.12) | 0.41 |
| Neuropathy—yes, n (%) | 17 (26.2) | 24 (36.9) | 0.26 |
| Retinopathy—yes, n (%) | 23 (35.4) | 22 (33.8) | 0.99 |
| CKD—yes, n (%) | 18 (27.7) | 13 (20.0) | 0.41 |
| CVD—yes, n (%) | 4 (6.2) | 1 (1.5) | 0.37 |
| Hypertension—yes, n (%) | 23 (35.4) | 34 (52.3) | 0.08 |
| Dyslipidemia—yes, n (%) | 28 (43.1) | 25 (38.5) | 0.72 |
| Smoking—yes, n (%) | 21 (32.3) | 21 (32.3) | 0.99 |
| Severe hypoglycemia—yes, n (%) | 11 (16.9) | 12 (18.5) | 0.99 |
| History of ketoacidosis—yes, n (%) | 13 (20.0) | 12 (18.5) | 0.99 |
| RAS inhibitor—yes, n (%) | 21 (32.3) | 21 (32.3) | 0.99 |
| Statin—yes, n (%) | 25 (38.5) | 17 (26.2) | 0.19 |
| IPRA Group | CTRL Group | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| N | 159 | 200 | |
| Severe hypoglycemia | 5 (3.1) | 14 (7.0) | 0.15 |
| Hospitalization due to ketosis/ketoacidosis | 2 (1.3) | 4 (2.0) | 0.70 |
| Hospitalization due to CVD | 1 (0.6) | 1 (0.5) | 0.99 |
| Urinary tract infections | 4 (2.5) | 1 (0.5) | 0.18 |
| Gastrointestinal symptoms | 2 (1.3) | 3 (1.5) | 0.99 |
| Dizziness/deafness | 3 (1.9) | 2 (1.0) | 0.66 |
| Dehydration | 0 (0.0) | 4 (2.0) | 0.13 |
| Upper respiratory tract infection | 1 (0.6) | 3 (1.5) | 0.63 |
| Oral infection | 0 (0.0) | 3 (1.5) | 0.26 |
| Weight loss | 2 (1.3) | 0 (0.0) | 0.20 |
| Skin rash | 1 (0.6) | 1 (0.5) | 0.99 |
| Liver dysfunction | 1 (0.6) | 1 (0.5) | 0.99 |
| Gout | 1 (0.6) | 1 (0.5) | 0.99 |
| After propensity score matching | |||
| N | 65 | 65 | |
| Severe hypoglycemia | 2 (3.1) | 2 (3.1) | 0.99 |
| Hospitalization due to ketosis/ketoacidosis | 0 (0.0) | 2 (3.1) | 0.50 |
| Hospitalization due to CVD | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | NA |
| Urinary tract infections | 3 (4.6) | 1 (1.5) | 0.62 |
| Gastrointestinal symptoms | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | NA |
| Dizziness/deafness | 2 (3.1) | 0 (0.0) | 0.50 |
| Dehydration | 0 (0.0) | 2 (3.1) | 0.50 |
| Upper respiratory tract infection | 1 (1.5) | 0 (0.0) | 0.99 |
| Oral infection | 0 (0.0) | 2 (3.1) | 0.50 |
| Weight loss | 1 (1.5) | 0 (0.0) | 0.99 |
| Skin rash | 1 (1.5) | 1 (1.5) | 0.99 |
| Liver dysfunction | 1 (1.5) | 1 (1.5) | 0.99 |
| Gout | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | NA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nakamura, Y.; Horie, I.; Yano, H.; Nomoto, H.; Fukui, T.; Yuyama, Y.; Kawamura, T.; Ueda, M.; Yamamoto, A.; Hirota, Y.; et al. Adjunct Therapy with Ipragliflozin Exerts Limited Effects on Kidney Protection in Type 1 Diabetes: A Retrospective Study Conducted at 25 Centers in Japan (IPRA-CKD). Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1287. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061287
Nakamura Y, Horie I, Yano H, Nomoto H, Fukui T, Yuyama Y, Kawamura T, Ueda M, Yamamoto A, Hirota Y, et al. Adjunct Therapy with Ipragliflozin Exerts Limited Effects on Kidney Protection in Type 1 Diabetes: A Retrospective Study Conducted at 25 Centers in Japan (IPRA-CKD). Biomedicines. 2025; 13(6):1287. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061287
Chicago/Turabian StyleNakamura, Yuta, Ichiro Horie, Hiroshi Yano, Hiroshi Nomoto, Tomoyasu Fukui, Yoshihiko Yuyama, Tomoyuki Kawamura, Mariko Ueda, Akane Yamamoto, Yushi Hirota, and et al. 2025. "Adjunct Therapy with Ipragliflozin Exerts Limited Effects on Kidney Protection in Type 1 Diabetes: A Retrospective Study Conducted at 25 Centers in Japan (IPRA-CKD)" Biomedicines 13, no. 6: 1287. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061287
APA StyleNakamura, Y., Horie, I., Yano, H., Nomoto, H., Fukui, T., Yuyama, Y., Kawamura, T., Ueda, M., Yamamoto, A., Hirota, Y., Kusunoki, Y., Nishida, K., Sekiguchi, D., Maeda, Y., Minami, M., Nagayama, A., Iwata, S., Minagawa, H., Furukawa, S., ... Abiru, N., on behalf of the IPRA-CKD Study Group. (2025). Adjunct Therapy with Ipragliflozin Exerts Limited Effects on Kidney Protection in Type 1 Diabetes: A Retrospective Study Conducted at 25 Centers in Japan (IPRA-CKD). Biomedicines, 13(6), 1287. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061287








