Merkel Cell Polyomavirus (MCPyV) and Its Possible Role in Head and Neck Cancers
Abstract
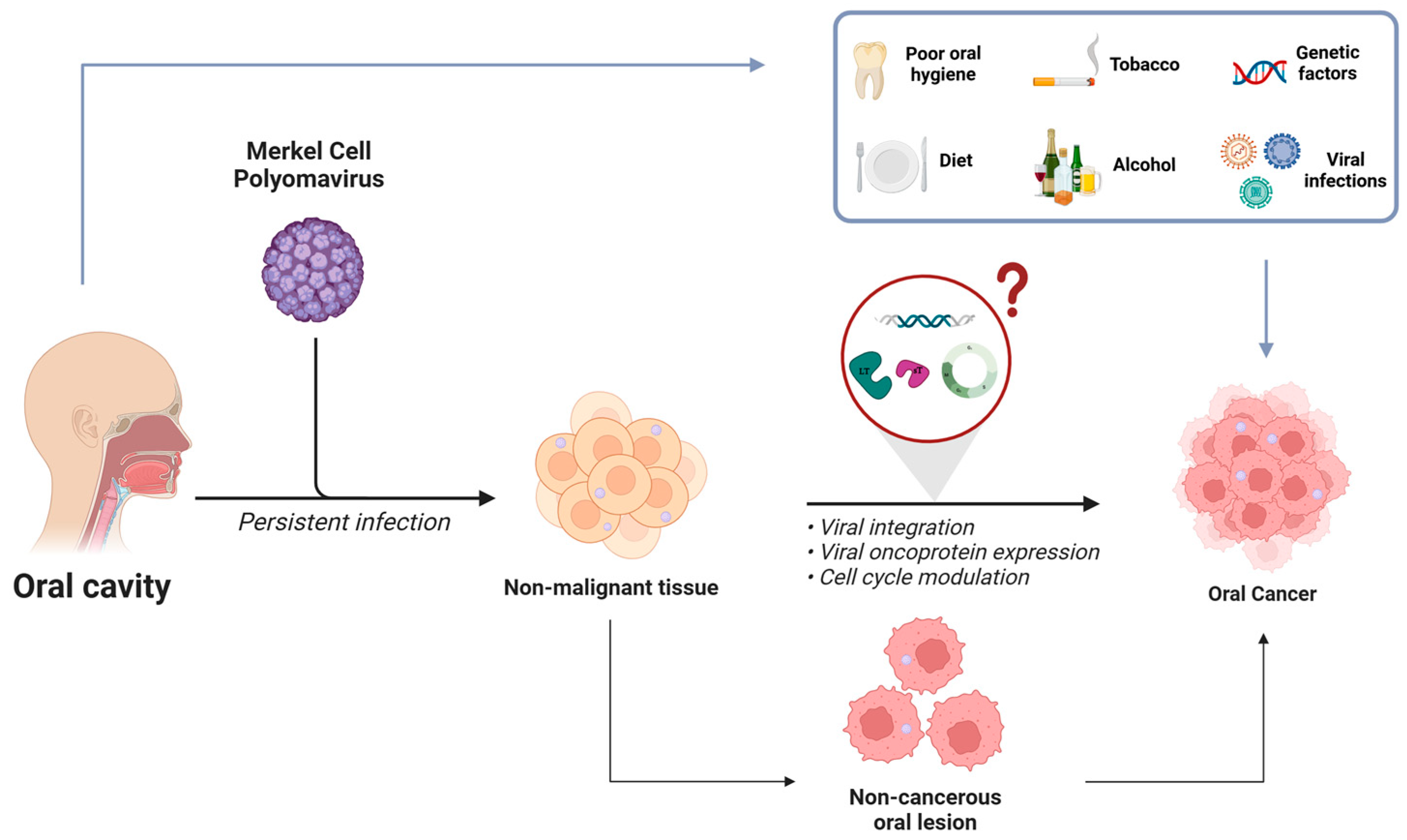
1. Introduction
2. Merkel Cell Polyomavirus (MCPyV) and Merkel Cell Carcinoma (MCC)
3. Merkel Cell Polyomavirus in Non-Cancerous Tissues and in Non-MCC Tumors
4. Merkel Cell Polyomavirus in Non-MCC Tumors Associated with HNCs
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dhull, A.K.; Atri, R.; Dhankhar, R.; Chauhan, A.K.; Kaushal, V. Major Risk Factors in Head and Neck Cancer: A Retrospective Analysis of 12-Year Experiences. World J. Oncol. 2018, 9, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samara, P.; Athanasopoulos, M.; Mastronikolis, S.; Kyrodimos, E.; Athanasopoulos, I.; Mastronikolis, N.S. The Role of Oncogenic Viruses in Head and Neck Cancers: Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Advancements in Detection Methods. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminski, B. Lymphomas of the head-and-neck region. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2021, 17, 1347–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. Head and Neck Tumours; IARC: Lyon, France, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- de Martel, C.; Georges, D.; Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Clifford, G.M. Global burden of cancer attributable to infections in 2018: A worldwide incidence analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2020, 8, e180–e190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, G.R.; Hyole, R.G.; Li, J. Head and neck cancer: Current challenges and future perspectives. Adv. Cancer Res. 2021, 152, 67–102. [Google Scholar]
- Marur, S.; Forastiere, A.A. Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Update on Epidemiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2016, 91, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warnakulasuriya, S. Causes of oral cancer—An appraisal of controversies. Br. Dent. J. 2009, 207, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payaradka, R.; Ramesh, P.S.; Vyas, R.; Patil, P.; Rajendra, V.K.; Kumar, M.; Shetty, V.; Devegowda, D. Oncogenic viruses as etiological risk factors for head and neck cancers: An overview on prevalence, mechanism of infection and clinical relevance. Arch. Oral. Biol. 2022, 143, 105526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Tie, Y.; Alu, A.; Ma, X.; Shi, H. Targeted therapy for head and neck cancer: Signaling pathways and clinical studies. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.E.; Burtness, B.; Leemans, C.R.; Lui, V.W.Y.; Bauman, J.E.; Grandis, J.R. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers. 2020, 6, 92, Erratum in Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2023, 9, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatini, M.E.; Chiocca, S. Human papillomavirus as a driver of head and neck cancers. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sturgis, E.M.; Wei, Q.; Spitz, M.R. Descriptive epidemiology and risk factors for head and neck cancer. Semin. Oncol. 2004, 31, 726–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poddar, A.; Aranha, R.R.; Muthukaliannan, G.K.; Nachimuthu, R.; Jayaraj, R. Head and neck cancer risk factors in India: Protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e020014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vučičević Boras, V.; Fučić, A.; Baranović, S.; Blivajs, I.; Milenović, M.; Bišof, V.; Rakušić, Z.; Ceppi, M.; Bruzzone, M. Environmental and behavioural head and neck cancer risk factors. Cent. Eur. J. Public Health 2019, 27, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashibe, M.; Brennan, P.; Benhamou, S.; Castellsague, X.; Chen, C.; Curado, M.P.; Dal Maso, L.; Daudt, A.W.; Fabianova, E.; Fernandez, L.; et al. Alcohol drinking in never users of tobacco, cigarette smoking in never drinkers, and the risk of head and neck cancer: Pooled analysis in the International Head and Neck Cancer Epidemiology Consortium. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2007, 99, 777–789, Erratum in J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2008, 100, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Rai, A.K.; Das, D.; Das, R.; Kumar, R.S.; Sarma, A.; Kataki, A.C.; Ramteke, A. Alcohol and tobacco increases risk of high risk HPV infection in head and neck cancer patients: Study from North-East Region of India. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, N.; Boffetta, P.; Wünsch Filho, V.; Eluf Neto, J.; Shangina, O.; Zaridze, D.; Curado, M.P.; Koifman, S.; Matos, E.; Menezes, A.; et al. Oral health and risk of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck and esophagus: Results of two multicentric case-control studies. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2007, 166, 1159–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, N.D.; Park, Y.; Subar, A.F.; Hollenbeck, A.R.; Leitzmann, M.F.; Schatzkin, A.; Abnet, C.C. Fruit and vegetable intake and head and neck cancer risk in a large United States prospective cohort study. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 122, 2330–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, C. Human Papillomavirus-Related Cancers. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 1018, 23–34. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, J.; Kist, L.F.; Pereira, S.B.; Quessada, M.A.; Petek, H.; Pille, A.; Maccari, J.G.; Mutlaq, M.P.; Nasi, L.A. Human papillomavirus infection: Epidemiology, biology, host interactions, cancer development, prevention, and therapeutics. Rev. Med. Virol. 2024, 34, e2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Robertson, E.S. Epstein-Barr Virus History and Pathogenesis. Viruses 2023, 15, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katano, H. Pathological Features of Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Infection. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1045, 357–376. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jia, L.; Gao, Y.; He, Y.; Hooper, J.D.; Yang, P. HBV induced hepatocellular carcinoma and related potential immunotherapy. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 159, 104992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, P.S.; Chang, Y. Why do viruses cause cancer? Highlights of the first century of human tumor virology. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 878–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras, A.; Sánchez, S.A.; Rodríguez-Medina, C.; Botero, J.E. The role and impact of viruses on cancer development. Periodontol. 2000 2024, 96, 170–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGlynn, K.A.; Petrick, J.L.; El-Serag, H.B. Epidemiology of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatology 2021, 73, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, M.; Naito, T.; Saito, M. Current perspectives in human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 infection and its associated diseases. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 867478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tempera, I.; Lieberman, P.M. Oncogenic viruses as entropic drivers of cancer evolution. Front. Virol. 2021, 1, 753366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, A.; Marques, N.; Crawford, N. Cancer and HIV: The Molecular Mechanisms of the Deadly Duo. Cancers 2024, 16, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leemans, C.R.; Snijders, P.J.F.; Brakenhoff, R.H. The Molecular Landscape of Head and Neck Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swiecicki, P.L.; Brennan, J.R.; Mierzwa, M.; Spector, M.E.; Brenner, J.C. Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Detection and Surveillance: Advances of Liquid Biomarkers. Laryngoscope 2019, 129, 1836–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, S.; Fischbein, N.J.; Baugnon, K.L.; Policeni, B.A.; Raghavan, P. Contemporary Imaging and Reporting Strategies for Head and Neck Cancer: MRI, FDG PET/MRI, NI-RADS, and Carcinoma of Unknown Primary-AJR Expert Panel Narrative Review. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2023, 220, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, G.J. Ludwik Gross, Sarah Stewart, and the 1950s discoveries of Gross murine leukemia virus and polyoma virus. Stud. Hist. Philos. Biol. Biomed. Sci. 2014, 48, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moens, U.; Krumbholz, A.; Ehlers, B.; Zell, R.; Johne, R.; Calvignac-Spencer, S.; Lauber, C. Biology, evolution, and medical importance of polyomaviruses: An update. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 54, 18–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazeli, M.M.; Heydari Sirat, S.; Shatizadeh Malekshahi, S. Novel Human Polyomaviruses Discovered From 2007 to the Present: An Update of Current Knowledge. Rev. Med. Virol. 2025, 35, e70017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Shuda, M.; Chang, Y.; Moore, P.S. Clonal Integration of a Polyomavirus in Human Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Science 2008, 319, 1096–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silling, S.; Kreuter, A.; Gambichler, T.; Meyer, T.; Stockfleth, E.; Wieland, U. Epidemiology of Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Infection and Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2022, 14, 6176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.M.; Cushman, C.H.; DeCaprio, J.A. Merkel Cell Polyomavirus: Oncogenesis in a Stable Genome. Viruses 2021, 14, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, P.; Sáenz Robles, M.T.; Pipas, J.M. Large T antigens of polyomaviruses: Amazing molecular machines. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 66, 213–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topalis, D.; Andrei, G.; Snoeck, R. The large tumor antigen: A “Swiss Army knife” protein possessing the functions required for the polyomavirus life cycle. Antivir. Res. 2013, 97, 122–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moens, U.; Passerini, S.; Falquet, M.; Sveinbjørnsson, B.; Pietropaolo, V. Phosphorylation of Human Polyomavirus Large and Small T Antigens: An Ignored Research Field. Viruses 2023, 15, 2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietropaolo, V.; Prezioso, C.; Moens, U. Merkel Cell Polyomavirus and Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, G.J.; Chen, C.J.; Sullivan, C.S. Merkel cell polyomavirus encodes a microRNA with the ability to autoregulate viral gene expression. Virology 2009, 383, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstatinell, A.; Coucheron, D.H.; Sveinbjørnsson, B.; Moens, U. MicroRNAs as Potential Biomarkers in Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1873. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.F.; Liu, W.; You, J. Characterization of molecular mechanisms driving Merkel cell polyomavirus oncogene transcription and tumorigenic potential. PLoS Pathog. 2023, 19, e1011598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prezioso, C.; Obregon, F.; Ambroselli, D.; Petrolo, S.; Checconi, P.; Rodio, D.M.; Coppola, L.; Nardi, A.; Vito, C.; Sarmati, L.; et al. Merkel Cell Polyomavirus (MCPyV) in the Context of Immunosuppression: Genetic Analysis of Noncoding Control Region (NCCR) Variability among a HIV-1-Positive Population. Viruses 2020, 12, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeCaprio, J.A. Molecular Pathogenesis of Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2021, 16, 69–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kean, J.M.; Rao, S.; Wang, M.; Garcea, R.L. Seroepidemiology of human polyomaviruses. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolstov, Y.L.; Pastrana, D.V.; Feng, H.; Becker, J.C.; Jenkins, F.J.; Moschos, S.; Chang, Y.; Buck, C.B.; Moore, P.S. Merkel cell polyomavirus infection II. MCV is a common human infection that can be detected by conformational capsid epitope immunoassays. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 125, 1250–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viscidi, R.P.; Rollison, D.E.; Sondak, V.K.; Silver, B.; Messina, J.L.; Giuliano, A.R.; Fulp, W.; Ajidahun, A.; Rivanera, D. Age-specific Seroprevalence of merkel cell polyomavirus, BK virus, and JC virus. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2011, 18, 1737–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamminga, S.; Van Der Meijden, E.; Feltkamp, M.C.W.; Zaaijer, H.L. Seroprevalence of fourteen human polyomaviruses determined in blood donors. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schowalter, R.M.; Pastrana, D.V.; Pumphrey, K.A.; Moyer, A.L.; Buck, C.B. Merkel cell polyomavirus and two previously unknown polyomaviruses are chronically shed from human skin. Cell Host Microbe 2010, 7, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Yang, R.; Payne, A.S.; Schowalter, R.M.; Spurgeon, M.E.; Lambert, P.F.; Xu, X.; Buck, C.B.; You, J. Identifying the Target Cells and Mechanisms of Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Infection. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 19, 775–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csoboz, B.; Rasheed, K.; Sveinbjørnsson, B.; Moens, U. Merkel cell polyomavirus and non-Merkel cell carcinomas: Guilty or circumstantial evidence? APMIS 2020, 128, 104–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsushita, M.; Kuwamoto, S.; Iwasaki, T.; Higaki-Mori, H.; Yashima, S.; Kato, M.; Murakami, I.; Horie, Y.; Kitamura, Y.; Hayashi, K. Detection of Merkel cell polyomavirus in the human tissues from 41 Japanese autopsy cases using polymerase chain reaction. Intervirology 2013, 56, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houben, R.; Celikdemir, B.; Kervarrec, T.; Schrama, D. Merkel Cell Polyomavirus: Infection, Genome, Transcripts and Its Role in Development of Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2023, 15, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motavalli Khiavi, F.; Nasimi, M.; Rahimi, H. Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Gene Expression and Mutational Analysis of Large Tumor Antigen in Non-Merkel Cell Carcinoma Tumors of Iranian Patients. Public Health Genom. 2021, 23, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starrett, G.J.; Marcelus, C.; Cantalupo, P.G.; Katz, J.P.; Cheng, J.; Akagi, K.; Thakuria, M.; Rabinowits, G.; Wang, L.C.; Symer, D.E.; et al. Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Exhibits Dominant Control of the Tumor Genome and Transcriptome in Virus-Associated Merkel Cell Carcinoma. mBio 2017, 8, e02079-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.F.; You, J. Merkel cell polyomavirus and associated Merkel cell carcinoma. Tumour Virus Res. 2022, 13, 200232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moens, U.; Prezioso, C.; Pietropaolo, V. Functional Domains of the Early Proteins and Experimental and Epidemiological Studies Suggest a Role for the Novel Human Polyomaviruses in Cancer. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 834368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuda, M.; Feng, H.; Kwun, H.J.; Rosen, S.T.; Gjoerup, O.; Moore, P.S.; Chang, Y. T antigen mutations are a human tumor-specific signature for Merkel cell polyomavirus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 16272–16277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesbacher, S.; Pfitzer, L.; Wiedorfer, K.; Angermeyer, S.; Borst, A.; Haferkamp, S.; Scholz, C.J.; Wobser, M.; Schrama, D.; Houben, R. RB1 is the crucial target of the Merkel cell polyomavirus Large T antigen in Merkel cell carcinoma cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 32956–32968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houben, R.; Grimm, J.; Willmes, C.; Weinkam, R.; Becker, J.C.; Schrama, D. Merkel cell carcinoma and Merkel cell polyomavirus: Evidence for hit-and-run oncogenesis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 254–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, X.; Diaz, J.; Tsang, S.H.; Buck, C.B.; You, J. Merkel cell polyomavirus large T antigen disrupts host genomic integrity and inhibits cellular proliferation. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 9173–9188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhaegen, M.E.; Mangelberger, D.; Harms, P.W.; Vozheiko, T.D.; Weick, J.W.; Wilbert, D.M.; Saunders, T.L.; Ermilov, A.N.; Bichakjian, C.K.; Johnson, T.M.; et al. Merkel cell polyomavirus small T antigen is oncogenic in transgenic mice. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, 135, 1415–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuda, M.; Kwun, H.J.; Feng, H.; Chang, Y.; Moore, P.S. Human Merkel cell polyomavirus small T antigen is an oncoprotein targeting the 4E-BP1 translation regulator. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 3623–3634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwun, H.J.; Shuda, M.; Camacho, C.J.; Gamper, A.M.; Thant, M.; Chang, Y.; Moore, P.S. Restricted protein phosphatase 2A targeting by Merkel cell polyomavirus small T antigen. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 4191–4200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Park, D.E.; Berrios, C.; White, E.A.; Arora, R.; Yoon, R.; Branigan, T.; Xiao, T.; Westerling, T.; Federation, A.; et al. Merkel cell polyomavirus recruits MYCL to the EP400 complex to promote oncogenesis. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwogu, N.; Ortiz, L.E.; Kwun, H.J. Surface charge of Merkel cell polyomavirus small T antigen determines cell transformation through allosteric FBW7 WD40 domain targeting. Oncogenesis 2020, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Sada, H.; Müller, M.; Mehta, R.; Toth, R.; Arthur, J.S.C.; Whitehouse, A.; Macdonald, A. The PP4R1 sub-unit of protein phosphatase PP4 is essential for inhibition of NF-κB by merkel polyomavirus small tumour antigen. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 25418–25432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stakaitytė, G.; Nwogu, N.; Dobson, S.J.; Knight, L.M.; Wasson, C.W.; Salguero, F.J.; Blackbourn, D.J.; Blair, G.E.; Mankouri, J.; Macdonald, A.; et al. Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Small T Antigen Drives Cell Motility via Rho-GTPase-Induced Filopodium Formation. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00940-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwogu, N.; Boyne, J.R.; Dobson, S.J.; Poterlowicz, K.; Blair, G.E.; Macdonald, A.; Mankouri, J.; Whitehouse, A. Cellular sheddases are induced by Merkel cell polyomavirus small tumour antigen to mediate cell dissociation and invasiveness. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassem, A.; Technau, K.; Kurz, A.K.; Pantulu, D.; Löning, M.; Kayser, G.; Stickeler, E.; Weyers, W.; Diaz, C.; Werner, M.; et al. Merkel cell polyomavirus sequences are frequently detected in nonmelanoma skin cancer of immunosuppressed patients. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 125, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dworkin, A.M.; Tseng, S.Y.; Allain, D.C.; Iwenofu, O.H.; Peters, S.B.; Toland, A.E. Merkel cell polyomavirus in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma of immunocompetent individuals. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2009, 129, 2868–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieland, U.; Scola, N.; Stolte, B.; Stucker, M.; Silling, S.; Kreuter, A. No evidence for a causal role of Merkel cell polyomavirus in keratoacanthoma. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2012, 67, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrama, D.; Groesser, L.; Ugurel, S.; Hafner, C.; Pastrana, D.V.; Buck, C.B.; Cerroni, L.; Theiler, A.; Becker, J.C. Presence of human polyomavirus 6 in mutation-specific BRAF inhibitor induced epithelial proliferations. JAMA Dermatol. 2014, 150, 1180–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arvia, R.; Sollai, M.; Pierucci, F.; Urso, C.; Massi, D.; Zakrzewska, K. Droplet digital PCR (ddPCR) vs quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) approach for detection and quantification of Merkel cell polyomavirus (MCPyV) DNA in formalin fixed paraffin embedded (FFPE) cutaneous biopsies. J. Virol. Methods 2017, 246, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purdie, K.J.; Proby, C.M.; Rizvi, H.; Griffin, H.; Doorbar, J.; Sommerlad, M.; Feltkamp, M.C.; der Meijden, E.V.; Inman, G.J.; South, A.P.; et al. The role of human papillomaviruses and polyomaviruses in BRAF-inhibitor induced cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma and benign squamoproliferative lesions. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramqvist, T.; Ursu, R.G.; Haeggblom, L.; Mirzaie, L.; Gahm, C.; Hammarstedt-Nordenvall, L.; Dalianis, T.; Näsman, A. Human polyomaviruses are not frequently present in cancer of the salivary glands. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 2871–2874. [Google Scholar]
- Scola, N.; Wieland, U.; Silling, S.; Altmeyer, P.; Stucker, M.; Kreuter, A. Prevalence of human polyomaviruses in common and rare types of non-Merkel cell carcinoma skin cancer. Br. J. Dermatol. 2012, 167, 1315–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imajoh, M.; Hashida, Y.; Nakajima, H.; Sano, S.; Daibata, M. Prevalence and viral DNA loads of three novel human polyomaviruses in skin cancers from Japanese patients. J. Dermatol. 2013, 40, 657–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellott, T.R.; Baez, C.F.; Almeida, S.G.; Venceslau, M.T.; Zalis, M.G.; Guimarães, M.A.; Rochael, M.C.; Luz, F.B.; Varella, R.B.; Almeida, J.R. Molecular prevalence of Merkel cell polyomavirus in nonmelanoma skin cancer in a Brazilian population. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2017, 42, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeggblom, L.; Franzen, J.; Nasman, A. Human polyomavirus DNA detection in keratoacanthoma and Spitz naevus: No evidence for a causal role. J. Clin. Pathol. 2017, 70, 451–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katano, H.; Ito, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Sato, Y.; Tsuji, T.; Matsuo, K.; Nakagawa, H.; Sata, T. Detection of Merkel cell polyomavirus in Merkel cell carcinoma and Kaposi’s sarcoma. J. Med. Virol. 2009, 81, 1951–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DuThanh, A.; Guillot, B.; Dereure, O.; Foulongne, V. Detection of Merkel cell and other human polyomavirus DNA in lesional and nonlesional skin from patients with Kaposi sarcoma. Br. J. Dermatol. 2015, 173, 1063–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urso, C.; Pierucci, F.; Sollai, M.; Arvia, R.; Massi, D.; Zakrzewska, K. Detection of Merkel cell poly-omavirus and human papillomavirus DNA in poro-carcinoma. J. Clin. Virol. 2016, 78, 71–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, I.; Matsushita, M.; Iwasaki, T.; Kuwamoto, S.; Kato, M.; Horie, Y.; Hayashi, K.; Gogusev, J.; Jaubert, F.; Nakamoto, S.; et al. High viral load of Merkel cell polyomavirus DNA sequences in Langerhans cell sarcoma tissues. Infect Agent Cancer 2014, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koburger, I.; Meckbach, D.; Metzler, G.; Fauser, U.; Garbe, C.; Bauer, J. Absence of Merkel cell polyoma virus in cutaneous melanoma. Exp. Dermatol. 2011, 20, 78–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ly, T.Y.; Walsh, N.M.; Pasternak, S. The spectrum of Merkel cell polyomavirus expression in Merkel cell carcinoma, in a variety of cutaneous neoplasms, and in neuroendocrine carcinomas from different anatomical sites. Hum. Pathol. 2012, 43, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, M.; Imajoh, M.; Ikawa, T.; Nakajima, H.; Kamioka, M.; Nemoto, Y.; Ujihara, T.; Uchiyama, J.; Matsuzaki, S.; Sano, S.; et al. Presence of Merkel cell polyomavirus in Japanese cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. J. Clin. Virol. 2011, 50, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashida, Y.; Imajoh, M.; Nemoto, Y.; Kamioka, M.; Taniguchi, A.; Taguchi, T.; Kume, M.; Orihashi, K.; Daibata, M. Detection of Merkel cell polyomavirus with a tumour-specific signature in non-small cell lung cancer. Br. J. Cancer. 2013, 108, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behdarvand, A.; Zamani, M.S.; Sadeghi, F.; Yahyapour, Y.; Vaziri, F.; Jamnani, F.R.; Nowruzi, B.; Fateh, A.; Siadat, S.D. Evaluation of Merkel cell polyomavirus in non-small cell lung cancer and adjacent normal cells. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 108, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.J.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, D.H. Clinical and prognostic significance of Merkel cell polyomavirus in nonsmall cell lung cancer. Medicine 2017, 96, e5413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bittar, H.E.T.; Pantanowitz, L. Merkel cell polyomavirus is not detected in lung adenocarcinomas by immunohistochemistry. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2016, 24, 427–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saláková, M.; Košlabová, E.; Vojtěchová, Z.; Tachezy, R.; Šroller, V. Detection of human polyomaviruses MCPyV, HPyV6, and HPyV7 in malignant and non-malignant tonsillar tissues. J. Med. Virol. 2016, 88, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herberhold, S.; Hellmich, M.; Panning, M.; Bartok, E.; Silling, S.; Akgül, B.; Wieland, U. Human polyomavirus and human papillomavirus prevalence and viral load in non-malignant tonsillar tissue and tonsillar carcinoma. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2017, 206, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chteinberg, E.; Klufah, F.; Rennspiess, D.; Mannheims, M.F.; Abdul-Hamid, M.A.; Losen, M.; Keijzers, M.; De Baets, M.H.; Kurz, A.K.; Zur Hausen, A. Low prevalence of Merkel cell polyomavirus in human epithelial thymic tumors. Thorac Cancer 2019, 10, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toracchio, S.; Foyle, A.; Sroller, V.; Reed, J.A.; Wu, J.; Kozinetz, C.A.; Butel, J.S. Lymphotropism of merkel cell polyomavirus infection, Nova Scotia. Canada. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 1702–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Gyarmati, P. Identification of merkel cell polyomavirus from a patient with acute myeloid leukemia. Genome Announc. 2017, 5, e01241-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashida, Y.; Imajoh, M.; Taniguchi, A.; Kamioka, M.; Daibata, M. Absence of merkel cell polyomavirus in monocytic leukemias. Acta Haematol. 2013, 130, 135–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepa Pantulu, N.; Pallasch, C.P.; Kurz, A.K.; Kassem, A.; Frenzel, L.; Sodenkamp, S.; Kvasnicka, H.M.; Wendtner, C.M.; Zur Hausen, A. Detection of a novel truncating Merkel cell polyomavirus large T antigen deletion in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Blood 2010, 116, 5280–5284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comar, M.; Cuneo, A.; Maestri, I.; Melloni, E.; Pozzato, G.; Soffritti, O.; Secchiero, P.; Zauli, G. Merkel-cell polyomavirus (MCPyV) is rarely associated to B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia (1 out of 50) samples and occurs late in the natural history of the disease. J. Clin. Virol. 2012, 55, 367–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imajoh, M.; Hashida, Y.; Taniguchi, A.; Kamioka, M.; Daibata, M. Novel human polyomaviruses, Merkel cell polyomavirus and human polyomavirus 9, in Japanese chronic lymphocytic leukemia cases. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2012, 5, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trizuljak, J.; Srovnal, J.; Plevová, K.; Brychtová, Y.; Semerád, L.; Bakešová, D.; Létalová, E.; Benedíková, A.; Mayer, J.; Hajdúch, M.; et al. Analysis of prognostic significance of Merkel cell polyomavirus in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2015, 15, 439–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loyo, M.; Guerrero-Preston, R.; Brait, M.; Hoque, M.O.; Chuang, A.; Kim, M.S.; Sharma, R.; Liégeois, N.J.; Koch, W.M.; Califano, J.A.; et al. Quantitative detection of Merkel cell virus in human tissues and possible mode of transmission. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 126, 2991–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smelov, V.; Bzhalava, D.; Arroyo Mühr, L.S.; Eklund, C.; Komyakov, B.; Gorelov, A.; Dillner, J.; Hultin, E. Detection of DNA viruses in prostate cancer. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Wang, T.; Zhu, H.; Guo, J.; Li, K.; Yao, Q.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, J.; He, C.; Chen, J.; et al. Multiplex PCR/mass spectrometry screening of biological carcinogenic agents in human mammary tumors. J. Clin. Virol. 2014, 61, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi-Vaziri, M.; Sadeghi, F.; Alamsi-Hashiani, A.; Haeri, H.; Monavari, S.H.; Keyvani, H. Merkel cell polyomavirus and human papillomavirus infections in cervical disease in Iranian women. Arch. Virol. 2015, 160, 1181–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahyapour, Y.; Sadeghi, F.; Alizadeh, A.; Rajabnia, R.; Siadati, S. Detection of Merkel cell polyomavirus and human papillomavirus in esophageal squamous cell carcinomas and non-cancerous esophageal samples in Northern Iran. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2016, 22, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.A.; Gheit, T.; Stellin, M.; Lupato, V.; Spinato, G.; Fuson, R.; Menegaldo, A.; Mckay-Chopin, S.; Dal Cin, E.; Tirelli, G.; et al. Oncogenic DNA viruses found in salivary gland tumors. Oral Oncol. 2017, 75, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.S.; Choi, Y.L.; Choi, J.S.; Roh, J.H.; Pyon, J.K.; Woo, K.J.; Lee, E.H.; Jang, K.T.; Han, J.; Park, C.S.; et al. Detection of Merkel cell polyomavirus in Merkel cell carcinomas and small cell carcinomas by PCR and immunohistochemistry. Histol. Histopathol. 2011, 26, 1231–1241. [Google Scholar]
- Toptan, T.; Yousem, S.A.; Ho, J.; Matsushima, Y.; Stabile, L.P.; Fernández-Figueras, M.T.; Bhargava, R.; Ryo, A.; Moore, P.S.; Chang, Y. Survey for human polyomaviruses in cancer. JCI Insight 2016, 1, e85562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sastre-Garau, X.; Peter, M.; Avril, M.F.; Laude, H.; Couturier, J.; Rozenberg, F.; Almeida, A.; Boitier, F.; Carlotti, A.; Couturaud, B.; et al. Merkel cell carcinoma of the skin: Pathological and molecular evidence for a causative role of MCV in oncogenesis. J. Pathol. 2009, 218, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yakkioui, Y.; Speel, E.M.; Van Overbeeke, J.J.; Boderie, M.J.M.; Pujari, S.; Hausen, A.Z.; Wolffs, P.F.G.; Temel, Y. Oncogenic viruses in skull base chordomas. World Neurosurg. 2018, 112, e7–e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, F.; Salehi-Vaziri, M.; Alizadeh, A.; Ghodsi, S.M.; Bokharaei-Salim, F.; Fateh, A.; Monavari, S.H.; Keyvani, H. Detection of Merkel cell polyomavirus large T-antigen sequences in human central nervous system tumors. J. Med. Virol. 2015, 87, 1241–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanio, S.; Matsushita, M.; Kuwamoto, S.; Horie, Y.; Kodani, I.; Murakami, I.; Ryoke, K.; Hayashi, K. Low prevalence of Merkel cell polyomavirus with low viral loads in oral and maxillofacial tumours or tumour-like lesions from immunocompetent patients: Absence of Merkel cell polyomavirus-associated neoplasms. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 3, 1301–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraud, G.; Ramqvist, T.; Pastrana, D.V.; Pavot, V.; Lindau, C.; Kogner, P.; Orrego, A.; Buck, C.B.; Allander, T.; Holm, S.; et al. DNA from KI, WU and Merkel cell polyomaviruses is not detected in childhood central nervous system tumours or neuroblastomas. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamiter, M.; Asarkar, A.; Rogers, D.; Moore-Medlin, T.; McClure, G.; Ma, X.; Vanchiere, J.; Nathan, C.O. A pilot study of Merkel cell polyomavirus in squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue. Oral Oncol. 2017, 74, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohebbi, E.; Noormohamadi, Z.; Sadeghi-Rad, H.; Sadeghi, F.; Yahyapour, Y.; Vaziri, F.; Rahimi, A.; Rahimi Jamnani, F.; Mehrabi, S.; Siadat, S.D.; et al. Low viral load of Merkel cell polyomavirus in Iranian patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Is it clinically important? J. Med. Virol. 2018, 90, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, J.P.; Blanco, R.; Osorio, J.C.; Oliva, C.; Diaz, M.J.; Carrillo-Beltrán, D.; Aguayo, R.; Castillo, A.; Tapia, J.C.; Calaf, G.M.; et al. Merkel cell polyomavirus detected in head and neck carcinomas from Chile. Infect. Agent. Cancer 2020, 15, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poluschkin, L.; Rautava, J.; Turunen, A.; Wang, Y.; Hedman, K.; Syrjänen, K.; Grenman, R.; Syrjänen, S. Polyomaviruses detectable in head and neck carcinomas. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 22642–22652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulder, F.J.; Klufah, F.; Janssen, F.M.E.; Farshadpour, F.; Willems, S.M.; de Bree, R.; Zur Hausen, A.; van den Hout, M.F.C.M.; Kremer, B.; Speel, E.J.M. Presence of Human Papillomavirus and Epstein-Barr Virus, but Absence of Merkel Cell Polyomavirus, in Head and Neck Cancer of Non-Smokers and Non-Drinkers. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 560434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Windon, M.; Fakhry, C.; Rooper, L.; Ha, P.; Schoppy, D.; Miles, B.; Koch, W.; Vosler, P.; Eisele, D.; D’Souza, G. The Role of Age and Merkel Cell Polyomavirus in Oral Cavity Cancers. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2020, 163, 1194–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasani Estalkhi, M.; Seyed Majidi, M.; Sadeghi, F.; Chehrazi, M.; Zebardast, A.; Hasanzadeh, A.; Yahyapour, Y. Prevalence of Merkel Cell Polyomavirus (MCPyV) in the Oral Cavity Biopsies in Northern Iran. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2021, 22, 3927–3932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passerini, S.; Babini, G.; Merenda, E.; Carletti, R.; Scribano, D.; Rosa, L.; Conte, A.L.; Moens, U.; Ottolenghi, L.; Romeo, U.; et al. Merkel Cell Polyomavirus in the Context of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Oral Potentially Malignant Disorders. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellott, T.R.; Luz, F.B.; Silva, A.K.F.D.; Varella, R.B.; Rochael, M.C.; Pantaleão, L. Merkel cell polyomavirus and its etiological relationship with skin tumors. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2023, 98, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Tissue (n) | Prevalence n (%) | Sample Type | Viral Load (Copies/Cell) | Viral Integration | Method | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oral tongue SCC (21) | 6 (28.6) | FFPE | NA | NA | PCR (LT) | [120] |
| Squamous cell tonsillar carcinoma (97) | 33 (34) | FFPE | NA | NA | qPCR (LT) | [97] |
| Non-malignant tonsillar tissue (103) | 10 (9.7) | |||||
| Non- malignant tonsillar tissue (40) | 4 (10) | Biopsy | 0.000004 | NA | PCR (LT) | [98] |
| Tonsillar carcinoma (38) | 8 (21.1) | 0.000064 | ||||
| SCC (50) | 8 (16) | FFPE | 0.0048 | NA | PCR (LT, VP1), qPCR (LT), RT-PCR (LT) | [121] |
| Non-cancerous adjacent normal tissue (50) | 1 (2) | 0.000026 | ||||
| SCC (119) | 0 (0) | FFPE | NA | NA | IHC (LT) | [124] |
| Oral brushes (54) | 1 (1.8) | FFPE | NA | NA | qPCR (LT) | [122] |
| SCC (120) | 15 (12.5) | |||||
| OCC (126) | 0 (0) | FFPE | NA | NA | IHC (LT) | [125] |
| OC (114) including | 28 (24.6) | FFPE | NA | qPCR (LT) | [126] | |
| SCC (35) | 7 (20) | 0.0232 | ||||
| LP (29) | 7 (24.1) | 0.000272 | ||||
| Dysplasia (14) | 3 (21.4) | 0.0202 | ||||
| IF (36) | 11 (30.6) | 0.000257 | ||||
| SCC (11) | 3 (27.3) | FFPE | 1.17 × 102 * | No integration | qPCR (sT) | [127] |
| PMD (12) | 4 (33.3) | 1.74 × 102 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Passerini, S.; Messina, S.; Moens, U.; Pietropaolo, V. Merkel Cell Polyomavirus (MCPyV) and Its Possible Role in Head and Neck Cancers. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1180. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051180
Passerini S, Messina S, Moens U, Pietropaolo V. Merkel Cell Polyomavirus (MCPyV) and Its Possible Role in Head and Neck Cancers. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(5):1180. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051180
Chicago/Turabian StylePasserini, Sara, Sara Messina, Ugo Moens, and Valeria Pietropaolo. 2025. "Merkel Cell Polyomavirus (MCPyV) and Its Possible Role in Head and Neck Cancers" Biomedicines 13, no. 5: 1180. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051180
APA StylePasserini, S., Messina, S., Moens, U., & Pietropaolo, V. (2025). Merkel Cell Polyomavirus (MCPyV) and Its Possible Role in Head and Neck Cancers. Biomedicines, 13(5), 1180. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051180







