Preclinical Research on Cinnamic Acid Derivatives for the Prevention of Liver Damage: Promising Therapies for Liver Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Testing
2.2. Chemical Products
Chemicals
2.3. Preparation of LQM717 and LQM755
2.3.1. Experimental Section
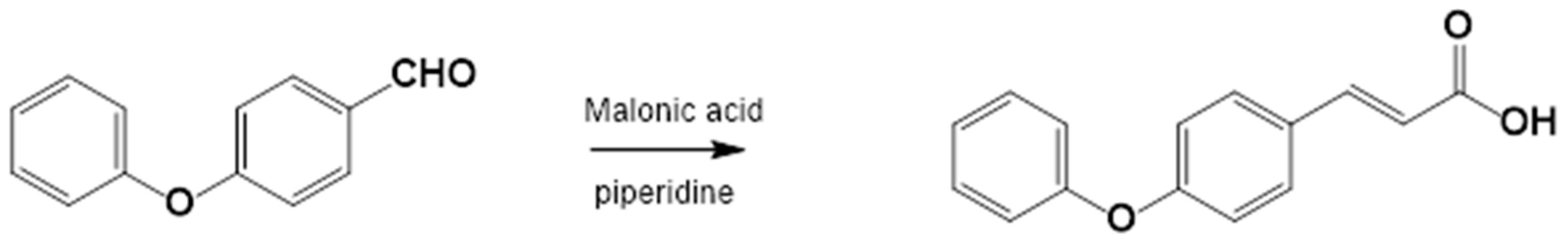
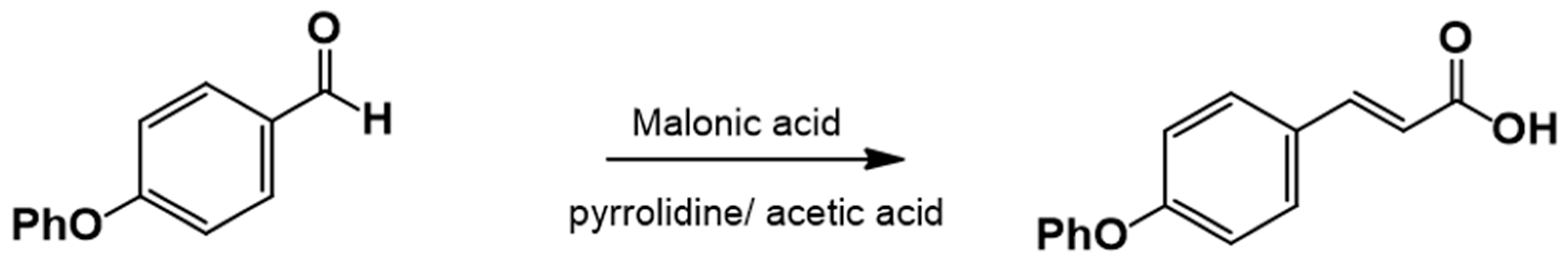
2.3.2. Procedure for the Synthesis of 3-(4-Phenoxyphenyl)-2-Propenoic Acid
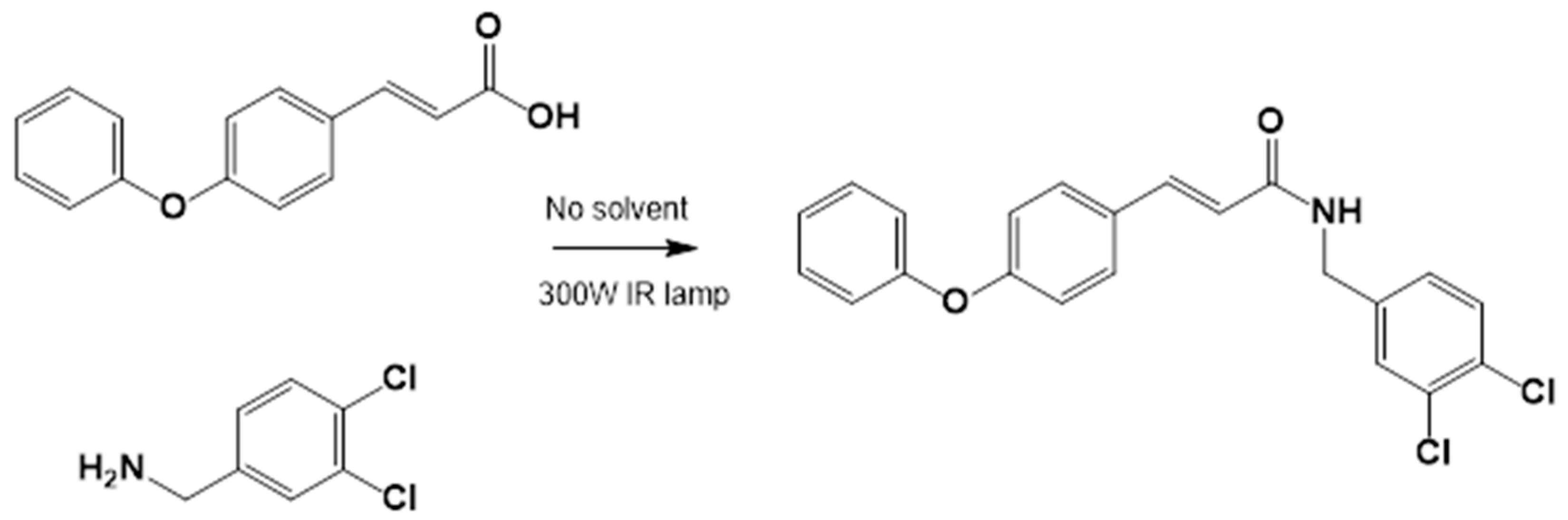
2.3.3. Amide Synthesis
2.4. Preparation of LQM717 and LQM755 for Intraperitoneal Administration
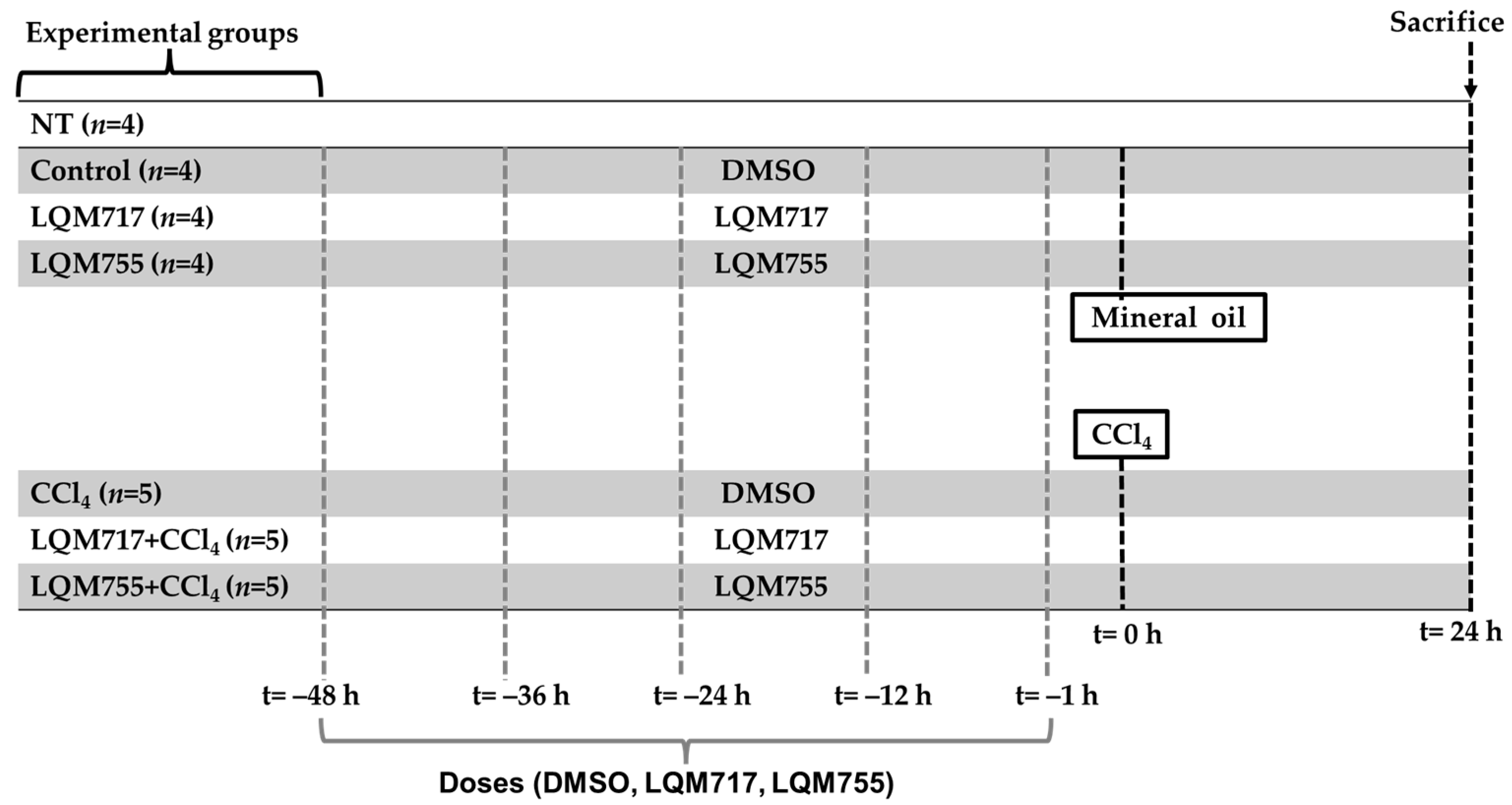
2.5. In Vivo Experimental Protocol
- i.
- NT (untreated): Without any administration or treatment.
- ii.
- Control: Five administrations of DMSO (100 µL, i.p.) and one administration of mineral oil (250 µL/100 g, p.o.), which are the vehicles for the compounds and CCl4, respectively.
- iii.
- LQM717: Rats pretreated with five doses of LQM717 and one administration of mineral oil.
- iv.
- LQM755: Rats pretreated with five doses of LQM755 and one administration of mineral oil.
- v.
- CCl4: Rats were treated five times with DMSO and were intoxicated with a sublethal dose of CCl4 (4 g/kg, p.o.).
- vi.
- LQM717 + CCl4: Rats pretreated with five doses of LQM717 and intoxicated with a sublethal dose of CCl4.
- vii.
- LQM755 + CCl4: Rats pretreated with five doses of LQM755 and intoxicated with a sublethal dose of CCl4.
2.6. Sacrifice of the Animals
2.7. In Situ Liver Evaluation
2.8. Histochemical Procedures
2.8.1. Paraffin Embedding Tissue Samples and Sectioning
2.8.2. H&E Staining
2.8.3. PAS Staining
2.8.4. Biochemical Marker of Liver Necrosis
2.8.5. Biochemical Markers of Cholestasis
2.8.6. Biochemical Markers of Liver Function
2.8.7. Statistical Analysis
2.8.8. Bioinformatic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Chemistry
3.1.1. Synthesis of 4-Phenoxy Cinnamic Acid
3.1.2. General Procedure for the Preparation of Amides
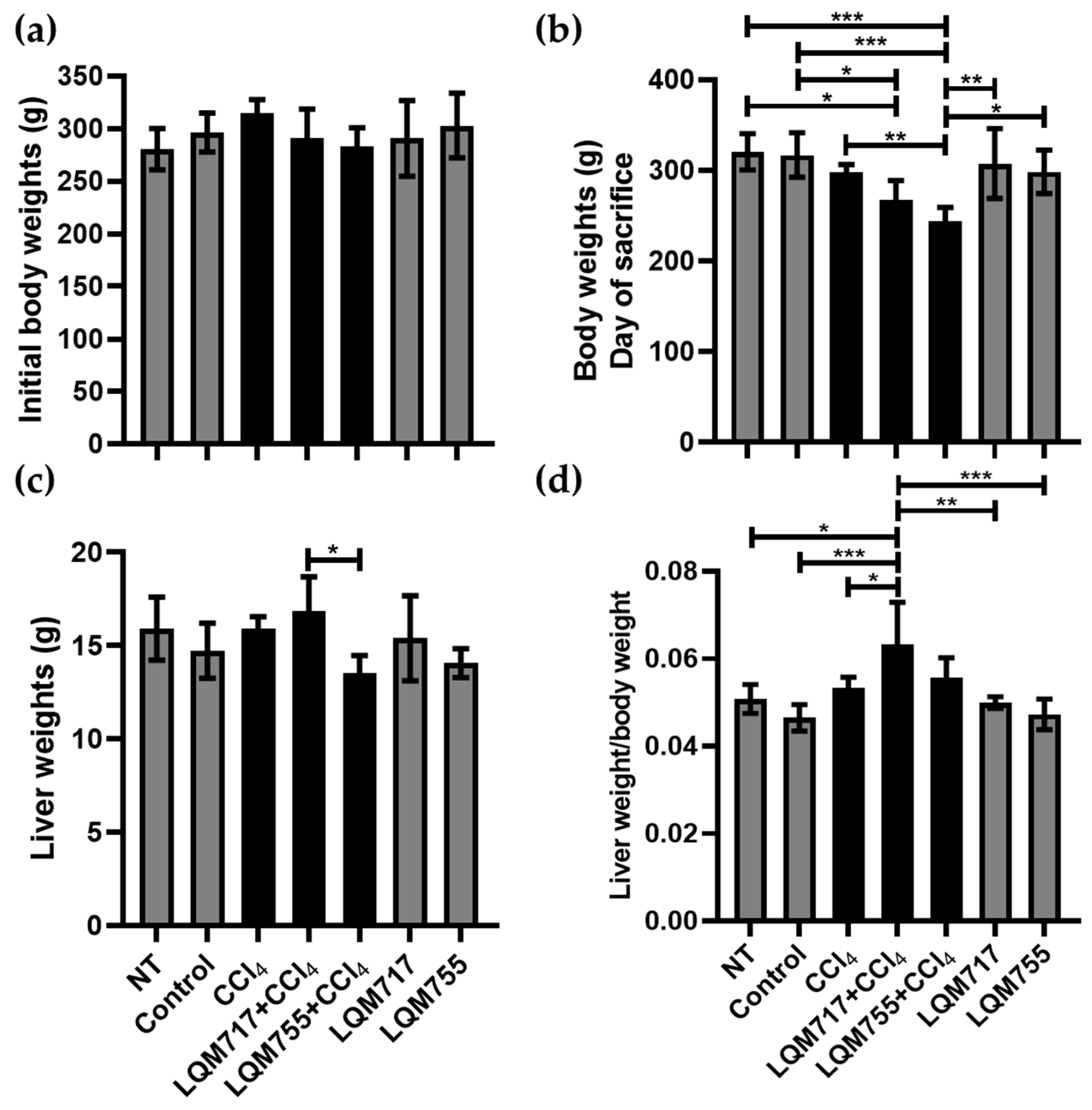
3.2. Body and Liver Weights
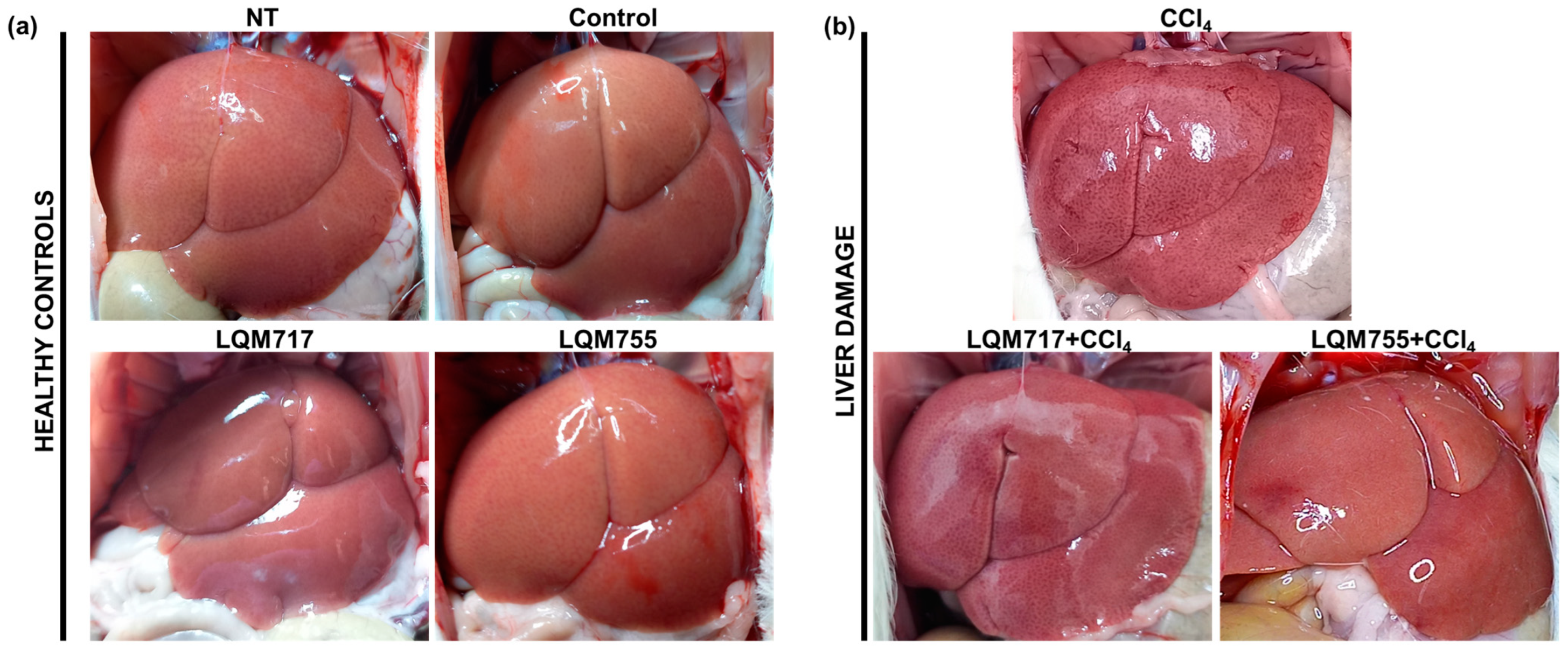
3.3. In Situ Liver Observations
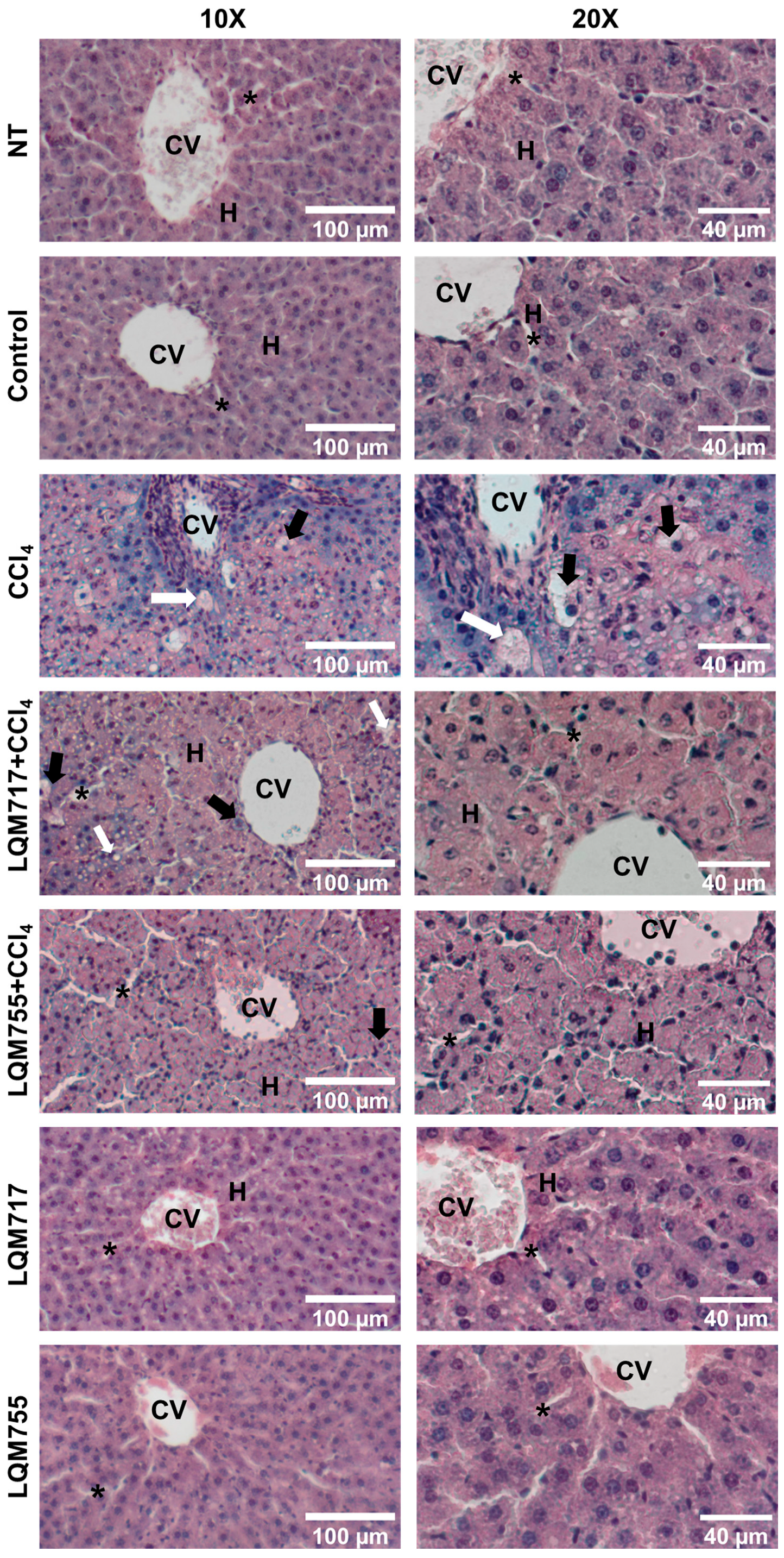
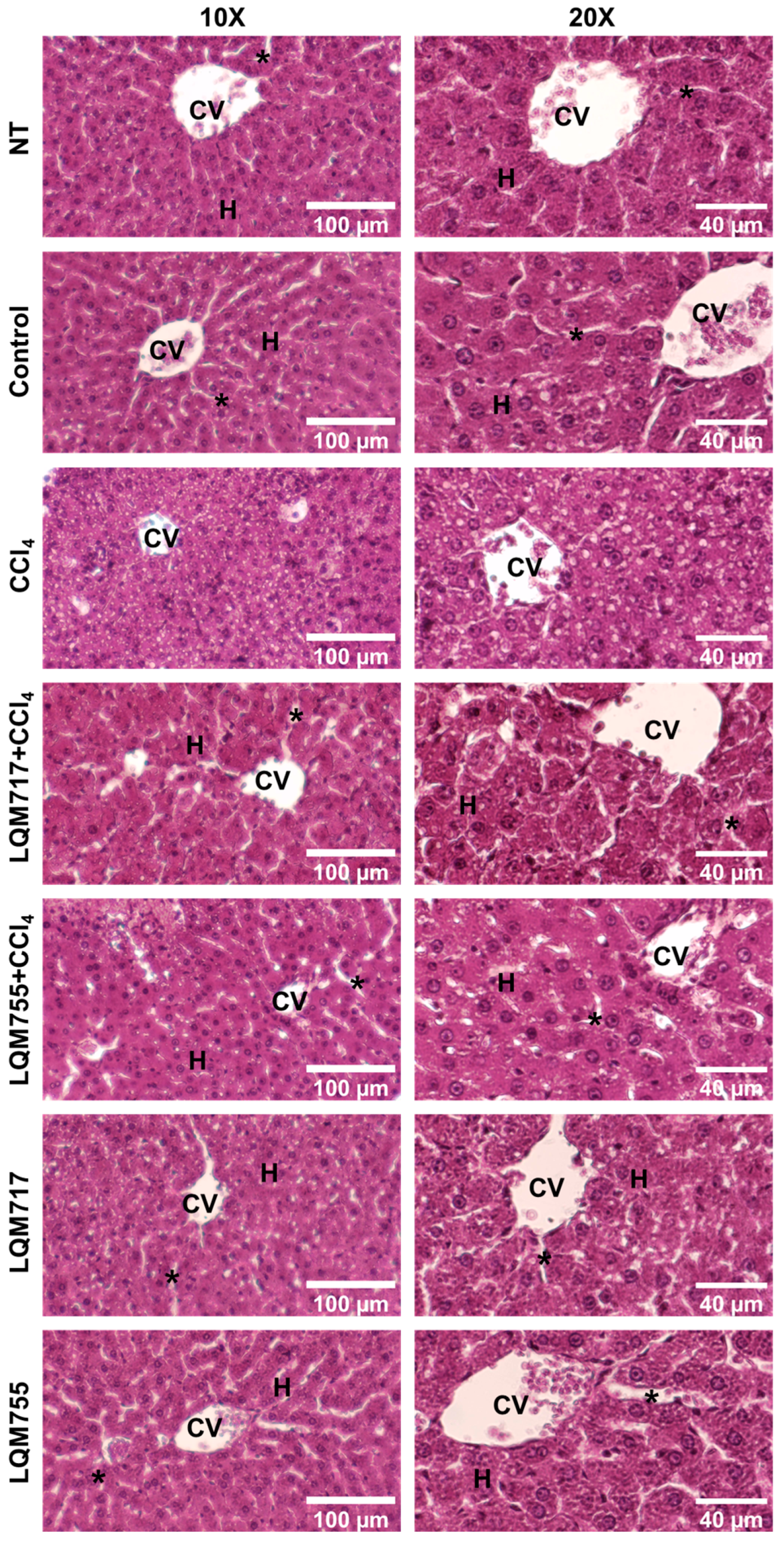
3.4. Evaluation of Microscopic Liver Damage via Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Staining
3.5. Liver Function Tests
3.6. Detection of Polysaccharides with Periodic Acid-Schiff (PAS) Staining
3.7. Identification of Possible Protein Targets in the Liver
4. Discussion
- (a)
- Carboxylesterase 1 (CES1, P23141) is involved in the detoxification of xenobiotics, and its inhibition is beneficial for the treatment of metabolic disorders, such as obesity and fatty liver disease [51];
- (b)
- CYP450 3A4 (P08684) is considered an important CYP450 whose function is to detoxify bile acids, and the stimulation of its activity could be useful for the treatment of cholestatis [52];
- (c)
- The DNA excision repair protein ERCC-1 (P07992) may influence survival time after chemotherapy [53].
- (a)
- MMP-1 (P03956);
- (b)
- MMP-9 (P14780);
- (c)
- MMP-12 (P39900).
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baviskar, K.; Kshirsagar, A.; Raut, H.; Shaikh, M.R.N. Overview: Global burden of liver disease. Int. J. Pharm. Chem. Anal. 2024, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devarbhavi, H.; Asrani, S.K.; Arab, J.P.; Nartey, Y.A.; Pose, E.; Kamath, P.S. Global burden of liver disease: 2023 update. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 516–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Yu, L. Role and therapeutic perspectives of extracellular vesicles derived from liver and adipose tissue in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Artif Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2024, 52, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zannad, F.; Sanyal, A.J.; Butler, J.; Ferreira, J.P.; Girerd, N.; Miller, V.; Pandey, A.; Parikh, C.R.; Ratziu, V.; Younossi, Z.M.; et al. MASLD and MASH at the crossroads of hepatology trials and cardiorenal metabolic trials. J. Intern. Med. 2024, 296, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Wong, G.; Anstee, Q.M.; Henry, L. The Global Burden of Liver Disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 21, 1978–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheemerla, S.; Balakrishnan, M. Global Epidemiology of Chronic Liver Disease. Clin. Liver Dis. 2021, 17, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittermann, T.; Shaked, A.; Goldberg, D.S. When Living Donor Liver Allografts Fail: Exploring the Outcomes of Retransplantation Using Deceased Donors. Am. J. Transplant. 2017, 17, 1097–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumgay, H.; Ferlay, J.; de Martel, C.; Georges, D.; Ibrahim, A.S.; Zheng, R.; Wei, W.; Lemmens, V.E.P.P.; Soerjomataram, I. Global, regional and national burden of primary liver cancer by subtype. Eur. J. Cancer. 2022, 161, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.A.; Jeong, S.; Jang, H.; Lee, D.H.; Joo, S.K.; Kim, W. Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease with Increased Alcohol Intake Increase the Risk of Developing Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Incident or Decompensated Cirrhosis: A Korean Nationwide Study. Liver Cancer 2023, 13, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhoute, X.; Pietri, O.; Pénaranda, G.; Wolf, T.; Beaurain, P.; Monnet, O.; Laquière, A.; Bonomini, J.; Neumann, F.; Levrel, O.; et al. Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma and Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Real-life Data on Liver Disease, Treatment and Prognosis. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2023, 11, 1106–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordan, J.D.; Kennedy, E.B.; Abou-Alfa, G.K.; Beal, E.; Finn, R.S.; Gade, T.P.; Goff, L.; Gupta, S.; Guy, J.; Hoang, H.T.; et al. Systemic Therapy for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: ASCO Guideline Update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 1830–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, L.; Chen, Y. Recent advances in systemic therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomark. Res. 2022, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, M. Recent Advances in Systemic Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma in an Aging Society: 2020 Update. Liver Cancer 2020, 9, 640–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danish, F.A.; Koul, S.S.; Subhani, F.R.; Rabbani, A.E.; Yasmin, S. Antiviral therapy in HCV-infected decompensated cirrhotics. Saudi J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, H.; Xu, Q.; Guo, H.Y.; Huang, X.; Chen, F.; Jin, L.; Quan, Z.S.; Shen, Q.K. Application of cinnamic acid in the structural modification of natural products: A review. Phytochemistry 2023, 206, 113532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contardi, M.; Lenzuni, M.; Fiorentini, F.; Summa, M.; Bertorelli, R.; Suarato, G.; Athanassiou, A. Hydroxycinnamic Acids and Derivatives Formulations for Skin Damages and Disorders: A Review. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Shahrajabian, M.H. Therapeutic Potential of Phenolic Compounds in Medicinal Plants-Natural Health Products for Human Health. Molecules 2023, 28, 1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcón-López, A.; Hernández, M.; Aguirre-Vidal, P.; Granados, L.A.; Vazquez Valadez, V.; Martínez-Soriano, P.; Briseño-Lugo, P.; Velázquez, A.; Rul-Ramírez, E.; Jiménez-Jiménez, M.; et al. Computational Insight and Anticancer Effect of Cinnamic Acid-Derivative Amide Compounds. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2024, 35, e20230195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macías-Pérez, J.R.; Beltrán-Ramírez, O.; Vásquez-Garzón, V.R.; Salcido-Neyoy, M.E.; Martínez-Soriano, P.A.; Ruiz-Sánchez, M.B.; Angeles, E.; Villa-Treviño, S. The effect of caffeic acid phenethyl ester analogues in a modified resistant hepatocyte model. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2013, 24, 394–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifford, M.N.; King, L.J.; Kerimi, A.; Pereira-Caro, M.G.; Williamson, G. Metabolism of phenolics in coffee and plant-based foods by canonical pathways: An assessment of the role of fatty acid β-oxidation to generate biologically-active and -inactive intermediates. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 3326–3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sova, M.; Saso, L. Natural Sources, Pharmacokinetics, Biological Activities and Health Benefits of Hydroxycinnamic Acids and Their Metabolites. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ketnawa, S.; Reginio, F.C., Jr.; Thuengtung, S.; Ogawa, Y. Changes in bioactive compounds and antioxidant activity of plant-based foods by gastrointestinal digestion: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 4684–4705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babaeenezhad, E.; Nouryazdan, N.; Nasri, M.; Ahmadvand, H.; Moradi Sarabi, M. Cinnamic acid ameliorate gentamicin-induced liver dysfunctions and nephrotoxicity in rats through induction of antioxidant activities. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, S.; Ashafaq, M.; Alshahrani, S.; Siddiqui, R.; Ahmed, R.A.; Khuwaja, G.; Islam, F. Cinnamon oil against acetaminophen-induced acute liver toxicity by attenuating inflammation, oxidative stress and apoptosis. Toxicol. Rep. 2020, 7, 1296–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Alvarez, V.; Bobadilla, R.A.; Muriel, P. Structure-hepatoprotective activity relationship of 3,4-dihydroxycinnamic acid (caffeic acid) derivatives. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2001, 21, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hu, Y.; He, B.; Li, L.; Tian, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Shang, H.; Zou, Z. Design, synthesis and evaluation of ursodeoxycholic acid-cinnamic acid hybrids as potential anti-inflammatory agents by inhibiting Akt/NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 260, 115785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Soriano, P.; Macías-Pérez, J.; Velázquez, A.; Camacho-Enriquez, B.; Pretelín-Castillo, G.; Ruiz-Sánchez, M.; Abrego-Reyes, V.; Villa-Treviño, S.; Angeles, E. Solvent-Free Synthesis of Carboxylic Acids and Amide Analogs of CAPE (Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester) under Infrared Irradiation Conditions. Green Sustain. Chem. 2015, 5, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NOM-062-ZOO-1999; Especificaciones Técnicas Para La Producción, Cuidado Y Uso De Los Animales De Laboratorio. Diario Oficial. 1999, p. 107. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/203498/NOM-062-ZOO-1999_220801.pdf (accessed on 12 May 2024).
- Syabani, D.M.; Eliyani, H.; Suharsono, S.; Rantam, F.A.; Ma’ruf, A. Postmortem Interval Estimation Time from Algormortis Temperature of Rats Expressed by MARS Model Approach. KnE Life Sci. 2017, 3, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, L.G. Manual of Histologic Staining Methods of the Armeed Forces Institute of Pathology, 3rd ed.; Blakiston Division, McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Zakout, Y.M.; Abdellah, M.A.; Abdallah, M.A.; Batran, S.A. Optimization of PAS stain and similar Schiff’s based methods for glycogen demonstration in liver tissue. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2024, 161, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitman, S.; Frankel, S. A colorimetric method for the determination of serum glutamic oxalacetic and glutamic pyruvic transaminases. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1957, 28, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmeyer, H.U.; Grassl, M.; Walter, H.E. Methods of Enzymatic Analysis, 3rd ed.; Bergmeyer, H.U.M., Ed.; Verlag Chemie: Deerfield Beach, FL, USA, 1983; Volume 2, pp. 269–270. [Google Scholar]
- Seifter, S.; Dayton, S. The estimation of glycogen with the anthrone reagent. Arch. Biochem. 1950, 25, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.; Yan, X.; Yang, Y.; Xu, J. Identifying Structure-Property Relationships through SMILES Syntax Analysis with Self-Attention Mechanism. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2019, 59, 914–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gfeller, D.; Grosdidier, A.; Wirth, M.; Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissTargetPrediction: A web server for target prediction of bioactive small molecules. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W32–W38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, K.; Goede, A.; Preissner, R.; Gohlke, B.O. SuperPred 3.0: Drug classification and target prediction—A machine learning approach. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W726–W731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaulton, A.; Bellis, L.J.; Bento, A.P.; Chambers, J.; Davies, M.; Hersey, A.; Light, Y.; McGlinchey, S.; Michalovich, D.; Al-Lazikani, B.; et al. ChEMBL: A large-scale bioactivity database for drug discovery. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D1100–D1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shen, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, S.; Zhang, W.; Liu, X.; Lai, L.; Pei, J.; Li, H. PharmMapper 2017 update: A web server for potential drug target identification with a comprehensive target pharmacophore database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W356–W360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelleher, K.J.; Sheils, T.K.; Mathias, S.L.; Yang, J.J.; Metzger, V.T.; Siramshetty, V.B.; Nguyen, D.T.; Jensen, L.J.; Vidović, D.; Schürer, S.C.; et al. Pharos 2023: An integrated resource for the understudied human proteome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D1405–D1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liang, L.; Yin, Z.; Lin, J. Improving chemical similarity ensemble approach in target prediction. J. Cheminform. 2016, 8, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, S.; Lee, B.; Yoon, S. TargetNet: Functional microRNA Target Prediction with Deep Neural Networks. Bioinformatics 2022, 38, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilson, M.K.; Liu, T.; Baitaluk, M.; Nicola, G.; Hwang, L.; Chong, J. BindingDB in 2015: A public database for medicinal chemistry, computational chemistry and systems pharmacology. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D1045–D1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldaba-Muruato, L.R.; Moreno, M.G.; Shibayama, M.; Tsutsumi, V.; Muriel, P. Protective effects of allopurinol against acute liver damage and cirrhosis induced by carbon tetrachloride: Modulation of NF-kappaB, cytokine production and oxidative stress. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1820, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, H.; Zhang, J.; Shang, D.; Zhu, C.; Xiang, X. The progress to establish optimal animal models for the study of acute-on-chronic liver failure. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1087274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Amin, A.S.M.; Menezes, R.G. Carbon Tetrachloride Toxicity. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Varela, M.L.; Mogildea, M.; Moreno, I.; Lopes, A. Acute Inflammation and Metabolism. Inflammation 2018, 41, 1115–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tohamy, A.A.; Aref, A.M.; Moneim, A.E.A.; Sayed, R.H.; Esmat, A.; Moneim, A. Cinnamic acid Attenuates Cisplatin-Induced Hepatotoxicity and Nephrotoxicity. J. Basic Environ. Sci. 2016, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Liu, T.; Tian, M.; Liu, C.; Ma, S.; Cao, H.; Bian, H.; Wang, L.; Feng, Y.; Qi, J. Albumin, an interesting and functionally diverse protein, varies from ‘native’ to ‘effective’ (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2024, 29, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Rosas, J.R.; Díaz-Torres, R.; Ramírez-Noguera, P.; López-Barrera, L.D.; Escobar-Chavez, J.J.; Ángeles, E.R. PLGA nanoparticles of a new cinnamic acid derivative inhibits cellular proliferation on breast cancer cell line MCF-7 in a PPARγ dependent way. Die Pharm. 2020, 75, 324–328. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.D.; Wang, Z.Z.; Liu, W.C.; Qian, X.K.; Zhu, Y.D.; Wang, T.G.; Pan, S.M.; Zou, L.W. Pyrazolone compounds could inhibit CES1 and ameliorates fat accumulation during adipocyte differentiation. Bioorg. Chem. 2024, 150, 107536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhao, K.N.; Chen, C. The role of CYP3A4 in the biotransformation of bile acids and therapeutic implication for cholestasis. Ann. Transl. Med. 2014, 2, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lentz, F.; Tran, A.; Rey, E.; Pons, G.; Tréluyer, J.M. Pharmacogenomics of fluorouracil, irinotecan, and oxaliplatin in hepatic metastases of colorectal cancer: Clinical implications. Am. J. Pharmacogenomics 2005, 5, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Guo, W.; Mao, C.; Shen, J.; Wan, M. Liver fibrosis: Pathological features, clinical treatment and application of therapeutic nanoagents. J. Mater Chem. B 2024, 12, 1446–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabir, U.; Gu, H.M.; Zhang, D.W. Extracellular matrix turnover: Phytochemicals target and modulate the dual role of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in liver fibrosis. Phytother. Res. 2023, 37, 4932–4962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taru, V.; Szabo, G.; Mehal, W.; Reiberger, T. Inflammasomes in chronic liver disease: Hepatic injury, fibrosis progression and systemic inflammation. J. Hepatol. 2024, 5, 895–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Cao, Y.; Lu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, J.; Che, J.; Zhuang, R.; Shao, J. Recent progress and applications of small molecule inhibitors of Keap1-Nrf2 axis for neurodegenerative diseases. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 264, 115998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, M.; Toribio, A.J.; Salem, Y.M.; Alexander, M.; Ferrey, A.; Swentek, L.; Tantisattamo, E.; Ichii, H. Nrf2 Signaling Pathway as a Key to Treatment for Diabetic Dyslipidemia and Atherosclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Rustamov, N.; Roh, Y.S. The Roles of NFR2-Regulated Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Quality Control in Chronic Liver Diseases. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Xiao, M.; Hu, S.; Wang, M. Keap1-Nrf2 pathway: A key mechanism in the occurrence and development of cancer. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1381467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Jin, Y.; Chen, X.; Ye, X.; Shen, X.; Lin, M.; Zeng, C.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, J. NF-κB in biology and targeted therapy: New insights and translational implications. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Rourke, S.A.; Shanley, L.C.; Dunne, A. The Nrf2-HO-1 system and inflammaging. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1457010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
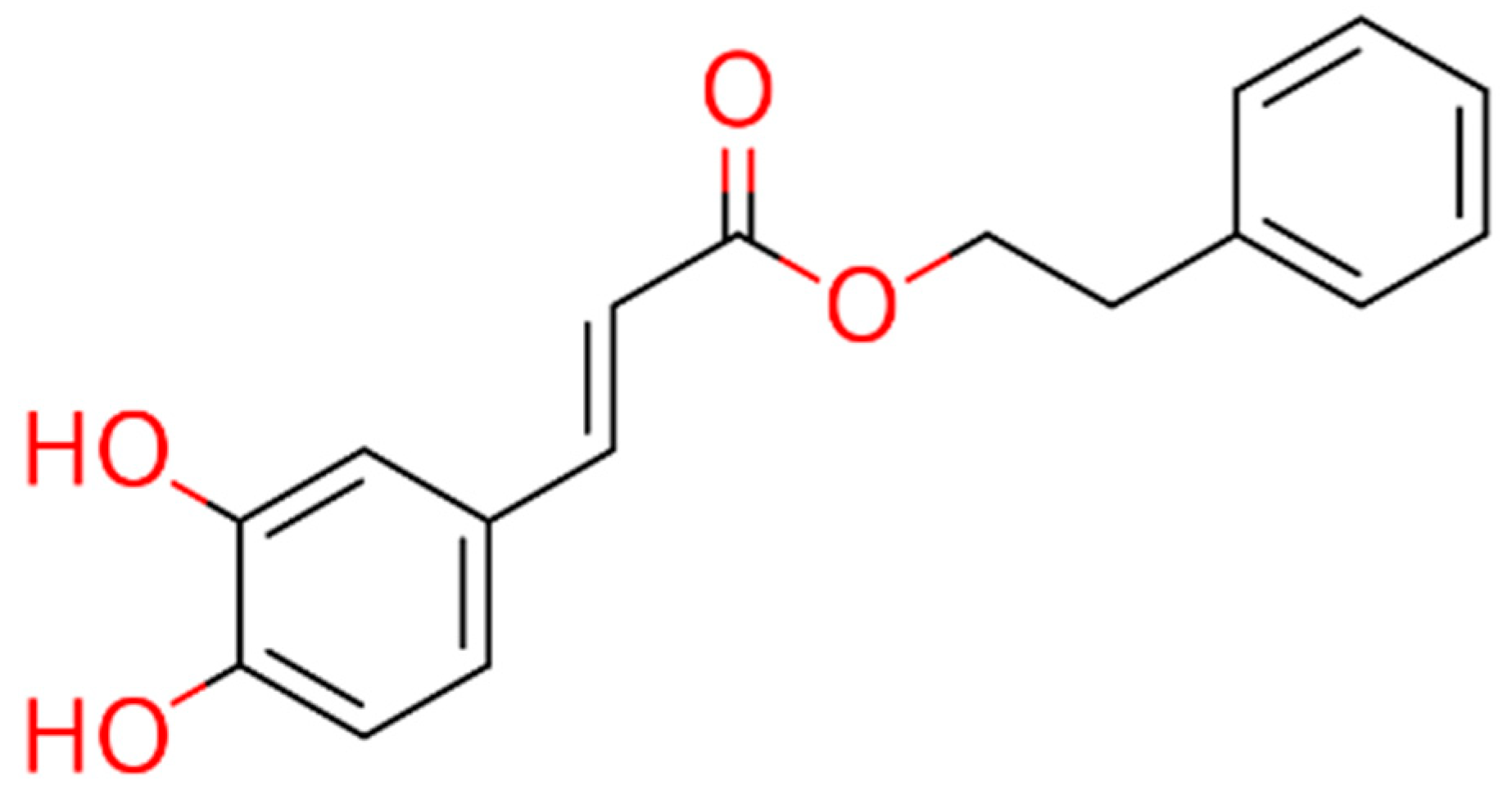


| Compound | LQM717 | LQM755 |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical structure | 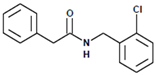 |  |
| Chemical name | N-(2-chlorobenzyl)-2-phenylacetamide | N-[(3,4-dichlorophenyl)methyl]-3-(4-phenoxyphenyl)-2-propenamide |
| Molecular weight | 259.73 g/mol | 398.29 g/mol |
| Physical characteristics | White solid | White crystalline solid |
| Compound | Dose | Vehicle |
|---|---|---|
| LQM717 | 20 mg/kg | 100 μL de DMSO |
| LQM755 | LQM717 equimolar dose | 100 μL de DMSO |
| Serum Samples | Liver Samples | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALT | ALP | GGT | Total Bilirubin | Direct Bilirubin | Albumin | Glycogen | |
| NT | 36.56 ± 16.61 abc**** | 35.24 ± 6.072 ab****c** | 14.13 ± 9.972 a****b** | 0.97 ± 0.326 a**b* | 0.47 ± 0.239 a** | 578.39 ± 24.11 a****b** | 2.08 ± 0.08 abc**** |
| Control | 39.92 ± 12.01 abc**** | 33.60 ± 3.691 ab****c*** | 7.88 ± 5.765 a****b** | 0.76 ± 0.679 a**b* | 0.56 ± 0.498 a** | 562.69 ± 20.3 a****b* | 1.91 ± 0.15 abc**** |
| CCl4 | 184.07 ± 14.83 b**c* | 253.22 ± 11.94 c**** | 210.34 ± 65.01 b*c*** | 25.86 ± 9.24 c* | 15.3 ± 9.372 | 471.73 ± 19.0 b*c** | 0.44 ± 0.02 bc* |
| LQM717 + CCl4 | 151.46 ± 14.65 a** | 220.92 ± 42.72 | 128.59 ± 58.4 a* | 25.47 ± 15.37 | 11.39 ± 4.644 | 509.08 ± 14.05 a* | 0.62 ± 0.11 a* |
| LQM755 + CCl4 | 161.21 ± 10.87 a* | 109.12 ± 35.86 a****b**** | 90.49 ± 32.76 a*** | 8.16 ± 6.24 a* | 6.27 ± 3.306 | 531.30 ± 18.07 a** | 0.64 ± 0.057 a* |
| LQM717 | 47.69 ± 8.044 abc**** | 46.31 ± 3.743 ab****c** | 12.85 ± 10.68 a****b** | 0.54 ± 0.49 a**b** | 0.32 ± 0.552 a** | 575.97 ± 29.61 a****b** | 2.02 ± 0.24 abc**** |
| LQM755 | 51.48 ± 4.022 abc**** | 40.93 ± 3.737 ab****c** | 15.14 ± 10.48 a****b** | 1.63 ± 0.65 a**b* | 0.31 ± 0.36 a** | 555.45 ± 10.43 a****b* | 1.98 ± 0.08 abc**** |
| Target Protein Name | Protein ID | Target Location and/or Function Human Protein Atlas | Database |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alanyl aminopeptidase | P15144 | Enriched cell type: hepatocytes/Protease angiogenesis | TN |
| Bifunctional epoxide hydrolase 2 | P34913 | Enriched cell type: hepatocytes/Lipid and xenobiotic metabolism | TN |
| 17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 | P37059 | Enriched cell type: hepatocytes and cholangiocytes/Lipid metabolism | BDB |
| Carbonic anhydrase 2 | P00918 | Enriched cell type: hepatocytes/Lyase | S |
| Carbonic anhydrase 5A, mitochondrial | P35218 | Enriched cell type: hepatocytes/Ureagenesis | S, SP |
| Carbonic anhydrase 9 * | Q16790 | Enriched cell type: cholangiocytes/Lyase | S |
| Carboxylesterase 1 | P23141 | Enriched cell type: hepatocytes/Lipid metabolism | TN |
| Carboxylesterase 2 | O00748 | Enriched cell type: hepatocytes/Lipid metabolism | TN |
| CYP450 2C9 * | P11712 | Enriched cell type: hepatocytes/Lipid metabolism | S |
| CYP450 3A4 | P08684 | Enriched cell type: hepatocytes/Lipid metabolism | S |
| Coagulation factor II, thrombin | P00734 | Enriched cell type: hepatocytes/Hemostasis | TN |
| DNA excision repair protein ERCC-1 * | P07992 | Liver/DNA repair | S |
| Folate hydrolase 1 * | Q04609 | Enriched cell type: hepatocytes/Multifunctional enzyme | TN |
| Histone deacetylase 1 * | Q13547 | Liver/Transcription regulation | P, S |
| Mitogen-activated protein kinase 8 * | P45983 | Liver/Proliferation and programmed cell death | P, S, TN |
| Perilipin-1 | O60240 | Enriched cell type: Hepatocytes/Lipid metabolism | TN |
| Perilipin-5 * | Q00G26 | Enriched cell type: Hepatocytes/Lipid metabolism | TN |
| Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src * | P12931 | Liver/Cell cycle | BDB |
| Solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 1 * | P11166 | Liver/Glucose transporter | SP |
| Target Protein Name | Protein ID | Target Location and/or Function Human Protein Atlas | Database |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amine oxidase [flavin-containing] B | P27338 | Enriched cell type: hepatocytes/Oxidative amine deamination | SP, TN |
| Broad substrate specificity ATP-binding cassette transporter ABCG2 | Q9UNQ0 | Enriched cell type: hepatocytes/Lipid transport | TN |
| C-C chemokine receptor type 2 | P41597 | Enriched cell type: Kupffer cells/Inflammatory response | TN |
| C5a anaphylatoxin chemotactic receptor 1 | P21730 | Enriched cell type: Kupffer cells/Chemotaxis | SP |
| Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (quinone), mitocondrial | Q02127 | Enriched cell type: hepatocytes/Pyrimidine biosynthesis | SP |
| Glycogen phosphorylase, liver form | P06737 | Enriched cell type: hepatocytes/Carbohydrate metabolism | P, S, TN |
| Histone deacetylase 2 * | Q92769 | Liver/Transcription regulation | TN |
| Histone deacetylase 5 * | Q9UQL6 | Liver/Transcription regulation | SP |
| Histone deacetylase 7 | Q8WUI4 | Liver/Transcription regulation | SP |
| Matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MMP-1) * | P03956 | Enriched cell type: Cholangiocytes/Collagen degradation | P, S, TN |
| Matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) | P08253 | Enriched cell type: hepatic stellate cells/Angiogenesis and collagen degradation | BDB, P, S, TN |
| Matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) * | P14780 | Liver/Collagen degradation | BDB, P, S, TN |
| Matrix metalloproteinase-12 (MMP-12) * | P39900 | Liver/Metalloprotease | TN |
| Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p65 subunit * | Q04206 | Liver/NF-kB Subunit | TN |
| Nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group H member 4 (Bile acid receptor) | Q96RI1 | Enriched cell type: hepatocytes and cholangiocytes/Bile acid transport | TN |
| Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor Alpha | Q07869 | Enriched cell type: hepatocytes/Transcription regulation | TN |
| Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma * | P37231 | Liver/Transcription regulation | TN |
| Polyunsaturated fatty acid 5-lipoxygenase | P09917 | Enriched cell type: Kupffer cells/Leukotriene biosynthesis | TN |
| Proteasome subunit beta type-2 * | P49721 | Liver/Protein degradation | SP |
| Transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 4 | Q9HBA0 | Enriched cell type: Kupffer cells and cholangiocytes/Ion transport | BDB |
| Transthyretin | P02766 | Enriched cell type: hepatocytes/Transport thyroid hormones | SP |
| Tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase 1 * | Q9NUW8 | Liver/DNA repair | SP |
| Vascular cell adhesion protein 1 | P19320 | Enriched cell type: Kupffer cells/Cell adhesion | TN |
| Target Protein Name | Protein ID | Target Location and/or Function Human Protein Atlas | Database |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apurinic/Apyrimidinic Endodeoxyribonuclease 1 * | P27695 | Liver/DNA repair and transcription regulation | SP |
| CYP450 2C19 | P33261 | Enriched cell type: hepatocytes/Lipid metabolism | TN, S |
| Histone deacetylase 6 | Q9UBN7 | Enriched cell type: hepatocytes/Transcription regulation | P, S, TN |
| M-phase inducer phosphatase 2 * | P30305 | Liver/Cell cycle | TN, SP |
| Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 | Q16236 | Liver/Antioxidant response | SP |
| Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 subunit | P19838 | Liver/NF-kB subunit | SP |
| Nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group I member 2 | O75469 | Enriched cell type: hepatocytes/Xenobiotic and drug metabolism | SP |
| Prostaglandin E2 receptor EP2 subtype | P43116 | Enriched cell type: Kupffer cells/G protein-coupled receptor | TN |
| Prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 1 | P23219 | Enriched cell type: hepatic stellate cells/Lipid and prostaglandin metabolism | SP |
| Sigma nonopioid intracellular receptor 1 | Q99720 | Enriched cell type: hepatocytes/Lipid transport | S, TN |
| Tachykinin receptor 2 | P21452 | Enriched cell type: Kupffer cells/G protein-coupled receptor | SP |
| Transcription intermediary factor 1-alpha * | O15164 | Liver/Regulation of cell proliferation | SP |
| Transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 1 | Q8NER1 | Enriched cell type: hepatocytes/Ion transport | BDB |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aldaba-Muruato, L.R.; Escalante-Hipólito, B.; Alarcón-López, A.Y.; Martínez-Soriano, P.A.; Angeles, E.; Macías-Pérez, J.R. Preclinical Research on Cinnamic Acid Derivatives for the Prevention of Liver Damage: Promising Therapies for Liver Diseases. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051094
Aldaba-Muruato LR, Escalante-Hipólito B, Alarcón-López AY, Martínez-Soriano PA, Angeles E, Macías-Pérez JR. Preclinical Research on Cinnamic Acid Derivatives for the Prevention of Liver Damage: Promising Therapies for Liver Diseases. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(5):1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051094
Chicago/Turabian StyleAldaba-Muruato, Liseth Rubí, Brayan Escalante-Hipólito, Aldo Yoshio Alarcón-López, Pablo A. Martínez-Soriano, Enrique Angeles, and José Roberto Macías-Pérez. 2025. "Preclinical Research on Cinnamic Acid Derivatives for the Prevention of Liver Damage: Promising Therapies for Liver Diseases" Biomedicines 13, no. 5: 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051094
APA StyleAldaba-Muruato, L. R., Escalante-Hipólito, B., Alarcón-López, A. Y., Martínez-Soriano, P. A., Angeles, E., & Macías-Pérez, J. R. (2025). Preclinical Research on Cinnamic Acid Derivatives for the Prevention of Liver Damage: Promising Therapies for Liver Diseases. Biomedicines, 13(5), 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051094







