Pharmacological Blocking of Adiponectin Receptors Induces Alzheimer’s Disease-like Neuropathology and Impairs Hippocampal Function
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Drug Administration
2.3. Behavioral Tests
2.3.1. Open Field Test (OFT)
2.3.2. Y-Maze Task
2.3.3. Novel Object Recognition Test
2.3.4. Elevated Plus Maze Test
2.3.5. Forced Swim Test
2.4. Tissue Preparation for Histochemistry
2.5. Immunohistochemistry Staining
2.6. Quantification of BrdU, Ki67, and DCX Positive Cells
2.7. Western Blot Analysis
2.8. Quantitative Reverse Transcription PCR
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
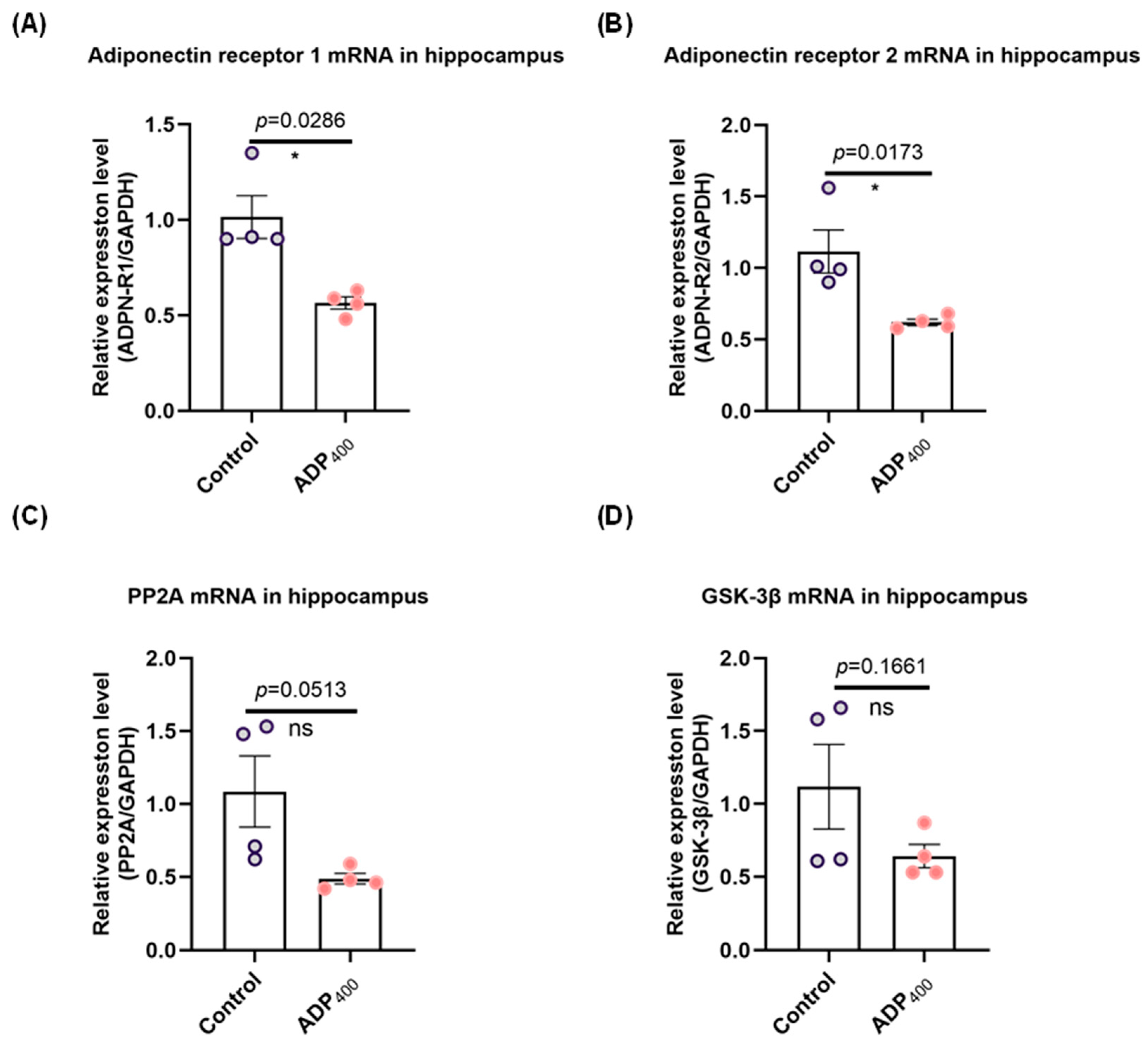
3.1. Blocking Adiponectin Receptors Downregulates Adiponectin Receptor Expression in the Hippocampus
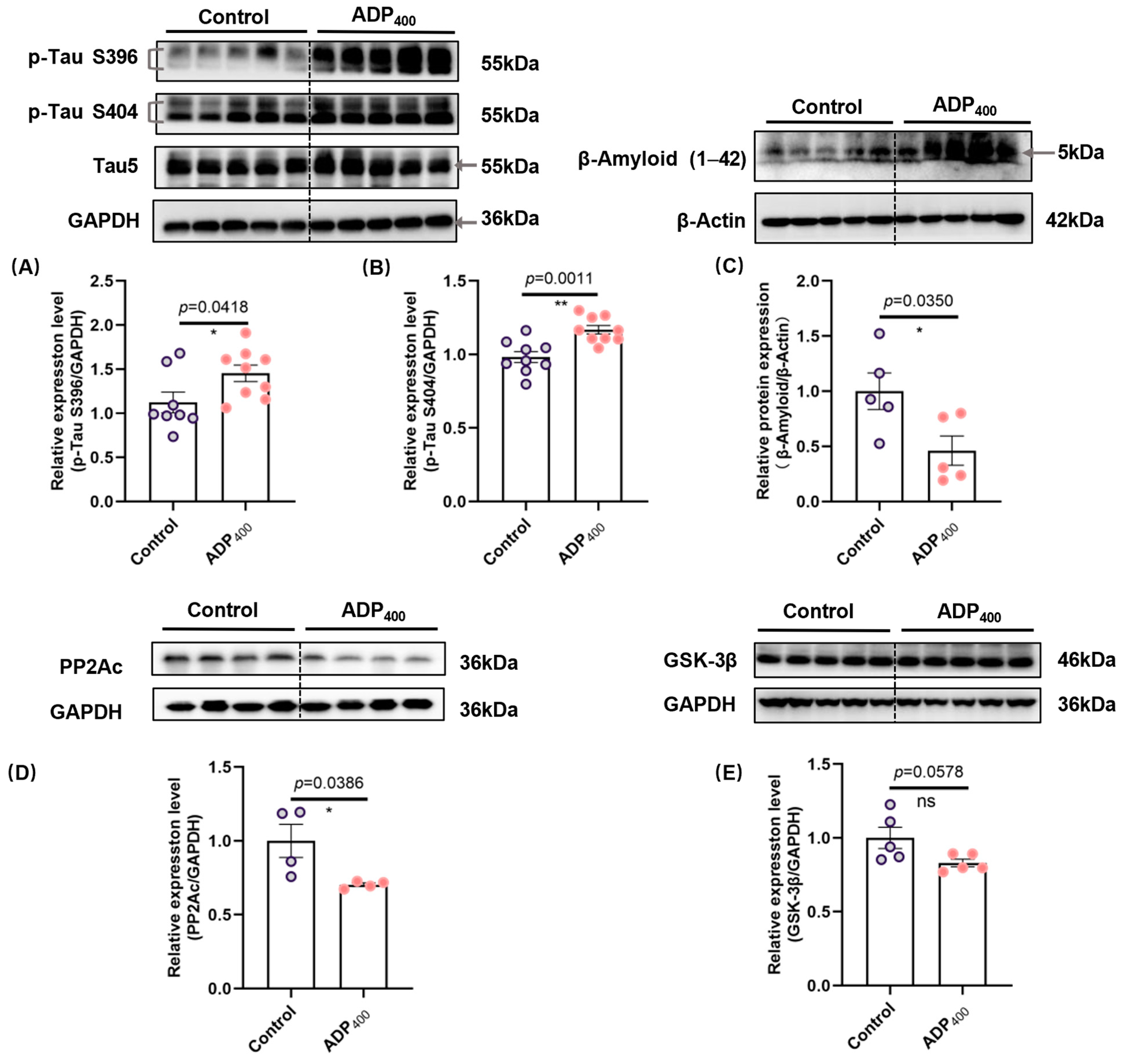
3.2. Blocking Adiponectin Receptors Induces Tau Hyperphosphorylation and Increases β-Amyloid Levels in the Hippocampus
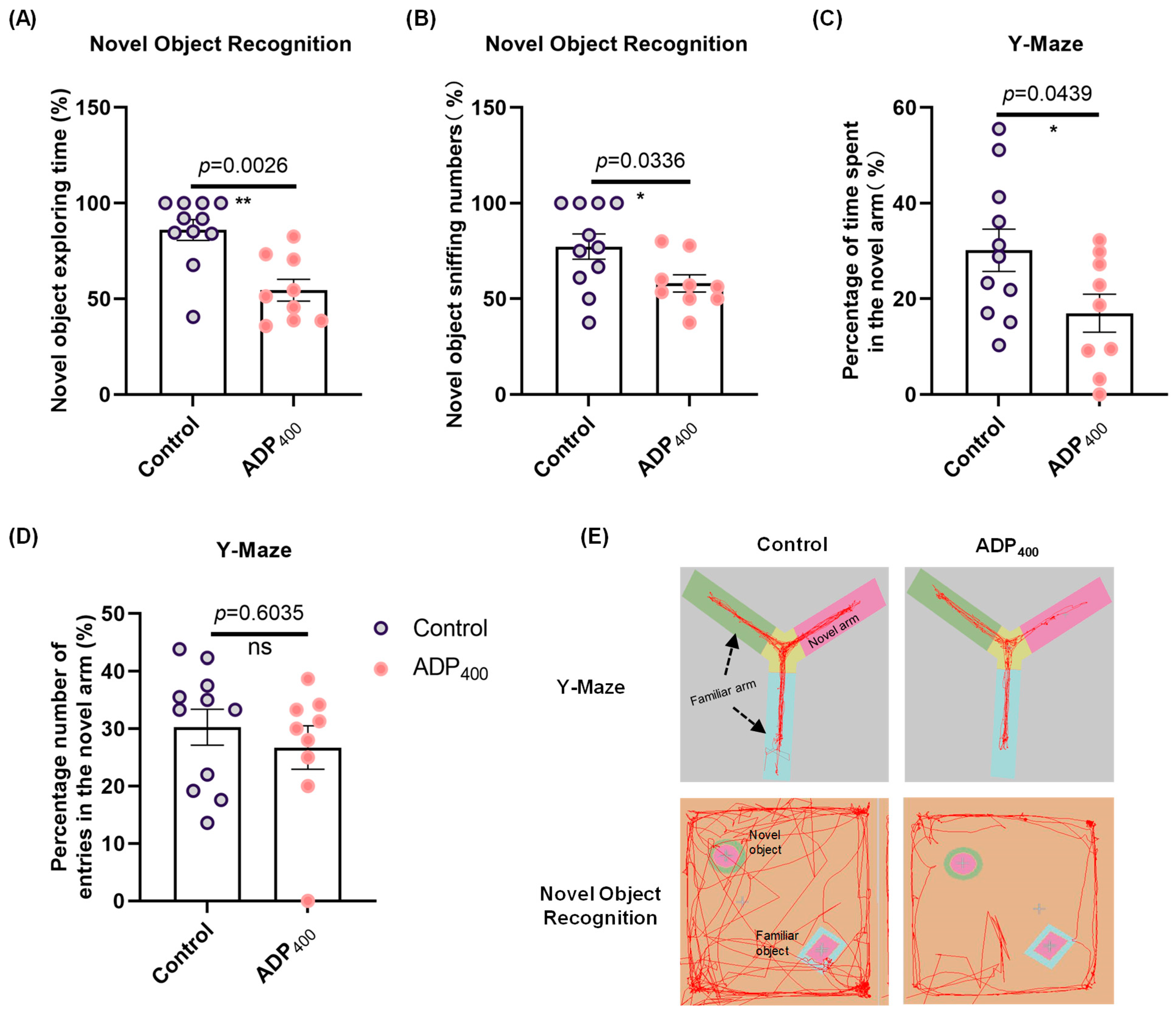
3.3. Blocking Adiponectin Receptors Induces Anxiety-like Behavior
3.4. Blocking Adiponectin Receptors Impairs Cognitive Function
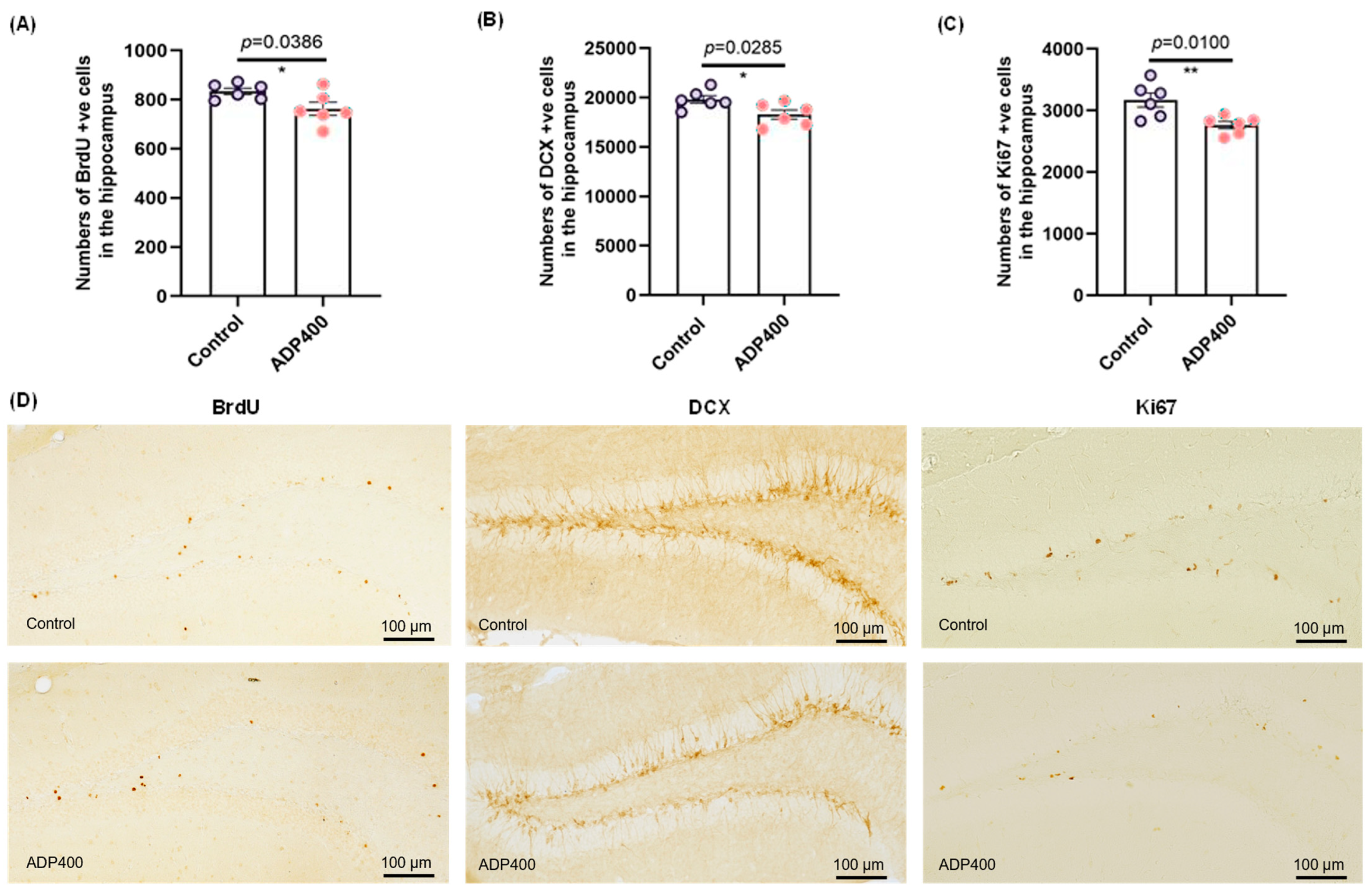
3.5. Blocking Adiponectin Receptors Reduces Hippocampal Neurogenesis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- 2024 Alzheimer’s Disease Facts and Figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2024, 20, 3708–3821. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilkaite, G.; Vogel, J.; Mattsson-Carlgren, N. Integrating Amyloid and Tau Imaging with Proteomics and Genomics in Alzheimer’s Disease. Cell Rep. Med. 2024, 5, 101735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayas, C.L.; Ávila, J. GSK-3 and Tau: A Key Duet in Alzheimer’s Disease. Cells 2021, 10, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Shi, J.; Yin, X.; Iqbal, K.; Grundke-Iqbal, I.; Gong, C.-X.; Liu, F. PP2A Regulates Tau Phosphorylation Directly and Also Indirectly via Activating GSK-3beta. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2010, 19, 1221–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L. Recent Advances in Alzheimer’s Disease: Mechanisms, Clinical Trials and New Drug Development Strategies. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowell, J.; Blunt, E.; Gupta, D.; Edison, P. Antidiabetic Agents as a Novel Treatment for Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Disease. Ageing Res. Rev. 2023, 89, 101979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, M.B.; Bhondge, H.M.; Wankhede, N.L.; Shende, P.V.; Thanekaer, R.P.; Aglawe, M.M. Navigating the Intersection: Diabetes and Alzheimer’s Intertwined Relationship. Ageing Res. Rev. 2024, 100, 102415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Wang, Z.H.; Kang, S.S.; Liu, X.; Xia, Y.; Chan, C.B. High-Fat Diet-Induced Diabetes Couples to Alzheimer’s Disease through Inflammation-Activated C/EBPβ/AEP Pathway. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 3396–3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Yao, S.Y.; Chen, Q.; Jin, H.; Du, M.Q.; Xue, Y.H. True or False? Alzheimer’s Disease Is Type 3 Diabetes: Evidences from Bench to Bedside. Ageing Res. Rev. 2024, 99, 102383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gils, V.; Rizzo, M.; Côté, J.; Viechtbauer, W.; Fanelli, G.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Wimberley, T.; Bulló, M.; Fernandez-Aranda, F.; Dalsgaard, S.; et al. The Association of Glucose Metabolism Measures and Diabetes Status with Alzheimer’s Disease Biomarkers of Amyloid and Tau: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2024, 159, 105604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, Y.Y.; Verdonschot, M.; McEvoy, C.T.; Peeters, G. Associations between Depression and Cognition, Mild Cognitive Impairment and Dementia in Persons with Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 185, 109227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straub, L.G.; Scherer, P.E. Metabolic Messengers: Adiponectin. Nat. Metab. 2019, 1, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Wu, X.; Wang, J.; Shi, Y.; Hu, Q.; Cui, W.; Bai, H.; Zhou, J.; Du, Y.; Han, L.; et al. Adiponectin/AdiopR1 Signaling Prevents Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Oxidative Injury after Traumatic Brain Injury in a SIRT3 Dependent Manner. Redox Biol. 2022, 54, 102390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, M.R.; Fasano, R.; Paolisso, G. Adiponectin and Cognitive Decline. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloemer, J.; Pinky, P.D.; Govindarajulu, M.; Hong, H.; Judd, R.; Amin, R.H.; Moore, T.; Dhanasekaran, M.; Reed, M.N.; Suppiramaniam, V. Role of Adiponectin in Central Nervous System Disorders. Neural Plast. 2018, 2018, 4593530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Sun, Q.; Chen, W.; Gao, Y.; Ye, J.; Chen, Y. New Advances of Adiponectin in Regulating Obesity and Related Metabolic Syndromes. J. Pharm. Anal. 2024, 14, 100913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, M.; Choubey, M.; Tirumalasetty, M.B.; Arbee, S.; Mohib, M.M.; Wahiduzzaman, M.; Mamun, M.A.; Uddin, M.B.; Mohiuddin, M.S. Adiponectin: A Promising Target for the Treatment of Diabetes and Its Complications. Life 2023, 13, 2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindzingre, L.; Bouaziz-Amar, E.; Mouton-Liger, F.; Cognat, E.; Dumurgier, J.; Vrillon, A.; Paquet, C.; Lilamand, M. The Role of Adiponectin in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Translational Review. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2024, 28, 100166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, R.C.-L.; Cheng, O.-Y.; Jian, M.; Kwan, J.S.-C.; Ho, P.W.-L.; Cheng, K.K.-Y.; Yeung, P.K.K.; Zhou, L.L.; Hoo, R.L.-C.; Chung, S.K.; et al. Chronic Adiponectin Deficiency Leads to Alzheimer’s Disease-like Cognitive Impairments and Pathologies through AMPK Inactivation and Cerebral Insulin Resistance in Aged Mice. Mol. Neurodegener. 2016, 11, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.W.; Abid, N.B.; Jo, M.H.; Jo, M.G.; Yoon, G.H.; Kim, M.O. Suppression of Adiponectin Receptor 1 Promotes Memory Dysfunction and Alzheimer’s Disease-like Pathologies. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, R.C.; Jian, M.; Ma, O.K.; Xiang, A.W.; Bunting, M.; Kwan, J.S. Liver-Specific Adiponectin Gene Therapy Suppresses Microglial NLRP3-Inflammasome Activation for Treating Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Neuroinflamm. 2024, 21, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horgusluoglu, E.; Neff, R.; Song, W.M.; Wang, M.; Wang, Q.; Arnold, M. Integrative metabolomics-genomics approach reveals key metabolic pathways and regulators of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2022, 18, 1260–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvanitakis, Z.; Capuano, A.W.; Tong, H.; Mehta, R.I.; Anokye-Danso, F.; Bennett, D.A. Associations of Serum Insulin and Related Measures With Neuropathology and Cognition in Older Persons With and Without Diabetes. Ann. Neurol. 2024, 95, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, T.; Rehman, S.U.; Khan, A.; Badshah, H.; Abid, N.B.; Kim, M.W. Adiponectin-mimetic novel nonapeptide rescues aberrant neuronal metabolic-associated memory deficits in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2021, 16, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, M.; Kwan, J.S.; Bunting, M.; Ng, R.C.; Chan, K.H. Adiponectin suppresses amyloid-β oligomer (AβO)-induced inflammatory response of microglia via AdipoR1-AMPK-NF-κB signaling pathway. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 1625, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Sterling, K.; Song, W. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in Alzheimer’s disease and its pharmaceutical potential. Transl. Neurodegener. 2022, 11, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dejanovic, B.; Sheng, M.; Hanson, J.E. Targeting Synapse Function and Loss for Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2024, 23, 23–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yau, S.Y.; Li, A.; Hoo, R.L.C.; Ching, Y.P.; Christie, B.R.; Lee, T.M.C.; Xu, A.; So, K.-F. Physical Exercise-Induced Hippocampal Neurogenesis and Antidepressant Effects Are Mediated by the Adipocyte Hormone Adiponectin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 15810–15815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.H.; Christie, B.R.; Praag, H.; Lin, K.; Siu, P.M.; Xu, A. AdipoRon Treatment Induces a Dose-Dependent Response in Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.; Sun, L.; Wang, J.; Sun, F.; Wang, W.; Wang, D. Role of Adiponectin-Notch Pathway in Cognitive Dysfunction Associated with Depression and in the Therapeutic Effect of Physical Exercise. Aging Cell 2021, 20, e13387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Ou, H.; Zhang, B.; Zheng, M.; Yan, L.; Chen, Y.; So, K.F.; Zhang, L. Treadmill Exercise Relieves Chronic Restraint Stress-Induced Cognitive Impairments in Mice Via Activating Protein Phosphatase 2A. Neurosci. Bull. 2021, 37, 1487–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada-Iwabu, M.; Yamauchi, T.; Iwabu, M.; Honma, T.; Hamagami, K.; Matsuda, K. A Small-Molecule AdipoR Agonist for Type 2 Diabetes and Short Life in Obesity. Nature 2013, 503, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Wang, J.; Meng, L.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, Y.; Yang, M. AdipoRon Promotes Amyloid-β Clearance through Enhancing Autophagy via Nuclear GAPDH-Induced Sirtuin 1 Activation in Alzheimer’s Disease. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2024, 181, 3039–3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zhang, W.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, J.; Li, Y. AdipoRon Ameliorates Synaptic Dysfunction and Inhibits Tau Hyper-Phosphorylation through the AdipoR/AMPK/mTOR Pathway in T2DM Mice. Neurochem. Res. 2024, 49, 2075–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGregor, E.R.; Lasky, D.J.; Rippentrop, O.J.; Clark, J.P.; Wright, S.; Jones, M.V.; Anderson, R.M. Reversal of neuronal tau pathology via adiponectin receptor activation. Commun. Biol. 2025, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otvos, L.; Knappe, D.; Hoffmann, R.; Kovalszky, I.; Olah, J.; Hewitson, T.D.; Stawikowska, R.; Stawikowski, M.; Cudic, P.; Lin, F.; et al. Development of Second Generation Peptides Modulating Cellular Adiponectin Receptor Responses. Front. Chem. 2014, 2, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tye, K.M.; Prakash, R.; Kim, S.Y.; Fenno, L.E.; Grosenick, L.; Zarabi, H. Amygdala Circuitry Mediating Reversible and Bidirectional Control of Anxiety. Nature 2011, 471, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinar, C.; Yau, S.Y.; Sharp, Z.; Shamei, A.; Fontaine, C.J.; Meconi, A.L. Effects of Voluntary Exercise on Cell Proliferation and Neurogenesis in the Dentate Gyrus of Adult FMR1 Knockout Mice. Brain Plast. 2018, 4, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Choe, K.; Lee, H.J.; Park, T.J.; Kim, M.O. Neuroprotective Effects of Osmotin in Parkinson’s Disease-Associated Pathology via the AdipoR1/MAPK/AMPK/mTOR Signaling Pathways. J. Biomed. Sci. 2023, 30, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Barua, S.; Jeong, Y.J.; Lee, J.E. Adiponectin: The Potential Regulator and Therapeutic Target of Obesity and Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congdon, E.E.; Ji, C.; Tetlow, A.M.; Jiang, Y.; Sigurdsson, E.M. Tau-Targeting Therapies for Alzheimer Disease: Current Status and Future Directions. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2023, 19, 715–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, C.S.; Baker, S.L.; Dobyns, L.; Janabi, M.; Jagust, W.J.; Harrison, T.M. Tau Accumulation and Atrophy Predict Amyloid Independent Cognitive Decline in Aging. Alzheimers Dement. 2024, 20, 2526–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Z.; He, J.L.; Guo, J.D.; McBride, S.; Narasimhan, H.; Kim, L. Changolkar Amyloid-β Plaques Enhance Alzheimer’s Brain Tau-Seeded Pathologies by Facilitating Neuritic Plaque Tau Aggregation. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 29–38. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Li, X.; Gao, W.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, L. Cornel Iridoid Glycoside Inhibits Tau Hyperphosphorylation via Regulating Cross-Talk Between GSK-3β and PP2A Signaling. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.-P.; Gan, G.-S.; Liu, Y.-M.; Xiao, J.-S.; Liu, H.-X.; Mei, B.; Zhang, J.-J. Adiponectin Attenuates Streptozotocin-Induced Tau Hyperphosphorylation and Cognitive Deficits by Rescuing PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β Pathway. Neurochem. Res. 2018, 43, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lam, J.B.; Lam, K.S.L.; Liu, J.; Lam, M.C.; Hoo, R.L.C.; Wu, D.; Cooper, G.J.S.; Xu, A. Adiponectin Modulates the Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3beta/Beta-Catenin Signaling Pathway and Attenuates Mammary Tumorigenesis of MDA-MB-231 Cells in Nude Mice. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 11462–11470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabe, R.; Tsuji, S.; Mochida, S.; Ikehara, T.; Usui, T.; Ohama, T.; Sato, K. A Stable Association with PME-1 May Be Dispensable for PP2A Demethylation—Implications for the Detection of PP2A Methylation and Immunoprecipitation. FEBS Open Bio. 2018, 8, 1486–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-J.; Lee, K.-W.; Oh, S.; Yan, R.; Zhang, J.; Beach, T.G.; Adler, C.H.; Voronkov, M.; Braithwaite, S.P.; Stock, J.B.; et al. Protein Phosphatase 2A and Its Methylation Modulating Enzymes LCMT-1 and PME-1 Are Dysregulated in Tauopathies of Progressive Supranuclear Palsy and Alzheimer Disease. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2018, 77, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Meng, F.; Garza, J.C.; Liu, J.; Lei, Y.; Kirov, S.A. Modulation of Depression-Related Behaviors by Adiponectin AdipoR1 Receptors in 5-HT Neurons. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 4205–4220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Tang, J.; Liang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhu, P.; Zhou, M. Running Exercise Alleviates Hippocampal Neuroinflammation and Shifts the Balance of Microglial M1/M2 Polarization through Adiponectin/AdipoR1 Pathway Activation in Mice Exposed to Chronic Unpre-Dictable Stress. Mol. Psychiatry 2024, 29, 2031–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Li, C.; Lei, Y.; Xu, S.; Zhao, D.; Lu, X.Y. Role of the Adipose PPARgamma-Adiponectin Axis in Susceptibility to Stress and Depression/Anxiety-Related Behaviors. Mol. Psychiatry 2017, 22, 1056–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yau, S.-Y.; Lee, T.H.-Y.; Li, A.; Xu, A.; So, K.-F. Adiponectin Mediates Running-Restored Hippocampal Neurogenesis in Streptozotocin-Induced Type 1 Diabetes in Mice. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.H.; Ahadullah Christie, B.R.; Lin, K.; Siu, P.M.F.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, T.F.; Komal, P.; Xu, A.; So, K.F.; Yau, S.Y. Chronic AdipoRon Treatment Mimics the Effects of Physical Exercise on Restoring Hippocampal Neuroplasticity in Diabetic Mice. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 4666–4681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Guo, M.; Zhang, D.; Cheng, S.Y.; Liu, M.; Ding, J.; Scherer, P.E.; Liu, F.; Lu, X.Y. Adiponectin Is Critical in Determining Susceptibility to Depressive Behaviors and Has Antidepressant-like Activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 12248–12253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, R.C.; Jian, M.; Ma, O.K.; Bunting, M.; Kwan, J.S.; Zhou, G.J. Chronic Oral Administration of adipoRon Reverses Cognitive Im-Pairments and Ameliorates Neuropathology in an Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Model. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 5669–5689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloemer, J.; Pinky, P.D.; Smith, W.D.; Bhattacharya, D.; Chauhan, A.; Govindarajulu, M.; Hong, H.; Dhanasekaran, M.; Judd, R.; Amin, R.H. Adiponectin Knockout Mice Display Cognitive and Synaptic Deficits. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Gene Name | Primer (5’ to 3’) |
|---|---|
| ADNR1-F | GAAAGACAACGACTACCTGCTAC |
| ADNR1-R | CGTCAAGATTCCCAGAAAGAG |
| ADNR2-F | CCACCATAGGGCAGATAGG |
| ADNR2-R | TGAACAAAGGCACCAGCAA |
| Ppp2ca-F | ATGGA CGAGA AGTTG TTCAC C |
| Ppp2ca-R | CAGTG ACTGG ACATC GAACC T |
| GSK-3β-F | CATCCTTATCCCTCCTCACGCT |
| GSK-3β-R | TATTGGTCTGTCCACGGTCTCC |
| GAPDH-F | TTCCTACCCCCAATGTATCCG |
| GAPDH-R | CATGAGGTCCACCACCCTGTT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, H.-H.; Ou, H.-N.; Yu, J.-S.; Yau, S.-Y.; Tsang, H.W.-H. Pharmacological Blocking of Adiponectin Receptors Induces Alzheimer’s Disease-like Neuropathology and Impairs Hippocampal Function. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051056
Guo H-H, Ou H-N, Yu J-S, Yau S-Y, Tsang HW-H. Pharmacological Blocking of Adiponectin Receptors Induces Alzheimer’s Disease-like Neuropathology and Impairs Hippocampal Function. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(5):1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051056
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Hui-Hui, Hai-Ning Ou, Jia-Sui Yu, Suk-Yu Yau, and Hector Wing-Hong Tsang. 2025. "Pharmacological Blocking of Adiponectin Receptors Induces Alzheimer’s Disease-like Neuropathology and Impairs Hippocampal Function" Biomedicines 13, no. 5: 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051056
APA StyleGuo, H.-H., Ou, H.-N., Yu, J.-S., Yau, S.-Y., & Tsang, H. W.-H. (2025). Pharmacological Blocking of Adiponectin Receptors Induces Alzheimer’s Disease-like Neuropathology and Impairs Hippocampal Function. Biomedicines, 13(5), 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051056







