Prediction of Kidney Function Improvement After Heart Transplantation
Abstract
1. Introduction
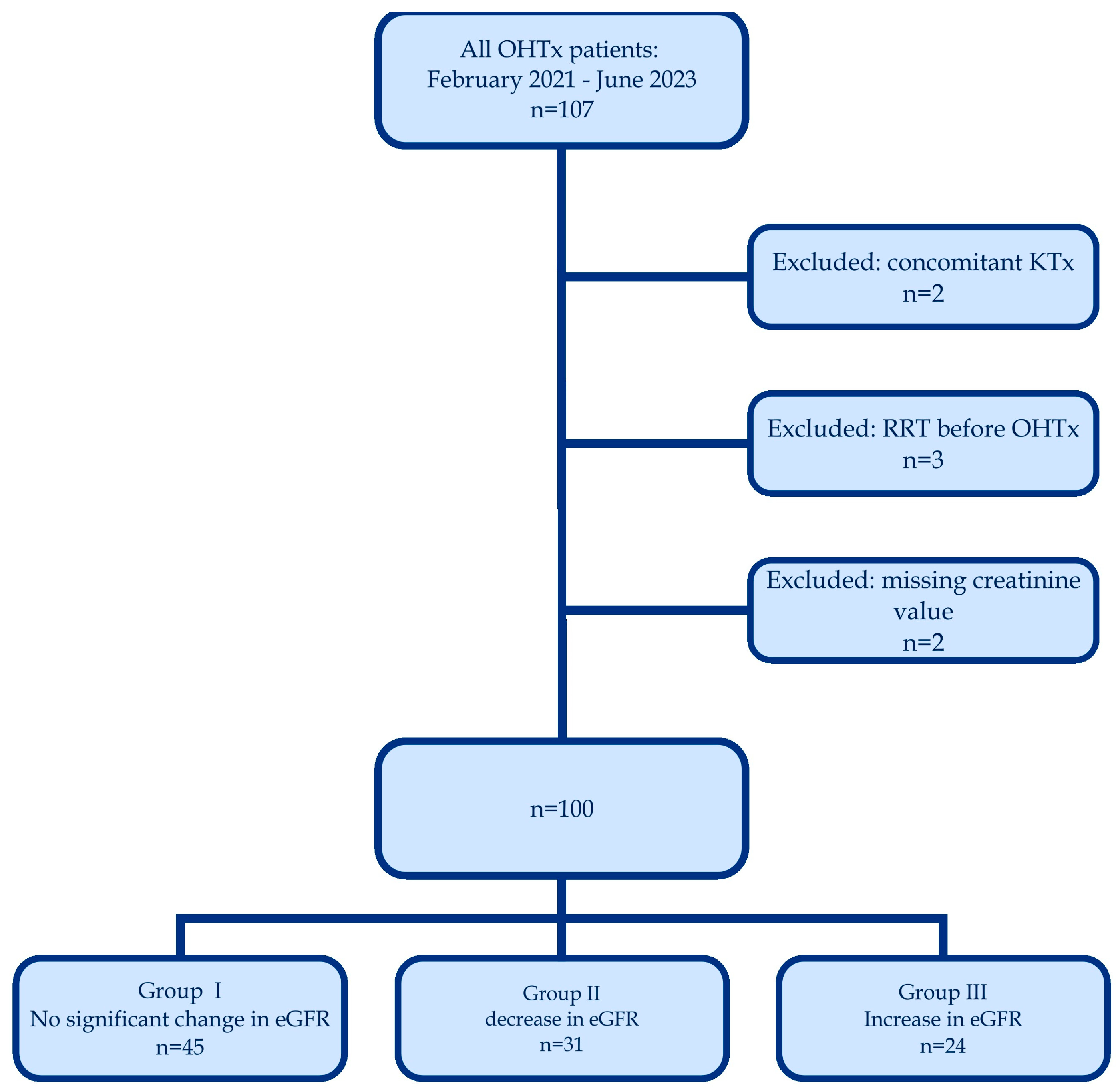
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
The Results Description
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HF | Heart failure |
| CRS | Cardiorenal syndrome |
| HTx | Heart transplantation |
| eGFR | Estimated glomerular filtration rate |
| RRT | Renal replacement therapy |
| NYHA | New York Heart Association |
| INTERMACS | Interagency Registry for Mechanically Assisted Circulatory Support |
| MDRD | Modification of Diet in Renal Disease |
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| NT-proBNP | N-terminal pro B-type natriuretic peptide |
| ALP | Alkaline phosphatase |
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| IABP | Intra-aortic balloon pump |
| ECMO | Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation |
| LVAD | Left ventricular assist device |
| ICD | Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator |
| CRT-D | Cardiac resynchronization therapy-defibrillator |
| CVP | Central venous pressure |
| PAS | Pulmonary artery systolic pressure |
| PAD | Pulmonary artery diastolic pressure |
| PAM | Pulmonary artery mean pressure |
| PCWP | Pulmonary capillary wedge pressure |
| CO | Cardiac output |
| CI | Cardiac index |
| CABG | Coronary artery bypass grafting |
| PCI | Percutaneous coronary interventions |
| TIA | Transient ischemic attack |
| AF | Atrial fibrillation |
| AFl | Atrial flutter |
| RAP | Right atrium pressure |
| PAPI | Pulmonary pulsatility index |
| INR | International normalized ratio |
| APTT | Activated partial thromboplastin clotting time |
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| GGTP | Gamma glutamyl transpeptidase |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| LDL | Low-density lipoprotein |
| ICU | Intensive care unit |
| mGFR | Measured glomerular filtration rate |
References
- Damman, K.; Valente, M.A.E.; Voors, A.A.; O’Connor, C.M.; van Veldhuisen, D.J.; Hillege, H.L. Renal impairment, worsening renal function, and outcome in patients with heart failure: An updated meta-analysis. Eur. Heart J. 2014, 35, 455–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Deursen, V.M.; Urso, R.; Laroche, C.; Damman, K.; Dahlström, U.; Tavazzi, L.; Maggioni, A.P.; Voors, A.A. Co-morbidities in patients with heart failure: An analysis of the European Heart Failure Pilot Survey. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2014, 16, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tedeschi, A.; Agostoni, P.; Pezzuto, B.; Corra’, U.; Scrutinio, D.; La Gioia, R.; Salvioni, E.; Mapelli, M.; Lagioia, R.; Vignati, C.; et al. Role of comorbidities in heart failure prognosis Part 2: Chronic kidney disease, elevated serum uric acid. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2020, 27, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baudry, G.; Sebbag, L.; Bourdin, J.; Hugon-Vallet, E.; Jobbe Duval, A.; Mewton, N.; Pozzi, M.; Rossignol, P.; Girerd, N. Haemodynamic parameters associated with renal function prior to and following heart transplantation. ESC Heart Fail. 2021, 8, 4944–4954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taiwo, A.A.; Khush, K.K.; Stedman, M.R.; Zheng, Y.; Tan, J.C. Longitudinal changes in kidney function following heart transplantation: Stanford experience. Clin. Transplant. 2018, 32, e13414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivey-Miranda, J.B.; Farrero-Torres, M.; Flores-Umanzor, E.; Santiago, E.; Perez-Villa, F. Predictors of Improvement in Renal Function After Heart Transplant. Exp. Clin. Transplant. 2019, 17, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolsrud, O.; Karason, K.; Holmberg, E.; Ricksten, S.E.; Felldin, M.; Samuelsson, O.; Dellgren, G. Renal function and outcome after heart transplantation. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2018, 155, 1593–1604.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, L.H.; Khush, K.K.; Cherikh, W.S.; Goldfarb, S.; Kucheryavaya, A.Y.; Levvey, B.J.; Meiser, B.; Ross, H.J.; Chambers, D.C.; Yusen, R.D.; et al. The Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: Thirty-fourth Adult Heart Transplantation Report—2017; Focus Theme: Allograft ischemic time. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2017, 36, 1037–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janus, N.; Launay-Vacher, V.; Sebbag, L.; Despins, P.; Epailly, E.; Pavie, A.; Dorent, R.; Durrbach, A.; Deray, G. Renal insufficiency, mortality, and drug management in heart transplant. Results of the CARIN study. Transpl. Int. 2014, 27, 931–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, A.P.; Vella, J.P. Acute Kidney Disease After Liver and Heart Transplantation. Transplantation 2016, 100, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delanaye, P.; Nellessen, E.; Grosch, S.; Depas, G.; Cavalier, E.; Defraigne, J.; Albert, A.; Chapelle, J.P.; Krzesinski, J.M. Creatinine-based formulae for the estimation of glomerular filtration rate in heart transplant recipients. Clin. Transplant. 2006, 20, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaffi, K.; Uhlig, K.; Perrone, R.D.; Ruthazer, R.; Rule, A.; Lieske, J.C.; Singh, A.K.; Weiner, D.E. Performance of Creatinine-Based GFR Estimating Equations in Solid-Organ Transplant Recipients. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2014, 63, 1007–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Howard, A.; Thomas, C.P. Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate at Transplant Listing and Other Predictors of Post-Heart Transplant Mortality and the Development of ESRD. Transplantation 2020, 104, 2444–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vella, A.; Labate, V.; Carenini, G.; Alfonzetti, E.; Milani, V.; Bandera, F.; Generati, G.; Cioffi, G.; D’Elia, E.; Dei Cas, A.; et al. Phenotyping congestion in acute heart failure by renal flow and right heart to pulmonary circulation coupling. ESC Heart Fail. 2023, 10, 3546–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudry, G.; Coutance, G.; Dorent, R.; Bauer, F.; Blanchart, K.; Boignard, A.; Roussel, J.C.; Leclercq, C.; Damy, T.; Girerd, N.; et al. Diuretic dose is a strong prognostic factor in ambulatory patients awaiting heart transplantation. ESC Heart Fail. 2023, 10, 2843–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodenas-Alesina, E.; Luis Scolari, F.; Wang, V.N.; Brahmbhatt, D.H.; Mihajlovic, V.; Fung, N.L.; Josiassen, J.; Deyell, M.W.; Cheung, C.C.; Ignaszewski, M.; et al. Improved mortality and haemodynamics with milrinone in cardiogenic shock due to acute decompensated heart failure. ESC Heart Fail. 2023, 10, 2577–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamson, C.; Cowan, L.M.; de Boer, R.A.; Diez, M.; Drożdż, J.; Dukát, A.; Filippatos, G.; Goncalvesova, E.; Katova, T.; Kosztin, A.; et al. Liver tests and outcomes in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: Findings from DAPA-HF. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2022, 24, 1856–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, L.A.; Felker, G.M.; Pocock, S.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Pfeffer, M.A.; Swedberg, K.; Wang, D.; Yusuf, S.; Michelson, E.L.; Granger, C.B.; et al. Liver function abnormalities and outcome in patients with chronic heart failure: Data from the Candesartan in Heart Failure: Assessment of Reduction in Mortality and Morbidity (CHARM) program. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2009, 11, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, T.; Rushton, S.N.; Parry, G.; Dark, J.H.; Sheerin, N.S. The impact of severe acute kidney injury requiring renal replacement therapy on survival and renal function of heart transplant recipients—A UK cohort study. Transpl. Int. 2020, 33, 1650–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Choi, J.O.; Cho, Y.H.; Sung, K.; Oh, J.; Cho, H.J.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, S.E.; Choe, W.S.; et al. Impact of preoperative renal replacement therapy on the clinical outcome of heart transplant patients. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Fu, L.; Wu, Y.; Xie, X.; Zhang, W.; Hou, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, M.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; et al. Risk factors of renal replacement therapy after heart transplantation: A retrospective single-center study. Ann. Transl. Med. 2022, 10, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoji, S.; Kuno, T.; Kohsaka, S.; Amiya, E.; Asleh, R.; Alvarez, P.; Patel, J.; Kobashigawa, J.A. Incidence and long-term outcome of heart transplantation patients who develop postoperative renal failure requiring dialysis. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2022, 41, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolsrud, O.; Ricksten, S.E.; Holmberg, E.; Felldin, M.; Karason, K.; Hammarsten, O.; Dellgren, G. Measured and not estimated glomerular filtration rate should be used to assess renal function in heart transplant recipients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2016, 31, 1182–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartfay, S.; Kolsrud, O.; Wessman, P.; Dellgren, G.; Karason, K. The trajectory of renal function following mechanical circulatory support and subsequent heart transplantation. ESC Heart Fail. 2022, 9, 2464–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jokinen, J.J.; Tikkanen, J.; Kukkonen, S.; Hämmäinen, P.; Lommi, J.; Sipponen, J.; Lemström, K.B. Natural course and risk factors for impaired renal function during the first year after heart transplantation. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2010, 29, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariño, A.; Garcia-Peña, A.; Muñoz-Velandia, O.M.; Cita-Pardo, J.E.; Betancourt, C. Evaluation of long-term kidney function following orthotopic heart transplantation. Transplant. Proc. 2022, 54, 769–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.; Kwon, H.J.; Yoo, H.; Kim, D.; Cho, Y.H.; Choi, J.O.; Lee, H.Y.; Cho, H.J.; Lee, S.E.; Choe, W.S.; et al. Clinical factors associated with renal outcome after heart transplantation. Int. Heart J. 2021, 62, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| All pts (100) | Group 1 (45) | Group 2 (31) | Group 3 (24) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic data: | |||||
| Sex—number of women N (%) | 18 (18%) | 8 (18%) | 6 (19%) | 4 (17%) | 0.966 |
| Age (years) | 54 (45–63) | 54 (47–62) | 51 (44–64) | 56.5 (46–64) | 0.610 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26.07 ± 4.25 | 26.75 ± 4.15 | 25.75 ± 4.25 | 24.97 ± 4.7 | 0.413 |
| Preoperative clinical data: | |||||
| Etiology of HF—number of ischemic HF N (%) | 43 (43%) | 22 (49%) | 11 (36%) | 10 (42%) | 0.509 |
| Use of inotropes/vasopressor N (%) | 40 (40%) | 23 (51%) | 7 (23%) | 10 (42%) | 0.044 |
| NYHA functional class: | 0.051 | ||||
| 1 and 2 N (%) | 14 (14%) | 4 (9%) | 8 (26%) | 2 (8%) | |
| 3 N (%) | 39 (39%) | 22 (49%) | 8 (26%) | 9 (38%) | |
| 4 N (%) | 30 (30%) | 11 (24%) | 8 (26%) | 11 (46%) | |
| INTERMACS profile | 0.219 | ||||
| 1–4 N (%) | 36 (53%) | 7 (10%) | 18 (26%) | 11 (16%) | |
| 5–7 N (%) | 32 (47%) | 11 (16%) | 16 (24%) | 5 (7%) | |
| IABP/ECMO/LVAD/Impella N (%) | 25 (25%) | 12 (27%) | 9 (29%) | 4 (17%) | 0.542 |
| Smoking. either now or in the past N (%) | 45 (45%) | 22 (49%) | 13 (42%) | 10 (42%) | 0.719 |
| ICD/CRT-D N (%) | 61 (61%) | 29 (64%) | 18 (58%) | 14 (58%) | 0.815 |
| CVP (mmHg) | 9 (6–14) | 7 (4.5–15) | 9 (6.5–12) | 10 (9–17) | 0.421 |
| PAS (mmHg) | 43.21 ± 14.38 | 42 ± 15.81 | 40.71 ± 14.97 | 47.69 ± 10.92 | 0.333 |
| PAD (mmHg) | 21 (16–26) | 19.5 (15.5–24) | 19 (16–30) | 24 (19.5–27) | 0.198 |
| PAM (mmHg) | 30 (23.5–36) | 28 (21–33) | 28 (21–37) | 33 (29–37) | 0.340 |
| PCWP (mmH)g | 20 (16–25) | 20 (15–25) | 19.5 (13.5–28) | 23 (19–25) | 0.424 |
| CO (thermodilution) (L/min) | 4.1 (3.5–4.7) | 4.09 (3.5–4.7) | 3.92 (3.47–4.4) | 4.45 (3.56–5.3) | 0.611 |
| CI (thermodilution). L/min/m2 | 2.07 (1.78–2.44) | 2.09 (1.84–2.44) | 2.08 (1.75–2.27) | 2.06 (1.78–2.70) | 0.831 |
| PAPI | 2.2 (1.5–3.3) | 2.4 (1.1–3.0) | 2.8 (1.7–3.3) | 2.9 (1.7–3.7) | 0.119 |
| RAP/PCWP | 0.46 (0.33–0.66) | 0.58 (0.35–0.80) | 0.49 (0.31–0.65) | 0.47 (0.40–0.65) | 0.475 |
| Comorbidities: | |||||
| Hypertension N (%) | 45 (45%) | 24 (53%) | 13 (42%) | 8 (33%) | 0.259 |
| Hyperlipidemia N (%) | 41 (41%) | 19 (42%) | 11 (36%) | 11 (46%) | 0.723 |
| Diabetes N (%) | 27 (27%) | 13 (29%) | 7 (23%) | 7 (29%) | 0.800 |
| Chronic kidney disease N (%) | 27 (27%) | 10 (22%) | 12 (39%) | 5 (21%) | 0.208 |
| Undergone CABG N (%) | 13 (13%) | 5 (11%) | 6 (19%) | 2 (8%) | 0.425 |
| Undergone PCI N (%) | 42 (42%) | 20 (44%) | 14 (45%) | 8 (33%) | 0.613 |
| Previous TIA/stroke N (%) | 12 (12%) | 6 (13%) | 2 (7%) | 4 (17%) | |
| AF/Afl N (%) | 48 (48%) | 19 (42%) | 18 (58%) | 11 (46%) | 0.568 |
| Preoperative Laboratory Data: | All Patients | Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 3 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hemoglobin (mg/dL) | 12.72 ± 2.03 | 12.54 ± 2.04 | 12.84 ± 1.91 | 13.1 ± 2.05 | 0.522 |
| Platelets (1000/mL) | 194 (161–240) | 200 (165–235) | 194 (150–269) | 179 (147–227) | 0.505 |
| INR | 1.3 (1.2–1.7) | 1.3 (1.1–1.5) | 1.4 (1.1–1.8) | 1.4 (1.2–1.8) | 0.686 |
| APTT (s) | 38 (33–46) | 37 (34–45) | 36 (31–54) | 39 (30–52) | 0.820 |
| Proteinuria (g) | 0.167 (0.1–0.875) | 0.1 (0.1–0.76) | 0.3 (0.1–1.09) | 0.3 (0.1–0.74) | 0.192 |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) | 1.27 (0.8–1.98) | 1.05 (0.78–1.92) | 0.95 (0.74–1.54) | 2.23 (1.51–2.99) | 0.000 |
| ALT (IU/L) | 29.83 (20.64–62) | 28.13 (20.13–38.47) | 34.33 (23–46.57) | 26.6 (19.55–349.97) | 0.557 |
| AST IU/L | 39.67 (26.33–61.67) | 37.8 (26.33–56) | 41 (27.45–61.67) | 36.86 (24.96–300.62) | 0.730 |
| ALP (IU/L) | 85.71 (63.7–107.3) | 82 (61.67–107.3) | 87.5 (64–99) | 91.33 (67.88–131) | 0.423 |
| GGTP (IU/L) | 83.9375 (48.13–156.58) | 84.5 (50.88–140) | 69.25 (35.3–141.37) | 115.83 (49–245) | 0.442 |
| Urea (mg/dL) | 50 (38.85–66.21) | 50.86 (40.8–66.25) | 42 (33.81–58.64) | 55.47 (44.67–75.54) | 0.040 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.13 (0.97–1.39) | 1.18 (1–1.5) | 1.05 (0.94–1.27) | 1.25 (1–1.43) | 0.128 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 68 (55.89–83.8) | 65.72 (50.67–79) | 77.57 (62.06–96.41) | 66.28 (54.56–78.58) | 0.052 |
| Uric acid (mg/dL) | 7.12 ±2.11 | 7.14 ± 2.27 | 7.12 ± 2.21 | 7.09 ± 1.73 | 0.996 |
| Total protein (g/dL) | 6.825 (6.12–7.3625) | 7.03 (6.12–7.36) | 6.95 (6–7.6) | 6.7 (6.2–7.13) | 0.754 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.7 (3.07–4.1) | 3.83 (3.33–4.14) | 3.48 (2.95–4.15) | 3.64 (3.11–3.87) | 0.344 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 11.97 (3.56–50.95) | 13.32 (5.06–46.85) | 11.55 (2.35–54.92) | 12.8 (3.05–55.77) | 0.735 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 126.86 ± 46.52 | 125.58 ± 31.11 | 130.4 ± 56.53 | 124.83 ± 58.61 | 0.921 |
| LDL (mg/dL) | 69.25 (48.25–92) | 64 (48.5–74) | 78 (66–116) | 69.25 (45–103) | 0.217 |
| Natrium (mmol/L) | 138 (137–140) | 139 (137–140) | 138 (136–140) | 137 (136–139) | 0.213 |
| Potassium (mmol/L) | 4.305 (4.091–4.5) | 4.3 (4.13–4.5) | 4.36 (4.07–4.58) | 4.28 (4.06–4.51) | 0.931 |
| Total calcium (mg/dL) | 9.04 (8.46–9.58) | 9 (8.6–9.4) | 9.4 (8.15–9.7) | 9.4 (8.7–10.6) | 0.232 |
| Inorganic phosphate (mg/dL) | 4.34 (3.2–5.1) | 3.5 (3–5) | 4.28 (3.48–5.8) | 4.8 (3.2–5.1) | 0.476 |
| Procalcitonin (ng/L) | 0.115 (0.043–0.45) | 0.1 (0.04–0.29) | 0.11 (0.05–0.54) | 0.15 (0.03–0.7) | 0.910 |
| Troponin (ng/mL) | 67 (16–1696) | 26 (11–819) | 246(26–2650) | 113 (18–1553) | 0.154 |
| NTproBNP (pg/mL) | 4219 (2228–8469) | 3820 (2419–6331) | 4244 (1587–6428) | 5245 (2789–12701) | 0.264 |
| MELD 3.0 score | 12.3 (8.6–17.2) | 11.0 (7.3–12.6) | 13.0 (7.5–17.1) | 16.1 (8.9–20.1) | 0.075 |
| Postoperative Laboratory Data: | All Patients | Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 3 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hemoglobin (mg/dL) | 10.75 ± 0.89 | 10.83 ± 0.94 | 10.62 ± 0.67 | 10.78 ± 1.07 | 0.482 |
| Platelets (1000/mL) | 209 (158–259) | 210 (156–264) | 209 (160–293) | 201 (154–245) | 0.474 |
| INR | 1.14 (1.09–1.23) | 1.15 (1.09–1.22) | 1.13 (1.08–1.3) | 1.14 (1.1–1.2) | 0.994 |
| APTT (s) | 32 (30–36) | 32 (31–36) | 33 (29–37) | 32 (30–36) | 0.764 |
| Proteinuria (g) | 0.17 (0.1–0.3) | 0.17 (0.1–0.3) | 0.19 (0.1–0.28) | 0.1 (0.1–0.47) | 0.806 |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) | 1.06 (0.68–1.58) | 0.99 (0.63–1.51) | 0.91 (0.65–1.18) | 1.41 (0.96–2.08) | 0.021 |
| ALT (IU/L) | 38.15 (26.07–69.75) | 38.07 (26.08–58.46) | 33.63 (21.15–105.71) | 40.36 (32.21–78.46) | 0.781 |
| AST (IU/L) | 38.23 (30.6–57.61) | 37.27 (30–57.61) | 38.71 (31.25–51.89) | 38.44 (31.37–61.14) | 0.813 |
| ALP (IU/L) | 95.71 (79.57–125.17) | 91.22 (80.69–123.86) | 96.46 (73.67–106.05) | 104.73 (79.71–170.5) | 0.356 |
| GGTP (IU/L) | 98.38 (67.14–156.6) | 112.28 (72–156.6) | 76.79 (61.63–122.71) | 133.92 (83.32–265) | 0.042 |
| Urea (mg/dL) | 66.35 (50–86) | 68.54 (50–85.25) | 69.5 (57.93–90.47) | 58.02 (41.86–75.17) | 0.102 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.33 (1.07–1.74) | 1.31 (1.1–1.68) | 1.67 (1.36–2.22) | 0.95 (0.76–1.21) | 0.000 |
| eGFR (ml/min/1.73 m2) | 66 (49.73–83.26) | 66 (52.37–74.93) | 52.62 (40.5–61.82) | 88.37 (77.97–114.36) | 0.000 |
| Uric acid (mg/dL) | 5.96 ±1.56 | 6.1 ± 1.75 | 6.32 ± 1.33 | 5.18 ± 1.28 | 0.034 |
| Total protein (g/dL) | 5.97 (5.5–6.39) | 6.13 (5.82–6.4) | 5.88 (5.47–6.33) | 5.6 (4.86–6.43) | 0.020 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.32 (3.09–3.58) | 3.35 (3.13–3.64) | 3.35 (2.88–3.57) | 3.26 (2.95–3.59) | 0.646 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 39.9 (26.01–65.39) | 44.55 (30.04–65.79) | 43.28 (26.91–81.71) | 30.11 (20.79–48.64) | 0.127 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 167.07 ± 40.74 | 161.82 ± 38.59 | 171.32 ± 46.43 | 171.78 ± 39.91 | 0.578 |
| LDL (mg/dL) | 95 (75–121.5) | 88.5 (74–109.25) | 106 (71.25–126) | 100.75 (89.08–136) | 0.254 |
| Natrium (mmol/L) | 138 (137–139) | 138(137–139) | 138 (136–140) | 138 (136–140) | 0.881 |
| Potassium (mmol/L) | 4.46 (4.23–4.68) | 4.42 (4.24–4.57) | 4.49 (4.24–4.72) | 4.49 (4.17–4.66) | 0.681 |
| Total calcium (mg/dL) | 8.86 (8.45–9.17) | 9.01 (8.56–9.27) | 8.74 (8.3–9.02) | 8.78 (8.49–9.1) | 0.187 |
| Inorganic phosphate (mg/dL) | 3.99 (3.53–4.83) | 3.85 (3.5–4.55) | 4.83 (4.07–5.4) | 3.37 (2.94–4.29) | 0.000 |
| Procalcitonin (ng/L) | 1.35 (0.4–3.22) | 1.17 (0.45–2.86) | 2.2 (0.43–5.18) | 0.75 (0.32–2.05) | 0.108 |
| Troponin (ng/mL) | 4325(2896–7267) | 4533.5 (2989–8725) | 4584 (3158–7267) | 3711(1399–6428) | 0.328 |
| NTproBNP (pg/mL) | 5837 (3086–9044) | 5979 (3624–9044) | 7068 (3944–14168) | 3820 (1920–8322) | 0.155 |
| MELD 3.0 score | 6.9 (4.1–9.5) | 7.6 (5.7–11.0) | 6.3 (3.7–10.0) | 5.4 (2.6–7.4) | 0.066 |
| Tacrolimus level (ng/mL) | 11.3 (9.4–13.9) | 11.7 (9.8–14.1) | 11.8 (9.0–14.1) | 11.2 (10.1–13.0) | 0.974 |
| Mycophenolate mofetil (ug/mL) | 1.90 (1.1–2.5) | 2.1 (1.6–2.5) | 1.6 (1.2–2.4) | 2.3 (0.9–2.8) | 0.670 |
| In-Hospital Course Data: | All Patients | Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 3 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Days in hospital | 36 (25–60) | 35 (25–55) | 34 (22–57) | 47 (31–78) | 0.1623 |
| Days in ICU | 7 (5–13) | 7 (4–14) | 8 (6–13) | 7 (4.5–10.5) | 0.5085 |
| Elective vs emergency (number of elective HTx) | 17 (17%) | 8 (18%) | 7 (23%) | 2 (8%) | 0.3479 |
| RRT after 3 months | 4 (4%) | 1 (2%) | 2 (7%) | 1 (4%) | |
| Deaths within 3 months (number of patients) | 16 (16) | 6 (13%) | 5 (16%) | 5 (21%) | 0.7439 |
| Postoperative RRT (number of patients) | 40 (40%) | 21 (47%) | 14 (45%) | 5 (21%) | 0.0785 |
| Infectious complications (number of patients) | 21 (21%) | 11 (24%) | 4 (13%) | 6 (25%) | 0.1273 |
| Rethoracotomy (number of patients) | 23 (23%) | 10 (22%) | 8 (26%) | 5 (21%) | 0.9626 |
| Right ventricular failure (number of patients) | 2 (2%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (3%) | 1 (4%) | 0.4213 |
| Pacemaker implantation (number of patients) | 6 (6%) | 3 (5%) | 1 (3%) | 2 (8%) | 0.7615 |
| Number of Patients | Univariate | Multivariate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p | |
| Sex—number of women (number of patients) | 100 | 0.94 (0.51–1.73) | 0.85 | ||
| Age (years) | 100 | 0.89 (0.86–1.05) | 0.76 | ||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 100 | 0.92 (0.79–1.07) | 0.3010 | ||
| Etiology of HF—number of ischemic HF (number of patients) | 100 | 0.94 (0.59–1.5) | 0.80 | ||
| Use of inotropes/vasopressor number of patients) | 100 | 1.05 (0.66–1.67) | 0.85 | ||
| NYHA functional class: (83) | 83 | ||||
| 1 and 2 (number of patients) | 0.98 (0.46–2.06) | 0.95 | |||
| 3 (number of patients) | 1.89 (0.19–1.56) | 0.10 | |||
| 4 (number of patients) | 0.54 (0.19–1.56) | 0.26 | |||
| IABP/ECMO/LVAD/Impella (number of patients) | 100 | 0.7 (0.39–1.27) | 0.24 | ||
| CVP (mmHg) | 67 | 1.05 (0.96–1.16) | 0.3030 | ||
| PAS (mmHg) | 67 | 1.03 (0.99–1.08) | 0.1460 | ||
| PAD (mmHg) | 67 | 1.03 (0.96–1.1) | 0.3910 | ||
| PAM (mmHg) | 67 | 1.03 (0.97–1.09) | 0.3090 | ||
| PCWP (mmH)g | 67 | 1.07 (0.98–1.17) | 0.1530 | ||
| CO (thermodilution), (l/min) | 67 | 1.04 (0.93–1.17) | 0.4830 | ||
| CI (thermodilution), l/min/m2 | 67 | 0.88 (0.27–2.82) | 0.8300 | ||
| Hypertension (number of patients) | 100 | 0.73 (0.45–1.17) | 0.19 | ||
| Hyperlipidemia (number of patients) | 100 | 1.14 (0.72–1.81) | 0.58 | ||
| Diabetes (number of patients) | 100 | 1.07 (0.65–1.79) | 0.78 | ||
| Chronic kidney disease (number of patients) | 100 | 0.8 (0.46–1.39) | 0.44 | ||
| Undergone CABG (number of patients) | 100 | 0.73 (0.33–1.62) | 0.44 | ||
| Undergone PCI (number of patients) | 100 | 764 (0.49–1.27) | 0.33 | ||
| Hemoglobin (mg/dL) | 100 | 1.12 (0.89–1.41) | 0.3450 | ||
| Platelets (1000/mL) | 100 | 1 (0.99–1) | 0.2550 | ||
| INR | 100 | 1.48 (0.66–3.31) | 0.3430 | ||
| APTT (s) | 100 | 1 (0.97–1.03) | 0.8830 | ||
| Proteinuria (g) | 100 | 0.73 (0.24–2.18) | 0.5710 | ||
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) | 100 | 1.66 (1.15–2.38) | 0.0070 | 1.66 (1.24–2.69) | 0.002 |
| ALT (IU/L) | 100 | 1 (1-1) | 0.0480 | ||
| AST, (IU/L) | 100 | 1 (1-1) | 0.0690 | ||
| ALP (IU/L) | 100 | 1.01 (1–1.02) | 0.0270 | ||
| GGTP (IU/L) | 100 | 1 (1–1.01) | 0.1130 | ||
| Urea (mg/dL) | 100 | 1.02 (1–1.04) | 0.0510 | ||
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 100 | 1.99 (0.71–5.56) | 0.1920 | ||
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 100 | 0.99 (0.97–1.01) | 0.2050 | ||
| Uric acid (mg/dL) | 100 | 0.99 (0.78–1.25) | 0.9380 | ||
| Total protein (g/dL) | 100 | 0.94 (0.54–1.65) | 0.8290 | ||
| Albumin (g/dL) | 100 | 0.81 (0.37–1.76) | 0.5890 | ||
| CRP (mg/L) | 100 | 1 (0.98–1.01) | 0.6940 | ||
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 100 | 1 (0.99–1.01) | 0.8400 | ||
| LDL (mg/dL) | 100 | 1 (0.99–1.02) | 0.6940 | ||
| Natrium (mmol/L) | 100 | 0.91 (0.79–1.05) | 0.2040 | ||
| Potassium (mmol/L) | 100 | 1.01 (0.98–1.04) | 0.5300 | ||
| Total calcium (mg/dL) | 100 | 2.12 (0.95–4.74) | 0.0680 | ||
| Inorganic phosphate (mg/dL) | 100 | 1.13 (0.67–1.92) | 0.6440 | ||
| Procalcitonin (ng/L) | 100 | 1.15 (0.96–1.39) | 0.1280 | ||
| Troponin (ng/mL) | 100 | 1 (1-1) | 0.6310 | ||
| NTproBNP (pg/mL) | 100 | 1 (1-1) | 0.0330 | ||
| Days in hospital | 100 | ||||
| Days in ICU | 100 | 1.03 (1–1.06) | 0.0640 | ||
| Elective vs emergency (number of elective HTx) | 100 | ||||
| Postoperative RRT (number of patients) | 100 | 0.55 (0.32–0.94) | 0.03 | 0.46 (0.24–0.88) | 0.02 |
| Infectious complications (number of patients) | 100 | 1.16 (0.68–2) | 0.58 | ||
| Rethoracotomy (number of patients) | 100 | 1 (0.56–1.77) | 1.00 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ptak, J.; Sokolski, M.; Wilk, M.; Waloszczyk, M.; Wiśniewski, K.; Krupka, D.; Makowska, P.; Cielecka, M.; Szwajkowski, M.; Rakowski, M.; et al. Prediction of Kidney Function Improvement After Heart Transplantation. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 933. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040933
Ptak J, Sokolski M, Wilk M, Waloszczyk M, Wiśniewski K, Krupka D, Makowska P, Cielecka M, Szwajkowski M, Rakowski M, et al. Prediction of Kidney Function Improvement After Heart Transplantation. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(4):933. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040933
Chicago/Turabian StylePtak, Jakub, Mateusz Sokolski, Mateusz Wilk, Mateusz Waloszczyk, Kacper Wiśniewski, Dominik Krupka, Paulina Makowska, Magdalena Cielecka, Maciej Szwajkowski, Mateusz Rakowski, and et al. 2025. "Prediction of Kidney Function Improvement After Heart Transplantation" Biomedicines 13, no. 4: 933. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040933
APA StylePtak, J., Sokolski, M., Wilk, M., Waloszczyk, M., Wiśniewski, K., Krupka, D., Makowska, P., Cielecka, M., Szwajkowski, M., Rakowski, M., Bochenek, M., Przybylski, R., & Zakliczyński, M. (2025). Prediction of Kidney Function Improvement After Heart Transplantation. Biomedicines, 13(4), 933. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040933







