Role of Educational Level in Kidney Transplant Outcomes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
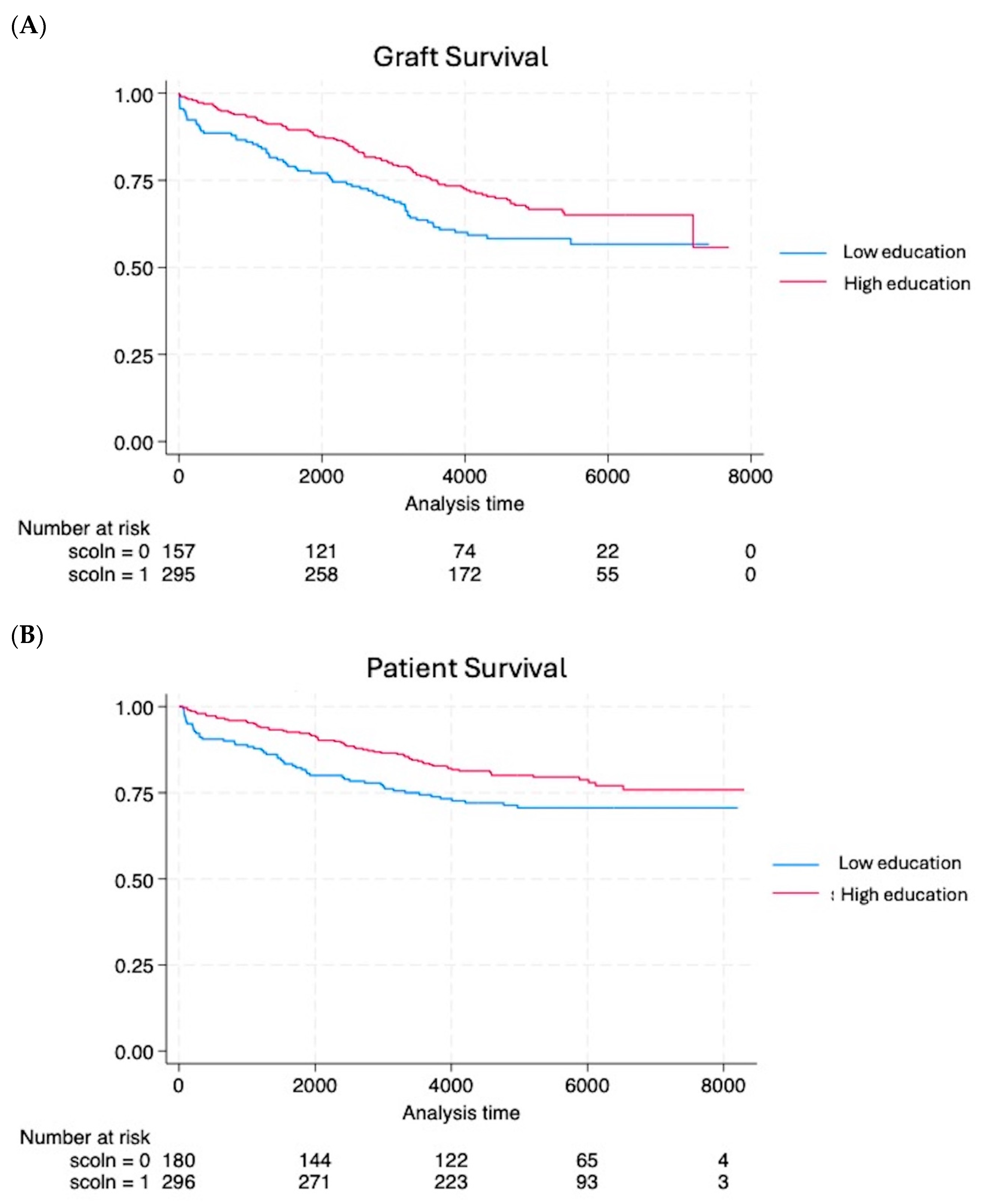
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Merion, R.M.; Goodrich, N.P.; Johnson, R.J.; McDonald, S.P.; Russ, G.R.; Gillespie, B.W.; Collett, D. Kidney transplant graft outcomes in 379 257 recipients on 3 continents. Am. J. Transplant. 2018, 18, 1914–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen-Bohlman, L.; Panzer, A.M.; Kindig, D.A. Health Literacy: A Prescription to End Confusion; Committee on Health Literacy, Board on Neuroscience and Behavioral Health, National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Berkman, N.D.; Sheridan, S.L.; Donahue, K.E.; Halpern, D.J.; Crotty, K. Low health literacy and health outcomes: An updated systematic review. Ann. Intern. Med. 2011, 155, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warsame, F.; Haugen, C.E.; Ying, H.; Garonzik-Wang, J.M.; Desai, N.M.; Hall, R.K.; Kambhampati, R.; Crews, D.C.; Purnell, T.S.; Segev, D.L.; et al. Limited health literacy and adverse outcomes among kidney transplant candidates. Am. J. Transplant. 2019, 19, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salter, M.L.; Orandi, B.; McAdams-DeMarco, M.A.; Law, A.; Meoni, L.A.; Jaar, B.G.; Sozio, S.M.; Kao, W.H.; Parekh, R.S.; Segev, D.L. Patient- and provider-reported information about transplantation and subsequent waitlisting. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 25, 2871–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salter, M.L.; Gupta, N.; King, E.; Bandeen-Roche, K.; Law, A.H.; McAdams-DeMarco, M.A.; Meoni, L.A.; Jaar, B.G.; Sozio, S.M.; Kao, W.H.; et al. Health-related and psychosocial concerns about transplantation among patients initiating dialysis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 9, 1940–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dageforde, L.A.; Box, A.; Feurer, I.D.; Cavanaugh, K.L. Understanding Patient Barriers to Kidney Transplant Evaluation. Transplantation 2015, 99, 1463–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, M.; Petgrave-Nelson, L.; Smith, K.D.; Perryman, J.P.; Clark, K.; Pastan, S.O.; Pearson, T.C.; Larsen, C.P.; Paul, S.; Patzer, R.E. Transplant Center Patient Navigator and Access to Transplantation among High-Risk Population: A Randomized, Controlled Trial. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 13, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillespie, A.; Hammer, H.; Lee, J.; Nnewihe, C.; Gordon, J.; Silva, P. Lack of listing status awareness: Results of a single-center survey of hemodialysis patients. Am. J. Transplant. 2011, 11, 1522–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pasquale, C.; Pistorio, M.L.; Corona, D.; Mistretta, A.; Zerbo, D.; Sinagra, N.; Giaquinta, A.; Tallarita, T.; Esker, B.; Mociskyte, D.; et al. Correlational study between psychic symptoms and quality of life among hemodialysis patients older than 55 years of age. Transplant. Proc. 2012, 44, 1876–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, J.A.; Mor, M.K.; Shields, A.M.; Sevick, M.A.; Palevsky, P.M.; Fine, M.J.; Arnold, R.M.; Weisbord, S.D. Prevalence and demographic and clinical associations of health literacy in patients on maintenance hemodialysis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 6, 1354–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, D.M.; Bradley, J.A.; Bradley, C.; Draper, H.; Dudley, C.; Fogarty, D.; Fraser, S.; Johnson, R.; Leydon, G.M.; Metcalfe, W.; et al. ATTOM investigators. Limited health literacy is associated with reduced access to kidney transplantation. Kidney Int. 2019, 95, 1244–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaboré, R.; Couchoud, C.; Macher, M.A.; Salomon, R.; Ranchin, B.; Lahoche, A.; Roussey-Kesler, G.; Garaix, F.; Decramer, S.; Pietrement, C.; et al. Age-Dependent Risk of Graft Failure in Young Kidney Transplant Recipients. Transplantation 2017, 101, 1327–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepeytre, F.; Dahhou, M.; Zhang, X.; Boucquemont, J.; Sapir-Pichhadze, R.; Cardinal, H.; Foster, B.J. Association of Sex with Risk of Kidney Graft Failure Differs by Age. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 3014–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boucquemont, J.; Pai, A.L.H.; Dharnidharka, V.R.; Hebert, D.; Furth, S.L.; Foster, B.J. Gender Differences in Medication Adherence Among Adolescent and Young Adult Kidney Transplant Recipients. Transplantation 2019, 103, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennerling, A.; Petersson, I.; Andersson, U.M.; Forsberg, A. Health Literacy among patients with end-stage kidney disease and kidney transplant recipients. Scand. J. Caring Sci. 2021, 35, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, D.M.; Fraser, S.; Dudley, C.; Oniscu, G.C.; Tomson, C.; Ravanan, R.; Roderick, P.; ATTOM investigators. Health literacy and patient outcomes in chronic kidney disease: A systematic review. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2018, 33, 1545–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, K.L.; Knoll, G.A.; Shariff, S.Z.; McArthur, E.; Garg, A.X.; Van Walraven, C.; Austin, P.C.; McCallum, M.K.; Quinn, R.R.; Tan, V.S.; et al. Socioeconomic Status and Kidney Transplant Outcomes in a Universal Healthcare System: A Population-based Cohort Study. Transplantation 2019, 103, 1024–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistretta, A.; Veroux, M.; Grosso, G.; Contarino, F.; Biondi, M.; Giuffrida, G.; Gagliano, M.; Giaquinta, A.; Zerbo, D.; Tallarita, T.; et al. Role of socioeconomic conditions on outcome in kidney transplant recipients. Transplant. Proc. 2009, 41, 1162–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Xia, X.; Lai, W.; Hao, X.; Wu, Y.; Lv, K.; Luo, Z.; Romão, E.A.; Ciancio, G.; Lv, C.; et al. Effects of recipient education disparity on living donor kidney transplant outcomes across different ethnic groups: A retrospective study in the United States. Trans. Androl. Urol. 2023, 12, 1137–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghods, A.J.; Nasrollahzadeh, D. Noncompliance with immunnosuppressive medications after renal transplantation. Exp. Clin. Transplant. 2003, 1, 39–47. [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb-Rumyantzev, A.S.; Sandhu, G.S.; Barenbaum, A.; Baird, B.C.; Patibandla, B.K.; Narra, A.; Koford, J.K.; Barenbaum, L. Education is associated with reduction in racial disparities in kidney transplant outcome. Clin. Transplant. 2012, 26, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hod, T.; Goldfarb-Rumyantzev, A.S. The role of disparities and socioeconomic factors in access to kidney transplantation and its outcome. Ren. Fail. 2014, 36, 1193–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schold, J.D.; Buccini, L.D.; Kattan, M.W.; Goldfarb, D.A.; Flechner, S.M.; Srinivas, T.R.; Poggio, E.D.; Fatica, R.; Kayler, L.K.; Sehgal, A.R. The association of community health indicators with outcomes for kidney transplant recipients in the United States. Arch. Surg. 2012, 147, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veroux, M.; Zerbo, D.; Basile, G.; Gozzo, C.; Sinagra, N.; Giaquinta, A.; Sanfiorenzo, A.; Veroux, P. Simultaneous Native Nephrectomy and Kidney Transplantation in Patients with Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veroux, M.; Sanfilippo, F.; Roscitano, G.; Giambra, M.; Giaquinta, A.; Riccioli, G.; Zerbo, D.; Corona, D.; Sorbello, M.; Veroux, P. Prevention of Delayed Graft Function in Kidney Transplant Recipients through a Continuous Infusion of the Prostaglandin Analogue Iloprost: A Single-Center Prospective Study. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsen, R.K.; Kirkeskov, L.; Riis, M.S.; Jacobsen, R.K.; Gronemann, F.H.; Osler, M.; Petersen, J.; Buus, N.H. Employment before and after initiation of dialysis or kidney transplantation- a Danish nationwide registry-based cohort study. BMC Nephrol. 2025, 26, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkeskov, L.; Carlsen, R.K.; Lund, T.; Buus, N.H. Employment of patients with kidney failure treated with dialysis or kidney transplantation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Nephrol. 2024, 22, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knobbe, T.J.; Kremer, D.; Abma, F.I.; Annema, C.; Berger, S.P.; Navis, G.J.; van der Mei, S.F.; Bültmann, U.; Visser, A.; Bakker, S.J.L.; et al. Employment Status and Work Functioning among Kidney Transplant Recipients. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 17, 1506–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, A.; Alma, M.A.; Bakker, S.J.L.; Bemelman, F.J.; Berger, S.P.; van der Boog, P.J.M.; Brouwer, S.; Hilbrands, L.B.; Standaar, D.S.M.; Stewart, R.E.; et al. Employment and ability to work after kidney transplantation in the Netherlands: The impact of preemptive versus non-preemptive kidney transplantation. Clin. Transplant. 2022, 36, e14757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubman-Nowak, M.; Dębska-Ślizień, A.; Renke, M. Employment after renal transplantation vs. the health locus of control and the quality of life. Int. J. Occup. Med. Environ. Health 2022, 35, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Park, J.; Jeong, J.; Jang, Y.; Kim, Y.C.; Kim, D.K.; Oh, K.H.; Joo, K.W.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, H. Changes in socioeconomic status and patient outcomes in kidney transplantation recipients in South Korea. Korean J. Transplant. 2023, 37, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Groups and their Characteristics | Low Educational Status (n = 161) | High Educational Status (n = 295) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Donor | |||
| Age (year) | 54.1 ± 16 | 48.7 ± 19.3 | 0.005 |
| Male sex (%) | 78 (48.7) | 108 (36.4) | 0.013 |
| Terminal serum creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.06 ± 0.3 | 1.20 ± 0.7 | 0.061 |
| Use of vasoactive amines (%) | 155 (96.8) | 275 (92.9) | 0.832 |
| Diabetes (%) | 8 (5) | 15 (5) | 0.343 |
| Cold ischemia time (h) | 16.6 ± 5.1 | 15.2 ± 5.8 | 0.017 |
| Cerebral hemorrhage/ischemia brain death (%) | 122 (76.2) | 185 (62.5) | 0.006 |
| Traumatic brain death (%) | 31 (19.3) | 95 (32.0) | 0.003 |
| Other causes of brain death | 8 (5) | 19 (6.4) | 0.617 |
| Stay in the ICU | 5 ± 3.4 | 5.1 ± 3.9 | 0.824 |
| Recipient | |||
| Age (year) | 52.08 ± 10.9 | 46.6 ± 12.4 | <0.001 |
| Male sex (%) | 94 (58.3) | 194 (65.7) | 0.138 |
| Pre-transplant panel reactive antibody (%) | 24 ± 8.9 | 19 ± 8.5 | 0.774 |
| BMI (mean, kg/m2) | 27.4 | 26.2 | 0.645 |
| Time on dialysis (mo) | 61.9 ± 60 | 41.3 ± 41 | <0.001 |
| Time on waiting list (mo) | 20.6 ± 28 | 18.9 ± 25 | 0.502 |
| Hemodialysis (%) | 159 (98.7) | 279 (94.5) | 0.885 |
| Peritoneal dialysis (%) | 0 (0) | 10 (3.3) | 0.433 |
| Pre-emptive | 1 (1.3) | 7 (2.3) | 0.173 |
| Dual transplant (%) | 16 (10) | 28 (9.4) | 0.883 |
| Delayed graft function (%) | 82 (51.2) | 80 (27.1) | <0.001 |
| Discontinuation of dialysis (dy) | 5.43 ± 3.1 | 3.3 ± 7.1 | 0.002 |
| Primary non-function (%) | 8 (5) | 6(2.5) | 0.733 |
| Acute rejection | 16 (6.7) | 25 (10.5) | 0.122 |
| Immunosuppression | |||
| Induction (basiliximab) | 45 (28.1) | 78 (23.1) | 0.753 |
| Induction (thymoglobuline) | 22 (13.7) | 44 (10) | 0.883 |
| Tacrolimus | 110 (68.5) | 204 (68.9) | 0.214 |
| MMF | 140 (87.5) | 250 (77.7) | 0.301 |
| Sirolimus | 24 (15) | 48 (10.9) | 0.112 |
| Cyclosporine | 25 (15.6) | 59 (23.1) | 0.108 |
| Everolimus | 12 (7.5) | 21 (7.9) | 0.323 |
| Hospital stay | 9.8 ± 3.4 | 10.5 ± 5.1 | 0.242 |
| Postoperative death (30-day) | 3 (1.8) | 4 (1.3) | 0.738 |
| Employed (%) | 52 (32.5) | 195 (66.1) | <0.001 |
| Part-time employed (%) | 2 (1.25) | 11 (3.7) | 0.128 |
| Housewife (%) | 24 (15) | 28 (9.4) | 0.080 |
| Retired (%) | 57 (35.6) | 31 (10.5) | <0.001 |
| Unemployed (%) | 12 (7.5) | 25 (8.4) | 0.702 |
| 1-year serum creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.41 ± 0.77 | 1.46 ± 0.80 | 0.490 |
| 5-year serum creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.66 ± 0.70 | 1.54 ± 0.78 | 0.189 |
| 10-year serum creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.65 ± 0.90 | 1.53 ± 0.78 | 0.367 |
| 1-year eGlomerular Filtration Rate (mL/min per 1.73 m2) | 65 ± 12.4 | 68 ± 9.5 | 0.012 |
| 5-year eGlomerular Filtration Rate (mL/min per 1.73 m2) | 61 ± 11.4 | 63 ± 10.4 | 0.048 |
| 10-year eGlomerular Filtration Rate (mL/min per 1.73 m2) | 58 ± 12.3 | 59 ± 11.8 | 0.633 |
| 1-year patient survival | 94.4% | 97.6% | 0.073 |
| 5-year patient survival | 85% | 92.5% | 0.011 |
| 10-year patient survival | 75.7% | 83.4% | 0.042 |
| 1-year graft survival | 88.1% | 96.2% | 0.0008 |
| 5-year graft survival | 77.6% | 88.8% | 0.001 |
| 10-year graft survival | 62.1% | 75% | 0.003 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leonforte, F.; Veroux, P.; Mistretta, A.; Giaquinta, A.; Giambra, M.M.; Zerbo, D.; Roscitano, G.; De Pasquale, C.; Pistorio, M.L.; D’Anna, A.; et al. Role of Educational Level in Kidney Transplant Outcomes. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 916. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040916
Leonforte F, Veroux P, Mistretta A, Giaquinta A, Giambra MM, Zerbo D, Roscitano G, De Pasquale C, Pistorio ML, D’Anna A, et al. Role of Educational Level in Kidney Transplant Outcomes. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(4):916. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040916
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeonforte, Francesco, Pierfrancesco Veroux, Antonio Mistretta, Alessia Giaquinta, Martina Maria Giambra, Domenico Zerbo, Giuseppe Roscitano, Concetta De Pasquale, Maria Luisa Pistorio, Antonio D’Anna, and et al. 2025. "Role of Educational Level in Kidney Transplant Outcomes" Biomedicines 13, no. 4: 916. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040916
APA StyleLeonforte, F., Veroux, P., Mistretta, A., Giaquinta, A., Giambra, M. M., Zerbo, D., Roscitano, G., De Pasquale, C., Pistorio, M. L., D’Anna, A., Cusmano, C., Granata, R., Riccioli, G., Scribano, M., & Veroux, M. (2025). Role of Educational Level in Kidney Transplant Outcomes. Biomedicines, 13(4), 916. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040916







