Engineered Expression of Hepatocyte Growth Factor Activator Inhibitor-1 (HAI-1) Reduces the Growth of Bladder Cancer Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Antibodies and Reagents
2.2. Cells and Cell Culture
2.3. RNA Extraction
2.4. Real-Time Quantitative PCR
2.5. Protein Extraction and Immunoblot Analysis
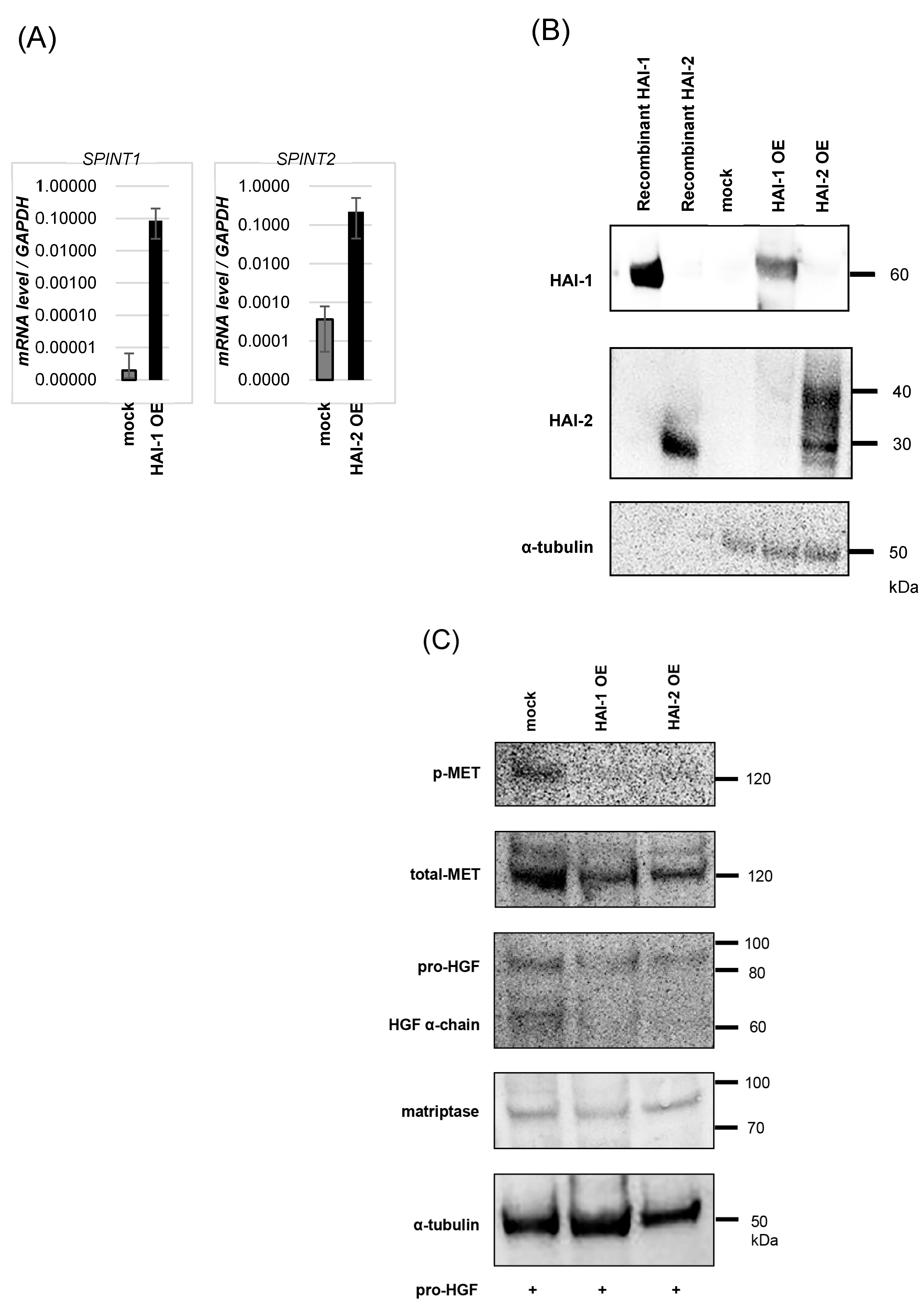
2.6. Establishment of Stably HAIs-Expressed KU-1 Cell Line, HAI-1 OE and HAI-2 OE
2.7. Knockdown of SPINT1 and SPINT2 in T24 Cell Line
2.8. Cell Proliferation Assay
2.9. Wound Healing Assay
2.10. Cell Invasion Assay
2.11. Animal Experiments
2.12. Immunohistochemistry
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
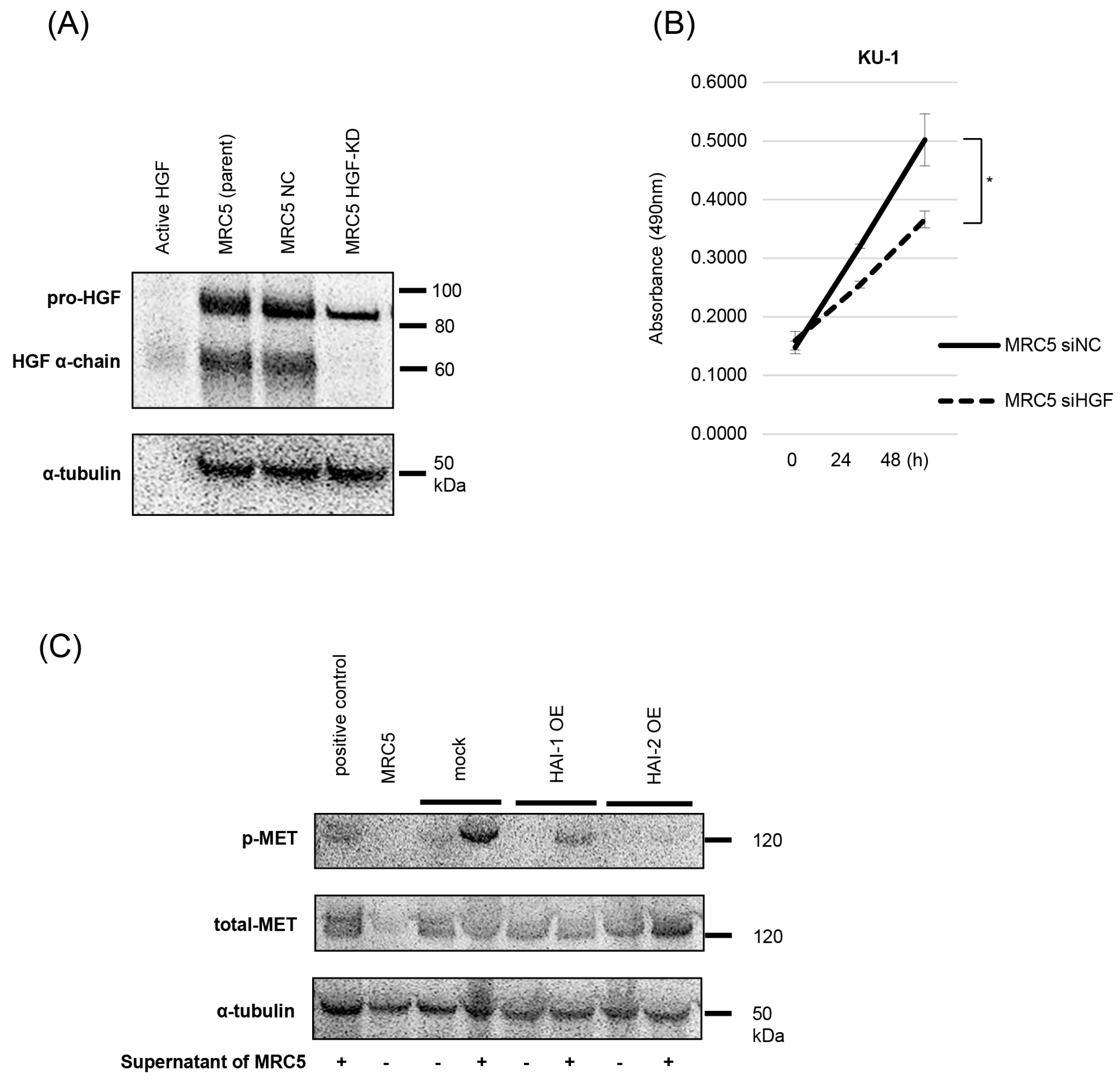
3.2. Inhibition of Pro-HGF Activation by HAIs
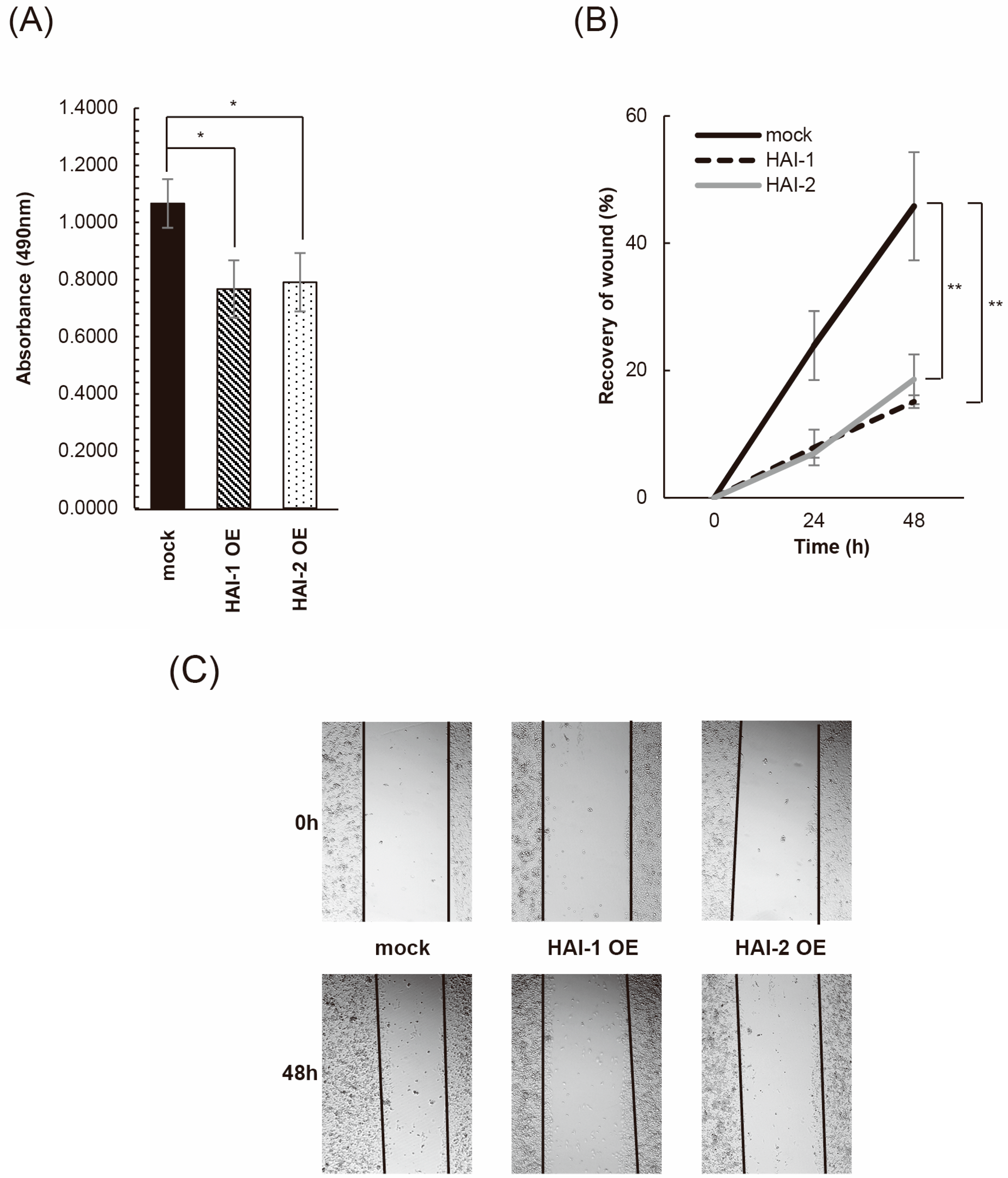
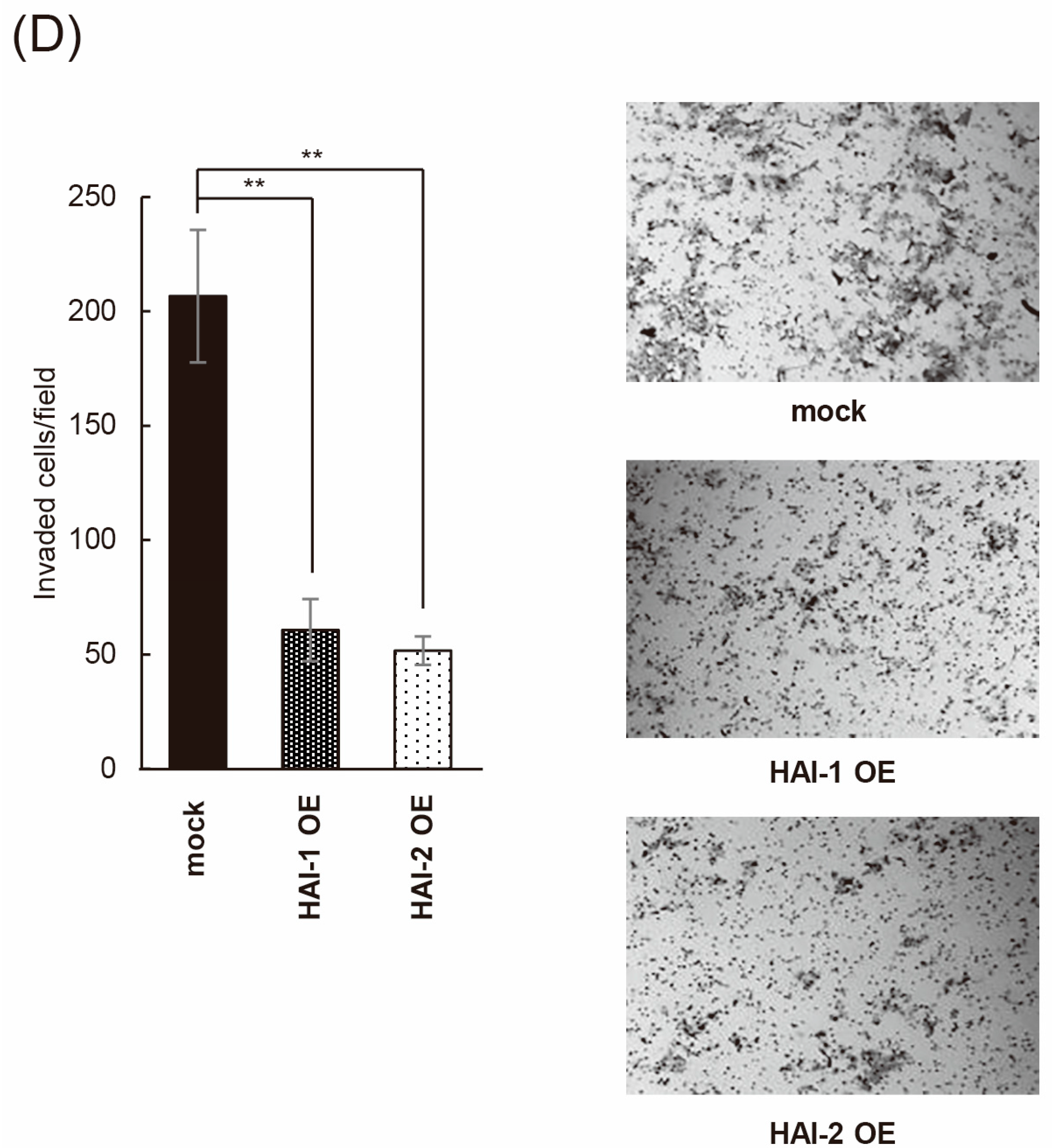
3.3. Inhibition of Bladder Cancer Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion by HAIs
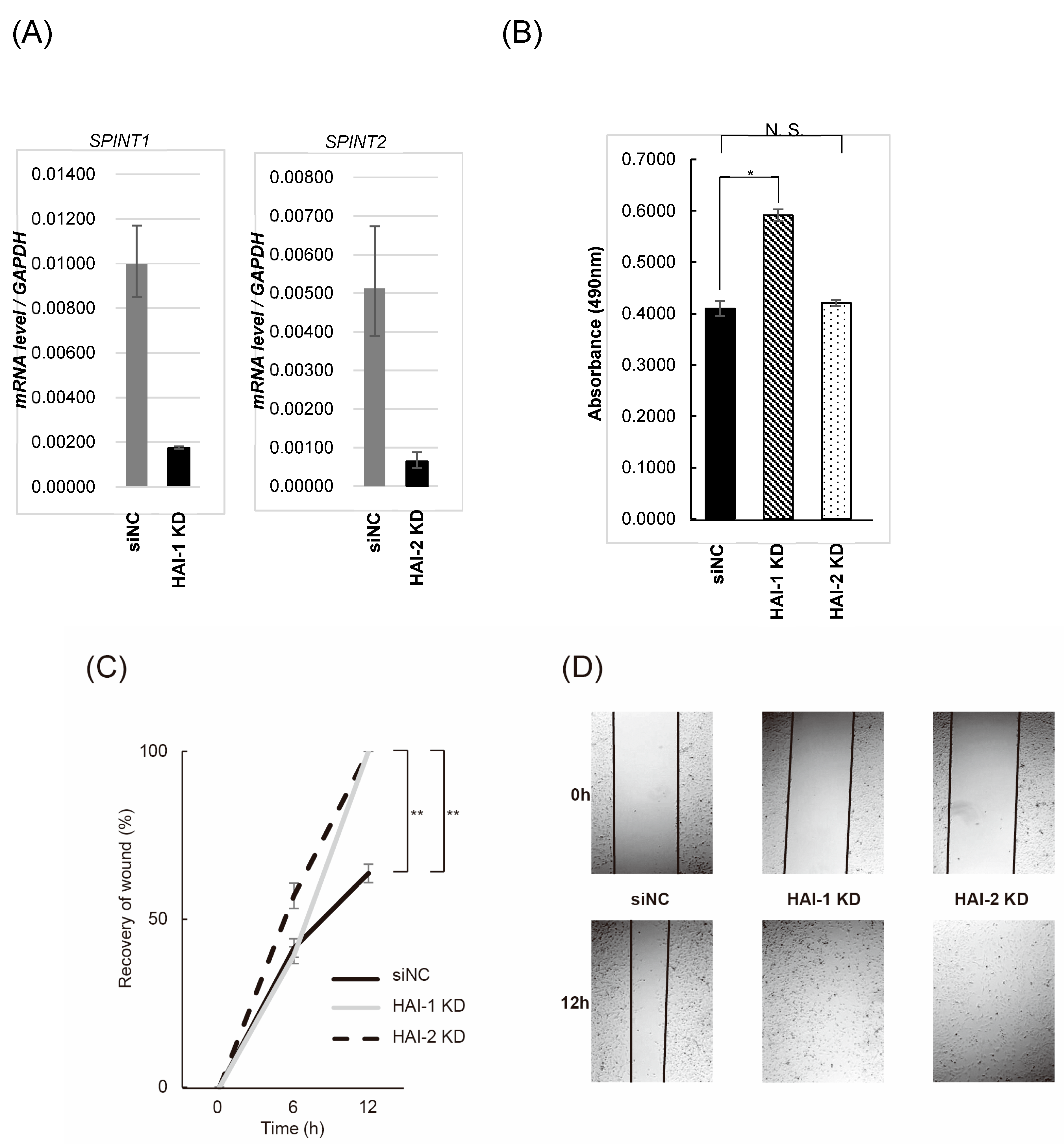
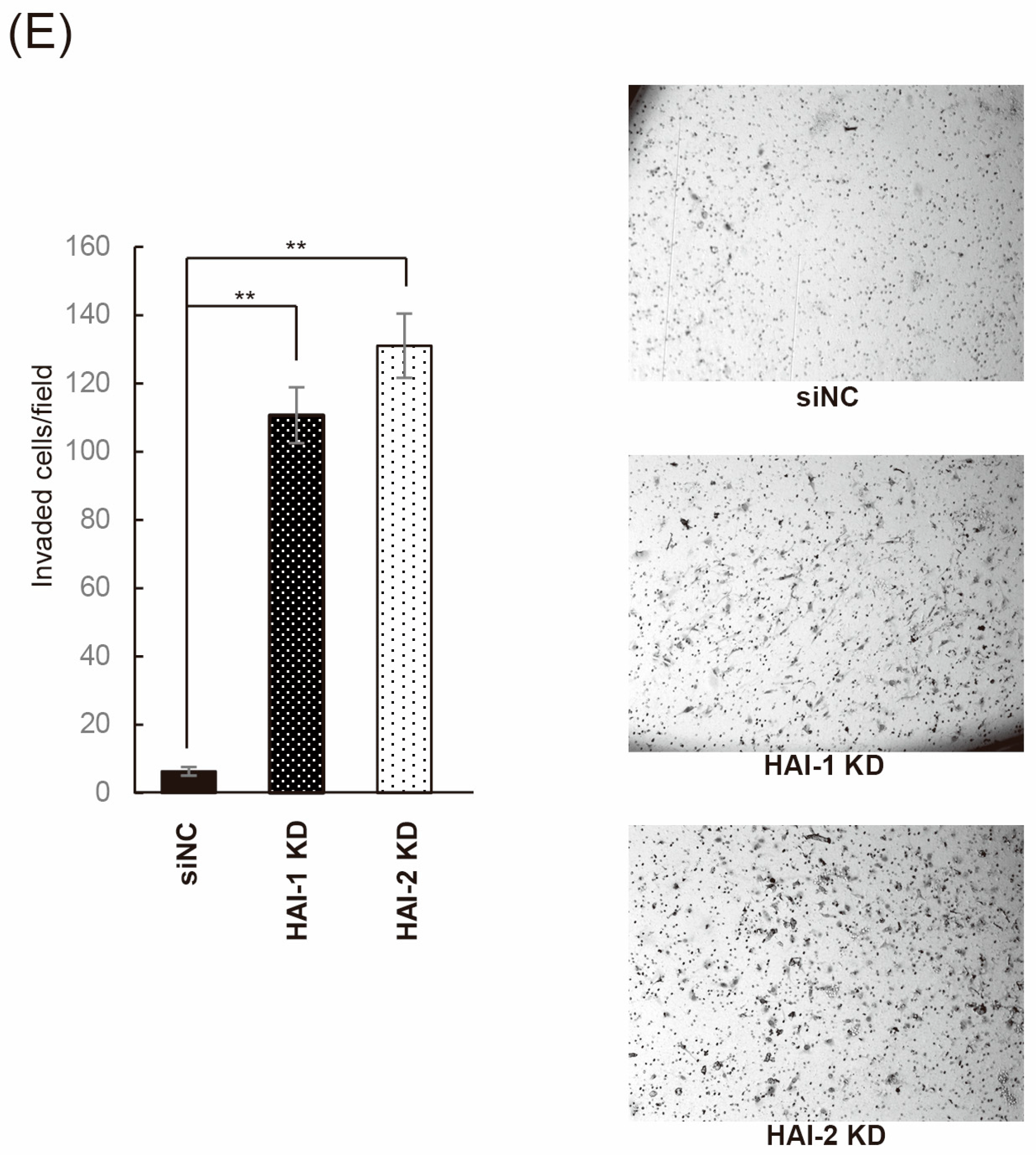
3.4. Effect on Bladder Cancer Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion by Knockdown of HAIs
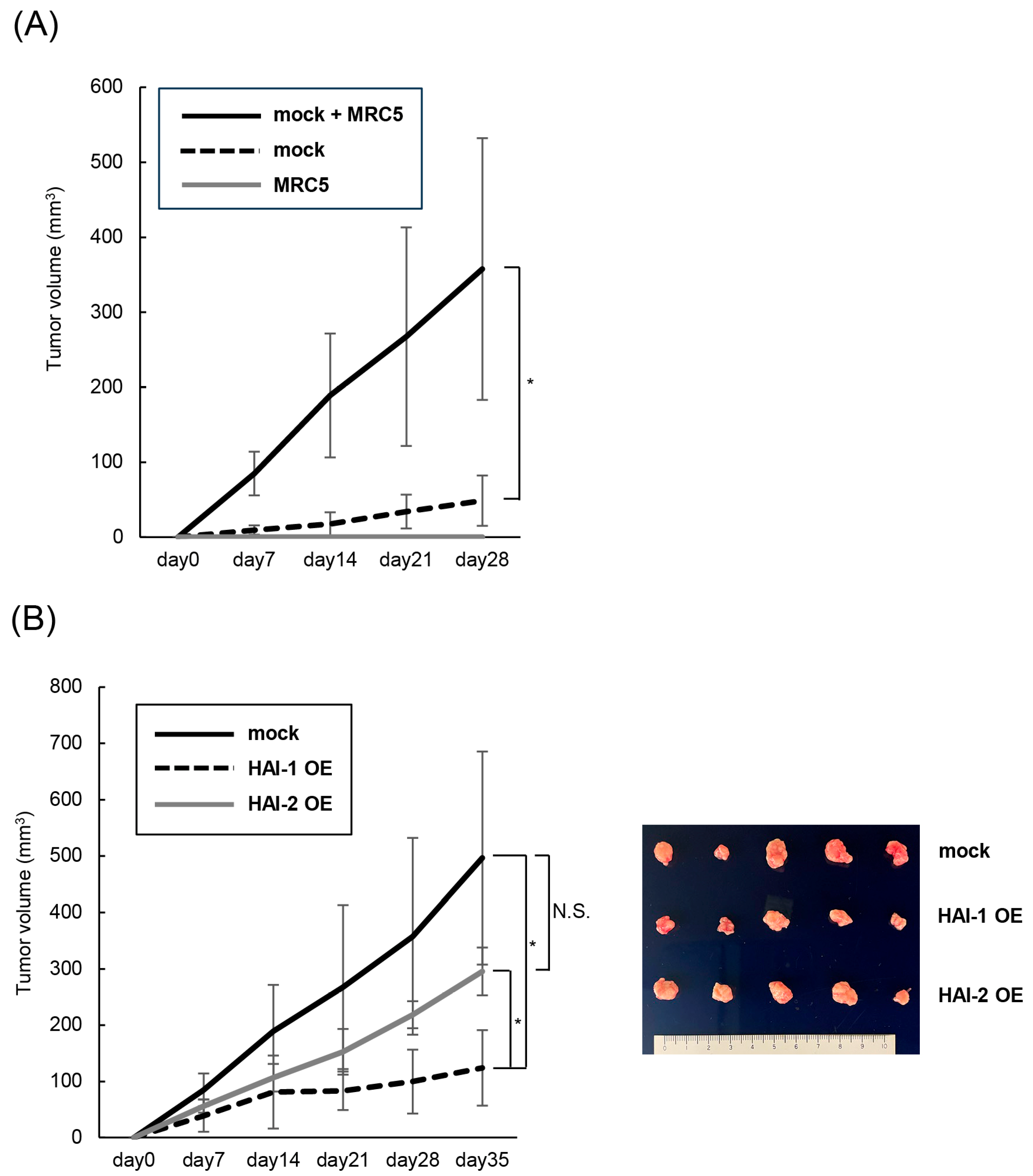
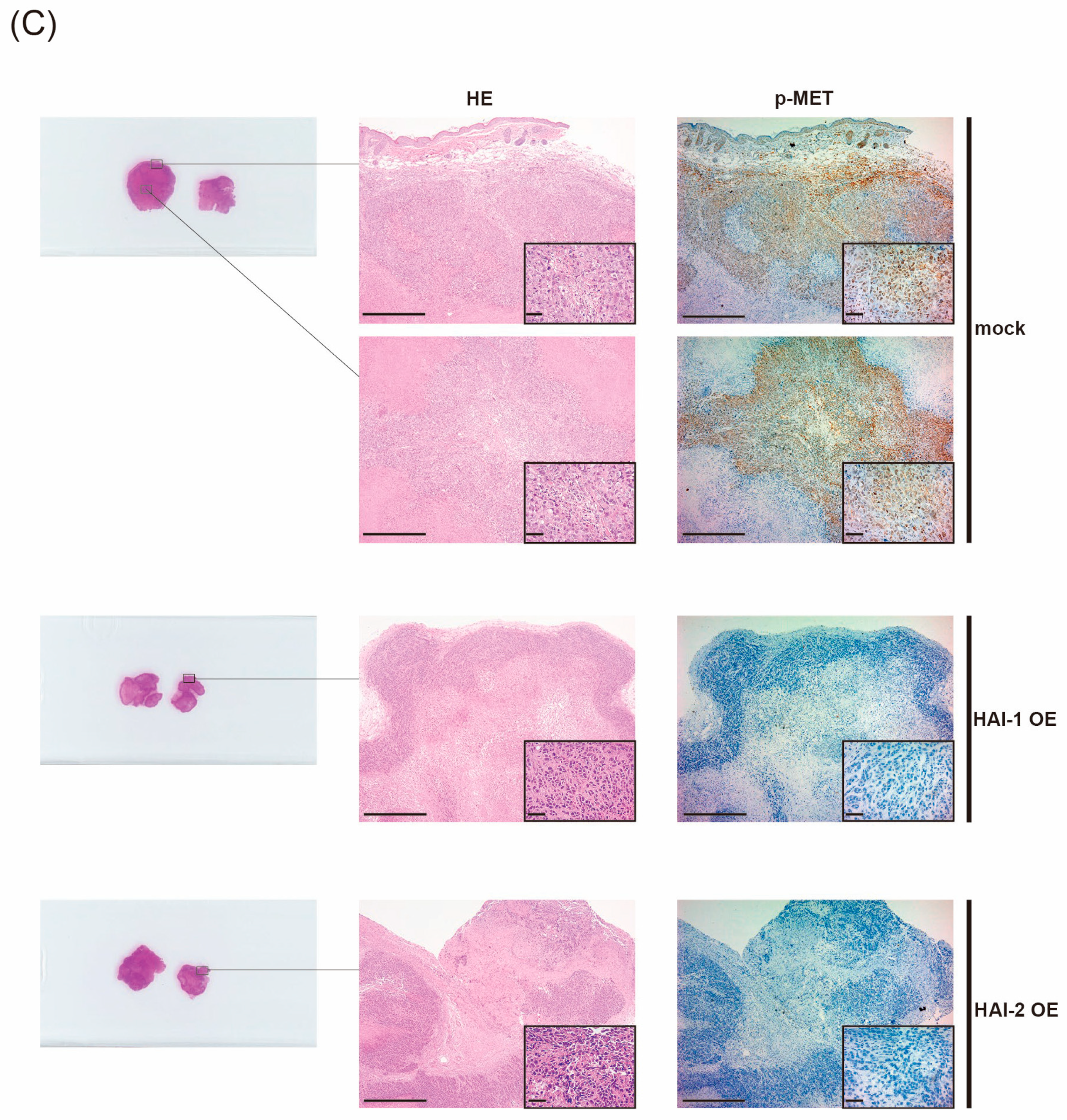
3.5. Therapeutic Effect of HAIs on Growth of Bladder Cancer, In Vivo Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HAI-1 | Hepatocyte growth factor inhibitor type 1 |
| HAI-2 | Hepatocyte growth factor inhibitor type 2 |
| MET | Hepatocyte growth factor receptor |
| HGF | Hepatocyte growth factor |
| Pro-HGF | HGF zymogen |
| MIBC | Muscle-invasive bladder cancer |
| SPINT | HAI coding gene |
| KLK5 | Human kallikrein-related peptidase 5 |
| HPN | Hepsin coding gene |
| ST-14 | Matriptase coding gene |
References
- Jubber, I.; Ong, S.; Bukavina, L.; Black, P.C.; Compérat, E.; Kamat, A.M.; Kiemeney, L.; Lawrentschuk, N.; Lerner, S.P.; Meeks, J.J.; et al. Epidemiology of Bladder Cancer in 2023: A Systematic Review of Risk Factors. Eur. Urol. 2023, 84, 176–190. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stein, J.P.; Lieskovsky, G.; Cote, R.; Groshen, S.; Feng, A.C.; Boyd, S.; Skinner, E.; Bochner, B.; Thangathurai, D.; Mikhail, M.; et al. Radical cystectomy in the treatment of invasive bladder cancer: Long-term results in 1054 patients. J. Clin. Oncol. 2001, 19, 666–675. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dyrskjøt, L.; Hansel, D.E.; Efstathiou, J.A.; Knowles, M.A.; Galsky, M.D.; Teoh, J.; Theodorescu, D. Bladder cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2023, 9, 58. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Powles, T.; Valderrama, B.P.; Gupta, S.; Bedke, J.; Kikuchi, E.; Hoffman-Censits, J.; Iyer, G.; Vulsteke, C.; Park, S.H.; Shin, S.J.; et al. EV-302 Trial Investigators. Enfortumab vedotin and pembrolizumab in untreated advanced urothelial cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 875–888. [Google Scholar]
- Powles, T.; Rosenberg, J.E.; Sonpavde, G.P.; Loriot, Y.; Durán, I.; Lee, J.L.; Matsubara, N.; Vulsteke, C.; Castellano, D.; Wu, C.; et al. Enfortumab vedotin in previously treated advanced urothelial carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1125–1135. [Google Scholar]
- Noriega-Guerra, H.; Freitas, V.M. Extracellular Matrix Influencing HGF/c-MET Signaling Pathway: Impact on Cancer Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukai, S.; Yamasaki, K.; Fujii, M.; Nagai, T.; Terada, N.; Kataoka, H.; Kamoto, T. Dysregulation of Type II Transmembrane Serine Proteases and Ligand-Dependent Activation of MET in Urological Cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, H.; Kawaguchi, M.; Fukushima, T.; Shimomura, T. Hepatocyte growth factor activator inhibitors (HAI-1 and HAI-2): Emerging key players in epithelial integrity and cancer. Pathol. Int. 2018, 68, 145–158. [Google Scholar]
- Gentile, A.; Trusolino, L.; Comoglio, P.M. The Met tyrosine kinase receptor in development and cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2008, 27, 85–94. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, C.E.; List, K. Cell surface-anchored serine proteases in cancer progression and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2019, 38, 357–387. [Google Scholar]
- Kawaguchi, M.; Kataoka, H. Mechanisms of hepatocyte growth factor activation in cancer tissues. Cancers 2014, 29, 1890–1904. [Google Scholar]
- Della Corte, C.M.; Fasano, M.; Papaccio, F.; Ciardiello, F.; Morgillo, F. Role of HGF-MET Signaling in Primary and Acquired Resistance to Targeted Therapies in Cancer. Biomedicines 2014, 2, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, K.; Mukai, S.; Nagai, T.; Nakahara, K.; Fujii, M.; Terada, N.; Ohno, A.; Sato, Y.; Toda, Y.; Kataoka, H.; et al. Matriptase-Induced Phosphorylation of MET is Significantly Associated with Poor Prognosis in Invasive Bladder Cancer; an Immunohistochemical Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roversi, F.M.; Olalla Saad, S.T.; Machado-Neto, J.A. Serine peptidase inhibitor Kunitz type 2 (SPINT2) in cancer development and progression. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 101, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Betsunoh, H.; Mukai, S.; Akiyama, Y.; Fukushima, T.; Minamiguchi, N.; Hasui, Y.; Osada, Y.; Kataoka, H. Clinical relevance of hepsin and hepatocyte growth factor activator inhibitor type 2 expression in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2007, 98, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Morris, M.R.; Gentle, D.; Abdulrahman, M.; Maina, E.N.; Gupta, K.; Banks, R.E.; Wiesener, M.S.; Kishida, T.; Yao, M.; The, B.; et al. Tumor suppressor activity and epigenetic inactivation of hepatocyte growth factor activator inhibitor type 2/SPINT2 in papillary and clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 4598–4606. [Google Scholar]
- Fujii, M.; Akioka, T.; Kimura, S.; Nagai, T.; Kiwaki, T.; Fukushima, T.; Mukai, S.; Kamoto, T. Possible role of combined therapy targeting MET and pro-HGF activation for renal cell carcinoma: Analysis by human HGF-producing SCID mice. Hum. Cell. 2023, 36, 775–785. [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka, H.; Miyata, S.; Uchinokura, S.; Itoh, H. Roles of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) activator and HGF activator inhibitor in the pericellular activation of HGF/scatter factor. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2003, 22, 223–236. [Google Scholar]
- Itoh, H.; Yamauchi, M.; Kataoka, H.; Hamasuna, R.; Kitamura, N.; Koono, M. Genomic structure and chromosomal localization of the human hepatocyte growth factor activator inhibitor type 1 and 2 genes. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 3351–3359. [Google Scholar]
- Saleem, M.; Adhami, V.M.; Zhong, W.; Longley, B.J.; Lin, C.Y.; Dickson, R.B.; Reagan-Shaw, S.; Jarrard, D.F.; Mukhtar, H. A novel biomarker for staging human prostate adenocarcinoma: Overexpression of matriptase with concomitant loss of its inhibitor, hepatocyte growth factor activator inhibitor-1. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2006, 5, 217–227. [Google Scholar]
- Yamauchi, M.; Kataoka, H.; Itoh, H.; Seguchi, T.; Hasui, Y.; Osada, Y. Hepatocyte growth factor activator inhibitor types 1 and 2 are expressed by tubular epithelium in kidney and down-regulated in renal cell carcinoma. J. Urol. 2004, 171, 890–896. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oberst, M.D.; Johnson, M.D.; Dickson, R.B.; Lin, C.Y.; Singh, B.; Stewart, M.; Williams, A.; al-Nafussi, A.; Smyth, J.F.; Gabra, H.; et al. Expression of the serine protease matriptase and its inhibitor HAI-1 in epithelial ovarian cancer: Correlation with clinical outcome and tumor clinicopathological parameters. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002, 8, 1101–1107. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, J.Y.; Dolled-Filhart, M.; Ocal, I.T.; Singh, B.; Lin, C.Y.; Dickson, R.B.; Rimm, D.L.; Camp, R.L. Tissue microarray analysis of hepatocyte growth factor/Met pathway components reveals a role for Met, matriptase, and hepatocyte growth factor activator inhibitor 1 in the progression of node-negative breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 1101–1105. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, K.; Hongo, A.; Kodama, J.; Hiramatsu, Y. The role of hepatocyte growth factor activator inhibitor (HAI)-1 and HAI-2 in endometrial cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 128, 2613–2624. [Google Scholar]
- Mukai, S.; Fukushima, T.; Naka, D.; Tanaka, H.; Osada, Y.; Kataoka, H. Activation of hepatocyte growth factor activator zymogen (pro-HGFA) by human kallikrein 1-related peptidases. FEBS J. 2008, 275, 1003–1017. [Google Scholar]
- Shinoda, Y.; Kozaki, K.; Imoto, I.; Obara, W.; Tsuda, H.; Mizutani, Y.; Shuin, T.; Fujioka, T.; Miki, T.; Inazawa, J. Association of KLK5 overexpression with invasiveness of urinary bladder carcinoma cells. J. Cancer Sci. 2007, 98, 1078–1086. [Google Scholar]
- Shimomura, T.; Denda, K.; Kitamura, A.; Kawaguchi, T.; Kito, M.; Kondo, J.; Kagaya, S.; Qin, L.; Takata, H.; Miyazawa, K.; et al. Hepatocyte growth factor activator inhibitor, a novel Kunitz-type serine protease inhibitor. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 6370–6376. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pereira, M.S.; de Almeida, G.C.; Pinto, F.; Viana-Pereira, M.; Reis, R.M. SPINT2 Deregulation in Prostate Carcinoma. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2016, 64, 32–41. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, C.H.; Teng, C.H.; Tu, Y.T.; Cheng, T.S.; Wu, S.R.; Ko, C.J.; Shyu, H.Y.; Lan, S.W.; Huang, H.P.; Tzeng, S.F.; et al. HAI-2 suppresses the invasive growth and metastasis of prostate cancer through regulation of matriptase. Oncogene 2014, 33, 4643–4652. [Google Scholar]
- Pennacchietti, S.; Cazzanti, M.; Bertotti, A.; Rideout, W.M., 3rd; Han, M.; Gyuris, J.; Perera, T.; Comoglio, P.M. Microenvironment-derived HGF overcomes genetically determined sensitivity to anti-MET drugs. Can. Res. 2014, 74, 6598–6660. [Google Scholar]
- Owusu, B.Y.; Bansal, N.; Venukadasula, P.K.; Ross, L.J.; Messick, T.E.; Goel, S.; Galemmo, R.A.; Klampfer, L. Inhibition of pro-HGF activation by SRI31215, a novel approach to block oncogenic HGF/MET signaling. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 29492–29506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venukadasula, P.K.; Owusu, B.Y.; Bansal, N.; Ross, L.J.; Hobrath, J.V.; Bao, D.; Truss, J.W.; Stackhouse, M.; Messick, T.E.; Klampfer, L.; et al. Design and Synthesis of Nonpeptide Inhibitors of Hepatocyte Growth Factor Activation. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Katayama, Y.; Akioka, T.; Kimura, S.; Fujii, M.; Nagai, T.; Kiwaki, T.; Kawaguchi, M.; Fukushima, T.; Sato, Y.; Mukai, S.; et al. Engineered Expression of Hepatocyte Growth Factor Activator Inhibitor-1 (HAI-1) Reduces the Growth of Bladder Cancer Cells. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 871. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040871
Katayama Y, Akioka T, Kimura S, Fujii M, Nagai T, Kiwaki T, Kawaguchi M, Fukushima T, Sato Y, Mukai S, et al. Engineered Expression of Hepatocyte Growth Factor Activator Inhibitor-1 (HAI-1) Reduces the Growth of Bladder Cancer Cells. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(4):871. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040871
Chicago/Turabian StyleKatayama, Yuichi, Takahiro Akioka, Shoichi Kimura, Masato Fujii, Takahiro Nagai, Takumi Kiwaki, Makiko Kawaguchi, Tsuyoshi Fukushima, Yuichiro Sato, Shoichiro Mukai, and et al. 2025. "Engineered Expression of Hepatocyte Growth Factor Activator Inhibitor-1 (HAI-1) Reduces the Growth of Bladder Cancer Cells" Biomedicines 13, no. 4: 871. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040871
APA StyleKatayama, Y., Akioka, T., Kimura, S., Fujii, M., Nagai, T., Kiwaki, T., Kawaguchi, M., Fukushima, T., Sato, Y., Mukai, S., Kamoto, T., & Sawada, A. (2025). Engineered Expression of Hepatocyte Growth Factor Activator Inhibitor-1 (HAI-1) Reduces the Growth of Bladder Cancer Cells. Biomedicines, 13(4), 871. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040871







