Observational Study of Microbial Colonization and Infection in Neurological Intensive Care Patients Based on Electronic Health Records
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Setting
2.2. Participants
2.3. Ethical Consideration
2.4. Data Collection Procedures
2.5. Microbiology
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Microbiology Results
3.3. Temporal Pathogen Patterns in Respiratory and Urine Samples During the 30-Day Period
3.4. Clinical and Microbiological Characteristics of Patients with and Without Pneumonia and Sepsis
3.5. Respiratory Pathogen Titers and Dynamics in Patients with and Without Pneumonia
3.6. Mono- and Polymicrobial Episodes in Patients with and Without Pneumonia
3.7. Multidrug-Resistant Bacterial Colonization in Patients with and Without Pneumonia and Sepsis
3.8. Antimicrobial Resistance in Pathogens Prioritized by the World Health Organization
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khellaf, A.; Khan, D.Z.; Helmy, A. Recent advances in traumatic brain injury. J. Neurol. 2019, 266, 2878–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olm-Shipman, C.; Moheet, A.M. Quality Improvement in Neurocritical Care. Crit. Care Clin. 2023, 39, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raj, R.; Bendel, S.; Reinikainen, M.; Hoppu, S.; Laitio, R.; Ala-Kokko, T.; Curtze, S.; Skrifvars, M.B. Costs, outcome and cost-effectiveness of neurocritical care: A multi-center observational study. Crit. Care 2018, 22, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Réa-Neto, Á.; Bernardelli, R.S.; De Oliveira, M.C.; David-João, P.G.; Kozesinski-Nakatani, A.C.; Falcão, A.L.E.; Kurtz, P.M.P.; Teive, H.A.G.; Neurocritical Brazil Study Group; Caltabeloti, F.; et al. Epidemiology and Disease Burden of Patients Requiring Neurocritical Care: A Brazilian Multicentre Cohort Study. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 18595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Annual Epidemiological Report for 2019–Healthcare Associated Infections Acquired in Intensive Care Units. In ECDC. Annual Epidemiological Report for 2018; ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Blot, S.; Ruppé, E.; Harbarth, S.; Asehnoune, K.; Poulakou, G.; Luyt, C.E.; Rello, J.; Klompas, M.; Depuydt, P.; Eckmann, C.; et al. Healthcare-associated infections in adult intensive care unit patients: Changes in epidemiology, diagnosis, prevention and contributions of new technologies. Intensive Crit. Care Nurs. 2022, 70, 103227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascia, L.; Sakr, Y.; Pasero, D.; Payen, D.; Reinhart, K.; Vincent, J.L.; Sepsis Occurrence in Acutely Ill Patients (SOAP) Investigators. Extracranial complications in patients with acute brain injury: A post-hoc analysis of the SOAP study. Intensive Care Med. 2008, 34, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, A.S.; Nicholson, J.; Lewis, A. Infection Prevention in the Neurointensive Care Unit: A Systematic Review. Neurocrit. Care 2019, 31, 196–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cefalu, J.E.; Barrier, K.M.; Davis, A.H. Wound Infections in Critical Care. Crit. Care Nurs. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 29, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magill, S.S.; O’Leary, E.; Janelle, S.J.; Thompson, D.L.; Dumyati, G.; Nadle, J.; Wilson, L.E.; Kainer, M.A.; Lynfield, R.; Greissman, S.; et al. Changes in prevalence of health care-associated infections in U.S. Hospitals. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 1732–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Li, H.; Lu, A.; Wu, S.; Lu, H.; Wen, W.; Wang, L.; Yuan, F. Prevalence, early predictors, and outcomes of sepsis in neurocritical illnesses: A prospective cohort study. Am. J. Infect. Control 2024, 52, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konar, S.; Maurya, I.; Shukla, D.P.; Maurya, V.P.; Deivasigamani, B.; Dikshit, P.; Mishra, R.; Agrawal, A. Intensive care unit management of traumatic brain injury patients. J. Neurointensive Care 2022, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, P.J.; Pittet, J.-F.; Kerby, J.D.; Bosarge, P.L.; Wagener, B.M. Acute brain trauma, lung injury, and pneumonia: More than just altered mental status and decreased airway protection. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2017, 313, L1–L115. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Busl, K.M. Healthcare-Associated Infections in the Neurocritical Care Unit. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2019, 19, 76. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Xiao, W.; Song, T.; Wang, S. Incidence, risk Factors, and outcomes of ventilator-associated pneumonia in traumatic brain injury: A meta-analysis. Neurocrit. Care 2020, 32, 272–285. [Google Scholar]
- Esnault, P.; Nguyen, C.; Bordes, J.; D’Aranda, E.; Montcriol, A.; Contargyris, C.; Cotte, J.; Goutorbe, P.; Joubert, C.; Dagain, A.; et al. Early-Onset Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia in Patients with Severe Traumatic Brain Injury: Incidence, Risk Factors, and Consequences in Cerebral Oxygenation and Outcome. Neurocrit. Care 2017, 27, 187–198. [Google Scholar]
- Meisel, C.; Schwab, J.M.; Prass, K.; Meisel, A.; Dirnagl, U. Central nervous system injury-induced immune deficiency syndrome. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2005, 6, 775–786. [Google Scholar]
- Chamorro, Á.; Meisel, A.; Planas, A.M.; Urra, X.; van de Beek, D.; Veltkamp, R. The immunology of acute stroke. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2012, 8, 401–410. [Google Scholar]
- Bansal, V.; Costantini, T.; Kroll, L.; Peterson, C.; Loomis, W.; Eliceiri, B.; Baird, A.; Wolf, P.; Coimbra, R. Traumatic brain injury and intestinal dysfunction: Uncovering the neuro-enteric axis. J. Neurotrauma 2009, 26, 1353–1359. [Google Scholar]
- Stanley, D.; Mason, L.J.; Mackin, K.E.; Srikhanta, Y.N.; Lyras, D.; Prakash, M.D.; Nurgali, K.; Venegas, A.; Hill, M.D.; Moore, R.J.; et al. Translocation and dissemination of commensal bacteria in post-stroke infection. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 1277–1284. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, R.; Shultz, S.R.; Robinson, M.J.; Belli, A.; Hibbs, M.L.; O’Brien, T.J.; Semple, B.D. Infections after a traumatic brain injury: The complex interplay between the immune and neurological systems. Brain Behav. Immun. 2019, 79, 63–74. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, P.; Song, Y.; Du, X.; Bai, L.; Hua, X.; Xiao, Y.; Yu, X. Intestinal barrier dysfunction following traumatic brain injury. Neurol. Sci. 2019, 40, 1105–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selassie, A.W.; Fakhry, S.M.; Ford, D.W. Population-based study of the risk of in-hospital death after traumatic brain injury: The role of sepsis. J. Trauma 2011, 71, 1226–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, D.; Kutsogiannis, D.J.; Sligl, W.I. Sepsis in Traumatic Brain Injury: Epidemiology and Outcomes. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 47, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Bacterial Priority Pathogens List, 2024: Bacterial Pathogens of Public Health Importance, to Guide Research, Development and Strategies to Prevent and Control Antimicrobial Resistance; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024; Available online: https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/376776 (accessed on 6 February 2025).
- Ture, Z.; Güner, R.; Alp, E. Antimicrobial stewardship in the intensive care unit. J. Intensive Med. 2022, 3, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Parejo, Y.; Gonzalez-Rubio, J.; Guerrero, J.G.; Sango, A.G.J.; Escribano, J.M.C.; Najera, A. Risk factors for colonisation by Multidrug-Resistant bacteria in critical care units. Intensive Crit. Care Nurs. 2025, 86, 103760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duhaniuc, A.; Păduraru, D.; Nastase, E.-V.; Trofin, F.; Iancu, L.-S.; Sima, C.-M.; Dorneanu, O.-S. Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria in Immunocompromised Patients. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, J.; Imani, S.; Zhou, A.; Zhao, Y.; Du, L.; Deng, S.; Li, J.; Wang, Q. Combatting resistance: Understanding multi-drug resistant pathogens in intensive care units. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 167, 115564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grechko, A.V.; Yadgarov, M.Y.; Yakovlev, A.A.; Berikashvili, L.B.; Kuzovlev, A.N.; Polyakov, P.A.; Kuznetsov, I.V.; Likhvantsev, V.V. Russian Intensive Care Dataset–RICD. Obs. Reanimatol. 2024, 20, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russian Intensive Care Dataset–RICD. Available online: https://fnkcrr-database.ru/ (accessed on 6 February 2025).
- Christian, M.D.; Hawryluck, L.; Wax, R.S.; Cook, T.; Lazar, N.M.; Herridge, M.S.; Muller, M.P.; Gowans, D.R.; Fortier, W.; Burkle, F.M. Development of a triage protocol for critical care during an influenza pandemic. CMAJ 2006, 175, 1377–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelfand, B.R. Nosocomial Pneumonia in Adults; Russian National Guidelines; MIA: Moscow, Russia, 2016. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Network NHS. Pneumonia (Ventilator-Associated [VAP] and Nonventilator-Associated Pneumonia [PNEU]) Event: Centre for Disease Control (CDC). 2021. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/nhsn/pdfs/pscmanual/6pscvapcurrent.pdf (accessed on 5 February 2025).
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Johnson, A.E.; Pollard, T.J.; Shen, L.; Lehman, L.W.; Feng, M.; Ghassemi, M.; Moody, B.; Szolovits, P.; Celi, L.A.; Mark, R.G. MIMIC-III, a freely accessible critical care database. Sci. Data 2016, 3, 160035. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zhu, Z.; Zhao, C.; Guo, Y.; Chen, D.; Wei, Y.; Jin, J. Central venous pressure measurement is associated with improved outcomes in septic patients: An analysis of the MIMIC-III database. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 433. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; He, Z.; Ren, J.; Wu, Y. Prediction model of in-hospital mortality in intensive care unit patients with cardiac arrest: A retrospective analysis of MIMIC -IV database based on machine learning. BMC Anesthesiol. 2023, 23, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Li, S.; Zheng, T.; Wu, J.; Fan, Y.; Liu, X.; Gong, W.; Xie, H.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; et al. Subphenotyping heterogeneous patients with chronic critical illness to guide individualised fluid balance treatment using machine learning: A retrospective cohort study. EClinicalMedicine 2023, 59, 101970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollard, T.J.; Johnson, A.E.W.; Raffa, J.D.; Celi, L.A.; Mark, R.G.; Badawi, O. The eICU Collaborative Research Database, a freely available multi-center database for critical care research. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180178. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, A.E.W.; Bulgarelli, L.; Shen, L.; Gayles, A.; Shammout, A.; Horng, S.; Pollard, T.J.; Hao, S.; Moody, B.; Gow, B.; et al. MIMIC-IV, a freely accessible electronic health record dataset. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 1. [Google Scholar]
- EUCAST. The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Routine and Extended Internal Quality Control for MIC Determination and Disk Diffusion as Recommended by EUCAST, Version 15.0. 2025. Available online: http://www.eucast.org (accessed on 18 March 2025).
- Kahlmeter, G. Redefining Susceptibility Testing Categories S, I, and R; European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST): Växjö, Sweden, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tay, W.H.; Chong, K.K.; Kline, K.A. Polymicrobial-Host Interactions during Infection. J. Mol. Biol. 2016, 428, 3355–3371. [Google Scholar]
- Bujang, M.A.; Sa’at, N.; Sidik, T.M.I.T.A.B.; Joo, L.C. Sample Size Guidelines for Logistic Regression from Observational Studies with Large Population: Emphasis on the Accuracy Between Statistics and Parameters Based on Real Life Clinical Data. Malays. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 25, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracheva, A.S.; Kashatnikova, D.A.; Redkin, I.V.; Zakharchenko, V.E.; Kuzovlev, A.N.; Salnikova, L.E. Genetics and Traumatic Brain Injury: Findings from an Exome-Based Study of a 50-Patient Case Series. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 10351–10368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polok, K.; Fronczek, J.; Putowski, Z.; Czok, M.; Guidet, B.; Jung, C.; de Lange, D.; Leaver, S.; Moreno, R.; Flatten, H.; et al. Validity of the total SOFA score in patients ≥ 80 years old acutely admitted to intensive care units: A post-hoc analysis of the VIP2 prospective, international cohort study. Ann. Intensive Care 2023, 13, 98. [Google Scholar]
- Pölkki, A.; Pekkarinen, P.T.; Takala, J.; Selander, T.; Reinikainen, M. Association of Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) components with mortality. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2022, 66, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Udekwu, P.; Kromhout-Schiro, S.; Vaslef, S.; Baker, C.; Oller, D. Glasgow Coma Scale score, mortality, and functional outcome in head-injured patients. J. Trauma 2004, 56, 1084–1089. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Armbruster, C.E.; Mobley, H.L.T.; Pearson, M.M. Pathogenesis of Proteus mirabilis Infection. EcoSal. Plus 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palusiak, A. Proteus mirabilis and Klebsiella pneumoniae as pathogens capable of causing co-infections and exhibiting similarities in their virulence factors. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 991657. [Google Scholar]
- Calvo, M.; Stefani, S.; Migliorisi, G. Bacterial Infections in Intensive Care Units: Epidemiological and Microbiological Aspects. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.; Chen, Y.H.; Lu, P.L.; Lin, W.R.; Chen, T.C.; Lin, C.Y. Proteus mirabilis urinary tract infection and bacteremia: Risk factors, clinical presentation, and outcomes. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2012, 45, 228–236. [Google Scholar]
- Abdallah, M.; Balshi, A. First literature review of carbapenem-resistant Providencia. New Microbes New Infect. 2018, 25, 16–23. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, A.D.; Pineles, L.; Belton, B.; Johnson, J.K.; Shardell, M.; Loeb, M.; Newhouse, R.; Dembry, L.; Braun, B.; Perencevich, E.N.; et al. Universal glove and gown use and acquisition of antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the ICU: A randomized trial. JAMA 2013, 310, 1571–1580. [Google Scholar]
- Slekovec, C.; Robert, J.; Berthelot, P.; van der Mee-Marquet, N.; Rogues, A.M.; Derouin, V.; Cholley, P.; Bertrand, X.; Gbaguidi-Haore, H.; DPCPYO Trial Group. Do Contact Precautions Reduce the Incidence of Intensive Care Unit-Acquired Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections? The DPCPYO (Detection and Contact Precautions for Patients with P. aeruginosa) Cluster-Randomized Crossover Trial. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, e2781–e2788. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, L.; Lopes, E.; Kishi, L.; Fraga, L.; Menegueti, M.; Gaspar, G.; Silva-Rocha, R.; Guazzaroni, M. Microbial Community Profiling in Intensive Care Units Expose Limitations in Current Sanitary Standards. Front. Public Health 2019, 7, 240. [Google Scholar]
- D’Souza, A.W.; Potter, R.F.; Wallace, M.; Shupe, A.; Patel, S.; Sun, X.; Gul, D.; Kwon, J.H.; Andleeb, S.; Burnham, C.-A.D.; et al. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Multidrug Resistant Bacteria on Intensive Care Unit Surfaces. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4569. [Google Scholar]
- Chopyk, J.; Akrami, K.; Bavly, T.; Shin, J.H.; Schwanemann, L.K.; Ly, M.; Kalia, R.; Xu, Y.; Kelley, S.T.; Malhotra, A.; et al. Temporal Variations in Bacterial Community Diversity and Composition throughout Intensive Care Unit Renovations. Microbiome 2020, 8, 86. [Google Scholar]
- Sommerstein, R.; Damonti, L.; Marschall, J.; Harbarth, S.; Gasser, M.; Kronenberg, A.; Buetti, N. Distribution of pathogens and antimicrobial resistance in ICU-bloodstream infections during hospitalization: A nationwide surveillance study. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16876. [Google Scholar]
- Torres, A.; Cilloniz, C.; Niederman, M.S.; Menéndez, R.; Chalmers, J.D.; Wunderink, R.G.; van der Poll, T. Pneumonia. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 25. [Google Scholar]
- Kashatnikova, D.A.; Khadzhieva, M.B.; Kolobkov, D.S.; Belopolskaya, O.B.; Smelaya, T.V.; Gracheva, A.S.; Kalinina, E.V.; Larin, S.S.; Kuzovlev, A.N.; Salnikova, L.E. Pneumonia and Related Conditions in Critically Ill Patients—Insights from Basic and Experimental Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Zhang, L. The hierarchy quorum sensing network in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Protein Cell 2015, 6, 26–41. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, N.G.; Nieto, V.; Kroken, A.R.; Jedel, E.; Grosser, M.R.; Hallsten, M.E.; Mettrucio, M.M.E.; Yahr, T.L.; Evans, D.J.; Fleiszig, S.M.J. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Can Diversify after Host Cell Invasion to Establish Multiple Intracellular Niches. mBio 2022, 13, e0274222. [Google Scholar]
- Kreitmann, L.; Helms, J.; Martin-Loeches, I.; Salluh, J.; Poulakou, G.; Pène, F.; Nseir, S. ICU-acquired infections in immunocompromised patients. Intensive Care Med. 2024, 50, 332–349. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, B.M.; Jabra-Rizk, M.A.; O’May, G.A.; Costerton, J.W.; Shirtliff, M.E. Polymicrobial interactions: Impact on pathogenesis and human disease. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 25, 193–213. [Google Scholar]
- Korgaonkar, A.; Trivedi, U.; Rumbaugh, K.P.; Whiteley, M. Community surveillance enhances Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence during polymicrobial infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 1059–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, M.; Difrancesco, L.F.; Liapikou, A.; Rinaudo, M.; Carbonara, M.; Li Bassi, G.; Gabarrus, A.; Torres, A. Polymicrobial intensive care unit-acquired pneumonia: Prevalence, microbiology and outcome. Crit. Care 2015, 19, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cillóniz, C.; Civljak, R.; Nicolini, A.; Torres, A. Polymicrobial community-acquired pneumonia: An emerging entity. Respirology 2016, 21, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vos, M.G.; Zagorski, M.; McNally, A.; Bollenbach, T. Interaction Networks, Ecological Stability, and Collective Antibiotic Tolerance in Polymicrobial Infections. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 10666–10671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, K.R.; Bell, T. Competition, not cooperation, dominates interactions among culturable microbial species. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, 1845–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Mohler, J.; Mahajan, S.D.; Schwartz, S.A.; Bruggemann, L.; Aalinkeel, R. Microbial Biofilm: A Review on Formation, Infection, Antibiotic Resistance, Control Measures, and Innovative Treatment. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiq, F.A.; Burmølle, M.; Heyndrickx, M.; Flint, S.; Lu, W.; Chen, W.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H. Community-wide changes reflecting bacterial interspecific interactions in multispecies biofilms. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 47, 338–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDaniel, M.S.; Lindgren, N.R.; Billiot, C.E.; Valladares, K.N.; Sumpter, N.A.; Swords, W.E. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Promotes Persistence of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia via Increased Adherence to Depolarized Respiratory Epithelium. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0384622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darch, S.E.; West, S.A.; Winzer, K.; Diggle, S.P. Density-dependent fitness benefits in quorum-sensing bacterial populations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 8259–8263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendueles, O.; Ghigo, J.M. Mechanisms of Competition in Biofilm Communities. Microbiol. Spectr. 2015, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
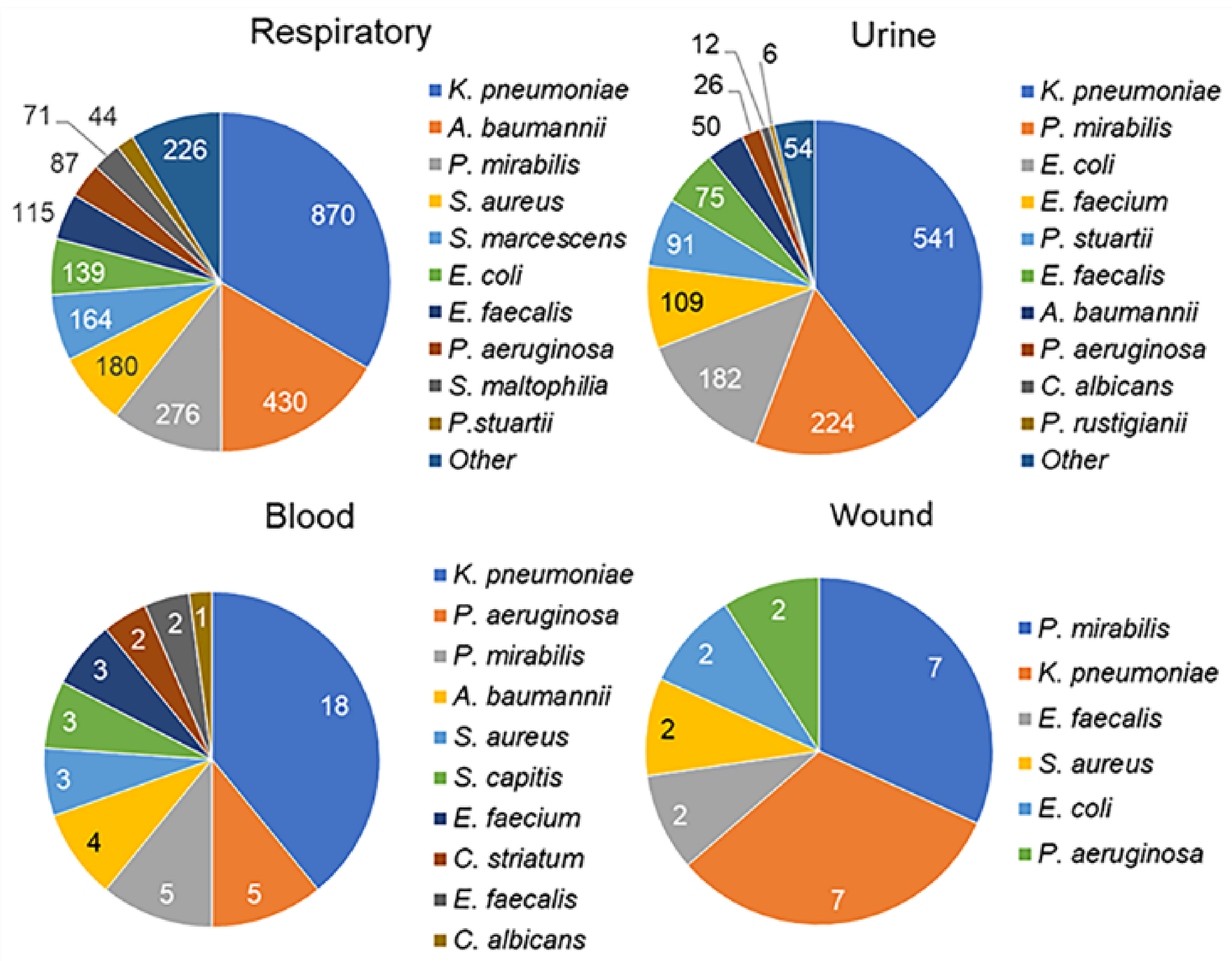


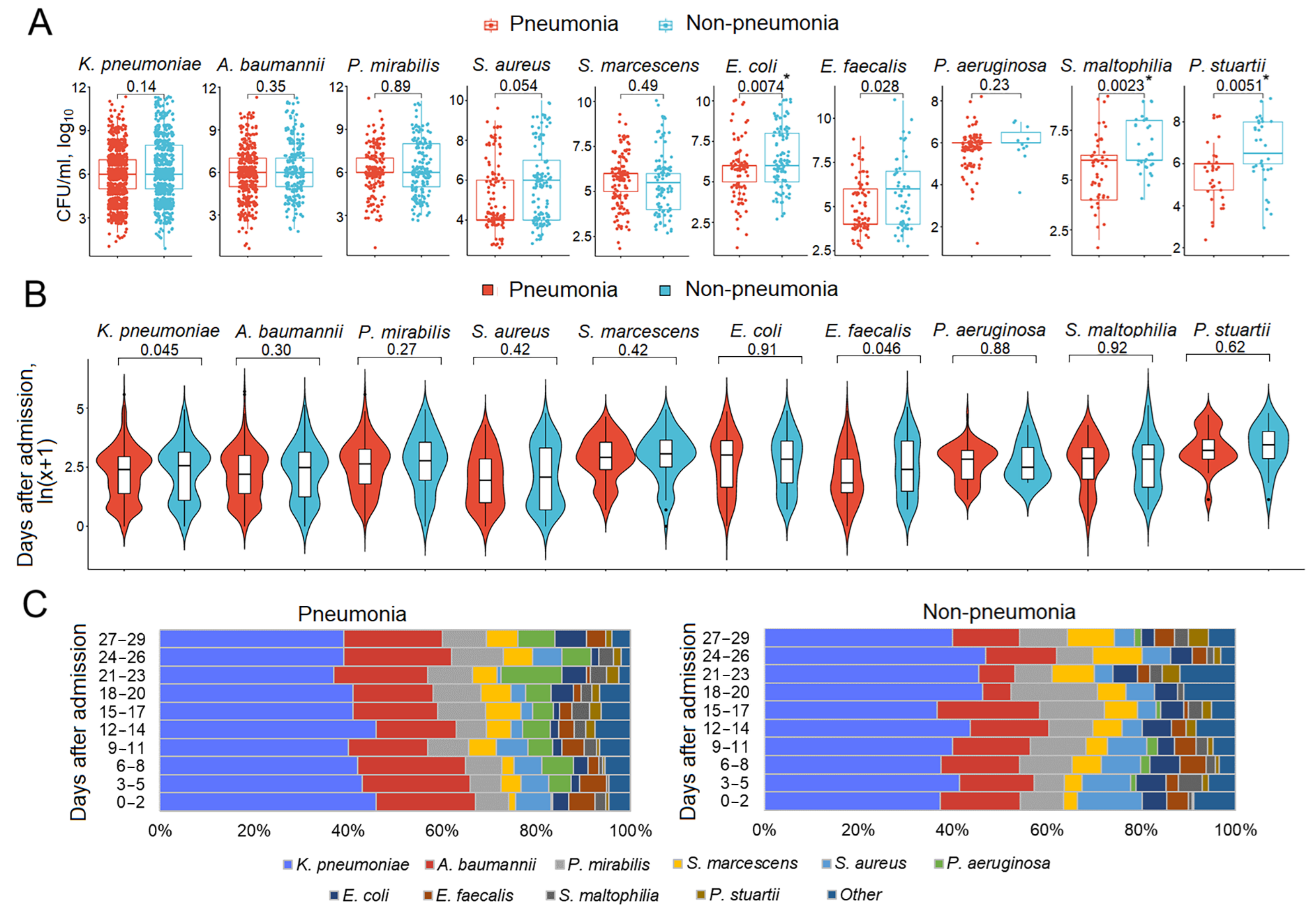



| Characteristics | n | % or Me (IQR) |
|---|---|---|
| General information | ||
| Male | 919 | 56.94 |
| Age | 1614 | 61 (47–72) |
| Transfer patients | 1487 | 92.13 |
| Admission department—ICU | 1577 | 97.71 |
| Sequential Organ Failure Assessment, SOFA (0–24) * | 1327 | 3 (2–5) |
| Glasgow coma scale, GCS (15–3) * | 1355 | 11 (8–14) |
| Primary disease | ||
| Intracerebral hemorrhage | 294 | 18.22 |
| Cerebral infarction | 681 | 42.19 |
| Intracranial injury | 267 | 16.54 |
| Other ** | 372 | 23.05 |
| Complications of primary disease | ||
| Mental disorder due to brain damage | 316 | 19.58 |
| Cerebral edema | 286 | 17.72 |
| Retinopathy and retinal vascular changes | 320 | 19.83 |
| Dysphagia | 142 | 8.80 |
| Tracheostomy | 585 | 36.25 |
| Flaccid neuropathic bladder | 420 | 26.02 |
| Anemia | 188 | 11.65 |
| Decubitus ulcer | 197 | 12.21 |
| Encephalopathy | 118 | 7.31 |
| Concurrent diseases | ||
| Hypertensive heart disease without heart failure, HHD without HF | 672 | 41.64 |
| Hypertensive heart disease with heart failure, HHD with HF | 285 | 17.66 |
| Atherosclerotic heart disease | 169 | 10.47 |
| Type 2 diabetes mellitus | 76 | 4.71 |
| Obesity (≥30 kg/m2) | 253 | 15.68 |
| Per-patient microbiology data | ||
| Positive culture | 1545 | 95.72 |
| Respiratory | 1244 | 80.52 |
| Urine | 966 | 62.52 |
| Blood | 44 | 2.85 |
| Eye, Ear, Nose, and Throat | 16 | 1.04 |
| Cerebrospinal fluid, CSF | 2 | 0.13 |
| Wound | 13 | 0.84 |
| Other | 8 | 0.52 |
| Hospital course | ||
| Pneumonia | 879 | 54.46 |
| Urinary tract infection (ICD-10: N39.0) | 36 | 2.23 |
| Sepsis/Septic shock | 54 | 3.35 |
| Death | 243 | 15.06 |
| Discharge department: ICU | 1035 | 64.13 |
| Discharge department: Neurorehabilitation | 285 | 17.66 |
| Discharge department: Palliative psychiatric ward | 294 | 18.22 |
| ICU stay, days *** | 998 | 25 (21–48) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gracheva, A.S.; Kuzovlev, A.N.; Salnikova, L.E. Observational Study of Microbial Colonization and Infection in Neurological Intensive Care Patients Based on Electronic Health Records. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 858. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040858
Gracheva AS, Kuzovlev AN, Salnikova LE. Observational Study of Microbial Colonization and Infection in Neurological Intensive Care Patients Based on Electronic Health Records. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(4):858. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040858
Chicago/Turabian StyleGracheva, Alesya S., Artem N. Kuzovlev, and Lyubov E. Salnikova. 2025. "Observational Study of Microbial Colonization and Infection in Neurological Intensive Care Patients Based on Electronic Health Records" Biomedicines 13, no. 4: 858. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040858
APA StyleGracheva, A. S., Kuzovlev, A. N., & Salnikova, L. E. (2025). Observational Study of Microbial Colonization and Infection in Neurological Intensive Care Patients Based on Electronic Health Records. Biomedicines, 13(4), 858. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040858






