Plasma Metabolic Profiles of Chronic and Recurrent Uveitis Treated by Artesunate in Lewis Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Animals
2.2. Animal Model of EAU and Drug Treatment
2.2.1. Induction of Antigen-Induced Uveitis (aEAU)
2.2.2. Induction of Adoptive tEAU and Drug Treatment
2.3. Clinical Evaluation
2.4. Histological Examinations
2.5. Plasma Untargeted Metabolomics Analysis
2.5.1. Collection of Plasma Samples
2.5.2. Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography (UHPLC)–Quadrupole Time-of-Fight (TOF) Mass Spectrometry (UHPLC-MS/MS) Analysis
2.6. Metabolomics Data Processing
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Alleviated Clinical Appearance of tEAU After ART Treatment
3.2. Reduced Histopathological Lesions of tEAU After ART Treatment
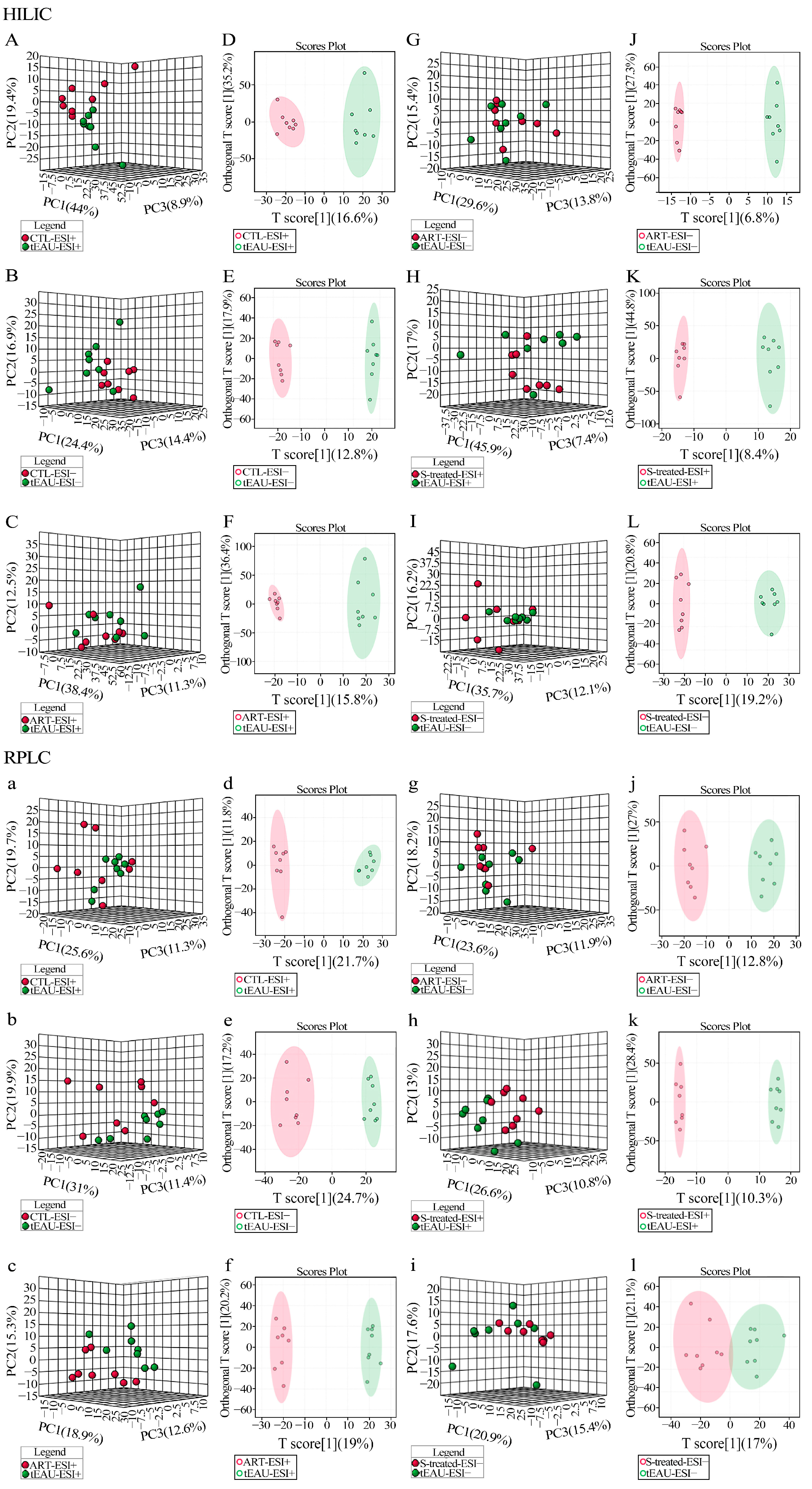
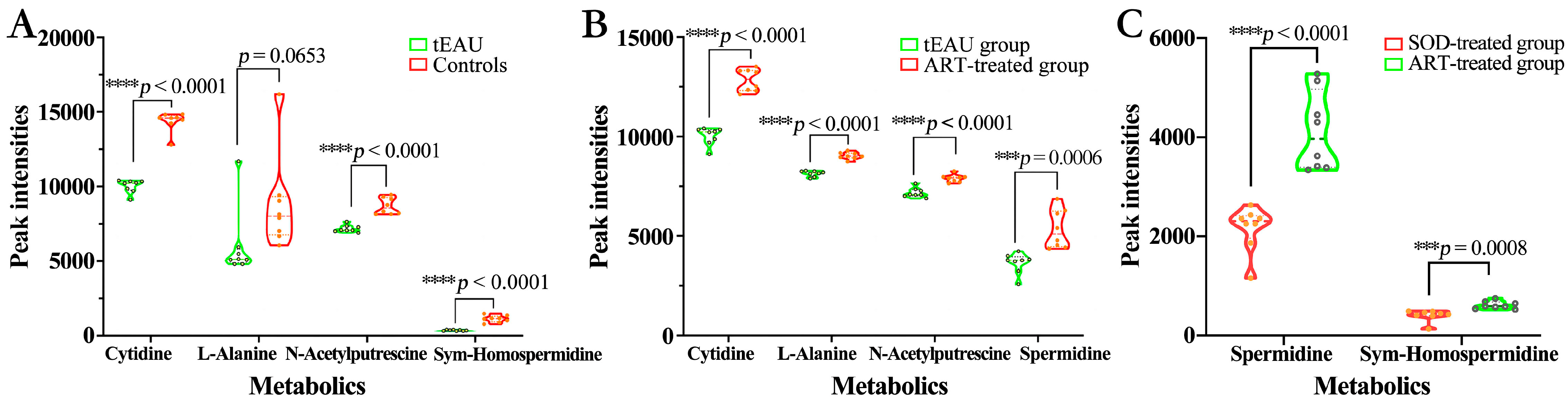
3.3. Altered Plasma Metabolomic Profiles After ART Treatment
Altered Metabolomic Profiles of Plasma in the tEAU Rat Model After ART Treatment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ART | Artesunate |
| EAU | Experimental autoimmune uveitis |
| IRBP | Inter-photoreceptor retinoid-binding protein |
| tEAU | Recurrent uveitis induced by IRBP R16 peptide-specific T-cells |
| SPF | Specific-pathogen-free |
| aEAU | Induction of antigen-induced uveitis |
| CFA | Complete Freund’s Adjuvant |
| APCs | Antigen-presenting cells |
| SOD | Sodium bicarbonate |
| QC | Quality control |
| UHPLC | Ultra-high performance liquid chromatography |
| TOF | Time-of-fight |
| MS | Mass spectrometry |
| PCA | Non-supervised principal component analysis |
| OPLS-DA | Orthogonal partial least-squares discriminant analysis |
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| VKH | Vogt–Koyanagi–Harada |
| BD | Behçet’s disease |
| CTL | Healthy control group |
References
- Caspi, R.R. A Look at Autoimmunity and Inflammation in the Eye. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 3073–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forrester, J.V.; Kuffova, L.; Dick, A.D. Autoimmunity, Autoinflammation, and Infection in Uveitis. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 189, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenthal, P.J. Artesunate for the Treatment of Severe Falciparum Malaria. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 1829–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, W.-Z.; Li, H.; Jiang, B.; Nandakumar, K.S.; Liu, K.-F.; Liu, L.-X.; Yu, X.-C.; Tan, H.-J.; Zhou, C. Therapeutic Effects of Artesunate on Lupus-Prone MRL/Lpr Mice Are Dependent on T Follicular Helper Cell Differentiation and Activation of JAK2-STAT3 Signaling Pathway. Phytomedicine 2019, 62, 152965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomé, R.; de Carvalho, A.C.; Alves da Costa, T.; Ishikawa, L.L.W.; de Campos Fraga-Silva, T.F.; Sartori, A.; de Oliveira, A.L.R.; Verinaud, L. Artesunate Ameliorates Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis by Inhibiting Leukocyte Migration to the Central Nervous System. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2016, 22, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, C.; Chen, G.; Shen, W.; Li, C.; Lin, W.; Lin, S.; Huang, H.; et al. Inhibitory Effect of the Antimalarial Agent Artesunate on Collagen-Induced Arthritis in Rats through Nuclear Factor Kappa B and Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling Pathway. Transl. Res. 2013, 161, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-X.; Zhang, X.-Q.; Yu, C.-G.; Huang, S.-L.; Xie, Y.; Dou, X.-T.; Liu, W.-J.; Zou, X.-P. Artesunate Exerts Protective Effects against Ulcerative Colitis via Suppressing Toll-like Receptor 4 and Its Downstream Nuclear factor-κB Signaling Pathways. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 20, 1321–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Feng, X.; Wen, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, B.; Hu, J.; Lu, L.; Zhuo, Y.; Fu, Y.; Qian, X.; et al. A Pilot Clinical Study of Intravitreal Injection of Artesunate for Ocular Neovascularization. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 35, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-Q.; Liu, H.-L.; Wang, G.-B.; Wu, P.-F.; Yan, T.; Xie, J.; Tang, Y.; Sun, L.-K.; Li, C. Effect of Artesunate on Endotoxin-Induced Uveitis in Rats. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 916–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percie du Sert, N.; Hurst, V.; Ahluwalia, A.; Alam, S.; Avey, M.T.; Baker, M.; Browne, W.J.; Clark, A.; Cuthill, I.C.; Dirnagl, U.; et al. The ARRIVE Guidelines 2.0: Updated Guidelines for Reporting Animal Research. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caspi, R.R. Experimental Autoimmune Uveoretinitis in the Rat and Mouse. Curr. Protoc. Immunol. 2003, 15, 15.6.1–15.6.20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkholder, B.M.; Jabs, D.A. Uveitis for the Non-Ophthalmologist. BMJ 2021, 372, m4979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Hong, X.; Lin, D.; Luo, X.; Zhu, M.; Mo, H. Artesunate Influences Th17/Treg Lymphocyte Balance by Modulating Treg Apoptosis and Th17 Proliferation in a Murine Model of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 13, 2267–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.-D.; Jing, J.; Wang, J.-W.; Yan, T.; Li, Q.-H.; Mo, Y.-Q.; Zheng, D.-H.; Gao, J.-L.; Nguyen, K.-A.; Dai, L. A Novel Function of Artesunate on Inhibiting Migration and Invasion of Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes from Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2019, 21, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Su, G.; Huang, X.; Chang, R.; Chen, Z.; Ye, Z.; Cao, Q.; Kijlstra, A.; Yang, P. Metabolomic Analysis of Aqueous Humor Identifies Aberrant Amino Acid and Fatty Acid Metabolism in Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada and Behcet’s Disease. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 587393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Li, M.; Su, Y.; Du, Y.; Wu, X.; Chen, X.; Song, Y.; Lai, L.; Cheng, H. Integrated Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Analyses of DNCB-Induced Atopic Dermatitis in Mice. Life Sci. 2023, 317, 121474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, B.; Pearce, E.L. Amino Assets: How Amino Acids Support Immunity. Cell Metab. 2020, 32, 154–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Tang, L.; Wang, J.-S. Assessment of the Adverse Impacts of Aflatoxin B1 on Gut-Microbiota Dependent Metabolism in F344 Rats. Chemosphere 2019, 217, 618–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheppard, K.; Yuan, J.; Hohn, M.J.; Jester, B.; Devine, K.M.; Söll, D. From One Amino Acid to Another: tRNA-Dependent Amino Acid Biosynthesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 1813–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, P.; Fox, P.L. Aminoacyl-tRNA Synthetases in Medicine and Disease. EMBO Mol. Med. 2013, 5, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.L.M.; Vitório, J.G.; de Paiva, M.J.N.; Porto, B.L.S.; Guimarães, H.C.; Canuto, G.A.B.; das Graças Carvalho, M.; de Souza, L.C.; de Toledo, J.S.; Caramelli, P.; et al. Frontotemporal Dementia: Plasma Metabolomic Signature Using Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 189, 113424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yin, X.; Wang, H.; Wu, X.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Fu, C.; Li, H.; Qiu, Y. Fecal Metabolomics and Potential Biomarkers for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, M.W.; Ilnytskyy, Y.; Golubov, A.; Metz, L.M.; Yong, V.W.; Kovalchuk, O. Global Transcriptome Profiling of Mild Relapsing-Remitting versus Primary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis. Eur. J. Neurol. 2018, 25, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ron-Harel, N.; Ghergurovich, J.M.; Notarangelo, G.; LaFleur, M.W.; Tsubosaka, Y.; Sharpe, A.H.; Rabinowitz, J.D.; Haigis, M.C. T Cell Activation Depends on Extracellular Alanine. Cell Rep. 2019, 28, 3011–3021.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trayhurn, P.; Van Heyningen, R. The Metabolism of Glutamate, Aspartate and Alanine in the Bovine Lens. Biochem. J. 1971, 124, 72P–73P. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitzer, L. Biosynthesis of Glutamate, Aspartate, Asparagine, L-Alanine, and D-Alanine. EcoSal Plus 2004, 1, 10-128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Kim, J.-H.; Hwangbo, H.; Kim, S.Y.; Ji, S.Y.; Kim, M.Y.; Cha, H.-J.; Park, C.; Hong, S.H.; Kim, G.-Y.; et al. Spermidine Attenuates Oxidative Stress-Induced Apoptosis via Blocking Ca2+ Overload in Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells Independently of ROS. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carriche, G.M.; Almeida, L.; Stüve, P.; Velasquez, L.; Dhillon-LaBrooy, A.; Roy, U.; Lindenberg, M.; Strowig, T.; Plaza-Sirvent, C.; Schmitz, I.; et al. Regulating T-Cell Differentiation through the Polyamine Spermidine. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 147, 335–348.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Ding, H.; Yu, X.; Meng, Y.; Li, J.; Guo, Q.; Zhou, H.; Shen, N. Spermidine Suppresses Inflammatory DC Function by Activating the FOXO3 Pathway and Counteracts Autoimmunity. iScience 2020, 23, 100807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Zheng, C.; Cao, J.; Cao, G.; Shou, P.; Lin, L.; Velletri, T.; Jiang, M.; Chen, Q.; Han, Y.; et al. Spermidine Alleviates Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis through Inducing Inhibitory Macrophages. Cell Death Differ. 2016, 23, 1850–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahalingam, S.S.; Pandiyan, P. Polyamines: Key Players in Immunometabolism and Immune Regulation. J. Cell Immunol. 2024, 6, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, M.; Lopata, A.L.; Dasouki, M.; Abdel Rahman, A.M. Metabolomics toward Personalized Medicine. Mass. Spectrom. Rev. 2019, 38, 221–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, J.; Bansback, N.; Barber, C.; Wells, G.; Hazlewood, G. Personalized Medicine in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Combining Biomarkers and Patient Preferences to Guide Therapeutic Decisions. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2022, 36, 101812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gong, X.; Fan, J.; Huang, H.; Xu, F.; Hu, K.; Liu, J.; Tan, Y.; Chen, F. Plasma Metabolic Profiles of Chronic and Recurrent Uveitis Treated by Artesunate in Lewis Rats. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 821. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040821
Gong X, Fan J, Huang H, Xu F, Hu K, Liu J, Tan Y, Chen F. Plasma Metabolic Profiles of Chronic and Recurrent Uveitis Treated by Artesunate in Lewis Rats. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(4):821. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040821
Chicago/Turabian StyleGong, Xinyi, Jingchuan Fan, Hui Huang, Fei Xu, Kaijiao Hu, Jianping Liu, Yi Tan, and Feilan Chen. 2025. "Plasma Metabolic Profiles of Chronic and Recurrent Uveitis Treated by Artesunate in Lewis Rats" Biomedicines 13, no. 4: 821. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040821
APA StyleGong, X., Fan, J., Huang, H., Xu, F., Hu, K., Liu, J., Tan, Y., & Chen, F. (2025). Plasma Metabolic Profiles of Chronic and Recurrent Uveitis Treated by Artesunate in Lewis Rats. Biomedicines, 13(4), 821. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040821



