Phosphorylation of MET Is Upregulated in Metastatic Sites of Renal Cell Carcinoma: Possible Role of MET and Hepatocyte Growth Factor Activation-Targeted Combined Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinicopathological Study Cohort
2.2. Antibodies and Reagents
2.3. Cell Culture
2.4. RNA Extraction
2.5. Real-Time Quantitative PCR
2.6. Protein Extraction and Immunoblot Analysis
2.7. Cell Proliferation Assay: Dual Inhibition by MET-I and HGFA-I
2.8. Wound-Healing Assay: Dual Inhibition by MET-I and HGFA-I
2.9. Immunohistochemistry and Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
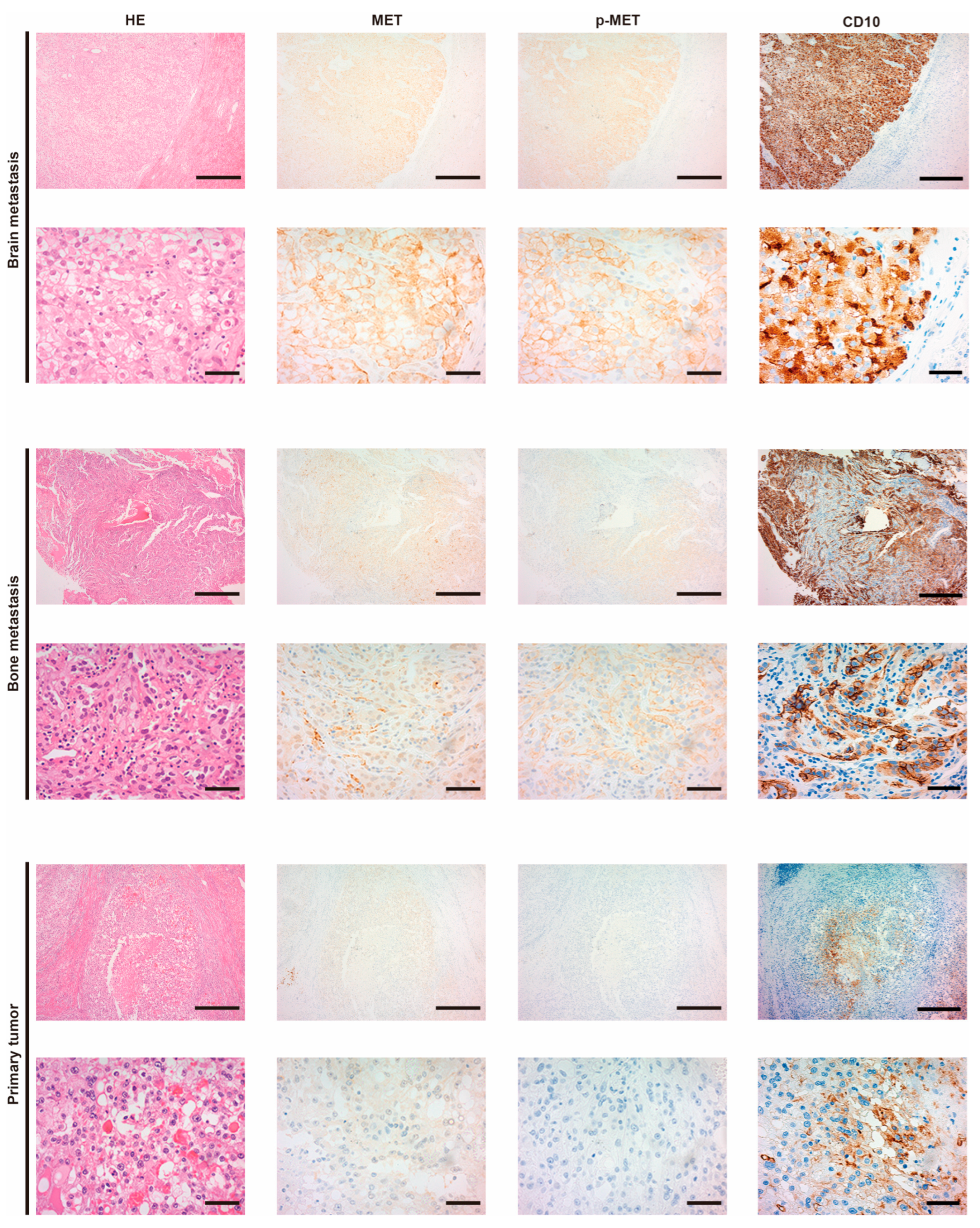
3.1. Expression of MET and the Phosphorylation in Metastatic RCC
3.2. Expression of HGF/MET Signaling-Related Molecules in RCC Cell Lines
3.3. Inhibition of MET Phosphorylation by MET-I and HGFA-I
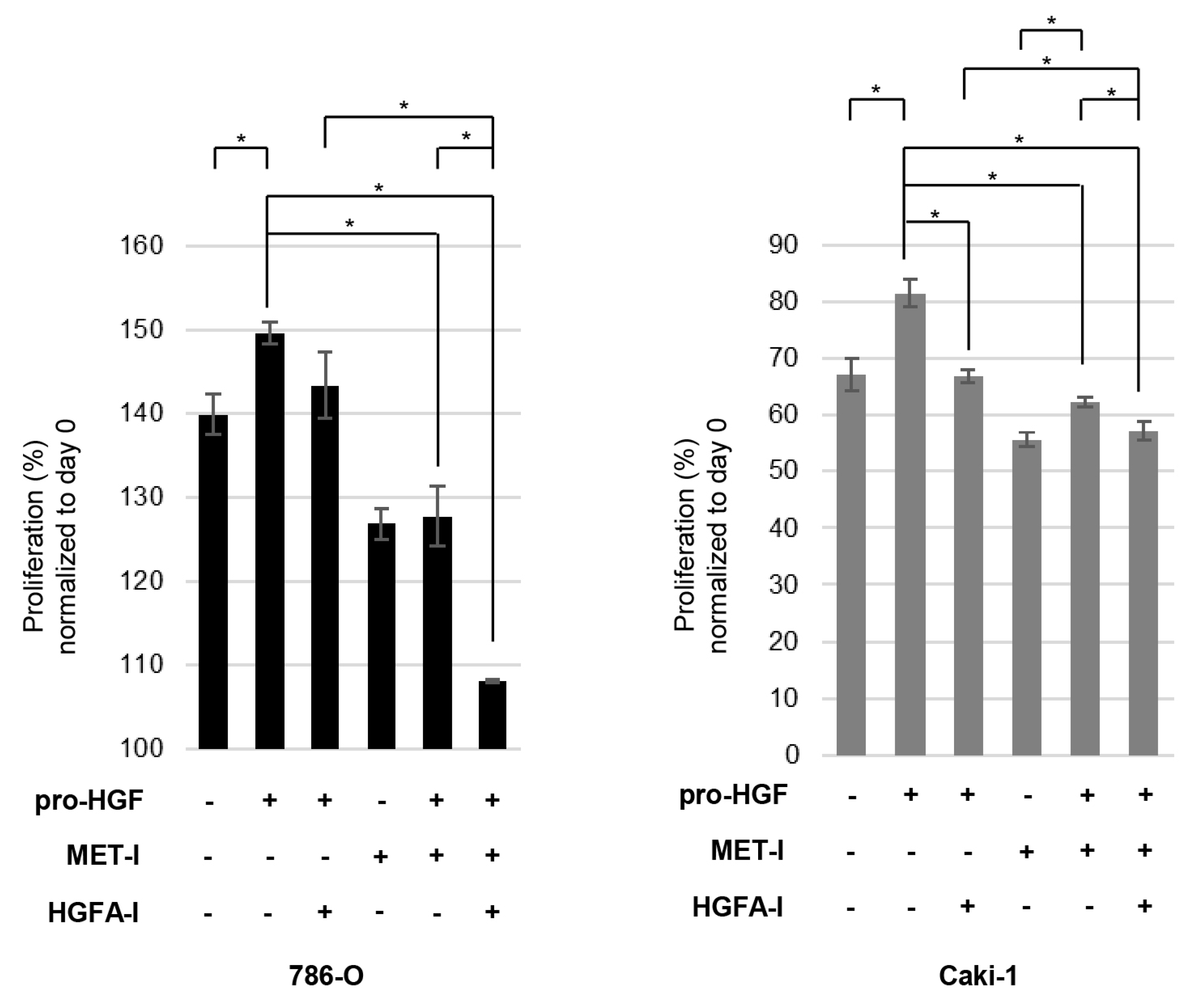
3.4. Inhibition of RCC Cell Proliferation by MET-I and HGFA-I
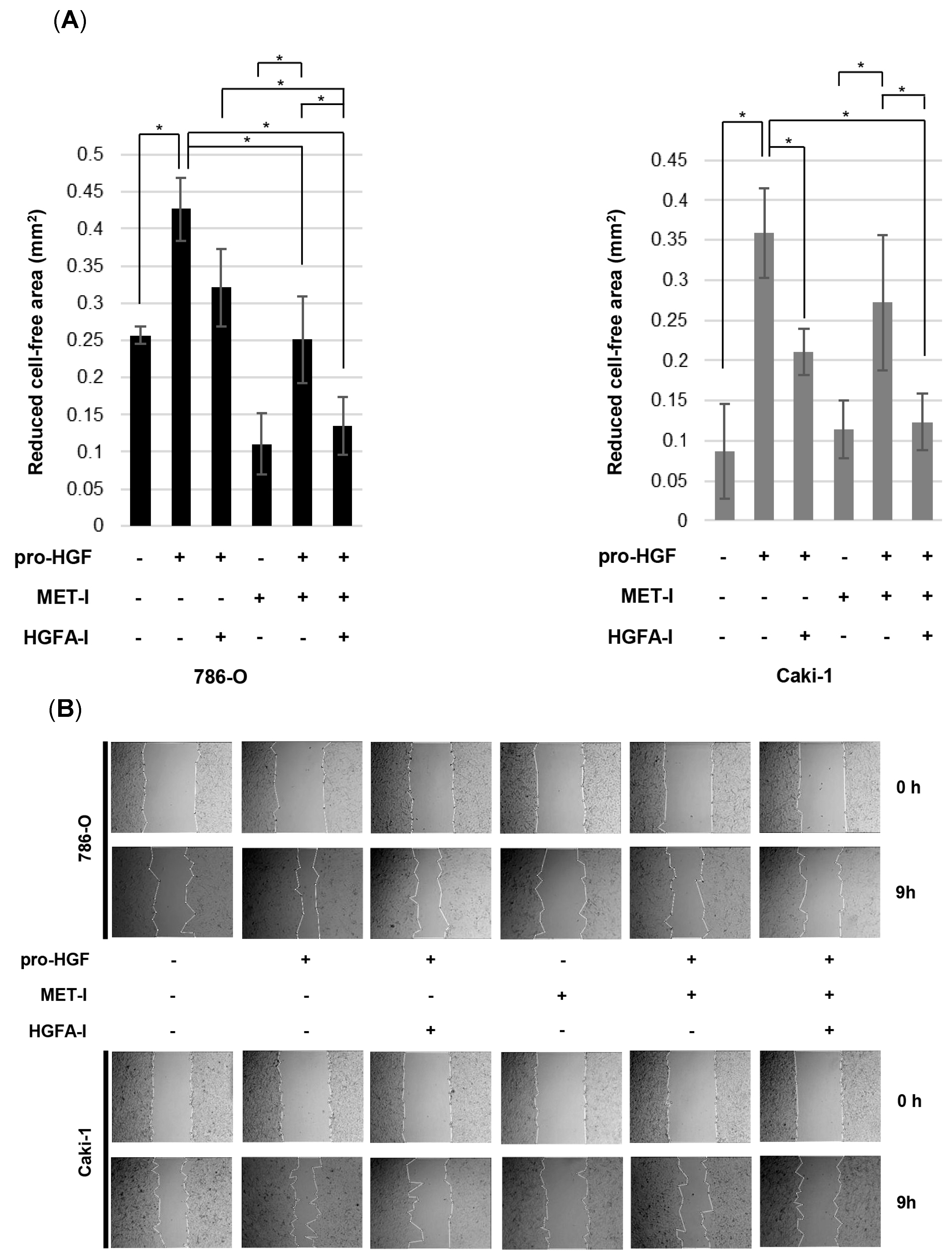
3.5. Inhibition of RCC Cell Motility by MET-I and HGFA-I
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MET | HGF receptor |
| HGF | Hepatocyte growth factor |
| Pro-HGF | HGF propeptide |
| HGFA | HGF activator |
| RCC | Renal cell carcinoma |
| mRCC | Metastatic renal cell carcinoma |
| TKI | Tyrosine kinase inhibitor |
| MET-I | MET inhibitor |
| HGFA-I | HGF-activator inhibitor |
| VEGFR | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| NSCLC | Non-small-cell lung cancer |
| HPN | Hepsin-coding gene |
| ST-14 | Matriptase-coding gene |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| CAF | Cancer-associated fibroblast |
References
- Kataoka, H.; Kawaguchi, M.; Fukushima, T.; Shimomura, T. Hepatocyte growth factor activator inhibitors (HAI-1 and HAI-2): Emerging key players in epithelial integrity and cancer. Pathol. Int. 2018, 68, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukai, S.; Yamasaki, K.; Fujii, M.; Nagai, T.; Terada, N.; Kataoka, H.; Kamoto, T. Dysregulation of type II transmembrane serine proteases and ligand-dependent activation of MET in urological cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Piotrowska, Z.; Hare, P.J.; Chen, H.; Mulvey, H.E.; Mayfield, A.; Noeen, S.; Kattermann, K.; Greenberg, M.; Williams, A.; et al. Three subtypes of lung cancer fibroblasts define distinct therapeutic paradigms. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 1531–1547.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Liu, W.; Liu, C.; Du, K.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, G.; Huang, Z.; Lin, S.; Cen, B.; Tian, Y.; et al. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Promote Radioresistance of Breast Cancer Cells via the HGF/c-Met Signaling Pathway. J. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2023, 116, 640–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.Y.; Kim, J.; Kim, M.A.; Choi, J.; Kim, W.H. Increased HGF Expression Induces Resistance to c-MET Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Gastric Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 1127–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, A.; Trusolino, L.; Comoglio, P.M. The Met tyrosine kinase receptor in development and cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2008, 27, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trusolino, L.; Bertotti, A.; Comoglio, P.M. MET signalling: Principles and functions in development, organ regeneration and cancer. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovar, E.A.; Graveel, C.R. MET in human cancer: Germline and somatic mutations. Ann. Transl. Med. 2017, 5, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recondo, G.; Che, J.; Jänne, P.A.; Awad, M.M. Targeting MET Dysregulation in Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 922–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escudier, B.; Powles, T.; Motzer, R.J.; Olencki, T.; Arén Frontera, O.; Oudard, S.; Rolland, F.; Tomczak, P.; Castellano, D.; Appleman, L.J.; et al. Cabozantinib, a New Standard of Care for Patients with Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma and Bone Metastases? Subgroup Analysis of the METEOR Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.J.; Powles, T.; Burotto, M.; Escudier, B.; Bourlon, M.T.; Shah, A.Y.; Suárez, C.; Hamzaj, A.; Porta, C.; Hocking, C.M.; et al. Nivolumab plus cabozantinib versus sunitinib in first-line treatment for advanced renal cell carcinoma (CheckMate 9ER): Long-term follow-up results from an open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 888–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motzer, R.J.; Penkov, K.; Haanen, J.; Rini, B.; Albiges, L.; Campbell, M.T.; Venugopal, B.; Kollmannsberger, C.; Negrier, S.; Uemura, M.; et al. Avelumab plus Axitinib versus Sunitinib for Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1103–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powles, T.; Plimack, E.R.; Soulières, D.; Waddell, T.; Stus, V.; Gafanov, R.; Nosov, D.; Pouliot, F.; Melichar, B.; Vynnychenko, I.; et al. Pembrolizumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib monotherapy as first-line treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma (KEYNOTE-426): Extended follow-up from a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 1563–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.J.; Porta, C.; Eto, M.; Powles, T.; Grünwald, V.; Hutson, T.E.; Alekseev, B.; Rha, S.Y.; Merchan, J.; Goh, J.C.; et al. CLEAR Trial Investigators. Lenvatinib Plus Pembrolizumab Versus Sunitinib in First-Line Treatment of Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma: Final Prespecified Overall Survival Analysis of CLEAR, a Phase III Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 1222–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, P.; El-Naggar, A.K.; Lin, S.H.; Pisters, L.L. Biological significance of c-met over expression in papillary renal cell carcinoma. J. Urol. 2002, 168, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harshman, L.C.; Choueiri, T.K. Targeting the hepatocyte growth factor/c-Met signaling pathway in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer J. 2013, 19, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betsunoh, H.; Mukai, S.; Akiyama, Y.; Fukushima, T.; Minamiguchi, N.; Hasui, Y.; Osada, Y.; Kataoka, H. Clinical relevance of hepsin and hepatocyte growth factor activator inhibitor type 2 expression in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2007, 98, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choueiri, T.K.; Escudier, B.; Powles, T.; Tannir, N.M.; Mainwaring, P.N.; Rini, B.I.; Hammers, H.J.; Donskov, F.; Roth, B.J.; Peltola, K.; et al. Cabozantinib versus everolimus in advanced renal cell carcinoma (METEOR): Final results from a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukai, S.; Yorita, K.; Kawagoe, Y.; Katayama, Y.; Nakahara, K.; Kamibeppu, T.; Sugie, S.; Tukino, H.; Kamoto, T.; Kataoka, H. Matriptase and MET are prominently expressed at the site of bone metastasis in renal cell carcinoma: Immunohistochemical analysis. Hum. Cell 2015, 28, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, K.; Mukai, S.; Nagai, T.; Nakahara, K.; Fujii, M.; Terada, N.; Ohno, A.; Sato, Y.; Toda, Y.; Kataoka, H.; et al. Matriptase-Induced Phosphorylation of MET is Significantly Associated with Poor Prognosis in Invasive Bladder Cancer; an Immunohistochemical Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukai, S.; Yorita, K.; Yamasaki, K.; Nagai, T.; Kamibeppu, T.; Sugie, S.; Kida, K.; Onizuka, C.; Tsukino, H.; Kamimura, T.; et al. Expression of human kallikrein 1-related peptidase 4 (KLK4) and MET phosphorylation in prostate cancer tissue: Immunohistochemical analysis. Hum. Cell 2015, 28, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.; De Bono, J.; Sternberg, C.; Le Moulec, S.; Oudard, S.; De Giorgi, U.; Krainer, M.; Bergman, A.; Hoelzer, W.; De Wit, R.; et al. Phase III Study of Cabozantinib in Previously Treated Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: COMET-1. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 3005–3013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Higgins, M.J.; Tolaney, S.M.; Come, S.E.; Smith, M.R.; Fornier, M.; Mahmood, U.; Baselga, J.; Yeap, B.Y.; Chabner, B.A.; et al. A Phase II Trial of Cabozantinib in Hormone Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer with Bone Metastases. Oncologist 2020, 25, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, Y.; Sagara, Y.; Kanda, S.; Hayashi, T.; Kanetake, H. Phosphorylated hepatocyte growth factor receptor/c-Met is associated with tumor growth and prognosis in patients with bladder cancer: Correlation with matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -7 and E-cadherin. Hum. Pathol. 2009, 40, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, J.; Seto, T.; Han, J.Y.; Reguart, N.; Garon, E.B.; Groen, H.J.M.; Tan, D.S.W.; Hida, T.; de Jonge, M.; Orlov, S.V.; et al. GEOMETRY mono-1 Investigators. Capmatinib in MET Exon 14-Mutated or MET-Amplified Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 944–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, P.K.; Felip, E.; Veillon, R.; Sakai, H.; Cortot, A.B.; Garassino, M.C.; Mazieres, J.; Viteri, S.; Senellart, H.; Van Meerbeeck, J.; et al. Tepotinib in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer with MET Exon 14 Skipping Mutations. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 931–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elisei, R.; Schlumberger, M.J.; Müller, S.P.; Schöffski, P.; Brose, M.S.; Shah, M.H.; Licitra, L.; Jarzab, B.; Medvedev, V.; Kreissl, M.C.; et al. Cabozantinib in progressive medullary thyroid cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3639–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liam, C.K.; Ahmad, A.R.; Hsia, T.C.; Zhou, J.; Kim, D.W.; Soo, R.A.; Cheng, Y.; Lu, S.; Shin, S.W.; Yang, J.C.; et al. Randomized Trial of Tepotinib Plus Gefitinib versus Chemotherapy in EGFR-Mutant NSCLC with EGFR Inhibitor Resistance Due to MET Amplification: INSIGHT Final Analysis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 29, 1879–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Offin, M.; Brannon, A.R.; Chang, J.; Chow, A.; Delasos, L.; Girshman, J.; Wilkins, O.; McCarthy, C.G.; Makhnin, A.; et al. MET Exon 14-altered Lung Cancers and MET Inhibitor Resistance. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thu, Y.M.; Suzawa, K.; Tomida, S.; Ochi, K.; Tsudaka, S.; Takatsu, F.; Date, K.; Matsuda, N.; Iwata, K.; Nakata, K.; et al. PAI-1 mediates acquired resistance to MET-targeted therapy in non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0300644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruickshanks, N.; Zhang, Y.; Hine, S.; Gibert, M.; Yuan, F.; Oxford, M.; Grello, C.; Pahuski, M.; Dube, C.; Guessous, F.; et al. Discovery and Therapeutic Exploitation of Mechanisms of Resistance to MET Inhibitors in Glioblastoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennacchietti, S.; Cazzanti, M.; Bertotti, A.; Rideout, W.M., 3rd; Han, M.; Gyuris, J.; Perera, T.; Comoglio, P.M.; Trusolino, L.; Michieli, P. Microenvironment-derived HGF overcomes genetically determined sensitivity to anti-MET drugs. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 6598–6609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basilico, C.; Modica, C.; Maione, F.; Vigna, E.; Comoglio, P.M. Targeting the MET oncogene by concomitant inhibition of receptor and ligand via an antibody-“decoy” strategy. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 143, 1774–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venukadasula, P.K.; Owusu, B.Y.; Bansal, N.; Ross, L.J.; Hobrath, J.V.; Bao, D.; Truss, J.W.; Stackhouse, M.; Messick, T.E.; Klampfer, L.; et al. Design and Synthesis of Nonpeptide Inhibitors of Hepatocyte Growth Factor Activation. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 7, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joffre, C.; Barrow, R.; Ménard, L.; Calleja, V.; Hart, I.R.; Kermorgant, S. A direct role for Met endocytosis in tumorigenesis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 827–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Age at Primary Treatment (Range) | 71 (39–86) |
|---|---|
| Gender | |
| Male | 22 |
| Female | 9 |
| pT stage | |
| T1 | 3 |
| T2 | 2 |
| T3a | 18 * |
| T3b | 5 |
| T4 | 4 |
| MET | p-MET | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pT Stage | + | − | p Value | + | − | p Value |
| ≤T2 | 4 | 1 | 0.9584 | 0 | 5 | 0.8540 |
| ≥T3 | 25 | 2 | 4 | 23 | ||
| Site | ||||||
| primary | 29 | 3 | 0.6253 | 4 | 28 | 0.0001 |
| metastasis | 37 | 7 | 31 | 13 | ||
| Metastatic Site | MET-Positive | p-MET-Positive | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lung | 12 | 9 | 14 |
| Bone | 6 | 6 | 8 |
| Lymph node | 5 | 3 | 5 |
| Subcutaneous | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Adrenal gland | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| Liver | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Pancreas | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| Retroperitoneum | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Brain | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Ureter | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Omentum | 1 | 1 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akioka, T.; Kimura, S.; Katayama, Y.; Fujii, M.; Kiwaki, T.; Kawaguchi, M.; Fukushima, T.; Sato, Y.; Mukai, S.; Kamoto, T.; et al. Phosphorylation of MET Is Upregulated in Metastatic Sites of Renal Cell Carcinoma: Possible Role of MET and Hepatocyte Growth Factor Activation-Targeted Combined Therapy. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 811. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040811
Akioka T, Kimura S, Katayama Y, Fujii M, Kiwaki T, Kawaguchi M, Fukushima T, Sato Y, Mukai S, Kamoto T, et al. Phosphorylation of MET Is Upregulated in Metastatic Sites of Renal Cell Carcinoma: Possible Role of MET and Hepatocyte Growth Factor Activation-Targeted Combined Therapy. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(4):811. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040811
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkioka, Takahiro, Shoichi Kimura, Yuichi Katayama, Masato Fujii, Takumi Kiwaki, Makiko Kawaguchi, Tsuyoshi Fukushima, Yuichiro Sato, Shoichiro Mukai, Toshiyuki Kamoto, and et al. 2025. "Phosphorylation of MET Is Upregulated in Metastatic Sites of Renal Cell Carcinoma: Possible Role of MET and Hepatocyte Growth Factor Activation-Targeted Combined Therapy" Biomedicines 13, no. 4: 811. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040811
APA StyleAkioka, T., Kimura, S., Katayama, Y., Fujii, M., Kiwaki, T., Kawaguchi, M., Fukushima, T., Sato, Y., Mukai, S., Kamoto, T., & Sawada, A. (2025). Phosphorylation of MET Is Upregulated in Metastatic Sites of Renal Cell Carcinoma: Possible Role of MET and Hepatocyte Growth Factor Activation-Targeted Combined Therapy. Biomedicines, 13(4), 811. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040811






