Telomere Length as Both Cause and Consequence in Type 1 Diabetes: Evidence from Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. IVs Selection
2.2.1. Identifying Exposure-Related IVs
2.2.2. Excluding Confounders
2.2.3. Identifying Outcome-Related IVs
2.3. MR Analysis
2.4. Multivariable MR Analysis
2.5. Sensitivity Analysis
3. Results
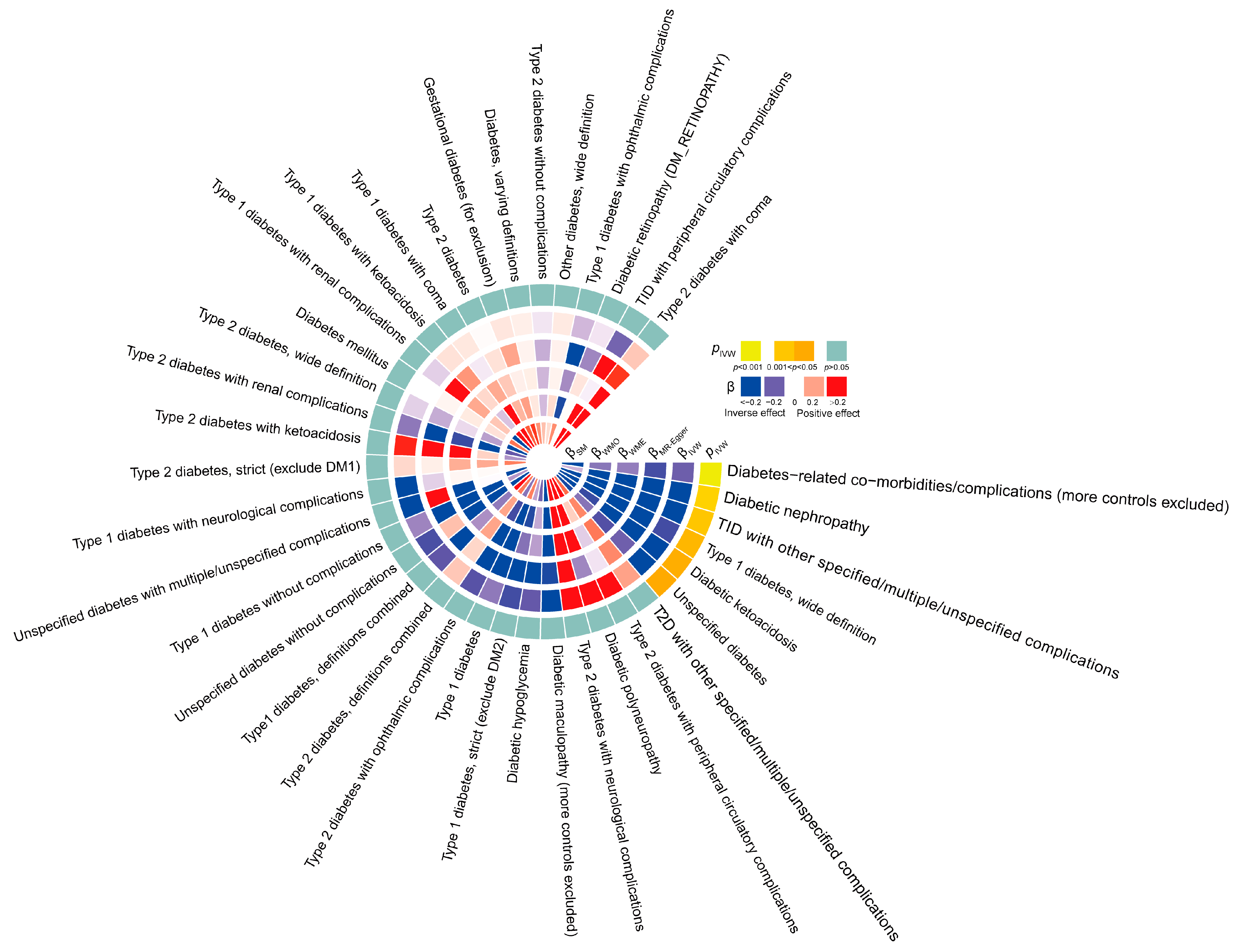
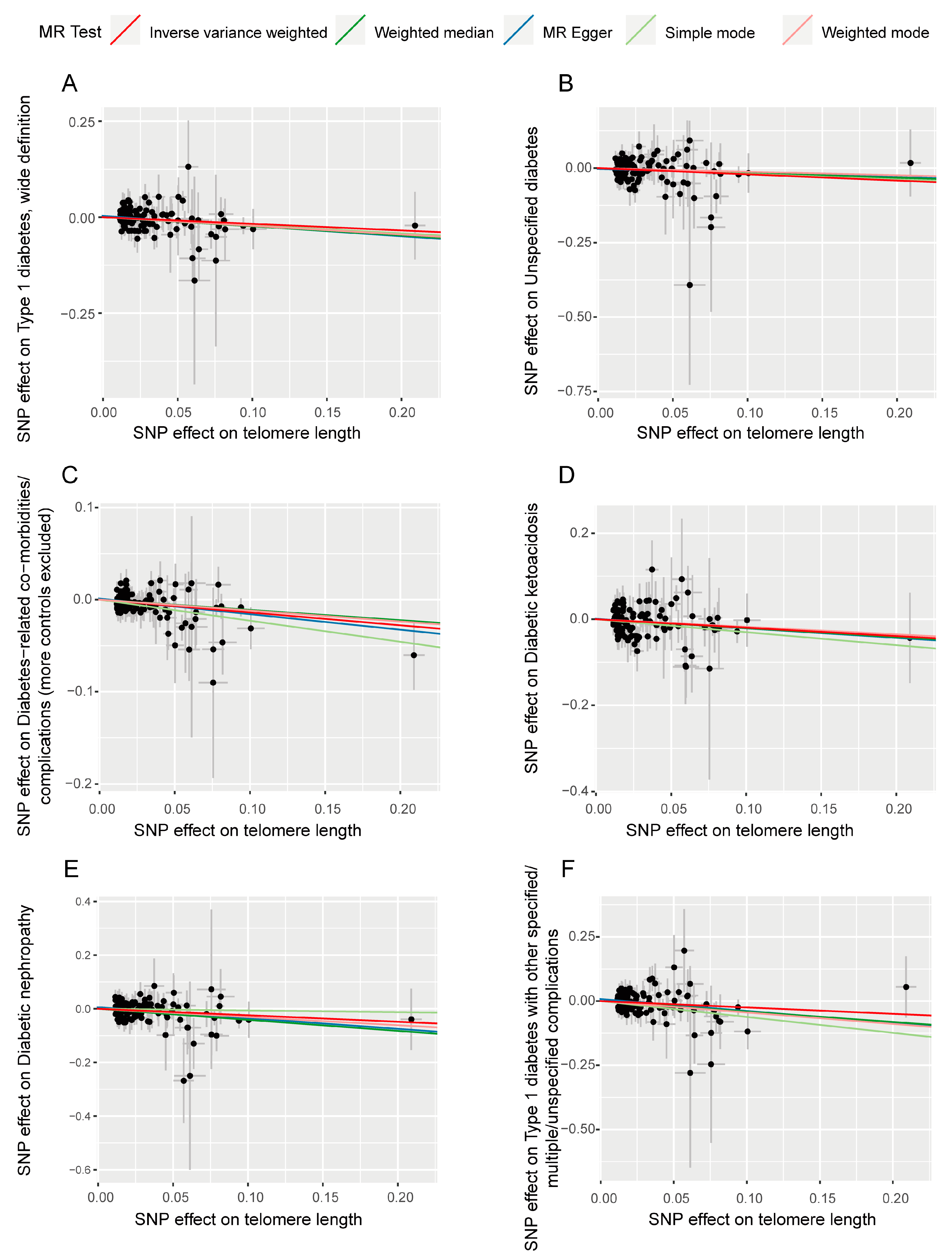
3.1. Forward Analysis Shows Different Causal Effects of TL on Diabetes Types and Its Complications
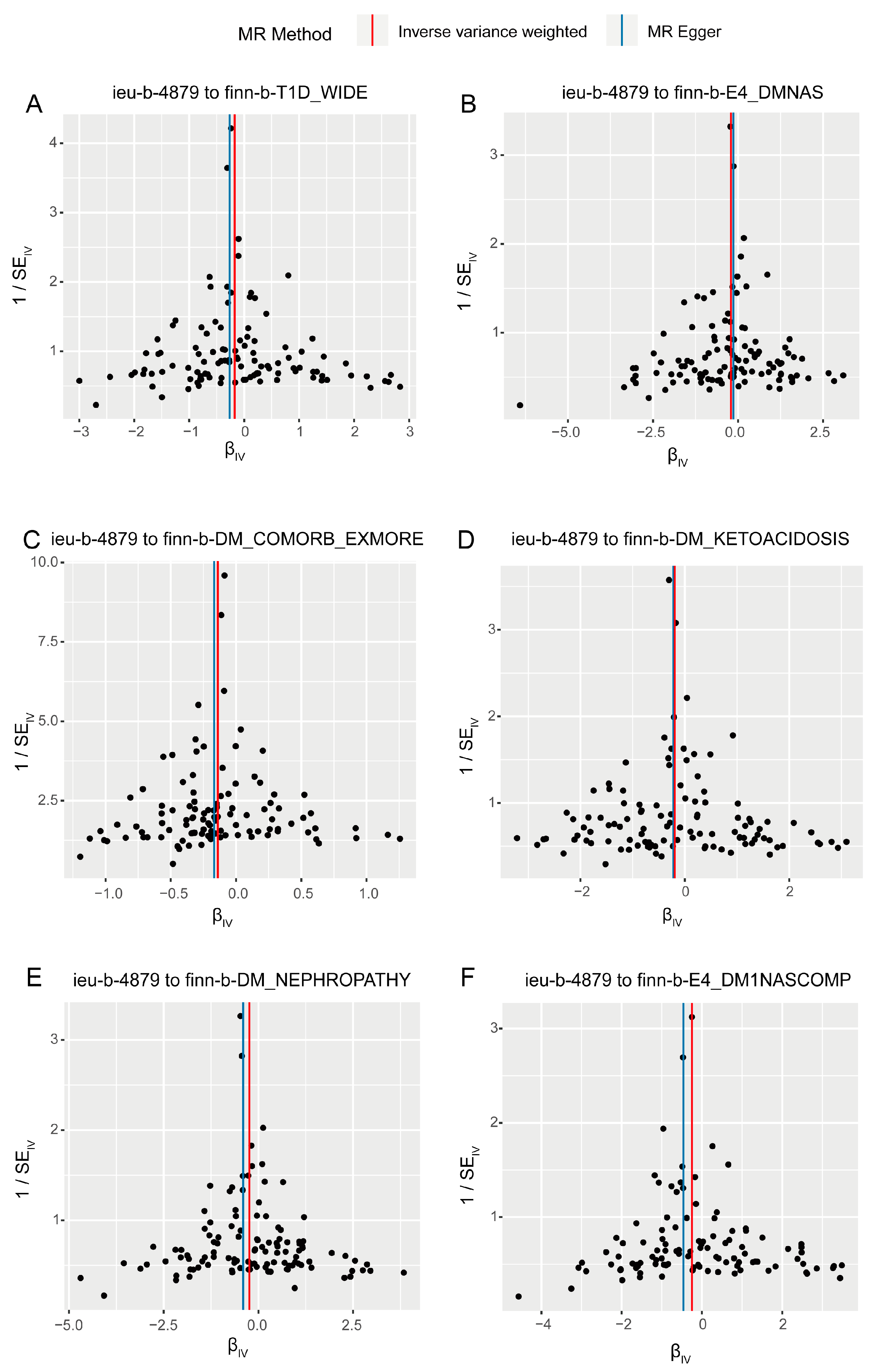
3.2. Sensitivity Analysis in Forward Analysis
3.3. Reverse Analysis Confirms Different Causal Effects of Diabetes Types and Complications on TL
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ghimire, K.; Kale, A.; Li, J.; Julovi, S.M.; O’Connell, P.; Grey, S.T.; Hawthorne, W.J.; Gunton, J.E.; Rogers, N.M. A metabolic role for CD47 in pancreatic β cell insulin secretion and islet transplant outcomes. Sci. Transl. Med. 2023, 15, eadd2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauvais-Jarvis, F. Aging, Male Sex, Obesity, and Metabolic Inflammation Create the Perfect Storm for COVID-19. Diabetes 2020, 69, 1857–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, H.; Du, W.; Wang, L. Preliminary evidence for the presence of multiple forms of cell death in diabetes cardiomyopathy. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharroubi, A.T.; Darwish, H.M. Diabetes mellitus: The epidemic of the century. World J. Diabetes 2015, 6, 850–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiMeglio, L.A.; Evans-Molina, C.; Oram, R.A. Type 1 diabetes. Lancet 2018, 391, 2449–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quattrin, T.; Mastrandrea, L.D.; Walker, L.S.K. Type 1 diabetes. Lancet 2023, 401, 2149–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, E.D.; Ingelfinger, J.R.; Kolko, J.; Linhales Barker, S.; Lopez, D.; Mejia, M.; Peek, M.; Reusch, J.E.B.; Rosen, C.J. Type 2 Diabetes—Controlling the Epidemic, Episode 2: After the Diagnosis—Making a Plan and Addressing Social Determinants of Health. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guber, C. Type 2 diabetes. Lancet 2005, 365, 1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shantikumar, S.; Caporali, A.; Emanueli, C. Role of microRNAs in diabetes and its cardiovascular complications. Cardiovasc. Res. 2012, 93, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bommer, C.; Heesemann, E.; Sagalova, V.; Manne-Goehler, J.; Atun, R.; Bärnighausen, T.; Vollmer, S. The global economic burden of diabetes in adults aged 20–79 years: A cost-of-illness study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017, 5, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hills, A.P.; Arena, R.; Khunti, K.; Yajnik, C.S.; Jayawardena, R.; Henry, C.J.; Street, S.J.; Soares, M.J.; Misra, A. Epidemiology and determinants of type 2 diabetes in south Asia. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018, 6, 966–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codd, V.; Wang, Q.; Allara, E.; Musicha, C.; Kaptoge, S.; Stoma, S.; Jiang, T.; Hamby, S.E.; Braund, P.S.; Bountziouka, V.; et al. Polygenic basis and biomedical consequences of telomere length variation. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 1425–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, F.T.; McGhie, J.D.; Chan, F.L.; Tang, M.C.; Anderson, M.A.; Mann, J.R.; Andy Choo, K.H.; Wong, L.H. PML bodies provide an important platform for the maintenance of telomeric chromatin integrity in embryonic stem cells. Nucleic Acids Res 2013, 41, 4447–4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, K.N.; Wu, M.; Bondy, S.C. Telomere shortening during aging: Attenuation by antioxidants and anti-inflammatory agents. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2017, 164, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banik, U.; Parasuraman, S.; Adhikary, A.K.; Othman, N.H. Curcumin: The spicy modulator of breast carcinogenesis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 36, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, K.J.; Vasu, V.; Griffin, D.K. Telomere Biology and Human Phenotype. Cells 2019, 8, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafirovic, S.; Macvanin, M.; Stanimirovic, J.; Obradovic, M.; Radovanovic, J.; Melih, I.; Isenovic, E. Association Between Telomere Length and Cardiovascular Risk: Pharmacological Treatments Affecting Telomeres and Telomerase Activity. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2022, 20, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhou, F.; Li, G.; Liu, J.; Lv, J.; Li, L.; Chang, D. Telomere length and the risk of cardiovascular diseases: A Mendelian randomization study. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 1012615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Pickett, H.A. Targeting telomeres: Advances in telomere maintenance mechanism-specific cancer therapies. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2022, 22, 515–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciejowski, J.; de Lange, T. Telomeres in cancer: Tumour suppression and genome instability. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vellingiri, B.; Balasubramani, K.; Iyer, M.; Raj, N.; Elangovan, A.; Song, K.; Yeo, H.C.; Jayakumar, N.; Kinoshita, M.; Thangarasu, R.; et al. Role of Telomeres and Telomerase in Parkinson’s Disease-A New Theranostics? Adv. Biol. 2023, 7, e2300097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.; Wei, C.; Zhu, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, G.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, D.; Yue, W.; Yu, H. Exploring the Causal Pathway From Telomere Length to Alzheimer’s Disease: An Update Mendelian Randomization Study. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitha, A.; Thanseem, I.; Vasu, M.M.; Viswambharan, V.; Poovathinal, S.A. Telomeres in neurological disorders. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2019, 90, 81–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kronenberg, F. Telomere length and chronic kidney disease: Cause or consequence? Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 980–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Carroll, L.; Joglekar, M.V.; Januszewski, A.S.; Wong, K.K.; Hardikar, A.A.; Jenkins, A.J.; Ma, R.C.W. Diabetes, metabolic disease, and telomere length. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.; Duffy, S.; Coulter, T.; Maxwell, A.P.; McKnight, A.J. Harnessing Genomic Analysis to Explore the Role of Telomeres in the Pathogenesis and Progression of Diabetic Kidney Disease. Genes 2023, 14, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojeda-Rodriguez, A.; Rangel-Zuñiga, O.A.; Arenas-de Larriva, A.P.; Gutierrez-Mariscal, F.M.; Torres-Peña, J.D.; Romero-Cabrera, J.L.; Podadera-Herreros, A.; García-Fernandez, H.; Porras-Pérez, E.; Luque, R.M.; et al. Telomere length as biomarker of nutritional therapy for prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus development in patients with coronary heart disease: CORDIOPREV randomised controlled trial. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argentieri, M.A.; Xiao, S.; Bennett, D.; Winchester, L.; Nevado-Holgado, A.J.; Ghose, U.; Albukhari, A.; Yao, P.; Mazidi, M.; Lv, J.; et al. Proteomic aging clock predicts mortality and risk of common age-related diseases in diverse populations. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 2450–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kivimäki, M.; Bartolomucci, A.; Kawachi, I. The multiple roles of life stress in metabolic disorders. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2023, 19, 10–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Pardeza, J.; López-Gil, J.F.; Huerta-Uribe, N.; Hormazábal-Aguayo, I.; Ojeda-Rodríguez, A.; Marti Del Moral, A.; Izquierdo, M.; García-Hermoso, A. Is physical fitness associated with leucocyte telomere length in youth with type 1 diabetes? Pediatr. Res. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, M.; Hoang, S.; Kannengiesser, C.; Potier, L.; Hadjadj, S.; Marre, M.; Roussel, R.; Velho, G.; Mohammedi, K. Leukocyte Telomere Length, DNA Oxidation, and Risk of Lower-Extremity Amputation in Patients With Long-standing Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 828–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, M.; Kannengiesser, C.; Hoang, S.; Potier, L.; Fumeron, F.; Venteclef, N.; Scheen, A.; Gautier, J.F.; Hadjadj, S.; Marre, M.; et al. Leukocyte telomere length, allelic variations in related genes and risk of coronary heart disease in people with long-standing type 1 diabetes. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2022, 21, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, N.M.; Holmes, M.V.; Davey Smith, G. Reading Mendelian randomisation studies: A guide, glossary, and checklist for clinicians. BMJ 2018, 362, k601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.; Davey Smith, G.; Davies, N.M.; Dudbridge, F.; Gill, D.; Glymour, M.M.; Hartwig, F.P.; Kutalik, Z.; Holmes, M.V.; Minelli, C.; et al. Guidelines for performing Mendelian randomization investigations: Update for summer 2023. Wellcome Open Res. 2019, 4, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, G.D.; Ebrahim, S. ‘Mendelian randomization’: Can genetic epidemiology contribute to understanding environmental determinants of disease? Int. J. Epidemiol. 2003, 32, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emdin, C.A.; Khera, A.V.; Kathiresan, S. Mendelian Randomization. JAMA 2017, 318, 1925–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, M.D.; Damask, A.; O’Keeffe, S.; Banerjee, N.; Li, D.; Watanabe, K.; Marketta, A.; Van Meter, M.; Semrau, S.; Horowitz, J.; et al. Common and rare variant associations with clonal haematopoiesis phenotypes. Nature 2022, 612, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurki, M.I.; Karjalainen, J.; Palta, P.; Sipilä, T.P.; Kristiansson, K.; Donner, K.M.; Reeve, M.P.; Laivuori, H.; Aavikko, M.; Kaunisto, M.A.; et al. FinnGen provides genetic insights from a well-phenotyped isolated population. Nature 2023, 613, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skrivankova, V.W.; Richmond, R.C.; Woolf, B.A.R.; Yarmolinsky, J.; Davies, N.M.; Swanson, S.A.; VanderWeele, T.J.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Timpson, N.J.; Dimou, N.; et al. Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology Using Mendelian Randomization: The STROBE-MR Statement. JAMA 2021, 326, 1614–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemani, G.; Zheng, J.; Elsworth, B.; Wade, K.H.; Haberland, V.; Baird, D.; Laurin, C.; Burgess, S.; Bowden, J.; Langdon, R.; et al. The MR-Base platform supports systematic causal inference across the human phenome. eLife 2018, 7, e34408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Yang, P.; Li, Y.; Liu, T.; Zha, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhang, J.; Feng, Z.; Li, M. New insights from bidirectional Mendelian randomization: Causal relationships between telomere length and mitochondrial DNA copy number in aging biomarkers. Aging 2024, 16, 7387–7404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Fu, Z.; Liao, J.; Liu, H.; Zhou, M. Exploring the Causal Effects of Mineral Metabolism Disorders on Telomere and Mitochondrial DNA: A Bidirectional Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Analysis. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawlor, D.A.; Harbord, R.M.; Sterne, J.A.; Timpson, N.; Davey Smith, G. Mendelian randomization: Using genes as instruments for making causal inferences in epidemiology. Stat. Med. 2008, 27, 1133–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrska-Bishop, M.; Evani, U.S.; Zhao, X.; Basile, A.O.; Abel, H.J.; Regier, A.A.; Corvelo, A.; Clarke, W.E.; Musunuri, R.; Nagulapalli, K.; et al. High-coverage whole-genome sequencing of the expanded 1000 Genomes Project cohort including 602 trios. Cell 2022, 185, 3426–3440.e3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-H.; Brown, D.W.; Machiela, M.J. LDtrait: An Online Tool for Identifying Published Phenotype Associations in Linkage Disequilibrium. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 3443–3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, S.; Thompson, S.G. Avoiding bias from weak instruments in Mendelian randomization studies. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 40, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, Q.; Geng, H.; Gao, Q.; Xu, M. The association between gut microbiome and PCOS: Evidence from meta-analysis and two-sample mendelian randomization. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1203902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Wang, N.; Luo, Y.; Ma, C.; Chen, Z.; Chenzhao, C.; Zhang, F.; Qi, X.; Xiong, W. A cause-effect relationship between Graves’ disease and the gut microbiome contributes to the thyroid-gut axis: A bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 977587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbanck, M.; Chen, C.Y.; Neale, B.; Do, R. Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.; Spiller, W.; Del Greco M, F.; Sheehan, N.; Thompson, J.; Minelli, C.; Davey Smith, G. Improving the visualization, interpretation and analysis of two-sample summary data Mendelian randomization via the Radial plot and Radial regression. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2018, 47, 1264–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemani, G.; Tilling, K.; Davey Smith, G. Orienting the causal relationship between imprecisely measured traits using GWAS summary data. PLoS Genet. 2017, 13, e1007081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.; Butterworth, A.; Thompson, S.G. Mendelian randomization analysis with multiple genetic variants using summarized data. Genet. Epidemiol. 2013, 37, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.C.; Holmes, M.V.; Burgess, S.; Asselbergs, F.W.; Jones, G.T.; Baas, A.F.; van ‘t Hof, F.N.; de Bakker, P.I.W.; Blankensteijn, J.D.; Powell, J.T.; et al. Genetic Association of Lipids and Lipid Drug Targets With Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm: A Meta-analysis. JAMA Cardiol. 2018, 3, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, S.; Thompson, S.G. Interpreting findings from Mendelian randomization using the MR-Egger method. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 32, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowden, J.; Davey Smith, G.; Haycock, P.C.; Burgess, S. Consistent Estimation in Mendelian Randomization with Some Invalid Instruments Using a Weighted Median Estimator. Genet. Epidemiol. 2016, 40, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, J.; Knoblauch, N.; Marcus, J.H.; Stephens, M.; He, X. Mendelian randomization accounting for correlated and uncorrelated pleiotropic effects using genome-wide summary statistics. Nat. Genet. 2020, 52, 740–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.; Foley, C.N.; Allara, E.; Staley, J.R.; Howson, J.M.M. A robust and efficient method for Mendelian randomization with hundreds of genetic variants. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, S.; Liao, M.; Zheng, Z.; Li, M.; Wei, X.; Liu, M.; Yang, L. Association between genetically predicted leukocyte telomere length and non-scarring alopecia: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1072573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, S.; Lu, M.; Cao, P.; Chen, T.; Li, S.; Xue, S.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Evaluating the impact of metformin targets on the risk of osteoarthritis: A mendelian randomization study. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2022, 30, 1506–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, E.; Spiller, W.; Bowden, J. Testing and correcting for weak and pleiotropic instruments in two-sample multivariable Mendelian randomization. Stat. Med. 2021, 40, 5434–5452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Hu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Yang, M.; Wu, F.; Peng, Y. Genetic causal relationship between age at menarche and benign oesophageal neoplasia identified by a Mendelian randomization study. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1113765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.; Bowden, J.; Fall, T.; Ingelsson, E.; Thompson, S.G. Sensitivity Analyses for Robust Causal Inference from Mendelian Randomization Analyses with Multiple Genetic Variants. Epidemiology 2017, 28, 30–42. [Google Scholar]
- Bowden, J.; Davey Smith, G.; Burgess, S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: Effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 44, 512–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Procházková Schrumpfová, P.; Fojtová, M.; Fajkus, J. Telomeres in Plants and Humans: Not So Different, Not So Similar. Cells 2019, 8, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teichroeb, J.H.; Kim, J.; Betts, D.H. The role of telomeres and telomerase reverse transcriptase isoforms in pluripotency induction and maintenance. RNA Biol. 2016, 13, 707–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalmykova, A. Telomere Checkpoint in Development and Aging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, S.M.; Samavarchi Tehrani, S.; Goodarzi, G.; Jamalpoor, Z.; Asadi, J.; Khelghati, N.; Qujeq, D.; Maniati, M. Shelterin Complex at Telomeres: Implications in Ageing. Clin. Interv. Aging 2020, 15, 827–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossiello, F.; Jurk, D.; Passos, J.F.; d’Adda di Fagagna, F. Telomere dysfunction in ageing and age-related diseases. Nat. Cell Biol. 2022, 24, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichikawa, Y.; Nishimura, Y.; Kurumizaka, H.; Shimizu, M. Nucleosome organization and chromatin dynamics in telomeres. Biomol. Concepts 2015, 6, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorini, E.; Santoni, A.; Colla, S. Dysfunctional telomeres and hematological disorders. Differ. Res. Biol. Divers. 2018, 100, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durham, A.L.; Speer, M.Y.; Scatena, M.; Giachelli, C.M.; Shanahan, C.M. Role of smooth muscle cells in vascular calcification: Implications in atherosclerosis and arterial stiffness. Cardiovasc. Res. 2018, 114, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calado, R.T.; Young, N.S. Telomere diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 2353–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, I.; Bhat, G.R.; Singh, V.; Kumar, R.; Bhanwer, A.J.; Bamezai, R.N.; Sharma, S.; Rai, E. Role of telomeres and associated maintenance genes in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A review. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2016, 122, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matveyenko, A.; Vella, A. Regenerative medicine in diabetes. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2015, 90, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2015 Healthcare Access and Quality Collaborators. Healthcare Access and Quality Index based on mortality from causes amenable to personal health care in 195 countries and territories, 1990–2015: A novel analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 2017, 390, 231–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Lee, K.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, M.Y.; Kim, J.R.; Lee, H.W.; Chung, Y.W.; Shin, H.I.; Kim, T.; Park, E.S.; et al. Selenoprotein W ensures physiological bone remodeling by preventing hyperactivity of osteoclasts. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yin, Y.; Ye, X.; Liu, K.; Zhu, H.; Wang, L.; Chiourea, M.; Okuka, M.; Ji, G.; Dan, J.; et al. Molecular insights into the heterogeneity of telomere reprogramming in induced pluripotent stem cells. Cell Res. 2012, 22, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Ge, Y.; Liu, D.; Songyang, Z. The role of telomere-binding modulators in pluripotent stem cells. Protein Cell 2020, 11, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toupance, S.; Simonici, S.; Labat, C.; Dumoulin, C.; Lai, T.P.; Lakomy, C.; Regnault, V.; Lacolley, P.; Dignat George, F.; Sabatier, F.; et al. Number and Replating Capacity of Endothelial Colony-Forming Cells are Telomere Length Dependent: Implication for Human Atherogenesis. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e020606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himbert, C.; Thompson, H.; Ulrich, C.M. Effects of Intentional Weight Loss on Markers of Oxidative Stress, DNA Repair and Telomere Length—A Systematic Review. Obes. Facts 2017, 10, 648–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, X.; Chen, S.; Zhang, S. Natural antisense transcripts in the biological hallmarks of cancer: Powerful regulators hidden in the dark. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Chen, X.; Huang, K.; Zheng, Q.; Fu, Y.; Ma, J.; Ren, X.; Xu, B.; Liu, P.; Liu, J.; et al. Urinary essential and toxic metal mixtures, and type 2 diabetes mellitus: Telomere shortening as an intermediary factor? J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 459, 132329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Zegher, F.; Díaz, M.; Ibáñez, L. Association Between Long Telomere Length and Insulin Sensitization in Adolescent Girls With Hyperinsulinemic Androgen Excess. JAMA Pediatr. 2015, 169, 787–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Karlsson, I.K.; Karlsson, R.; Tillander, A.; Reynolds, C.A.; Pedersen, N.L.; Hägg, S. Exploring the Causal Pathway From Telomere Length to Coronary Heart Disease: A Network Mendelian Randomization Study. Circ. Res. 2017, 121, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Jia, W.; Lyu, Y.; Su, D.; Bai, M.; Shen, J.; Qiao, J.; Han, T.; Liu, W.; Chen, J.; et al. Pwp1 regulates telomere length by stabilizing shelterin complex and maintaining histone H4K20 trimethylation. Cell Discov. 2019, 5, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shay, J.W.; Wright, W.E. Senescence and immortalization: Role of telomeres and telomerase. Carcinogenesis 2005, 26, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, G.; Solari, F.; Mateescu, B.; Karaca, M.; Castel, J.; Bourachot, B.; Magnan, C.; Billaud, M.; Mechta-Grigoriou, F. Oxidative stress contributes to aging by enhancing pancreatic angiogenesis and insulin signaling. Cell Metab. 2008, 7, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voican, C.S.; Perlemuter, G. Insulin resistance and oxidative stress: Two therapeutic targets in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2011, 54, 388–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Yu, Y.; Yu, X.; Zhang, M.; Yang, Y. The changes of leukocyte telomere length and telomerase activity after sitagliptin intervention in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes. Diabetes/Metab. Res. Rev. 2015, 31, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okitsu, T.; Kobayashi, N.; Jun, H.S.; Shin, S.; Kim, S.J.; Han, J.; Kwon, H.; Sakaguchi, M.; Totsugawa, T.; Kohara, M.; et al. Transplantation of reversibly immortalized insulin-secreting human hepatocytes controls diabetes in pancreatectomized pigs. Diabetes 2004, 53, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.E.; Newgard, C.B. Mechanisms controlling pancreatic islet cell function in insulin secretion. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 142–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusminski, C.M.; Bickel, P.E.; Scherer, P.E. Targeting adipose tissue in the treatment of obesity-associated diabetes. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2016, 15, 639–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Luk, A.O.; Shi, M.; Huang, C.; Jiang, G.; Yang, A.; Wu, H.; Lim, C.K.P.; Tam, C.H.T.; Fan, B.; et al. Shortened Leukocyte Telomere Length Is Associated With Glycemic Progression in Type 2 Diabetes: A Prospective and Mendelian Randomization Analysis. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, F.; Luk, A.O.; Wu, H.; Tam, C.H.T.; Lim, C.K.P.; Fan, B.; Jiang, G.; Carroll, L.; Yang, A.; Lau, E.S.H.; et al. Relative leucocyte telomere length is associated with incident end-stage kidney disease and rapid decline of kidney function in type 2 diabetes: Analysis from the Hong Kong Diabetes Register. Diabetologia 2022, 65, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, K.K.; Cheng, F.; Mao, D.; Lim, C.K.P.; Tam, C.H.T.; Wang, C.C.; Yuen, L.Y.; Chan, M.H.M.; Ho, C.S.; Joglekar, M.V.; et al. Vitamin D Levels During Pregnancy Are Associated with Offspring Telomere Length: A Longitudinal Mother-Child Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, e3901–e3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Shen, Y.; He, J.; Shen, Y.; Zhu, W.; Wu, X.; Xiao, M. Longer leukocyte telomere length increases cardiovascular mortality in type 2 diabetes patients. J. Diabetes 2023, 15, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, A.J.; Syreeni, A.; Mutter, S.; Januszewski, A.S.; Groop, P.H. Telomeres in clinical diabetes research—Moving towards precision medicine in diabetes care? Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 194, 110178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeeri, M.; Didari, T.; Khalid, M.; Mohammadi-Nejad, S.; Daghighi, S.M.; Farhadi, R.; Rahimifard, M.; Bayrami, Z.; Haghi-Aminjan, H.; Foroumadi, R.; et al. Molecular Evidence of the Inhibitory Potential of Melatonin against NaAsO2-Induced Aging in Male Rats. Molecules 2021, 26, 6603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastmanesh, R. Potential of melatonin to treat or prevent age-related macular degeneration through stimulation of telomerase activity. Med. Hypotheses 2011, 76, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennisi, G.; Bruzzaniti, P.; Burattini, B.; Piaser Guerrato, G.; Della Pepa, G.M.; Sturiale, C.L.; Lapolla, P.; Familiari, P.; La Pira, B.; D’Andrea, G.; et al. Advancements in Telomerase-Targeted Therapies for Glioblastoma: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrivankova, V.W.; Richmond, R.C.; Woolf, B.A.R.; Davies, N.M.; Swanson, S.A.; VanderWeele, T.J.; Timpson, N.J.; Higgins, J.P.; Dimou, N.; Langenberg, C.; et al. Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology using Mendelian Randomisation (STROBE-MR): Explanation and Elaboration. BMJ 2021, 375, n2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Method | Nsnp | B | SE | p-Value | Adjusting Insulin * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type1 diabetes, definitions combined to TL | |||||
| MR Egger | 14 | 0.0081 | 0.002 | 3.88 × 10−³ | |
| Weighted median | 14 | 0.0075 | 0.002 | 3.28 × 10−5 | |
| IVW | 14 | 0.0064 | 0.002 | 2.42 × 10−5 | 2.63 × 10−1 |
| Simple mode | 14 | 0.0065 | 0.004 | 1.48 × 10−1 | |
| Weighted mode | 14 | 0.0072 | 0.002 | 1.72 × 10−3 | |
| Type 1 diabetes, strict (exclude DM2) to TL | |||||
| MR Egger | 17 | 0.0077 | 0.002 | 2.67 × 10−3 | |
| Weighted median | 17 | 0.0073 | 0.002 | 3.95 × 10−5 | |
| IVW | 17 | 0.0060 | 0.001 | 4.08 × 10−5 | 2.77 × 10−1 |
| Simple mode | 17 | 0.0066 | 0.004 | 1.23 × 10−1 | |
| Weighted mode | 17 | 0.0072 | 0.002 | 1.12 × 10−3 | |
| Type 1 diabetes without complications to TL | |||||
| MR Egger | 31 | 0.0066 | 0.002 | 1.53 × 10−3 | |
| Weighted median | 31 | 0.0059 | 0.002 | 6.27 × 10−4 | |
| IVW | 31 | 0.0051 | 0.001 | 2.64 × 10−4 | 2.90 × 10−1 |
| Simple mode | 31 | 0.0064 | 0.005 | 1.91 × 10−1 | |
| Weighted mode | 31 | 0.0056 | 0.002 | 1.95 × 10−3 | |
| Diabetic hypoglycemia to TL | |||||
| MR Egger | 16 | 0.0046 | 0.005 | 3.49 × 10−1 | |
| Weighted median | 16 | 0.0061 | 0.004 | 9.10 × 10−2 | |
| IVW | 16 | 0.0055 | 0.003 | 4.16 × 10−2 | 9.78 × 10−1 |
| Simple mode | 16 | 0.0059 | 0.006 | 3.73 × 10−1 | |
| Weighted mode | 16 | 0.0059 | 0.004 | 1.19 × 10−1 | |
| Diabetic retinopathy to TL | |||||
| MR Egger | 16 | −0.0248 | 0.012 | 5.77 × 10−2 | |
| Weighted median | 16 | −0.0132 | 0.008 | 8.17 × 10−2 | |
| IVW | 16 | −0.0113 | 0.006 | 4.19 × 10−2 | 7.34 × 10−1 |
| Simple mode | 16 | −0.0002 | 0.013 | 9.87 × 10−1 | |
| Weighted mode | 16 | −0.0164 | 0.008 | 5.63 × 10−2 | |
| Type 1 diabetes with coma to TL | |||||
| MR Egger | 16 | 0.0031 | 0.001 | 5.62 × 10−2 | |
| Weighted median | 16 | 0.0026 | 0.001 | 6.60 × 10−2 | |
| IVW | 16 | 0.0025 | 0.001 | 2.54 × 10−2 | 4.09 × 10−1 |
| Simple mode | 16 | 0.0047 | 0.002 | 6.97 × 10−2 | |
| Weighted mode | 16 | 0.0025 | 0.001 | 9.32 × 10−2 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, G.; Chen, R.; Liu, S.; Cai, S.; Feng, Z. Telomere Length as Both Cause and Consequence in Type 1 Diabetes: Evidence from Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 774. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040774
Wei G, Chen R, Liu S, Cai S, Feng Z. Telomere Length as Both Cause and Consequence in Type 1 Diabetes: Evidence from Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(4):774. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040774
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Guanping, Ruiping Chen, Shupeng Liu, Shenhua Cai, and Zhijun Feng. 2025. "Telomere Length as Both Cause and Consequence in Type 1 Diabetes: Evidence from Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization" Biomedicines 13, no. 4: 774. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040774
APA StyleWei, G., Chen, R., Liu, S., Cai, S., & Feng, Z. (2025). Telomere Length as Both Cause and Consequence in Type 1 Diabetes: Evidence from Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization. Biomedicines, 13(4), 774. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040774






