Using a Natural Triterpenoid to Unlock the Antitumor Effects of Autophagy in B-Cell Lymphoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines
2.2. Triterpenoids and Cellular Cytotoxicity Assays
2.3. Caspase Activation and Inhibition Assays
2.4. Western Blot Analysis
2.5. TMRE Staining
2.6. In Vivo Tumor Induction and Evaluation
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
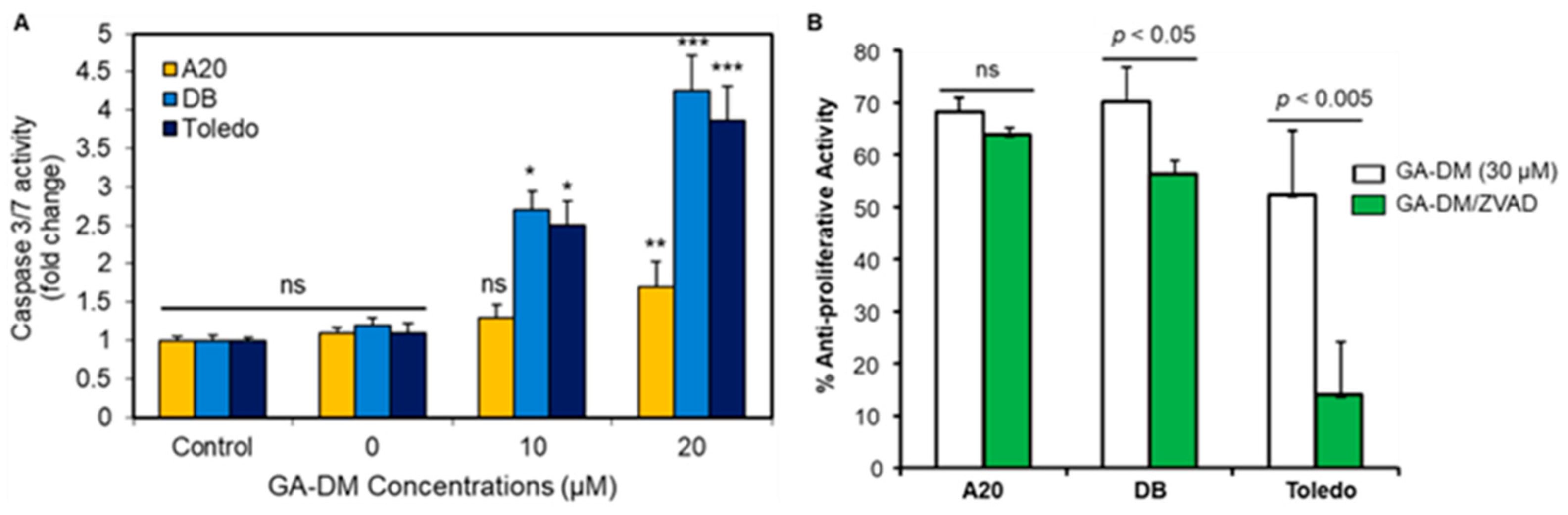
3.1. Anti-Proliferative Activity by the Natural Product GA-DM
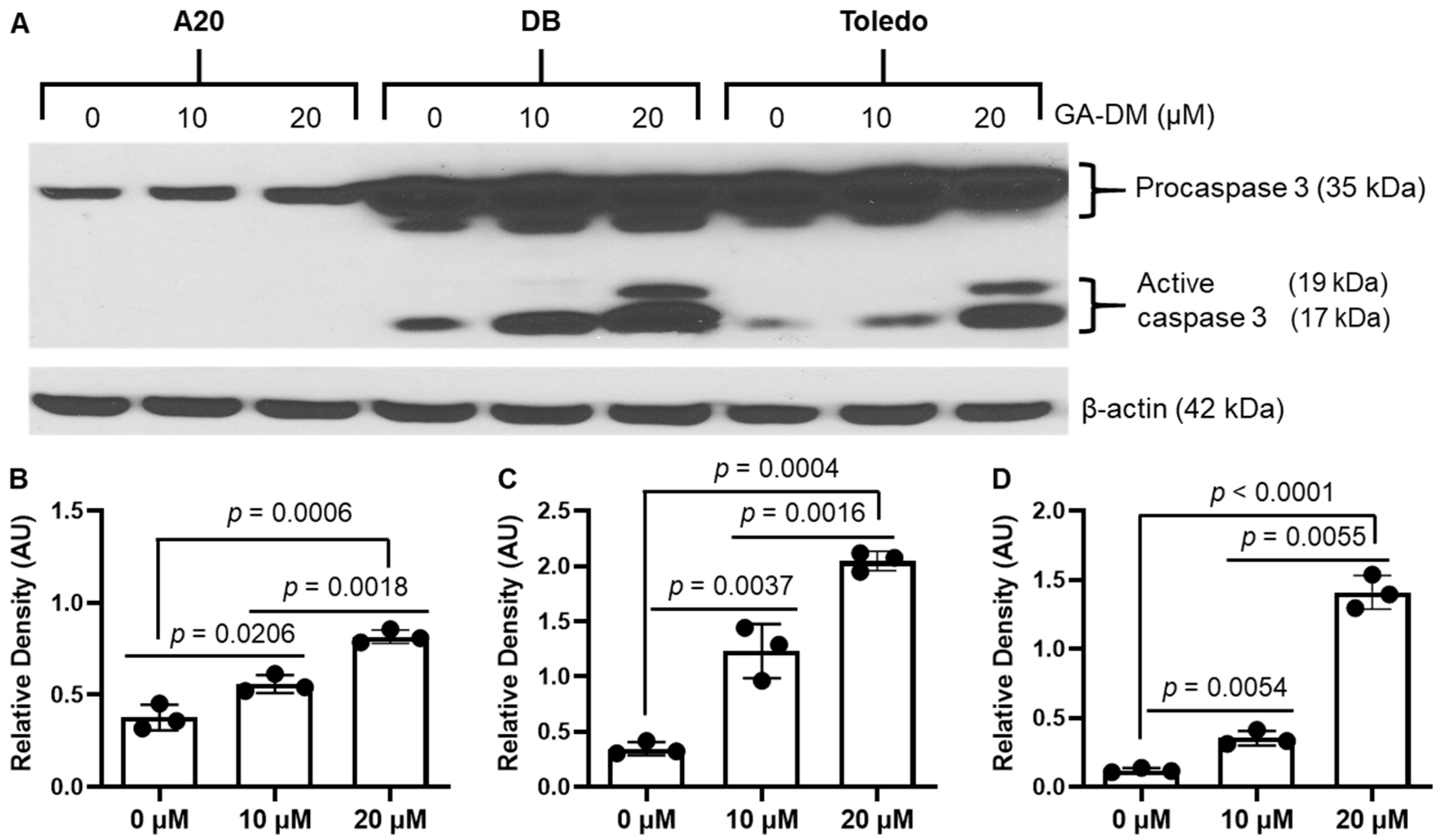
3.2. GA-DM Differentially Activates Caspase Processing in Human and Mouse B-Cell Lymphomas
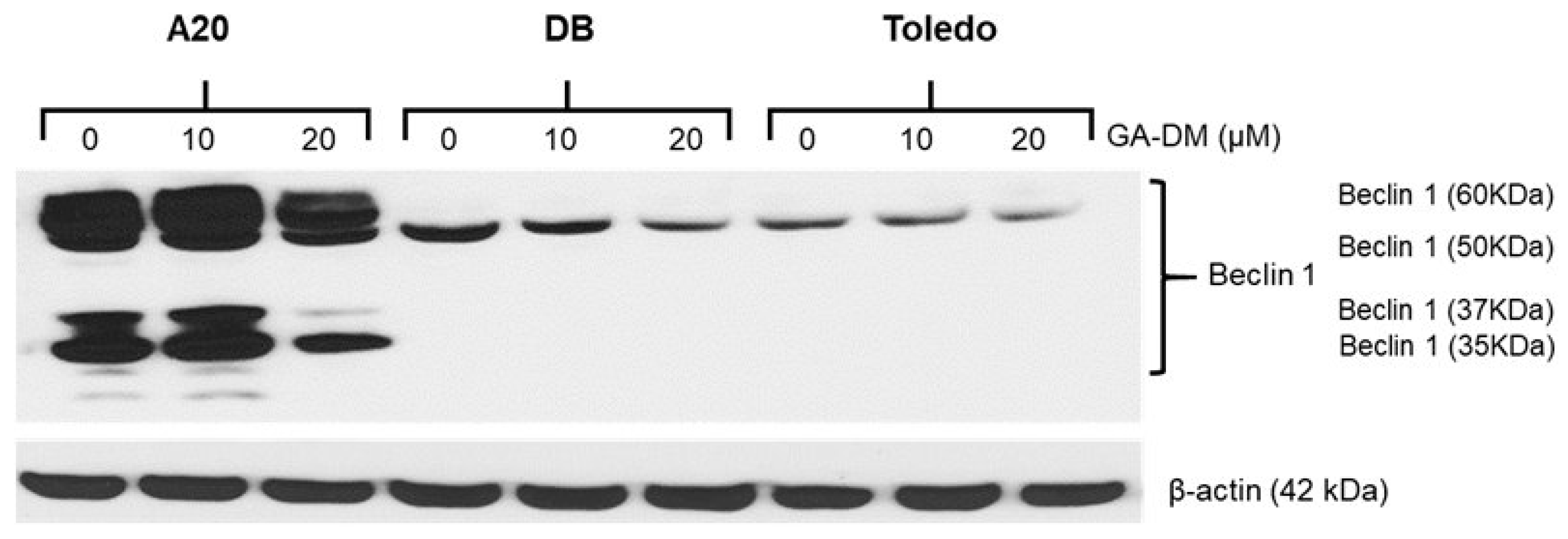
3.3. GA-DM Induces Autophagy in Mouse A20 Lymphoma Cells
3.4. Effects of GA-DM on the Mitochondrial Membrane Potential in Mouse and Human Lymphoma Cells
3.5. In Vivo Antitumor Efficacy of GA-DM
4. Discussion
5. Possible Clinical Implications and Limitations of GA-DM Treatment
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shingleton, J.; Wang, J.; Baloh, C.; Dave, T.; Davis, N.; Happ, L.; Jadi, O.; Kositsky, R.; Li, X.; Love, C.; et al. Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas: Malignancies Arising from Mature B Cells. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2021, 11, a034843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luitel, P.; Thapaliya, I.; Paudel, S.; Khanal, S.; Shah, R.; Sapkota Upadhya, P. Diffuse large B cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma complicated with jejunal stricture and perforation. Int. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2024, 124, 110375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakkoli, M.; Barta, S.K. 2024 Update: Advances in the risk stratification and management of large B-cell lymphoma. Am. J. Hematol. 2023, 98, 1791–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crees, Z.D.; Ghobadi, A. Cellular Therapy Updates in B-Cell Lymphoma: The State of the CAR-T. Cancers 2021, 13, 5181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayala, E.; Tomblyn, M. Hematopoietic cell transplantation for lymphomas. Cancer Control 2011, 18, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mey, U.; Hitz, F.; Lohri, A.; Pederiva, S.; Taverna, C.; Tzankov, A.; Meier, O.; Yeow, K.; Renner, C. Diagnosis and treatment of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2012, 142, w13511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, E.S.; Pittaluga, S. Aggressive B-cell lymphomas: A review of new and old entities in the WHO classification. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 2011, 2011, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morton, L.M.; Wang, S.S.; Devesa, S.S.; Hartge, P.; Weisenburger, D.D.; Linet, M.S. Lymphoma incidence patterns by WHO subtype in the United States, 1992–2001. Blood 2006, 107, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.; Howell, D.; Patmore, R.; Jack, A.; Roman, E. Incidence of haematological malignancy by sub-type: A report from the Haematological Malignancy Research Network. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 105, 1684–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, C.; Murawski, N.; Wiesen, M.H.; Held, G.; Poeschel, V.; Zeynalova, S.; Wenger, M.; Nickenig, C.; Peter, N.; Lengfelder, E.; et al. The role of sex and weight on rituximab clearance and serum elimination half-life in elderly patients with DLBCL. Blood 2012, 119, 3276–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liedtke, M.; Hamlin, P.A.; Moskowitz, C.H.; Zelenetz, A.D. Surveillance imaging during remission identifies a group of patients with more favorable aggressive NHL at time of relapse: A retrospective analysis of a uniformly-treated patient population. Ann. Oncol. 2006, 17, 909–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabbri, N.; Mussetti, A.; Sureda, A. Second-line treatment of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: Evolution of options. Semin. Hematol. 2023, 60, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Testa, U.; Leone, G.; Pelosi, E.; Castelli, G.; Hohaus, S. CAR-T Cell Therapy in Large B Cell Lymphoma. Mediterr. J. Hematol. Infect. Dis. 2023, 15, e2023066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Z.; Yang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yu, Q. Apoptosis, autophagy, necroptosis, and cancer metastasis. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, U.; Roy, R.; Ghosh, S.; Chakrabarti, G. The interplay between autophagy and apoptosis: Its implication in lung cancer and therapeutics. Cancer Lett. 2024, 585, 216662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, A.; Radwan, F.F.; Doonan, B.P.; God, J.M.; Zhang, L.; Bell, P.D.; Haque, A. A possible cross-talk between autophagy and apoptosis in generating an immune response in melanoma. Apoptosis 2012, 17, 1066–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igney, F.H.; Krammer, P.H. Immune escape of tumors: Apoptosis resistance and tumor counterattack. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2002, 71, 907–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Cho, S.W. The Evasion Mechanisms of Cancer Immunity and Drug Intervention in the Tumor Microenvironment. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 868695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanwar, J.; Taskeen, M.; Mohammad, I.; Huo, C.; Chan, T.H.; Dou, Q.P. Recent advances on tea polyphenols. Front. Biosci. 2012, 4, 111–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balunas, M.J.; Su, B.; Brueggemeier, R.W.; Kinghorn, A.D. Natural products as aromatase inhibitors. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2008, 8, 646–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monga, M.; Sausville, E.A. Developmental therapeutics program at the NCI: Molecular target and drug discovery process. Leukemia 2002, 16, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cragg, G.M.; Grothaus, P.G.; Newman, D.J. Impact of natural products on developing new anti-cancer agents. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 3012–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boh, B.; Berovic, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhi-Bin, L. Ganoderma lucidum and its pharmaceutically active compounds. Biotechnol. Annu. Rev. 2007, 13, 265–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Chang, Q.; Wong, L.K.; Chong, F.S.; Li, R.C. Triterpene antioxidants from ganoderma lucidum. Phytother. Res. 1999, 13, 529–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, I.; Liu, J.; Shimizu, K.; Sato, M.; Kukita, A.; Kukita, T.; Kondo, R. Regulation of osteoclastogenesis by ganoderic acid DM isolated from Ganoderma lucidum. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 602, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.; Gu, X.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Z. Chemotherapeutic and targeted drugs-induced immunogenic cell death in cancer models and antitumor therapy: An update review. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1152934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Ding, C.; Zhu, W.; Li, X.; Chen, T.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, T.C.; Ma, W. Chemotherapeutic drugs induce oxidative stress associated with DNA repair and metabolism modulation. Life Sci. 2022, 289, 120242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeng, E. Apoptosis (programmed cell death) and its signals—A review. Braz. J. Biol. 2021, 81, 1133–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debnath, J.; Gammoh, N.; Ryan, K.M. Autophagy and autophagy-related pathways in cancer. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2023, 24, 560–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Gao, H.; Su, X. Autophagy-related signaling pathways are involved in cancer (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Y.; Yu, Q.J.; Zhang, R.D.; Liu, B. Core signaling pathways of survival/death in autophagy-related cancer networks. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2011, 43, 1263–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brech, A.; Ahlquist, T.; Lothe, R.A.; Stenmark, H. Autophagy in tumour suppression and promotion. Mol. Oncol. 2009, 3, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Kang, J.; Fu, C. The independence of and associations among apoptosis, autophagy, and necrosis. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2018, 3, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Shao, Y.; Li, C. Different types of cell death and their shift in shaping disease. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takacs-Vellai, K. Apoptosis and Autophagy, Different Modes of Cell Death: How to Utilize Them to Fight Diseases? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radwan, F.F.; Hossain, A.; God, J.M.; Leaphart, N.; Elvington, M.; Nagarkatti, M.; Tomlinson, S.; Haque, A. Reduction of myeloid-derived suppressor cells and lymphoma growth by a natural triterpenoid. J. Cell Biochem. 2015, 116, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, B.M.; Radwan, F.F.Y.; Hossain, A.; Doonan, B.P.; Hathaway-Schrader, J.D.; God, J.M.; Voelkel-Johnson, C.V.; Banik, N.L.; Reddy, S.V.; Haque, A. Endoplasmic reticulum stress, autophagic and apoptotic cell death, and immune activation by a natural triterpenoid in human prostate cancer cells. J. Cell Biochem. 2019, 120, 6264–6276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radwan, F.F.; Zhang, L.; Hossain, A.; Doonan, B.P.; God, J.M.; Haque, A. Mechanisms regulating enhanced human leukocyte antigen class II-mediated CD4 + T cell recognition of human B-cell lymphoma by resveratrol. Leuk. Lymphoma 2012, 53, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- God, J.M.; Cameron, C.; Figueroa, J.; Amria, S.; Hossain, A.; Kempkes, B.; Bornkamm, G.W.; Stuart, R.K.; Blum, J.S.; Haque, A. Elevation of c-MYC disrupts HLA class II-mediated immune recognition of human B cell tumors. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 1434–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council (US) Committee for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, 8th ed.; National Academies Press (US): Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polcyn, R.; Capone, M.; Matzelle, D.; Hossain, A.; Chandran, R.; Banik, N.L.; Haque, A. Enolase inhibition alters metabolic hormones and inflammatory factors to promote neuroprotection in spinal cord injury. Neurochem. Int. 2020, 139, 104788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radwan, F.F.; Perez, J.M.; Haque, A. Apoptotic and Immune Restoration Effects of Ganoderic Acids Define a New Prospective for Complementary Treatment of Cancer. J. Clin. Cell. Immunol. 2011, S3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bata, N.; Cosford, N.D.P. Cell Survival and Cell Death at the Intersection of Autophagy and Apoptosis: Implications for Current and Future Cancer Therapeutics. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2021, 4, 1728–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Q.; Liu, Y.; Li, X. The interaction mechanism between autophagy and apoptosis in colon cancer. Transl. Oncol. 2020, 13, 100871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shalini, S.; Dorstyn, L.; Dawar, S.; Kumar, S. Old, new and emerging functions of caspases. Cell Death Differ. 2015, 22, 526–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonkin-Reeves, A.; Giuliani, C.M.; Price, J.T. Inhibition of autophagy; an opportunity for the treatment of cancer resistance. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1177440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bialik, S.; Dasari, S.K.; Kimchi, A. Autophagy-dependent cell death—Where, how and why a cell eats itself to death. J. Cell Sci. 2018, 131, 215152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nano, M.; Mondo, J.A.; Harwood, J.; Balasanyan, V.; Montell, D.J. Cell survival following direct executioner-caspase activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2216531120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, C.H.; Kumar, S. Caspases in metabolic disease and their therapeutic potential. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 1010–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.Y.; Moon, D.O.; Choi, Y.H.; Lee, J.D.; Kim, G.Y. Bcl-2 and caspase-3 are major regulators in Agaricus blazei-induced human leukemic U937 cell apoptosis through dephoshorylation of Akt. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 30, 1432–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Virgilio, L.; Silva-Lucero, M.D.; Flores-Morelos, D.S.; Gallardo-Nieto, J.; Lopez-Toledo, G.; Abarca-Fernandez, A.M.; Zacapala-Gomez, A.E.; Luna-Munoz, J.; Montiel-Sosa, F.; Soto-Rojas, L.O.; et al. Autophagy: A Key Regulator of Homeostasis and Disease: An Overview of Molecular Mechanisms and Modulators. Cells 2022, 11, 2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirawan, E.; Vanden Berghe, T.; Lippens, S.; Agostinis, P.; Vandenabeele, P. Autophagy: For better or for worse. Cell Res. 2012, 22, 43–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wu, Y.; Meng, S.; Xu, P.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Hu, X.; Ouyang, L.; Wang, G. Selective autophagy in cancer: Mechanisms, therapeutic implications, and future perspectives. Mol. Cancer 2024, 23, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubas, A.; Dikic, I. A guide to the regulation of selective autophagy receptors. FEBS J. 2022, 289, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Liao, M.; Qin, R.; Zhu, S.; Peng, C.; Fu, L.; Chen, Y.; Han, B. Regulated cell death (RCD) in cancer: Key pathways and targeted therapies. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Towers, C.G.; Wodetzki, D.; Thorburn, A. Autophagy and cancer: Modulation of cell death pathways and cancer cell adaptations. J. Cell Biol. 2020, 219, e201909033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yao, S.; Yang, H.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y. Autophagy: Regulator of cell death. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, M.A.; Fraile-Martinez, O.; de Leon-Oliva, D.; Boaru, D.L.; Lopez-Gonzalez, L.; Garcia-Montero, C.; Alvarez-Mon, M.A.; Guijarro, L.G.; Torres-Carranza, D.; Saez, M.A.; et al. Autophagy in Its (Proper) Context: Molecular Basis, Biological Relevance, Pharmacological Modulation, and Lifestyle Medicine. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2024, 20, 2532–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mele, L.; Del Vecchio, V.; Liccardo, D.; Prisco, C.; Schwerdtfeger, M.; Robinson, N.; Desiderio, V.; Tirino, V.; Papaccio, G.; La Noce, M. The role of autophagy in resistance to targeted therapies. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2020, 88, 102043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, R.; Zeh, H.J.; Lotze, M.T.; Tang, D. The Beclin 1 network regulates autophagy and apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2011, 18, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platini, F.; Perez-Tomas, R.; Ambrosio, S.; Tessitore, L. Understanding autophagy in cell death control. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2010, 16, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiuri, M.C.; Zalckvar, E.; Kimchi, A.; Kroemer, G. Self-eating and self-killing: Crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Doonan, B.P.; Radwan, F.F.Y.; Banik, N.L.; Haque, A. Using a Natural Triterpenoid to Unlock the Antitumor Effects of Autophagy in B-Cell Lymphoma. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 445. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13020445
Doonan BP, Radwan FFY, Banik NL, Haque A. Using a Natural Triterpenoid to Unlock the Antitumor Effects of Autophagy in B-Cell Lymphoma. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(2):445. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13020445
Chicago/Turabian StyleDoonan, Bently P., Faisal F. Y. Radwan, Naren L. Banik, and Azizul Haque. 2025. "Using a Natural Triterpenoid to Unlock the Antitumor Effects of Autophagy in B-Cell Lymphoma" Biomedicines 13, no. 2: 445. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13020445
APA StyleDoonan, B. P., Radwan, F. F. Y., Banik, N. L., & Haque, A. (2025). Using a Natural Triterpenoid to Unlock the Antitumor Effects of Autophagy in B-Cell Lymphoma. Biomedicines, 13(2), 445. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13020445






