Ultrasound-Guided Versus Traditional Refill of Intrathecal Infusion Pumps: A Prospective Quasi-Experimental Clinical Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Background
1.2. The Study
2. Methods
2.1. Design
2.2. Study Setting and Sampling
2.3. Inclusion/Exclusion Criteria
2.4. Study Interventions
2.4.1. Traditional Method
2.4.2. Ultrasound-Guided Method
2.5. Data Collection
2.6. Data Analysis
2.7. Ethical Considerations
3. Results
3.1. Patients’ Characteristics
3.2. Factors Associated with Procedural Pain and Complications During Intrathecal Refills
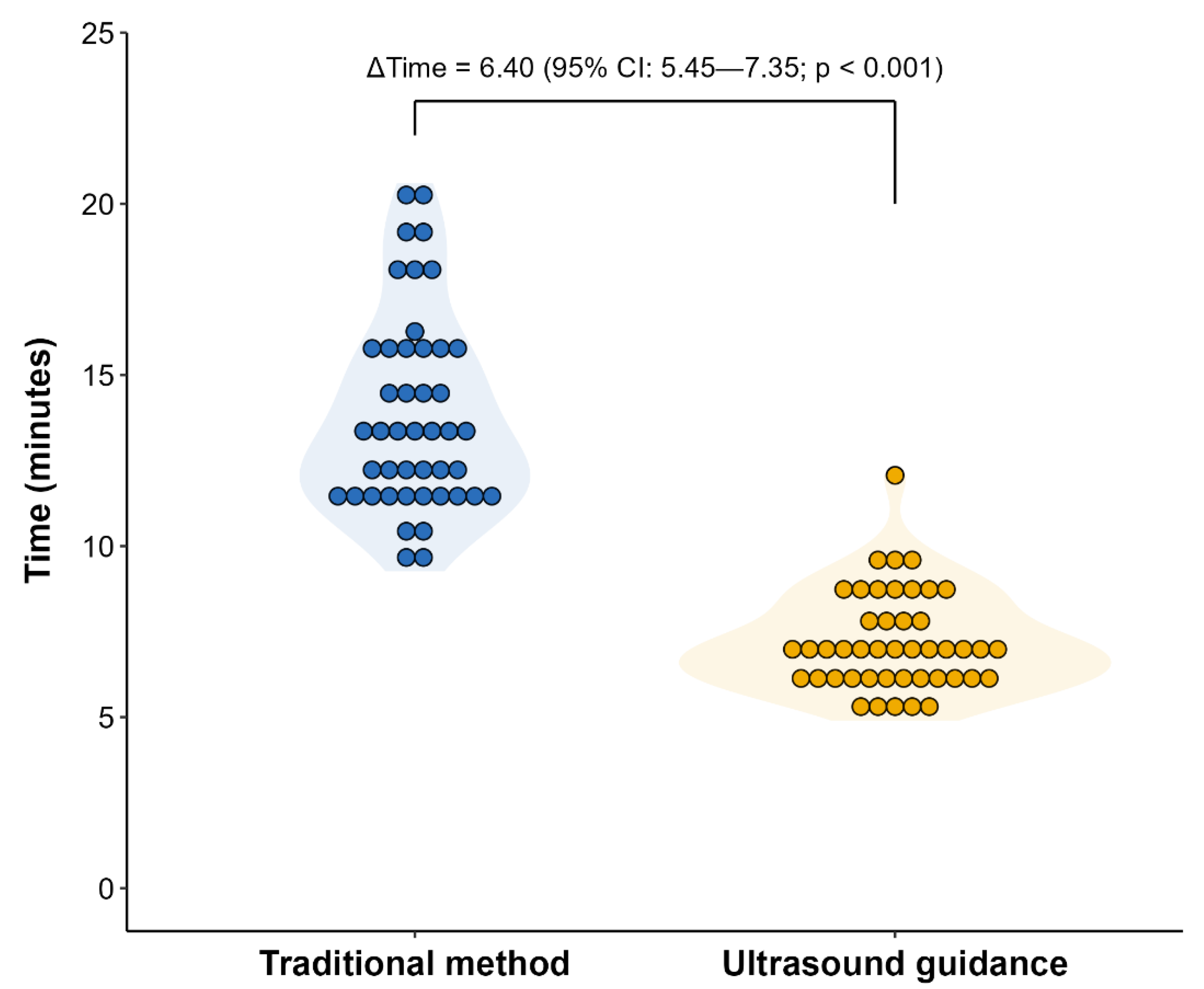
3.3. Comparison of Refill Duration and Pain Between Both Methods
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raja, S.N.; Carr, D.B.; Cohen, M.; Finnerup, N.B.; Flor, H.; Gibson, S.; Keefe, F.J.; Mogil, J.S.; Ringkamp, M.; Sluka, K.A.; et al. The revised International Association for the Study of Pain definition of pain: Concepts, challenges, and compromises. Pain 2020, 161, 1976–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallerand, A.H.; Musto, S.; Polomano, R.C. Nursing’s role in cancer pain management. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2011, 15, 250–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, D.S.; McGee, S.J. Pain as a global public health priority. BMC Public Health 2011, 11, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahawar, B.; Kannan, A.; Mahawar, V.; Srinivasan, S. Intrathecal pain pumps in pain relief. Clin. Radiol. 2023, 78, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deer, T.R.; Pope, J.E.; Hayek, S.M.; Bux, A.; Buchser, E.; Eldabe, S.; De Andrés, J.A.; Erdek, M.; Patin, D.; Grider, J.S.; et al. The Polyanalgesic Consensus Conference (PACC): Recommendations on Intrathecal Drug Infusion Systems Best Practices and Guidelines. Neuromodulation 2017, 20, 96–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldabe, S.; Duarte, R.; Thomson, S.; Bojanic, S.; Farquhar-Smith, P.; Bagchi, S.; Farquhar, L.; Wetherill, B.; Copley, S. Intrathecal drug delivery for the management of pain and spasticity in adults: British Pain Society’s recommendations for best clinical practice. Br. J. Pain 2024, 20494637241280356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmiento, I.M.N.; Santos, J.R.H.; Villegas, S.T.; Ramos, A.J.; Hurtado, G.C.; Huerta, J.C.T. Bomba de infusión intratecal implantable en pacientes con dolor crónico. Evaluación de la discapacidad y la calidad de vida. Rev. Soc. Esp. Dolor 2010, 17, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saulino, M.; Gofeld, M. “Sonology” of programmable intrathecal pumps. Neuromodulation 2014, 17, 696–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gofeld, M.; McQueen, C.K. Ultrasound-guided intrathecal pump access and prevention of the pocket fill. Pain Med. 2011, 12, 607–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurdle, M.F.; Locketz, A.J.; Smith, J. A technique for ultrasound-guided intrathecal drug-delivery system refills. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2007, 86, 250–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, H. Ultrasound-Guided Localization of Difficult-to-Access Refill Port of the Intrathecal Pump Reservoir. Neuromodulation 2009, 12, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peccora, C.D.; Ross, E.L.; Hanna, G.M. Aberrant intrathecal pump refill: Ultrasound-guided aspiration of a substantial quantity of subcutaneous hydromorphone. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2013, 38, 544–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maneyapanda, M.B.; Chang Chien, G.C.; Mattie, R.; Amorapanth, P.; Reger, C.; McCormick, Z.L. Ultrasound guidance for technically challenging intrathecal baclofen pump refill: Three cases and procedure description. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2016, 95, 692–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, P.; Mazzon, G.; Sarra, V.M.; Tacconi, L.; Manganotti, P. The use ultrasound guided for refilling intrathecal baclofene pump in complicated clinical cases: A practical approach. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 57, 194–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Eslava, J.S.; Barahona-Correa, J.E.; Moreno, D.A.; Bonilla, A. Usefulness of ultrasound: Intrathecal pump refill in the management of chronic pain. A case report. Colomb. J. Anesthesiol. 2018, 46, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, S.; Ferreira, A.; Calado, D.; Hatia, M.; Faria, F. Ultrasound-Guided Intrathecal Baclofen Pump Refilling Method for Management of Spasticity in a Complex Clinical Case. Cureus 2022, 14, e31537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, S.N.; Wei, D.; Reger, C. Ultrasound guidance versus landmark guidance for intrathecal baclofen pump refill: A randomized pilot study. PM&R 2023, 15, 1425–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singa, R.M.; Buvanendran, A.; McCarthy, R.J. A Comparison of Refill Procedures and Patient Outcomes Following Ultrasound-Guided and Template-Guided Intrathecal Drug Delivery Systems with Recessed Ports. Neuromodulation 2020, 23, 938–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthys, C.; Jacobs, M.; Rossat, J.; Perruchoud, C. Accuracy of Template Versus Ultrasound Identification of the Reservoir Access Port of Intrathecal Drug Delivery System. Neuromodulation 2020, 23, 944–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maino, P.; van Kuijk, S.M.J.; Perez, R.S.G.M.; Koetsier, E. Refill Procedures of Intrathecal Drug Delivery Systems with a Recessed Fill Port on the Pump Surface: A Prospective Comparison Study of Ultrasound-Guided vs. Blind Refill Technique. Neuromodulation 2019, 22, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2008, 61, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado, D.A.; Lambert, B.S.; Boutris, N.; McCulloch, P.C.; Robbins, A.B.; Moreno, M.R.; Harris, J.D. Validation of Digital Visual Analog Scale Pain Scoring with a Traditional Paper-based Visual Analog Scale in Adults. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. Glob. Res. Rev. 2018, 2, e088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, B.; Cordero Tous, N.; Reinoso-Cobo, A.; Cortés-Martín, J.; Sánchez-García, J.C.; Rodríguez-Blanque, R.; Gálvez Mateos, R. Ultrasound-Guided Localization of the Refill Port for Intrathecal Infusion Pump Recharge: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 7178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, J.A.; Lotz, N.M. Intrathecal pain management: A team-based approach. J. Pain Res. 2017, 10, 2565–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderveer, B.L.; Ruf, K.; Street, S.; McDowell, S. We Did IT Together: Implementing a Strategy to Safely Manage Patients with Implanted Intrathecal Pumps. Pain Manag. Nurs. 2022, 23, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piquin, S.; Batardière, É.; Buron, L.; Légé, É.; Leroy, C.; Mourin, P. Nursing management of patients with intrathecal pumps in oncology. Rev. Infirm. 2021, 70, 47–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristic | n = 45 1 |
|---|---|
| Sex | |
| Female | 20 (44.4%) |
| Male | 25 (55.6%) |
| Age, years | |
| Min-Max | 33.0–82.0 |
| Mean (SD) | 56.7 (10.9) |
| Median (Q1–Q3) | 56.0 (51.0–64.0) |
| Medical history | |
| Postsurgical spinal pain | 13 (28.9%) |
| Lumbar pain / spinal degenerative disease | 16 (35.6%) |
| Chronic widespread musculoskeletal pain | 11 (24.4%) |
| Structural musculoskeletal abnormalities | 1 (2.2%) |
| Tumors / Rare diseases | 3 (6.7%) |
| Other | 1 (2.2%) |
| Intrathecal medication type | |
| Ziconotide | 7 (15.6%) |
| Morphine | 38 (84.4%) |
| Time between procedures, days | |
| Min-Max | 21.0–94.0 |
| Mean (SD) | 64.7 (21.5) |
| Median (Q1–Q3) | 72.0 (49.0–84.0) |
| Variable 1 | Traditional Method 2 | Ultrasound Guidance 2 | Adjusted Difference (95% CI) 3 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Self-reported procedural pain | 5.91 (5.20, 6.62) | 2.76 (2.27, 3.24) | −3.16 (−4.02, −2.30) | <0.001 |
| Stratified analysis | ||||
| Sex | ||||
| Female | 6.74 (5.70, 7.79) | 3.11 (2.48, 3.74) | −3.63 (−4.68, −2.59) | <0.001 |
| Male | 5.25 (4.42, 6.07) | 2.47 (1.97, 2.97) | −2.77 (−3.59, −1.95) | <0.001 |
| Refill duration, fixed at 10 min | 5.12 (4.05, 6.20) | 3.03 (2.40, 3.67) | −2.09 (−3.55, −0.63) | 0.005 |
| Time between procedures, fixed at 72 days | 5.62 (4.89, 6.35) | 2.61 (2.14, 3.09) | −3.01 (−3.84, −2.18) | <0.001 |
| Intrathecal medication type | ||||
| Ziconotide | 6.51 (4.89, 8.14) | 3.06 (2.20, 3.91) | −3.46 (−4.67, −2.24) | <0.001 |
| Morphine | 5.80 (5.06, 6.54) | 2.70 (2.21, 3.19) | −3.10 (−3.95, −2.24) | <0.001 |
| Medical history | ||||
| Postsurgical spinal pain | 5.77 (4.62, 6.92) | 2.69 (2.06, 3.33) | −3.08 (−4.05, −2.11) | <0.001 |
| Lumbar pain/spinal degenerative disease | 5.90 (4.84, 6.97) | 2.72 (2.12, 3.33) | −3.18 (−4.14, −2.23) | <0.001 |
| Chronic widespread musculoskeletal pain | 5.66 (4.44, 6.88) | 2.70 (2.03, 3.38) | −2.95 (−3.95, −1.96) | <0.001 |
| Structural musculoskeletal abnormalities | 8.14 (3.50, 12.8) | 3.86 (1.60, 6.11) | −4.29 (−6.96, −1.61) | 0.002 |
| Tumors/Rare diseases | 6.69 (4.21, 9.17) | 2.98 (1.80, 4.15) | −3.71 (−5.34, −2.09) | <0.001 |
| Other | 6.08 (2.08, 10.07) | 2.92 (0.966, 4.88) | −3.15 (−5.38, −0.92) | 0.006 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carrasco, B.L.; Martínez-Linares, J.M.; Ávila-Cabreja, J.A.; Cortés-Martín, J.; Piqueras-Sola, B.; Tous, N.C.; Mateos, R.G. Ultrasound-Guided Versus Traditional Refill of Intrathecal Infusion Pumps: A Prospective Quasi-Experimental Clinical Study. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2671. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112671
Carrasco BL, Martínez-Linares JM, Ávila-Cabreja JA, Cortés-Martín J, Piqueras-Sola B, Tous NC, Mateos RG. Ultrasound-Guided Versus Traditional Refill of Intrathecal Infusion Pumps: A Prospective Quasi-Experimental Clinical Study. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(11):2671. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112671
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarrasco, Beatriz Lechuga, Jose Manuel Martínez-Linares, José Alejandro Ávila-Cabreja, Jonathan Cortés-Martín, Beatriz Piqueras-Sola, Nicolás Cordero Tous, and Rafael Gálvez Mateos. 2025. "Ultrasound-Guided Versus Traditional Refill of Intrathecal Infusion Pumps: A Prospective Quasi-Experimental Clinical Study" Biomedicines 13, no. 11: 2671. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112671
APA StyleCarrasco, B. L., Martínez-Linares, J. M., Ávila-Cabreja, J. A., Cortés-Martín, J., Piqueras-Sola, B., Tous, N. C., & Mateos, R. G. (2025). Ultrasound-Guided Versus Traditional Refill of Intrathecal Infusion Pumps: A Prospective Quasi-Experimental Clinical Study. Biomedicines, 13(11), 2671. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112671







