Predicting and Treating Pulmonary Fibrosis with Proteomic Biomarker Investigations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Challenges of IPF
3. Protein Analysis Through Different Types of Mass Spectrometry Relevant for IPF Research
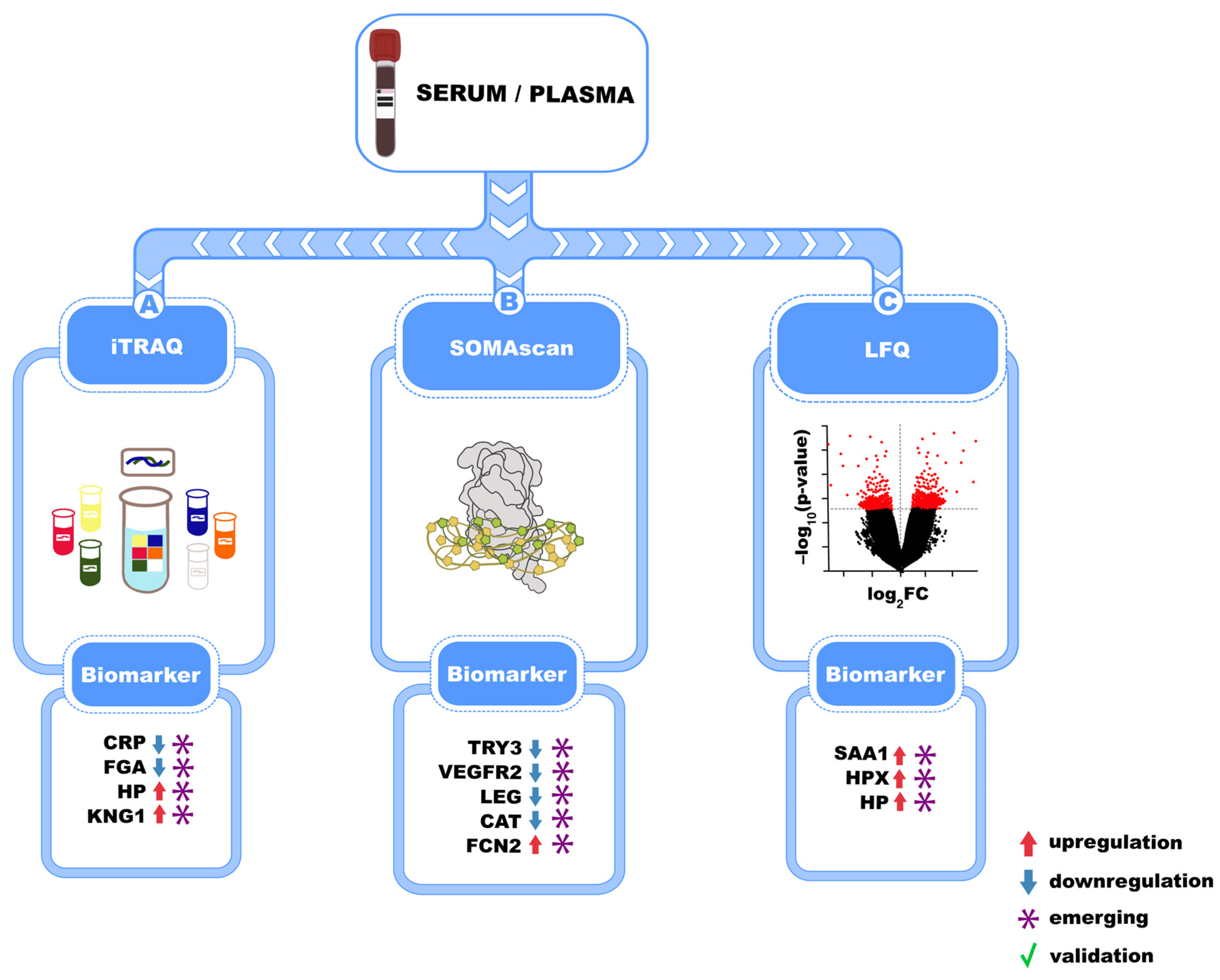
4. Mass Spectrometry-Based Serum and Plasma Biomarkers in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
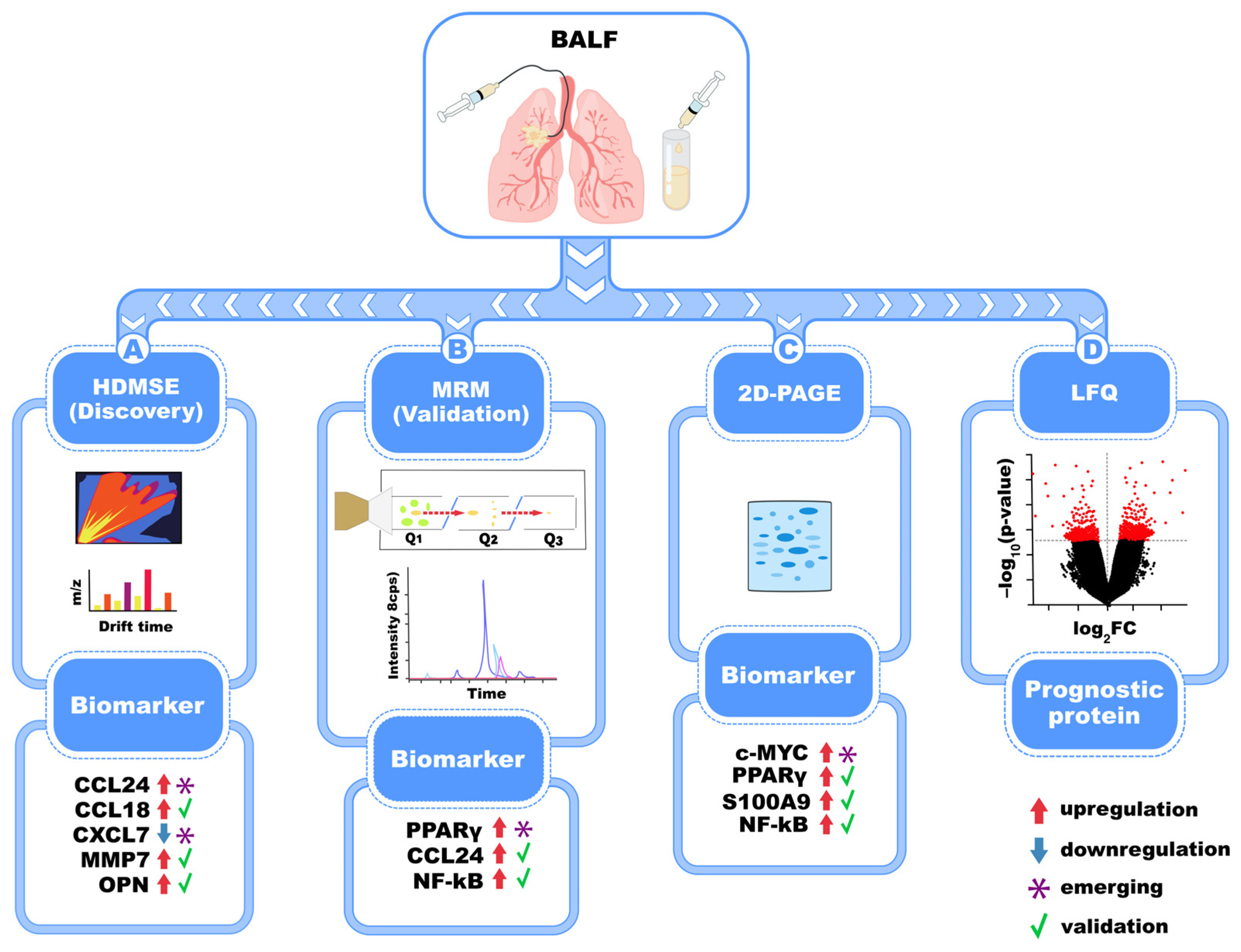
5. Biomarkers of IPF Identified in BALF Fluid Through Proteomics
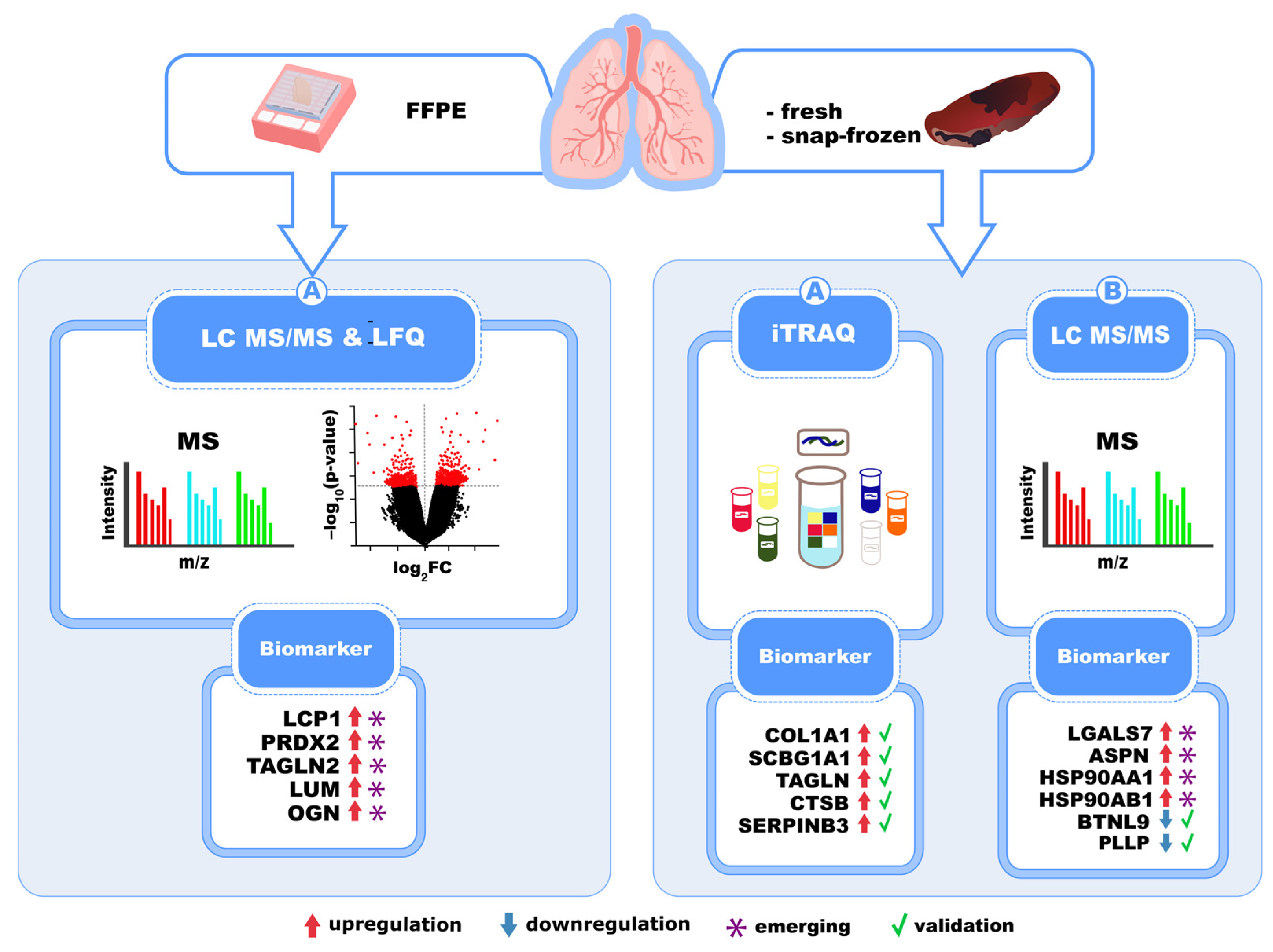
6. Biomarkers of IPF Identified in Lung Tissues Through Proteomics
New Insight into Biomarker Identification Through Spatial Proteomics
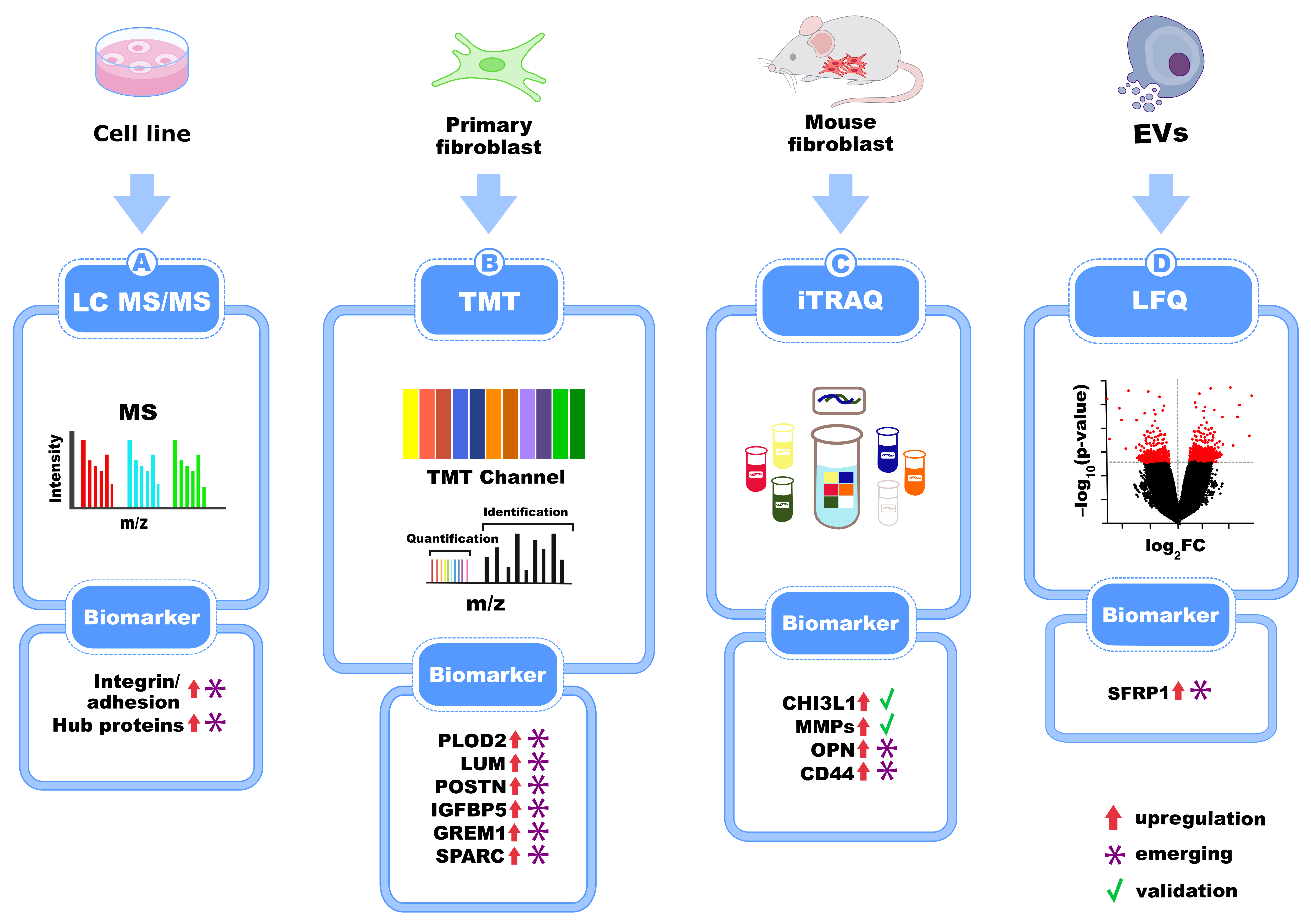
7. Biomarkers of IPF Identified in Pulmonary Cell Lines and Primary Cells from IPF Patients
New Insights in Biomarker Discovery with Single-Cell Proteomics
8. Key Validated Protein Biomarkers in IPF
| Biomarker | Biological Role/Source | Diagnostic/Prognostic Value | Strengths | Limitations | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MMP-7 (Matrix Metalloproteinase-7) | ECM remodeling enzyme secreted by alveolar epithelium and macrophages | Elevated in IPF; baseline levels predict poor survival | Strong predictor of progression; frequently validated; independent in multivariate models | Not IPF-specific; elevated in other ILDs; cutoff variability | [68,76] |
| KL-6 (Krebs von den Lungen-6/MUC1) | Marker of type II pneumocyte injury | High in IPF; inversely correlates with FVC and DLCO; associated with disease progression | Highly sensitive; useful for monitoring | Limited specificity; variation across studies and platforms | [43,67,77,78,79,80] |
| Surfactant proteins A and D (SP-A, SP-D) | Alveolar epithelial cell products involved in surfactant metabolism and immune response | Increased in IPF; especially SP-D correlates with disease severity and outcomes | Well established in serum and BAL; measurable in standard biofluids | SP-A less consistent; levels influenced by inflammation | [39] |
| CCL18 (Chemokine [C-C motif] ligand 18) | Produced by alveolar macrophages; involved in immune cell recruitment and collagen production | Elevated in IPF; predictive of FVC decline and survival | Promising prognostic marker; measurable in serum | Lacks disease specificity; varies across cohorts | [33,41,81,82,83,84] |
| Periostin | ECM protein secreted by activated fibroblasts; marker of fibrosis and tissue remodeling | Elevated in some IPF cohorts; may correlate with progression or acute exacerbations | Novel marker; may reflect fibroblast activity | Fewer studies; requires further validation | [85,86,87,88] |
9. AI-Powered Proteomics: A New Era in Translational Medicine
10. Clinical Translation of Proteomics from Bench to Bedside in IPF
Current Limitations in the Clinical Translation of Proteomics
11. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 2D | Two-Dimensional |
| 2D-PAGE | Two-Dimensional Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis |
| 16S rRNA | 16S Ribosomal Ribonucleic Acid |
| AAV DTR | Adeno-Associated Virus Diphtheria Toxin Receptor |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| ASPN | Asporin |
| ATS | American Thoracic Society |
| BALF | Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid |
| BALF-EVs | Extracellular Vesicles Isolated from Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid |
| BTNL9 | Butyrophilin Like 9 |
| CCL | CC-Chemokine Ligand |
| CCL17, 22, 25, 28 | Chemokine (C-C motif) Ligands |
| CCL18 | Chemokine (C-C motif) Ligand 18 |
| CCD19Lu | Normal Human Lung Fibroblast Cell Line |
| CD44 | Cluster of Differentiation 44 |
| ChIP-Seq | Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Sequencing |
| CLIA | Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments |
| COL1A1 | Collagen Type I Alpha 1 Chain |
| COPD | Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease |
| CRP | C-Reactive Protein |
| CyTOF | Cytometry by Time of Flight |
| CCT6A | Chaperonin Containing TCP1 Subunit 6A |
| DIA | Data-Independent Acquisition |
| DIGE | Differential Gel Electrophoresis |
| DLCO | Diffusion Lung Carbon Monoxide |
| ECM | Extracellular Matrix |
| ELISA | Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| ERS | European Respiratory Society |
| ESI | Electrospray Ionization |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| FF | Fibroblastic Foci |
| FFPE | Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded (Tissue) |
| FGF | Fibroblast Growth Factor |
| FVC | Forced Vital Capacity |
| GC-MS | Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry |
| GREM1 | Gremlin 1 |
| HDMSE | High-Definition Mass Spectrometry with Data-Dependent Acquisition |
| HP | Haptoglobin |
| HPX | Hemopexin |
| HRCT | High-Resolution Computed Tomography |
| HRMS | High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry |
| HSP90AA1 | Heat Shock Protein 90 Alpha Family Class A Member 1 |
| HSP90AB1 | Heat Shock Protein 90 Alpha Family Class B Member 1 |
| IIP | Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonia |
| IGFBP5 | Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein 5 |
| IL | Interleukin |
| ILD | Interstitial Lung Disease |
| IPF | Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis |
| iTRAQ | Isobaric Tags for Relative and Absolute Quantitation |
| KL-6 | Krebs von den Lungen-6 |
| LASSO | Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator |
| LC-MS | Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry |
| LC-MS/MS | Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry |
| LCP1 | Lymphocyte Cytosolic Protein 1 |
| LDHA | Lactate Dehydrogenase A |
| LGALS7 | Galectin-7 |
| LL29, LL97A | IPF-derived Human Lung Fibroblast Cell Lines |
| LFQ | Label-Free Quantification |
| LTBP1 | Latent Transforming Growth Factor Beta Binding Protein 1 |
| LUM | Lumican |
| MALDI | Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization |
| MALDI-TOF MS | Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization–Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry |
| MALDI-ToF/ToF | Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-Flight/Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry |
| MIF | Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor |
| MIMECAN (OGN) | Mimecan |
| MMP | Matrix Metalloproteinase |
| MMPs | Matrix Metalloproteinases |
| MS | Mass Spectrometry |
| MS/MS | Tandem Mass Spectrometry |
| MUC5B | Mucin 5B |
| NF-kB | Nuclear Factor Kappa-Light-Chain-Enhancer of Activated B Cells |
| NMR | Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |
| OGN | Mimecan |
| OPN | Osteopontin |
| PC37 | 37-Protein Classifier |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| PDE4B | Phosphodiesterase 4B |
| PLOD2 | Procollagen-Lysine, 2-Oxoglutarate 5-Dioxygenase 2 |
| POSTN | Periostin |
| PPARγ | Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma |
| PRDX2 | Peroxiredoxin-2 |
| ProCanFDL | Proteomics Cancer Federated Deep Learning |
| PTMs | Post-Translational Modifications |
| RNA-Seq | RNA Sequencing |
| RCT | Randomized Controlled Trial |
| SAA1 | Serum Amyloid A1 |
| SCGB1A1 | Secretoglobin Family 1A Member 1 |
| SCoPE | Single-Cell Proteomics by Mass Spectrometry |
| SERPINB3 | Serpin Family B Member 3 |
| SFRP1 | Secreted Frizzled-Related Protein 1 |
| SNP | Single Nucleotide Polymorphism |
| SOMAmer | Slow-Off Rate-Modified Aptamer |
| SP-A | Surfactant Protein A |
| SP-D | Surfactant Protein D |
| SPARC | Secreted Protein Acidic and Rich in Cysteine |
| STRING | Search Tool for the Retrieval of Interacting Genes/Proteins |
| SSc | Systemic Sclerosis |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| TAGLN2 | Transgelin 2 |
| TERC | Telomerase RNA Component |
| TERT | Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase |
| TGF-β | Transforming Growth Factor Beta |
| Th2 | T Helper Type 2 |
| TMT | Tandem Mass Tag |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha |
| UIP | Usual Interstitial Pneumonia |
| VEGF | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor |
| VOCs | Volatile Organic Compounds |
References
- Moss, B.J.; Ryter, S.W.; Rosas, I.O. Pathogenic Mechanisms Underlying Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2022, 17, 515–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, S.; Tonelli, R.; Murray, M.; Samarelli, A.V.; Spagnolo, P. Environmental Causes of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, C.; Cottin, V. Epidemiology and Real-Life Experience in Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2022, 28, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biondini, D.; Balestro, E.; Sverzellati, N.; Cocconcelli, E.; Bernardinello, N.; Ryerson, C.J.; Spagnolo, P. Acute Exacerbations of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (AE-IPF): An Overview of Current and Future Therapeutic Strategies. Expert. Rev. Respir. Med. 2020, 14, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clynick, B.; Corte, T.J.; Jo, H.E.; Stewart, I.; Glaspole, I.N.; Grainge, C.; Maher, T.M.; Navaratnam, V.; Hubbard, R.; Hopkins, P.M.A.; et al. Biomarker Signatures for Progressive Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2022, 59, 2101181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Steen, J.A.; Mann, M. Mass-Spectrometry-Based Proteomics: From Single Cells to Clinical Applications. Nature 2025, 638, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aebersold, R.; Mann, M. Mass-Spectrometric Exploration of Proteome Structure and Function. Nature 2016, 537, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, G.; Collard, H.R.; Egan, J.J.; Martinez, F.J.; Behr, J.; Brown, K.K.; Colby, T.V.; Cordier, J.-F.; Flaherty, K.R.; Lasky, J.A.; et al. An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Statement: Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Evidence-Based Guidelines for Diagnosis and Management. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 788–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, D.A.; Travis, W.D.; Müller, N.L.; Galvin, J.R.; Hansell, D.M.; Grenier, P.A.; King, J.; Talmadge, E. Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias: CT Features. Radiology 2005, 236, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selman, M.; Pardo, A. The Leading Role of Epithelial Cells in the Pathogenesis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Cell Signal 2020, 66, 109482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarelli, A.V.; Tonelli, R.; Heijink, I.; Martin Medina, A.; Marchioni, A.; Bruzzi, G.; Castaniere, I.; Andrisani, D.; Gozzi, F.; Manicardi, L.; et al. Dissecting the Role of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Cause or Solution. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 692551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerri, S.; Monari, M.; Guerrieri, A.; Donatelli, P.; Bassi, I.; Garuti, M.; Luppi, F.; Betti, S.; Bandelli, G.; Carpano, M.; et al. Real-Life Comparison of Pirfenidone and Nintedanib in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A 24-Month Assessment. Respir. Med. 2019, 159, 105803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, P.W.; Albera, C.; Bradford, W.Z.; Costabel, U.; Glassberg, M.K.; Kardatzke, D.; King, T.E.; Lancaster, L.; Sahn, S.A.; Szwarcberg, J.; et al. Pirfenidone in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (CAPACITY): Two Randomised Trials. Lancet 2011, 377, 1760–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richeldi, L.; Azuma, A.; Cottin, V.; Kreuter, M.; Maher, T.M.; Martinez, F.J.; Oldham, J.M.; Valenzuela, C.; Clerisme-Beaty, E.; Gordat, M.; et al. Nerandomilast in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2025, 392, 2193–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velázquez-Enríquez, J.M.; Ramírez-Hernández, A.A.; Navarro, L.M.S.; Reyes-Avendaño, I.; González-García, K.; Jiménez-Martínez, C.; Castro-Sánchez, L.; Sánchez-Chino, X.M.; Vásquez-Garzón, V.R.; Baltiérrez-Hoyos, R. Proteomic Analysis Reveals Differential Expression Profiles in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Cell Lines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodbelt, J.S. Deciphering Combinatorial Post-Translational Modifications by Top-down Mass Spectrometry. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2022, 70, 102180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradian, A.; Kalli, A.; Sweredoski, M.J.; Hess, S. The Top-down, Middle-down, and Bottom-up Mass Spectrometry Approaches for Characterization of Histone Variants and Their Post-Translational Modifications. Proteomics 2014, 14, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Po, A.; Eyers, C.E. Top-Down Proteomics and the Challenges of True Proteoform Characterization. J. Proteome Res. 2023, 22, 3663–3675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.M.; Smith, L.M. Overview and Considerations in Bottom-up Proteomics. Analyst 2023, 148, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plantier, L.; Smolinska, A.; Fijten, R.; Flamant, M.; Dallinga, J.; Mercadier, J.J.; Pachen, D.; d’Ortho, M.P.; van Schooten, F.J.; Crestani, B.; et al. The Use of Exhaled Air Analysis in Discriminating Interstitial Lung Diseases: A Pilot Study. Respir. Res. 2022, 23, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, E.A.; Baker, J.; Aggarwal, P.; Hughes, D.M.; Nwosu, A.C.; Boyd, M.T.; Mayland, C.R.; Mason, S.; Ellershaw, J.; Probert, C.S.; et al. GC-MS Techniques Investigating Potential Biomarkers of Dying in the Last Weeks with Lung Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, T.J.; Xie, H.; Bandhakavi, S.; Popko, J.; Mohan, A.; Carlis, J.V.; Higgins, L. iTRAQ Reagent-Based Quantitative Proteomic Analysis on a Linear Ion Trap Mass Spectrometer. J. Proteome Res. 2007, 6, 4200–4209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Principi, L.; Ferrini, E.; Ciccimarra, R.; Pagani, L.; Chinello, C.; Previtali, P.; Smith, A.; Villetti, G.; Zoboli, M.; Ravanetti, F.; et al. Proteomic Fingerprint of Lung Fibrosis Progression and Response to Therapy in Bleomycin-Induced Mouse Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aichler, M.; Kunzke, T.; Buck, A.; Sun, N.; Ackermann, M.; Jonigk, D.; Gaumann, A.; Walch, A. Molecular Similarities and Differences from Human Pulmonary Fibrosis and Corresponding Mouse Model: MALDI Imaging Mass Spectrometry in Comparative Medicine. Lab. Investig. 2018, 98, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stainer, A.; Faverio, P.; Busnelli, S.; Catalano, M.; Della Zoppa, M.; Marruchella, A.; Pesci, A.; Luppi, F. Molecular Biomarkers in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: State of the Art and Future Directions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Peng, F.; Zhou, Y. Biomarkers in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Current Insight and Future Direction. Chin. Med. J. Pulm. Crit. Care Med. 2024, 2, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, T.J.; Kaminski, N.; Baribaud, F.; Flavin, S.; Brodmerkel, C.; Horowitz, D.; Li, K.; Choi, J.; Vuga, L.J.; Lindell, K.O.; et al. Peripheral Blood Proteins Predict Mortality in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 185, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, N.; Hu, M.; Khalil, R.A. Biochemical and Biological Attributes of Matrix Metalloproteinases. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2017, 147, 1–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, F.; Kaminski, N.; Eugui, E.; Allard, J.; Yakhini, Z.; Ben-Dor, A.; Lollini, L.; Morris, D.; Kim, Y.; DeLustro, B.; et al. Gene Expression Analysis Reveals Matrilysin as a Key Regulator of Pulmonary Fibrosis in Mice and Humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 6292–6297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosas, I.O.; Richards, T.J.; Konishi, K.; Zhang, Y.; Gibson, K.; Lokshin, A.E.; Lindell, K.O.; Cisneros, J.; Macdonald, S.D.; Pardo, A.; et al. MMP1 and MMP7 as Potential Peripheral Blood Biomarkers in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. PLoS Med. 2008, 5, e93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuliá-Peris, L.; Carreres-Rey, C.; Gabasa, M.; Alcaraz, J.; Carretero, J.; Pereda, J. Matrix Metalloproteinases and Their Inhibitors in Pulmonary Fibrosis: EMMPRIN/CD147 Comes into Play. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasse, A.; Probst, C.; Bargagli, E.; Zissel, G.; Toews, G.B.; Flaherty, K.R.; Olschewski, M.; Rottoli, P.; Müller-Quernheim, J. Serum CC-Chemokine Ligand 18 Concentration Predicts Outcome in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 179, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamai, K.; Iwamoto, H.; Ishikawa, N.; Horimasu, Y.; Masuda, T.; Miyamoto, S.; Nakashima, T.; Ohshimo, S.; Fujitaka, K.; Hamada, H.; et al. Comparative Study of Circulating MMP-7, CCL18, KL-6, SP-A, and SP-D as Disease Markers of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Dis. Markers 2016, 2016, 4759040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, M.; Izuhara, K.; Ohta, S.; Ono, J.; Hoshino, T. Ability of Periostin as a New Biomarker of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1132, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayama, G.; Arima, K.; Kanaji, T.; Toda, S.; Tanaka, H.; Shoji, S.; McKenzie, A.N.J.; Nagai, H.; Hotokebuchi, T.; Izuhara, K. Periostin: A Novel Component of Subepithelial Fibrosis of Bronchial Asthma Downstream of IL-4 and IL-13 Signals. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2006, 118, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, M.; Hoshino, T.; Kitasato, Y.; Sakazaki, Y.; Kawayama, T.; Fujimoto, K.; Ohshima, K.; Shiraishi, H.; Uchida, M.; Ono, J.; et al. Periostin, a Matrix Protein, Is a Novel Biomarker for Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias. Eur. Respir. J. 2011, 37, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Alessandro, M.; Bergantini, L.; Cameli, P.; Pieroni, M.; Refini, R.M.; Sestini, P.; Bargagli, E. Serum Concentrations of KL-6 in Patients with IPF and Lung Cancer and Serial Measurements of KL-6 in IPF Patients Treated with Antifibrotic Therapy. Cancers 2021, 13, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashley, S.L.; Xia, M.; Murray, S.; O’Dwyer, D.N.; Grant, E.; White, E.S.; Flaherty, K.R.; Martinez, F.J.; Moore, B.B. Six-SOMAmer Index Relating to Immune, Protease and Angiogenic Functions Predicts Progression in IPF. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xin, Q.; Wu, Z.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Niu, R. Application of Isobaric Tags for Relative and Absolute Quantification (iTRAQ) Coupled with Two-Dimensional Liquid Chromatography/Tandem Mass Spectrometry in Quantitative Proteomic Analysis for Discovery of Serum Biomarkers for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 4146–4153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldham, J.M.; Huang, Y.; Bose, S.; Ma, S.-F.; Kim, J.S.; Schwab, A.; Ting, C.; Mou, K.; Lee, C.T.; Adegunsoye, A.; et al. Proteomic Biomarkers of Survival in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2024, 209, 1111–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, M.W.; Morrison, L.D.; Todd, J.L.; Snyder, L.D.; Thompson, J.W.; Soderblom, E.J.; Plonk, K.; Weinhold, K.J.; Townsend, R.; Minnich, A.; et al. Quantitative Proteomics of Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 1238–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargagli, E.; Carleo, A.; Bianchi, L.; Gagliardi, A.; Prasse, A.; Perari, M.G.; Refini, R.M.; Bini, L.; Rottoli, P. A System Biology Study of BALF from Patients Affected by Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) and Healthy Controls. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2014, 8, 932–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, A.; Sakamoto, N.; Ishimatsu, Y.; Kakugawa, T.; Nakashima, S.; Hara, S.; Adachi, M.; Fujita, H.; Mukae, H.; Kohno, S. S100A9 in BALF Is a Candidate Biomarker of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Respir. Med. 2012, 106, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rottoli, P.; Magi, B.; Perari, M.G.; Liberatori, S.; Nikiforakis, N.; Bargagli, E.; Cianti, R.; Bini, L.; Pallini, V. Cytokine Profile and Proteome Analysis in Bronchoalveolar Lavage of Patients with Sarcoidosis, Pulmonary Fibrosis Associated with Systemic Sclerosis and Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Proteomics 2005, 5, 1423–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, L.T.; Rekowski, M.J.; Koestler, D.C.; Yorozuya, T.; Saito, A.; Azeem, I.; Harrison, A.; Demoruelle, M.K.; Boomer, J.; England, B.R.; et al. Proteomic Profiling of Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid Uncovers Protein Clusters Linked to Survival in Idiopathic Forms of Interstitial Lung Disease. ERJ Open Res. 2024, 10, 00192-2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darville, L.N.F.; Lockhart, J.H.; Putty Reddy, S.; Fang, B.; Izumi, V.; Boyle, T.A.; Haura, E.B.; Flores, E.R.; Koomen, J.M. A Fast-Tracking Sample Preparation Protocol for Proteomics of Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Tumor Tissues. Methods Mol. Biol. 2024, 2823, 193–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Liu, W.; Ju, Z.; Tamboli, P.; Jonasch, E.; Mills, G.B.; Lu, Y.; Hennessy, B.T.; Tsavachidou, D. An Efficient Procedure for Protein Extraction from Formalin-Fixed, Paraffin-Embedded Tissues for Reverse Phase Protein Arrays. Proteome Sci. 2012, 10, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarelli, A.V.; Tonelli, R.; Raineri, G.; Bruzzi, G.; Andrisani, D.; Gozzi, F.; Marchioni, A.; Costantini, M.; Fabbiani, L.; Genovese, F.; et al. Proteomic Profiling of Formalin-Fixed Paraffine-Embedded Tissue Reveals Key Proteins Related to Lung Dysfunction in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1275346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Li, H.; Gao, Y.; Liu, C.; Qiu, T.; Wu, H.; Cao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, H.; Chen, J.; et al. Quantitative Proteomic Characterization of Lung Tissue in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Clin. Proteom. 2019, 16, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.; Sun, S.; Wang, J.; Cheng, Z.J.; Lei, K.C.; Xue, M.; Zhang, T.; Huang, H.; Zhang, X.D.; Sun, B. Integrative Omics Analysis Identifies Biomarkers of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, J.A.; Dingle, L.; Montero, M.A.; Venkateswaran, R.V.; Blaikley, J.F.; Lawless, C.; Schwartz, M.A. The UIP/IPF Fibroblastic Focus Is a Collagen Biosynthesis Factory Embedded in a Distinct Extracellular Matrix. JCI Insight 2022, 7, e156115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Jin, L.; Wang, X.; Cui, B.; Yang, Y.; Duggan, L.; Schwartz Sterman, A.; Lloyd, S.M.; Hazelwood, L.A.; Chaudhary, N.; et al. Novel Integration of Spatial and Single-Cell Omics Data Sets Enables Deeper Insights into IPF Pathogenesis. Proteomes 2025, 13, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandran, R.R.; Vijayaraj, P.; Garcia-Milian, R.; King, J.; Castillo, K.; Chen, L.; Kwon, Y.; William, S.; Rickabaugh, T.M.; Langerman, J.; et al. Loss of Cell Junctional Components and Matrix Alterations Drive Cell Desquamation and Fibrotic Changes in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. bioRxiv 2024. preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griesser, E.; Gesell, M.; Veyel, D.; Lamla, T.; Geillinger-Kästle, K.; Rist, W. Whole Lung Proteome of an Acute Epithelial Injury Mouse Model in Comparison to Spatially Resolved Proteomes. Proteomics 2023, 23, 2100414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullenbrock, S.; Liu, F.; Szak, S.; Hronowski, X.; Gao, B.; Juhasz, P.; Sun, C.; Liu, M.; McLaughlin, H.; Xiao, Q.; et al. Systems Analysis of Transcriptomic and Proteomic Profiles Identifies Novel Regulation of Fibrotic Programs by miRNAs in Pulmonary Fibrosis Fibroblasts. Genes. 2018, 9, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Latta, V.; Cecchettini, A.; Comelli, L.; Ucciferri, N.; Di Primio, C.; Terreni, M.; Burchielli, S.; Pelosi, G.; Rocchiccioli, S.; Morales, M. A Proteomics Approach to the Study of Bleomycin- Induced Lung Fibrosis. J. Transl. Sci. 2018, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadota, T.; Kosaka, N.; Fujita, Y.; Araya, J.; Kuwano, K.; Ochiya, T. Chapter 13—Extracellular Vesicles in Fibrotic Diseases: New Applications for Fibrosis Diagnosis and Treatment. In Exosomes; Edelstein, L., Smythies, J., Quesenberry, P., Noble, D., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 307–323. ISBN 978-0-12-816053-4. [Google Scholar]
- Shaba, E.; Landi, C.; Carleo, A.; Vantaggiato, L.; Paccagnini, E.; Gentile, M.; Bianchi, L.; Lupetti, P.; Bargagli, E.; Prasse, A.; et al. Proteome Characterization of BALF Extracellular Vesicles in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Unveiling Undercover Molecular Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adduri, R.S.R.; Cai, K.; Velasco-Alzate, K.; Vasireddy, R.; Miller, J.W.; de Frías, S.P.; de Frías, F.P.; Horimasu, Y.; Iwamoto, H.; Hattori, N.; et al. Plasma Extracellular Vesicle Proteins as Promising Noninvasive Biomarkers for Diagnosis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. J. Extracell. Biol. 2023, 2, e98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgy, O.; Mayr, C.H.; Schenesse, D.; Papakonstantinou, E.F.; Ballester, B.; Sengupta, A.; She, Y.; Hu, Q.; Melo-Narvaéz, M.C.; Jain, E.; et al. Fibroblast-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Contain SFRP1 and Mediate Pulmonary Fibrosis. JCI Insight 2024, 9, e168889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandura, D.R.; Baranov, V.I.; Ornatsky, O.I.; Antonov, A.; Kinach, R.; Lou, X.; Pavlov, S.; Vorobiev, S.; Dick, J.E.; Tanner, S.D. Mass Cytometry: Technique for Real Time Single Cell Multitarget Immunoassay Based on Inductively Coupled Plasma Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 6813–6822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, A.J.; Spelke, D.P.; Xu, Z.; Kang, C.-C.; Schaffer, D.V.; Herr, A.E. Single-Cell Western Blotting. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 749–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darmanis, S.; Gallant, C.J.; Marinescu, V.D.; Niklasson, M.; Segerman, A.; Flamourakis, G.; Fredriksson, S.; Assarsson, E.; Lundberg, M.; Nelander, S.; et al. Simultaneous Multiplexed Measurement of RNA and Proteins in Single Cells. Cell Rep. 2016, 14, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blume, J.E.; Manning, W.C.; Troiano, G.; Hornburg, D.; Figa, M.; Hesterberg, L.; Platt, T.L.; Zhao, X.; Cuaresma, R.A.; Everley, P.A.; et al. Rapid, Deep and Precise Profiling of the Plasma Proteome with Multi-Nanoparticle Protein Corona. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.-Y.; Huang, M.; Wang, X.-K.; Zhu, Y.; Li, J.-S.; Wong, C.C.L.; Fang, Q. Nanoliter-Scale Oil-Air-Droplet Chip-Based Single Cell Proteomic Analysis. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 5430–5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budnik, B.; Levy, E.; Harmange, G.; Slavov, N. SCoPE-MS: Mass Spectrometry of Single Mammalian Cells Quantifies Proteome Heterogeneity during Cell Differentiation. Genome Biol. 2018, 19, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Du, T.; Yang, L.; Wu, L. Research Progress of KL-6 in Respiratory System Diseases. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2024, 61, 599–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulito-Cueto, V.; Atienza-Mateo, B.; Batista-Liz, J.C.; Sebastián Mora-Gil, M.; Mora-Cuesta, V.M.; Iturbe-Fernández, D.; Izquierdo Cuervo, S.; Aguirre Portilla, C.; Blanco, R.; López-Mejías, R. Matrix Metalloproteinases and Their Tissue Inhibitors as Upcoming Biomarker Signatures of Connective Tissue Diseases-Related Interstitial Lung Disease: Towards an Earlier and Accurate Diagnosis. Mol. Med. 2025, 31, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, D.; Khan, M.S.; Sue, T.; Ali, M.; Jahan, U.M.S.; Atiquzzaman, M.; Khatun, M.; Islam, M.K.; Keya, R.B.; Hasan, A.; et al. Targeting MMP-7 in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: An Integrative in Vivo and in Silico Evaluation of the Therapeutic Potential of Tylophora Indica. Comput. Biol. Med. 2025, 196, 110867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.A.; Stewart, I.; Saini, G.; Robinson, K.A.; Jenkins, R.G. A Systematic Review of Blood Biomarkers with Individual Participant Data Meta-Analysis of Matrix Metalloproteinase-7 in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2022, 59, 2101612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, E.S.; Xia, M.; Murray, S.; Dyal, R.; Flaherty, C.M.; Flaherty, K.R.; Moore, B.B.; Cheng, L.; Doyle, T.J.; Villalba, J.; et al. Plasma Surfactant Protein-D, Matrix Metalloproteinase-7, and Osteopontin Index Distinguishes Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis from Other Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 194, 1242–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, P.K.; Bozyk, P.D.; Bentley, J.K.; Popova, A.P.; Birch, C.M.; Wilke, C.A.; Fry, C.D.; White, E.S.; Sisson, T.H.; Tayob, N.; et al. Periostin Promotes Fibrosis and Predicts Progression in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2012, 303, L1046–L1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, S.; Okamoto, M.; Fujimoto, K.; Sakamoto, N.; Takahashi, K.; Yamamoto, H.; Kushima, H.; Ishii, H.; Akasaka, K.; Ono, J.; et al. The Usefulness of Monomeric Periostin as a Biomarker for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaeeyan, H.; Arabfard, M.; Rasouli, H.R.; Shahriary, A.; Gh, B.F.N.M. Evaluation of Common Protein Biomarkers Involved in the Pathogenesis of Respiratory Diseases with Proteomic Methods: A Systematic Review. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2023, 11, e1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Yao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wei, W.; Yin, B.; Huang, M.; Yuan, P.; Chen, R.; Wang, F.; Wu, S.; et al. Evaluating the Diagnostic and Therapeutic Significance of KL-6 in Patients with Interstitial Lung Diseases. Heliyon 2024, 10, e27561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.M.; Tan, D.B.A.; Tedja, C.; Cooper, W.A.; Jo, H.E.; Grainge, C.; Glaspole, I.N.; Goh, N.; Ellis, S.; Hopkins, P.M.A.; et al. Pre-Treatment MMP7 Predicts Progressive Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis in Antifibrotic Treated Patients. Respirology 2025, 30, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhao, D.; Hu, D. Induced Sputum KL-6 Combined with HRCT Scoring for Diagnosing and Monitoring Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Biomol. Biomed. 2025, 26, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonella, F.; Vegas Sanchez, M.C.; d’Alessandro, M.; Millan-Billi, P.; Santos, R.F.; Schröder, N.; Bastos, H.N.; Molina-Molina, M.; Pernaute, O.S.; Villegas, D.C.; et al. Serum KL-6 as a Biomarker to Predict Progression at One Year in Interstitial Lung Disease. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 35243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choe, E.J.; Jang, J.H.; Park, J.H.; Jung, S.Y.; Her, M.; Lee, J.H. Role of Blood Krebs von Lungen-6 in Predicting Acute Exacerbation in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0323784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.W. Predictive Biomarkers and Novel Treatments for the Progressive Fibrosing Phenotype in Interstitial Lung Disease Associated with Connective Tissue Disease. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unterman, A.; Zhao, A.Y.; Neumark, N.; Schupp, J.C.; Ahangari, F.; Cosme, C.; Sharma, P.; Flint, J.; Stein, Y.; Ryu, C.; et al. Single-Cell Profiling Reveals Immune Aberrations in Progressive Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2024, 210, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliskan, C.; Seeliger, B.; Jäger, B.; Fuge, J.; Welte, T.; Terwolbeck, O.; Freise, J.; van Moorsel, C.H.M.; Zhang, Y.; Prasse, A. Genetic Variation in CCL18 Gene Influences CCL18 Expression and Correlates with Survival in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis—Part B. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiertz, I.A.; Moll, S.A.; Seeliger, B.; Barlo, N.P.; van der Vis, J.J.; Korthagen, N.M.; Rijkers, G.T.; Ruven, H.J.T.; Grutters, J.C.; Prasse, A.; et al. Genetic Variation in CCL18 Gene Influences CCL18 Expression and Correlates with Survival in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Part A. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Höhne, K.; Wagenknecht, A.; Maier, C.; Engelhard, P.; Goldmann, T.; Schließmann, S.J.; Plönes, T.; Trepel, M.; Eibel, H.; Müller-Quernheim, J.; et al. Pro-Fibrotic Effects of CCL18 on Human Lung Fibroblasts Are Mediated via CCR6. Cells 2024, 13, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, M.; Fujimoto, K.; Johkoh, T.; Kawaguchi, A.; Mukae, H.; Sakamoto, N.; Ogura, T.; Ikeda, S.; Kondoh, Y.; Yamano, Y.; et al. A Prospective Cohort Study of Periostin as a Serum Biomarker in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Treated with Nintedanib. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 22977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshihara, T.; Nanri, Y.; Nunomura, S.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Feghali-Bostwick, C.; Ajito, K.; Murakami, S.; Mawatari, M.; Izuhara, K. Periostin Plays a Critical Role in the Cell Cycle in Lung Fibroblasts. Respir. Res. 2020, 21, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpagnano, G.E.; Soccio, P.; Scioscia, G.; Palladino, G.P.; Foschino Barbaro, M.P.; Lacedonia, D. The Potential Role of Airways Periostin in the Clinical Practice of Patients Affected by Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Rejuvenation Res. 2021, 24, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Liu, H.; Yin, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Ding, Z. The Significance of Periostin in the Diagnosis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Prediction of Acute Exacerbations. J. Thorac. Dis. 2025, 17, 1364–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, M.; Kumar, C.; Zeng, W.-F.; Strauss, M.T. Artificial Intelligence for Proteomics and Biomarker Discovery. Cell Syst. 2021, 12, 759–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gessulat, S.; Schmidt, T.; Zolg, D.P.; Samaras, P.; Schnatbaum, K.; Zerweck, J.; Knaute, T.; Rechenberger, J.; Delanghe, B.; Huhmer, A.; et al. Prosit: Proteome-Wide Prediction of Peptide Tandem Mass Spectra by Deep Learning. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- How Is AI Shaping Proteomics and Multiomics? Available online: http://www.technologynetworks.com/immunology/articles/how-is-ai-shaping-proteomics-and-multiomics-395403 (accessed on 24 July 2025).
- Wang, L.; Zhu, M.; Li, Y.; Yan, P.; Li, Z.; Chen, X.; Yang, J.; Pan, X.; Zhao, H.; Wang, S.; et al. Serum Proteomics Identifies Biomarkers Associated With the Pathogenesis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2023, 22, 100524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Ma, S.-F.; Oldham, J.M.; Adegunsoye, A.; Zhu, D.; Murray, S.; Kim, J.S.; Bonham, C.; Strickland, E.; Linderholm, A.L.; et al. Machine Learning of Plasma Proteomics Classifies Diagnosis of Interstitial Lung Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2024, 210, 444–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, P.; Ammar, R.; Thompson, J.R.; Luo, Y.; Streltsov, D.; Porteous, M.; McCoubrey, C.; Cantu, E.; Beers, M.F.; Jarai, G.; et al. Integrated Plasma Proteomics and Lung Transcriptomics Reveal Novel Biomarkers in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Respir. Res. 2021, 22, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajiri, M.; Okamoto, M.; Fujimoto, K.; Johkoh, T.; Ono, J.; Tominaga, M.; Azuma, K.; Kawayama, T.; Ohta, S.; Izuhara, K.; et al. Serum Level of Periostin Can Predict Long-Term Outcome of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Respir. Investig. 2015, 53, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosack, C.S.; Page, A.-L.; Klatser, P.R. A Guide to Aid the Selection of Diagnostic Tests. Bull. World Health Organ. 2017, 95, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.-L.; Lai, C.-T.; Reyes, A.J.; Yang, H.-C.; Lu, J.-Y.; Shih, S.-R.; Chen, K.-Y.; Hoofnagle, A.N.; Yu, S.-L.; Bocik, W.; et al. Lessons Learned: Establishing a CLIA-Equivalent Laboratory for Targeted Mass Spectrometry Assays—Navigating the Transition from Research to Clinical Practice. Clin. Proteom. 2024, 21, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lathrop, J.T.; Jeffery, D.A.; Shea, Y.R.; Scholl, P.F.; Chan, M.M. US Food and Drug Administration Perspectives on Clinical Mass Spectrometry. Clin. Chem. 2016, 62, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Thomas, S.N. Impact of VALID Act Implementation on Mass Spectrometry-Based Clinical Proteomic Laboratory Developed Tests. J. Mass Spectrom. Adv. Clin. Lab. 2023, 28, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina-Pinelo, S.; Pastor, M.D.; Paz-Ares, L. VeriStrat: A Prognostic and/or Predictive Biomarker for Advanced Lung Cancer Patients? Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2014, 8, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Selvarajan, S.; Zang, Z.; Liu, W.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W.; Chen, H.; Li, L.; Cai, X.; et al. Artificial Intelligence Defines Protein-Based Classification of Thyroid Nodules. Cell Discov. 2022, 8, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
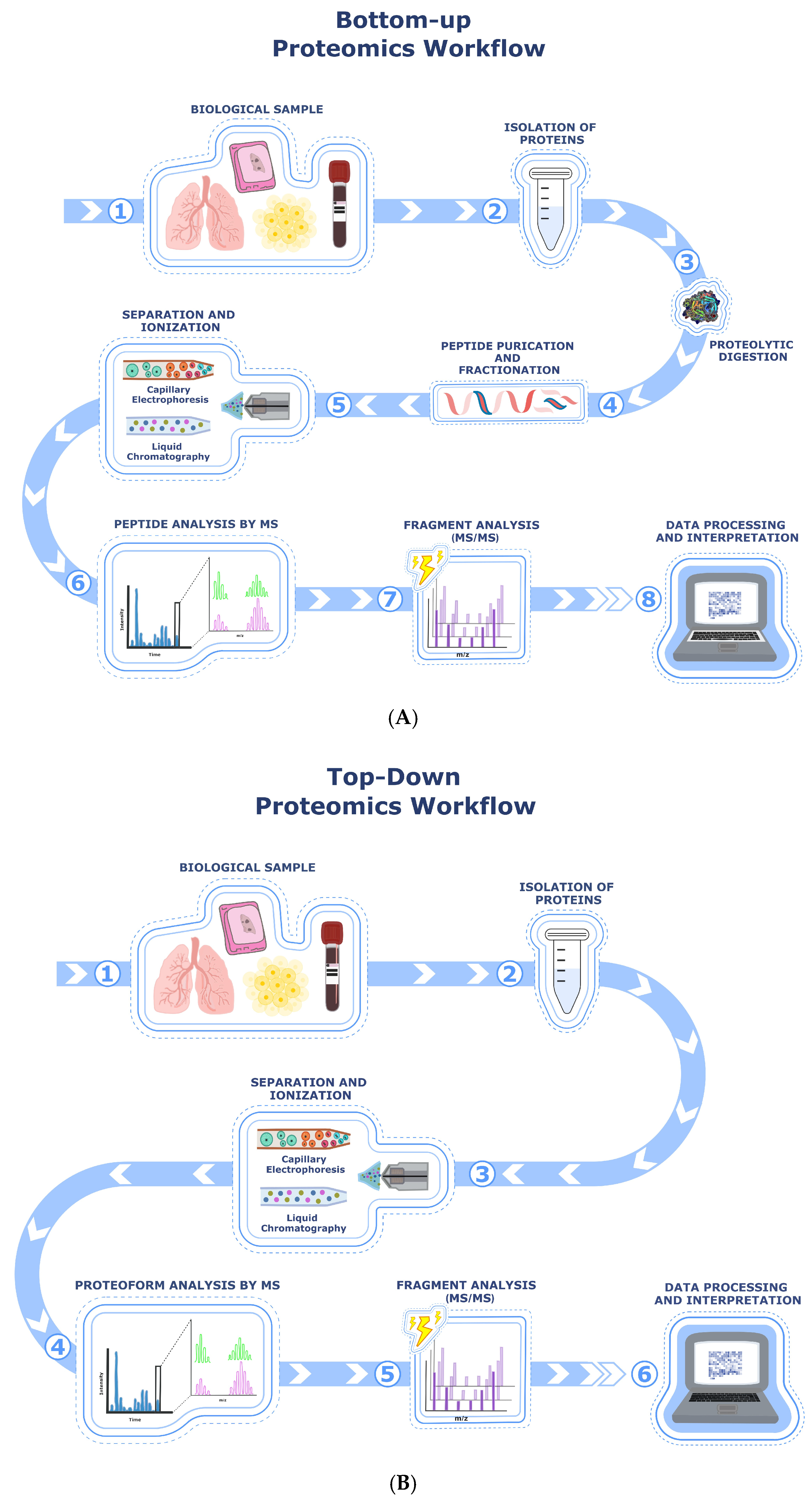
| Mass Spectrometry Technique | Identified Biomarkers | Activated Molecular Pathway | Sample Type | Reference(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GC-MS | Acetone, other VOCs | Oxidative stress, inflammation | Exhaled breath (VOCs) | [23] |
| LC-MS/MS | MMP-7, MMP-1, MMP-10 | ECM remodeling | Plasma/serum | [34,35,36,37,38] |
| LC-MS/MS | CCL18 | Inflammation, immunoregulation | Plasma/serum | [39,40] |
| LC-MS/MS | Periostin | TGF-β, IL-4, IL-13 signaling | Plasma/serum | [41,42,43] |
| LC-MS/MS | SP-A, SP-D, KL-6 | Immune response, alveolar regeneration | Serum | [33,40,44] |
| SOMAscan (aptamer-based) | VEGFR2, Ficolin-2, Legumain, Cathepsin, ICOS, Trypsin-3 | IPF progression (not specified) | Plasma | [45] |
| iTRAQ + LC-MS/MS | CRP, Fibrinogen-α, Haptoglobin, Kininogen-1 | Systemic inflammation | Plasma | [46] |
| Quantitative proteomics | SAA1, Haptoglobin, Hemopexin | Inflammation, oxidative stress, ECM | Plasma | [47] |
| HDMSE, MRM, 2D-PAGE, MALDI-ToF | MMP-7, CXCL7, CCL18, S100A9, ILs, MIF, Calgranulin B, CCL24 | Inflammation, ECM remodeling, cellular signaling | BALF | [48,49,50,51,52] |
| LC-MS/MS (FFPE tissue) | LCP1, PRDX2, TAGLN2, LUM, OGN | TGF-β, cell adhesion, ECM | Lung tissue (FFPE) | [15] |
| iTRAQ + LC-MS/MS | COL1A1, SCGB1A1, HSP90AA1/AB1, LGALS7, ASPN | ECM production and remodeling | Fresh lung tissue | [55] |
| LCM-MS, spatial proteomics | TGF-β1/2/3, LTBP1, FN1, SFRP1 | TGF-β signaling, ECM remodeling, EMT | Laser-captured lung tissue sections | [57,58,59,60] |
| Label-free LC-MS/MS | >80 proteins (e.g., POSTN, IGFBP5, SPARC) | Matrisome, cell adhesion, ECM signaling | Primary cell lines (fibroblasts) | [61,62] |
| LC-MS/MS (EVs from BALF and plasma) | SFRP1, signaling proteins, cytokines, cytoskeletal proteins | WNT/β-catenin, cell–cell communication | EVs from BALF and plasma | [63,64,65,66,67] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Raineri, G.; Samarelli, A.V.; Tonelli, R.; Masciale, V.; Aramini, B.; Petrachi, T.; Bruzzi, G.; Gozzi, F.; Trasforini, E.; Esposito, A.; et al. Predicting and Treating Pulmonary Fibrosis with Proteomic Biomarker Investigations. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2656. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112656
Raineri G, Samarelli AV, Tonelli R, Masciale V, Aramini B, Petrachi T, Bruzzi G, Gozzi F, Trasforini E, Esposito A, et al. Predicting and Treating Pulmonary Fibrosis with Proteomic Biomarker Investigations. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(11):2656. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112656
Chicago/Turabian StyleRaineri, Giulia, Anna Valeria Samarelli, Roberto Tonelli, Valentina Masciale, Beatrice Aramini, Tiziana Petrachi, Giulia Bruzzi, Filippo Gozzi, Ester Trasforini, Angela Esposito, and et al. 2025. "Predicting and Treating Pulmonary Fibrosis with Proteomic Biomarker Investigations" Biomedicines 13, no. 11: 2656. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112656
APA StyleRaineri, G., Samarelli, A. V., Tonelli, R., Masciale, V., Aramini, B., Petrachi, T., Bruzzi, G., Gozzi, F., Trasforini, E., Esposito, A., Azzali, F., Dominici, M., Eccher, A., Cerri, S., & Clini, E. (2025). Predicting and Treating Pulmonary Fibrosis with Proteomic Biomarker Investigations. Biomedicines, 13(11), 2656. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112656









