Potential Risk of Cutaneous Melanoma Attributable to Medication Use: A Mendelian Randomization Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
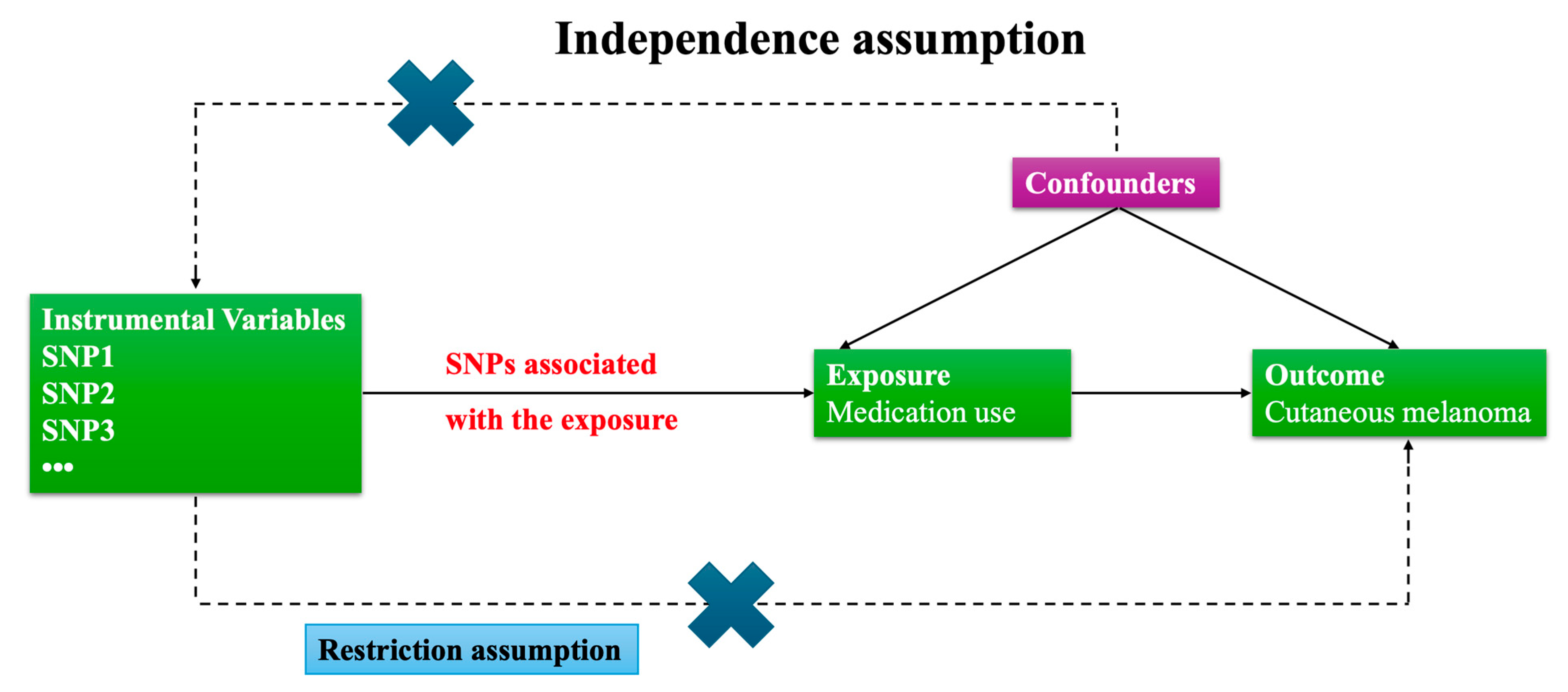
2.1. Research Framework
- (1)
- Relevance: The genetic instruments (IVs) are strongly associated with the exposure (medication use).
- (2)
- Independence from confounders: The IVs are not associated with confounders of the exposure–outcome relationship.
- (3)
- Exclusion restriction: The IVs affect the outcome (cutaneous melanoma) only through the exposure, not via alternative pathways.
2.2. Data Acquisition
2.3. Instrumental Variable Selection
2.4. MR Analyses
2.5. Sensitivity Analysis
2.6. Instrument Pleiotropy and Confounder Screening
2.7. Additional Analyses and Statistical Corrections
3. Results
3.1. Selection of Instrumental Variables (IVs)
3.2. Mendelian Randomization Analysis
3.3. Sensitivity and Pleiotropy Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| (GWASs) | Genome-Wide Association Studies |
| (MR) | Mendelian randomization |
| (DALYs) | Disability-adjusted life years |
| (NSAIDs) | Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications |
| (COX) | Cyclooxygenase |
| (IVW) | Inverse variance weighted method |
| (WME) | Weighted median estimation |
| (GORD) | Gastro-esophageal reflux disease |
References
- Arnold, M.; Singh, D.; Laversanne, M.; Vignat, J.; Vaccarella, S.; Meheus, F.; Cust, A.E.; de Vries, E.; Whiteman, D.C.; Bray, F. Global Burden of Cutaneous Melanoma in 2020 and Projections to 2040. JAMA Dermatol. 2022, 158, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, L.E.; Shalin, S.C.; Tackett, A.J. Current state of melanoma diagnosis and treatment. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2019, 20, 1366–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, P.; Knabel, P.; Fleischer, A.B., Jr. United States burden of melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancer from 1990 to 2019. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2021, 85, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortes, C.; Mastroeni, S.; Zappalà, A.R.; Passarelli, F.; Ricci, F.; Abeni, D.; Michelozzi, P. Early inflammatory biomarkers and melanoma survival. Int. J. Dermatol. 2023, 62, 752–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caini, S.; Gandini, S.; Sera, F.; Raimondi, S.; Fargnoli, M.C.; Boniol, M.; Armstrong, B.K. Meta-analysis of risk factors for cutaneous melanoma according to anatomical site and clinico-pathological variant. Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 3054–3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powe, D.G.; Voss, M.J.; Zänker, K.S.; Habashy, H.O.; Green, A.R.; Ellis, I.O.; Entschladen, F. Beta-blocker drug therapy reduces secondary cancer formation in breast cancer and improves cancer specific survival. Oncotarget 2010, 1, 628–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musselman, R.P.; Bennett, S.; Li, W.; Mamdani, M.; Gomes, T.; van Walraven, C.; Boushey, R.; Al-Obeed, O.; Al-Omran, M.; Auer, R.C. Association between perioperative beta blocker use and cancer survival following surgical resection. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 44, 1164–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobos, J.; Kenessey, I.; Tímár, J.; Ladányi, A. Glucocorticoid receptor expression and antiproliferative effect of dexamethasone on human melanoma cells. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2011, 17, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, A.; Thomsen, H.F.; Engebjerg, M.C.; Olesen, A.B.; Friis, S.; Karagas, M.R.; Sørensen, H.T. Use of oral glucocorticoids and risk of skin cancer and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: A population-based case-control study. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 100, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Lin, J.A.; Chang, C.L.; Wu, S.Y.; Zhang, J. Association between long-term opioid use and cancer risk in patients with chronic pain: A propensity score-matched cohort study. Br. J. Anaesth. 2022, 129, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamizu, K.; Furuta, S.; Hamada, Y.; Yamashita, A.; Kuzumaki, N.; Narita, M.; Doi, K.; Katayama, S.; Nagase, H.; Yamashita, J.K.; et al. κ Opioids inhibit tumor angiogenesis by suppressing VEGF signaling. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannesdottir, S.A.; Chang, E.T.; Mehnert, F.; Schmidt, M.; Olesen, A.B.; Sørensen, H.T. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and the risk of skin cancer: A population-based case-control study. Cancer 2012, 118, 4768–4776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz-Motilva, V.; Martorell-Calatayud, A.; Nagore, E. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and melanoma. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2012, 18, 3966–3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Rahmoun, M.; Ghiasvand, R.; Cairat, M.; Mahamat-Saleh, Y.; Cervenka, I.; Severi, G.; Boutron-Ruault, M.C.; Robsahm, T.E.; Kvaskoff, M.; Fournier, A. Statin Use and Skin Cancer Risk: A Prospective Cohort Study. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2022, 142, 1318–1325.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Dai, S.; Lou, D.; Wang, T.; Wang, S.; Zheng, Z. Association between statins exposure and risk of skin cancer: An updated meta-analysis. Int. J. Dermatol. 2023, 62, 1332–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.; Thompson, S.G. Mendelian Randomization: Methods for Using Genetic Variants in Causal Estimation; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Li, Q.; Cao, Z.; Wu, J. Multicenter proteome-wide Mendelian randomization study identifies causal plasma proteins in melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancers. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Nakayama, T.; Asaba, K. Systematic proteome-wide Mendelian randomization to prioritize causal plasma proteins for skin cancers. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrivankova, V.W.; Richmond, R.C.; Woolf, B.A.R.; Yarmolinsky, J.; Davies, N.M.; Swanson, S.A.; VanderWeele, T.J.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Timpson, N.J.; Dimou, N.; et al. Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology Using Mendelian Randomization: The STROBE-MR Statement. JAMA 2021, 326, 1614–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Byrne, E.M.; Zheng, Z.; Kemper, K.E.; Yengo, L.; Mallett, A.J.; Yang, J.; Visscher, P.M.; Wray, N.R. Genome-wide association study of medication-use and associated disease in the UK Biobank. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Zheng, Z.; Fang, H.; Yang, J. A generalized linear mixed model association tool for biobank-scale data. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 1616–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, S.; Butterworth, A.; Thompson, S.G. Mendelian randomization analysis with multiple genetic variants using summarized data. Genet. Epidemiol. 2013, 37, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartwig, F.P.; Davey Smith, G.; Bowden, J. Robust inference in summary data Mendelian randomization via the zero modal pleiotropy assumption. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 46, 1985–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowden, J.; Davey Smith, G.; Burgess, S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: Effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 44, 512–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowden, J.; Davey Smith, G.; Haycock, P.C.; Burgess, S. Consistent Estimation in Mendelian Randomization with Some Invalid Instruments Using a Weighted Median Estimator. Genet. Epidemiol. 2016, 40, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.; Del Greco, M.F.; Minelli, C.; Zhao, Q.; Lawlor, D.A.; Sheehan, N.A.; Thompson, J.; Davey Smith, G. Improving the accuracy of two-sample summary-data Mendelian randomization: Moving beyond the NOME assumption. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2019, 48, 728–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, S.; Thompson, S.G. Interpreting findings from Mendelian randomization using the MR-Egger method. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 32, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, J.S.; MacGregor, S. Implementing MR-PRESSO and GCTA-GSMR for pleiotropy assessment in Mendelian randomization studies from a practitioner’s perspective. Genet. Epidemiol. 2019, 43, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demenais, F.; Margaritte-Jeannin, P.; Barnes, K.C.; Cookson, W.O.C.; Altmüller, J.; Ang, W.; Barr, R.G.; Beaty, T.H.; Becker, A.B.; Beilby, J.; et al. Multiancestry association study identifies new asthma risk loci that colocalize with immune-cell enhancer marks. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim, R.P.; Koumbourlis, A.C. Tolerance & resistance to β2-agonist bronchodilators. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2013, 14, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matarrese, P.; Maccari, S.; Ascione, B.; Vona, R.; Vezzi, V.; Stati, T.; Grò, M.C.; Marano, G.; Ambrosio, C.; Molinari, P. Crosstalk between β2- and α2-Adrenergic Receptors in the Regulation of B16F10 Melanoma Cell Proliferation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Switzer, B.; Puzanov, I.; Gandhi, S.; Repasky, E.A. Targeting beta-adrenergic receptor pathways in melanoma: How stress modulates oncogenic immunity. Melanoma Res. 2024, 34, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.Y.; Chen, F. β2AR is a potential biomarker for prognosis of malignant melanoma. Genom. Appl. Biol. 2019, 38, 4800–4805. [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, P.J. Inhaled Corticosteroids. Pharmaceuticals 2010, 3, 514–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obrador, E.; Salvador-Palmer, R.; López-Blanch, R.; Oriol-Caballo, M.; Moreno-Murciano, P.; Estrela, J.M. Survival Mechanisms of Metastatic Melanoma Cells: The Link between Glucocorticoids and the Nrf2-Dependent Antioxidant Defense System. Cells 2023, 12, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.A.; Gupta, A.K.; Vujcic, B.; Piccinin, M. Use of opioid analgesics in skin disorders: Results from a nationally representative US sample. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2015, 26, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasdogan, A.; Sullivan, R.J.; Katalinic, A.; Lebbe, C.; Whitaker, D.; Puig, S.; van de Poll-Franse, L.V.; Massi, D.; Schadendorf, D. Cutaneous melanoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2025, 11, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davey, M.G.; Miller, N.; McInerney, N.M. A Review of Epidemiology and Cancer Biology of Malignant Melanoma. Cureus 2021, 13, e15087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Wang, H.; Song, W.; Feng, J.; Hou, S. Lipid-lowering medications and risk of malignant melanoma: A Mendelian randomization study. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1408972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Du, H.; An, K.; He, L.; Li, J.; Li, S. Values and preferences of medication use in patients for primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular diseases: A mixed-methods exploratory study. Chin. General. Pract. J. 2024, 1, 100022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, R.K. The alarming rise of lifestyle diseases and their impact on public health: A comprehensive overview and strategies for overcoming the epidemic. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2025, 30, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faje, A.T.; Lawrence, D.; Flaherty, K.; Freedman, C.; Fadden, R.; Rubin, K.; Cohen, J.; Sullivan, R.J. High-dose glucocorticoids for the treatment of ipilimumab-induced hypophysitis is associated with reduced survival in patients with melanoma. Cancer 2018, 124, 3706–3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
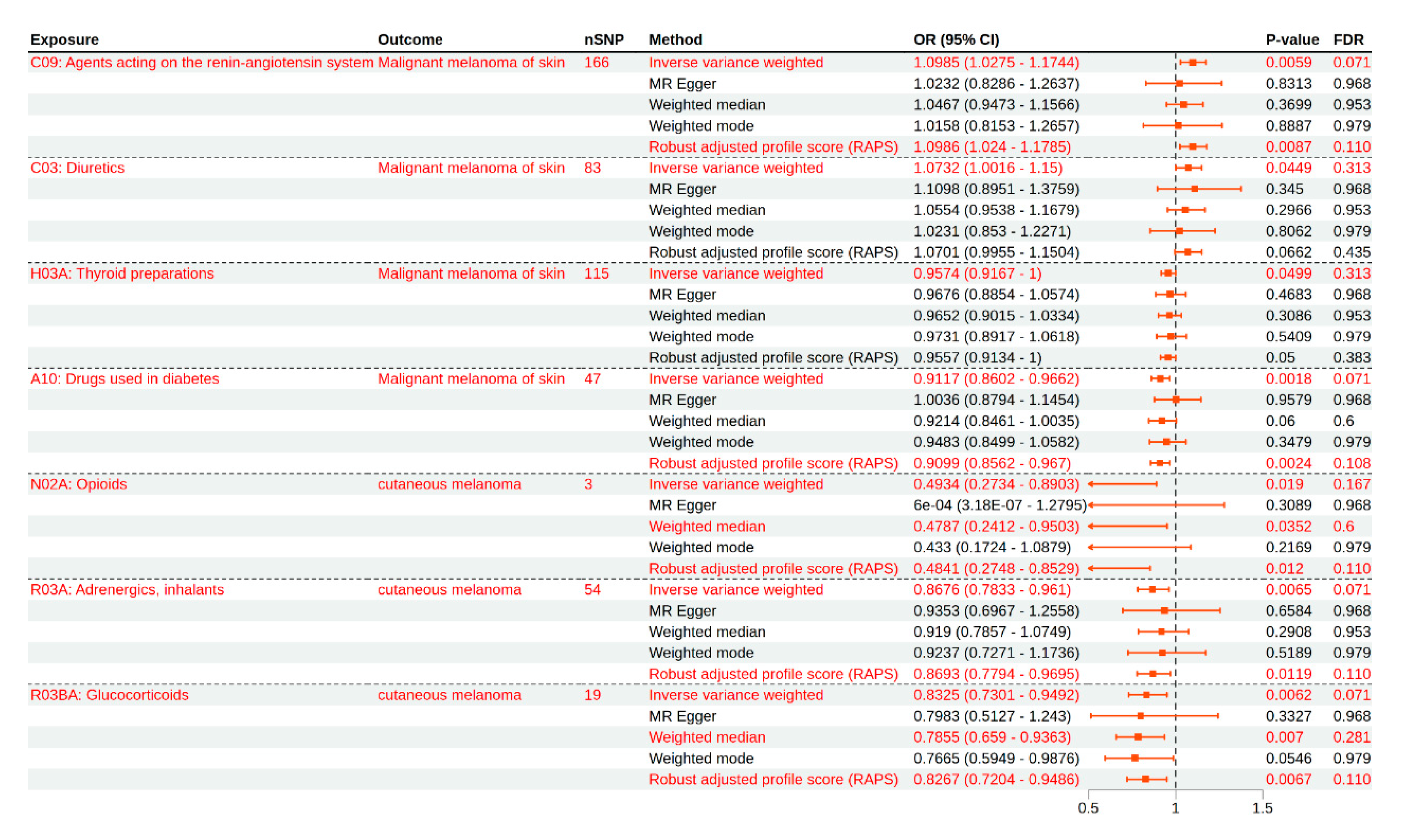
| Exposure | Outcome | Number of SNPs | Method | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | FDR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C09: Agents acting on the renin–angiotensin system | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 166 | Inverse variance weighted | 1.0985 (1.0275–1.1744) | 0.0059 | 0.0712 |
| MR Egger | 1.0232 (0.8286–1.2637) | 0.8313 | 0.9686 | |||
| Weighted median | 1.0467 (0.9473–1.1566) | 0.3699 | 0.9535 | |||
| Weighted mode | 1.0158 (0.8153–1.2657) | 0.8887 | 0.9795 | |||
| Robust adjusted profile score (RAPS) | 1.0986 (1.024–1.1785) | 0.0087 | 0.1108 | |||
| C09: Agents acting on the renin–angiotensin system | Cutaneous melanoma | 165 | Inverse variance weighted | 1.0385 (0.9452–1.141) | 0.4316 | 0.8291 |
| MR Egger | 0.82 (0.6154–1.0927) | 0.1774 | 0.9089 | |||
| Weighted median | 1.008 (0.8769–1.1586) | 0.9108 | 0.9535 | |||
| Weighted mode | 0.9473 (0.6385–1.4054) | 0.7882 | 0.9795 | |||
| Robust adjusted profile score (RAPS) | 1.0416 (0.9438–1.1495) | 0.4181 | 0.9159 | |||
| C03: Diuretics | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 83 | Inverse variance weighted | 1.0732 (1.0016–1.15) | 0.0449 | 0.3138 |
| MR Egger | 1.1098 (0.8951–1.3759) | 0.345 | 0.9686 | |||
| Weighted median | 1.0554 (0.9538–1.1679) | 0.2966 | 0.9535 | |||
| Weighted mode | 1.0231 (0.853–1.2271) | 0.8062 | 0.9795 | |||
| Robust adjusted profile score (RAPS) | 1.0701 (0.9955–1.1504) | 0.0662 | 0.4351 | |||
| C03: Diuretics | Cutaneous melanoma | 89 | Inverse variance weighted | 1.0318 (0.9321–1.1421) | 0.5463 | 0.9244 |
| MR Egger | 1.0956 (0.7872–1.5249) | 0.5896 | 0.9686 | |||
| Weighted median | 0.9406 (0.8081–1.0949) | 0.4296 | 0.9535 | |||
| Weighted mode | 0.7402 (0.5086–1.0771) | 0.1195 | 0.9795 | |||
| Robust adjusted profile score (RAPS) | 1.0321 (0.9201–1.1577) | 0.59 | 0.9642 | |||
| C08: Calcium channel blockers | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 89 | Inverse variance weighted | 1.0619 (0.992–1.1367) | 0.0837 | 0.3763 |
| MR Egger | 1.1229 (0.9061–1.3917) | 0.2925 | 0.9686 | |||
| Weighted median | 1.0317 (0.9307–1.1436) | 0.5529 | 0.9535 | |||
| Weighted mode | 1.0551 (0.8944–1.2447) | 0.5264 | 0.9795 | |||
| Robust adjusted profile score (RAPS) | 1.0569 (0.9841–1.135) | 0.1285 | 0.4748 | |||
| C08: Calcium channel blockers | Cutaneous melanoma | 92 | Inverse variance weighted | 0.9871 (0.896–1.0875) | 0.7928 | 0.9357 |
| MR Egger | 0.9797 (0.722–1.3293) | 0.8954 | 0.9686 | |||
| Weighted median | 0.9929 (0.8585–1.1483) | 0.9232 | 0.9535 | |||
| Weighted mode | 1.0083 (0.7256–1.4013) | 0.9607 | 0.9795 | |||
| Robust adjusted profile score (RAPS) | 0.9824 (0.8874–1.0875) | 0.7316 | 0.9642 | |||
| H03A: Thyroid preparations | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 115 | Inverse variance weighted | 0.9574 (0.9167–1) | 0.0499 | 0.3138 |
| MR Egger | 0.9676 (0.8854–1.0574) | 0.4683 | 0.9686 | |||
| Weighted median | 0.9652 (0.9015–1.0334) | 0.3086 | 0.9535 | |||
| Weighted mode | 0.9731 (0.8917–1.0618) | 0.5409 | 0.9795 | |||
| Robust adjusted profile score (RAPS) | 0.9557 (0.9134–1) | 0.05 | 0.383 | |||
| H03A: Thyroid preparations | Cutaneous melanoma | 116 | Inverse variance weighted | 0.9477 (0.89–1.0092) | 0.0941 | 0.3763 |
| MR Egger | 0.9105 (0.7885–1.0514) | 0.2041 | 0.9089 | |||
| Weighted median | 0.9146 (0.8248–1.014) | 0.09 | 0.7203 | |||
| Weighted mode | 0.8998 (0.7953–1.0179) | 0.0962 | 0.9795 | |||
| Robust adjusted profile score (RAPS) | 0.9436 (0.8838–1.0075) | 0.0825 | 0.4461 | |||
| C07: Beta blocking agents | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 57 | Inverse variance weighted | 1.0629 (0.9584–1.1787) | 0.2478 | 0.6413 |
| MR Egger | 1.3246 (0.8948–1.9609) | 0.1658 | 0.9089 | |||
| Weighted median | 1.0111 (0.889–1.15) | 0.8665 | 0.9535 | |||
| Weighted mode | 0.9685 (0.7773–1.2068) | 0.7765 | 0.9795 | |||
| Robust adjusted profile score (RAPS) | 1.0586 (0.9553–1.173) | 0.2769 | 0.7077 | |||
| C07: Beta blocking agents | Cutaneous melanoma | 54 | Inverse variance weighted | 1.0116 (0.8876–1.153) | 0.8625 | 0.9357 |
| MR Egger | 0.9781 (0.6107–1.5665) | 0.927 | 0.9686 | |||
| Weighted median | 0.9744 (0.8045–1.1803) | 0.7911 | 0.9535 | |||
| Weighted mode | 0.8886 (0.5475–1.4423) | 0.6346 | 0.9795 | |||
| Robust adjusted profile score (RAPS) | 1.024 (0.8923–1.1752) | 0.7356 | 0.9642 | |||
| C10AA: HMG CoA reductase inhibitors | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 87 | Inverse variance weighted | 1.0653 (0.9842–1.1531) | 0.1175 | 0.3977 |
| MR Egger | 0.997 (0.8595–1.1566) | 0.9686 | 0.9686 | |||
| Weighted median | 1.0795 (0.9548–1.2205) | 0.2217 | 0.9535 | |||
| Weighted mode | 1.0715 (0.9276–1.2378) | 0.3505 | 0.9795 | |||
| Robust adjusted profile score (RAPS) | 1.0585 (0.9747–1.1495) | 0.1767 | 0.4782 | |||
| C10AA: HMG CoA reductase inhibitors | Cutaneous melanoma | 85 | Inverse variance weighted | 1.0866 (0.9751–1.2107) | 0.1326 | 0.4167 |
| MR Egger | 1.0268 (0.8457–1.2467) | 0.7899 | 0.9686 | |||
| Weighted median | 1.0098 (0.8455–1.206) | 0.914 | 0.9535 | |||
| Weighted mode | 1.0504 (0.8504–1.2973) | 0.6496 | 0.9795 | |||
| Robust adjusted profile score (RAPS) | 1.0962 (0.9796–1.2267) | 0.1093 | 0.4572 | |||
| A10: Drugs used in diabetes | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 47 | Inverse variance weighted | 0.9117 (0.8602–0.9662) | 0.0018 | 0.0712 |
| MR Egger | 1.0036 (0.8794–1.1454) | 0.9579 | 0.9686 | |||
| Weighted median | 0.9214 (0.8461–1.0035) | 0.06 | 0.6 | |||
| Weighted mode | 0.9483 (0.8499–1.0582) | 0.3479 | 0.9795 | |||
| Robust adjusted profile score (RAPS) | 0.9099 (0.8562–0.967) | 0.0024 | 0.1083 | |||
| A10: Drugs used in diabetes | Cutaneous melanoma | 49 | Inverse variance weighted | 0.9883 (0.9134–1.0693) | 0.7698 | 0.9357 |
| MR Egger | 0.9475 (0.7921–1.1334) | 0.5578 | 0.9686 | |||
| Weighted median | 0.9964 (0.8829–1.1245) | 0.9535 | 0.9535 | |||
| Weighted mode | 0.994 (0.8677–1.1388) | 0.9317 | 0.9795 | |||
| Robust adjusted profile score (RAPS) | 0.9871 (0.9089–1.072) | 0.7576 | 0.9642 | |||
| N02A: Opioids | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 3 | Inverse variance weighted | 0.849 (0.5965–1.2086) | 0.3636 | 0.8 |
| MR Egger | 2.0287 (0.0016–2618.2156) | 0.8783 | 0.9686 | |||
| Weighted median | 0.9264 (0.5858–1.4651) | 0.7436 | 0.9535 | |||
| Weighted mode | 1.0082 (0.5805–1.7509) | 0.9795 | 0.9795 | |||
| Robust adjusted profile score (RAPS) | 0.847 (0.581–1.2349) | 0.3881 | 0.8926 | |||
| N02A: Opioids | Cutaneous melanoma | 3 | Inverse variance weighted | 0.4934 (0.2734–0.8903) | 0.019 | 0.167 |
| MR Egger | 6 × 10−4 (3.18 × 10−7–1.2795) | 0.3089 | 0.9686 | |||
| Weighted median | 0.4787 (0.2412–0.9503) | 0.0352 | 0.6 | |||
| Weighted mode | 0.433 (0.1724–1.0879) | 0.2169 | 0.9795 | |||
| Robust adjusted profile score (RAPS) | 0.4841 (0.2748–0.8529) | 0.012 | 0.1108 | |||
| C02: Antihypertensives | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 4 | Inverse variance weighted | 0.9702 (0.8149–1.155) | 0.7337 | 0.9357 |
| MR Egger | 0.341 (0.0019–60.0168) | 0.7229 | 0.9686 | |||
| Weighted median | 0.9523 (0.7857–1.1543) | 0.6187 | 0.9535 | |||
| Weighted mode | 0.9422 (0.7246–1.2252) | 0.6871 | 0.9795 | |||
| Robust adjusted profile score (RAPS) | 0.9701 (0.8044–1.1701) | 0.7511 | 0.9642 | |||
| C02: Antihypertensives | Cutaneous melanoma | 4 | Inverse variance weighted | 0.8924 (0.6476–1.2296) | 0.4863 | 0.8916 |
| MR Egger | 0.038 (8.01 × 10−7–1799.4876) | 0.6119 | 0.9686 | |||
| Weighted median | 0.9098 (0.662–1.2502) | 0.5599 | 0.9535 | |||
| Weighted mode | 0.9436 (0.5583–1.5948) | 0.8423 | 0.9795 | |||
| Robust adjusted profile score (RAPS) | 0.8882 (0.6408–1.231) | 0.4765 | 0.9642 | |||
| C01D: Vasodilators used in cardiac diseases | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 2 | Inverse variance weighted | 1.0158 (0.7987–1.2919) | 0.8983 | 0.9357 |
| Robust adjusted profile score (RAPS) | 1.0159 (0.7892–1.3077) | 0.9024 | 0.9642 | |||
| C01D: Vasodilators used in cardiac diseases | Cutaneous melanoma | 2 | Inverse variance weighted | 0.8952 (0.5749–1.394) | 0.6242 | 0.9357 |
| Robust adjusted profile score (RAPS) | 0.967 (0.6625–1.4114) | 0.8618 | 0.9642 | |||
| M01A: Anti-inflammatory and antirheumatic products, non-steroids | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 6 | Inverse variance weighted | 0.9754 (0.6532–1.4566) | 0.9032 | 0.9357 |
| MR Egger | 0.61 (0.0274–13.5924) | 0.7705 | 0.9686 | |||
| Weighted median | 0.9435 (0.5861–1.519) | 0.811 | 0.9535 | |||
| Weighted mode | 0.7593 (0.3974–1.4508) | 0.4425 | 0.9795 | |||
| Robust adjusted profile score (RAPS) | 0.968 (0.6284–1.4912) | 0.8828 | 0.9642 | |||
| M01A: Anti-inflammatory and antirheumatic products, non-steroids | Cutaneous melanoma | 4 | Inverse variance weighted | 1.0399 (0.5307–2.038) | 0.9091 | 0.9357 |
| MR Egger | 0.8255 (0.0049–138.6755) | 0.9482 | 0.9686 | |||
| Weighted median | 1.1797 (0.5594–2.4878) | 0.6643 | 0.9535 | |||
| Weighted mode | 1.4986 (0.6099–3.6819) | 0.4427 | 0.9795 | |||
| Robust adjusted profile score (RAPS) | 1.0412 (0.5297–2.0468) | 0.9068 | 0.9642 | |||
| R03A: Adrenergics, inhalants | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 48 | Inverse variance weighted | 0.9374 (0.871–1.0089) | 0.0849 | 0.3763 |
| MR Egger | 0.9678 (0.788–1.1887) | 0.7565 | 0.9686 | |||
| Weighted median | 0.9664 (0.8672–1.077) | 0.5365 | 0.9535 | |||
| Weighted mode | 0.9913 (0.847–1.1601) | 0.9134 | 0.9795 | |||
| Robust adjusted profile score (RAPS) | 0.9353 (0.8662–1.0098) | 0.0873 | 0.4461 | |||
| R03A: Adrenergics, inhalants | Cutaneous melanoma | 54 | Inverse variance weighted | 0.8676 (0.7833–0.961) | 0.0065 | 0.0712 |
| MR Egger | 0.9353 (0.6967–1.2558) | 0.6584 | 0.9686 | |||
| Weighted median | 0.919 (0.7857–1.0749) | 0.2908 | 0.9535 | |||
| Weighted mode | 0.9237 (0.7271–1.1736) | 0.5189 | 0.9795 | |||
| Robust adjusted profile score (RAPS) | 0.8693 (0.7794–0.9695) | 0.0119 | 0.1108 | |||
| R03BA: Glucocorticoids | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 17 | Inverse variance weighted | 0.9509 (0.8616–1.0494) | 0.3169 | 0.734 |
| MR Egger | 0.7243 (0.5201–1.0088) | 0.0757 | 0.9089 | |||
| Weighted median | 0.923 (0.804–1.0595) | 0.2549 | 0.9535 | |||
| Weighted mode | 0.8363 (0.6806–1.0276) | 0.1083 | 0.9795 | |||
| Robust adjusted profile score (RAPS) | 0.9444 (0.8478–1.0519) | 0.2979 | 0.7213 | |||
| R03BA: Glucocorticoids | Cutaneous melanoma | 19 | Inverse variance weighted | 0.8325 (0.7301–0.9492) | 0.0062 | 0.0712 |
| MR Egger | 0.7983 (0.5127–1.243) | 0.3327 | 0.9686 | |||
| Weighted median | 0.7855 (0.659–0.9363) | 0.007 | 0.2817 | |||
| Weighted mode | 0.7665 (0.5949–0.9876) | 0.0546 | 0.9795 | |||
| Robust adjusted profile score (RAPS) | 0.8267 (0.7204–0.9486) | 0.0067 | 0.1108 | |||
| M05B: Drugs affecting bone structure and mineralization | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 11 | Inverse variance weighted | 1.032 (0.8843–1.2045) | 0.6893 | 0.9357 |
| MR Egger | 0.6195 (0.3002–1.2781) | 0.2272 | 0.9089 | |||
| Weighted median | 1.0158 (0.8612–1.1983) | 0.8521 | 0.9535 | |||
| Weighted mode | 1.052 (0.8186–1.3519) | 0.7005 | 0.9795 | |||
| Robust adjusted profile score (RAPS) | 1.015 (0.8611–1.1964) | 0.8588 | 0.9642 | |||
| M05B: Drugs affecting bone structure and mineralization | Cutaneous melanoma | 11 | Inverse variance weighted | 0.8885 (0.7549–1.0457) | 0.1549 | 0.4259 |
| MR Egger | 0.5807 (0.2663–1.2662) | 0.2049 | 0.9089 | |||
| Weighted median | 0.8601 (0.6909–1.0708) | 0.1776 | 0.9535 | |||
| Weighted mode | 0.8344 (0.5909–1.1782) | 0.3279 | 0.9795 | |||
| Robust adjusted profile score (RAPS) | 0.8868 (0.7457–1.0545) | 0.1741 | 0.4782 | |||
| S01E: Antiglaucoma preparations and miotics | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 12 | Inverse variance weighted | 1.0028 (0.9331–1.0778) | 0.9383 | 0.9383 |
| MR Egger | 1.1416 (0.9417–1.3839) | 0.2073 | 0.9089 | |||
| Weighted median | 1.0056 (0.9113–1.1097) | 0.9107 | 0.9535 | |||
| Weighted mode | 1.0237 (0.9139–1.1467) | 0.6936 | 0.9795 | |||
| Robust adjusted profile score (RAPS) | 1.0021 (0.9254–1.0851) | 0.9588 | 0.9642 | |||
| S01E: Antiglaucoma preparations and miotics | Cutaneous melanoma | 12 | Inverse variance weighted | 1.0186 (0.9121–1.1374) | 0.744 | 0.9357 |
| MR Egger | 0.75 (0.549–1.0246) | 0.1008 | 0.9089 | |||
| Weighted median | 0.9372 (0.8125–1.0811) | 0.3733 | 0.9535 | |||
| Weighted mode | 0.8963 (0.7495–1.0719) | 0.2556 | 0.9795 | |||
| Robust adjusted profile score (RAPS) | 1.016 (0.901–1.1457) | 0.7958 | 0.9642 | |||
| N02BA: Salicylic acid and derivatives | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 7 | Inverse variance weighted | 0.9535 (0.721–1.2609) | 0.7382 | 0.9357 |
| MR Egger | 0.8693 (0.3767–2.0057) | 0.7559 | 0.9686 | |||
| Weighted median | 0.9498 (0.6512–1.3854) | 0.7892 | 0.9535 | |||
| Weighted mode | 0.9272 (0.5568–1.5439) | 0.7811 | 0.9795 | |||
| Robust adjusted profile score (RAPS) | 0.9404 (0.6985–1.266) | 0.6855 | 0.9642 | |||
| N02BA: Salicylic acid and derivatives | Cutaneous melanoma | 10 | Inverse variance weighted | 0.9376 (0.6488–1.355) | 0.7318 | 0.9357 |
| MR Egger | 1.3303 (0.4619–3.8312) | 0.6112 | 0.9686 | |||
| Weighted median | 1.0405 (0.6674–1.6222) | 0.8608 | 0.9535 | |||
| Weighted mode | 1.13 (0.491–2.6004) | 0.7804 | 0.9795 | |||
| Robust adjusted profile score (RAPS) | 0.9448 (0.6355–1.4047) | 0.7791 | 0.9642 | |||
| R06A: Antihistamines for systemic use | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 8 | Inverse variance weighted | 1.0232 (0.8421–1.2432) | 0.8177 | 0.9357 |
| MR Egger | 0.8562 (0.2704–2.7115) | 0.8007 | 0.9686 | |||
| Weighted median | 1.0115 (0.7952–1.2866) | 0.926 | 0.9535 | |||
| Weighted mode | 1.0153 (0.7312–1.4097) | 0.9304 | 0.9795 | |||
| Robust adjusted profile score (RAPS) | 1.0208 (0.8365–1.2457) | 0.8395 | 0.9642 | |||
| R06A: Antihistamines for systemic use | Cutaneous melanoma | 8 | Inverse variance weighted | 0.9595 (0.7553–1.2191) | 0.7352 | 0.9357 |
| MR Egger | 2.9939 (0.8739–10.2575) | 0.1315 | 0.9089 | |||
| Weighted median | 0.9149 (0.6649–1.2588) | 0.5848 | 0.9535 | |||
| Weighted mode | 0.7714 (0.4687–1.2696) | 0.3412 | 0.9795 | |||
| Robust adjusted profile score (RAPS) | 0.9603 (0.744–1.2395) | 0.756 | 0.9642 | |||
| A02B: Drugs for peptic ulcers and gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 5 | Inverse variance weighted | 1.0987 (0.6533–1.8478) | 0.7227 | 0.9357 |
| MR Egger | 0.0676 (0.0032–1.4381) | 0.1826 | 0.9089 | |||
| Weighted median | 1.1083 (0.6519–1.884) | 0.7042 | 0.9535 | |||
| Weighted mode | 1.0863 (0.5387–2.1905) | 0.8284 | 0.9795 | |||
| Robust adjusted profile score (RAPS) | 1.0484 (0.6058–1.8143) | 0.866 | 0.9642 | |||
| A02B: Drugs for peptic ulcers and gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) | Cutaneous melanoma | 5 | Inverse variance weighted | 0.6647 (0.4015–1.1005) | 0.1124 | 0.3977 |
| MR Egger | 0.5052 (0.0213–11.9822) | 0.701 | 0.9686 | |||
| Weighted median | 0.7571 (0.399–1.4366) | 0.3945 | 0.9535 | |||
| Weighted mode | 0.8053 (0.3286–1.9736) | 0.6606 | 0.9795 | |||
| Robust adjusted profile score (RAPS) | 0.6618 (0.3856–1.1359) | 0.1342 | 0.4748 | |||
| N02BE: Anilides | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 6 | Inverse variance weighted | 0.8311 (0.536–1.2886) | 0.4083 | 0.8291 |
| MR Egger | 1.1435 (0.0541–24.1589) | 0.9355 | 0.9686 | |||
| Weighted median | 0.9822 (0.5975–1.6144) | 0.9434 | 0.9535 | |||
| Weighted mode | 0.9856 (0.4704–2.0653) | 0.9709 | 0.9795 | |||
| Robust adjusted profile score (RAPS) | 0.8657 (0.5328–1.4063) | 0.5601 | 0.9642 | |||
| N02BE: Anilides | Cutaneous melanoma | 7 | Inverse variance weighted | 0.7463 (0.4402–1.265) | 0.2771 | 0.6773 |
| MR Egger | 2.6883 (0.0802–90.1552) | 0.6048 | 0.9686 | |||
| Weighted median | 0.5378 (0.2877–1.0053) | 0.052 | 0.6 | |||
| Weighted mode | 0.4773 (0.1795–1.2697) | 0.189 | 0.9795 | |||
| Robust adjusted profile score (RAPS) | 0.6967 (0.4133–1.1743) | 0.1749 | 0.4782 | |||
| N02C: Antimigraine preparations | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 13 | Inverse variance weighted | 1.0387 (0.9446–1.1421) | 0.4334 | 0.8291 |
| MR Egger | 0.9788 (0.5059–1.894) | 0.9505 | 0.9686 | |||
| Weighted median | 1.0073 (0.8976–1.1304) | 0.9015 | 0.9535 | |||
| Weighted mode | 0.9935 (0.8373–1.1789) | 0.9418 | 0.9795 | |||
| Robust adjusted profile score (RAPS) | 1.0193 (0.9333–1.1132) | 0.6709 | 0.9642 | |||
| N02C: Antimigraine preparations | Cutaneous melanoma | 13 | Inverse variance weighted | 1.0382 (0.928–1.1615) | 0.5131 | 0.903 |
| MR Egger | 0.7122 (0.3382–1.4998) | 0.3908 | 0.9686 | |||
| Weighted median | 1.0652 (0.9139–1.2414) | 0.419 | 0.9535 | |||
| Weighted mode | 1.0876 (0.8315–1.4227) | 0.5513 | 0.9795 | |||
| Robust adjusted profile score (RAPS) | 1.0369 (0.9212–1.1671) | 0.5484 | 0.9642 | |||
| N06A: Antidepressants | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 1 | Robust adjusted profile score (RAPS) | 0.7943 (0.3369–1.8727) | 0.5986 | 0.9642 |
| N06A: Antidepressants | Cutaneous melanoma | 1 | Robust adjusted profile score (RAPS) | 1.0533 (0.322–3.4458) | 0.9315 | 0.9642 |
| B01A: Antithrombotic agents | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 9 | Inverse variance weighted | 1.0172 (0.789–1.3113) | 0.8956 | 0.9357 |
| MR Egger | 0.8049 (0.3888–1.6663) | 0.5771 | 0.9686 | |||
| Weighted median | 0.9784 (0.7018–1.3639) | 0.8974 | 0.9535 | |||
| Weighted mode | 0.9669 (0.563–1.6605) | 0.9059 | 0.9795 | |||
| Robust adjusted profile score (RAPS) | 1.0107 (0.775–1.3181) | 0.9372 | 0.9642 | |||
| B01A: Antithrombotic agents | Cutaneous melanoma | 13 | Inverse variance weighted | 0.9836 (0.7278–1.3294) | 0.9144 | 0.9357 |
| MR Egger | 1.3796 (0.5997–3.1742) | 0.4649 | 0.9686 | |||
| Weighted median | 1.0373 (0.6939–1.5508) | 0.8582 | 0.9535 | |||
| Weighted mode | 1.3109 (0.5537–3.1038) | 0.5496 | 0.9795 | |||
| Robust adjusted profile score (RAPS) | 0.9928 (0.7232–1.3627) | 0.9642 | 0.9642 | |||
| L04: Immunosuppressants | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 2 | Inverse variance weighted | 0.9325 (0.8605–1.0106) | 0.0886 | 0.3763 |
| Robust adjusted profile score (RAPS) | 0.9324 (0.8579–1.0134) | 0.0996 | 0.4572 | |||
| L04: Immunosuppressants | Cutaneous melanoma | 2 | Inverse variance weighted | 0.9228 (0.8283–1.028) | 0.1448 | 0.4247 |
| Robust adjusted profile score (RAPS) | 0.9228 (0.8252–1.0319) | 0.1585 | 0.4782 |
| Exposure | Outcome | Raw | Global Test p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p-Value | |||
| C09: Agents acting on the renin–angiotensin system | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 1.0985 (1.0302–1.1714) | 0.0047 | 0.7398 |
| C09: Agents acting on the renin–angiotensin system | Cutaneous melanoma | 1.0385 (0.9497–1.1356) | 0.4088 | 0.8078 |
| C03: Diuretics | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 1.0732 (1.0057–1.1454) | 0.0361 | 0.7728 |
| C03: Diuretics | Cutaneous melanoma | 1.0318 (0.9321–1.1421) | 0.5478 | 0.275 |
| C08: Calcium channel blockers | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 1.0619 (0.9951–1.1331) | 0.0734 | 0.7192 |
| C08: Calcium channel blockers | Cutaneous melanoma | 0.9871 (0.9047–1.0770) | 0.7710 | 0.9045 |
| H03A: Thyroid preparations | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 0.9574 (0.9234–0.9927) | 0.0200 | 0.993 |
| H03A: Thyroid preparations | Cutaneous melanoma | 0.9477 (0.8954–1.0030) | 0.0661 | 0.9348 |
| C07: Beta blocking agents | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 1.0629 (0.9584–1.1787) | 0.2527 | 0.0752 |
| C07: Beta blocking agents | Cutaneous melanoma | 1.0116 (0.8981–1.1396) | 0.8498 | 0.805 |
| C10AA: HMG CoA reductase inhibitors | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 1.0653 (0.9964–1.1390) | 0.0670 | 0.9815 |
| C10AA: HMG CoA reductase inhibitors | Cutaneous melanoma | 1.0866 (0.9872–1.1959) | 0.0934 | 0.9247 |
| A10: Drugs used in diabetes | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 0.9117 (0.8672–0.9585) | 0.0007 | 0.9018 |
| A10: Drugs used in diabetes | Cutaneous melanoma | 0.9883 (0.9158–1.0665) | 0.7635 | 0.6068 |
| C02: Antihypertensives | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 0.9702 (0.9249–1.0177) | 0.3029 | 0.975 |
| C02: Antihypertensives | Cutaneous melanoma | 0.8924 (0.6476–1.2296) | 0.5364 | 0.2502 |
| M01A: Anti-inflammatory and antirheumatic products, non-steroids | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 0.9754 (0.6532–1.4566) | 0.9079 | 0.3383 |
| M01A: Anti-inflammatory and antirheumatic products, non-steroids | Cutaneous melanoma | 1.0399 (0.5307–2.0380) | 0.9164 | 0.3513 |
| R03A: Adrenergics, inhalants | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 0.9374 (0.8726–1.0070) | 0.0834 | 0.5812 |
| R03A: Adrenergics, inhalants | Cutaneous melanoma | 0.8676 (0.7833–0.9610) | 0.0087 | 0.4147 |
| R03BA: Glucocorticoids | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 0.9509 (0.8623–1.0487) | 0.3283 | 0.4442 |
| R03BA: Glucocorticoids | Cutaneous melanoma | 0.8325 (0.7560–0.9167) | 0.0015 | 0.9403 |
| M05B: Drugs affecting bone structure and mineralization | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 1.0320 (0.8843–1.2045) | 0.6977 | 0.1475 |
| M05B: Drugs affecting bone structure and mineralization | Cutaneous melanoma | 0.8885 (0.7788–1.0136) | 0.1090 | 0.7827 |
| S01E: Antiglaucoma preparations and miotics | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 1.0028 (0.9331–1.0778) | 0.9397 | 0.3787 |
| S01E: Antiglaucoma preparations and miotics | Cutaneous melanoma | 1.0186 (0.9121–1.1374) | 0.7501 | 0.288 |
| N02BA: Salicylic acid and derivatives | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 0.9535 (0.7210–1.2609) | 0.7495 | 0.4637 |
| N02BA: Salicylic acid and derivatives | Cutaneous melanoma | 0.9376 (0.6488–1.3550) | 0.7397 | 0.1655 |
| R06A: Antihistamines for systemic use | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 1.0232 (0.8421–1.2432) | 0.8243 | 0.312 |
| R06A: Antihistamines for systemic use | Cutaneous melanoma | 0.9595 (0.7597–1.2120) | 0.7391 | 0.495 |
| A02B: Drugs for peptic ulcers and gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 1.0987 (0.6533–1.8478) | 0.7406 | 0.151 |
| A02B: Drugs for peptic ulcers and gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) | Cutaneous melanoma | 0.6647 (0.4653–0.9497) | 0.0883 | 0.7485 |
| N02BE: Anilides | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 0.8311 (0.5360–1.2886) | 0.4459 | 0.2148 |
| N02BE: Anilides | Cutaneous melanoma | 0.7463 (0.4402–1.2650) | 0.3188 | 0.2253 |
| N02C: Antimigraine preparations | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 1.0387 (0.9446–1.1421) | 0.4486 | 0.1557 |
| N02C: Antimigraine preparations | Cutaneous melanoma | 1.0382 (0.9461–1.1391) | 0.4444 | 0.7472 |
| B01A: Antithrombotic agents | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 1.0172 (0.8252–1.2537) | 0.8773 | 0.6837 |
| B01A: Antithrombotic agents | Cutaneous melanoma | 0.9836 (0.7278–1.3294) | 0.9162 | 0.3003 |
| Exposure | Outcome | Heterogeneity | Pleotropy | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q Statistic (IVW) | p-Value | MR-Egger Intercept | p-Value | ||
| C09: Agents acting on the renin–angiotensin system | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 152.4217 | 0.7498 | 0.0039 | 0.488 |
| C09: Agents acting on the renin–angiotensin system | Cutaneous melanoma | 147.9214 | 0.811 | 0.0128 | 0.0897 |
| C03: Diuretics | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 72.632 | 0.7608 | −0.0024 | 0.7479 |
| C03: Diuretics | Cutaneous melanoma | 95.8575 | 0.2658 | −0.0042 | 0.7091 |
| C08: Calcium channel blockers | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 80.1599 | 0.7119 | −0.004 | 0.5917 |
| C08: Calcium channel blockers | Cutaneous melanoma | 73.6709 | 0.9076 | 0.0005 | 0.9594 |
| H03A: Thyroid preparations | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 78.7658 | 0.9951 | −0.0012 | 0.7899 |
| H03A: Thyroid preparations | Cutaneous melanoma | 93.6669 | 0.9278 | 0.0041 | 0.5452 |
| C07: Beta blocking agents | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 72.1946 | 0.0714 | −0.0145 | 0.2593 |
| C07: Beta blocking agents | Cutaneous melanoma | 43.9047 | 0.8089 | 0.0022 | 0.8846 |
| C10AA: HMG CoA reductase inhibitors | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 61.2164 | 0.9802 | 0.005 | 0.3039 |
| C10AA: HMG CoA reductase inhibitors | Cutaneous melanoma | 65.969 | 0.9269 | 0.0045 | 0.4933 |
| A10: Drugs used in diabetes | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 34.0802 | 0.903 | −0.012 | 0.1198 |
| A10: Drugs used in diabetes | Cutaneous melanoma | 44.8823 | 0.6014 | 0.0054 | 0.6097 |
| N02A: Opioids | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 1.5901 | 0.4516 | −0.057 | 0.8508 |
| N02A: Opioids | Cutaneous melanoma | 3.0697 | 0.2155 | 0.4393 | 0.3356 |
| C02: Antihypertensives | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 0.2257 | 0.9733 | 0.1139 | 0.73 |
| C02: Antihypertensives | Cutaneous melanoma | 4.7457 | 0.1914 | 0.3436 | 0.6233 |
| C01D: Vasodilators used in cardiac diseases | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 0.7753 | 0.3786 | NA | NA |
| C01D: Vasodilators used in cardiac diseases | Cutaneous melanoma | 2.8943 | 0.0889 | NA | NA |
| M01A: Anti-inflammatory and antirheumatic products, non-steroids | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 6.121 | 0.2946 | 0.0214 | 0.7795 |
| M01A: Anti-inflammatory and antirheumatic products, non-steroids | Cutaneous melanoma | 3.8206 | 0.2815 | 0.011 | 0.9368 |
| R03A: Adrenergics, inhalants | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 44.5975 | 0.5726 | −0.0029 | 0.7461 |
| R03A: Adrenergics, inhalants | Cutaneous melanoma | 55.5037 | 0.3806 | −0.0067 | 0.5958 |
| R03BA: Glucocorticoids | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 15.7594 | 0.4699 | 0.0295 | 0.1124 |
| R03BA: Glucocorticoids | Cutaneous melanoma | 9.7239 | 0.9405 | 0.0045 | 0.8482 |
| M05B: Drugs affecting bone structure and mineralization | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 15.3649 | 0.1193 | 0.0615 | 0.1919 |
| M05B: Drugs affecting bone structure and mineralization | Cutaneous melanoma | 6.537 | 0.7683 | 0.0516 | 0.3026 |
| S01E: Antiglaucoma preparations and miotics | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 11.8261 | 0.3769 | −0.0255 | 0.1875 |
| S01E: Antiglaucoma preparations and miotics | Cutaneous melanoma | 12.7507 | 0.3099 | 0.0562 | 0.0691 |
| N02BA: Salicylic acid and derivatives | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 6.0431 | 0.4184 | 0.0068 | 0.8252 |
| N02BA: Salicylic acid and derivatives | Cutaneous melanoma | 13.2612 | 0.1511 | −0.027 | 0.5071 |
| R06A: Antihistamines for systemic use | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 8.6941 | 0.2754 | 0.0169 | 0.7685 |
| R06A: Antihistamines for systemic use | Cutaneous melanoma | 6.6625 | 0.4648 | −0.1096 | 0.1144 |
| A02B: Drugs for peptic ulcers and gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 7.6852 | 0.1038 | 0.1377 | 0.169 |
| A02B: Drugs for peptic ulcers and gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) | Cutaneous melanoma | 2.003 | 0.7352 | 0.0139 | 0.8744 |
| N02BE: Anilides | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 7.6643 | 0.1757 | −0.0159 | 0.8456 |
| N02BE: Anilides | Cutaneous melanoma | 8.2897 | 0.2176 | −0.0653 | 0.5015 |
| N02C: Antimigraine preparations | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 17.2075 | 0.142 | 0.0088 | 0.8618 |
| N02C: Antimigraine preparations | Cutaneous melanoma | 8.2093 | 0.7686 | 0.0561 | 0.3373 |
| B01A: Antithrombotic agents | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 5.4223 | 0.7116 | 0.0185 | 0.5226 |
| B01A: Antithrombotic agents | Cutaneous melanoma | 13.8993 | 0.3072 | −0.0263 | 0.4107 |
| L04: Immunosuppressants | Malignant melanoma of the skin | 0.7494 | 0.3867 | NA | NA |
| L04: Immunosuppressants | Cutaneous melanoma | 0.2824 | 0.5951 | NA | NA |
| Exposure | Outcome | Correct_Causal_Direction | Steiger_Pval |
|---|---|---|---|
| A02B: Drugs for peptic ulcers and gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) | Cutaneous melanoma | TRUE | 1.02 × 10−27 |
| A02B: Drugs for peptic ulcers and gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) | Malignant melanoma of the skin | TRUE | 3.21 × 10−25 |
| A10: Drugs used in diabetes | Cutaneous melanoma | TRUE | 0 |
| A10: Drugs used in diabetes | Malignant melanoma of the skin | TRUE | 0 |
| B01A: Antithrombotic agents | Cutaneous melanoma | TRUE | 1.7 × 10−115 |
| B01A: Antithrombotic agents | Malignant melanoma of the skin | TRUE | 2.9 × 10−101 |
| C01D: Vasodilators used in cardiac diseases | Cutaneous melanoma | TRUE | 2.01 × 10−17 |
| C01D: Vasodilators used in cardiac diseases | Malignant melanoma of the skin | TRUE | 2.53 × 10−18 |
| C02: Antihypertensives | Cutaneous melanoma | TRUE | 1.45 × 10−19 |
| C02: Antihypertensives | Malignant melanoma of the skin | TRUE | 1.01 × 10−22 |
| C03: Diuretics | Cutaneous melanoma | TRUE | 0 |
| C03: Diuretics | Malignant melanoma of the skin | TRUE | 0 |
| C07: Beta blocking agents | Cutaneous melanoma | TRUE | 0 |
| C07: Beta blocking agents | Malignant melanoma of the skin | TRUE | 0 |
| C08: Calcium channel blockers | Cutaneous melanoma | TRUE | 0 |
| C08: Calcium channel blockers | Malignant melanoma of the skin | TRUE | 0 |
| C09: Agents acting on the renin–angiotensin system | Cutaneous melanoma | TRUE | 0 |
| C09: Agents acting on the renin–angiotensin system | Malignant melanoma of the skin | TRUE | 0 |
| C10AA: HMG CoA reductase inhibitors | Cutaneous melanoma | TRUE | 0 |
| C10AA: HMG CoA reductase inhibitors | Malignant melanoma of the skin | TRUE | 0 |
| H03A: Thyroid preparations | Cutaneous melanoma | TRUE | 0 |
| H03A: Thyroid preparations | Malignant melanoma of the skin | TRUE | 0 |
| L04: Immunosuppressants | Cutaneous melanoma | TRUE | 1.37 × 10−73 |
| L04: Immunosuppressants | Malignant melanoma of the skin | TRUE | 1.89 × 10−67 |
| M01A: Anti-inflammatory and antirheumatic products, non-steroids | Cutaneous melanoma | TRUE | 7.89 × 10−29 |
| M01A: Anti-inflammatory and antirheumatic products, non-steroids | Malignant melanoma of the skin | TRUE | 4.83 × 10−32 |
| M05B: Drugs affecting bone structure and mineralization | Cutaneous melanoma | TRUE | 3.74 × 10−60 |
| M05B: Drugs affecting bone structure and mineralization | Malignant melanoma of the skin | TRUE | 5.2 × 10−55 |
| N02A: Opioids | Cutaneous melanoma | TRUE | 1.12 × 10−13 |
| N02A: Opioids | Malignant melanoma of the skin | TRUE | 2.26 × 10−15 |
| N02BA: Salicylic acid and derivatives | Cutaneous melanoma | TRUE | 3.89 × 10−69 |
| N02BA: Salicylic acid and derivatives | Malignant melanoma of the skin | TRUE | 3.59 × 10−62 |
| N02BE: Anilides | Cutaneous melanoma | TRUE | 4.47 × 10−46 |
| N02BE: Anilides | Malignant melanoma of the skin | TRUE | 7.22 × 10−39 |
| N02C: Antimigraine preparations | Cutaneous melanoma | TRUE | 1.77 × 10−88 |
| N02C: Antimigraine preparations | Malignant melanoma of the skin | TRUE | 1.6 × 10−79 |
| N06A: Antidepressants | Cutaneous melanoma | TRUE | 3.16 × 10−7 |
| N06A: Antidepressants | Malignant melanoma of the skin | TRUE | 1.02 × 10−6 |
| R03A: Adrenergics, inhalants | Cutaneous melanoma | TRUE | 0 |
| R03A: Adrenergics, inhalants | Malignant melanoma of the skin | TRUE | 0 |
| R03BA: Glucocorticoids | Cutaneous melanoma | TRUE | 2.6 × 10−192 |
| R03BA: Glucocorticoids | Malignant melanoma of the skin | TRUE | 5.5 × 10−174 |
| R06A: Antihistamines for systemic use | Cutaneous melanoma | TRUE | 1.76 × 10−45 |
| R06A: Antihistamines for systemic use | Malignant melanoma of the skin | TRUE | 2.92 × 10−42 |
| S01E: Antiglaucoma preparations and miotics | Cutaneous melanoma | TRUE | 2.7 × 10−103 |
| S01E: Antiglaucoma preparations and miotics | Malignant melanoma of the skin | TRUE | 8.89 × 10−96 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wan, H.; Zhong, L.; Su, J.; Zhao, Q.; Tominaga, M.; Takamori, K.; Ma, H.; Xia, T.; Zhang, D. Potential Risk of Cutaneous Melanoma Attributable to Medication Use: A Mendelian Randomization Approach. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2477. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102477
Wan H, Zhong L, Su J, Zhao Q, Tominaga M, Takamori K, Ma H, Xia T, Zhang D. Potential Risk of Cutaneous Melanoma Attributable to Medication Use: A Mendelian Randomization Approach. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(10):2477. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102477
Chicago/Turabian StyleWan, Huiying, Ling Zhong, Jia Su, Qiaofeng Zhao, Mitsutoshi Tominaga, Kenji Takamori, Hang Ma, Tian Xia, and Dingding Zhang. 2025. "Potential Risk of Cutaneous Melanoma Attributable to Medication Use: A Mendelian Randomization Approach" Biomedicines 13, no. 10: 2477. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102477
APA StyleWan, H., Zhong, L., Su, J., Zhao, Q., Tominaga, M., Takamori, K., Ma, H., Xia, T., & Zhang, D. (2025). Potential Risk of Cutaneous Melanoma Attributable to Medication Use: A Mendelian Randomization Approach. Biomedicines, 13(10), 2477. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102477






