Transepidermal Delivery of Calcium Hydroxyapatite (CaHA) Microneedling: A Novel Approach for Inducing Collagen Types III and IV
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval
2.2. Preparation of CaHA and Hyaluronidase
Fluorescent Labeling of Calcium Hydroxyapatite
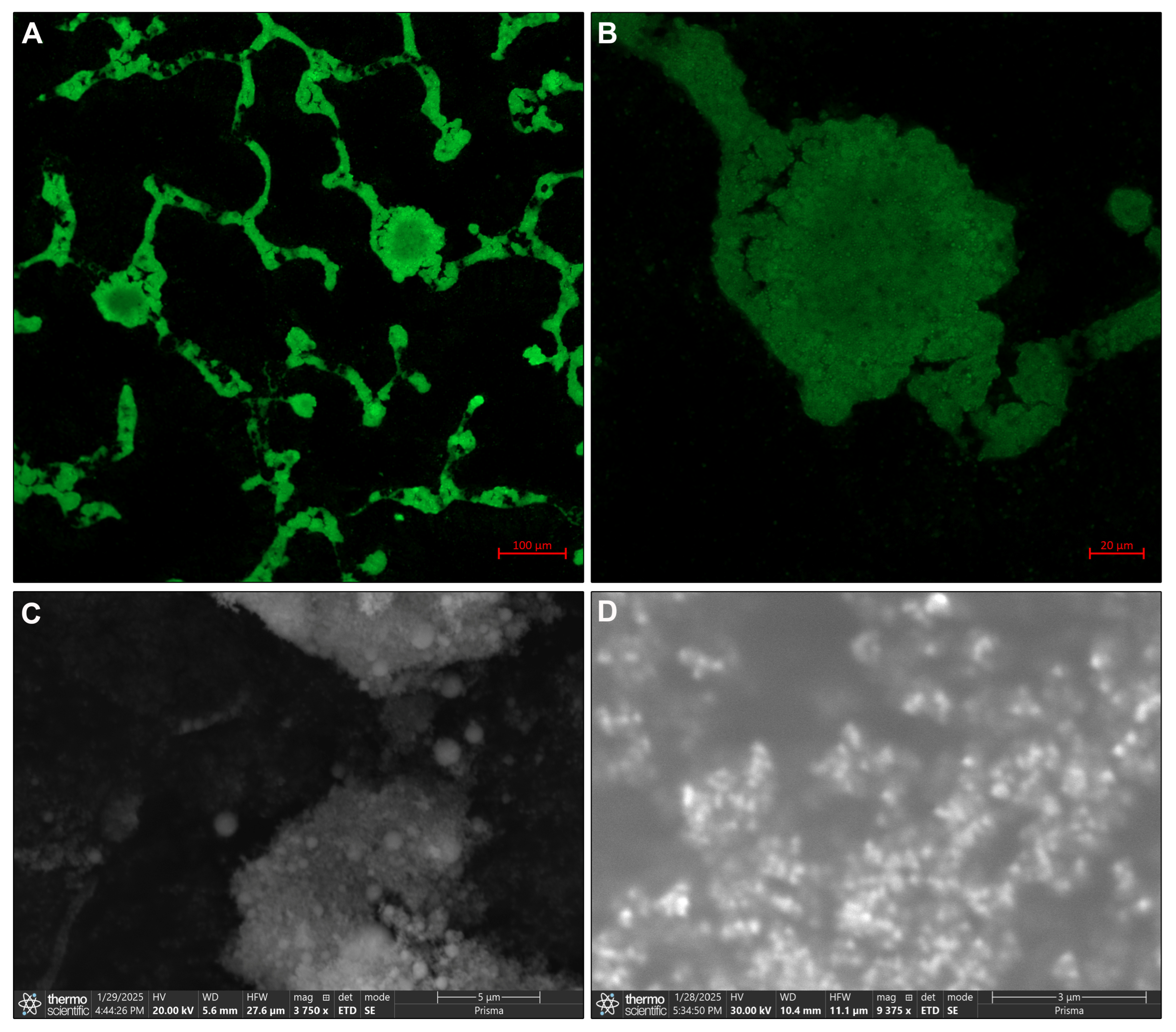
2.3. Morphological and Structural Analysis
2.4. Transepidermal Delivery Protocol
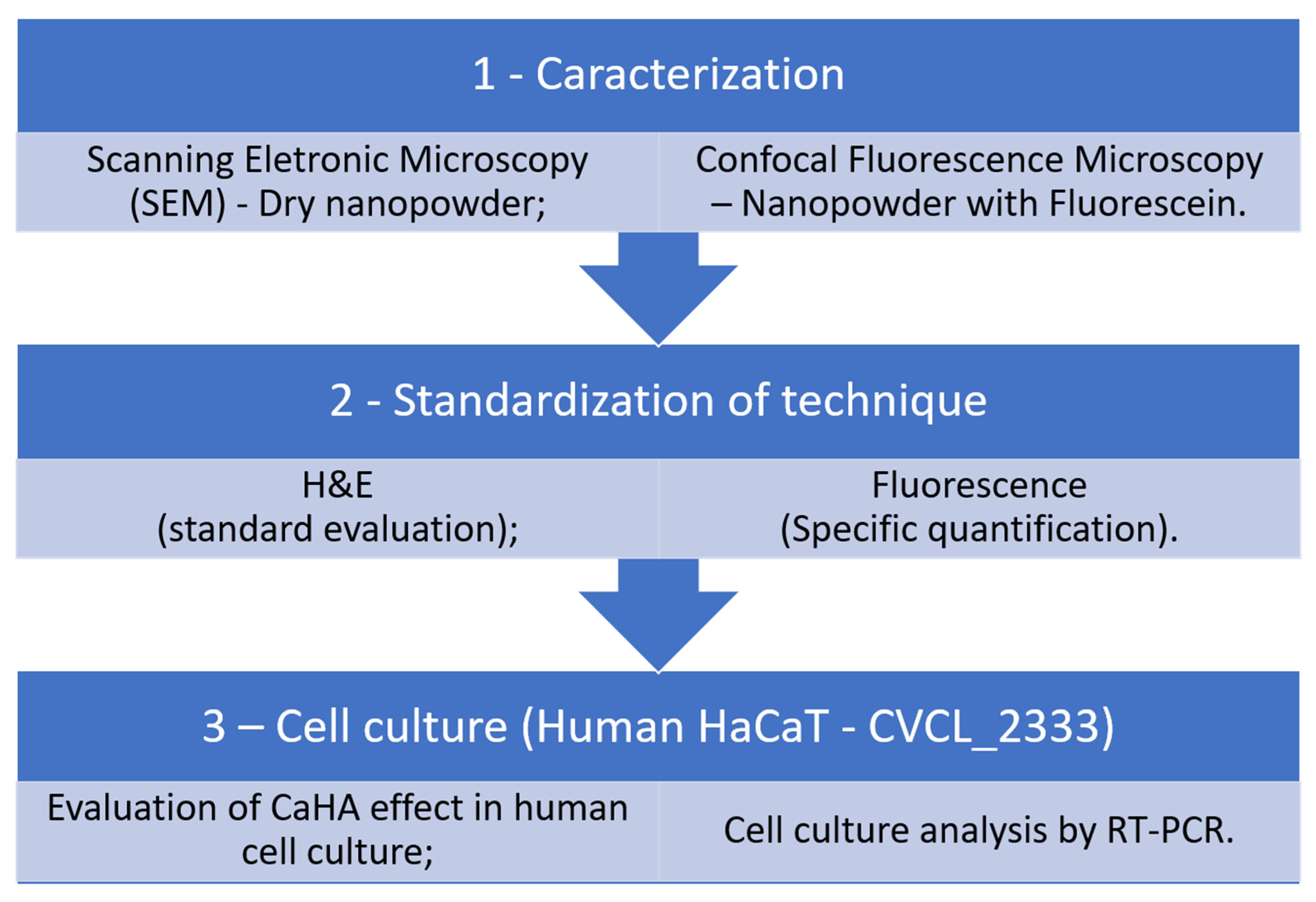
2.5. Experimental Design
- Group 1: Topical CaHA and intense microneedling (1 min), no hyaluronidase.
- Group 2: Same as Group 1 and topical hyaluronidase.
- Group 3: CaHA aspirated into microneedling pen and intense microneedling.
- Group 4: Same as Group 3 and topical hyaluronidase.
- Group 5: Light microneedling with CaHA-loaded pen.
- Group 6: Hyaluronidase injected, then light microneedling with CaHA.
- Group 7: Topical hyaluronidase before light microneedling with CaHA.
- Group 8: Negative control (no treatment).
- Group 9: Positive control (direct injection of CaHA, no hyaluronidase).
2.6. Ex Vivo Skin Permeation Analysis
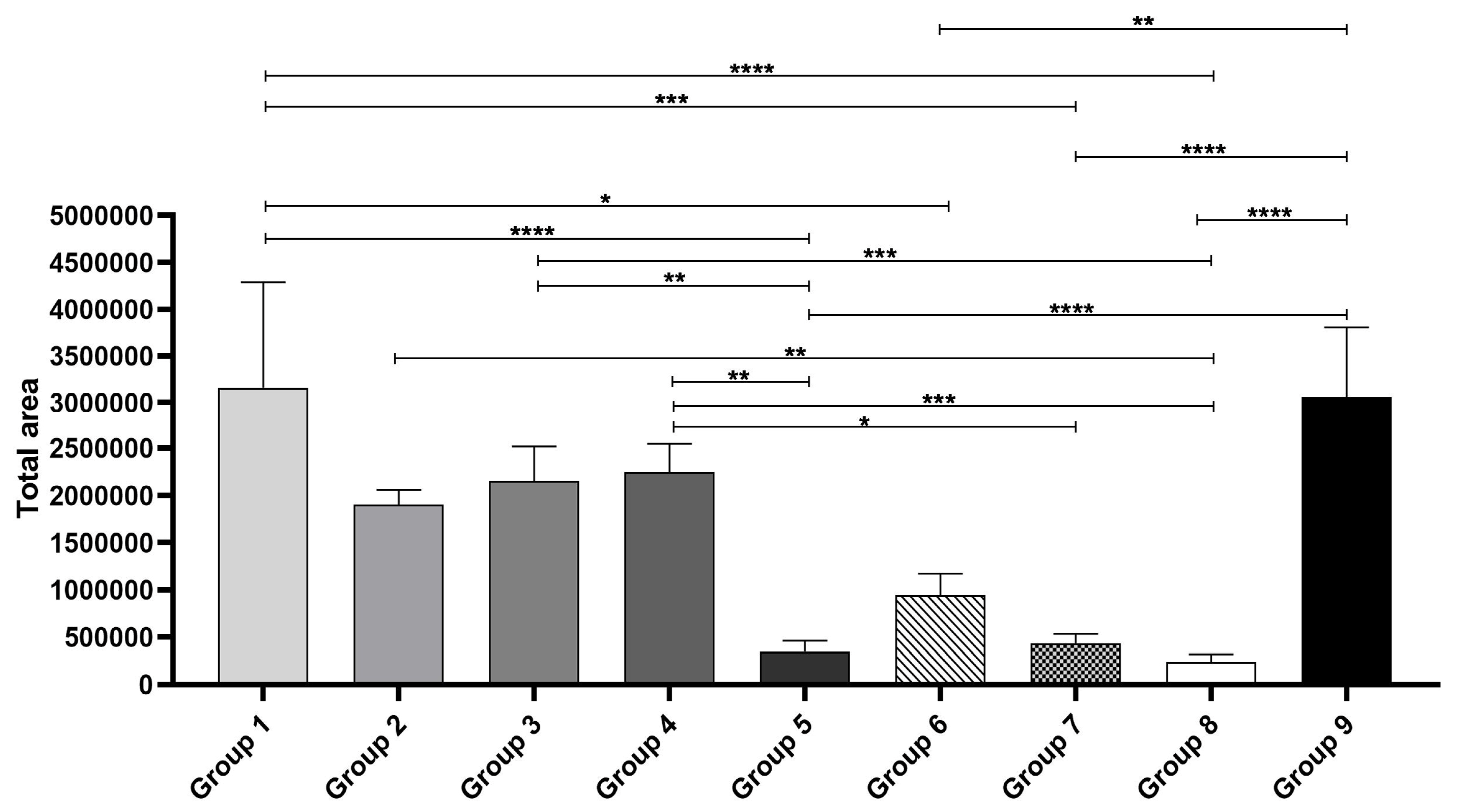
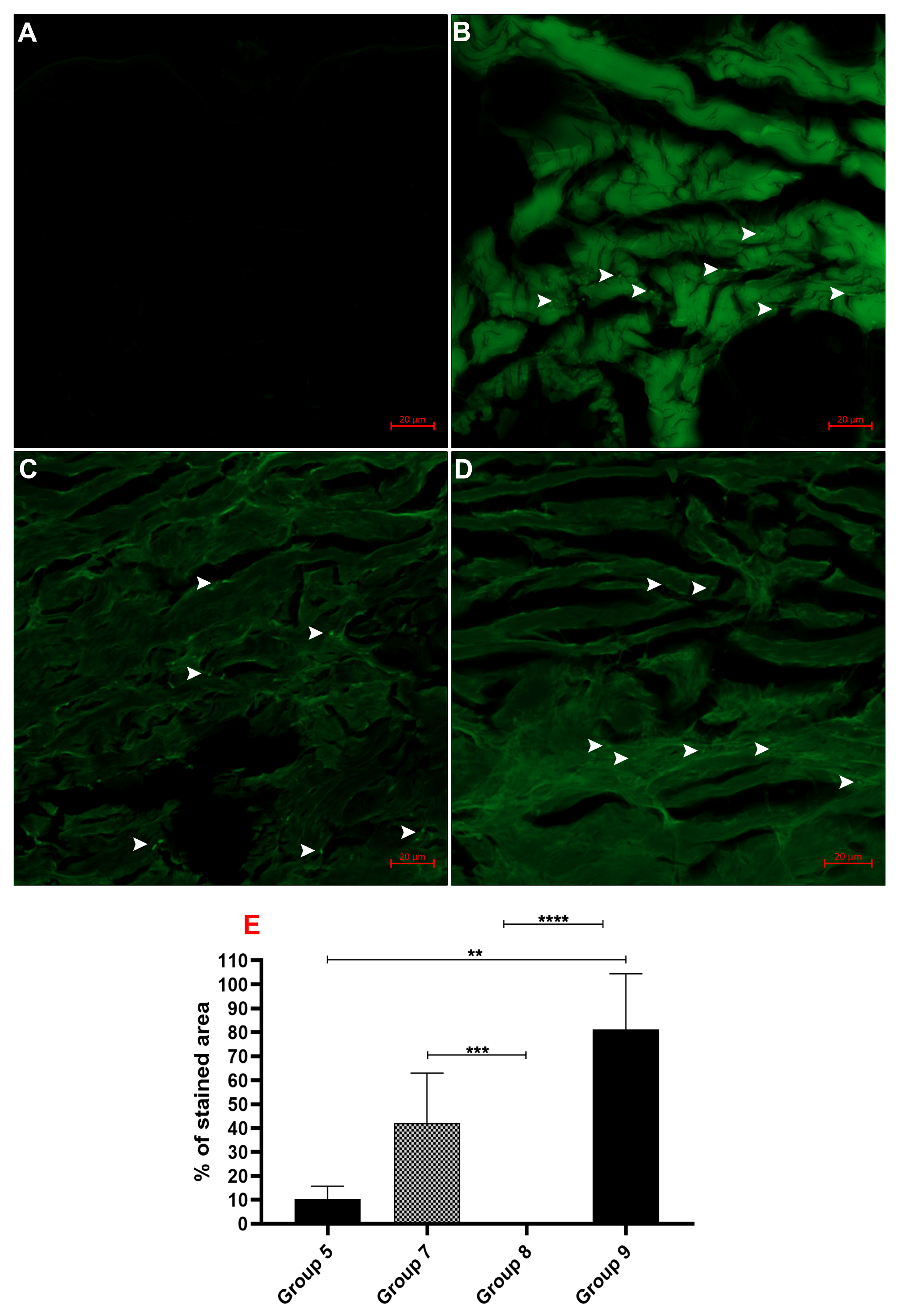
Quantification of CaHA Distribution
2.7. Cell Culture
2.8. Expression by Real-Time PCR
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. CaHA Morphology
3.2. Histological Insights
3.3. Fluorescence Imaging
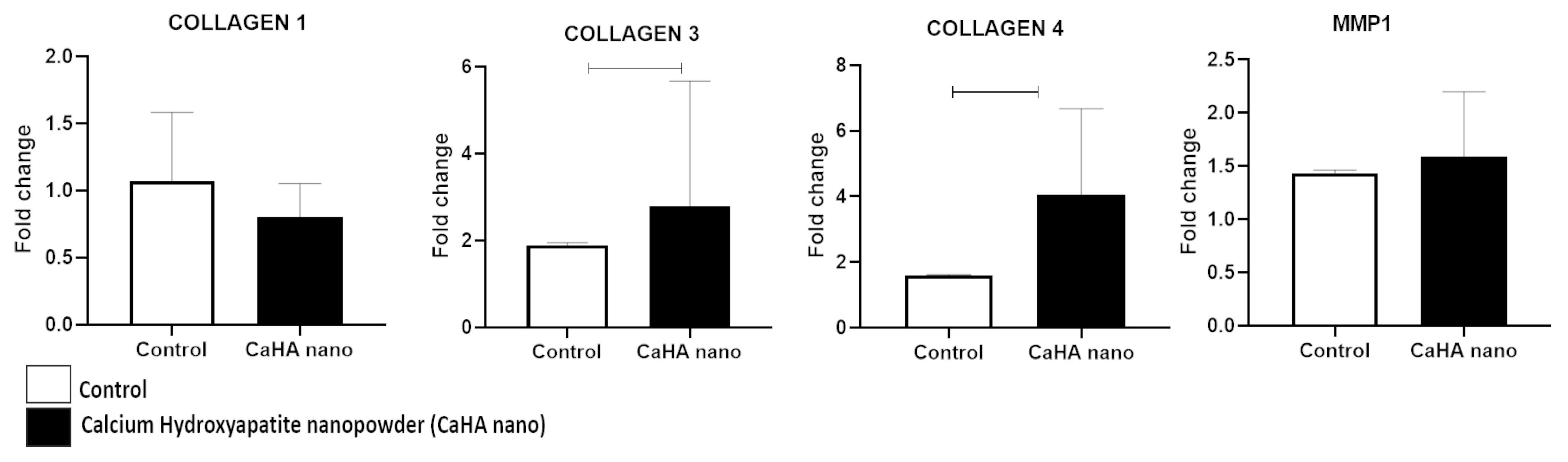
3.4. Biological Activity of CaHA
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bariya, S.H.; Gohel, M.C.; Mehta, T.A.; Sharma, O.P. Microneedles: An emerging transdermal drug delivery system. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2012, 64, 11–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karatas, E.; Koc, K.; Yilmaz, M.; Aydin, H.M. Characterization and Comparative Investigation of Hydroxyapatite/Carboxymethyl Cellulose (CaHA/CMC) Matrix for Soft Tissue Augmentation in a Rat Model. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 31586–31600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scardua, N.; Rovaris, D.P.; Moreira, K.M.S.; Guimaraes, A.L.S.; Scardua, M.T. Supraperiosteal technique protocol for forehead filling with a mixture of calcium hydroxyapatite and hyaluronic acid: Double-blind, randomized controlled clinical trial. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2024, 23, 4116–4122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiri, M.; Mecani, R.; Niehot, C.D.; Phillips, T.; Kolb, J.; Daughtry, H.; Muka, T. Skin regeneration-related mechanisms of Calcium Hydroxylapatite (CaHA): A systematic review. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1195934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldie, K.; Chernoff, G.; Corduff, N.; Davies, O.; van Loghem, J.; Viscomi, B. Consensus Agreements on Regenerative Aesthetics: A Focus on Regenerative Biostimulation with Calcium Hydroxylapatite. Dermatol. Surg. 2024, 50, S172–S176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadick, N.S.; Katz, B.E.; Roy, D. A multicenter, 47-month study of safety and efficacy of calcium hydroxylapatite for soft tissue augmentation of nasolabial folds and other areas of the face. Dermatol. Surg. 2007, 33, S122–S126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ma, Y.; He, G.; Ma, S.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y. Pilose antler extract restores type I and III collagen to accelerate wound healing. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 161, 114510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumann, L.; Bernstein, E.F.; Weiss, A.S.; Bates, D.; Humphrey, S.; Silberberg, M.; Daniels, R. Clinical Relevance of Elastin in the Structure and Function of Skin. Aesthet. Surg. J. Open Forum 2021, 3, ojab019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, G.J.; Wang, Z.Q.; Datta, S.C.; Varani, J.; Kang, S.; Voorhees, J.J. Pathophysiology of premature skin aging induced by ultraviolet light. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 337, 1419–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowag, B.; Casabona, G.; Kippenberger, S.; Zoller, N.; Hengl, T. Calcium hydroxylapatite microspheres activate fibroblasts through direct contact to stimulate neocollagenesis. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2023, 22, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panse, G.; Bossuyt, V.; Ko, C.J. Metastatic serous carcinoma presenting as inflammatory carcinoma over the breast-Report of two cases and literature review. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2018, 45, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunzler, C.; Hartmann, C.; Nowag, B.; Shah, R.; El-Banna, R.; Backfisch, S.; Schafer, D.; Hengl, T.; Hagedorn, N. Comparison of Physicochemical Characteristics and Biostimulatory Functions in Two Calcium Hydroxyapatite-Based Dermal Fillers. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2023, 22, 910–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Tsoi, L.C.; Billi, A.C.; Ward, N.L.; Harms, P.W.; Zeng, C.; Maverakis, E.; Kahlenberg, J.M.; Gudjonsson, J.E. Cytokinocytes: The diverse contribution of keratinocytes to immune responses in skin. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e142067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugwu, N.; Xun, H.; Dover, J.S.; Boustany, A.N.; Chung, H.J. Histological Assessment of the Effectiveness of Microneedling Device-Assisted Filler Delivery. Dermatol. Surg. 2024, 50, 829–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahar-Shany, K.; Ravid, A.; Koren, R. Upregulation of MMP-9 production by TNFalpha in keratinocytes and its attenuation by vitamin D. J. Cell. Physiol. 2010, 222, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scardua, M.T.; Scardua, N.; Fernanda Ismail, M.; Junior, W.B.; Carpinteiro, I.M.C.; Costa, A.L.O.; Guimaraes, A.L.S. The Use of Medium-Deep Peelings to Treat Melasma: A Case Series Study. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2025, 24, e70291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, J.C.; Gomes, E.P.; Fonseca-Silva, T.; Velloso, N.A.; Vieira, L.T.; Fernandes, M.F.; Santos, S.H.; Neto, J.F.; De-Paula, A.M.; Guimaraes, A.L. Fluoxetine reduces periodontal disease progression in a conditioned fear stress model in rats. J. Periodontal Res. 2013, 48, 632–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duraes, C.P.; Fonseca, L.L.; Santos, S.H.S.; Filho, A.P.S.; Silveira, M.F.; Queiroz, L.; Lacerda, A.S.M.; de Paula, A.M.B.; Farias, L.C.; Guimaraes, A.L.S. Effect of photobiomodulation on rat parotid gland cells after ionizing radiation-an experimental study in animal model-Part 1. J. Stomatol. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraga, C.A.; de Oliveira, M.V.; de Oliveira, E.S.; Barros, L.O.; Santos, F.B.; Gomez, R.S.; De-Paula, A.M.; Guimaraes, A.L. A high HIF-1alpha expression genotype is associated with poor prognosis of upper aerodigestive tract carcinoma patients. Oral. Oncol. 2012, 48, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, R.G.; Farias, L.C.; da Silva Menezes, A.S.; de Oliveira, E.S.C.S.; Tabosa, A.T.L.; Chagas, P.V.F.; Santiago, L.; Santos, S.H.S.; de Paula, A.M.B.; Guimaraes, A.L.S. Treatment of mucositis with combined 660- and 808-nm-wavelength low-level laser therapy reduced mucositis grade, pain, and use of analgesics: A parallel, single-blind, two-arm controlled study. Lasers Med. Sci. 2018, 33, 1813–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingos, P.L.B.; Souza, M.G.; Guimaraes, T.A.; Santos, E.S.; Farias, L.C.; de Carvalho Fraga, C.A.; Jones, K.M.; Santos, S.H.S.; de Paula, A.M.B.; Guimaraes, A.L.S. Hypoxia reduces the E-cadherin expression and increases OSCC cell migration regardless of the E-cadherin methylation profile. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2017, 213, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, D.J.; Kim, H.J. Microneedles in Action: Microneedling and Microneedles-Assisted Transdermal Delivery. Polymers 2022, 14, 1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yutskovskaya, Y.; Kogan, E.; Leshunov, E. A randomized, split-face, histomorphologic study comparing a volumetric calcium hydroxylapatite and a hyaluronic acid-based dermal filler. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2014, 13, 1047–1052. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.E.; Allen, B.G.; Weeks, D.L. Using PhiC31 integrase to mediate insertion of DNA in Xenopus embryos. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 917, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casabona, G.; Marchese, P. Calcium Hydroxylapatite Combined with Microneedling and Ascorbic Acid is Effective for Treating Stretch Marks. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2017, 5, e1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merati, M.; Woods, C.; Reznik, N.; Parker, L. An Assessment of Microneedling with Topical Growth Factors for Facial Skin Rejuvenation: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Aesthet. Dermatol. 2020, 13, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liebl, H.; Kloth, L.C. Skin cell proliferation stimulated by microneedles. J. Am. Coll. Clin. Wound Spec. 2012, 4, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.C.; Lin, Z.Z.; Zhang, Z.D.; Xie, S.; Xie, G.H. Comparing the Effectiveness of Platelet-Rich Plasma Alone Versus Combined With Microneedles or Radiofrequency for Neck Wrinkle Treatment. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2025, 24, e16651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, E.; Choo, J.P.S.; Rao, P.; Webb, W.R.; Carruthers, J.D.A.; Rahman, E. A Systematic Review on the Effectiveness and Safety of Combining Biostimulators with Botulinum Toxin, Dermal Fillers, and Energy-Based Devices. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2025, 49, 2809–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badran, K.W.; Nabili, V. Lasers, Microneedling, and Platelet-Rich Plasma for Skin Rejuvenation and Repair. Facial Plast. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 26, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.L. Platelet-Rich Plasma for Skin Rejuvenation: Facts, Fiction, and Pearls for Practice. Facial Plast. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 27, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakih-Gomez, N.; Kadouch, J. Combining Calcium Hydroxylapatite and Hyaluronic Acid Fillers for Aesthetic Indications: Efficacy of an Innovative Hybrid Filler. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2022, 46, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, A.; Cohen, B.; Haimovic, A.; Elbuluk, N. Microneedling: A Comprehensive Review. Dermatol. Surg. 2017, 43, 321–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tey, R.V.; Haldankar, P.; Joshi, V.R.; Raj, R.; Maradi, R. Variability in Platelet-Rich Plasma Preparations Used in Regenerative Medicine: A Comparative Analysis. Stem Cells Int. 2022, 2022, 3852898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, Y.J.; Koo, D.W.; Lee, J.S. Late Onset Foreign Body Reaction due to Poly-L-Lactic Acid Facial Injections for Cosmetic Purpose. Ann. Dermatol. 2020, 32, 519–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Dong, C. Poly-L-Lactic acid increases collagen gene expression and synthesis in cultured dermal fibroblast (Hs68) through the TGF-beta/Smad pathway. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2023, 22, 1213–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thums, M.A.; Payeras, M.R.; Cherubini, K.; Koth, V.S.; Salum, F.G. Clinical and Histological Effects of Calcium Hydroxyapatite Filler in the Orofacial Region: A Study in Rats. Dermatol. Surg. 2024, 50, 939–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalifian, S.; McCarthy, A.D.; Yoelin, S.G. Hyperdiluting Calcium Hydroxylapatite with Platelet-Rich Plasma and Hyaluronidase for Improving Neck Laxity and Wrinkle Severity. Cureus 2024, 16, e63969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Costa, A.L.O.; Barcellos, F.V.C.; Mariano, M.T.S.; Santos, E.M.; Queiroz, L.d.R.P.; Santos, E.P.; de Melo, V.R.O.; Santos, S.H.S.; Farias, L.C.; de Paula, A.M.B.; et al. Transepidermal Delivery of Calcium Hydroxyapatite (CaHA) Microneedling: A Novel Approach for Inducing Collagen Types III and IV. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2463. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102463
Costa ALO, Barcellos FVC, Mariano MTS, Santos EM, Queiroz LdRP, Santos EP, de Melo VRO, Santos SHS, Farias LC, de Paula AMB, et al. Transepidermal Delivery of Calcium Hydroxyapatite (CaHA) Microneedling: A Novel Approach for Inducing Collagen Types III and IV. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(10):2463. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102463
Chicago/Turabian StyleCosta, Andréia Luiza Oliveira, Fernando Veloso Caldeira Barcellos, Maria Tereza Scardua Mariano, Eloá Mangabeira Santos, Lorena dos Reis Pereira Queiroz, Erivelton Pereira Santos, Vitória Regina Oliveira de Melo, Sérgio Henrique Sousa Santos, Lucyana Conceição Farias, Alfredo Maurício Batista de Paula, and et al. 2025. "Transepidermal Delivery of Calcium Hydroxyapatite (CaHA) Microneedling: A Novel Approach for Inducing Collagen Types III and IV" Biomedicines 13, no. 10: 2463. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102463
APA StyleCosta, A. L. O., Barcellos, F. V. C., Mariano, M. T. S., Santos, E. M., Queiroz, L. d. R. P., Santos, E. P., de Melo, V. R. O., Santos, S. H. S., Farias, L. C., de Paula, A. M. B., & Guimarães, A. L. S. (2025). Transepidermal Delivery of Calcium Hydroxyapatite (CaHA) Microneedling: A Novel Approach for Inducing Collagen Types III and IV. Biomedicines, 13(10), 2463. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102463








