Endoscopic Bariatric Therapies for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: Mechanistic Insights and Metabolic Implications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Pathophysiology of MASLD
3. Mechanistic Basis of Weight Loss-Induced MASLD Improvement
3.1. Caloric Restriction and Fat Mobilization
3.2. Hormonal Modulation
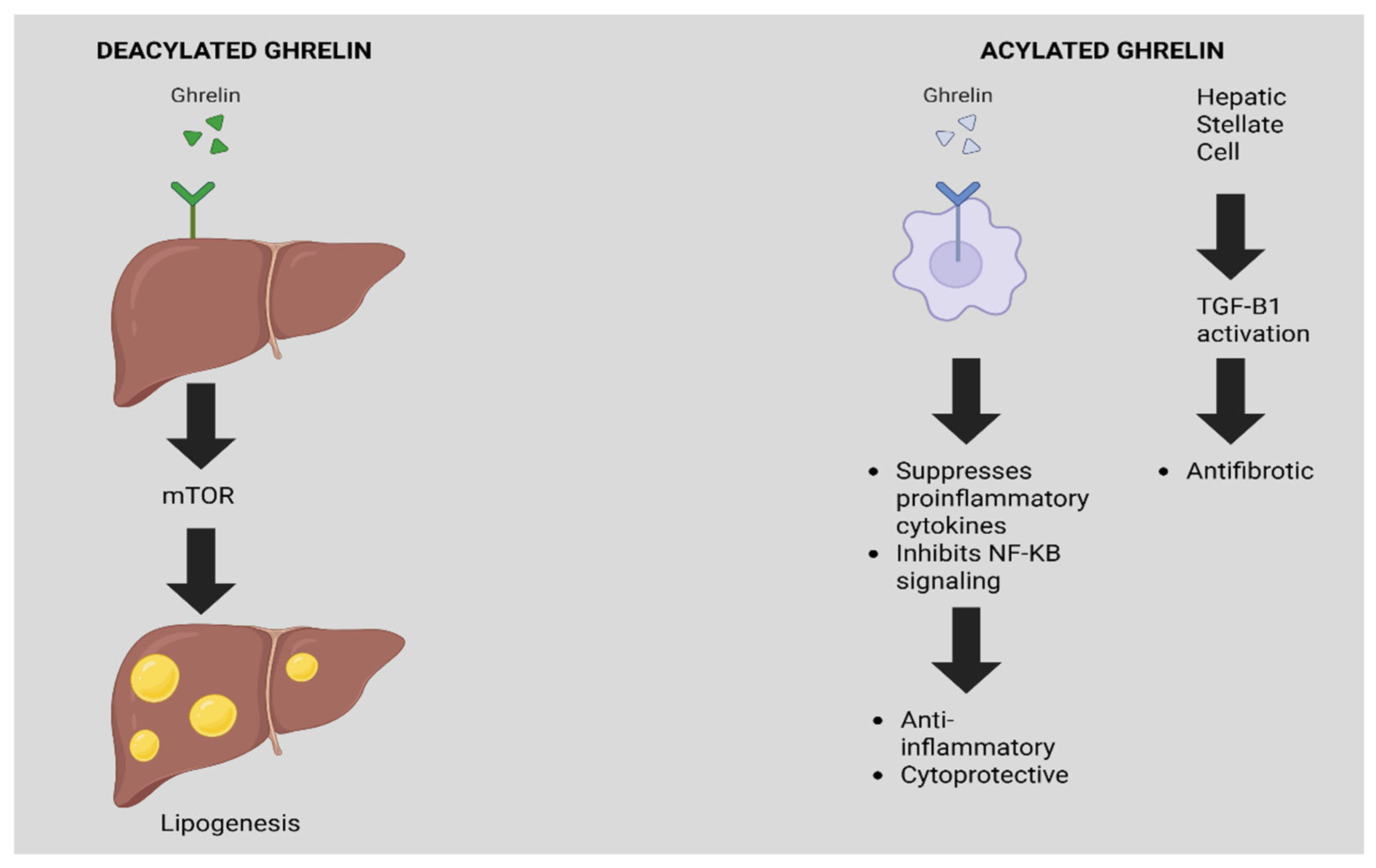
3.3. Ghrelin
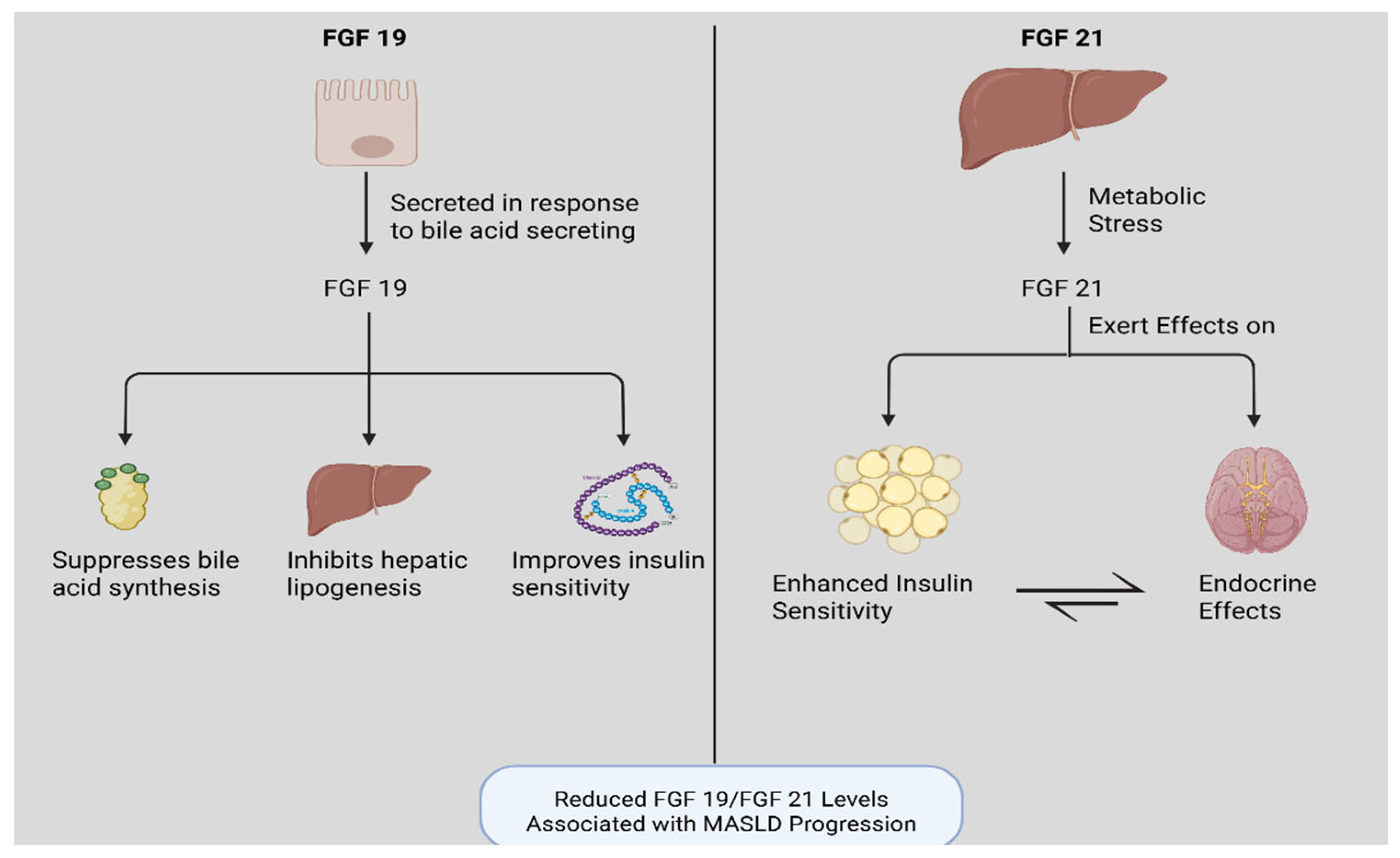
3.4. Fibroblast Growth Factor 19 and 21 (FGF19/FGF21)
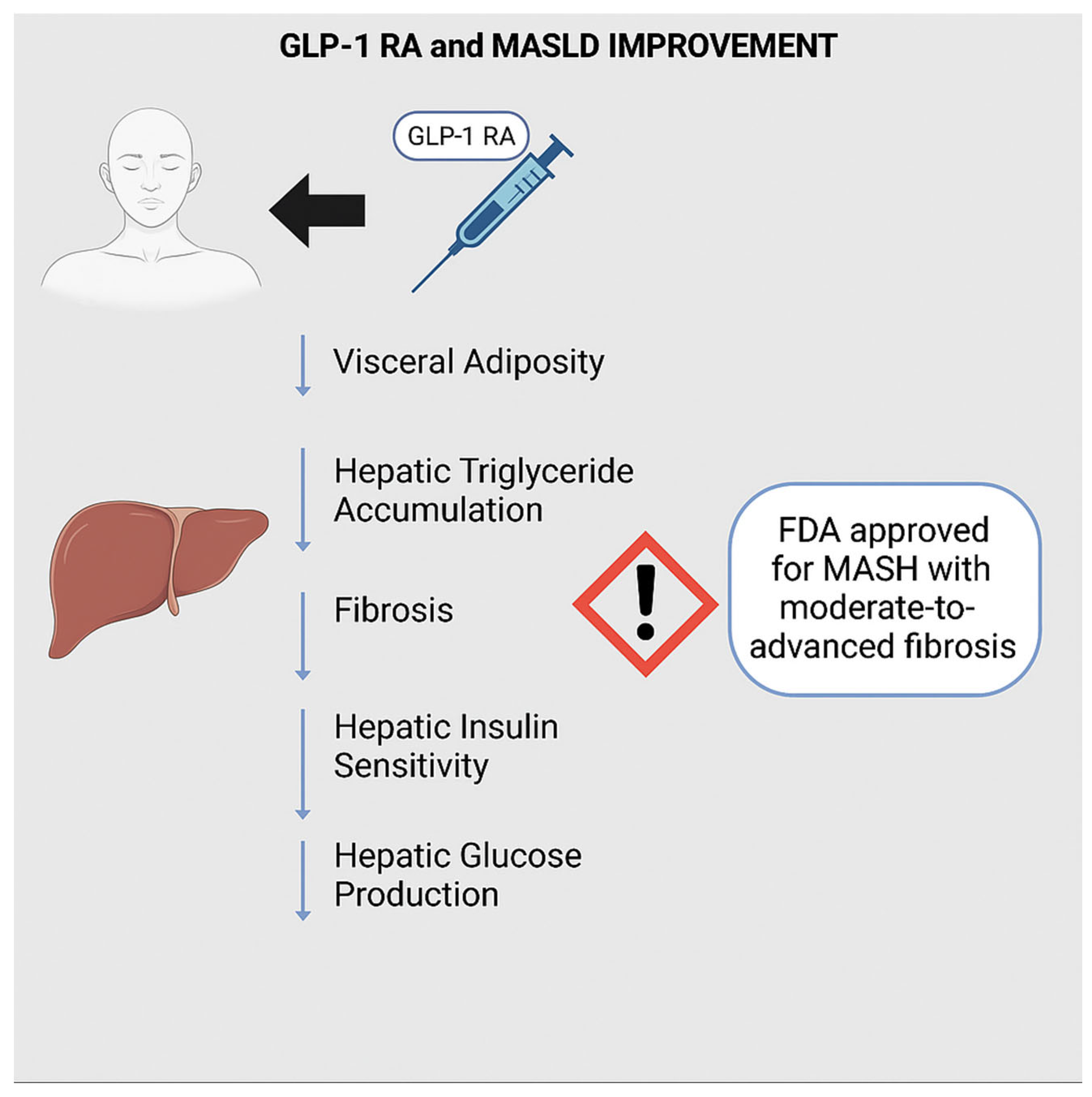
3.5. Glucagon-like Peptide 1 (GLP-1)
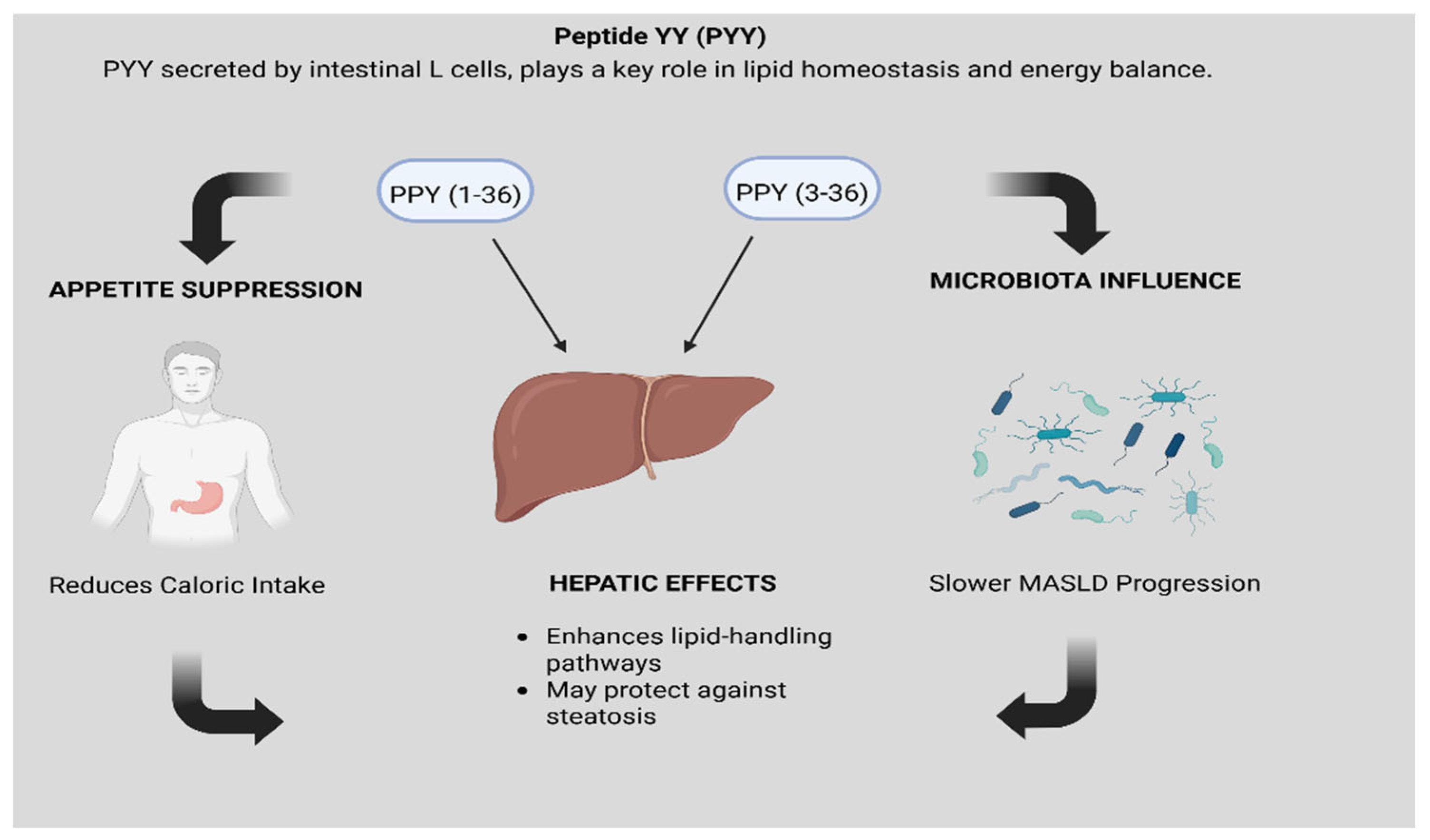
3.6. Peptide YY (PYY)
3.7. Microbiome
3.8. Endoscopic Bariatric Therapies (EBTs)
3.9. Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty (ESG)
3.10. Intragastric Balloon (IGB)
3.11. Duodenal-Jejunal Bypass Liner (DJBL)
3.12. Duodenal Mucosal Resurfacing (DMR)
4. EBTs and MASLD: Emerging Evidence
4.1. Mechanistic Pathways for Improvement in MASLD Outcomes
4.2. Current EBT Outcomes in MASLD
4.3. ESG
4.4. IGB
4.5. DJBL
4.6. DMR
5. Patient Selection for Endoscopic Bariatric Therapies
6. Safety Considerations of Endoscopic Bariatric Therapies
- ESG: ESG is generally well tolerated, with most adverse events limited to transient abdominal pain, nausea, or reflux symptoms. The need for hospitalization is low compared to surgical sleeve gastrectomy, but careful patient selection and post-procedure monitoring remain essential [70].
- IGB: Intolerance, manifested as persistent nausea, vomiting, or abdominal pain, is the most common reason for early removal. Balloon deflation with migration into the small bowel is rare but may lead to obstruction. Ulceration and, rarely, gastric perforation have also been described [48].
- DJBL: Although DJBL can significantly improve glycemic control and steatosis, adverse events remain a limiting factor. Device migration and spontaneous early removal occur in a small percentage of cases. Hepatic abscess formation, though uncommon, is one of the most serious complications and has led to early termination of some clinical trials. Other risks include GI bleeding and obstruction at the liner’s distal tip [71].
- DMR: DMR is generally well tolerated, with mild GI symptoms (e.g., abdominal pain, diarrhea) as the most frequent adverse events. However, mucosal injury carries a theoretical risk of strictures, ulceration, or delayed bleeding, underscoring the need for ongoing safety monitoring as this technology evolves [68].
7. Limitations
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Busebee, B.; Ghusn, W.; Cifuentes, L.; Acosta, A. Obesity: A Review of Pathophysiology and Classification. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2023, 98, 1842–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flegal, K.M.; Kit, B.K.; Orpana, H.; Graubard, B.I. Association of all-cause mortality with overweight and obesity using standard body mass index categories: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Jama 2013, 309, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Golabi, P.; Paik, J.M.; Henry, A.; Van Dongen, C.; Henry, L. The global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH): A systematic review. Hepatology 2023, 77, 1335–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahnazarian, V.; Ramai, D.; Sarkar, A. Endoscopic bariatric therapies for treating obesity: A learning curve for gastroenterologists. Transl. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 4, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Dayyeh, B.K.; Edmundowicz, S.; Thompson, C.C. Clinical Practice Update: Expert Review on Endoscopic Bariatric Therapies. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 716–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, W.K.; Chuah, K.H.; Rajaram, R.B.; Lim, L.L.; Ratnasingam, J.; Vethakkan, S.R. Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD): A State-of-the-Art Review. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2023, 32, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado-Rojas, A.D.C.; Zuarth-Vázquez, J.M.; Uribe, M.; Barbero-Becerra, V.J. Insulin resistance and Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD): Pathways of action of hypoglycemic agents. Ann. Hepatol. 2024, 29, 101182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsiki, N.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Mantzoros, C.S. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and dyslipidemia: An update. Metabolism 2016, 65, 1109–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallianou, N.G.; Kounatidis, D.; Psallida, S.; Vythoulkas-Biotis, N.; Adamou, A.; Zachariadou, T.; Kargioti, S.; Karampela, I.; Dalamaga, M. NAFLD/MASLD and the Gut-Liver Axis: From Pathogenesis to Treatment Options. Metabolites 2024, 14, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zazueta, A.; Valenzuela-Pérez, L.; Ortiz-López, N.; Pinto-León, A.; Torres, V.; Guiñez, D.; Aliaga, N.; Merino, P.; Sandoval, A.; Covarrubias, N.; et al. Alteration of Gut Microbiota Composition in the Progression of Liver Damage in Patients with Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskridge, W.; Cryer, D.R.; Schattenberg, J.M.; Gastaldelli, A.; Malhi, H.; Allen, A.M.; Noureddin, M.; Sanyal, A.J. Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis: The Patient and Physician Perspective. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshaer, A.; Chascsa, D.M.H.; Lizaola-Mayo, B.C. Exploring Varied Treatment Strategies for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD). Life 2024, 14, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, J.E.; Ramos-Roman, M.A.; Valdez, M.J.; Browning, J.D.; Rogers, T.; Parks, E.J. Weight loss in MASLD restores the balance of liver fatty acid sources. J. Clin. Investig. 2025, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Corey, K.E.; Lim, J.K. AGA Clinical Practice Update on Lifestyle Modification Using Diet and Exercise to Achieve Weight Loss in the Management of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Expert Review. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 912–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobbie, L.J.; Burgess, J.; Hamid, A.; Nevitt, S.J.; Hydes, T.J.; Alam, U.; Cuthbertson, D.J. Effect of a Low-Calorie Dietary Intervention on Liver Health and Body Weight in Adults with Metabolic-Dysfunction Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) and Overweight/Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Li, F.; Yan, H.; Chang, X.; Yao, X.; Yang, X.; Wu, S.; Suo, Y.; Zhu, X.; Wang, C.; et al. Intermittent compared with continuous calorie restriction for treatment of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: A randomized clinical trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2025, 121, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsagoni, C.N.; Papatheodoridis, G.V.; Ioannidou, P.; Deutsch, M.; Alexopoulou, A.; Papadopoulos, N.; Papageorgiou, M.V.; Fragopoulou, E.; Kontogianni, M.D. Improvements in clinical characteristics of patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, after an intervention based on the Mediterranean lifestyle: A randomised controlled clinical trial. Br. J. Nutr. 2018, 120, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilar-Gomez, E.; Martinez-Perez, Y.; Calzadilla-Bertot, L.; Torres-Gonzalez, A.; Gra-Oramas, B.; Gonzalez-Fabian, L.; Friedman, S.L.; Diago, M.; Romero-Gomez, M. Weight Loss Through Lifestyle Modification Significantly Reduces Features of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 367–378.e365; quiz e314–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haigh, L.; Kirk, C.; El Gendy, K.; Gallacher, J.; Errington, L.; Mathers, J.C.; Anstee, Q.M. The effectiveness and acceptability of Mediterranean diet and calorie restriction in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 1913–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, T.S.; Luu, K.; Lagishetty, V.; Sedighian, F.; Woo, S.L.; Dreskin, B.W.; Katzka, W.; Chang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Arias-Jayo, N.; et al. The Intestinal Microbiome Predicts Weight Loss on a Calorie-Restricted Diet and Is Associated with Improved Hepatic Steatosis. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 718661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchay, M.S.; Choudhary, N.S.; Ramos-Molina, B. Pathophysiological underpinnings of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2025, 328, C1637–C1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heeren, J.; Scheja, L. Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease and lipoprotein metabolism. Mol. Metab. 2021, 50, 101238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson-Meyer, D.E.; Heilbronn, L.K.; Redman, L.M.; Newcomer, B.R.; Frisard, M.I.; Anton, S.; Smith, S.R.; Alfonso, A.; Ravussin, E. Effect of calorie restriction with or without exercise on insulin sensitivity, beta-cell function, fat cell size, and ectopic lipid in overweight subjects. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 1337–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Most, J.; Gilmore, L.A.; Smith, S.R.; Han, H.; Ravussin, E.; Redman, L.M. Significant improvement in cardiometabolic health in healthy nonobese individuals during caloric restriction-induced weight loss and weight loss maintenance. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 314, E396–E405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alisi, A.; Ceccarelli, S.; Panera, N.; Prono, F.; Petrini, S.; De Stefanis, C.; Pezzullo, M.; Tozzi, A.; Villani, A.; Bedogni, G.; et al. Association between Serum Atypical Fibroblast Growth Factors 21 and 19 and Pediatric Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; Gallego-Escuredo, J.M.; Catalán, V.; Rodríguez, A.; Domingo, P.; Moncada, R.; Valentí, V.; Salvador, J.; Giralt, M.; Villarroya, F.; et al. FGF19 and FGF21 serum concentrations in human obesity and type 2 diabetes behave differently after diet- or surgically-induced weight loss. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falamarzi, K.; Malekpour, M.; Tafti, M.F.; Azarpira, N.; Behboodi, M.; Zarei, M. The role of FGF21 and its analogs on liver associated diseases. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 967375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego-Durán, R.; Ampuero, J.; Maya-Miles, D.; Pastor-Ramírez, H.; Montero-Vallejo, R.; Rivera-Esteban, J.; Álvarez-Amor, L.; Pareja, M.J.; Rico, M.C.; Millán, R.; et al. Fibroblast growth factor 21 is a hepatokine involved in MASLD progression. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2024, 12, 1056–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, J.P.; Morgan, D.A.; Sullivan, A.I.; Fu, X.; Inigo-Vollmer, M.; Burgess, S.C.; Meyerholz, D.K.; Rahmouni, K.; Potthoff, M.J. FGF21 reverses MASH through coordinated actions on the CNS and liver. Cell Metab. 2025, 37, 1515–1529.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Headland, M.L.; Clifton, P.M.; Keogh, J.B. Effects of Weight Loss on FGF-21 in Human Subjects: An Exploratory Study. Int. J. Env. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milani, I.; Codini, M.; Guarisco, G.; Chinucci, M.; Gaita, C.; Leonetti, F.; Capoccia, D. Hepatokines and MASLD: The GLP1-Ras-FGF21-Fetuin-A Crosstalk as a Therapeutic Target. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghusn, W.; Hurtado, M.D. Glucagon-like Receptor-1 agonists for obesity: Weight loss outcomes, tolerability, side effects, and risks. Obes. Pillars 2024, 12, 100127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghusn, W.; Fansa, S.; Anazco, D.; Tama, E.; Nicolalde, B.; Gala, K.; De la Rosa, A.; Sacoto, D.; Cifuentes, L.; Campos, A.; et al. Weight loss and cardiovascular disease risk outcomes of semaglutide: A one-year multicentered study. Int. J. Obes. 2024, 48, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abushamat, L.A.; Shah, P.A.; Eckel, R.H.; Harrison, S.A.; Barb, D. The Emerging Role of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists for the Treatment of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 22, 1565–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabut, J.M.; Drucker, D.J. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor-based Therapeutics for Metabolic Liver Disease. Endocr. Rev. 2023, 44, 14–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochoń, J.; Kalinowski, P.; Szymanek-Majchrzak, K.; Grąt, M. Role of gut-liver axis and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in the treatment of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 30, 2964–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyal, A.J.; Newsome, P.N.; Kliers, I.; Østergaard, L.H.; Long, M.T.; Kjær, M.S.; Cali, A.M.G.; Bugianesi, E.; Rinella, M.E.; Roden, M.; et al. Phase 3 Trial of Semaglutide in Metabolic Dysfunction–Associated Steatohepatitis. New Engl. J. Med. 2025, 392, 2089–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevola, R.; Epifani, R.; Imbriani, S.; Tortorella, G.; Aprea, C.; Galiero, R.; Rinaldi, L.; Marfella, R.; Sasso, F.C. GLP-1 receptor agonists in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Current evidence and future perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowie, K. Semaglutide: FDA approves weight loss jab to treat severe liver disease. BMJ 2025, 390, r1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.C.; Hämmerle, C.M.; Lee, I.C.; Turner, N.; Nguyen, A.D.; Riepler, S.J.; Lin, S.; Sainsbury, A.; Herzog, H.; Zhang, L. Adult-onset PYY overexpression in mice reduces food intake and increases lipogenic capacity. Neuropeptides 2012, 46, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, Q.; Luo, F.; Li, B.; Li, Z.; Guo, Z.; Chen, Z.; Wu, W.; Hu, M. Gut microbiota and metabolic biomarkers in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Hepatol. Commun. 2024, 8, e0310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aron-Wisnewsky, J.; Warmbrunn, M.V.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Clément, K. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Modulating Gut Microbiota to Improve Severity? Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1881–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Vitetta, L. Gut Microbiota Metabolites in NAFLD Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.S.; Katzka, W.; Yang, J.C.; Chang, C.; Arias-Jayo, N.; Lagishetty, V.; Balioukova, A.; Chen, Y.; Dutson, E.; Li, Z.; et al. Microbial changes from bariatric surgery alters glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide and prevents fatty liver disease. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2167170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craciun, C.-I.; Neag, M.-A.; Catinean, A.; Mitre, A.-O.; Rusu, A.; Bala, C.; Roman, G.; Buzoianu, A.-D.; Muntean, D.-M.; Craciun, A.-E. The Relationships between Gut Microbiota and Diabetes Mellitus, and Treatments for Diabetes Mellitus. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portincasa, P.; Bonfrate, L.; Vacca, M.; De Angelis, M.; Farella, I.; Lanza, E.; Khalil, M.; Wang, D.Q.; Sperandio, M.; Di Ciaula, A. Gut Microbiota and Short Chain Fatty Acids: Implications in Glucose Homeostasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghusn, W.; Calderon, G.; Abu Dayyeh, B.K.; Acosta, A. Mechanism of action and selection of endoscopic bariatric therapies for treatment of obesity. Clin. Endosc. 2024, 57, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tate, C.M.; Geliebter, A. Intragastric Balloon Treatment for Obesity: Review of Recent Studies. Adv. Ther. 2017, 34, 1859–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohde, U.; Hedbäck, N.; Gluud, L.L.; Vilsbøll, T.; Knop, F.K. Effect of the EndoBarrier Gastrointestinal Liner on obesity and type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2016, 18, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghusn, W.; Zeineddine, J.; Betancourt, R.S.; Gajjar, A.; Yang, W.; Robertson, A.G.; Ghanem, O.M. Advances in Metabolic Bariatric Surgeries and Endoscopic Therapies: A Comprehensive Narrative Review of Diabetes Remission Outcomes. Medicina 2025, 61, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Hwang, H.; Shin, H.; Kim, B.H.; Kang, S.H.; Yoo, J.-J.; Choi, M.Y.; Lee, D.e.; Jun, D.W.; Cho, Y. Bariatric intervention improves metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis in patients with obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2024, 30, 561–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.; Xia, Y.; Pan, H.; Zhou, X.; Yu, M.; Ji, F. Duodenal-jejunal bypass ameliorates MASLD in rats by regulating gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism through FXR pathways. Hepatol. Commun. 2025, 9, e0615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Dayyeh, B.K.; Bazerbachi, F.; Graupera, I.; Cardenas, A.M.D. Endoscopic bariatric and metabolic therapies for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 1246–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitharaju, V.; Ragheb, J.; Firkins, S.; Patel, R.; Simons-Linares, C.R. Endoscopic bariatric and metabolic therapies and its effect on metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: A review of the current literature. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2025, 21, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gala, K.; Ghusn, W.; Fansa, S.; Abu Dayyeh, B.K.; Ghanem, O.M.; Kellogg, T.; Acosta, A. Effects of Heterozygous Variants in the Leptin-Melanocortin Pathway on Transoral Outlet Reduction After Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass: A Case–Control Study and Review of Literature. Obes. Surg. 2023, 33, 1284–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajifathalian, K.; Mehta, A.; Ang, B.; Skaf, D.; Shah, S.L.; Saumoy, M.; Dawod, Q.; Dawod, E.; Shukla, A.; Aronne, L.; et al. Improvement in insulin resistance and estimated hepatic steatosis and fibrosis after endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2021, 93, 1110–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunes, B.C.M.; de Moura, D.T.H.; Kum, A.S.T.; de Oliveira, G.H.P.; Hirsch, B.S.; Ribeiro, I.B.; Gomes, I.L.C.; de Oliveira, C.P.M.; Mahmood, S.; Bernardo, W.M.; et al. Impact of Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Obes. Surg. 2023, 33, 2917–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagtap, N.; Kalapala, R.; Katakwar, A.; Sharma, M.; Aslam, M.; Gupta, R.; Rao, P.N.; Goud, R.; Tandan, M.; Kanakagiri, H.; et al. Endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty—Minimally invasive treatment for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and obesity. Indian J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 40, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jirapinyo, P.; Jaroenlapnopparat, A.; Zucker, S.D.; Thompson, C.C. Combination Therapy of Endoscopic Gastric Remodeling with GLP-1RA for the Treatment of MASLD. Obes. Surg. 2024, 34, 1471–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomone, F.; Currenti, W.; Magrì, G.; Boškoski, I.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Galvano, F. Effects of intragastric balloon in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and advanced fibrosis. Liver Int. 2021, 41, 2112–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoko, O.; Maharaj, T.; Boland, F.; Cheriyan, D.; Ryan, J. Meta-analysis: Impact of intragastric balloon therapy on NAFLD-related parameters in patients with obesity. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2024, 59, 8–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-M.; Low, H.C.; Lim, L.G.; Dan, Y.Y.; Aung, M.O.; Cheng, C.L.; Wee, A.; Lim, S.G.; Ho, K.Y. Intragastric balloon significantly improves nonalcoholic fatty liver disease activity score in obese patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A pilot study. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2012, 76, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dijk, A.M.; de Vries, M.; El-Morabit, F.; Bac, S.T.; Mundt, M.W.; van der Schuit, L.E.; Hirdes, M.M.C.; Kara, M.; de Bruijne, J.; van Meer, S.; et al. Intra-gastric balloon with lifestyle modification: A promising therapeutic option for overweight and obese patients with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2023, 18, 2271–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, V.B.; Thompson, C.C.; Kumar, N.; Ciarleglio, M.M.; Deng, Y.; Laine, L. Effect of Intragastric Balloons on Liver Enzymes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2016, 61, 2477–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraghavan, R.; Sarin, S.K.; Bharadwaj, A.; Anand, L.; Maiwall, R.; Choudhury, A.; Benjamin, J.; Kanal, U.; Jamwal, K.D. Intragastric Balloon in Obese Compensated Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Cirrhosis Patients Is Safe and Achieves Significant Weight Reduction at 6-Months. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2023, 68, 1035–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jonge, C.; Rensen, S.S.; Koek, G.H.; Joosten, M.F.; Buurman, W.A.; Bouvy, N.D.; Greve, J.W. Endoscopic duodenal-jejunal bypass liner rapidly improves plasma parameters of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 11, 1517–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlas, T.; Petroff, D.; Feisthammel, J.; Beer, S.; Blüher, M.; Schütz, T.; Lichtinghagen, R.; Hoffmeister, A.; Wiegand, J. Endoscopic Bariatric Treatment with Duodenal-Jejunal Bypass Liner Improves Non-invasive Markers of Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis. Obes. Surg. 2022, 32, 2495–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mingrone, G.; Van Baar, A.C.; Devière, J.; Hopkins, D.; Moura, E.; Cercato, C.; Rajagopalan, H.; Lopez-Talavera, J.C.; White, K.; Bhambhani, V. Safety and efficacy of hydrothermal duodenal mucosal resurfacing in patients with type 2 diabetes: The randomised, double-blind, sham-controlled, multicentre REVITA-2 feasibility trial. Gut 2022, 71, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadefi, A.; Verset, L.; Pezzullo, M.; Rosewick, N.; Degré, D.; Gustot, T.; Moreno, C.; Devière, J.; Trépo, E. Endoscopic duodenal mucosal resurfacing for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH): A pilot study. Endosc. Int. Open 2021, 9, E1792–E1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu Dayyeh, B.K.; Bazerbachi, F.; Vargas, E.J.; Sharaiha, R.Z.; Thompson, C.C.; Thaemert, B.C.; Teixeira, A.F.; Chapman, C.G.; Kumbhari, V.; Ujiki, M.B.; et al. Endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty for treatment of class 1 and 2 obesity (MERIT): A prospective, multicentre, randomised trial. Lancet 2022, 400, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruban, A.; Miras, A.D.; Glaysher, M.A.; Goldstone, A.P.; Prechtl, C.G.; Johnson, N.; Chhina, N.; Al-Najim, W.; Aldhwayan, M.; Klimowska-Nassar, N.; et al. Duodenal-Jejunal Bypass Liner for the management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Obesity: A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial. Ann. Surg. 2022, 275, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouillard, N.A.; Barnett, S.D.; Zhang, X.; Kam, L.; Manikat, R.; Cheung, R.; Nguyen, M.H. Bariatric surgery reduces long-term mortality in patients with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease and cirrhosis. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2025, 31, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Procedure | Mechanism | Weight Loss Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty (ESG) | Endoscopic suturing device plicates the greater curvature of the stomach, creating a tubular reduced-calorie reservoir without resection or incisions | 15–20% TBWL over 12–18 months |
| Intragastric Balloon (IGB) | Saline- or gas-filled balloon occupies gastric lumen space, triggering stretch receptors and promoting early satiety | 10–15% TBWL during 6-month indwelling period |
| Duodenal-Jejunal Bypass Liner (DJBL) | 60 cm impermeable sleeve anchored in the duodenal bulb, bypassing nutrient exposure in proximal small intestine and mimicking Roux-en-Y bypass physiology | ~12% TBWL, 20–25% excess body weight reduction at 12 months |
| Duodenal Mucosal Resurfacing (DMR) | Hydrothermal ablation of duodenal mucosa disrupts maladaptive nutrient sensing and regenerates epithelium | ~5% TBWL over 6–12 months |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghusn, W.; Sridharan, M.; Fromer, R.; Ozdemir, M.; Haff, M.G.; Vargas, E.J. Endoscopic Bariatric Therapies for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: Mechanistic Insights and Metabolic Implications. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2437. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102437
Ghusn W, Sridharan M, Fromer R, Ozdemir M, Haff MG, Vargas EJ. Endoscopic Bariatric Therapies for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: Mechanistic Insights and Metabolic Implications. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(10):2437. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102437
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhusn, Wissam, Mira Sridharan, Rachel Fromer, Muhammet Ozdemir, Madeleine G. Haff, and Eric J. Vargas. 2025. "Endoscopic Bariatric Therapies for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: Mechanistic Insights and Metabolic Implications" Biomedicines 13, no. 10: 2437. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102437
APA StyleGhusn, W., Sridharan, M., Fromer, R., Ozdemir, M., Haff, M. G., & Vargas, E. J. (2025). Endoscopic Bariatric Therapies for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: Mechanistic Insights and Metabolic Implications. Biomedicines, 13(10), 2437. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102437







