Assessing Plasma C-Peptide Levels and Their Relationship with Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients with Prediabetes and Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
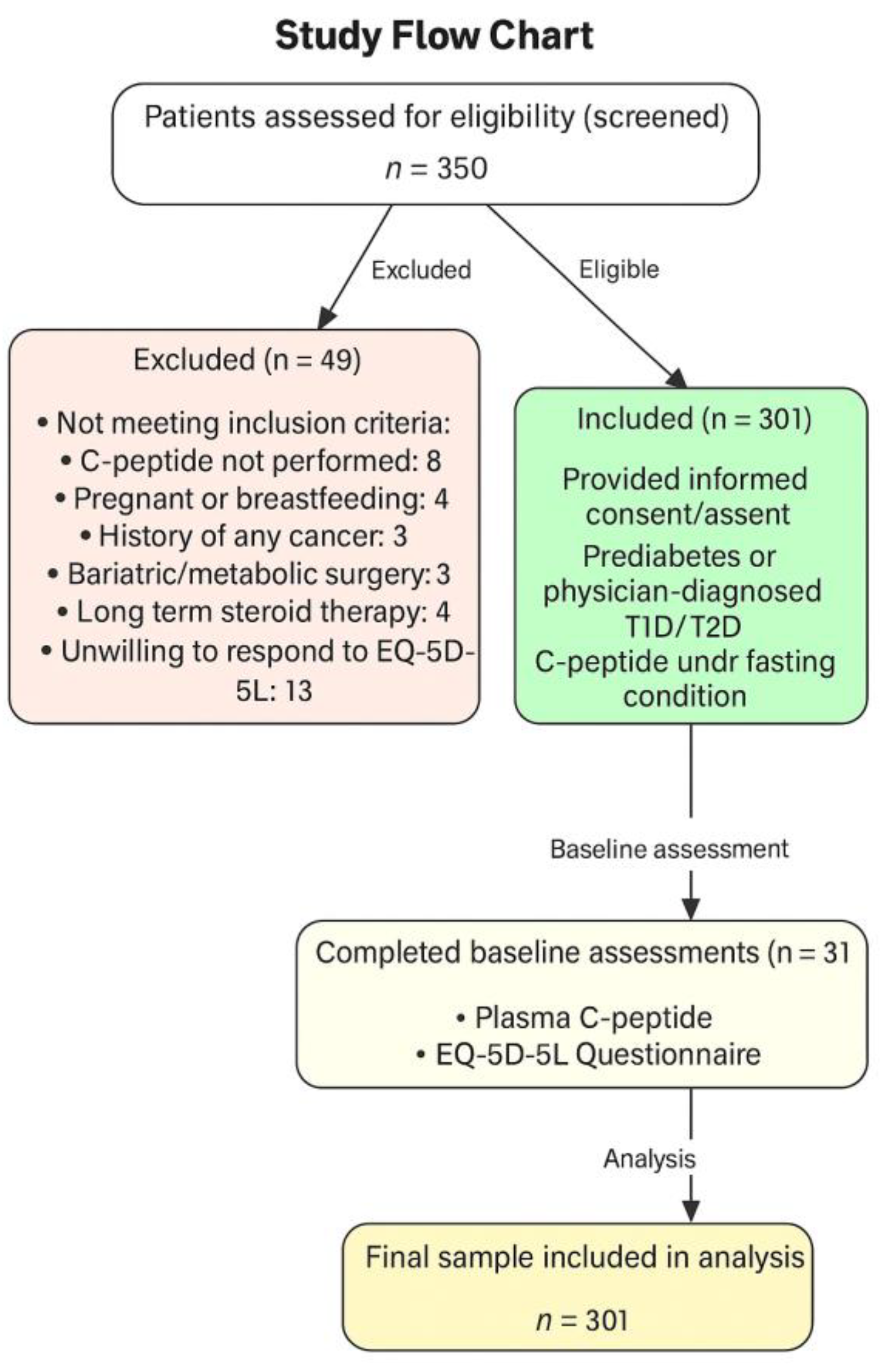
2.1. Participants and Study Design
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Study Endpoints/Outcome Measures
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
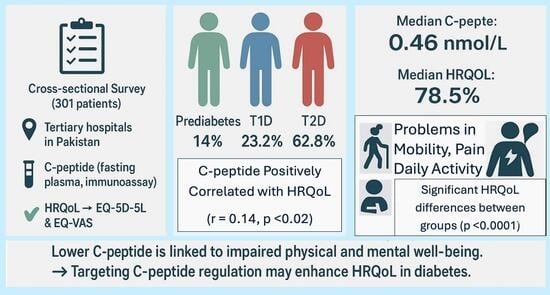
3.1. Patient Characteristics at Baseline
3.2. Primary Outcome Measures
3.2.1. EQ-5D-5L System
3.2.2. C-Peptide and Its Relation to the HRQoL
3.3. Secondary Outcome Measures
HRQoL Across Different Types of Diabetes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| C-peptide | Connecting peptide |
| T1D | Type 1 diabetes |
| T2D | Type 2 diabetes |
| HRQoL | Health-related Quality of Life |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| EQ-5D-5L | EuroQoL Five Dimensions Five Levels |
| SF-36 | Short Form 36 Health Survey |
| WHOQOL-BREF | World Health Organization Quality of Life-BREF |
| SZH | Sheikh Zayed hospital |
| MH | Mayo hospital |
| PU | University of the Punjab |
| HbA1c | Hemoglobin A1C |
| GADA | GAD/anti-islet |
| EQ VAS | EuroQol Visual Analog |
Appendix A
References
- Chen, J.; Huang, Y.; Liu, C.; Chi, J.; Wang, Y.; Xu, L. The role of C-peptide in diabetes and its complications: An updated review. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1256093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, A.; Shafiee-Nick, R. Pathological consequences of C-peptide deficiency in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. World J. Diabetes 2015, 6, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yosten, G.L.; Maric-Bilkan, C.; Luppi, P.; Wahren, J. Physiological effects and therapeutic potential of proinsulin C-peptide. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 307, E955–E968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dakroub, A.; Dbouk, A.; Asfour, A.; Nasser, S.A.; El-Yazbi, A.F.; Sahebkar, A.; Eid, A.A.; Iratni, R.; Eid, A.H. C-peptide in diabetes: A player in a dual hormone disorder? J. Cell. Physiol. 2024, 239, e31212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essa, B.S.; Meena, M.Q. Potential of Fasting C-peptide to Glucose Ratio and Triglyceride Glucose Index as Markers for beta-Cell Dysfunction and Insulin Resistance in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes on Insulin Therapy. Cureus 2024, 16, e66543. [Google Scholar]
- Aviles-Santa, M.L.; Monroig-Rivera, A.; Soto-Soto, A.; Lindberg, N.M. Current State of Diabetes Mellitus Prevalence, Awareness, Treatment, and Control in Latin America: Challenges and Innovative Solutions to Improve Health Outcomes Across the Continent. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2020, 20, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkinson, C.; Stewart-Brown, S.; Petersen, S.; Paice, C. Assessment of the SF-36 version 2 in the United Kingdom. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 1999, 53, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, M.; Sheikhvatan, M.; Montazeri, A.; Sheikhfathollahi, M. Reliability of World Health Organization’s Quality of Life-BREF versus Short Form 36 Health Survey questionnaires for assessment of quality of life in patients with coronary artery disease. J. Cardiovasc. Med. 2009, 10, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herdman, M.; Gudex, C.; Lloyd, A.; Janssen, M.; Kind, P.; Parkin, D.; Bonsel, G.; Badia, X. Development and preliminary testing of the new five-level version of EQ-5D (EQ-5D-5L). Qual. Life Res. 2011, 20, 1727–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satterley, N. Healthy, Prosperous Lives for All: The European Health Equity Status Report; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019; Available online: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/346044/WHO-EURO-2019-3536-43295-60680-eng.pdf?sequence=3 (accessed on 17 December 2024).
- Maddaloni, E.; Bolli, G.B.; Frier, B.M.; Little, R.R.; Leslie, R.D.; Pozzilli, P.; Buzzetti, R. C-peptide determination in the diagnosis of type of diabetes and its management: A clinical perspective. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2022, 24, 1912–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, A.G.; Hattersley, A.T. The clinical utility of C-peptide measurement in the care of patients with diabetes. Diabet. Med. 2013, 30, 803–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-Nejem, R.; Hannon, T.S. Insulin Dynamics and Pathophysiology in Youth-Onset Type 2 Diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 109, 2411–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chesser, H.; Srinivasan, S.; Puckett, C.; Gitelman, S.E.; Wong, J.C. Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Adolescents and Young Adults With Type 2 Diabetes Can Improve Quality of Life. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2024, 18, 911–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, P.; Weiskirchen, R. The Role of Obesity in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus-An Overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, P.N.; Collins, K.S.; Lam, A.; Karpen, S.R.; Greeno, B.; Walker, F.; Lozano, A.; Atabakhsh, E.; Ahmed, S.T.; Marinac, M.; et al. C-peptide and metabolic outcomes in trials of disease modifying therapy in new-onset type 1 diabetes: An individual participant meta-analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2023, 11, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanBuecken, D.E.; Greenbaum, C.J. Residual C-peptide in type 1 diabetes: What do we really know? Pediatr. Diabetes 2014, 15, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Cheng, B.; Kui, C.; Wang, Y. C-peptide, glycaemic control, and diabetic complications in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A real-world study. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2022, 38, e3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorgjerd, E.P.; Asvold, B.O.; Grill, V. Low C-peptide together with a high glutamic acid decarboxylase autoantibody level predicts progression to insulin dependence in latent autoimmune diabetes in adults: The HUNT study. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021, 23, 2539–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludvigsson, J. The clinical potential of low-level C-peptide secretion. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2016, 16, 933–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubitosi-Klug, R.A.; Braffett, B.H.; Hitt, S.; Arends, V.; Uschner, D.; Jones, K.; Diminick, L.; Karger, A.B.; Paterson, A.D.; Roshandel, D.; et al. Residual beta cell function in long-term type 1 diabetes associates with reduced incidence of hypoglycemia. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e143011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoeff, K.; Marfil-Garza, B.A.; Dajani, K.; Bigam, D.L.; Anderson, B.; Kin, T.; Lam, A.; O’Gorman, D.; Senior, P.A.; Shapiro, A.M.J. C-peptide Targets and Patient-centered Outcomes of Relevance to Cellular Transplantation for Diabetes. Transplantation 2023, 107, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzilli, P.; Bosi, E.; Cirkel, D.; Harris, J.; Leech, N.; Tinahones, F.J.; Vantyghem, M.C.; Vlasakakis, G.; Ziegler, A.G.; Janmohamed, S. Randomized 52-week Phase 2 Trial of Albiglutide Versus Placebo in Adult Patients With Newly Diagnosed Type 1 Diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, e2192–e2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourhoseingholi, M.A.; Vahedi, M.; Rahimzadeh, M. Sample size calculation in medical studies. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Bed Bench 2013, 6, 14–17. [Google Scholar]
- Basit, A.; Fawwad, A.; Qureshi, H.; Shera, A.S.; Members, N. Prevalence of diabetes, pre-diabetes and associated risk factors: Second National Diabetes Survey of Pakistan (NDSP), 2016–2017. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e020961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roudijk, B.; Ludwig, K.; Devlin, N. EQ-5D-5L Value Set Summaries. In Value Sets for EQ-5D-5L: A Compendium, Comparative Review & User Guide; Devlin, N., Roudijk, B., Ludwig, K., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 55–212. [Google Scholar]
- Jyani, G.; Sharma, A.; Prinja, S.; Kar, S.S.; Trivedi, M.; Patro, B.K.; Goyal, A.; Purba, F.D.; Finch, A.P.; Rajsekar, K.; et al. Development of an EQ-5D Value Set for India Using an Extended Design (DEVINE) Study: The Indian 5-Level Version EQ-5D Value Set. Value Health 2022, 25, 1218–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staples, T.L. Expansion and evolution of the R programming language. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2023, 10, 221550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jankowska, A.; Mlynczak, K.; Golicki, D. Validity of EQ-5D-5L health-related quality of life questionnaire in self-reported diabetes: Evidence from a general population survey. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2021, 19, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, G.; Garin, O.; Pardo, Y.; Vilagut, G.; Pont, A.; Suarez, M.; Neira, M.; Rajmil, L.; Gorostiza, I.; Ramallo-Farina, Y.; et al. Validity of the EQ-5D-5L and reference norms for the Spanish population. Qual. Life Res. 2018, 27, 2337–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seng, J.J.B.; Kwan, Y.H.; Fong, W.; Phang, J.K.; Lui, N.L.; Thumboo, J.; Leung, Y.Y. Validity and reliability of EQ-5D-5L among patients with axial spondyloarthritis in Singapore. Eur. J. Rheumatol. 2020, 7, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, F.; Ameri, H.; Madadizadeh, F.; Reza Aghaei, M. Health-related quality of life and its associated factors in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. SAGE Open Med. 2020, 8, 2050312120965314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.N.; Cheng, A.Y.Y.; Robinson, D.J. Emotional, Psychological, and Social Well-being Experience of Long-Term Living with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Patient-Psychiatrist-Endocrinologist Perspective. Diabetes Ther. 2024, 15, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahromi, M.K.; Ahmadirad, H.; Jamshidi, S.; Farhadnejad, H.; Mokhtari, E.; Shahrokhtabar, T.; Tavakkoli, S.; Teymoori, F.; Mirmiran, P. The association of serum C-peptide with the risk of cardiovascular events: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2023, 15, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majaliwa, E.S.; Muze, K.C.; Ndayongeje, J.; Mfinanga, S.G.; Mmbaga, B.T.; Ramaiya, K. Correlation of C-Peptide with Complications Observed in Children and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes in Tanzania: A Cross-Sectional Survey. Glob. Pediatr. Health 2023, 10, 2333794X231159790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, R.; Balci, M.K. Relationship between C peptide and chronic complications in type-2 diabetes mellitus. J. Natl. Med. Assoc. 2005, 97, 1113–1118. [Google Scholar]
- De Sonnaville, J.J.; Snoek, F.J.; Colly, L.P.; Deville, W.; Wijkel, D.; Heine, R.J. Well-being and symptoms in relation to insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 1998, 21, 919–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, Y.M.; Wang, L.J.; Mao, H.X.; Lou, X.Y.; Zhu, Y.J.; Zhu, Y.H. Correlation of lower 2 h C-peptide and elevated evening cortisol with high levels of depression in type 2 diabetes mellitus. BMC Psychiatry 2020, 20, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barmpagianni, A.; Karamanakos, G.; Anastasiou, I.A.; Kountouri, A.; Lambadiari, V.; Liatis, S. The relationship between residual insulin secretion and subclinical cardiovascular risk indices in young adults with type 1 diabetes. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2025, 39, 108946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, V.; Sousa, M.E.; Lopes, S.C.; Lages, A.S. Metabolic impact of residual C-peptide secretion in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Arch. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 68, e230503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryk, A.; Losiewicz, A.; Michalak, A.; Fendler, W. Biological Activity of c-Peptide in Microvascular Complications of Type 1 Diabetes-Time for Translational Studies or Back to the Basics? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makrilakis, K.; Liatis, S.; Tsiakou, A.; Stathi, C.; Papachristoforou, E.; Perrea, D.; Katsilambros, N.; Kontodimopoulos, N.; Niakas, D. Comparison of health-related quality of Life (HRQOL) among patients with pre-diabetes, diabetes and normal glucose tolerance, using the 15D-HRQOL questionnaire in Greece: The DEPLAN study. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2018, 18, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arian, M.; Mirmohammadkhani, M.; Ghorbani, R.; Soleimani, M. Health-related quality of life (HRQoL) in beta-thalassemia major (beta-TM) patients assessed by 36-item short form health survey (SF-36): A meta-analysis. Qual. Life Res. 2019, 28, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veelen, A.; Erazo-Tapia, E.; Oscarsson, J.; Schrauwen, P. Type 2 diabetes subgroups and potential medication strategies in relation to effects on insulin resistance and beta-cell function: A step toward personalised diabetes treatment? Mol. Metab. 2021, 46, 101158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.H.; Yue, J.; Jiang, Y.H.; Yang, M.L.; Gu, Z.C.; Ma, J.; Li, H. Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitors Use Improves the Satisfaction With Anti-diabetic Agent Treatment: A Questionnaire-based Propensity Score-matched Study. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 787704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, S.; Bayoumi, A.M.; Abrahao, A.B.K.; Trudeau, M.; Pritchard, K.I.; Li, C.N.; Mitsakakis, N.; Liu, G.; Krahn, M. Implementing routine collection of EQ-5D-5L in a breast cancer outpatient clinic. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0307225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuan, W.C.; Chee, K.H.; Kasim, S.; Lim, K.K.; Dujaili, J.A.; Lee, K.K.; Teoh, S.L. Validity and measurement equivalence of EQ-5D-5L questionnaire among heart failure patients in Malaysia: A cohort study. J. Med. Econ. 2024, 27, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pongsachareonnont, P.F.; Sakthong, P.; Chaikitmongkol, V.; Tsutsumi, W.D.; Bhoomibunchoo, C.; Hurst, C.P.; Teerawattananon, Y.; Kulvichit, K. Health Utility Values Among Patients With Diabetic Retinopathy, Wet Age-Related Macular Degeneration, and Cataract in Thailand: A Multicenter Survey Using Time Trade-Off, EQ-5D-5L, and Health Utility Index 3. Value Health Reg. Issues 2024, 44, 101030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, H.; James, S.; Brown, F.; Gaca, M.; O’Neal, D.; Tran-Duy, A.; Devlin, N.; Kelly, R.; Ekinci, E.I. Health-related quality of life assessment in health economic analyses involving type 2 diabetes. Diabet. Med. 2024, 41, e15418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, L.; Costa, B.; Pereira, M.; Silva, A.; Santos, J.; Saldanha, L.; Silva, I.; Magalhaes, P.; Schmidt, S.; Vale, N. Advancing Precision Medicine: A Review of Innovative In Silico Approaches for Drug Development, Clinical Pharmacology and Personalized Healthcare. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyani, R.R.; Allende-Vigo, M.Z.; Antinori-Lent, K.J.; Close, K.L.; Das, S.R.; Deroze, P.; Edelman, S.V.; El Sayed, N.A.; Kerr, D.; Neumiller, J.J.; et al. Prioritizing Patient Experiences in the Management of Diabetes and Its Complications: An Endocrine Society Position Statement. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 109, 1155–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, D.; Andresen-Bundus, H.; Pagonas, N.; Jaehn, P.; Ukena, C.; Godde, K.; Holmberg, C.; Ritter, O.; Sasko, B. Adverse socioeconomic factors are associated with a widening gap in one-year health-related quality of life after acute myocardial infarction. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 19791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyono, D.; Kim, S. Impact of comorbidities on health-related quality of life in diabetic patients: Evidence from a South Korean population-based panel study. Sci. Prog. 2025, 108, 368504251328770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Characteristics | Prediabetes, n = 42 | T1D, n = 70 | T2D, n = 189 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age at visit (years) * | 36.55 ± 13.4 | 22.9 ± 7.0 | 30.3 ± 8.5 |
| Sex male/female * | 21 (50%)/21 (50%) | 33 (47.2%)/37 (52.8%) | 124 (65.6%)/65 (34.4%) |
| BMI, n = 281 (prediabetes = 42, T1D = 67, T2D = 172) ** | |||
| <18.5 kg/m2 | 2 (4.8%) | 6 (8.9%) | 12 (7%) |
| BMI 18.5 to <25 kg/m2 * | 6 (14.3%) | 33 (49.2%) | 48 (27.9%) |
| BMI 25 to <30 kg/m2 | 15 (35.7%) | 16 (23.8%) | 50 (29.1%) |
| BMI ≥30 kg/m2 * | 14 (33.3%) | 12 (17.9%) | 62 (36.0%) |
| Ever smoked * | 8 (19.0%) | 8 (11.4%) | 29 (16.9%) |
| SBP (mmHg) | 116.5 (110.8–121.8) | 114 (107.5–122.5) | 120 (111–128) |
| DBP (mmHg) * | 68.5 (63.8–77.5) | 67 (61.5–74) | 71 (64–80) |
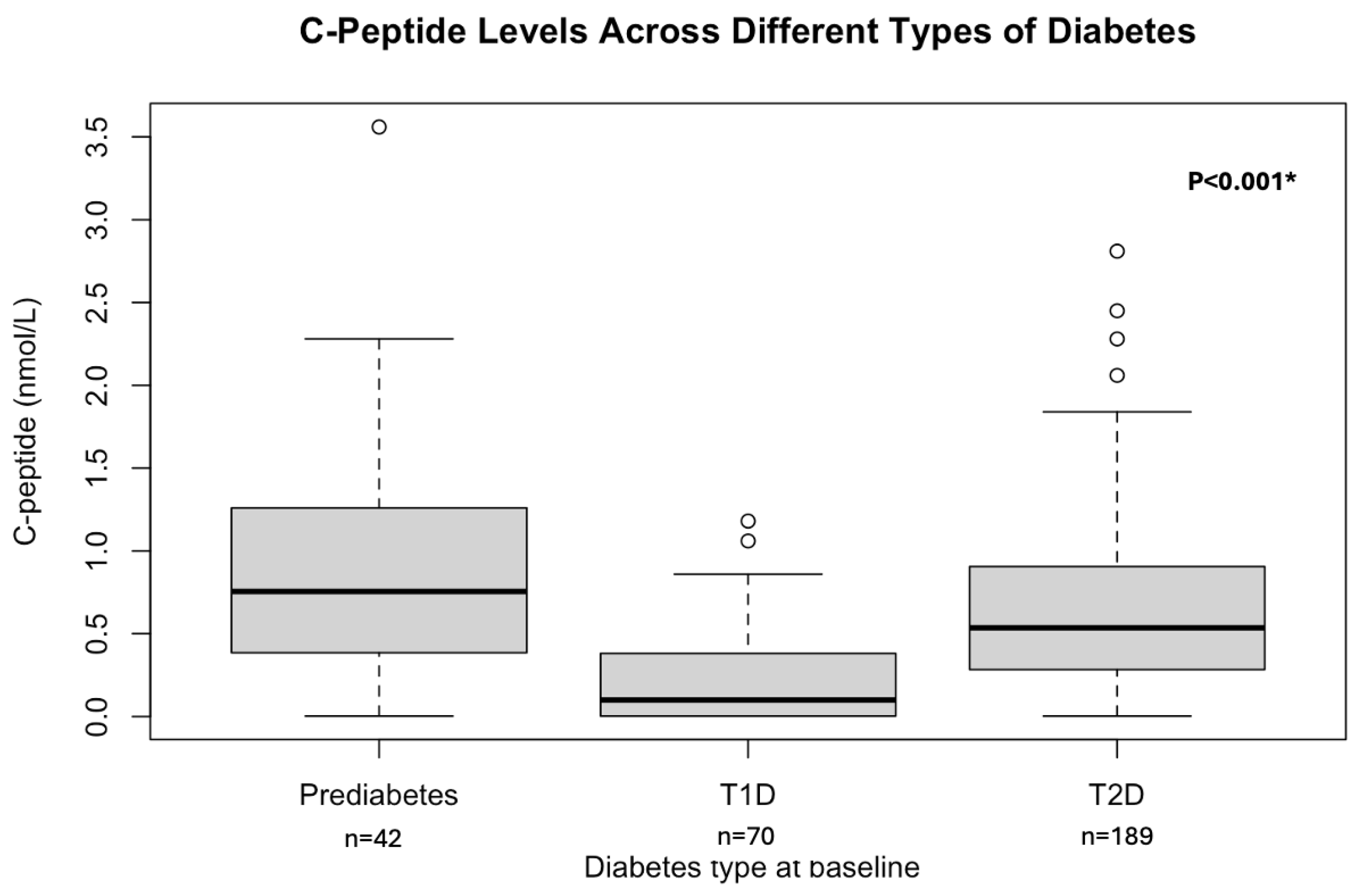
| C-peptide (fasting), nmol/L * | 0.76 (0.39–1.2) | 0.09 (0.003–0.38) | 0.54 (0.3–0.9) |
| Hba1C (%) * | 5.9 (5.7–6.2) | 10.2 (8.3–12.1) | 9.9 (8.3–11.9) |
| Plasma glucose (fasting), nmol/L * | 6.5 (5.5–7.6) | 12.8 (8.3–16.6) | 11.3 (7.8–16.1) |
| EQ-5D-5L | Mobility (%) | Self-Care (%) | Usual Activity (%) | Pain/Discomfort (%) | Anxiety/Depression (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No problem | 199 (66.1%) | 260 (86.4%) | 235 (78.1%) | 156 (51.5) | 151 (50.2%) |
| Slight problem | 79 (26.2%) | 33 (11%) | 41 (13.6%) | 98 (32.6%) | 99 (32.9%) |
| Moderate problem | 13 (4.3%) | 5 (1.7%) | 22 (7.3) | 37 (12.3%) | 42 (14%) |
| Severe problem | 6 (2%) | 2 (0.7%) | 2 (0.7%) | 8 (2.7%) | 7 (2.3) |
| Extreme problem | 4 (1.3%) | 1 (0.3%) | 1 (0.3%) | 2 (0.7%) | 2 (0.7%) |
| EQ VAS Score | |||||
| Mean | SD | Median | 25th percentile | 75th percentile | |
| EQ VAS Score | 0.801 | 0.128 | 0.85 | 0.70 | 0.90 |
| HRQoL | Prediabetes (n = 42) | T1D (n = 70) | T2D (n = 189) | All (n = 301) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mobility issues | 4 (9.5%) | 52 (74.3%) | 110 (58.2%) | 166 (55.1%) | <0.0001 ** |
| Self-care difficulties | 4 (9.5%) | 45 (64.3%) | 106 (56.1%) | 155 (51.5%) | <0.00001 ** |
| Disruptions in usual activities | 4 (9.5%) | 48 (68.6%) | 112 (59.3%) | 164 (54.5%) | <0.00001 ** |
| Pain/discomfort | 4 (9.5%) | 53 (75.7%) | 113 (59.8%) | 170 (56.5%) | <0.0004 ** |
| Anxiety/depression | 4 (9.5%) | 51 (72.9%) | 115 (60.6%) | 170 (56.5%) | <0.04 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iqbal, S.; Reverté-Villarroya, S.; Rizvi, N.B.; Butt, H.; Clúa-Espuny, J.L. Assessing Plasma C-Peptide Levels and Their Relationship with Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients with Prediabetes and Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2423. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102423
Iqbal S, Reverté-Villarroya S, Rizvi NB, Butt H, Clúa-Espuny JL. Assessing Plasma C-Peptide Levels and Their Relationship with Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients with Prediabetes and Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(10):2423. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102423
Chicago/Turabian StyleIqbal, Sajid, Silvia Reverté-Villarroya, Nayab Batool Rizvi, Hira Butt, and Josep Lluís Clúa-Espuny. 2025. "Assessing Plasma C-Peptide Levels and Their Relationship with Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients with Prediabetes and Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes" Biomedicines 13, no. 10: 2423. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102423
APA StyleIqbal, S., Reverté-Villarroya, S., Rizvi, N. B., Butt, H., & Clúa-Espuny, J. L. (2025). Assessing Plasma C-Peptide Levels and Their Relationship with Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients with Prediabetes and Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes. Biomedicines, 13(10), 2423. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102423