Spectrum of Pathogenic Variants of the ATP7B Gene and Genotype–Phenotype Correlation in Eastern Eurasian Patient Cohorts with Wilson’s Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Isolation of Genomic DNA
2.2.2. Polymerase Chain Reaction
2.2.3. Purification of PCR Fragments
2.2.4. Sanger DNA Sequencing
2.2.5. DNA Sequencing Data Analysis
2.2.6. Analysis of Patient Data on Symptoms of WD
3. Results
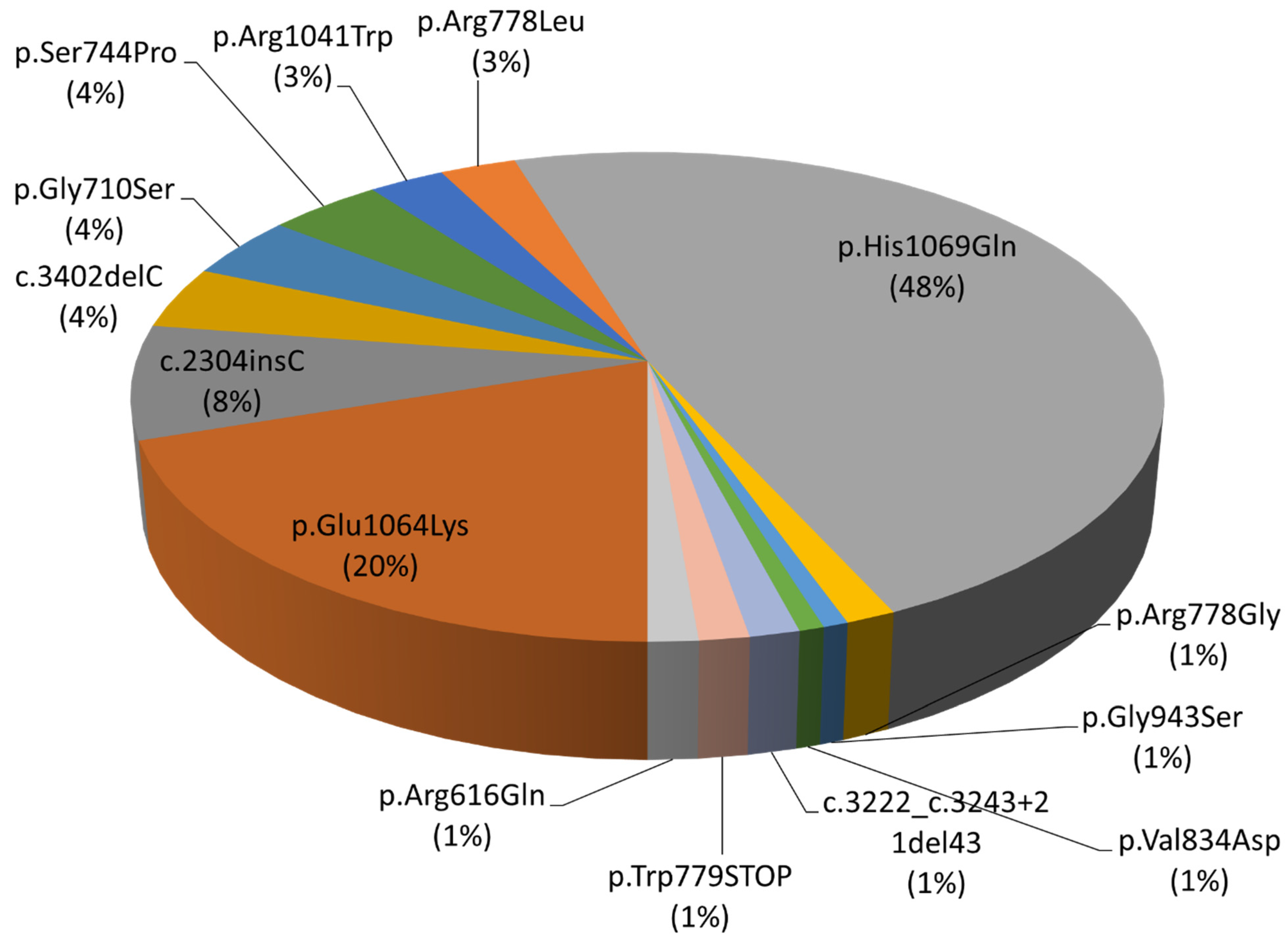
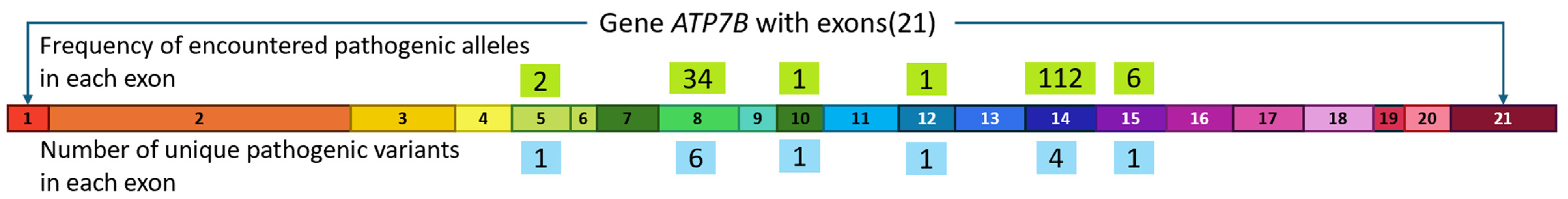
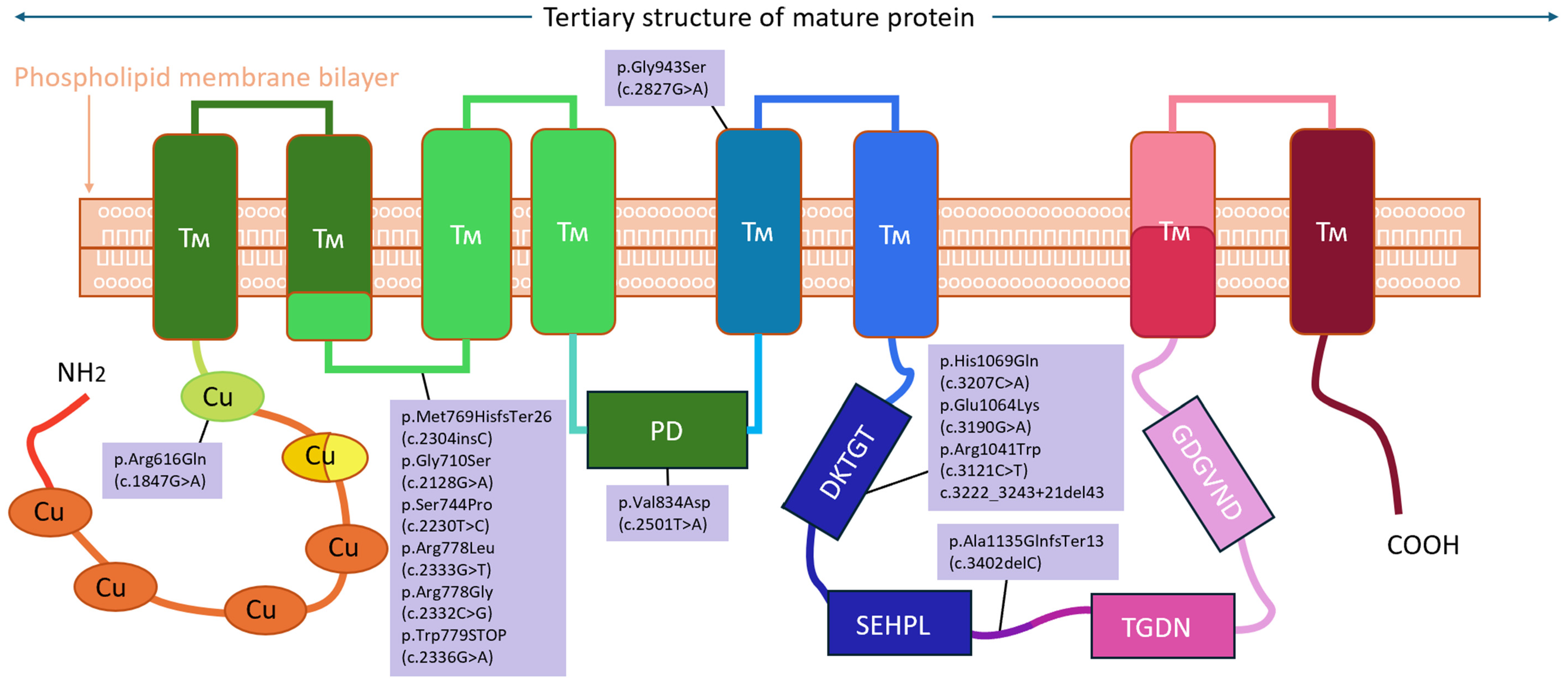
3.1. Spectrum of ATP7B Pathogenic Variants
3.2. General Characteristics of Patients with WD Taken for the Study of Genotype–Phenotype Correlation
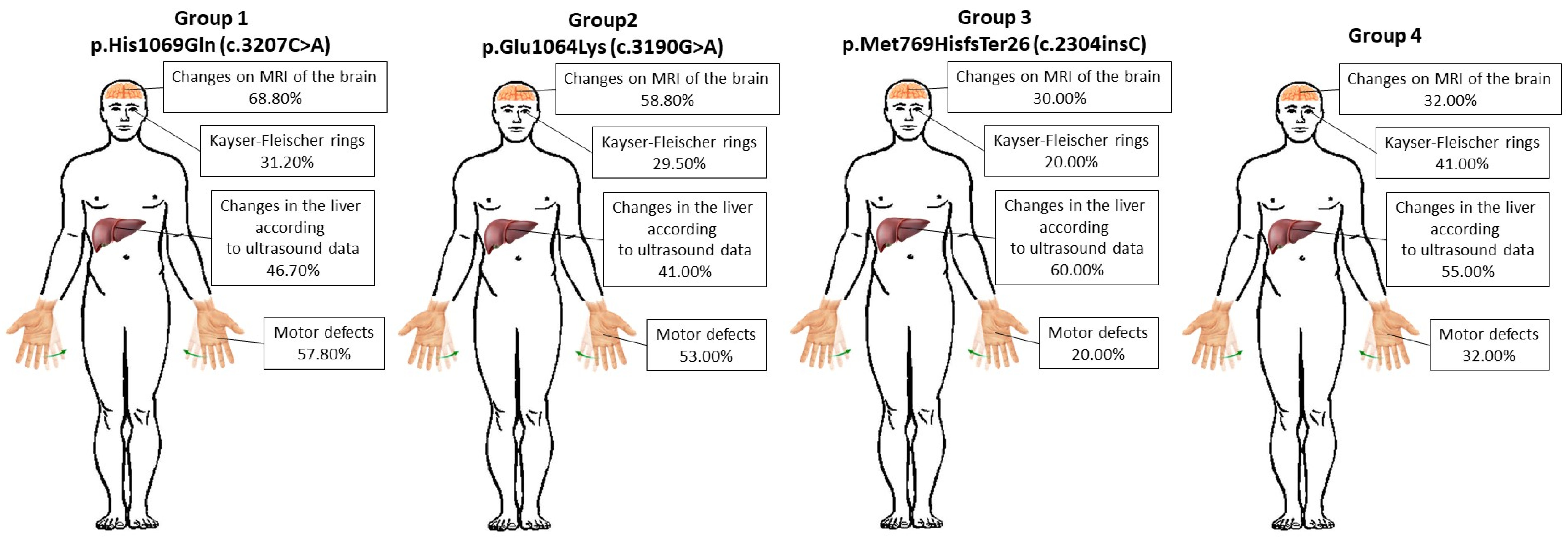
3.3. Establishment of Genotype–Phenotype Correlation in Patients with WD
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Asnov, A.Y.; Sokolov, A.A.; Volgina, S.A. Providing Medical Care and Drug Supply to Patients Suffering from Life-Threatening and Chronic Progressive Rare Diseases. Wilson’s Disease (Hepatolenticular Degeneration). Problems of Standardization in Healthcare 2015; no. 5–6, pp. 30–35. (In Russian). Available online: https://neurology.ru/book/federalnye-klinicheskie-rekomendacii-po.html (accessed on 3 November 2024).
- Bull, P.C.; Thomas, G.R.; Rommens, J.M.; Forbes, J.R.; Cox, D.W. The Wilson disease gene is a putative copper transporting P-type ATPase similar to the Menkes gene. Nat. Genet. 1993, 5, 327–337, Erratum in Nat. Genet. 1994, 6, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Compston, A. Progressive lenticular degeneration: A familial nervous disease associated with cirrhosis of the liver, by S. A. Kinnier Wilson, (From the National Hospital, and the Laboratory of the National Hospital, Queen Square, London) Brain 1912: 34; 295-509. Brain. 2009, 132 Pt 8, 1997–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalioti, V.; Tsubota, A.; Sandoval, I.V. Disorders in Hepatic Copper Secretion: Wilson’s Disease and Pleomorphic Syndromes. Semin. Liver Dis. 2017, 37, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for Study of Liver. EASL clinical practice guidelines: Wilson’s disease. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 671–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferenci, P.; Stremmel, W.; Członkowska, A.; Szalay, F.; Viveiros, A.; Stättermayer, A.F.; Bruha, R.; Houwen, R.; Pop, T.L.; Stauber, R.; et al. Age and Sex but Not ATP7B Genotype Effectively Influence the Clinical Phenotype of Wilson Disease. Hepatology 2019, 69, 1464–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferenci, P.; Członkowska, A.; Merle, U.; Ferenc, S.; Gromadzka, G.; Yurdaydin, C.; Vogel, W.; Bruha, R.; Schmidt, H.T.; Stremmel, W. Late-onset Wilson’s disease. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 1294–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korman, J.D.; Volenberg, I.; Balko, J.; Webster, J.; Schiodt, F.V.; Squires, R.H., Jr.; Fontana, R.J.; Lee, W.M.; Schilsky, M.L.; Pediatric and Adult Acute Liver Failure Study Groups. Screening for Wilson disease in acute liver failure: A comparison of currently available diagnostic tests. Hepatology 2008, 48, 1167–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Roberts, E.A.; Schilsky, M.L.; American Association for Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD). Diagnosis and treatment of Wilson disease: An update. Hepatology 2008, 47, 2089–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, A.; Nevitt, S.J.; Tuohy, O.; Cook, P. Biomarkers for diagnosis of Wilson’s disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 2019, CD012267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bost, M.; Piguet-Lacroix, G.; Parant, F.; Wilson, C.M. Molecular analysis of Wilson patients: Direct sequencing and MLPA analysis in the ATP7B gene and Atox1 and COMMD1 gene analysis. J.Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2012, 26, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayazutdinova, G.M.; Shchagina, O.A.; Karunas, A.S.; Vyalova, N.V.; Sokolov, A.A.; Polyakov, A.V. Spectrum of pathogenic variants in the ATP7B gene in Russian patients with Wilson–Konovalov disease. Genetics 2019, 55, 1433–1441. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffey, A.J.; Durkie, M.; Hague, S.; McLay, K.; Emmerson, J.; Lo, C.; Klaffke, S.; Joyce, C.J.; Dhawan, A.; Hadzic, N.; et al. A genetic study of Wilson’s disease in the United Kingdom. Brain. 2013, 136, 1476–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Collet, C.; Laplanche, J.L.; Page, J.; Morel, H.; Woimant, F.; Poujois, A. High genetic carrier frequency of Wilson’s disease in France: Discrepancies with clinical prevalence. BMC Med. Genet. 2018, 19, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedoussis, G.V.; Genschel, J.; Sialvera, T.E.; Bochow, B.; Manolaki, N.; Manios, Y.; Tsafantakis, E.; Schmidt, H. Wilson disease: High prevalence in a mountainous area of Crete. Ann. Hum. Genet. 2005, 69, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zappu, A.; Magli, O.; Lepori, M.B.; Dessi, V.; Diana, S.; Incollu, S.; Kanavakis, E.; Nicolaidou, P.; Manolaki, N.; Fretzayas, A.; et al. High incidence and allelic homogeneity of Wilson disease in 2 isolated populations: A prerequisite for efficient disease prevention programs. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2008, 47, 334–338. [Google Scholar]
- Cocos, R.; Sendroiu, A.; Schipor, S.; Bohiltea, L.C.; Sendroiu, I.; Raicu, F. Genotype-phenotype correlations in a mountain population community with high prevalence of Wilson’s disease: Genetic and clinical homogeneity. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, P.; Ala, A.; Askari, F.K.; Czlonkowska, A.; Hilgers, R.D.; Poujois, A.; Roberts, E.A.; Sandahl, T.D.; Weiss, K.H.; Ferenci, P.; et al. Designing Clinical Trials in Wilson’s Disease. Hepatology 2021, 74, 3460–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ohura, T.; Abukawa, D.; Shiraishi, H.; Yamaguchi, A.; Arashima, S.; Hiyamuta, S.; Tada, K.; Iinuma, K. Pilot study of screening for Wilson disease using dried blood spots obtained from children seen at outpatient clinics. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 1999, 22, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, S.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Jang, Y.J.; Kim, S.N.; Shin, H.C.; Park, S.Y.; Han, H.S.; Yu, E.S.; Yoo, H.W.; Lee, J.S.; et al. Pilot study of mass screening for Wilson’s disease in Korea. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2002, 76, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beinhardt, S.; Leiss, W.; Stattermayer, A.F.; Graziadei, I.; Zoller, H.; Stauber, R.; Maieron, A.; Datz, C.; Steindl-Munda, P.; Hofer, H.; et al. Long-term outcomes of patients with Wilson disease in a large Austrian cohort. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 12, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poujois, A.; Woimant, F. Wilson’s disease: A 2017 update. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2018, 42, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, K.S.; Seto, W.K.; Fung, J.; Mak, L.Y.; Lai, C.L.; Yuen, M.F. Epidemiology and natural history of Wilson’s disease in the Chinese: A territory-based study in Hong Kong between 2000 and 2016. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 7716–7726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, C.S.; Wu, J.F.; Chen, H.L.; Hsu, H.Y.; Chang, M.H.; Ni, Y.H. Modality of treatment and potential outcome of Wilson disease in Taiwan: A population-based longitudinal study. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2018, 117, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, C.; Waldenstrom, E.; Westermark, K.; Landegre, U.; Syvanen, A.C. Determination of the frequencies of ten allelic variants of the Wilson disease gene (ATP7B), in pooled DNA samples. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2000, 8, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenney, S.M.; Cox, D.W. Sequence variation database for the Wilson disease copper transporter, ATP7B. Hum. Mutat. 2007, 28, 1171–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, G.R.; Roberts, E.A.; Walshe, J.M.; Cox, D.W. Haplotypes and mutations in Wilson disease. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1995, 56, 1315–1319. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Margarit, E.; Bach, V.; Gómez, D.; Bruguera, M.; Jara, P.; Queralt, R.; Ballesta, F. Pathogenic variant analysis of Wilson disease in the Spanish population—Identification of a prevalent substitution and eight novel pathogenic variants in the ATP7B gene. Clin. Genet. 2005, 68, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loudianos, G.; Dessi, V.; Lovicu, M.; Angius, A.; Nurchi, A.; Sturniolo, G.C.; Marcellini, M.; Zancan, L.; Bragetti, P.; Akar, N.; et al. Further delineation of the molecular pathology of Wilson disease in the Mediterranean population. Hum. Mutat. 1998, 12, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.; Dedoussis, G.V. Geographic distribution of ATP7B pathogenic variants in Wilson disease. Ann. Hum. Biol. 2016, 43, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Dmitriev, O.Y.; Nokhrin, S.; Braiterman, L.; Hubbard, A.L.; Lutsenko, S. Cellular copper levels determine the phenotype of the Arg875 variant of ATP7B/Wilson disease protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 5390–5395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Santhosh, S.; Shaji, R.V.; Eapen, C.E.; Jayanthi, V.; Malathi, S.; Chandy, M.; Stanley, M.; Selvi, S.; Kurian, G.; Chandy, G.M. ATP7B mutations in families in a predominantly southern Indian cohort of Wilson’s disease patients. Ind. J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 25, 277–282. [Google Scholar]
- Al Jumah, M.; Majumdar, R.; Al Rajeh, S.; Awada, A.; Al Zaben, A.; Al Traif, I.; Al Jumah, A.R.; Rehana, Z. A clinical and genetic study of 56 Saudi Wilson disease patients: Identification of Saudi-specific mutations. Eur. J. Neurol. 2004, 11, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firneisz, G.; Szonyi, L.; Ferenci, P.; Willheim, C.; Horvath, A.; Folhoffer, A.; Tulassay, Z.; Szalay, F. The other pathogenic variant is found: Follow-up of an exceptional family with Wilson disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 99, 2504–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simsek Papur, O.; Akman, S.A.; Cakmur, R.; Terzioglu, O. Mutation analysis of ATP7B gene in Turkish Wilson disease patients: Identification of five novel mutations. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2013, 56, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moller, L.B.; Ott, P.; Lund, C.; Horn, N. Homozygosity for a gross partial gene deletion of the C-terminal end of ATP7B in a Wilson patient with hepatic and no neurological manifestations. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2005, 138, 340–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stapelbroek, J.M.; Bollen, C.W.; van Amstel, J.K.; van Erpecum, K.J.; van Hattum, J.; van den Berg, L.H.; Klomp, L.W.; Houwen, R.H. The HIS1069GLN pathogenic variant in ATP7B is associated with late and neurologic presentation in Wilson disease: Results of a meta-analysis. J. Hepatol. 2004, 41, 758–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panagiotakaki, E.; Tzetis, M.; Manolaki, N.; Loudianos, G.; Papatheodorou, A.; Manesis, E.; Nousia-Arvanitakis, S.; Syriopoulou, V.; Kanavakis, E. Genotype-phenotype correlations for a wide spectrum of pathogenic variants in the Wilson disease gene (ATP7B). Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2004, 131, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.B.; Chernov, I.; Zhang, H.T.; Ross, B.M.; Das, K.; Lutsenko, S.; Parano, E.; Pavone, L.; Evgrafov, O.; Ivanova-Smolenskaya, I.A.; et al. Identification and analysis of mutations in the Wilson disease gene (ATP7B): Population frequencies, genotype-phenotype correlation, and functional analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1997, 61, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacob, R.; Iacob, S.; Nastase, A.; Vagu, C.; Ene, A.M.; Constantinescu, A.; Anghel, D.; Banica, C.; Paslaru, L.; Coriu, D.; et al. The His1069Gln mutation in the ATP7B gene in Romanian patients with Wilson’s disease referred to a tertiary gastroenterology center. J. Gastrointest. Liver Dis. 2012, 21, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Caca, K.; Ferenci, P.; Kühn, H.J.; Polli, C.; Willgerodt, H.; Kunath, B.; Hermann, W.; Mössner, J.; Berr, F. High. prevalence of the H1069Q mutation in East German patients with Wilson disease: Rapid detection of mutations by limited sequencing and phenotype-genotype analysis. J. Hepatol. 2001, 35, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loudianos, G.; Kostic, V.; Solinas, P.; Lovicu, M.; Dessì, V.; Svetel, M.; Major, T.; Cao, A. Characterization of the molecular defect in the ATP7B gene in Wilson disease patients from Yugoslavia. Genet. Test. 2003, 7, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrabelova, S.; Letocha, O.; Borsky, M.; Kozak, L. Mutation analysis of the ATP7B gene and genotype/phenotype correlation in 227 patients with Wilson disease. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2005, 86, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todorov, T.; Savov, A.; Jelev, H.; Panteleeva, E.; Konstantinova, D.; Krustev, Z.; Mihaylova, V.; Tournev, I.; Tankova, L.; Tzolova, N.; et al. Spectrum of mutations in the Wilson disease gene (ATP7B) in the Bulgarian population. Clin. Genet. 2005, 68, 474–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gromadzka, G.; Schmidt, H.H.; Genschel, J.; Bochow, B.; Rodo, M.; Tarnacka, B.; Litwin, T.; Chabik, G.; Członkowska, A. Frameshift and nonsense pathogenic variants in the gene for ATPase7B are associated with severe impairment of copper metabolism and with an early clinical manifestation of Wilson’s disease. Clin. Genet. 2005, 68, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zali, N.; Mohebbi, S.R.; Esteghamat, S.; Chiani, M.; Haghighi, M.M.; Hosseini-Asl, S.M.; Derakhshan, F.; Mohammad-Alizadeh, A.H.; Malek-Hosseini, S.A.; Zali, M.R. Prevalence of ATP7B Gene Pathogenic variants in Iranian Patients With Wilson Disease. Hepat. Mon. 2011, 11, 890–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Abdel Ghaffar, T.Y.; Elsayed, S.M.; Elnaghy, S.; Shadeed, A.; Elsobky, E.S.; Schmidt, H. Phenotypic and genetic characterization of a cohort of pediatric Wilson disease patients. BMC Pediatr. 2011, 11, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garbuz, M.M.; Ovchinnikova, A.A.; Kumeiko, V.V. Design, Optimization and Validation of the ARMS PCR Protocol for the Rapid Diagnosis of Wilson’s Disease Using a Panel of 14 Common Pathogenic variants for the European Population. Genes 2022, 13, 1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, N.; Fujiwara, J.; Ohnishi, S.; Sato, M.; Kodama, H.; Kohsaka, T.; Inui, A.; Fujisawa, T.; Tamai, H.; Ida, S.; et al. Effects of long-term zinc treatment in Japanese patients with Wilson disease: Efficacy, stability, and copper metabolism. Transl. Res. 2010, 156, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, N.; Tsivkovskii, R.; Tsivkovskaia, N.; Lutsenko, S. The copper-transporting ATPases, menkes and wilson disease proteins, have distinct roles in adult and developing cerebellum. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 9640–9645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dusek, P.; Roos, P.M.; Litwin, T.; Schneider, S.A.; Flaten, T.P.; Aaseth, J. The neurotoxicity of iron, copper and manganese in Parkinson’s and Wilson’s diseases. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2015, 31, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asanov, A.Y.; Sokolov, A.A.; Volgina, S.Y. Federal Clinical Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Wilson-Konovalov Disease (Hepatolenticular Degeneration). Ministry of Health of Russia. 2013. 71p. (In Russian). Available online: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/okazanie-meditsinskoy-pomoschi-i-lekarstvennoe-obespecheniya-patsientov-stradayuschih-zhizneugrozhayuschimi-i-hronicheskimi (accessed on 2 November 2024).
- Członkowska, A.; Litwin, T.; Chabik, G. Wilson disease: Neurologic features. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2017, 142, 101–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woimant, F.; Poujois, A.; Bloch, A.; Jordi, T.; Laplanche, J.L.; Morel, H.; Collet, C. A novel deep intronic variant in ATP7B in five unrelated families affected by Wilson disease. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2020, 8, e1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pop, T.L.; Grama, A.; Stefanescu, A.C.; Willheim, C.; Ferenci, P. Acute liver failure with hemolytic anemia in children with Wilson’s disease: Genotype-phenotype correlations? World J. Hepatol. 2021, 13, 1428–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cooper, D.N.; Ball, E.V.; Stenson, P.D.; Phillips, A.D.; Evans, K.; Heywood, S.; Hayden, M.J.; Chapman, M.M.; Mort, M.E.; Azevedo, L.; et al. The Human Gene Mutation Database. Qiagen. Available online: http://www.hgmd.cf.ac.uk/ac/index.php (accessed on 22 April 2021).
- Manolaki, N.; Nikolopoulou, G.; Daikos, G.L.; Panagiotakaki, E.; Tzetis, M.; Roma, E.; Kanavakis, E.; Syriopoulou, V.P. Wilson disease in children: Analysis of 57 cases. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2009, 48, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couchonnal, E.; Bouchard, S.; Sandahl, T.D.; Pagan, C.; Lion-François, L.; Guillaud, O.; Habes, D.; Debray, D.; Lamireau, T.; Broué, P.; et al. ATP7B variant spectrum in a French pediatric Wilson disease cohort. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2021, 64, 104305, Erratum in Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2021, 64, 104341. Erratum in Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2022, 65, 104453.. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merle, U.; Weiss, K.H.; Eisenbach, C.; Tuma, S.; Ferenci, P.; Stremmel, W. Truncating mutations in the Wilson disease gene ATP7B are associated with very low serum ceruloplasmin oxidase activity and an early onset of Wilson disease. BMC Gastroenterol. 2010, 10, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lee, B.H.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Jin, H.Y.; Kim, K.J.; Lee, J.J.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, G.H.; Choi, J.H.; Kim, K.M.; et al. Distinct clinical courses according to presenting phenotypes and their correlations to ATP7B mutations in a large Wilson’s disease cohort. Liver Int. 2011, 31, 831–839, Erratum in Liver Int. 2011, 31, 1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, W.; Li, X.; Pei, P.; Dong, T.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J. Clinical and genetic characterization of a large cohort of patients with Wilson’s disease in China. Transl. Neurodegener. 2022, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]

| Exon | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| 2A | CATTGTTTTCCATTTTCTCAGTG | CCGATGGCACATATTTCACAG |
| 2B | CTTGCCAGTCATGTGTGAAGT | CAGAAGATAAAGGTCTCTTTGG |
| 2C | GATATTGAGCGGTTACAAAGCA | ACTCCCTTCGGCTCCATC |
| 2D | GACCCTTCTTGTACCAGCC | CTCACCTATACCACCATCC |
| 3 | GACAATGAACCCTCACCAAG | GAATACGAGGTCTATACGCAG |
| 4 | CCACCCAGAGTGTTACAGC | CTAATCACAAAGATGGATGTGTC |
| 5 | CTGCCTGTTACCTAGACTC | CATCTTTCTCTTACCCATTCAC |
| 6 | CCCACAAAGTCTACTGAGG | GCTAATCCAGGAGGAAGGC |
| 7 | CTTAAACTGTGTCCTCAGAAG | GGAAGGGAGAGGTCTGC |
| 8 | GCCCATCACAGAGGAAGAA | GAGATTTGTTTACTGAAGGAGC |
| 9 | GGTGGATAGCAAGTAACGC | GAGAGTGGTGATCTTACTGTG |
| 10 + 11 | GCAAATACAGTGTAACTATTGTAAC | CCCAGAACTCTTCACATAATTTC |
| 12 | CCAATCTTTATCCATGCTTGTG | GTGACTGTTTATCCTACTCTG |
| 13 | CCTTATTGAACTCTCAACCTG | CTCTGTTGCTACTGTTGTTATTC |
| 14 | CTGAGATTGAACGACAGAGG | GTGAGGAATAAAAGAGCATTGG |
| 15 | CGCTTTCCGCTGCTCTC | CAGAGGCAATCACTGCTGG |
| 16 | CACAAGAGGTGCTTACAAGG | CTGAAATTAAGAGAGGAAGGC |
| 17 | CACTCGTAATCCTATTCCTTG | GGAGTACAGCTCAGTGCTG |
| 18 + 19 | GCTGCTATCTGATACCTTTTG | CTGGGAGACAGAAGCCTTT |
| 20 | GAACATCAGGGCGAGTGG | GAATGGGAAATGAGAGGCAAG |
| 21A | GAATGGCTCAGATGCTGTTG | GCAGGATGACTGGACATATC |
| 21B | CAGGGATGAGGAGCAGTAC | GCAGGGTTGCGAGGGG |
| 21C | GTACATAGTCTGTTCCTTTTCTC | CACGAGGTGACAGTCAGAA |
| 21D | CATGGGAAACGTATGTGTGC | GGTTGGTTGGGAGGATTAGA |
| 21E | GGATTAAATTCTGGGTGAAACC | GGCTGAAAACAAGGAAAACACA |
| 21F | CCTTCACCTTGGATGGTTAG | CTGACCACGCATCTCACTC |
| Exon | Protein Domain | Position in cDNA | Position in Protein | Pathogenic Variant Effect | Number of Alleles |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | Transmembrane | c.1847G>A | p.Arg616Gln | Loss of function | 2 (1%) |
| 8 | Transmembrane | c.2304insC | p.Met769HisfsTer26 | Frame shift | 11 (8%) |
| c.2128G>A | p.Gly710Ser | Loss of function | 6 (4%) | ||
| c.2230T>C | p.Ser744Pro | Loss of function | 6 (4%) | ||
| c.2333G>T | p.Arg778Leu | Loss of function | 4 (3%) | ||
| c.2332C>G | p.Arg778Gly | Loss of function | 2 (1%) | ||
| c.2336G>A | p.Trp779STOP | Stop codon formation | 2 (1%) | ||
| 10 | Transmembrane | c.2501T>A | p.Val834Asp | Loss of function | 1 (1%) |
| 12 | Transmembrane | c.2827G>A | p.Gly943Ser | Loss of function | 1 (1%) |
| 14 | ATP-binding | c.3207C>A | p.His1069Gln | Loss of function | 70 (48%) |
| c.3190G>A | p.Glu1064Lys | Loss of function | 29 (20%) | ||
| c.3121C>T | p.Arg1041Trp | Loss of function | 4 (3%) | ||
| c.3222_3243+21del43 | - | Protein maturation disorder | 2 (1%) | ||
| 15 | ATP-binding | c.3402delC | p.Ala1135GlnfsTer13 | Frame shift | 6 (4%) |
| Total number of patients analyzed | 100 | |
| Patient gender | Male | 52 (52%) |
| Female | 48 (48%) | |
| Average age of patients at the time of visiting a doctor | 24.5 years | |
| Average age of onset of WD | 19.6 years | |
| Average length of observation with a doctor | 8.9 years | |
| Patient’s region of origin | Descendants of immigrants from regions bordering Eastern Europe, Ukraine, Belarus, Poland—65% Descendants of immigrants from central Russia and Siberia—29% Asian patients—4% Immigrants from Azerbaijan—2% | |
| Indicators | p.His1069Gln (c.3207C>A) | p.Glu1064Lys (c.3190G>A) | p.Met769HisfsTer26 (c.2304insC) | 4th Group | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient gender | Male | 48.89% | 52.94% | 30% | 68.18% |
| Female | 51.11% | 47.06% | 70% | 31.82% | |
| Average age of patients at the time of the study | 17.6 | 19.3 | 26.2 | 34.7 | |
| Region of residence | Primorsky Territory—62.2%; Khabarovsk Territory—22.2%; Kamchatka—8.9%; Sakhalin—6.7%. | Primorsky Territory—52.9%; Khabarovsk Territory—29.4%; Kamchatka—5.9%; Sakhalin—11.8%. | Primorsky Territory—20%; Khabarovsk Territory—0%; Kamchatka—50%; Sakhalin—30%. | Primorsky Territory—36.4%; Khabarovsk Territory—31.8%; Kamchatka—13.6%; Sakhalin—18.2%. | |
| Symptoms | p.His1069Gln (c.3207C>A) | p.Glu1064Lys (c.3190G>A) | p.Met769HisfsTer26 (c.2304insC) | 4th Group | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age of disease onset ± SD (p = 0.86) | First 10 years | 40.00 ± 4.36% | 35.00 ± 1.53% | 30.00 ± 1.53% | 32.00 ± 0.58% |
| 10–20 years | 37.80 ± 4.36% | 41.00 ± 1.53% | 50.00 ± 1.53% | 32.00% ± 0.58% | |
| After 20 years | 22.20 ± 4.36% | 24.00 ± 1.53% | 20.00 ± 1.53% | 36.00% ± 0.58% | |
| Primary symptoms ± SD (p = 0.09) | Paroxysmal conditions | 35.50 ± 1.53% | 41.00 ± 4.16% | 50.00 ± 1.53% | 59.00 ± 5.51% |
| Motor defects | 57.80 ± 1.53% | 53.00 ± 4.16% | 20.00 ± 1.53% | 32.00 ± 5.51% | |
| Other symptoms | 6.70 ± 1.53% | 6.00 ± 4.16% | 30.00 ± 1.53% | 9.00 ± 5.51% | |
| Changes on MRI of the brain ± SD (p = 0.59) | 68.80 ± 12.23% | 58.80 ± 12.23% | 30.00 ± 12.23% | 32.00 ± 12.23% | |
| Changes in the liver according to ultrasound data ± SD (p = 0.59) | 46.70 ± 7.09% | 41.00 ± 7.09% | 60.00 ± 7.09% | 55.00 ± 7.09% | |
| Kayser–Fleischer rings ± SD (p = 0.59) | 31.20 ± 5.48% | 29.50 ± 5.48% | 20.00 ± 5.48% | 41.00 ± 5.48% | |
| Severe impairment of mental, intellectual, and cognitive functions ± SD (p = 0.59) | 26.60 ± 4.72% | 23.80 ± 4.72% | 2.00 ± 4.72% | 14.00 ± 4.72% | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garbuz, M.; Ovchinnikova, E.; Ovchinnikova, A.; Vinokurova, V.; Aristarkhova, Y.; Kuziakova, O.; Mashurova, M.; Kumeiko, V. Spectrum of Pathogenic Variants of the ATP7B Gene and Genotype–Phenotype Correlation in Eastern Eurasian Patient Cohorts with Wilson’s Disease. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2833. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122833
Garbuz M, Ovchinnikova E, Ovchinnikova A, Vinokurova V, Aristarkhova Y, Kuziakova O, Mashurova M, Kumeiko V. Spectrum of Pathogenic Variants of the ATP7B Gene and Genotype–Phenotype Correlation in Eastern Eurasian Patient Cohorts with Wilson’s Disease. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(12):2833. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122833
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarbuz, Mikhail, Elena Ovchinnikova, Anna Ovchinnikova, Valeriya Vinokurova, Yulya Aristarkhova, Olga Kuziakova, Mariya Mashurova, and Vadim Kumeiko. 2024. "Spectrum of Pathogenic Variants of the ATP7B Gene and Genotype–Phenotype Correlation in Eastern Eurasian Patient Cohorts with Wilson’s Disease" Biomedicines 12, no. 12: 2833. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122833
APA StyleGarbuz, M., Ovchinnikova, E., Ovchinnikova, A., Vinokurova, V., Aristarkhova, Y., Kuziakova, O., Mashurova, M., & Kumeiko, V. (2024). Spectrum of Pathogenic Variants of the ATP7B Gene and Genotype–Phenotype Correlation in Eastern Eurasian Patient Cohorts with Wilson’s Disease. Biomedicines, 12(12), 2833. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122833





