Beneficial Actions of 4-Methylumbelliferone in Type 1 Diabetes by Promoting β Cell Renewal and Inhibiting Dedifferentiation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
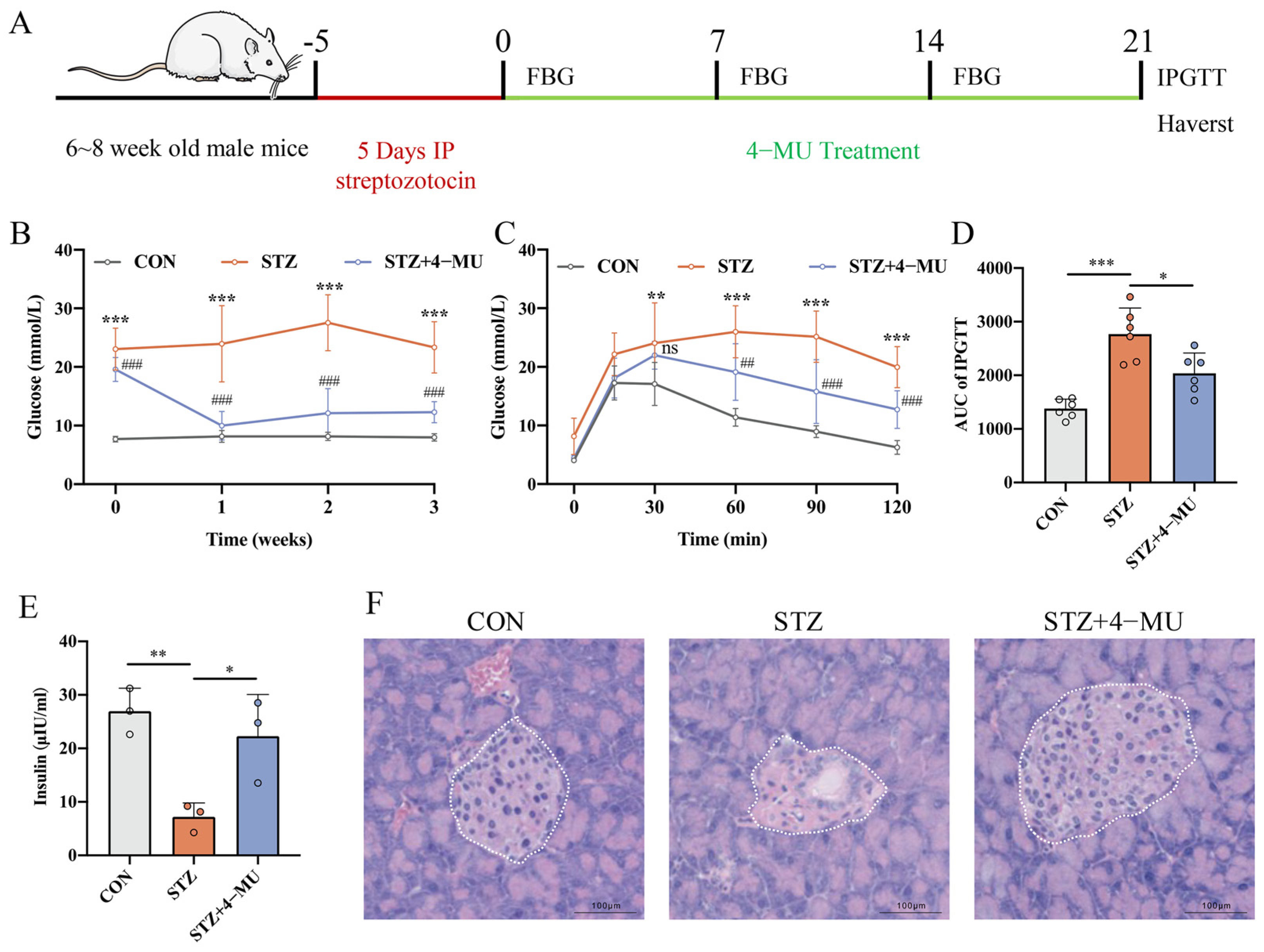
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Measurement of Blood Glucose Levels
2.4. Intraperitoneal Glucose Tolerance Test (IPGTT)
2.5. Histological Examination
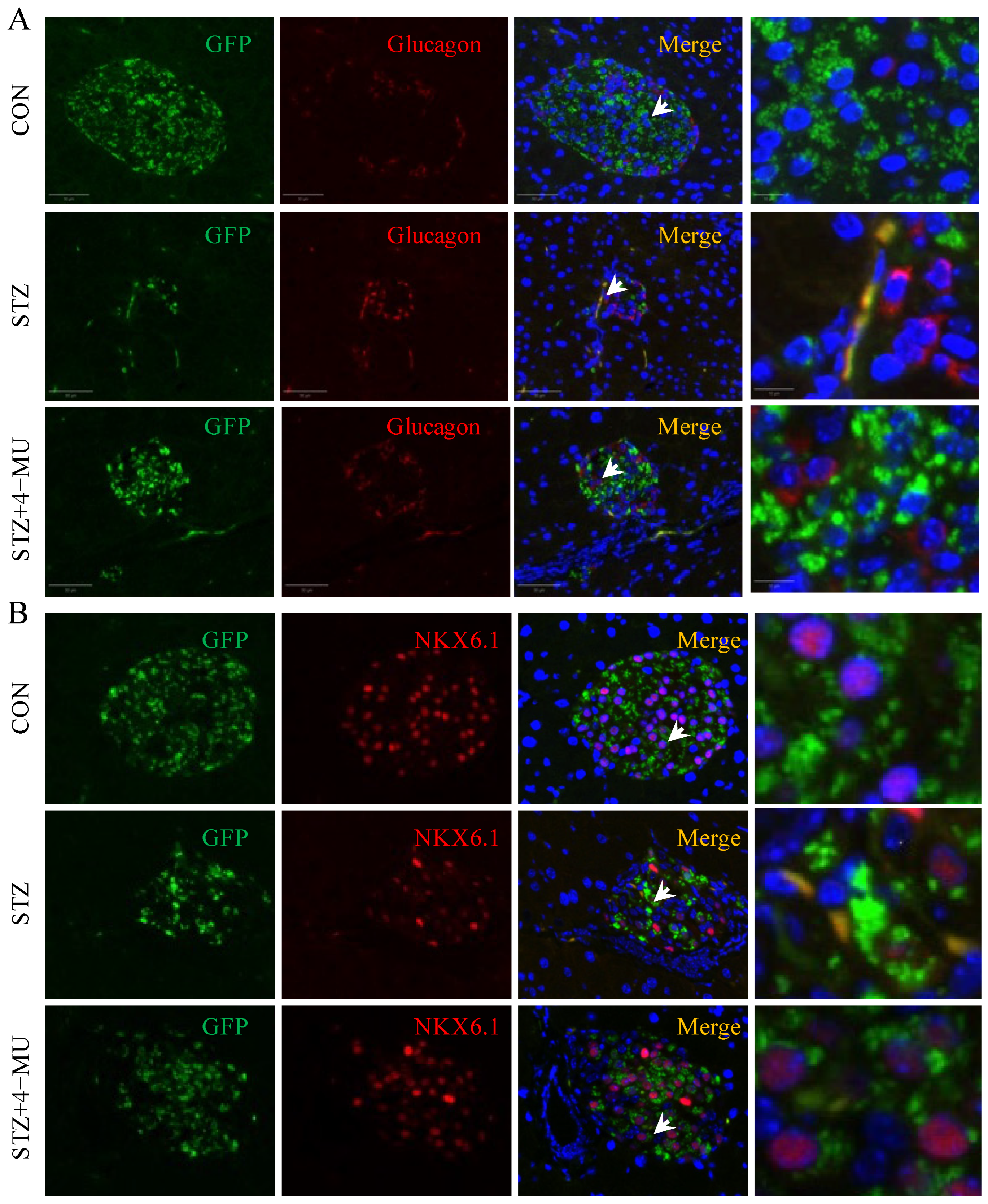
2.6. Immunofluorescent Staining and Quantification
2.7. Isolation and Culture of Primary Pancreatic Islets
2.8. Treatment of Islets with STZ and 4-MU
2.9. Islet Viability Assessment In Vitro
2.10. Insulin Secretion Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.11. RNA Isolation, Reverse Transcription, and Quantitative PCR
- NKX6.1 Sense: ATCTTCTGGCCCGGAGTG;
- NKX6.1 Anti Sense: TCTCTCTGGTCCTGCCAAG;
- PDX1 Sense: GACCTTTCCCGAATGGAACC;
- PDX1 Anti Sense: GTTCCGCTGTGTAAGCACC;
- β-actin Sense: TGCGTGACATCAAAGAGAAG;
- β-actin Anti Sense: GATGCCACAGGATTCCATA.
3. Results
3.1. 4-MU Regulated Blood Glucose Levels and Improved Diabetic Symptoms
3.2. 4-MU Increases β Cells Number, and Decreases α Cell Number in STZ-Induced T1D Mice
3.3. 4-MU Alleviates Inflammation and Promotes β Cell Renewal in STZ-Induced T1D Mice
3.4. 4-MU Inhibited β Cell Dedifferentiation
3.5. 4-MU Can Protect Islets from STZ-Induced Damage, Inhibit β Cell Dedifferentiation and Enhance Islet Insulin Secretion In Vitro
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lam, C.J.; Chatterjee, A.; Shen, E.; Cox, A.R.; Kushner, J.A. Low-Level Insulin Content Within Abundant Non-beta Islet Endocrine Cells in Long-standing Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes 2019, 68, 598–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Redondo, P.; Izpisua Belmonte, J.C. Tailored chromatin modulation to promote tissue regeneration. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 97, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Buffonge, S.; Ramnath, R.; Jenner, S.; Fawaz, S.; Arkill, K.P.; Neal, C.; Verkade, P.; White, S.J.; Hezzell, M.; et al. Endothelial glycocalyx is damaged in diabetic cardiomyopathy: Angiopoietin 1 restores glycocalyx and improves diastolic function in mice. Diabetologia 2022, 65, 879–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; He, X.; Cai, P.; Li, T.; Peng, R.; Dang, J.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Huang, F.; Shi, G.; et al. Induced regulatory T cells suppress Tc1 cells through TGF-β signaling to ameliorate STZ-induced type 1 diabetes mellitus. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 698–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaszewska, E.; Dobrowolski, P.; Muszynski, S.; Donaldson, J.; Golynski, M.; Zwolska, J.; Szadkowski, M.; Oseka, M.; Mielnik-Blaszczak, M.; Balicki, I. Longitudinal Analysis of Bone Metabolic Markers and Bone Mechanical Properties in STZ-Induced Diabetic Rats. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kataoka, M.; Kawamuro, Y.; Shiraki, N.; Miki, R.; Sakano, D.; Yoshida, T.; Yasukawa, T.; Kume, K.; Kume, S. Recovery from diabetes in neonatal mice after a low-dose streptozotocin treatment. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 430, 1103–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rankin, M.M.; Kushner, J.A. Adaptive beta-cell proliferation is severely restricted with advanced age. Diabetes 2009, 58, 1365–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Qian, Y.; Jiang, H.; He, Y.; Dai, H.; Chen, Y.; Xia, Z.; Liang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, R.; et al. Genetic lineage tracing identifies adaptive mechanisms of pancreatic islet beta cells in various mouse models of diabetes with distinct age of initiation. Sci. China Life Sci. 2024, 67, 504–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, N.; de la Zerda, A.; Kaber, G.; Johnson, P.Y.; Hu, K.H.; Kratochvil, M.J.; Yadava, K.; Zhao, W.; Cui, Y.; Navarro, G.; et al. Hyaluronan content governs tissue stiffness in pancreatic islet inflammation. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, N.; Kaber, G.; Johnson, P.Y.; Gebe, J.A.; Preisinger, A.; Falk, B.A.; Sunkari, V.G.; Gooden, M.D.; Vernon, R.B.; Bogdani, M.; et al. Inhibition of hyaluronan synthesis restores immune tolerance during autoimmune insulitis. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 3928–3940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, A.C. Type 1 diabetes mellitus: Much progress, many opportunities. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e142242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, E.L.; Dayan, C.M.; Chatenoud, L.; Sumnik, Z.; Simmons, K.M.; Szypowska, A.; Gitelman, S.E.; Knecht, L.A.; Niemoeller, E.; Tian, W.; et al. Teplizumab and beta-Cell Function in Newly Diagnosed Type 1 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 2151–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warshauer, J.T.; Bluestone, J.A.; Anderson, M.S. New Frontiers in the Treatment of Type 1 Diabetes. Cell Metab. 2020, 31, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuipers, H.F.; Rieck, M.; Gurevich, I.; Nagy, N.; Butte, M.J.; Negrin, R.S.; Wight, T.N.; Steinman, L.; Bollyky, P.L. Hyaluronan synthesis is necessary for autoreactive T-cell trafficking, activation, and Th1 polarization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 1339–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreichenko, I.N.; Tsitrina, A.A.; Fokin, A.V.; Gabdulkhakova, A.I.; Maltsev, D.I.; Perelman, G.S.; Bulgakova, E.V.; Kulikov, A.M.; Mikaelyan, A.S.; Kotelevtsev, Y.V. 4-methylumbelliferone Prevents Liver Fibrosis by Affecting Hyaluronan Deposition, FSTL1 Expression and Cell Localization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsitrina, A.A.; Halimani, N.; Andreichenko, I.N.; Sabirov, M.; Nesterchuk, M.; Dashenkova, N.O.; Romanov, R.; Bulgakova, E.V.; Mikaelyan, A.; Kotelevtsev, Y. 4-Methylumbelliferone Targets Revealed by Public Data Analysis and Liver Transcriptome Sequencing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pibuel, M.A.; Poodts, D.; Sias, S.A.; Byrne, A.; Hajos, S.E.; Franco, P.G.; Lompardia, S.L. 4-Methylumbelliferone enhances the effects of chemotherapy on both temozolomide-sensitive and resistant glioblastoma cells. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 9356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, N.; Kuipers, H.F.; Frymoyer, A.R.; Ishak, H.D.; Bollyky, J.B.; Wight, T.N.; Bollyky, P.L. 4-methylumbelliferone treatment and hyaluronan inhibition as a therapeutic strategy in inflammation, autoimmunity, and cancer. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandoch, M.; Flogel, U.; Virtue, S.; Maier, J.K.; Jelenik, T.; Kohlmorgen, C.; Feldmann, K.; Ostendorf, Y.; Castaneda, T.R.; Zhou, Z.; et al. 4-Methylumbelliferone improves the thermogenic capacity of brown adipose tissue. Nat. Metab. 2019, 1, 546–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, M.; Kinoshita, Y.; Satoh, I.; Shinbori, C.; Suzuki, H.; Yamada, M.; Watanabe, T.; Satoh, K. Ability of cyclohexenonic long-chain fatty alcohol to reverse diabetes-induced cystopathy in the rat. Eur. Urol. 2007, 51, 479–487; discussion 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunachalam, K.; Parimelazhagan, T. Antidiabetic activity of Ficus amplissima Smith. bark extract in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 147, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Z.; Cao, Y.; Wen, Q.; Zhang, H.; Fang, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Xi, Y.; Luo, Z.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Dapagliflozin ameliorates diabetes-induced spermatogenic dysfunction by modulating the adenosine metabolism along the gut microbiota-testis axis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, N.; Kaber, G.; Sunkari, V.G.; Marshall, P.L.; Hargil, A.; Kuipers, H.F.; Ishak, H.D.; Bogdani, M.; Hull, R.L.; Grandoch, M.; et al. Inhibition of hyaluronan synthesis prevents β-cell loss in obesity-associated type 2 diabetes. Matrix Biol. 2023, 123, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Ni, F.; Sun, D.; Peng, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, X.; Li, S.; Qi, X.; He, X.; Li, M.; et al. Glucagon Enhances Chemotherapy Efficacy By Inhibition of Tumor Vessels in Colorectal Cancer. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, e2307271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zeng, X.; Liu, Z.; Chen, X.; Li, L.; Luo, R.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Lu, Y.; et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells protect hepatocytes from lipotoxicity through alleviation of endoplasmic reticulum stress by restoring SERCA activity. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 2976–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Li, R.; Cao, J.; Song, X.; Ma, W.; Liu, T.; Wang, L.; Zou, J.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Z.; et al. The inhibition of FKBP5 protects beta-cell survival under inflammation stress via AKT/FOXO1 signaling. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.S.; Song, G.J.; Jun, H.S. Betacellulin-Induced alpha-Cell Proliferation Is Mediated by ErbB3 and ErbB4, and May Contribute to beta-Cell Regeneration. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 605110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tan, S.B.; Guo, Z.G. CD47 decline in pancreatic islet cells promotes macrophage-mediated phagocytosis in type I diabetes. World J. Diabetes 2020, 11, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santarsiero, A.; Todisco, S.; Convertini, P.; De Leonibus, C.; Infantino, V. Transcriptional Regulation and Function of Malic Enzyme 1 in Human Macrophage Activation. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell-Thompson, M.; Fu, A.; Kaddis, J.S.; Wasserfall, C.; Schatz, D.A.; Pugliese, A.; Atkinson, M.A. Insulitis and β-Cell Mass in the Natural History of Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes 2016, 65, 719–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apaolaza, P.S.; Balcacean, D.; Zapardiel-Gonzalo, J.; Rodriguez-Calvo, T. The extent and magnitude of islet T cell infiltration as powerful tools to define the progression to type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 2023, 66, 1129–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gribben, C.; Lambert, C.; Messal, H.A.; Hubber, E.L.; Rackham, C.; Evans, I.; Heimberg, H.; Jones, P.; Sancho, R.; Behrens, A. Ductal Ngn3-expressing progenitors contribute to adult beta cell neogenesis in the pancreas. Cell Stem Cell 2023, 30, 498–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cinti, F.; Bouchi, R.; Kim-Muller, J.Y.; Ohmura, Y.; Sandoval, P.R.; Masini, M.; Marselli, L.; Suleiman, M.; Ratner, L.E.; Marchetti, P.; et al. Evidence of beta-Cell Dedifferentiation in Human Type 2 Diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 1044–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Wen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tan, X.; Chen, X.; Zhu, X.; Wei, C.; Chen, L.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J. Hollow mesoporous ruthenium nanoparticles conjugated bispecific antibody for targeted anti-colorectal cancer response of combination therapy. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 9661–9678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuyama, K.; Chera, S.; van Gurp, L.; Oropeza, D.; Ghila, L.; Damond, N.; Vethe, H.; Paulo, J.A.; Joosten, A.M.; Berney, T.; et al. Diabetes relief in mice by glucose-sensing insulin-secreting human alpha-cells. Nature 2019, 567, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluestone, J.A.; Buckner, J.H.; Herold, K.C. Immunotherapy: Building a bridge to a cure for type 1 diabetes. Science 2021, 373, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eizirik, D.L.; Colli, M.L.; Ortis, F. The role of inflammation in insulitis and β-cell loss in type 1 diabetes. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2009, 5, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdani, M.; Johnson, P.Y.; Potter-Perigo, S.; Nagy, N.; Day, A.J.; Bollyky, P.L.; Wight, T.N. Hyaluronan and hyaluronan-binding proteins accumulate in both human type 1 diabetic islets and lymphoid tissues and associate with inflammatory cells in insulitis. Diabetes 2014, 63, 2727–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, N.; Kuipers, H.F.; Marshall, P.L.; Wang, E.; Kaber, G.; Bollyky, P.L. Hyaluronan in immune dysregulation and autoimmune diseases. Matrix Biol. 2019, 78–79, 292–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, C.O.; Nagy, N.; Bollyky, P.L. Extracellular matrix and the maintenance and loss of peripheral immune tolerance in autoimmune insulitis. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2018, 55, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebe, J.A.; Gooden, M.D.; Workman, G.; Nagy, N.; Bollyky, P.L.; Wight, T.N.; Vernon, R.B. Modulation of hyaluronan synthases and involvement of T cell-derived hyaluronan in autoimmune responses to transplanted islets. Matrix Biol. Plus 2021, 9, 100052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuipers, H.F.; Nagy, N.; Ruppert, S.M.; Sunkari, V.G.; Marshall, P.L.; Gebe, J.A.; Ishak, H.D.; Keswani, S.G.; Bollyky, J.; Frymoyer, A.R.; et al. The pharmacokinetics and dosing of oral 4-methylumbelliferone for inhibition of hyaluronan synthesis in mice. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2016, 185, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Mouslem, A.K.; Khalil, H.E.; Emeka, P.M.; Alotaibi, G. Investigation of the Chemical Composition, Antihyperglycemic and Antilipidemic Effects of Bassia eriophora and Its Derived Constituent, Umbelliferone on High-Fat Diet and Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. Molecules 2022, 27, 6941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villalba, A.; Rodriguez-Fernandez, S.; Perna-Barrull, D.; Ampudia, R.M.; Gomez-Munoz, L.; Pujol-Autonell, I.; Aguilera, E.; Coma, M.; Cano-Sarabia, M.; Vazquez, F.; et al. Repurposed Analog of GLP-1 Ameliorates Hyperglycemia in Type 1 Diabetic Mice Through Pancreatic Cell Reprogramming. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eizirik, D.L.; Pasquali, L.; Cnop, M. Pancreatic β-cells in type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus: Different pathways to failure. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2020, 16, 349–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Zhang, M.; Zeng, S.; Huang, Y.; Qin, M.; Nasri, U.; Santamaria, P.; Riggs, A.D.; Jin, L.; Zeng, D. Reversal of autoimmunity by mixed chimerism enables reactivation of β cells and transdifferentiation of α cells in diabetic NOD mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 31219–31230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimkulrat, S.D.; Bernstein, M.N.; Ni, Z.; Brown, J.; Kendziorski, C.; Blum, B. The Anna Karenina Model of beta-Cell Maturation in Development and Their Dedifferentiation in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes 2021, 70, 2058–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Cui, X.; Li, F.; Xia, L.; Wei, T.; Liu, J.; Fu, W.; Yang, J.; Hong, T.; Wei, R. Glucagon receptor blockage inhibits β-cell dedifferentiation through FoxO1. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 324, E97–E113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanday, N.; Flatt, P.R.; Irwin, N.; Moffett, R.C. Liraglutide and sitagliptin counter beta- to alpha-cell transdifferentiation in diabetes. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 245, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarnobat, D.; Moffett, R.C.; Gault, V.A.; Tanday, N.; Reimann, F.; Gribble, F.M.; Flatt, P.R.; Irwin, N. Effects of long-acting GIP, xenin and oxyntomodulin peptide analogues on alpha-cell transdifferentiation in insulin-deficient diabetic Glu(CreERT2);ROSA26-eYFP mice. Peptides 2020, 125, 170205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Cui, X.; Feng, J.; Gu, L.; Lang, S.; Wei, T.; Yang, J.; Liu, J.; Le, Y.; Wang, H.; et al. Dapagliflozin promotes beta cell regeneration by inducing pancreatic endocrine cell phenotype conversion in type 2 diabetic mice. Metabolism 2020, 111, 154324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, P.L.; Nagy, N.; Kaber, G.; Barlow, G.L.; Ramesh, A.; Xie, B.J.; Linde, M.H.; Haddock, N.L.; Lester, C.A.; Tran, Q.L.; et al. Hyaluronan synthesis inhibition impairs antigen presentation and delays transplantation rejection. Matrix Biol. 2021, 96, 69–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, W.; Yang, S.; Yu, X.; Zhu, S.; Wang, X.; Sun, F.; Liang, S.; Wang, X.; Zhao, G.; Gao, B. Beneficial Actions of 4-Methylumbelliferone in Type 1 Diabetes by Promoting β Cell Renewal and Inhibiting Dedifferentiation. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2790. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122790
Zhang W, Yang S, Yu X, Zhu S, Wang X, Sun F, Liang S, Wang X, Zhao G, Gao B. Beneficial Actions of 4-Methylumbelliferone in Type 1 Diabetes by Promoting β Cell Renewal and Inhibiting Dedifferentiation. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(12):2790. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122790
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Wencheng, Shuo Yang, Xinwen Yu, Shanshan Zhu, Xin Wang, Fei Sun, Shengru Liang, Xiaoguang Wang, Guohong Zhao, and Bin Gao. 2024. "Beneficial Actions of 4-Methylumbelliferone in Type 1 Diabetes by Promoting β Cell Renewal and Inhibiting Dedifferentiation" Biomedicines 12, no. 12: 2790. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122790
APA StyleZhang, W., Yang, S., Yu, X., Zhu, S., Wang, X., Sun, F., Liang, S., Wang, X., Zhao, G., & Gao, B. (2024). Beneficial Actions of 4-Methylumbelliferone in Type 1 Diabetes by Promoting β Cell Renewal and Inhibiting Dedifferentiation. Biomedicines, 12(12), 2790. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122790




