Adalimumab Autoantibodies in Uveitis Patients: Do We Need Routine Drug Monitoring?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Laboratory Testing
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring
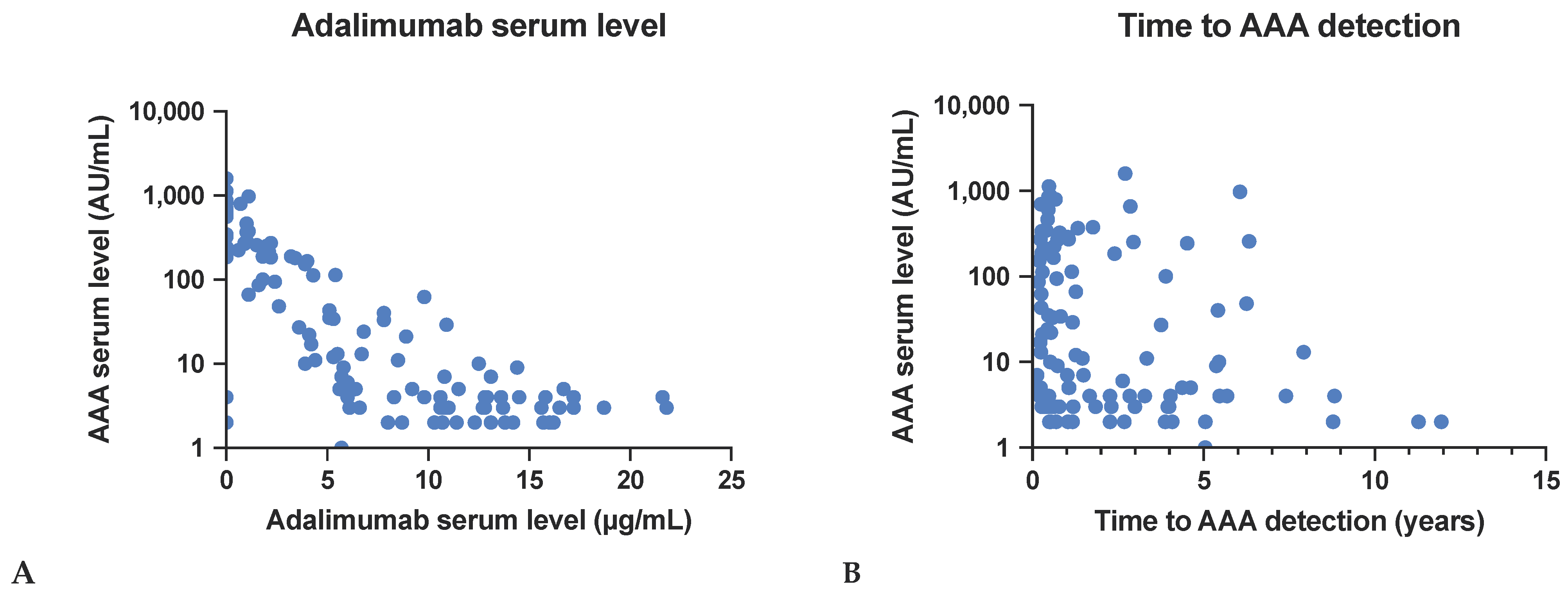
3.2.1. Effect on Adalimumab Serum Levels
3.2.2. Time to AAA Detection
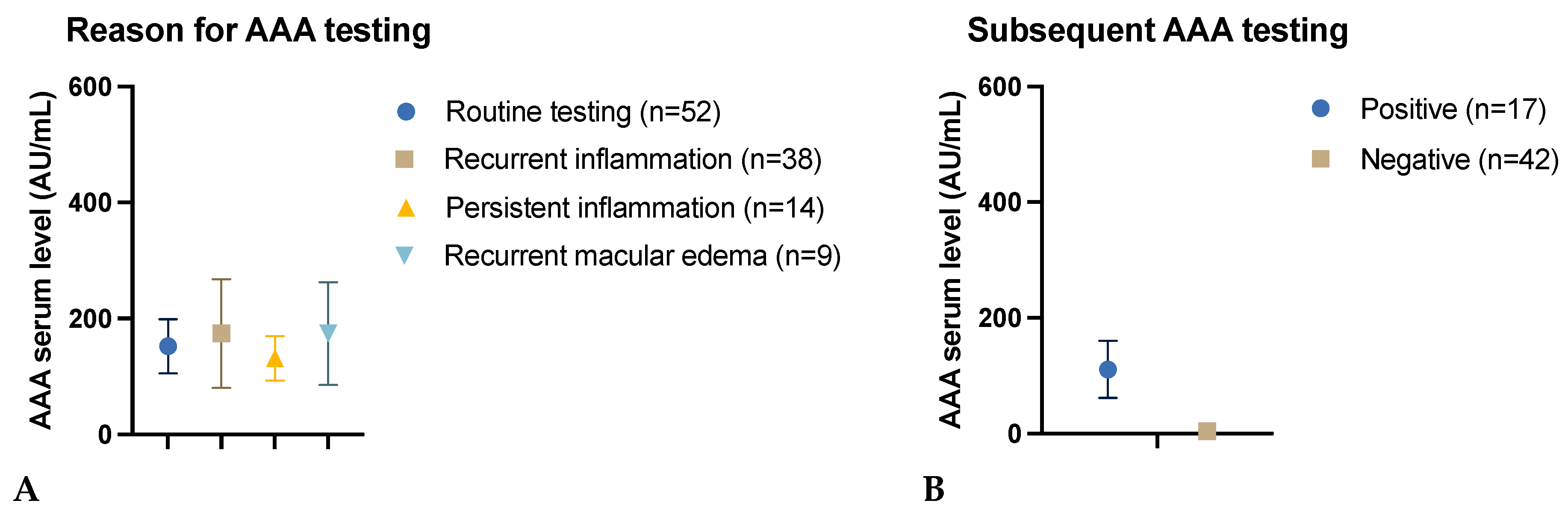
3.2.3. Reason for AAA Testing
3.2.4. Impact of the Initial Test Result on Subsequent AAA Testing
3.3. Factors Affecting AAA Formation
3.3.1. Effect of Age
3.3.2. Effect of Gender
3.3.3. Effect of Concomitant Systemic Disease
3.3.4. Effect of Uveitis Type
3.3.5. Effect of Additional Immunosuppression
3.3.6. Effect of Previous Immunosuppression
3.3.7. Effect of Adalimumab Interruption
3.3.8. Effect of Adalimumab 80 Mg Induction
4. Discussion
4.1. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring
4.1.1. Adalimumab Serum Level and Transient Antibodies
4.1.2. Timing of the Antibody Test
4.2. Factors Affecting AAA Formation
4.2.1. Uveitis in Systemic Autoimmune Diseases
4.2.2. Additional Immunosuppression
4.2.3. Adalimumab Interruption
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Durrani, O.M.; Tehrani, N.N.; Marr, J.E.; Moradi, P.; Stavrou, P.; Murray, P.I. Degree, duration, and causes of visual loss in uveitis. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2004, 88, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaffe, G.J.; Dick, A.D.; Brézin, A.P.; Nguyen, Q.D.; Thorne, J.E.; Kestelyn, P.; Barisani-Asenbauer, T.; Franco, P.; Heiligenhaus, A.; Scales, D.; et al. Adalimumab in Patients with Active Noninfectious Uveitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 932–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleyer, U.; Al-Mutairi, S.; Murphy, C.C.; Hamam, R.; Hammad, S.; Nagy, O.; Szepessy, Z.; Guex-Crosier, Y.; Julian, K.; Habot-Wilner, Z.; et al. Impact of adalimumab in patients with active non-infectious intermediate, posterior, and panuveitis in real-life clinical practice: HOPE study. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2023, 107, 1892–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Schouwenburg, P.A.; van de Stadt, L.A.; de Jong, R.N.; van Buren, E.E.; Kruithof, S.; de Groot, E.; Hart, M.; van Ham, S.M.; Rispens, T.; Aarden, L.; et al. Adalimumab elicits a restricted anti-idiotypic antibody response in autoimmune patients resulting in functional neutralisation. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atiqi, S.; Hooijberg, F.; Loeff, F.C.; Rispens, T.; Wolbink, G.J. Immunogenicity of TNF-Inhibitors. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehin, J.E.; Goll, G.L.; Brun, M.K.; Jani, M.; Bolstad, N.; Syversen, S.W. Assessing Immunogenicity of Biologic Drugs in Inflammatory Joint Diseases: Progress Toward Personalized Medicine. BioDrugs 2022, 36, 731–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartelds, G.M.; Krieckaert, C.L.; Nurmohamed, M.T.; van Schouwenburg, P.A.; Lems, W.F.; Twisk, J.W.; Dijkmans, B.A.; Aarden, L.; Wolbink, G.J. Development of antidrug antibodies against adalimumab and association with disease activity and treatment failure during long-term follow-up. JAMA 2011, 305, 1460–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero-Coma, M.; Calleja-Antolín, S.; Garzo-García, I.; Nuñez-Garnés, A.M.; Álvarez-Castro, C.; Franco-Benito, M.; de Morales, J.G.R. Adalimumab for Treatment of Noninfectious Uveitis: Immunogenicity and Clinical Relevance of Measuring Serum Drug Levels and Antidrug Antibodies. Ophthalmology 2016, 123, 2618–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachón-Suárez, D.I.; Zárate-Pinzón, L.; Cifuentes-González, C.; Rojas-Carabali, W.; Mejía-Salgado, G.; Pineda, J.S.; Peña-Pulgar, L.F.; de-la-Torre, A. Immunogenicity of Adalimumab in Patients with Non-Infectious Uveitis: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ocul. Immunol. Inflamm. 2024, 32, 1539–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eurelings, L.E.; Missotten, T.O.; van Velthoven, M.E.; Van Daele, P.L.; Van Laar, J.A.; van Hagen, P.M.; Thiadens, A.A.; Rombach, S.M. Long-Term Follow-up of Patients With Uveitis Treated With Adalimumab: Response Rates and Reasons for Discontinuation of Therapy. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 240, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieckaert, C.L.; van Tubergen, A.; Gehin, J.E.; Hernández-Breijo, B.; Le Mélédo, G.; Balsa, A.; Böhm, P.; Cucnik, S.; Elkayam, O.; Goll, G.L.; et al. EULAR points to consider for therapeutic drug monitoring of biopharmaceuticals in inflammatory rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 82, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheifetz, A.S.; Abreu, M.T.; Afif, W.; Cross, R.K.; Dubinsky, M.C.; Loftus, E.V., Jr.; Osterman, M.T.; Saroufim, A.; Siegel, C.A.; Yarur, A.J.; et al. A Comprehensive Literature Review and Expert Consensus Statement on Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Biologics in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 116, 2014–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syversen, S.W.; Jørgensen, K.K.; Goll, G.L.; Brun, M.K.; Sandanger, Ø.; Bjørlykke, K.H.; Sexton, J.; Olsen, I.C.; Gehin, J.E.; Warren, D.J.; et al. Effect of Therapeutic Drug Monitoring vs Standard Therapy During Maintenance Infliximab Therapy on Disease Control in Patients With Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2021, 326, 2375–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascual-Salcedo, D.; Plasencia, C.; del Valle, L.G.; Casla, T.L.; Arribas, F.; Villalba, A.; Bonilla, G.; Granados, E.L.; Mola, E.M.; Balsa, A. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring (TDM) in Rheumatic Day Clinic Enables to Reduce Pharmaceutical Cost Maintaining Clinical Efficacy. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, A227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Arango, C.; Gorostiza, I.; Úcar, E.; García-Vivar, M.L.; Pérez, C.E.; De Dios, J.R.; Alvarez, B.; Ruibal-Escribano, A.; Stoye, C.; Vasques, M.; et al. Cost-Effectiveness of Therapeutic Drug Monitoring-Guided Adalimumab Therapy in Rheumatic Diseases: A Prospective, Pragmatic Trial. Rheumatol. Ther. 2021, 8, 1323–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieckaert, C.L.M.; Nair, S.C.; Nurmohamed, M.T.; Van Dongen, C.J.J.; Lems, W.F.; Lafeber, F.P.J.G.; Bijlsma, J.W.J.; Koffijberg, H.; Wolbink, G.; Welsing, P.M.J. Personalised treatment using serum drug levels of adalimumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: An evaluation of costs and effects. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikhonova, I.A.; Yang, H.; Bello, S.; Salmon, A.; Robinson, S.; Hemami, M.R.; Dodman, S.; Kharechko, A.; Haigh, R.C.; Jani, M.; et al. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for monitoring TNF-alpha inhibitors and antibody levels in people with rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol. Assess. 2021, 25, 1–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leinonen, S.T.; Aalto, K.; Kotaniemi, K.M.; Kivelä, T.T. Anti-adalimumab antibodies in juvenile idiopathic arthritis-related uveitis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2017, 35, 1043–1046. [Google Scholar]
- Bellur, S.; McHarg, M.; Kongwattananon, W.; Vitale, S.; Sen, H.N.; Kodati, S. Antidrug Antibodies to Tumor Necrosis Factor α Inhibitors in Patients With Noninfectious Uveitis. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2023, 141, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Zhu, R.; Wu, J.; Xue, L.; Gu, M.; Miao, L. Early Adalimumab and Anti-Adalimumab Antibody Levels for Prediction of Primary Nonresponse in Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2020, 13, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodoraki, E.; Orfanoudaki, E.; Foteinogiannopoulou, K.; Andreou, N.P.; Gazouli, M.; Koutroubakis, I.E. Effect of antinuclear antibodies on pharmacokinetics of anti-TNF therapy in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2022, 37, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brun, M.K.; Goll, G.L.; Jørgensen, K.K.; Sexton, J.; Gehin, J.E.; Sandanger, Ø.; Olsen, I.C.; Klaasen, R.A.; Warren, D.J.; Mørk, C.; et al. Risk factors for anti-drug antibody formation to infliximab: Secondary analyses of a randomised controlled trial. J. Intern. Med. 2022, 292, 477–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bromeo, A.J.; Karaca, I.; Ghoraba, H.H.; Lyu, X.; Than, N.T.T.; Ongpalakorn, P.; Shin, Y.U.; Uludag, G.; Tran, A.N.T.; Thng, Z.X.; et al. Risk factors for development of anti-adalimumab antibodies in non-infectious uveitis. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Characteristic | Mean ± SD 1 |
|---|---|
| Age | 42.5 years (±17.1) |
| Adalimumab anti-drug antibodies (AAA) serum level | 158.1 AU/mL (±283.1) |
| Adalimumab serum level | 6.9 µg/mL (±5.8) |
| Time to detection of AAA | 2.1 years (±2.5) |
| Uveitis subtype | Number of patients |
| Posterior uveitis | 42 |
| Intermediate uveitis | 32 |
| Anterior uveitis | 24 |
| Panuveitis | 16 |
| Total | 114 |
| Specific ocular diseases | Number of patients |
| Punctate inner choroidopathy | 7 |
| Multifocal choroiditis | 6 |
| Serpiginous choroiditis | 6 |
| Birdshot retinochoroiditis | 4 |
| Sympathetic ophthalmia | 3 |
| Frosted branch angiitis | 1 |
| Acute zonal occult outer retinopathy | 1 |
| Acute posterior multifocal placoid pigment epitheliopathy | 1 |
| Idiopathic retinitis vasculitis aneurysms and neuroretinitis | 1 |
| Idiopathic | 38 |
| Systemic autoimmune diseases | Number of patients |
| Ankylosing spondylitis | 12 |
| Sarcoidosis | 9 |
| Juvenile idiopathic arthritis (ANA-positive) | 9 (100%) |
| Vogt–Koyanagi–Harada disease | 7 |
| Behçet’s disease | 6 |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | 5 |
| Psoriasis | 3 |
| Tubulointerstitial nephritis and uveitis syndrome | 1 |
| Systemic lupus erythematosus | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
zur Bonsen, L.S.; Knecht, V.A.; Rübsam, A.; Pohlmann, D.; Pleyer, U. Adalimumab Autoantibodies in Uveitis Patients: Do We Need Routine Drug Monitoring? Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2782. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122782
zur Bonsen LS, Knecht VA, Rübsam A, Pohlmann D, Pleyer U. Adalimumab Autoantibodies in Uveitis Patients: Do We Need Routine Drug Monitoring? Biomedicines. 2024; 12(12):2782. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122782
Chicago/Turabian Stylezur Bonsen, Lynn S., Vitus A. Knecht, Anne Rübsam, Dominika Pohlmann, and Uwe Pleyer. 2024. "Adalimumab Autoantibodies in Uveitis Patients: Do We Need Routine Drug Monitoring?" Biomedicines 12, no. 12: 2782. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122782
APA Stylezur Bonsen, L. S., Knecht, V. A., Rübsam, A., Pohlmann, D., & Pleyer, U. (2024). Adalimumab Autoantibodies in Uveitis Patients: Do We Need Routine Drug Monitoring? Biomedicines, 12(12), 2782. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122782







