Integrative Multi-Omics Analysis Reveals Critical Molecular Networks Linking Intestinal-System Diseases to Colorectal Cancer Progression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy and Literature Screening
2.2. Data Preprocessing and Identification of DEG
Up-regulated if adj. p-value < 0.01 & logFC ≥ 1.0,
Down-regulated if adj. p-value < 0.01 & logFC ≤ −1.0.
2.3. Pathway and Functional Enrichment Analysis
2.4. Identification of Hub Genes
2.5. Survival Analysis
Z ≤ −2 Underexpress
2 < Z > −2 Normal (Unaltered)
2.6. The ROC Curve Analysis and Expression Analysis
2.7. Sample Collection and Immunohistochemical Staining Evaluation
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Data Analysis Flowchart
3.2. Gene Expression Analysis
3.3. Pathway and Functional Association Analysis
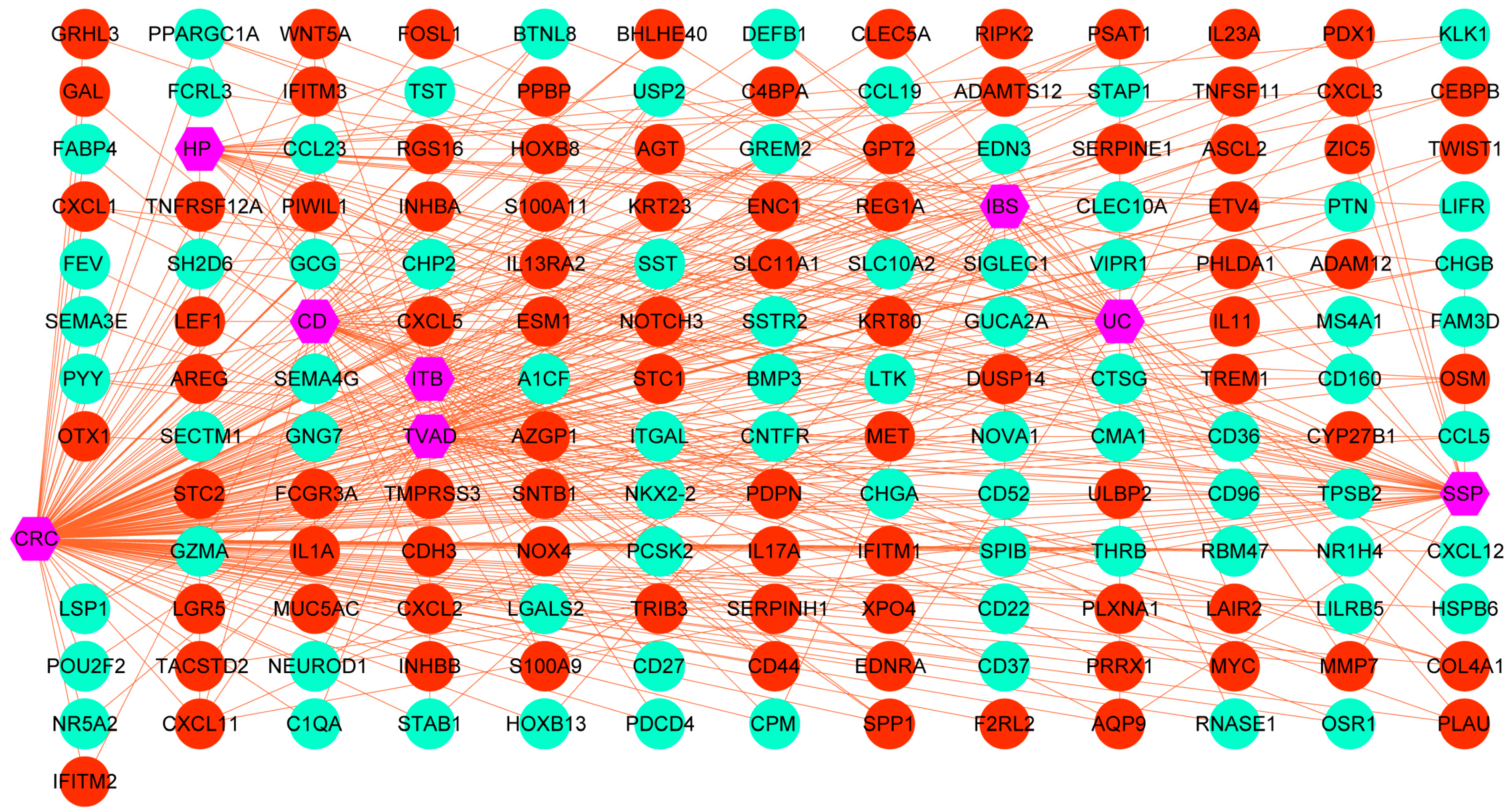
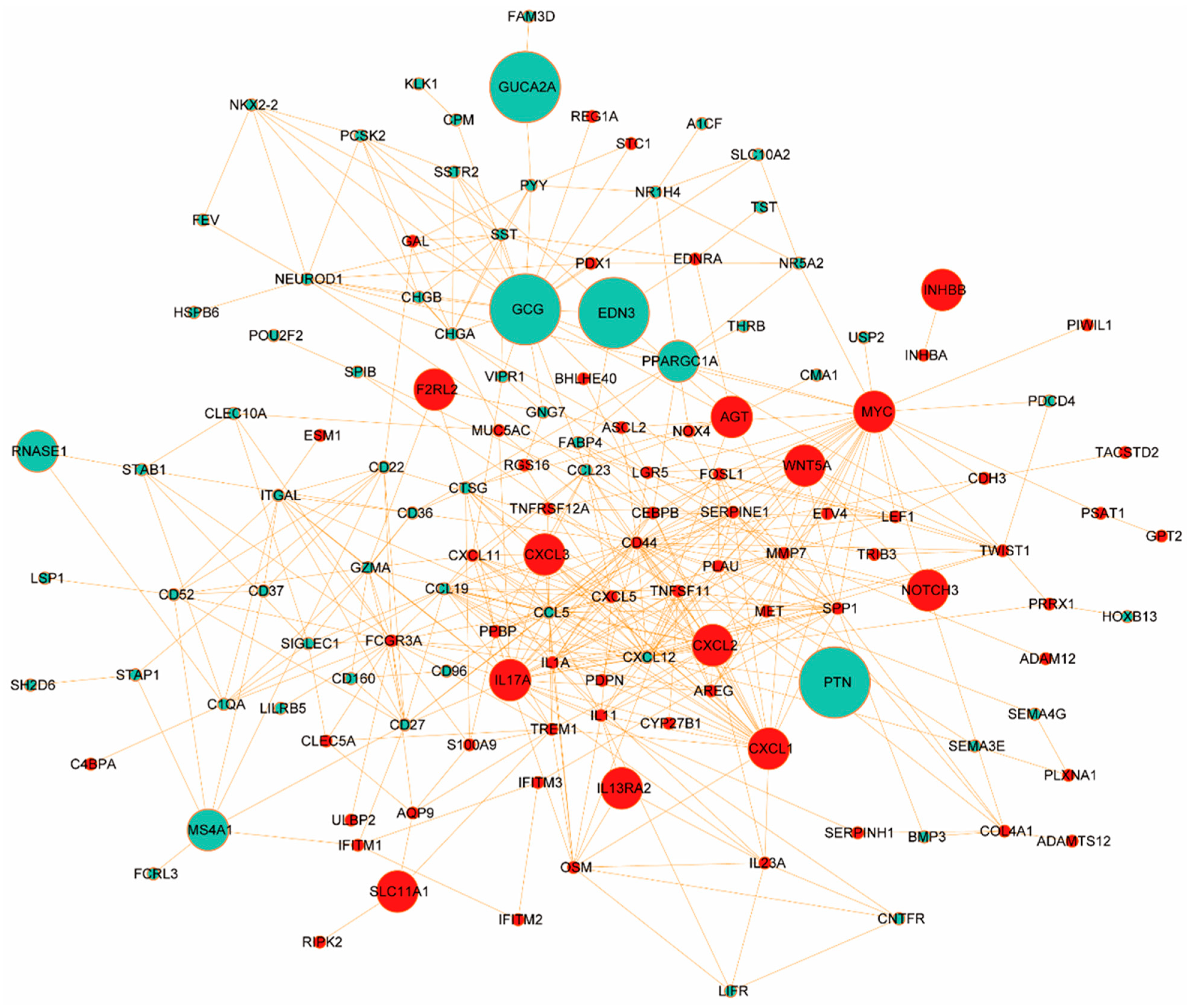
3.4. Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) Analysis
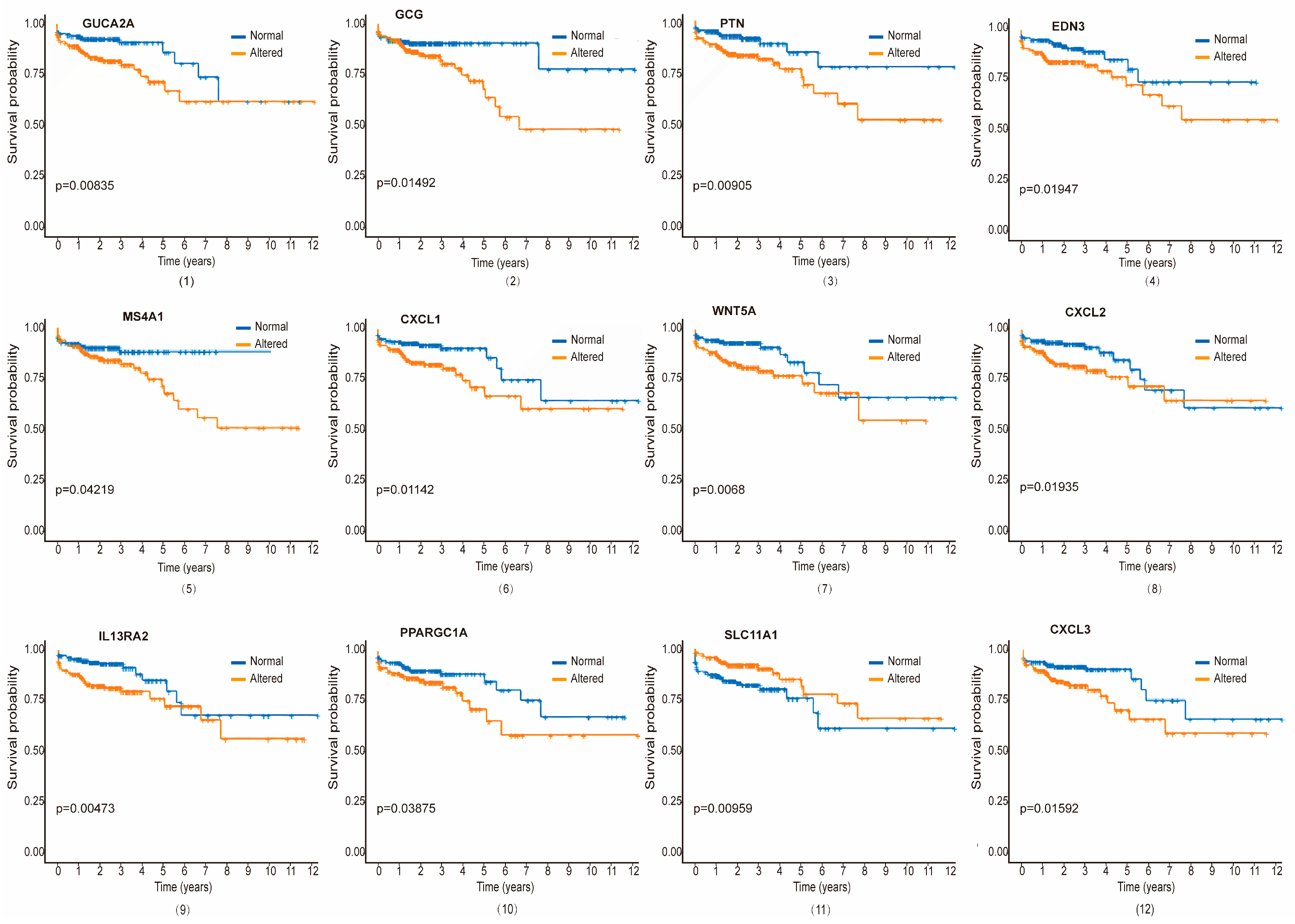
3.5. Validation of Hub Proteins with Survival Analysis
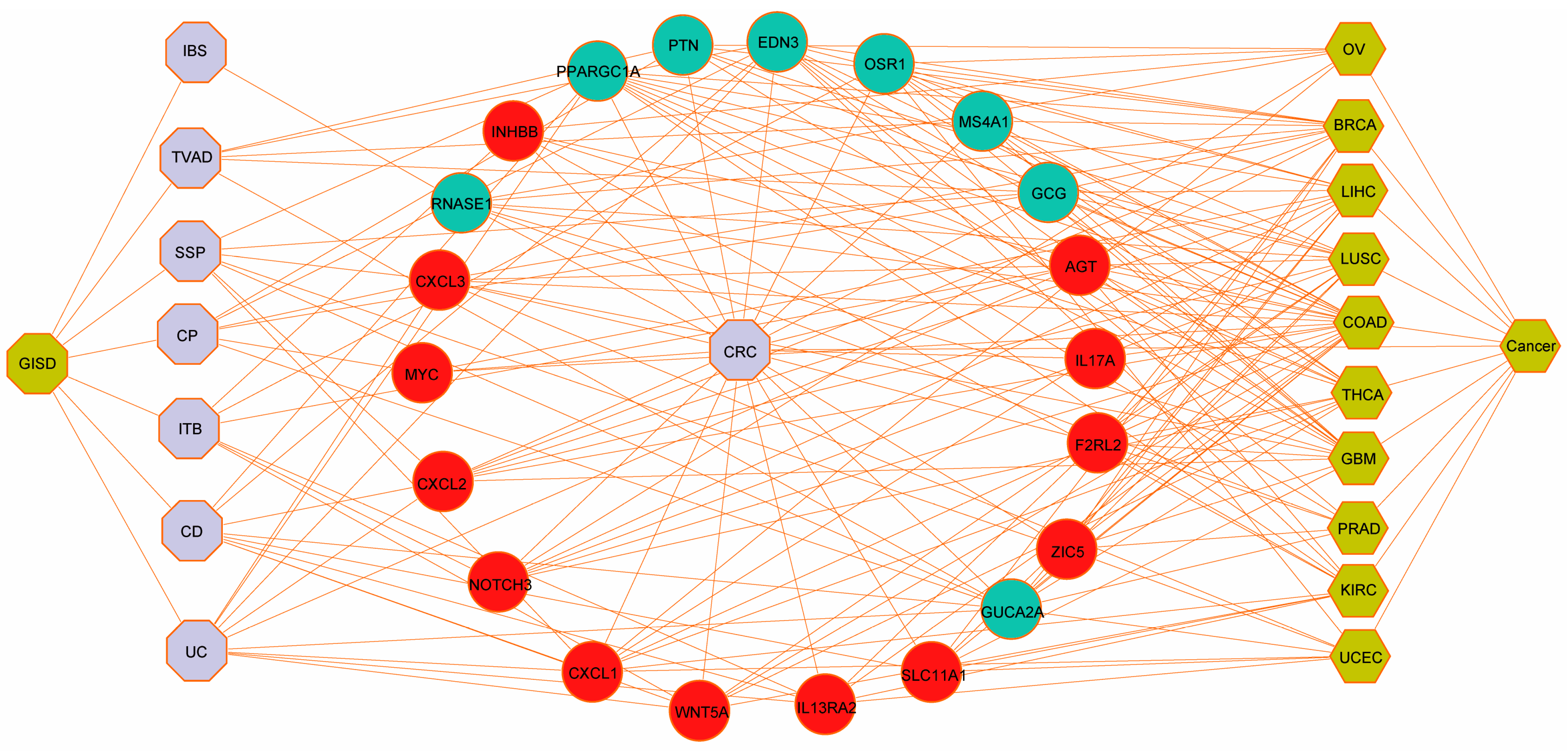
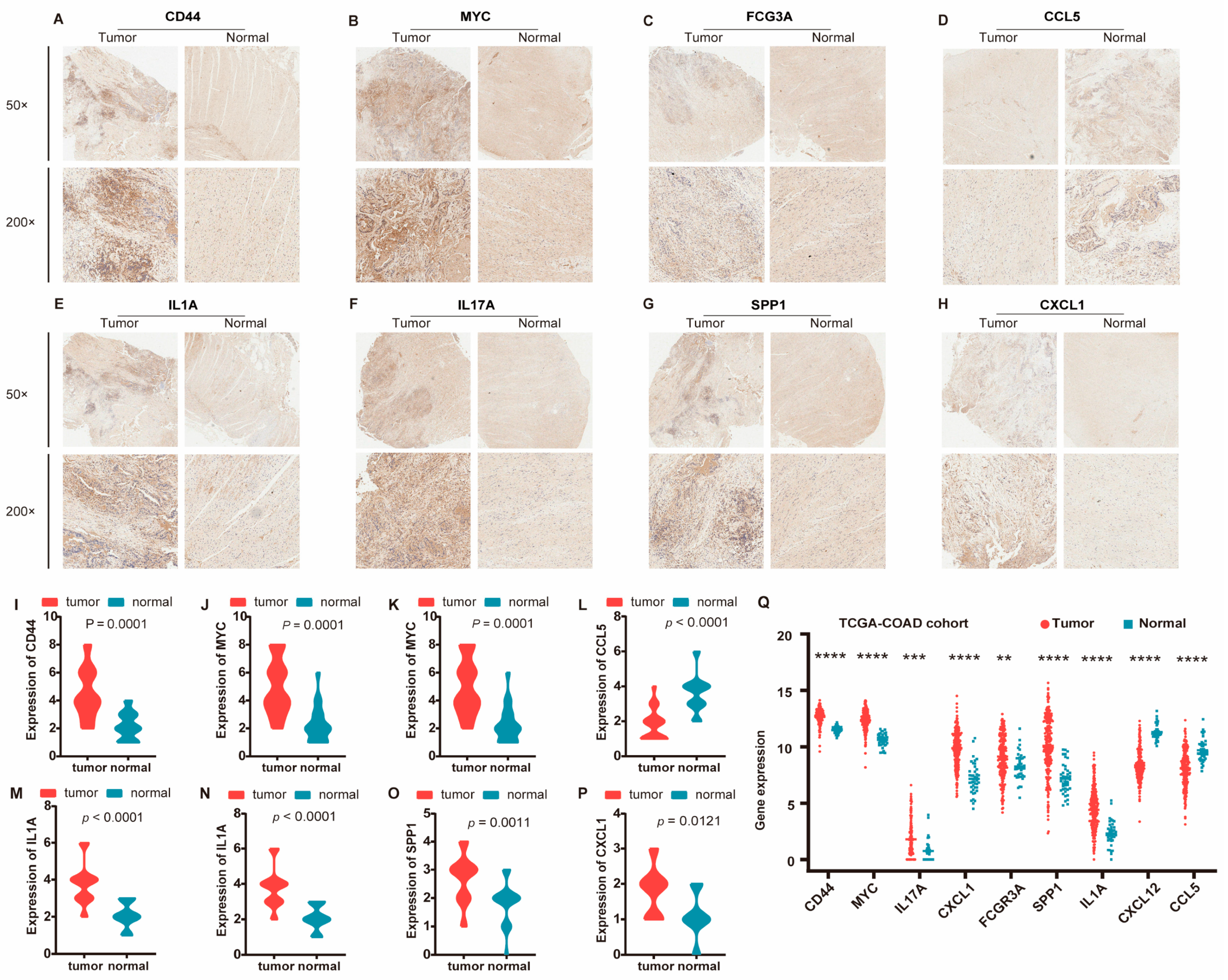
3.6. Validation Against Gold-Standard Databases and Immunohistochemical Verification
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Valderas, J.M.; Starfield, B.; Sibbald, B.; Salisbury, C.; Roland, M. Defining comorbidity: Implications for understanding health and health services. Ann. Fam. Med. 2009, 7, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreutzburg, T.; Peters, F.; Rieß, H.C.; Hischke, S.; Marschall, U.; Kriston, L.; L’Hoest, H.; Sedrakyan, A.; Debus, E.S.; Behrendt, C.A. Editor’s Choice—Comorbidity Patterns Among Patients with Peripheral Arterial Occlusive Disease in Germany: A Trend Analysis of Health Insurance Claims Data. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2020, 59, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merluzzi, T.V.; Philip, E.J.; Gomer, B.; Heitzmann Ruhf, C.A.; Kim, D. Comorbidity, Functional Impairment, and Emotional Distress: A Coping Mediation Model for Persons with Cancer. Ann. Behav. Med. A Publ. Soc. Behav. Med. 2021, 55, 994–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boakye, D.; Rillmann, B.; Walter, V.; Jansen, L.; Hoffmeister, M.; Brenner, H. Impact of comorbidity and frailty on prognosis in colorectal cancer patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2018, 64, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Leersum, N.J.; Janssen-Heijnen, M.L.G.; Wouters, M.W.J.M.; Rutten, H.J.T.; Coebergh, J.W.; Tollenaar, R.A.E.M.; Lemmens, V.E.P.P. Increasing prevalence of comorbidity in patients with colorectal cancer in the South of the Netherlands 1995–2010. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 132, 2157–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostenfeld, E.B.; Nørgaard, M.; Thomsen, R.W.; Iversen, L.H.; Jacobsen, J.B.; Søgaard, M. Comorbidity and survival of Danish patients with colon and rectal cancer from 2000–2011: A population-based cohort study. Clin. Epidemiol. 2013, 5, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iversen, L.H.; Nørgaard, M.; Jacobsen, J.; Laurberg, S.; Sørensen, H.T. The impact of comorbidity on survival of Danish colorectal cancer patients from 1995 to 2006—A population-based cohort study. Dis. Colon Rectum 2009, 52, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erichsen, R.; Horváth-Puhó, E.; Iversen, L.H.; Lash, T.L.; Sørensen, H.T. Does comorbidity interact with colorectal cancer to increase mortality? A nationwide population-based cohort study. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 2005–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bopanna, S.; Ananthakrishnan, A.N.; Kedia, S.; Yajnik, V.; Ahuja, V. Risk of colorectal cancer in Asian patients with ulcerative colitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 2, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellokumpu, I.; Kairaluoma, M.; Mecklin, J.P.; Kellokumpu, H.; Väyrynen, V.; Wirta, E.V.; Sihvo, E.; Kuopio, T.; Seppälä, T.T. Impact of Age and Comorbidity on Multimodal Management and Survival from Colorectal Cancer: A Population-Based Study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castano-Milla, C.; Chaparro, M.; Gisbert, J.P. Systematic review with meta-analysis: The declining risk of colorectal cancer in ulcerative colitis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 39, 645–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieszczy, P.; Kaminski, M.F.; Franczyk, R.; Loberg, M.; Kobiela, J.; Rupinska, M.; Kocot, B.; Rupinski, M.; Holme, O.; Wojciechowska, U.; et al. Colorectal Cancer Incidence and Mortality After Removal of Adenomas During Screening Colonoscopies. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.K.; Jensen, C.D.; Levin, T.R.; Doubeni, C.A.; Zauber, A.G.; Chubak, J.; Kamineni, A.S.; Schottinger, J.E.; Ghai, N.R.; Udaltsova, N.; et al. Long-term Risk of Colorectal Cancer and Related Death After Adenoma Removal in a Large, Community-based Population. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 884–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Wu, K.; Ogino, S.; Giovannucci, E.L.; Chan, A.T.; Song, M. Association Between Risk Factors for Colorectal Cancer and Risk of Serrated Polyps and Conventional Adenomas. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 355–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvvuri, A.; Chandrasekar, V.T.; Srinivasan, S.; Narimiti, A.; Dasari, C.; Nutalapati, V.; Kennedy, K.F.; Spadaccini, M.; Antonelli, G.; Desai, M.; et al. Risk of Colorectal Cancer and Cancer Related Mortality After Detection of Low-risk or High-risk Adenomas, Compared With No Adenoma, at Index Colonoscopy: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 1986–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Click, B.; Pinsky, P.F.; Hickey, T.; Doroudi, M.; Schoen, R.E. Association of Colonoscopy Adenoma Findings with Long-term Colorectal Cancer Incidence. JAMA 2018, 319, 2021–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Hang, D.; Wu, K.; Nayor, J.; Drew, D.A.; Giovannucci, E.L.; Ogino, S.; Chan, A.T.; Song, M. Long-term Risk of Colorectal Cancer After Removal of Conventional Adenomas and Serrated Polyps. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 852–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Wu, W.; Wu, C.; Li, M.; Sun, F.; Zheng, L.; Liu, G.; Li, X.; Yun, Z.; Tang, J.; et al. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine signature in circulating cell-free DNA as a potential diagnostic factor for early-stage colorectal cancer and precancerous adenoma. Mol. Oncol. 2021, 15, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Emilsson, L.; Bozorg, S.R.; Nguyen, L.H.; Joshi, A.D.; Staller, K.; Nayor, J.; Chan, A.T.; Ludvigsson, J.F. Risk of colorectal cancer incidence and mortality after polypectomy: A Swedish record-linkage study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Yamano, H.O.; Yamamoto, E.; Matushita, H.O.; Aoki, H.; Yoshikawa, K.; Takagi, R.; Harada, E.; Nakaoka, M.; Yoshida, Y.; et al. Endoscopic and molecular characterization of colorectal sessile serrated adenoma/polyps with cytologic dysplasia. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2017, 86, 1131–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett-Hartman, A.N.; Chubak, J.; Hua, X.; Ziebell, R.; Kamineni, A.; Zhu, L.C.; Upton, M.P.; Malen, R.C.; Hardikar, S.; Newcomb, P.A. The association between colorectal sessile serrated adenomas/polyps and subsequent advanced colorectal neoplasia. Cancer Causes Control 2019, 30, 979–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aust, D.E.; Baretton, G.B.; Members of the Working Group GIPotGSoP. Serrated polyps of the colon and rectum (hyperplastic polyps, sessile serrated adenomas, traditional serrated adenomas, and mixed polyps)-proposal for diagnostic criteria. Virchows Arch. Int. J. Pathol. 2010, 457, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, W.; Hoskin, P.; Henry, A.; Gomez-Iturriaga, A.; Robinson, A.; Nikapota, A. Short-term Toxicity of High Dose Rate Brachytherapy in Prostate Cancer Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 30, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirashima, T.; Tamura, Y.; Han, Y.; Hashimoto, S.; Tanaka, A.; Shiroyama, T.; Morishita, N.; Suzuki, H.; Okamoto, N.; Akada, S.; et al. Efficacy and safety of concurrent anti-Cancer and anti-tuberculosis chemotherapy in Cancer patients with active Mycobacterium tuberculosis: A retrospective study. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirashima, T.; Nagai, T.; Shigeoka, H.; Tamura, Y.; Yoshida, H.; Kawahara, K.; Kondoh, Y.; Sakai, K.; Hashimoto, S.; Fujishima, M.; et al. Comparison of the clinical courses and chemotherapy outcomes in metastatic colorectal cancer patients with and without active Mycobacterium tuberculosis or Mycobacterium kansasii infection: A retrospective study. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oka, P.; Parr, H.; Barberio, B.; Black, C.J.; Savarino, E.V.; Ford, A.C. Global prevalence of irritable bowel syndrome according to Rome III or IV criteria: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 908–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fond, G.; Loundou, A.; Hamdani, N.; Boukouaci, W.; Dargel, A.; Oliveira, J.; Roger, M.; Tamouza, R.; Leboyer, M.; Boyer, L. Anxiety and depression comorbidities in irritable bowel syndrome (IBS): A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2014, 264, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wang, J.; Ye, Z.; Wang, J.; Liao, X.; Liv, M.; Svn, Z. Risk of Colorectal Cancer in Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Meta-Analysis of Population-Based Observational Studies. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 819122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, I.; Simren, M. The overlap between irritable bowel syndrome and organic gastrointestinal diseases. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 6, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, B.K.; Noone, A.M.; Mariotto, A.B.; Simard, E.P.; Boscoe, F.P.; Henley, S.J.; Jemal, A.; Cho, H.; Anderson, R.N.; Kohler, B.A.; et al. Annual Report to the Nation on the status of cancer, 1975-2010, featuring prevalence of comorbidity and impact on survival among persons with lung, colorectal, breast, or prostate cancer. Cancer 2014, 120, 1290–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, T.; Wilhite, S.E.; Ledoux, P.; Evangelista, C.; Kim, I.F.; Tomashevsky, M.; Marshall, K.A.; Phillippy, K.H.; Sherman, P.M.; Holko, M.; et al. NCBI GEO: Archive for functional genomics data sets—Update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D991–D995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, H.; Jiang, S.; Li, R.; Li, W.; Chen, H.; Bo, X. A survey and evaluation of Web-based tools/databases for variant analysis of TCGA data. Brief. Bioinform. 2019, 20, 1524–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galamb, O.; Wichmann, B.; Sipos, F.; Spisák, S.; Krenács, T.; Tóth, K.; Leiszter, K.; Kalmár, A.; Tulassay, Z.; Molnár, B. Dysplasia-carcinoma transition specific transcripts in colonic biopsy samples. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delker, D.A.; McGettigan, B.M.; Kanth, P.; Pop, S.; Neklason, D.W.; Bronner, M.P.; Burt, R.W.; Hagedorn, C.H. RNA sequencing of sessile serrated colon polyps identifies differentially expressed genes and immunohistochemical markers. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.R.; Chiang, J.M.; Lim, S.N.; Su, M.Y.; Chen, T.H.; Huang, S.W.; Chen, C.W.; Wu, R.C.; Tsai, C.L.; Lin, Y.H.; et al. Dynamic bioenergetic alterations in colorectal adenomatous polyps and adenocarcinomas. EBioMedicine 2019, 44, 334–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandborn, W.J.; Feagan, B.G.; Marano, C.; Zhang, H.; Strauss, R.; Johanns, J.; Adedokun, O.J.; Guzzo, C.; Colombel, J.F.; Reinisch, W.; et al. Subcutaneous golimumab induces clinical response and remission in patients with moderate-to-severe ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 85–95, quiz e14–e85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhove, W.; Peeters, P.M.; Staelens, D.; Schraenen, A.; Van der Goten, J.; Cleynen, I.; De Schepper, S.; Van Lommel, L.; Reynaert, N.L.; Schuit, F.; et al. Strong Upregulation of AIM2 and IFI16 Inflammasomes in the Mucosa of Patients with Active Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 2673–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, V.; Subodh, S.; Tuteja, A.; Mishra, V.; Garg, S.K.; Gupta, N.; Makharia, G.; Acharya, S.K. Genome-wide gene expression analysis for target genes to differentiate patients with intestinal tuberculosis and Crohn’s disease and discriminative value of FOXP3 mRNA expression. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2016, 4, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swan, C.; Duroudier, N.P.; Campbell, E.; Zaitoun, A.; Hastings, M.; Dukes, G.E.; Cox, J.; Kelly, F.M.; Wilde, J.; Lennon, M.G.; et al. Identifying and testing candidate genetic polymorphisms in the irritable bowel syndrome (IBS): Association with TNFSF15 and TNFalpha. Gut 2013, 62, 985–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Q.; Li, B.; Cai, X.; Lv, Z.; Cai, S.; Zhong, Y.; Wen, B. Transcriptomic Analyses of the Adenoma-Carcinoma Sequence Identify Hallmarks Associated with the Onset of Colorectal Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 704531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, R.; Jurickova, I.; Ballard, E.; Bonkowski, E.; Han, X.; Xu, H.; Denson, L.A. Activation of an IL-6:STAT3-dependent transcriptome in pediatric-onset inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2008, 14, 446–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.H.; Rana, H.K.; Peng, S.; Hu, X.; Chen, C.; Quinn, J.M.; Moni, M.A. Bioinformatics and machine learning methodologies to identify the effects of central nervous system disorders on glioblastoma progression. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbaa365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torcivia-Rodriguez, J.; Dingerdissen, H.; Chang, T.C.; Mazumder, R. A Primer for Access to Repositories of Cancer-Related Genomic Big Data. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1878, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.H.; Peng, S.; Hu, X.; Chen, C.; Rahman, M.R.; Uddin, S.; Quinn, J.M.; Moni, M.A. A Network-Based Bioinformatics Approach to Identify Molecular Biomarkers for Type 2 Diabetes that Are Linked to the Progression of Neurological Diseases. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Nastou, K.C.; Lyon, D.; Kirsch, R.; Pyysalo, S.; Doncheva, N.T.; Legeay, M.; Fang, T.; Bork, P.; et al. The STRING database in 2021: Customizable protein-protein networks, and functional characterization of user-uploaded gene/measurement sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D605–D612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Shannon, C.P.; Gautier, B.; Rohart, F.; Vacher, M.; Tebbutt, S.J.; Lê Cao, K.A. DIABLO: An integrative approach for identifying key molecular drivers from multi-omics assays. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 3055–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Lu, D.; Sun, K.; Xu, Y.; Hu, P.; Li, X.; Xu, F. Identification of biomarkers associated with diagnosis and prognosis of colorectal cancer patients based on integrated bioinformatics analysis. Gene 2019, 692, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Disease Name | GEO Number | Tissues | Platform | Location | Control Samples | Case Samples | Sigt. Genes | UpReg. Genes | DownReg. Genes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TVAD | GSE4183 | biopsy samples | Affymetrix Human Genome U133 Plus 2.0 Array | Hungary | 8 | 15 | 1744 | 1096 | 648 |
| TVAD | GSE164541 | Triplicate tissue samples | Illumina HiSeq 2500 | China | 5 | 5 | 1121 | 214 | 907 |
| CD | GSE26305 | biopsy samples | Illumina HumanWG-6 v3.0 expression beadchip | India | 2 | 2 | 440 | 228 | 212 |
| CD | GSE59071 | biopsy samples | Affymetrix Human Gene 1.0 ST Array | Belgium | 11 | 8 | 693 | 167 | 526 |
| CRC | TCGA | biopsy samples | High-throughput sequencing | USA Canada | 51 | 647 | 2141 | 1169 | 972 |
| CRC | GSE164541 | Triplicate tissue samples | Illumina HiSeq 2500 | China | 5 | 5 | 2082 | 710 | 1372 |
| ITB | GSE26305 | biopsy samples | Illumina HumanWG-6 v3.0 expression beadchip | India | 2 | 2 | 877 | 564 | 313 |
| UC | GSE92415 | biopsy samples | Affymetrix HT HG-U133+ PM Array Plate | Europe | 21 | 87 | 1187 | 366 | 821 |
| UC | GSE9686 | biopsy samples | Affymetrix GeneChip Human Genome U133 Plus 2.0 Array | USA | 5 | 8 | 2013 | 751 | 1262 |
| IBS | GSE36701 | biopsy samples | Affymetrix Human Genome U133 Plus 2.0 Array | UK | 77 | 87 | 2137 | 0 | 2137 |
| SSPs | GSE46513 | biopsy samples | Illumina HiSeq 2000 | USA | 8 | 7 | 746 | 336 | 410 |
| HP | GSE81804 | biopsy samples | Affymetrix Human Gene 2.0 ST Array | China (Taiwan) | 5 | 5 | 340 | 94 | 246 |
| ISD | Gene Symbol | Univariate Cox | Multivariate Cox | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | HR.95L | HR.95H | p Value | HR | HR.95L | HR.95H | p Value | ||
| TVAD | GUCA2A | 1.00002 | 1.00001 | 1.00004 | 0.00500 | 1.00144 | 1.00078 | 1.00210 | 0.00002 |
| GCG | 1.00009 | 1.00001 | 1.00016 | 0.00207 | 1.04378 | 1.02168 | 1.06636 | 0.00009 | |
| MS4A1 | 1.00016 | 1.00000 | 1.00032 | 0.04845 | 1.05744 | 1.01616 | 1.10041 | 0.03981 | |
| PTN | 0.97874 | 0.96409 | 0.99361 | 0.00523 | 1.00011 | 1.00006 | 1.00017 | 0.00003 | |
| EDN3 | 1.00075 | 1.00008 | 1.00142 | 0.02923 | 1.00038 | 1.00011 | 1.00064 | 0.00513 | |
| CD | GUCA2A | 1.00002 | 1.00001 | 1.00004 | 0.00500 | 1.00144 | 1.00078 | 1.00210 | 0.00002 |
| EDN3 | 1.00075 | 1.00008 | 1.00142 | 0.02923 | 1.00038 | 1.00011 | 1.00064 | 0.00513 | |
| CXCL1 | 0.99876 | 0.99777 | 0.99974 | 0.00131 | 1.01249 | 1.00631 | 1.01871 | 0.00007 | |
| WNT5A | 0.99887 | 0.99816 | 0.99958 | 0.00172 | 1.02524 | 1.01432 | 1.03627 | 0.00000 | |
| CXCL2 | 0.99921 | 0.99853 | 0.99990 | 0.02483 | 1.00091 | 1.00039 | 1.00143 | 0.00065 | |
| IL13RA2 | 1.00003 | 1.00001 | 1.00005 | 0.00057 | 1.06190 | 1.03580 | 1.08866 | 0.00000 | |
| SLC11A1 | 1.00046 | 1.00010 | 1.00081 | 0.00119 | 1.38585 | 1.18743 | 1.61742 | 0.00003 | |
| PPARGC1A | 0.99987 | 0.99975 | 1.00000 | 0.04510 | 1.00033 | 1.00002 | 1.00063 | 0.02638 | |
| UC | GUCA2A | 1.00002 | 1.00001 | 1.00004 | 0.00500 | 1.00144 | 1.00078 | 1.00210 | 0.00002 |
| EDN3 | 1.00075 | 1.00008 | 1.00142 | 0.02923 | 1.00038 | 1.00011 | 1.00064 | 0.00513 | |
| CXCL1 | 0.99876 | 0.99777 | 0.99974 | 0.00131 | 1.01249 | 1.00631 | 1.01871 | 0.00007 | |
| WNT5A | 0.99887 | 0.99816 | 0.99958 | 0.00172 | 1.02524 | 1.01432 | 1.03627 | 0.00000 | |
| CXCL2 | 0.99921 | 0.99853 | 0.99990 | 0.02483 | 1.00091 | 1.00039 | 1.00143 | 0.00065 | |
| IL13RA2 | 1.00003 | 1.00001 | 1.00005 | 0.00057 | 1.06190 | 1.03580 | 1.08866 | 0.00000 | |
| PPARGC1A | 0.99987 | 0.99975 | 1.00000 | 0.04510 | 1.00033 | 1.00002 | 1.00063 | 0.02638 | |
| CXCL3 | 1.00016 | 1.00002 | 1.00030 | 0.00225 | 1.04923 | 1.02417 | 1.07490 | 0.00010 | |
| AGT | 1.00082 | 1.00043 | 1.00122 | 0.00005 | 1.00710 | 1.00419 | 1.01001 | 0.00000 | |
| HP | GUCA2A | 1.00002 | 1.00001 | 1.00004 | 0.00500 | 1.00144 | 1.00078 | 1.00210 | 0.00002 |
| GCG | 1.00009 | 1.00001 | 1.00016 | 0.00207 | 1.04378 | 1.02168 | 1.06636 | 0.00009 | |
| PTN | 0.97874 | 0.96409 | 0.99361 | 0.00523 | 1.00011 | 1.00006 | 1.00017 | 0.00003 | |
| EDN3 | 1.00075 | 1.00008 | 1.00142 | 0.02923 | 1.00038 | 1.00011 | 1.00064 | 0.00513 | |
| CXCL3 | 1.00016 | 1.00002 | 1.00030 | 0.00225 | 1.04923 | 1.02417 | 1.07490 | 0.00010 | |
| MYC | 1.00086 | 1.00008 | 1.00164 | 0.03002 | 1.01964 | 1.00500 | 1.03449 | 0.00840 | |
| SSP | GUCA2A | 1.00002 | 1.00001 | 1.00004 | 0.00500 | 1.00144 | 1.00078 | 1.00210 | 0.00002 |
| GCG | 1.00009 | 1.00001 | 1.00016 | 0.00207 | 1.04378 | 1.02168 | 1.06636 | 0.00009 | |
| CXCL1 | 0.99876 | 0.99777 | 0.99974 | 0.00131 | 1.01249 | 1.00631 | 1.01871 | 0.00007 | |
| CXCL2 | 0.99921 | 0.99853 | 0.99990 | 0.02483 | 1.00091 | 1.00039 | 1.00143 | 0.00065 | |
| PPARGC1A | 0.99987 | 0.99975 | 1.00000 | 0.04510 | 1.00033 | 1.00002 | 1.00063 | 0.02638 | |
| CXCL3 | 1.00016 | 1.00002 | 1.00030 | 0.00225 | 1.04923 | 1.02417 | 1.07490 | 0.00010 | |
| ZIC5 | 1.00016 | 1.00002 | 1.00031 | 0.03053 | 1.00001 | 1.00000 | 1.00002 | 0.01373 | |
| ITB | WNT5A | 0.99887 | 0.99816 | 0.99958 | 0.00172 | 1.02524 | 1.01432 | 1.03627 | 0.00000 |
| IL13RA2 | 1.00003 | 1.00001 | 1.00005 | 0.00057 | 1.06190 | 1.03580 | 1.08866 | 0.00000 | |
| NOTCH3 | 0.98949 | 0.98012 | 0.99895 | 0.02952 | 1.00129 | 1.00038 | 1.00220 | 0.00561 | |
| OSR1 | 1.00007 | 1.00002 | 1.00013 | 0.00140 | 1.00135 | 1.00068 | 1.00202 | 0.00008 | |
| INHBB | 1.00008 | 1.00005 | 1.00012 | 0.00002 | 1.00767 | 1.00467 | 1.01069 | 0.00000 | |
| AGT | 1.00082 | 1.00043 | 1.00122 | 0.00005 | 1.00710 | 1.00419 | 1.01001 | 0.00000 | |
| IBS | RNASE1 | 1.00824 | 1.00112 | 1.01541 | 0.02315 | 1.04461 | 1.01940 | 1.07044 | 0.00046 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ji, S.; Hu, H.; Zhu, R.; Guo, D.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, T.; Zou, C.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, G. Integrative Multi-Omics Analysis Reveals Critical Molecular Networks Linking Intestinal-System Diseases to Colorectal Cancer Progression. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2656. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122656
Ji S, Hu H, Zhu R, Guo D, Liu Y, Yang Y, Li T, Zou C, Jiang Y, Liu G. Integrative Multi-Omics Analysis Reveals Critical Molecular Networks Linking Intestinal-System Diseases to Colorectal Cancer Progression. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(12):2656. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122656
Chicago/Turabian StyleJi, Shiliang, Haoran Hu, Ruifang Zhu, Dongkai Guo, Yujing Liu, Yang Yang, Tian Li, Chen Zou, Yiguo Jiang, and Guilai Liu. 2024. "Integrative Multi-Omics Analysis Reveals Critical Molecular Networks Linking Intestinal-System Diseases to Colorectal Cancer Progression" Biomedicines 12, no. 12: 2656. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122656
APA StyleJi, S., Hu, H., Zhu, R., Guo, D., Liu, Y., Yang, Y., Li, T., Zou, C., Jiang, Y., & Liu, G. (2024). Integrative Multi-Omics Analysis Reveals Critical Molecular Networks Linking Intestinal-System Diseases to Colorectal Cancer Progression. Biomedicines, 12(12), 2656. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122656






