Next-Generation Sequencing of Chinese Children with Congenital Hearing Loss Reveals Rare and Novel Variants in Known and Candidate Genes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Clinical Evaluation
2.2. Whole-Exome Sequencing and Data Analyses
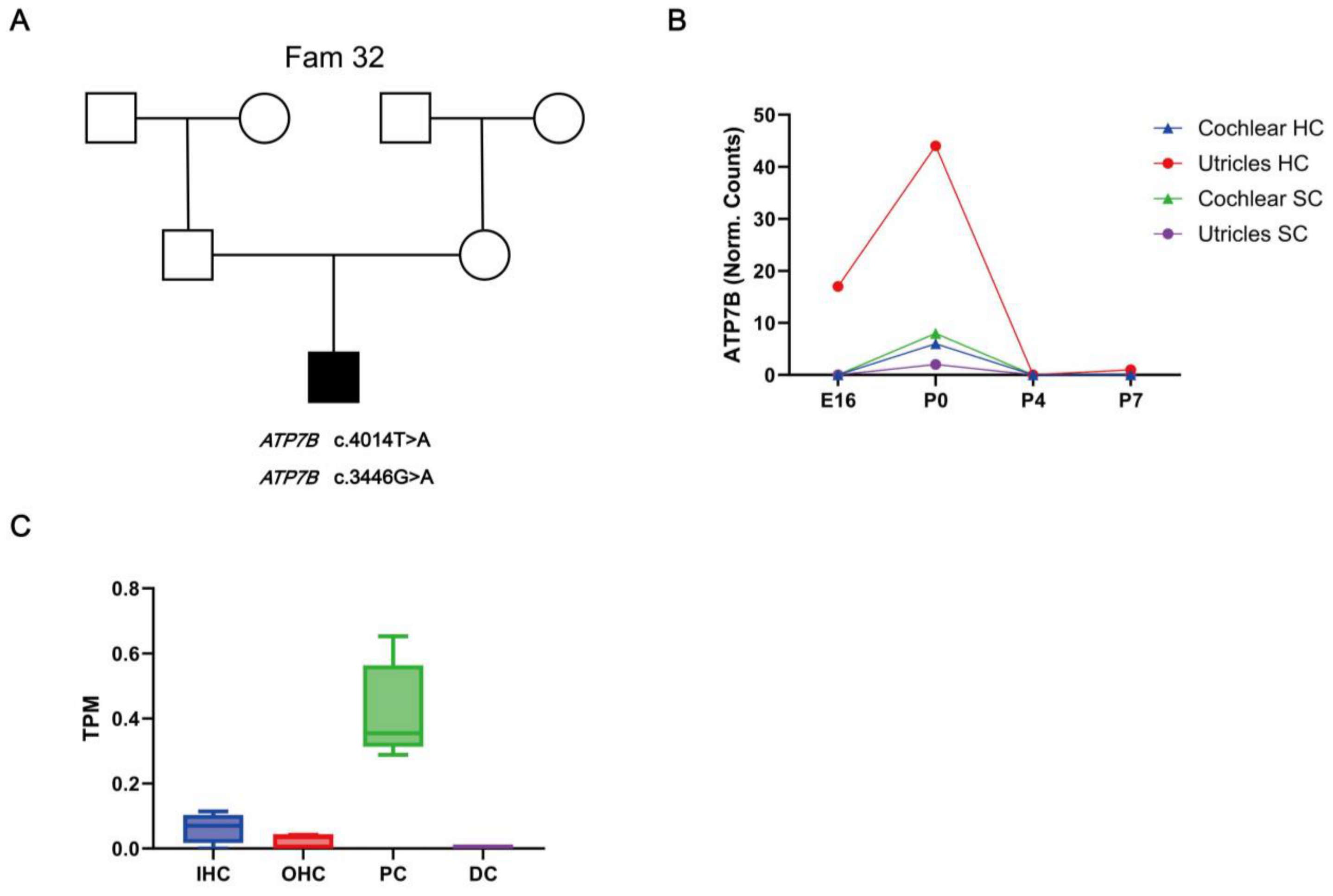
2.3. RNA Expression Profiling of ATP7B in Mice Cochlear Tissues
2.4. Immunofluorescence of ATP7B Expression in Cochlear Tissue
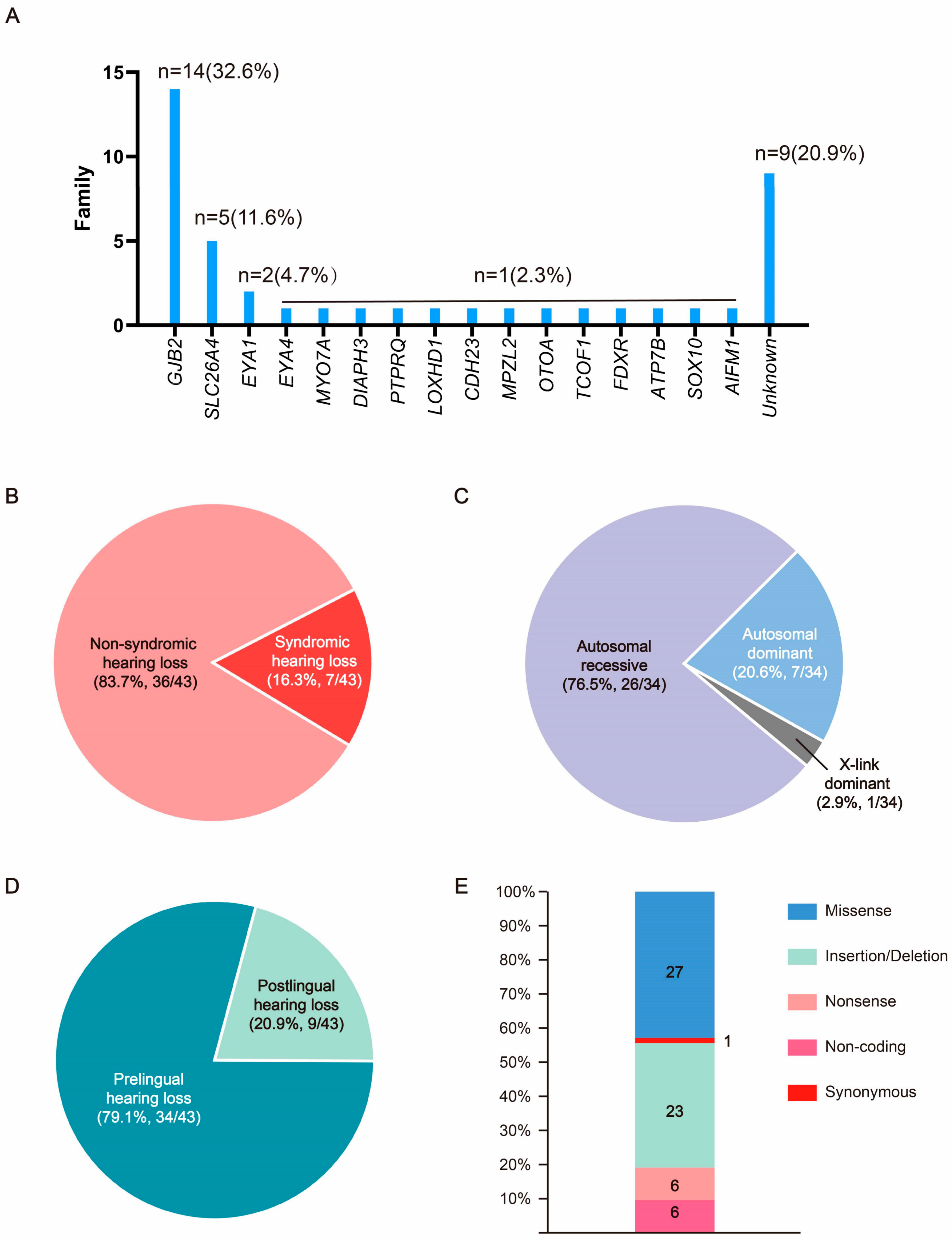
3. Results
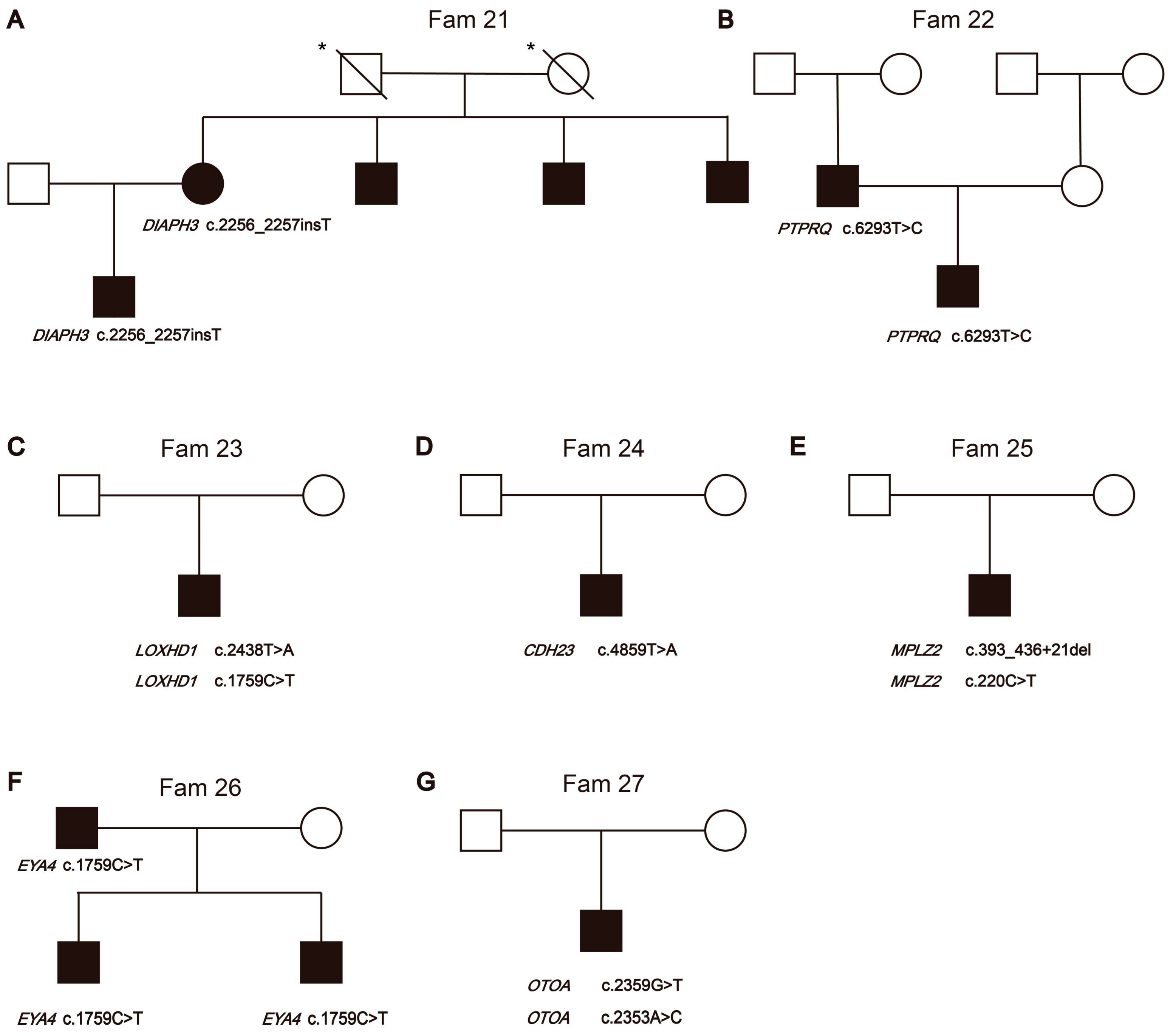
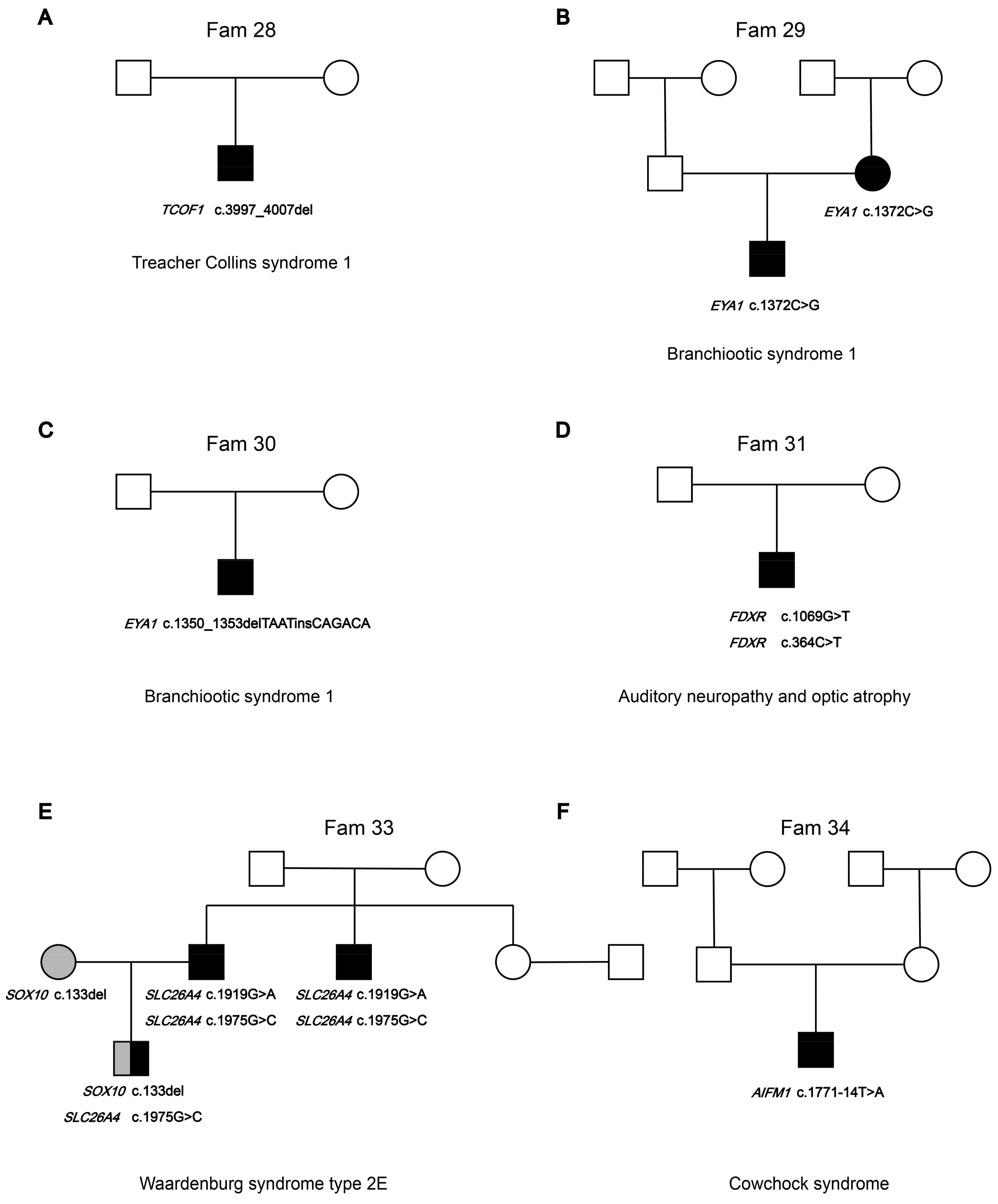
3.1. The Pedigree Analysis of the Families in This Cohort
3.2. Bioinformatic and Molecular Analysis
3.2.1. Non-Syndromic Hearing Loss Gene Variants
3.2.2. Syndromic Hearing Loss Gene Variants
3.2.3. Hearing Loss Candidate Gene Variants
3.3. Expression of HL Candidate Genes ATP7B in the Mouse Inner Ear
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Korver, A.M.H.; Smith, R.J.H.; Van Camp, G.; Schleiss, M.R.; Bitner-Glindzicz, M.A.K.; Lustig, L.R.; Usami, S.-I.; Boudewyns, A.N. Congenital hearing loss. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2017, 3, 16094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, L.L.; Tucci, D.L. Hearing Loss in Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2465–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wonkam, A.; Adadey, S.M.; Schrauwen, I.; Aboagye, E.T.; Wonkam-Tingang, E.; Esoh, K.; Popel, K.; Manyisa, N.; Jonas, M.; Dekock, C.; et al. Exome sequencing of families from Ghana reveals known and candidate hearing impairment genes. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://hereditaryhearingloss.org (accessed on 20 October 2024).
- Jin, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, S.; Xiang, J.; Peng, Z.; Sun, Y. Analysis of the Results of Cytomegalovirus Testing Combined with Genetic Testing in Children with Congenital Hearing Loss. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, P.; Yu, F.; Han, B.; Liu, X.; Wang, G.; Li, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, X.; Huang, D.; Kang, D.; et al. GJB2 mutation spectrum in 2063 Chinese patients with nonsyndromic hearing impairment. J. Transl. Med. 2009, 7, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, P.; Yu, F.; Han, B.; Yuan, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, G.; Liu, X.; He, J.; Huang, D.; Kang, D.; et al. The prevalence of the 235delC GJB2 mutation in a Chinese deaf population. Genet. Med. 2007, 9, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Kim, A.R.; Han, J.H.; Kim, S.D.; Kim, S.H.; Koo, J.-W.; Oh, S.H.; Choi, B.Y. Outcome of Cochlear Implantation in Prelingually Deafened Children According to Molecular Genetic Etiology. Ear Hear. 2017, 38, e316–e324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, R.J.; Walsh, T.; Mandell, J.B.; Aburayyan, A.; Lee, M.K.; Gulsuner, S.; Horn, D.L.; Ou, H.C.; Sie, K.C.Y.; Mancl, L.; et al. Association of Genetic Diagnoses for Childhood-Onset Hearing Loss With Cochlear Implant Outcomes. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2023, 149, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tropitzsch, A.; Schade-Mann, T.; Gamerdinger, P.; Dofek, S.; Schulte, B.; Schulze, M.; Fehr, S.; Biskup, S.; Haack, T.B.; Stöbe, P.; et al. Variability in Cochlear Implantation Outcomes in a Large German Cohort With a Genetic Etiology of Hearing Loss. Ear Hear. 2023, 44, 1464–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivero, R.J.; Fan, K.; Angeli, S.; Balkany, T.J.; Liu, X.Z. Cochlear implantation in common forms of genetic deafness. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2010, 74, 1107–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.-H.; Wu, H.-P.; Wu, C.-M.; Chiang, Y.-T.; Hsu, J.S.; Tsai, C.-Y.; Wang, H.; Tseng, L.-H.; Chen, P.-Y.; Yang, T.-H.; et al. Cochlear Implantation Outcomes in Patients with Auditory Neuropathy Spectrum Disorder of Genetic and Non-Genetic Etiologies: A Multicenter Study. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, G.; Yao, J.; Wu, B.; Liu, T.; Wei, Q.; Liu, C.; Lu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, H.; Yang, X.; et al. Identification of OSBPL2 as a novel candidate gene for progressive nonsyndromic hearing loss by whole-exome sequencing. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, A.; Vuckovic, D.; Krishnamoorthy, N.; Rubinato, E.; Ambrosetti, U.; Castorina, P.; Franzè, A.; Vozzi, D.; La Bianca, M.; Cappellani, S.; et al. Next-generation sequencing identified SPATC1L as a possible candidate gene for both early-onset and age-related hearing loss. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2019, 27, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharadwaj, T.; Schrauwen, I.; Rehman, S.; Liaqat, K.; Acharya, A.; Giese, A.P.J.; Nouel-Saied, L.M.; Nasir, A.; Everard, J.L.; Pollock, L.M.; et al. ADAMTS1, MPDZ, MVD, and SEZ6: Candidate genes for autosomal recessive nonsyndromic hearing impairment. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2022, 30, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Liang, Y.; Huang, B.; Sun, J.; Chen, K. Report of rare and novel mutations in candidate genes in a cohort of hearing-impaired patients. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2022, 10, e1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-Z.; Jin, Y.; Chen, S.; Xu, K.; Xie, L.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, X.-H.; Sun, Y.; Kong, W.-J. F-Actin Dysplasia Involved in Organ of Corti Deformity in Gjb2 Knockdown Mouse Model. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 14, 808553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Xiong, Y.; Gu, X.; Zeng, S.; Chen, W. Research progress in delineating the pathological mechanisms of GJB2-related hearing loss. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1208406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Jin, Y.; Song, N.; Chen, S.; Shen, J.; Xie, W.; Sun, X.; Peng, Z.; Sun, Y. Comprehensive genetic testing improves the clinical diagnosis and medical management of pediatric patients with isolated hearing loss. BMC Med. Genom. 2022, 15, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Ma, X.; Lin, K.; Huang, R.; Bi, X.; Ming, C.; Li, L.; Li, X.; Li, G.; Zhao, L.; et al. Genetic screening of a Chinese cohort of children with hearing loss using a next-generation sequencing panel. Hum. Genom. 2023, 17, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Cao, Z.; Su, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cai, R.; Chen, J.; Gao, B.; Han, M.; Li, X.; Zhang, D.; et al. Molecular diagnose of a large hearing loss population from China by targeted genome sequencing. J. Hum. Genet. 2022, 67, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-C.; Tsai, C.-Y.; Lin, Y.-H.; Chen, P.-Y.; Lin, P.-H.; Cheng, Y.-F.; Wu, C.-M.; Lin, Y.-H.; Lee, C.-Y.; Erdenechuluun, J.; et al. Genetic Epidemiology and Clinical Features of Hereditary Hearing Impairment in the Taiwanese Population. Genes 2019, 10, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, P.; Xu, B.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, C.; Chen, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Y. Analysis of GJB2 Gene Mutations in 1330 Deafness Cases of Major Ethnic Groups in Northwest China. Inq. J. Health Care Organ. Provis. Financ. 2022, 59, 469580211055571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Dai, P.; Huang, D.-L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, G.-J.; Zhu, Q.-W.; Liu, X.; Han, D.-Y. Prevalence of GJB2 mutations in Uigur and Han ethnic populations with deafness in Xinjiang region of China. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2007, 87, 2977–2981. [Google Scholar]
- Ohtsuka, A.; Yuge, I.; Kimura, S.; Namba, A.; Abe, S.; Van Laer, L.; Van Camp, G.; Usami, S.-I. GJB2 deafness gene shows a specific spectrum of mutations in Japan, including a frequent founder mutation. Hum. Genet. 2003, 112, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, S.H.; Park, K.; Park, H.-J.; Chun, Y.-M.; Kim, H.-N. Connexin26 mutations associated with nonsyndromic hearing loss. Laryngoscope 2000, 110, 1535–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Chen, S.; Kong, W.; He, M.; Sun, Y. Genotypic and Allelic Frequencies of GJB2 Variants and Features of Hearing Phenotypes in the Chinese Population of the Dongfeng-Tongji Cohort. Genes 2023, 14, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oguchi, T.; Ohtsuka, A.; Hashimoto, S.; Oshima, A.; Abe, S.; Kobayashi, Y.; Nagai, K.; Matsunaga, T.; Iwasaki, S.; Nakagawa, T.; et al. Clinical features of patients with GJB2 (connexin 26) mutations: Severity of hearing loss is correlated with genotypes and protein expression patterns. J. Hum. Genet. 2005, 50, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukada, K.; Nishio, S.; Usami, S.; Deafness Gene Study Consortium. A large cohort study of GJB2 mutations in Japanese hearing loss patients. Clin. Genet. 2010, 78, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-M.; Ko, H.-C.; Tsou, Y.-T.; Lin, Y.-H.; Lin, J.-L.; Chen, C.-K.; Chen, P.-L.; Wu, C.-C. Long-Term Cochlear Implant Outcomes in Children with GJB2 and SLC26A4 Mutations. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Jin, Y.; Xie, L.; Xie, W.; Xu, K.; Qiu, Y.; Bai, X.; Zhang, H.-M.; Liu, X.-Z.; Wang, X.-H.; et al. A Novel Spontaneous Mutation of the SOX10 Gene Associated with Waardenburg Syndrome Type II. Neural Plast. 2020, 2020, 9260807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, S.; Sun, Y.; Kong, W. Nonsyndromic deafness due to compound heterozygous mutation of the CDH23 gene. J. Clin. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2021, 35, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Liu, X.; Zong, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Sun, Y. Novel compound heterozygous variants in MARVELD2 causing autosomal recessive hearing loss in two Chinese families. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2024, 12, e2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Ding, Y.; Hu, Y. Identifications of the novel mutants on MYO7A in a family with non-syndromic hereditary deafness. J. Clin. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2022, 36, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Hu, P.; Yuan, L.; Xiong, W.; Xu, H.; Yi, J.; Yang, Z.; Deng, X.; Guo, Y.; Deng, H. A homozygous MYO7A mutation associated to Usher syndrome and unilateral auditory neuropathy spectrum disorder. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 4241–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Liu, X.-Z.; Xie, L.; Xie, W.; Chen, S.; Sun, Y. Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing Identified Novel Compound Heterozygous Variants in the PTPRQ Gene Causing Autosomal Recessive Hearing Loss in a Chinese Family. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 884522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, Z.; Shi, X.; Zong, Y.; Sun, Y. The Effects of Viral Infections on the Molecular and Signaling Pathways Involved in the Development of the PAOs. Viruses 2024, 16, 1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corriols-Noval, P.; Simón, E.C.L.; Cadiñanos, J.; Diñeiro, M.; Capín, R.; Aguado, R.G.; Marcos, M.C.; Angulo, C.M.; Farpón, R.C. Clinical Impact of Genetic Diagnosis of Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Adults. Otol. Neurotol. 2022, 43, 1125–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloan-Heggen, C.M.; Bierer, A.O.; Shearer, A.E.; Kolbe, D.L.; Nishimura, C.J.; Frees, K.L.; Ephraim, S.S.; Shibata, S.B.; Booth, K.T.; Campbell, C.A.; et al. Comprehensive genetic testing in the clinical evaluation of 1119 patients with hearing loss. Hum. Genet. 2016, 135, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, H.; Yu, L.; Wang, A.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; et al. Next-generation sequencing facilitates genetic diagnosis and improves the management of patients with hearing loss in clinical practice. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2022, 161, 111258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghezzi, D.; Sevrioukova, I.; Invernizzi, F.; Lamperti, C.; Mora, M.; D’Adamo, P.; Novara, F.; Zuffardi, O.; Uziel, G.; Zeviani, M. Severe X-linked mitochondrial encephalomyopathy associated with a mutation in apoptosis-inducing factor. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2010, 86, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooton-Kee, C.R. Therapeutic implications of impaired nuclear receptor function and dysregulated metabolism in Wilson’s disease. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 251, 108529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Ni, W.; Chen, W.-J.; Wan, B.; Zhao, G.-X.; Shi, Z.-Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, N.; Yu, L.; Xu, J.-F.; et al. Spectrum and Classification of ATP7B Variants in a Large Cohort of Chinese Patients with Wilson’s Disease Guides Genetic Diagnosis. Theranostics 2016, 6, 638–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhou, W.; Huang, Y.; Yin, H.; Jin, Y.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, A.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, B. Presumed missense and synonymous mutations in ATP7B gene cause exon skipping in Wilson disease. Liver Int. 2018, 38, 1504–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huster, D.; Kühne, A.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Raines, L.; Jantsch, V.; Noe, J.; Schirrmeister, W.; Sommerer, I.; Sabri, O.; Berr, F.; et al. Diverse functional properties of Wilson disease ATP7B variants. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 947–956.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, C.J.; Yi, F.; Dayuha, R.; Duong, P.; Horslen, S.; Camarata, M.; Coskun, A.K.; Houwen, R.H.J.; Pop, T.L.; Zoller, H.; et al. Direct Measurement of ATP7B Peptides Is Highly Effective in the Diagnosis of Wilson Disease. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 2367–2382.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wungjiranirun, M.; Sharzehi, K. Wilson’s Disease. Semin. Neurol. 2023, 43, 626–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouider-Khouja, N. Wilson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. Park. Relat. Disord. 2009, 15 (Suppl. S3), S126–S129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Xiong, Y.; Hu, Y.; He, H.; Chen, W.; Sun, Y. Next-Generation Sequencing of Chinese Children with Congenital Hearing Loss Reveals Rare and Novel Variants in Known and Candidate Genes. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2657. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122657
Jin Y, Liu X, Zhang Q, Xiong Y, Hu Y, He H, Chen W, Sun Y. Next-Generation Sequencing of Chinese Children with Congenital Hearing Loss Reveals Rare and Novel Variants in Known and Candidate Genes. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(12):2657. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122657
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Yuan, Xiaozhou Liu, Qiong Zhang, Ying Xiong, Yao Hu, Haixia He, Wei Chen, and Yu Sun. 2024. "Next-Generation Sequencing of Chinese Children with Congenital Hearing Loss Reveals Rare and Novel Variants in Known and Candidate Genes" Biomedicines 12, no. 12: 2657. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122657
APA StyleJin, Y., Liu, X., Zhang, Q., Xiong, Y., Hu, Y., He, H., Chen, W., & Sun, Y. (2024). Next-Generation Sequencing of Chinese Children with Congenital Hearing Loss Reveals Rare and Novel Variants in Known and Candidate Genes. Biomedicines, 12(12), 2657. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122657






