Functional Characterization of Two Novel Intron 4 SERPING1 Gene Splice Site Pathogenic Variants in Families with Hereditary Angioedema
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
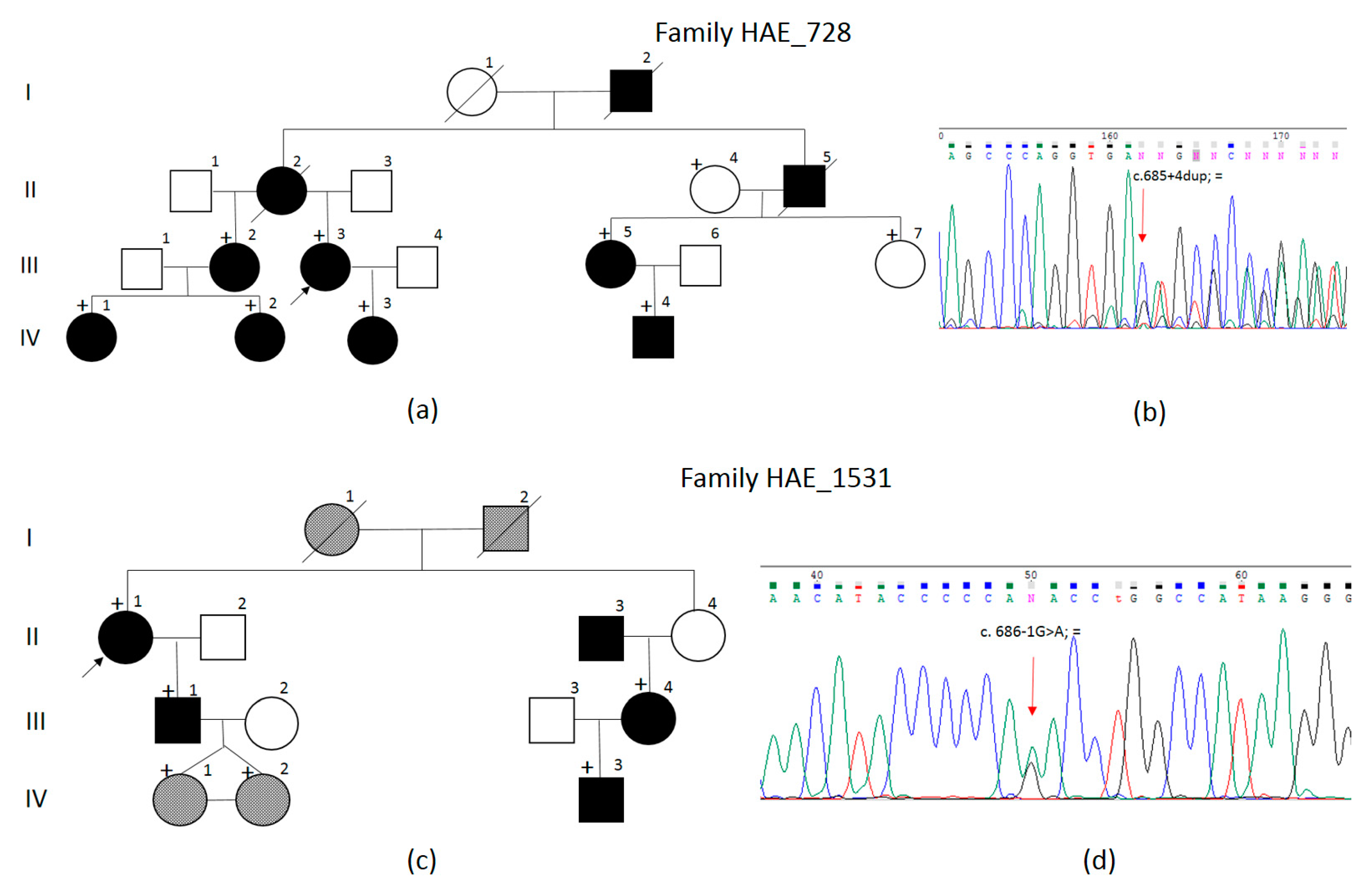
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nzeako, U.C.; Frigas, E.; Tremaine, W.J. Hereditary Angioedema: A Broad Review for Clinicians. Arch. Intern. Med. 2001, 161, 2417–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewald, G.; Bork, K. Missense Mutations in the Coagulation Factor XII (Hageman Factor) Gene in Hereditary Angioedema with Normal C1 Inhibitor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 343, 1286–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bork, K.; Wulff, K.; Steinmüller-Magin, L.; Brænne, I.; Staubach-Renz, P.; Witzke, G.; Hardt, J. Hereditary Angioedema with a Mutation in the Plasminogen Gene. Allergy 2018, 73, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bafunno, V.; Firinu, D.; D’Apolito, M.; Cordisco, G.; Loffredo, S.; Leccese, A.; Bova, M.; Barca, M.P.; Santacroce, R.; Cicardi, M.; et al. Mutation of the Angiopoietin-1 Gene (ANGPT1) Associates with a New Type of Hereditary Angioedema. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ariano, A.; D’Apolito, M.; Bova, M.; Bellanti, F.; Loffredo, S.; D’Andrea, G.; Intrieri, M.; Petraroli, A.; Maffione, A.B.; Spadaro, G.; et al. A Myoferlin Gain-of-Function Variant Associates with a New Type of Hereditary Angioedema. Allergy 2020, 75, 2989–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suffritti, C.; Zanichelli, A.; Maggioni, L.; Bonanni, E.; Cugno, M.; Cicardi, M. High-Molecular-Weight Kininogen Cleavage Correlates with Disease States in the Bradykinin-Mediated Angioedema Due to Hereditary C1-Inhibitor Deficiency. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2014, 44, 1503–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bork, K.; Wulff, K.; Möhl, B.S.; Steinmüller-Magin, L.; Witzke, G.; Hardt, J.; Meinke, P. Novel Hereditary Angioedema Linked with a Heparan Sulfate 3-O-Sulfotransferase 6 Gene Mutation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 148, 1041–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drouet, C.; López-Lera, A.; Ghannam, A.; López-Trascasa, M.; Cichon, S.; Ponard, D.; Parsopoulou, F.; Grombirikova, H.; Freiberger, T.; Rijavec, M.; et al. SERPING1 Variants and C1-INH Biological Function: A Close Relationship with C1-INH-HAE. Front. Allergy 2022, 3, 835503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghebrehiwet, B.; Kaplan, A.P.; Joseph, K.; Peerschke, E.I.B. The Complement and Contact Activation Systems: Partnership in Pathogenesis beyond Angioedema. Immunol. Rev. 2016, 274, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponard, D.; Gaboriaud, C.; Charignon, D.; Ghannam, A.; Wagenaar-Bos, I.G.A.; Roem, D.; López-Lera, A.; López-Trascasa, M.; Tosi, M.; Drouet, C. SERPING1 Mutation Update: Mutation Spectrum and C1 Inhibitor Phenotypes. Hum. Mutat. 2020, 41, 38–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grymová, T.; Grodecká, L.; Souček, P.; Freiberger, T. SERPING1 Exon 3 Splicing Variants Using Alternative Acceptor Splice Sites. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 107, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grombirikova, H.; Bily, V.; Soucek, P.; Kramarek, M.; Hakl, R.; Ballonova, L.; Ravcukova, B.; Ricna, D.; Kozena, K.; Kratochvilova, L.; et al. Systematic Approach Revealed SERPING1 Splicing-Affecting Variants to Be Highly Represented in the Czech National HAE Cohort. J. Clin. Immunol. 2023, 43, 1974–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baralle, D.; Lucassen, A.; Buratti, E. Missed Threads. The Impact of Pre-mRNA Splicing Defects on Clinical Practice. EMBO Rep. 2009, 10, 810–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buratti, E.; Baralle, M.; Baralle, F.E. Defective Splicing, Disease and Therapy: Searching for Master Checkpoints in Exon Definition. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 3494–3510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, L.C.; Whiley, P.J.; Houdayer, C.; Hansen, T.V.O.; Vega, A.; Santamarina, M.; Blanco, A.; Fachal, L.; Southey, M.C.; Lafferty, A.; et al. Evaluation of a 5-Tier Scheme Proposed for Classification of Sequence Variants Using Bioinformatic and Splicing Assay Data: Inter-Reviewer Variability and Promotion of Minimum Reporting Guidelines. Hum. Mutat. 2013, 34, 1424–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grodecká, L.; Hujová, P.; Kramárek, M.; Kršjaková, T.; Kováčová, T.; Vondrášková, K.; Ravčuková, B.; Hrnčířová, K.; Souček, P.; Freiberger, T. Systematic Analysis of Splicing Defects in Selected Primary Immunodeficiencies-Related Genes. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 180, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Francioli, L.C.; Goodrich, J.K.; Collins, R.L.; Kanai, M.; Wang, Q.; Alföldi, J.; Watts, N.A.; Vittal, C.; Gauthier, L.D.; et al. A Genome-Wide Mutational Constraint Map Quantified from Variation in 76,156 Human Genomes. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaganathan, K.; Kyriazopoulou Panagiotopoulou, S.; McRae, J.F.; Darbandi, S.F.; Knowles, D.; Li, Y.I.; Kosmicki, J.A.; Arbelaez, J.; Cui, W.; Schwartz, G.B.; et al. Predicting Splicing from Primary Sequence with Deep Learning. Cell 2019, 176, 535–548.e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Nguyen, T.Y.D.; Cygan, K.J.; Çelik, M.H.; Fairbrother, W.G.; Avsec, Ž.; Gagneur, J. MMSplice: Modular Modeling Improves the Predictions of Genetic Variant Effects on Splicing. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebsgaard, S.M.; Korning, P.G.; Tolstrup, N.; Engelbrecht, J.; Rouzé, P.; Brunak, S. Splice Site Prediction in Arabidopsis thaliana Pre-mRNA by Combining Local and Global Sequence Information. Nucleic Acids Res. 1996, 24, 3439–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leman, R.; Parfait, B.; Vidaud, D.; Girodon, E.; Pacot, L.; Le Gac, G.; Ka, C.; Ferec, C.; Fichou, Y.; Quesnelle, C.; et al. SPiP: Splicing Prediction Pipeline, a Machine Learning Tool for Massive Detection of Exonic and Intronic Variant Effects on mRNA Splicing. Hum Mutat. 2022, 43, 2308–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimura, C.; Kiyohara, C.; Fukushi, J.-I.; Hirose, T.; Ohsawa, I.; Tahira, T.; Horiuchi, T. Clinical and Genetic Features of Hereditary Angioedema with and without C1-Inhibitor (C1-INH) Deficiency in Japan. Allergy 2021, 76, 3529–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harigaya, Y.; Parker, R. No-Go Decay: A Quality Control Mechanism for RNA in Translation. WIREs RNA 2010, 1, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ando, T.; Torii, R.; Kazuta, T.; Endo, T.; Araki, A.; Horiuchi, T.; Terao, S.; Katsuno, M. Hereditary Angioedema Type 1 with Recurrent Dizziness. Intern. Med. 2019, 58, 1961–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roche, O.; Blanch, A.; Duponchel, C.; Fontán, G.; Tosi, M.; López-Trascasa, M. Hereditary Angioedema: The Mutation Spectrum of SERPING1/C1NH in a Large Spanish Cohort. Hum. Mutat. 2005, 26, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gösswein, T.; Kocot, A.; Emmert, G.; Kreuz, W.; Martinez-Saguer, I.; Aygören-Pürsün, E.; Rusicke, E.; Bork, K.; Oldenburg, J.; Müller, C.R. Mutational Spectrum of the C1INH (SERPING1) Gene in Patients with Hereditary Angioedema. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2008, 121, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Human Gene Mutation Database|QIAGEN Digital Insights. Bioinformatics Software|QIAGEN Digital Insights. Available online: https://www.hgmd.cf.ac.uk/ (accessed on 19 December 2023).
- Pappalardo, E.; Caccia, S.; Suffritti, C.; Tordai, A.; Zingale, L.C.; Cicardi, M. Mutation Screening of C1 Inhibitor Gene in 108 Unrelated Families with Hereditary Angioedema: Functional and Structural Correlates. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 3536–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colobran, R.; Lois, S.; de la Cruz, X.; Pujol-Borrell, R.; Hernández-González, M.; Guilarte, M. Identification and Characterization of a Novel Splice Site Mutation in the SERPING1 Gene in a Family with Hereditary Angioedema. Clin. Immunol. 2014, 150, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| cDNA Variant | Functional Proof | In Vitro Effect | In Silico Effect (SpliceAI (ΔScore)) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| c.685+1G>T | no | Skipping of exon 4 (1); Shortening of exon 4 by 36 bp (0.71) | [28] | |
| c.685+1G>A | no | Skipping of exon 4 (1); Shortening of exon 4 by 36 bp (0.68) | [26] | |
| c.685+1del | MGA *, BDR * | MGA: skipping of exon 4, activation of cryptic intronic sites. BDR: skipping of exon 4 and exons 4–5 | Skipping of exon 4 (1); Shortening of exon 4 by 1 bp (NMD) (0.68) | [16] |
| c.685+2T>G | no | Skipping of exon 4 (0.99); Shortening of exon 4 by 36 bp (0.74) | [28] | |
| c.685+2T>A | BDR | Skipping of exon 4. Decrease in the expression of the aberrant transcript due to NGD * | Skipping of exon 4 (1); Shortening of exon 4 by 36 bp (0.62) | [29] |
| c.685+2_685+13del | MGA, BDR | MGA: skipping of exon 4, activation of cryptic intronic sites. BDR: skipping of exon 4 and exons 4–6 | Skipping of exon 4 (1); Shortening of exon 4 by 36 bp (0.56) | [16] |
| c.685+4dup | BDR | BDR: exon 4 shortened by 36 bp. Decrease in the expression of the aberrant transcript due to NGD | Skipping of exon 4 (0.03); Shortening of exon 4 by 36 bp (0.19) | [this study] |
| c.685+5G>A | no | Skipping of exon 4 (0.04); Shortening of exon 4 by 36 bp (0.20) | [10] | |
| c.685+5G>T | no | Skipping of exon 4 (0.04); Shortening of exon 4 by 36 bp (0.20) | [10] | |
| c.685+31G>A | no | No effect | [6] | |
| c.686-7C>G | BDR | Activation of the cryptic intronic site, inclusion of 2 amino acid residues (+6 nucleotides) | Skipping of exon 5 (0.92); Elongation of exon 5 by 6 bp (0.99) | [12,25] |
| c.686-12A>G | MGA | Activation of the intronic cryptic site, elongation by 11 nucleotides, NMD * | Skipping of exon 5 (0.71); Elongation of exon 5 by 11 bp (0.94) | [16] |
| c.686-1G>A | BDR | Skipping of exon 5 | Skipping of exon 5 (0.97); Shortening of exon 5 by 1 bp (0.60) | [this study] |
| c.686-1G>T | no | Skipping of exon 5 (0.96); Shortening of exon 5 by 1 bp (0.66) | [22] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shchagina, O.; Gracheva, E.; Chukhrova, A.; Bliznets, E.; Bychkov, I.; Kutsev, S.; Polyakov, A. Functional Characterization of Two Novel Intron 4 SERPING1 Gene Splice Site Pathogenic Variants in Families with Hereditary Angioedema. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12010072
Shchagina O, Gracheva E, Chukhrova A, Bliznets E, Bychkov I, Kutsev S, Polyakov A. Functional Characterization of Two Novel Intron 4 SERPING1 Gene Splice Site Pathogenic Variants in Families with Hereditary Angioedema. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(1):72. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12010072
Chicago/Turabian StyleShchagina, Olga, Elena Gracheva, Alyona Chukhrova, Elena Bliznets, Igor Bychkov, Sergey Kutsev, and Aleksander Polyakov. 2024. "Functional Characterization of Two Novel Intron 4 SERPING1 Gene Splice Site Pathogenic Variants in Families with Hereditary Angioedema" Biomedicines 12, no. 1: 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12010072
APA StyleShchagina, O., Gracheva, E., Chukhrova, A., Bliznets, E., Bychkov, I., Kutsev, S., & Polyakov, A. (2024). Functional Characterization of Two Novel Intron 4 SERPING1 Gene Splice Site Pathogenic Variants in Families with Hereditary Angioedema. Biomedicines, 12(1), 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12010072








