Integrating Chinese Herbs and Western Medicine for New Wound Dressings Through Handheld Electrospinning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Precursor Solutions
2.3. Preparation of YB-CIP Beaded Fiber by Electrospinning
2.4. Characterization
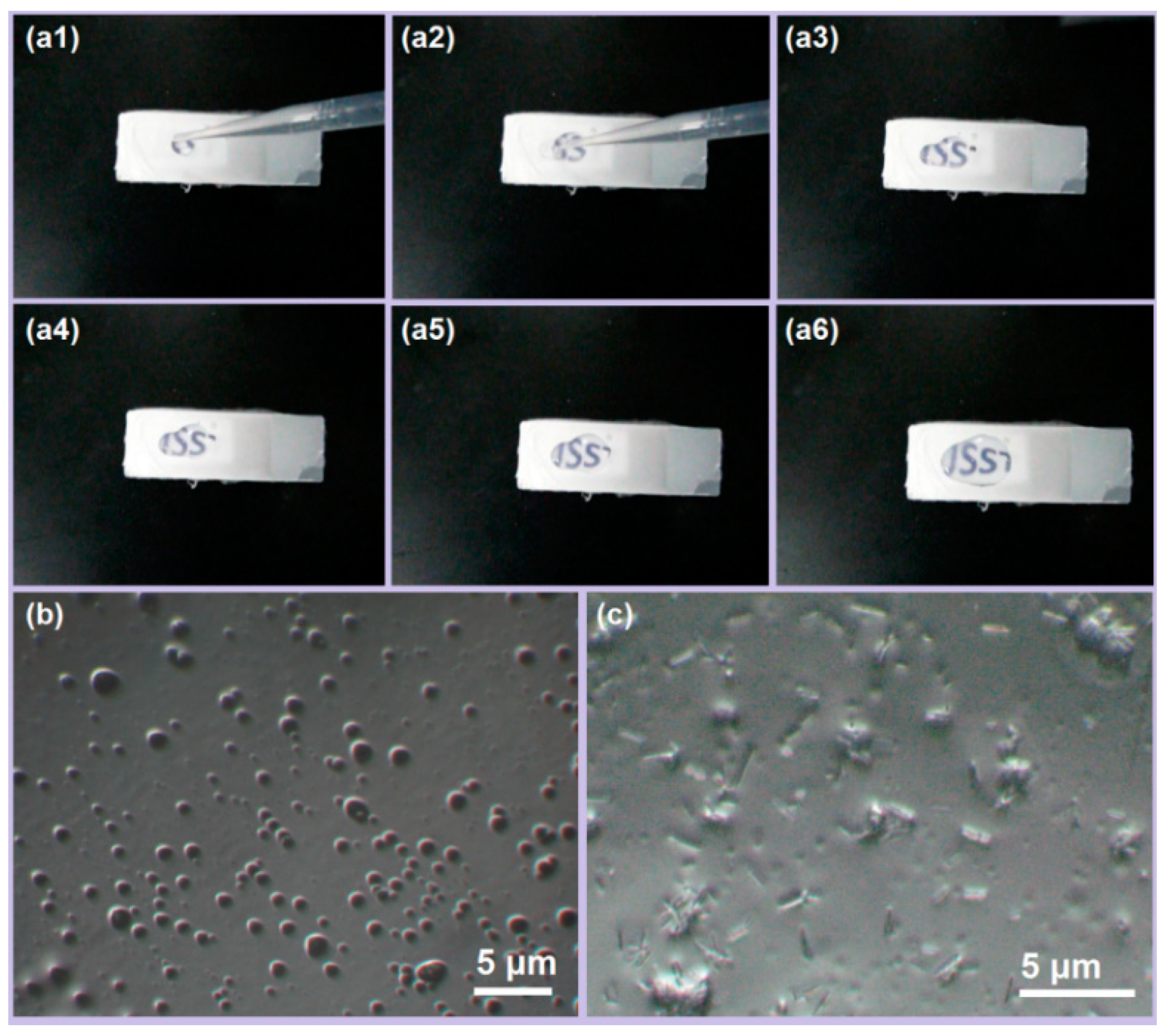
2.4.1. Analysis of Morphology
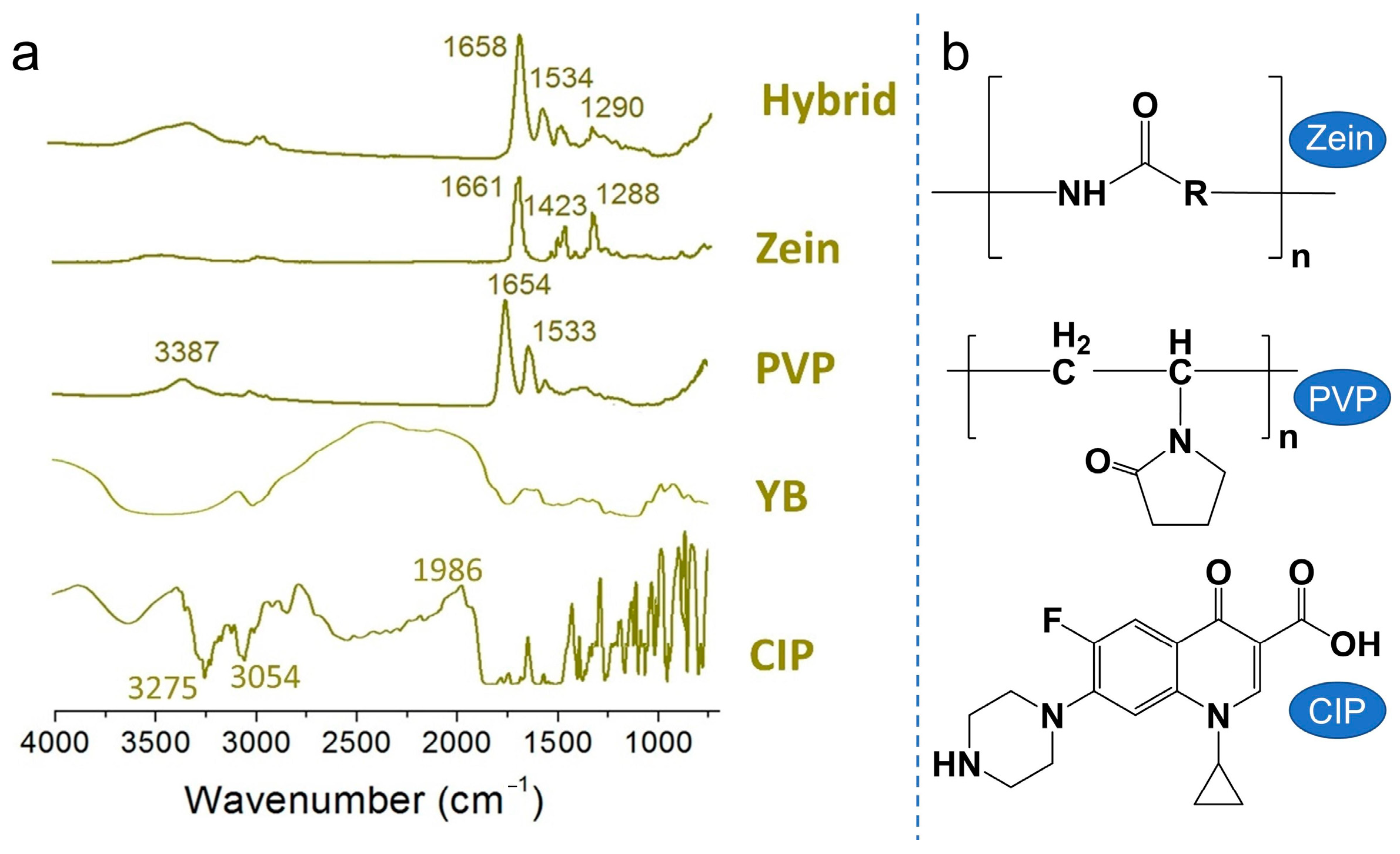
2.4.2. XRD and FTIR Analysis
2.5. Fast Dissolution Performance
2.6. In Vitro Drug Release
2.7. Antibacterial Performances of Nanofibers
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and discussion
3.1. The Sequential EHDA Process
3.2. Morphology of Product
3.3. Physical State and Compatibility of Components
3.4. Rapid Disintegration of YB-CIP Beaded Nanofiber Membrane
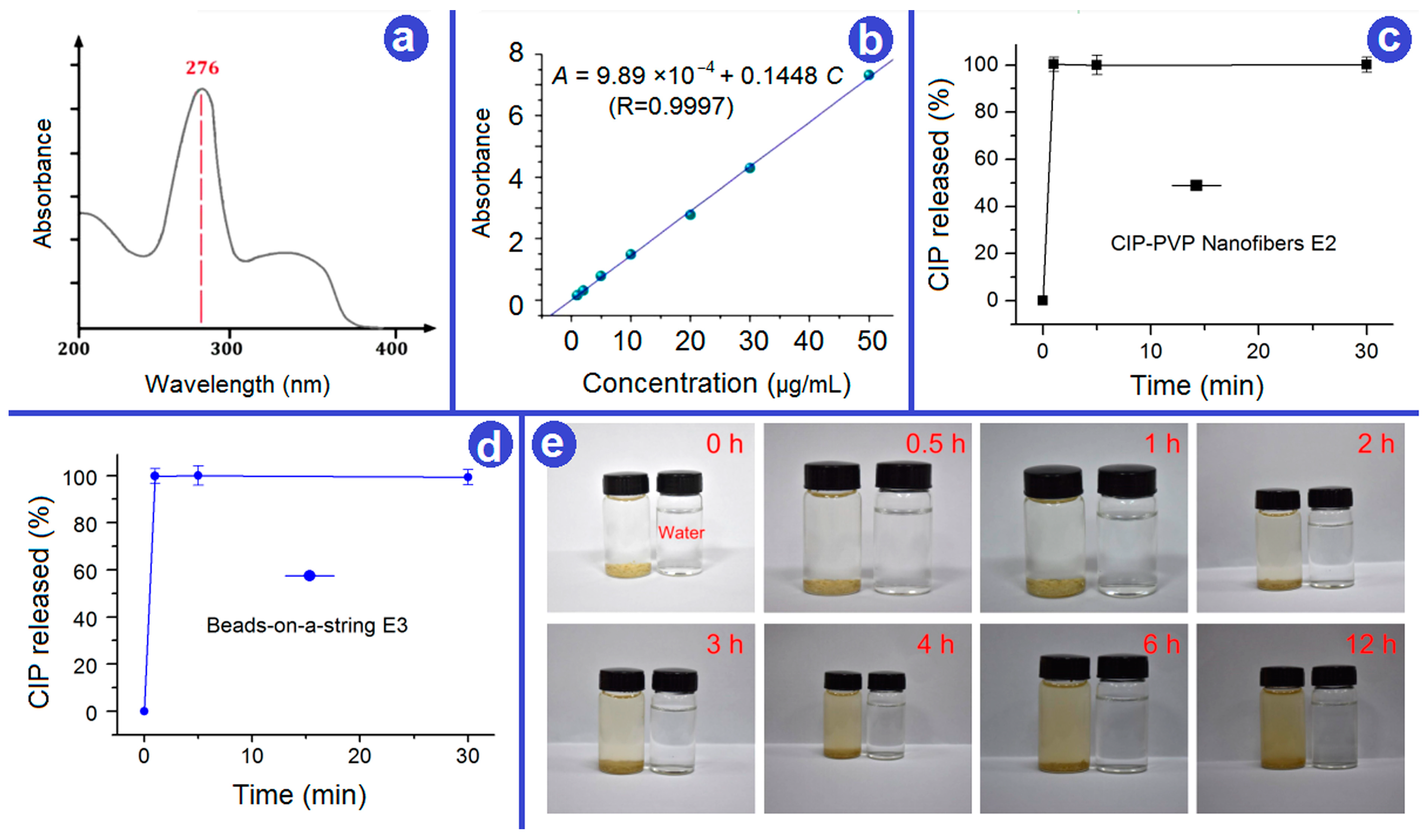
3.5. In Vitro Drug Release
3.6. Analysis of Antibacterial Performances
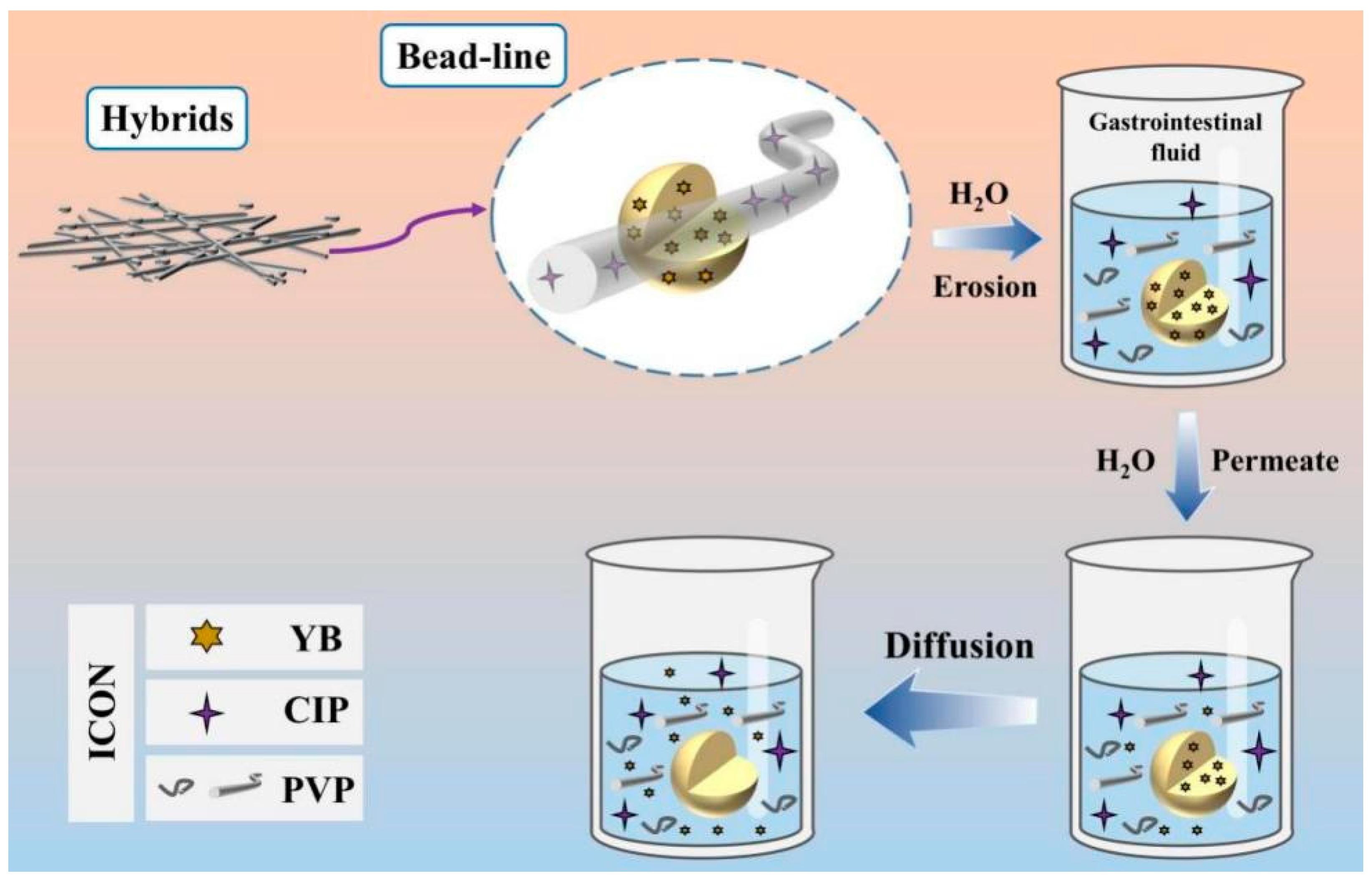
3.7. Release Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tung, N.-T.; Dong, T.-H.-Y.; Tran, C.-S.; Nguyen, T.-K.-T.; Chi, S.-C.; Dao, D.-S.; Nguyen, D.-H. Integration of lornoxicam nanocrystals into hydroxypropyl methylcellulose-based sustained release matrix to form a novel biphasic release system. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 209, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adala, I.; Ramis, J.; Ntone Moussinga, C.; Janowski, I.; Amer, M.H.; Bennett, A.J.; Alexander, C.; Rose, F.R.A.J. Mixed polymer and bioconjugate core/shell electrospun fibers for biphasic protein release. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 4120–4133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conceicao, J.; Adeoye, O.; Cabral-Marques, H.; Concheiro, A.; Alvarez-Lorenzo, C.; Sousa Lobo, J.M. Carbamazepine bilayer tablets combining hydrophilic and hydrophobic cyclodextrins as a quick/slow biphasic release system. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 101611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Dong, Y.; Shen, Y.; Hou, A.; Quan, G.; Pan, X.; Wu, C. Bilayer dissolving microneedle array containing 5-fluorouracil and triamcinolone with biphasic release profile for hypertrophic scar therapy. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 2400–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Yu, W.; Qian, X.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Ji, J. Dissolving microneedles with a biphasic release of antibacterial agent and growth factor to promote wound healing. Biomater. Sci. 2022, 10, 2409–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabakoglu, S.; Kolbuk, D.; Sajkiewicz, P. Multifluid electrospinning for multi-drug delivery systems: Pros and cons, challenges, and future directions. Biomater. Sci. 2022, 11, 37–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, A.; Rehman, T.U.; Rehan, Z.A.; Noreen, R.; Iqbal, S.; Batool, S.; Qayyum, M.A.; Ahmed, T.; Farooq, T. Development of polymeric nanofibers blended with extract of neem (azadirachta indica), for potential biomedical applications. Front. Mater. 2022, 9, 1042304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brimo, N.; Serdaroglu, D.C.; Uysal, B. Comparing antibiotic pastes with electrospun nanofibers as modern drug delivery systems for regenerative endodontics. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2022, 19, 904–917. [Google Scholar]
- Kuang, G.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhou, D.; Lu, X.; Jing, X.; Huang, Y. Biphasic drug release from electrospun polyblend nanofibers for optimized local cancer treatment. Biomater. Sci. 2018, 6, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Ge, R.L.; Zhang, F.; Yu, D.G.; Liu, Z.P.; Li, X.; Shen, H.; Williams, G.R. Electrospun fibers with blank surface and inner drug gradient for improving sustained release. Biomater. Adv. 2023, 150, 213404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Xu, G.; Kharaghani, D.; Nishino, M.; Song, K.H.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, I.S. Electrospun tri-layered zein/PVP-GO/zein nanofiber mats for providing biphasic drug release profiles. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 531, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalek, M.A.A.; Gaber, S.A.A.; El-Domany, R.A.; El-Kemary, M.A. Photoactive electrospun cellulose acetate/polyethylene oxide/methylene blue and trilayered cellulose acetate/polyethylene oxide/silk fibroin/ciprofloxacin nanofibers for chronic wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 193, 1752–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejeta, F.; Gabriel, T.; Joseph, N.M.; Belete, A. Formulation, optimization and in vitro evaluation of fast disintegrating tablets of salbutamol sulphate using a combination of superdisintegrant and subliming agent. Curr. Drug Delivery 2022, 19, 129–141. [Google Scholar]
- Kose, M.D.; Ungun, N.; Bayraktar, O. Eggshell membrane based turmeric extract loaded orally disintegrating films. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2022, 19, 547–559. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.-F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Pan, B.; Liu, M.-L. Ciprofloxacin derivatives and their antibacterial activities. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 146, 599–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, H.; Wang, P.; Cong, Y.; Dong, W.; Li, L. Preparation of ciprofloxacin-based carbon dots with high antibacterial activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, C.-T.; Wang, Z.J.; Chow, M.S.S.; Lam, C.W.K. Herb-herb combination for therapeutic enhancement and advancement: Theory, practice and future perspectives. Molecules 2013, 18, 5125–5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallmann, E.; Sabała, P. Organic and conventional herbs quality reflected by their antioxidant compounds concentration. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, N.; Yang, Z. (Eds.) Novel Drug Delivery Systems for Chinese Medicines; Springer: Singapore, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Feng, C. Chiral fiber supramolecular hydrogels for tissue engineering. Wires. Nanomed. Nanobi. 2023, 15, e1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Bai, Z.; Huang, S.; Jiang, K.; Liu, L.; Wang, X. The effect of angiogenesis-based scaffold of mesoporousbioactive glass nanofiber on osteogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guadagno, L.; Raimondo, M.; Vertuccio, L.; Lamparelli, E.P.; Ciardulli, M.C.; Longo, P.; Mariconda, A.; Della Porta, G.; Longo, R. Electrospun membranes designed for burst release of new gold-complexes inducing apoptosis of melanoma cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Ossa, J.G.; Danti, S.; Salsano, J.E.; Azimi, B.; Tempesti, V.; Barbani, N.; Digiacomo, M.; Macchia, M.; Uddin, M.J.; Cristallini, C.; et al. Electrospun poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate)/olive leaf extract fiber mesh as prospective bio-based scaffold for wound healing. Molecules 2022, 27, 6208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Feng, N. Application of nmp and neusilin US2-integrated liquisolid technique in mini-tablets for improving the physical performances and oral bioavailability of liposoluble supercritical fluid extracts. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 81, 104205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xia, Q.; Wu, T.; He, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Hou, X.; He, Y.; Ruan, S.; Wang, Z.; et al. A novel multi-functionalized multicellular nanodelivery system for non-small cell lung cancer photochemotherapy. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Q.; Ruan, H.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Pei, L.; Hu, H.; He, Z.; Wu, T.; Ruan, S.; Guo, T.; et al. Keratinocyte membrane-mediated nanodelivery system with dissolving microneedles for targeted therapy of skin diseases. Biomaterials 2021, 278, 121142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, I.S. A review of sustained drug release studies from nanofiber hydrogels. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malekmohammadi, S.; Sedghi Aminabad, N.; Sabzi, A.; Zarebkohan, A.; Razavi, M.; Vosough, M.; Bodaghi, M.; Maleki, H. Smart and biomimetic 3D and 4D printed composite hydrogels: Opportunities for different biomedical applications. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javed, B.; Zhao, X.; Cui, D.; Curtin, J.; Tian, F. Enhanced anticancer response of curcumin- and piperine-loaded lignin-g-p (NIPAM-co-DMAEMA) gold nanogels against U-251 MG glioblastoma multiforme. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Feng, C. Aniline dimers serving as stable and efficient transfer units for intermolecular charge-carrier transmission. iScience 2023, 26, 105762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleemardani, M.; Zare, P.; Seifalian, A.; Bagher, Z.; Seifalian, A.M. Graphene-based materials prove to be a promising candidate for nerve regeneration following peripheral nerve injury. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Hou, J.; Yu, D.G.; Li, S.; Zhu, J.; Chen, Z. Electrospun tri-layer nanodepots for sustained release of acyclovir. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 846, 156471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.-F.; Zhu, L.-F.; Liu, J.; Ali, A.; Zaman, A.; Ahmad, Z.; Chen, X.; Chang, M.-W. Novel core-shell fiber delivery system for synergistic treatment of cervical cancer. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 59, 101865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, Z.I.; Topuz, F.; Kilic, M.E.; Durgun, E.; Uyar, T. Encapsulation of antioxidant beta-carotene by cyclodextrin complex electrospun nanofibers: Solubilization and stabilization of beta-carotene by cyclodextrins. Food Chem. 2023, 423, 136284. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Yu, X.; Cui, J.; Yu, F.; Liu, M.; Chen, Y.; Wu, J.; Sun, B.; Mo, X. Development of biodegradable polymeric stents for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.-C.; Zhang, C.; Ahmad, Z.; Huang, J.; Li, J.-S.; Chang, M.-W. Designer fibers from 2D to 3D-simultaneous and controlled engineering of morphology, shape and size. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, P.; Yu, D.-G.; Zhu, Y. Biphasic drug release from electrospun structures. Exp. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2023, 20, 621–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Dai, Y.; Fu, J.; Yan, C.; Yu, D.-G.; Yi, T. Dual-step controlled release of berberine hydrochloride from the trans-scale hybrids of nanofibers and microparticles. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaeei, S.; Mansurian, M.; Asare-Addo, K.; Nokhodchi, A. Metronidazole-and amoxicillin-loaded PLGA and PCL nanofibers as potential drug delivery systems for the treatment of periodontitis: In vitro and in vivo evaluations. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, Q.; Gao, J.; He, J.; Zhang, H.; Ding, J. Stereo coverage and overall stiffness of biomaterial arrays underly parts of topography effects on cell adhesion. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 6142–6155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Geng, C.; Shen, H.; Zhang, Q.; Miao, Y.; Wu, J.; Ouyang, R.; Zhou, S. Two hawks with one arrow: A review on bifunctional scaffolds for photothermal therapy and bone regeneration. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Q.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Silva, D.Z.; Ruiz, M.E.L.; Ouyang, R.; Liu, B.; Miao, Y. Recent development of rhenium-based materials in the application of diagnosis and tumor therapy. Molecules 2023, 28, 2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivan, M.; Madheswaran, D.; Hauzerova, S.; Novotny, V.; Hedvicakova, V.; Jencova, V.; Kostakova, E.K.; Schindler, M.; Lukas, D. AC electrospinning: Impact of high voltage and solvent on the electrospinnability and productivity of polycaprolactone electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds. Mater. Today Chem. 2022, 26, 101025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ahmad, Z.; Huang, J.; Li, J.-S.; Chang, M.-W. Multi-compartment centrifugal electrospinning based composite fibers. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 330, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Liu, Y.; Bai, Y.; Shi, H.; Zhou, W.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yu, D.-G. Recent combinations of electrospinning with photocatalytic technology for treating polluted water. Catalysts 2023, 13, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, A.F.; Favretto, M.; Paquis, R.; Estevinho, B.N. Co-encapsulation of epigallocatechin-3-Gallate and vitamin B12 in zein microstructures by electrospinning/electrospraying technique. Molecules 2023, 28, 2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Yang, Z.; Kang, S.; Yu, D.-G.; Chen, X.; Shao, J. A sequential electrospinning of a coaxial and blending process for creating double-layer hybrid films to sense glucose. Sensors 2023, 23, 3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guler, E.; Nur Hazar-Yavuz, A.; Tatar, E.; Morid Haidari, M.; Sinemcan Ozcan, G.; Duruksu, G.; Graça, M.P.F.; Kalaskar, D.M.; Gunduz, O.; Emin Cam, M. Oral empagliflozin-loaded tri-layer core-sheath fibers fabricated using tri-axial electrospinning: Enhanced in vitro and in vivo antidiabetic performance. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 635, 122716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Sun, C.; Lin, H.; Li, G.; Lian, Z.; Song, R.; Zhuang, S.; Zhang, D. Electrospun bi-decorated BixBiyOz/TiO2 flexible carbon nanofibers and their applications on degradating of organic pollutants under solar radiation. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 150, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, Z.; Chen, Y.; Huang, J.; Lei, Z.; Qian, X.; Lai, Y.; Zhang, S. A quadruple biomimetic hydrophilic/hydrophobic janus composite material integrating Cu(OH)2 micro-needles and embedded bead-on-string nanofiber membrane for efficient fog harvesting. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 455, 140863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.-G.; Xu, L. Impact evaluations of articles in current drug delivery based on web of science. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2023, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhong, M.; Song, N.; Wang, C.; Lu, X. General synthesis of pt and ni co-doped porous carbon nanofibers to boost HER performance in both acidic and alkaline solutions. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2023, 34, 107359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.-C.; Yuan, Q.; Ahmad, Z.; Huang, J.; Li, J.-S.; Chang, M.-W. Controlled morphing of microbubbles to beaded nanofibers via electrically forced thin film stretching. Polymers 2017, 9, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Yu, J.; Li, Z.; Ding, B. Self-healing fibrous membranes. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2022, 61, e202208949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Song, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Lu, X.; Wang, C. Electrospun nanofibers: Current progress and applications in food systems. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2022, 70, 1391–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, D.-G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.-N. Progress of electrospun nanofibrous carriers for modifications to drug release profiles. J. Func. Biomater. 2022, 13, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Lu, Y.; Yang, H.; Yu, D.-G.; Lu, X. The influence of the ultrasonic treatment of working fluids on electrospun amorphous solid dispersions. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023, 10, 1184767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.; Hou, S.; Chen, X.; Yu, D.-G.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Williams, R.G. Energy-saving electrospinning with a concentric teflon-core rod spinneret to create medicated nanofibers. Polymers 2020, 12, 2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Jiang, W.; Zhou, J.; Yu, D.-G.; Liu, H. The applications of ferulic-acid-loaded fibrous films for fruit preservation. Polymers 2022, 14, 4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.G.; Rajan, T.P. A review on electrospinning of natural bio herbs blended with polyvinyl alcohol nanofibres for biomedical applications. J. Nat. Fibers 2022, 19, 11984–12003. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Li, X.; Liu, P.; Zhang, M.; Wang, C.; Zhang, B. Multifunctional chitosan/polycaprolactone nanofiber scaffolds with varied dual-drug release for wound-healing applications. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 4666–4676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraiva, M.M.; Campelo, M.D.S.; Câmara Neto, J.F.; Lima, A.B.N.; Silva, G.D.A.; Dias, A.T.D.F.F.; Ricardo, N.M.P.S.; Kaplan, D.L.; Ribeiro, M.E.N.P. Alginate/polyvinyl alcohol films for wound healing: Advantages and challenges. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2023, 111, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajalli, N.; Pourmadadi, M.; Yazdian, F.; Abdouss, M.; Rashedi, H.; Rahdar, A. PVA Based Nanofiber Containing GO Modified with Cu Nanoparticles and Loaded Curcumin; High Antibacterial Activity with Acceleration Wound Healing. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2023, 20, 1569–1583. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grosu, O.-M.; Dragostin, O.-M.; Gardikiotis, I.; Chitescu, C.L.; Lisa, E.L.; Zamfir, A.-S.; Confederat, L.; Dragostin, I.; Dragan, M.; Stan, C.D.; et al. Experimentally Induced Burns in Rats Treated with Innovative Polymeric Films Type Therapies. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.; Thanki, A.; Viradia, D.; Shah, P.A. Honey-based Silver Sulfadiazine Microsponge-Loaded Hydrogel: In vitro and In vivo Evaluation for Burn Wound Healing. Curr. Drug. Deliv. 2023, 20, 608–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alosaimi, A.M.; Alorabi, R.O.; Katowah, D.F.; Al-Thagafi, Z.T.; Alsolami, E.S.; Hussein, M.A.; Qutob, M.; Rafatullah, M. Recent biomedical applications of coupling nanocomposite polymeric materials reinforced with variable carbon nanofillers. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deineka, V.; Sulaieva, O.; Pernakov, M.; Korniienko, V.; Husak, Y.; Yanovska, A.; Yusupova, A.; Tkachenko, Y.; Kalinkevich, O.; Zlatska, A.; et al. Hemostatic and tissue regeneration performance of novel electrospun chitosan-based materials. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, N.; Hu, W.; Wang, J. Lignin-based porous biomaterials for medical and pharmaceutical applications. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.-G.; Du, Y.; Chen, J.; Song, W.; Zhou, T. A Correlation Analysis between Undergraduate Students’ Safety Behaviors in the Laboratory and Their Learning Efficiencies. Behav. Sci. 2023, 13, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Zhou, X.; Xiao, B.; Duan, L.; Zhu, Z. Mucus-penetrating silk fibroin-based nanotherapeutics for efficient treatment of ulcerative colitis. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivan, M.; Madheswaran, D.; Valtera, J.; Kostakova, E.K.; Lukas, D. Alternating current electrospinning: The impacts of various high-voltage signal shapes and frequencies on the spinnability and productivity of polycaprolactone nanofibers. Mater. Des. 2022, 213, 110308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Dai, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, P.; Zhou, W.; Yu, D.-G.; Ge, R. Fast and convenient delivery of fluidextracts liquorice through electrospun core-shell nanohybrids. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1172133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Lv, G.; Bu, W. Redox dyshomeostasis strategy for tumor therapy based on nanomaterials chemistry. Chem. Sci. 2022, 13, 2202–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Li, H.; Bu, W. A forward vision for chemodynamic therapy: Issues and opportunities. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202210415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Y.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; Shi, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wu, F.; Jiang, X.; Yang, W.; Zhang, L.; et al. Reactive metal boride nanoparticles trap lipopolysaccharide and peptidoglycan for bacteria-infected wound healing. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, P.K.; Kuppusamy, U.R.; Chua, K.H.; Arumugam, B. Emerging Strategies to Improve the Stability and Bioavailability of Insulin: An Update on Formulations and Delivery Approaches. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2022, 19, 1141–1162. [Google Scholar]
- Assi, S.; El Hajj, H.; Hayar, B.; Pisano, C.; Saad, W.; Darwiche, N. Development and Challenges of Synthetic Retinoid Formulations in Cancer. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2022, 20, 1314–1326. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, D.G.; Huang, C. Electrospun Biomolecule-Based Drug Delivery Systems. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.-G.; Zhao, P. The Key Elements for Biomolecules to Biomaterials and to Bioapplications. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
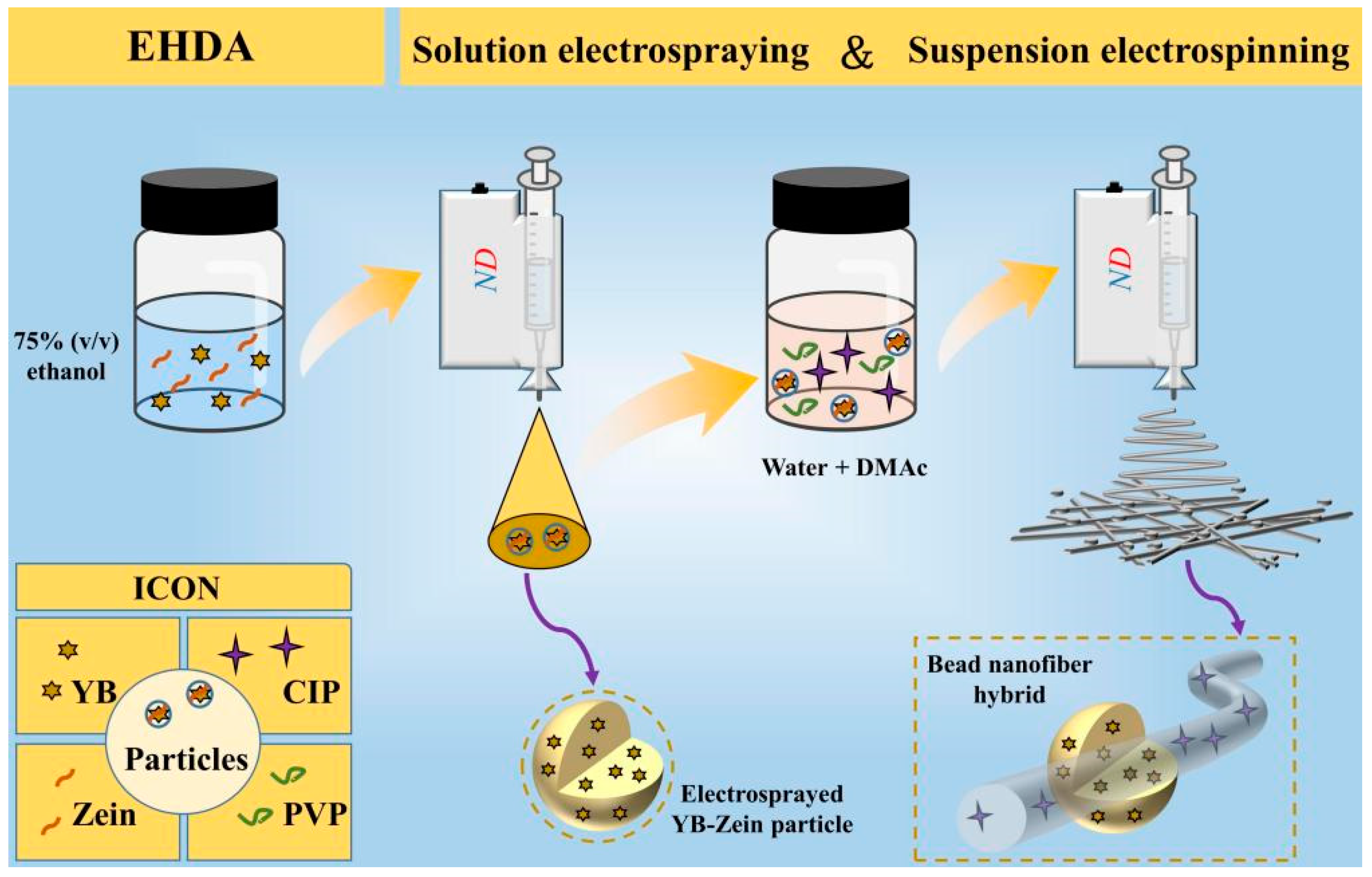

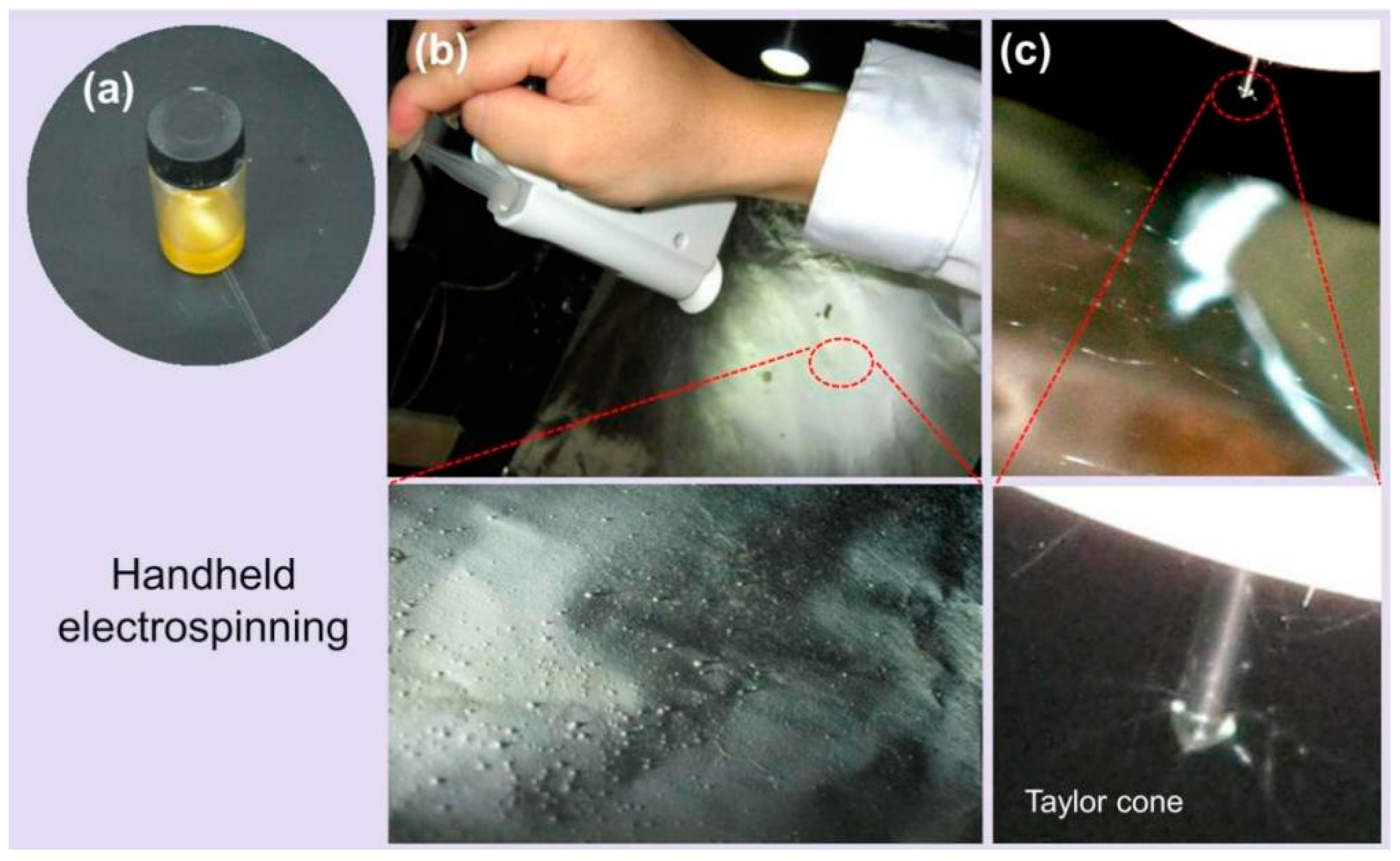
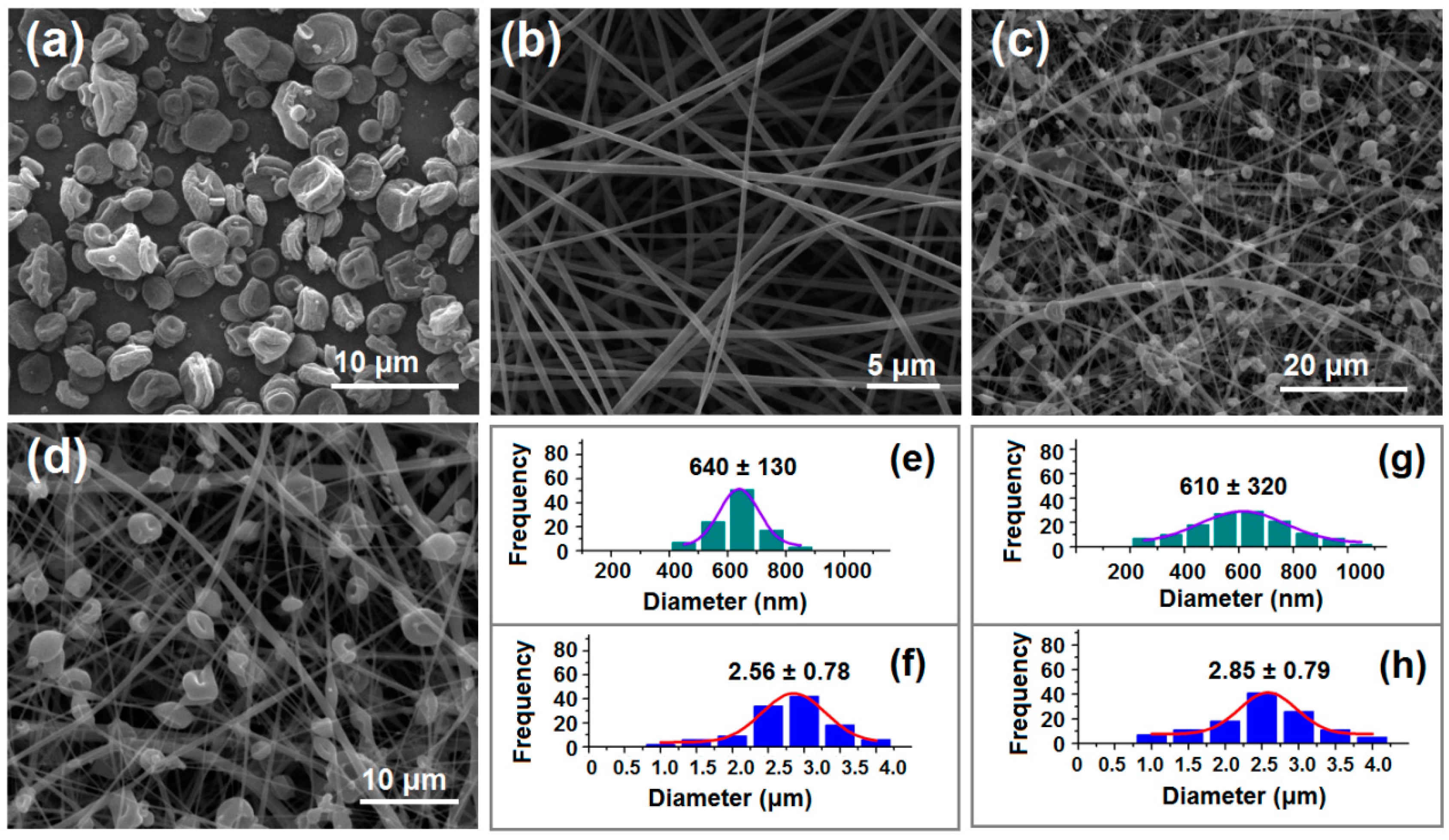
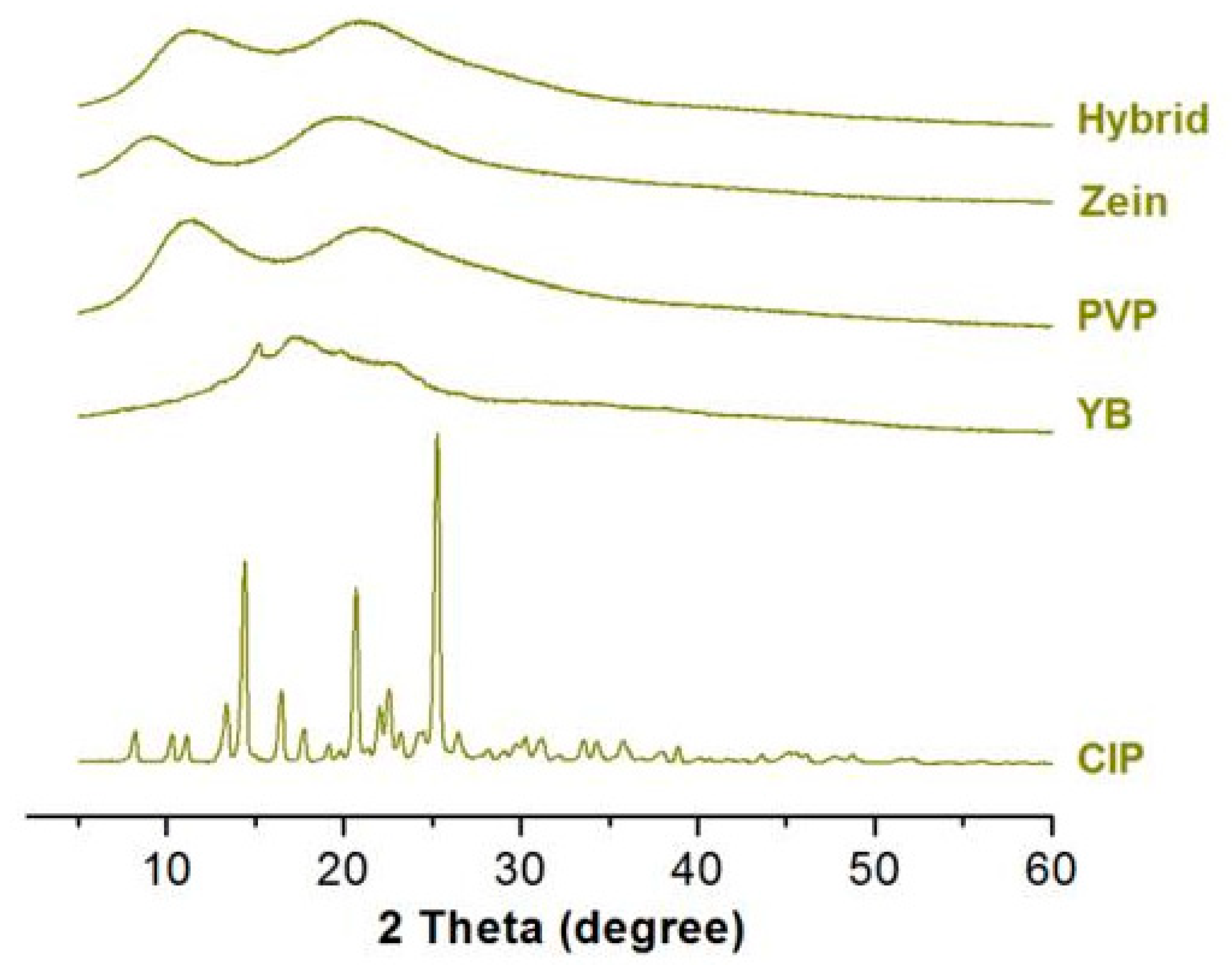

| No. | EHDA Process | Working Fluid | Experimental Conditions | Drug Contents | Morphology | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V (kV) | D (cm) | |||||
| E1 | Electrospraying | Fluid 1 a | 20 | 20 | 20.0% YB | Particles |
| E2 | Electrospinning | Fluid 2 b | Cell | 20 | 20.0% CIP | Fibers |
| E3 | Sequential EHDA process | Fluid 3 c | Cell | 20 | 15% (YB) & 5% (CIP) | Hybrids |
| Bacteria | Samples | Initial CFU | CFU after 2 h | CFU after 6 h | CFU after 12 h |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CFU (ABE%) | CFU (ABE%) | CFU (ABE%) | |||
| Wb800 | YB | 1.5 × 105 | 2.8 × 104 (88.3%) | 1.4 × 104 (98.7%) | 6.7 × 103 (99.9%) |
| E1 | 1.5 × 105 | 4.7 × 104 (80.4%) | 2.4 × 104 (97.8%) | 8.5 × 103 (99.9%) | |
| E2 | 1.5 × 105 | 1.2 × 103 (99.5%) | 2.8 × 102 (>99.9%) | 1.9 × 102 (>99.9%) | |
| E3 | 1.5 × 105 | 2.1 × 104 (91.3%) | 3.6 × 102 (>99.9%) | 2.1 × 102 (>99.9%) | |
| Blank | 1.5 × 105 | 2.4 × 105 | 1.1 × 106 | 7.3 × 106 | |
| Escherichia coli dh5α | YB | 1.5 × 105 | 5.1 × 104 (81.1%) | 2.2 × 104 (98.1%) | 4.7 × 103 (99.9%) |
| E1 | 1.5 × 105 | 7.4 × 104 (72.6%) | 3.5 × 104 (97.1%) | 5.3 × 103 (99.9%) | |
| E2 | 1.5 × 105 | 4.2 × 103 (98.4%) | 8.9 × 102 (>99.9%) | 3.4 × 102 (>99.9%) | |
| E3 | 1.5 × 105 | 7.6 × 103 (97.2%) | 1.3 × 103 (>99.9%) | 5.7 × 102 (>99.9%) | |
| Blank | 1.5 × 105 | 2.7 × 105 | 1.2 × 106 | 8.1 × 106 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, J.; Wang, L.; Gong, W.; Wang, B.; Yu, D.-G.; Zhu, Y. Integrating Chinese Herbs and Western Medicine for New Wound Dressings Through Handheld Electrospinning. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2146. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11082146
Zhou J, Wang L, Gong W, Wang B, Yu D-G, Zhu Y. Integrating Chinese Herbs and Western Medicine for New Wound Dressings Through Handheld Electrospinning. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(8):2146. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11082146
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Jianfeng, Liangzhe Wang, Wenjian Gong, Bo Wang, Deng-Guang Yu, and Yuanjie Zhu. 2023. "Integrating Chinese Herbs and Western Medicine for New Wound Dressings Through Handheld Electrospinning" Biomedicines 11, no. 8: 2146. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11082146
APA StyleZhou, J., Wang, L., Gong, W., Wang, B., Yu, D.-G., & Zhu, Y. (2023). Integrating Chinese Herbs and Western Medicine for New Wound Dressings Through Handheld Electrospinning. Biomedicines, 11(8), 2146. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11082146







