PRISMA Systematic Literature Review, including with Meta-Analysis vs. Chatbot/GPT (AI) regarding Current Scientific Data on the Main Effects of the Calf Blood Deproteinized Hemoderivative Medicine (Actovegin) in Ischemic Stroke
Abstract
1. Introduction
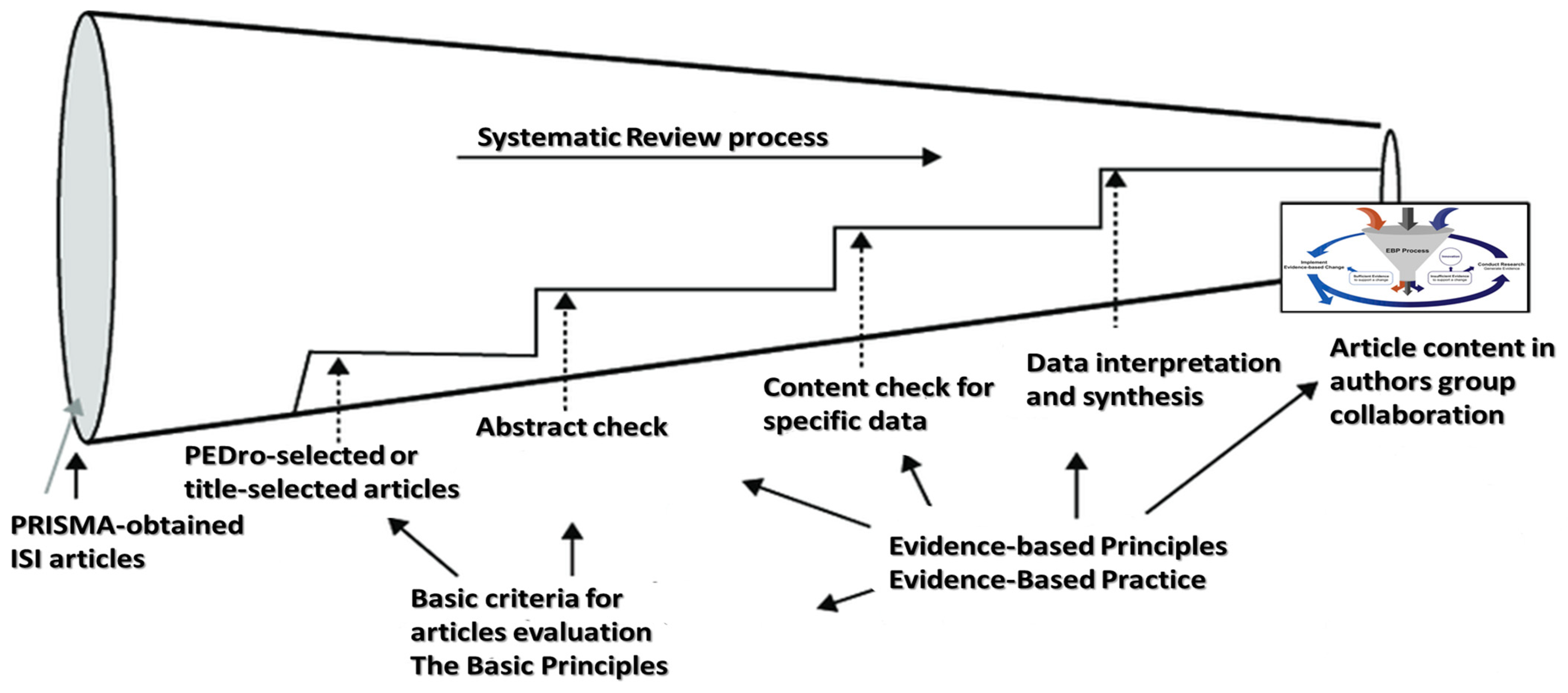
2. Methods
3. Chatbot (AI) Interrogation Regarding Actovegin® in Ischemic Stroke
4. Results Seen as Progress in the Last Three Years Resulting from PRISMA-Type Systematic Review
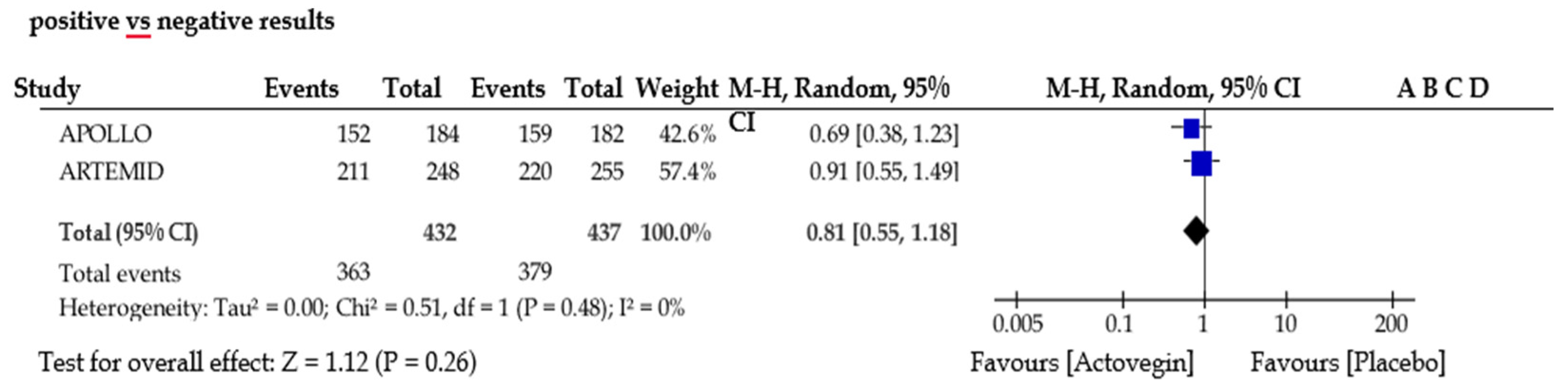
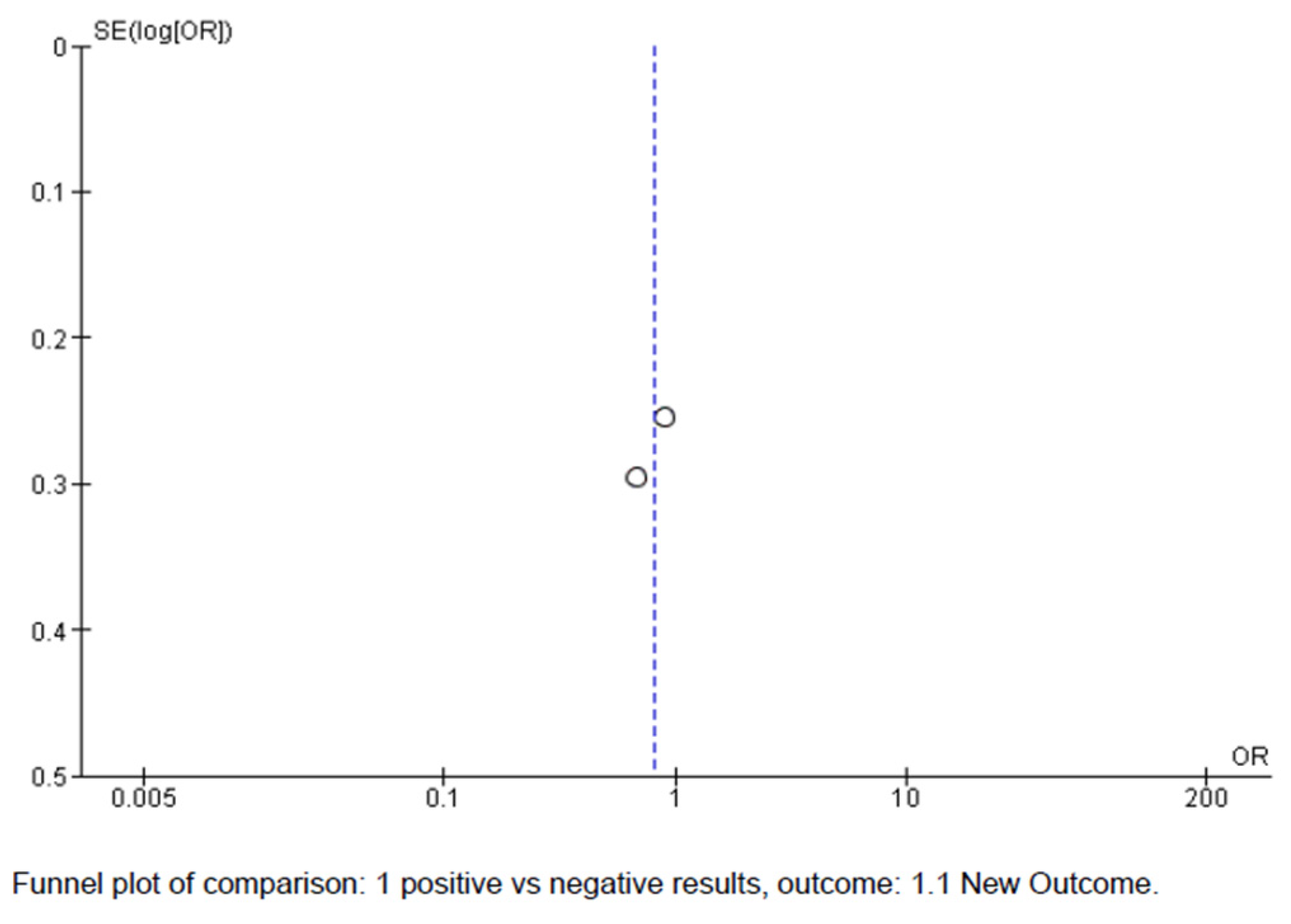
5. Meta-Analysis
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mu, Q.; Xue, Y.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, Q.; Wan, J.; Liu, P.; Liu, J.; Qu, Y.; Huang, C.; et al. Advances in the therapy of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury with natural product-based nanoparticles. Nano TransMed 2022, 1, e9130009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firan, F.C.; Romila, A.; Onose, G. Current Synthesis and Systematic Review of Main Effects of Calf Blood Deproteinized Medicine (Actovegin®) in Ischemic Stroke. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onose, G.; Anghelescu, A.; Blendea, D.; Ciobanu, V.; Daia, C.; Firan, F.C.; Oprea, M.; Spinu, A.; Popescu, C.; Ionescu, A.; et al. Cellular and Molecular Targets for Non-Invasive, Non-Pharmacological Therapeutic/Rehabilitative Interventions in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Young, W.; Ziad, A.; Hooshang, S.; Alok, S.; Dafin, M.; Shiqing, F.; Lin, C. Beijing Declaration of International Association of Neurorestoratology. J. Neurorestoratol. 2015, 3, 121–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleindorfer, D.O.; Towfighi, A.; Chaturvedi, S.; Cockroft, K.M.; Gutierrez, J.; Lombardi-Hill, D.; Kamel, H.; Kernan, W.N.; Kittner, S.J.; Leira, E.C.; et al. 2021 Guideline for the Prevention of Stroke in Patients with Stroke and Transient Ischemic Attack: A Guideline From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2021, 52, e364–e467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawanduzy, C.A.; Earl, E.; Mayer, G.; Lucke-Wold, B. Pediatric Stroke: A Review of Common Etiologies and Management Strategies. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmlinger, M.W.; Kriebel, M.; Ziegler, D. Neuroprotective and Anti-Oxidative Effects of the Hemodialysate Actovegin on Primary Rat Neurons in Vitro. NeuroMol. Med. 2011, 13, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guekht, A.; Skoog, I.; Edmundson, S.; Zakharov, V.; Korczyn, A.D. ARTEMIDA Trial (A Randomized Trial of Efficacy, 12 Months International Double-Blind Actovegin): A Randomized Controlled Trial to Assess the Efficacy of Actovegin in Poststroke Cognitive Impairment. Stroke 2017, 48, 1262–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichl, F.-X.; Högg, C.; Liu, F.; Schwarz, M.; Teupser, D.; Hickel, R.; Bloch, W.; Schweikl, H.; Thomas, P.; Summer, B. Actovegin® reduces PMA-induced inflammation on human cells. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2020, 120, 1671–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Guo, A.; Sun, M.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q. Neuroprotective Effects of Deproteinized Calf Serum in Ischemic Stroke. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 636494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanzadeh, S.; Lucke-Wold, B.; Eshghyar, F.; Rezaei, K.; Clark, A. The Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio in Poststroke Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Dis. Markers 2022, 2022, 1983455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machicao, F.; Muresanu, D.F.; Hundsberger, H.; Pflüger, M.; Guekht, A. Pleiotropic neuroprotective and metabolic effects of Actovegin’s mode of action. J. Neurol. Sci. 2012, 322, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvagno, M.; ChatGPT; Taccone, F.S.; Gerli, A.G. Can artificial intelligence help for scientific writing? Crit. Care 2023, 27, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Følstad, A.; Araujo, T.; Law, E.L.-C.; Brandtzaeg, P.B.; Papadopoulos, S.; Reis, L.; Baez, M.; Laban, G.; McAllister, P.; Ischen, C.; et al. Future directions for chatbot research: An interdisciplinary research agenda. Computing 2021, 103, 2915–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; Moher, D.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. PRISMA 2020 explanation and elaboration: Updated guidance and exemplars for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberger, D.C.; Blechschmidt, V.; Timmerman, H.; Wolff, A.; Treede, R.-D. Challenges of neuropathic pain: Focus on diabetic neuropathy. J. Neural Transm. 2020, 127, 589–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardlaw, J.M.; Debette, S.; Jokinen, H.; De Leeuw, F.-E.; Pantoni, L.; Chabriat, H.; Staals, J.; Doubal, F.; Rudilosso, S.; Eppinger, S.; et al. ESO Guideline on covert cerebral small vessel disease. Eur. Stroke J. 2021, 6, CXI–CLXII. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Jian, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, X.; Pu, B.; Gu, L.; Xion, X. Janus Kinase Inhibition Ameliorates Ischemic Stroke Injury and Neuroinflammation Through Reducing NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation via JAK2/STAT3 Pathway Inhibition. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 714943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, L.; Alattar, A.; Tan, Z.; Shah, F.A.; Ali, T.; Alshaman, R.; Koh, P.O.; Li, S. A Potent Antioxidant Endogenous Neurohormone Melatonin, Rescued MCAO by Attenuating Oxidative Stress-Associated Neuroinflammation. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, T.J.; Richard, E.; Teuschl, Y.; Gattringer, T.; Hafdi, M.; O’brien, J.T.; Merriman, N.; Gillebert, C.; Huyglier, H.; Verdelho, A.; et al. European Stroke Organisation and European Academy of Neurology joint guidelines on post-stroke cognitive impairment. Eur. Stroke J. 2021, 6, 42192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhao, T.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, F.; Cen, J.; Duan, S. Curcumin Derivative Cur20 Attenuated Cerebral Ischemic Injury by Antioxidant Effect and HIF-1α/VEGF/TFEB-Activated Angiogenesis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 648107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadeev, K.A.; Smirnov, A.S.; Zhigalova, O.P.; Bazhina, P.S.; Tumialis, A.V.; Golokhvast, K.S. Too Real to Be Virtual: Autonomic and EEG Responses to Extreme Stress Scenarios in Virtual Reality. Behav. Neurol. 2020, 2020, 5758038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Ruan, J.; Zhang, L.; Fu, F. Jieyu Anshen Granule, a Chinese Herbal Formulation, Exerts Effects on Poststroke Depression in Rats. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2020, 2020, 7469068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silina, E.V.; Manturova, N.E.; Litvitskiy, P.F.; Stupin, V.A. Comparative Analysis of the Effectiveness of Some Biological Injected Wound Healing Stimulators and Criteria for Its Evaluation. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 4869–4883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoica, S.I.; Bleotu, C.; Ciobanu, V.; Ionescu, A.M.; Albadi, I.; Onose, G.; Munteanu, C. Considerations about Hypoxic Changes in Neuraxis Tissue Injuries and Recovery. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurkin, D.V.; Bakulin, D.A.; Morkovin, E.I.; Kalatanova, A.V.; Makarenko, I.E.; Dorotenko, A.R.; Kovalev, N.S.; Dubrovina, M.A.; Verkholyak, D.V.; Abrosimova, E.E.; et al. Neuroprotective action of Cortexin, Cerebrolysin and Actovegin in acute or chronic brain ischemia in rats. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0254493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- la Fleur, P.; Baizhaxynova, A.; Reynen, E.; Kaunelis, D.; Galiyeva, D. Actovegin in the management of patients after ischemic stroke: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0270497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, M.; Birinci, B.; Haberal, B.; Atılgan, A.O.; Demirkale, I. In vivo study of the role of hyaluronic acid, N-acetyl cysteine, and deproteinized calf serum on injury-induced cartilage degeneration. Jt. Dis. Relat. Surg. 2023, 34, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthon, P.; Nairn, A.; Money, A. Through the Paradigm Funnel: A Conceptual Tool for Literature Analysis. Mark. Educ. Rev. 2003, 13, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Willik, E.M.; van Zwet, E.W.; Hoekstra, T.; van Ittersum, F.J.; Hemmelder, M.H.; Zoccali, C.; Jager, K.J.; Dekker, F.W.; Meuleman, Y. Funnel plots of patient-reported outcomes to evaluate health-care quality: Basic principles, pitfalls and considerations. Nephrology 2021, 26, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finch, P.M. The evidence funnel: Highlighting the importance of research literacy in the delivery of evidence informed complementary health care. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2007, 11, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchu, S.; Diaz, M.J.; Ladehoff, L.; Root, K.; Lucke-Wold, B. Utilizing the Ethereum blockchain for retrieving and archiving augmented reality surgical navigation data. Explor. Drug Sci. 2023, 1, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porche, K.; Maciel, C.B.; Lucke-Wold, B.; Robicsek, S.A.; Chalouhi, N.; Brennan, M.; Busl, K.M. Preoperative prediction of postoperative urinary retention in lumbar surgery: A comparison of regression to multilayer neural network. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2022, 36, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, A.P. Towards Strong AI with Analog Neural Chips. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Seville, Spain, 12–14 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kuleshov, A.; Prokhorov, S. Domain Dependence of Definitions Required to Standardize and Compare Performance Characteristics of Weak AI Systems. In Proceedings of the 2019 Artificial Intelligence Applications and Innovations Conference—IC-AIAI 2019, Crete, Greece, 17–20 June 2019; pp. 62–65. [Google Scholar]
- Hassani, H.; Silva, E.S. The Role of ChatGPT in Data Science: How AI-Assisted Conversational Interfaces Are Revolutionizing the Field. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2023, 7, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiliu, O. Analysis of neuroprotective medication in patients with neurocognitive disorders: The efficacy and tolerability of highly purified animal tissues extracts. Rom. J. Mil. Med. 2022, 125, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.Y.F. The Role of Actovegin in Muscle Injuries. Doctoral Dissertation, Cardiff University, Cardiff, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Suchkov, I.A.; Mzhavanadze, N.D.; Bogachev, V.Y.; Bokuchava, M.; Kuznetsov, M.R.; Lukyanov, Y.V.; Kelimbetov, R.; Pang, H.; Araslanov, S.A. Efficacy and safety of Actovegin in the treatment of intermittent claudication: Results of an international, multicenter, placebo-controlled, randomized, phase IIIb clinical trial (APOLLO). Int. Angiol. 2022, 41, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skoog, I.; Korczyn, A.D.; Guekht, A. Neuroprotection in vascular dementia: A future path. J. Neurol. Sci. 2012, 322, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haupt, C.E.; Law, H.; Marks, M. AI-Generated Medical Advice—GPT and Beyond. JAMA 2023, 329, 1349–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lister, K.; Coughlan, T.; Iniesto, F.; Freear, N.; Devine, P. Accessible Conversational User Interfaces Considerations for Design. In Proceedings of the 17th International Web for All Conference—Web4All 2020, Taipei, Taiwan, 20–21 April 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Okonkwo, C.W.; Ade-Ibijola, A. Chatbots applications in education: A systematic review. Comput. Educ. Artif. Intell. 2021, 2, 100033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
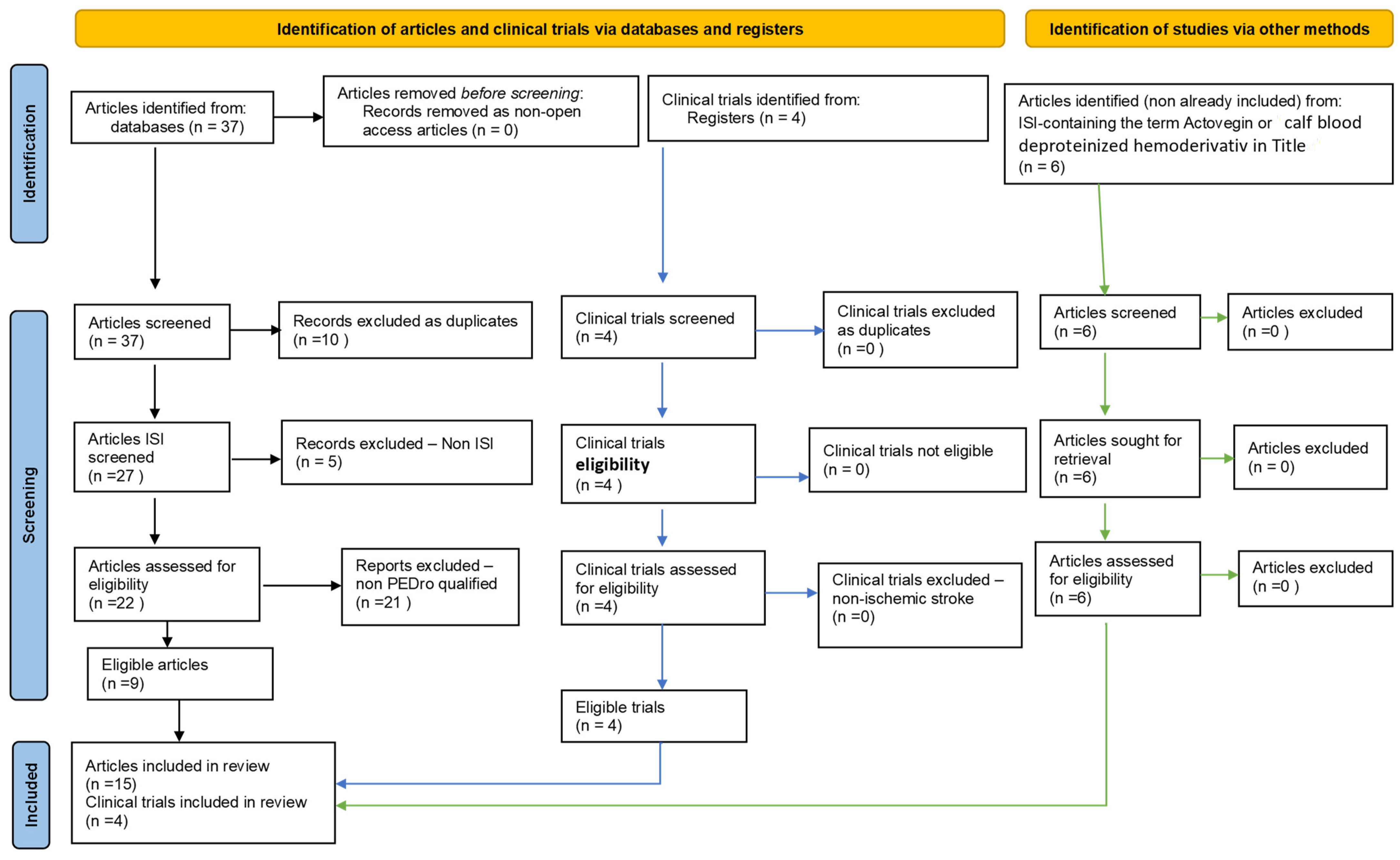
| Keywords | Elsevier | PubMed | PMC | PEDro | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| “stroke” + “Actovegin” | 0 | 3 | 27 | 0 | 30 |
| “stroke” + “calf blood deproteinized hemoderivative” | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| “stroke” + “calf blood deproteinized hemodialysate” | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| “Actovegin” + “pleiotropic” | 0 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 7 |
| “calf blood deproteinized hemoderivative” + “pleiotropic” | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| “calf blood deproteinized hemodialysate” + “pleiotropic” | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 0 | 3 | 34 | 0 | 37 |
| Reference | Keywords | Publication_Year | Isi_Citation_Count | References_Count | PEDRO_Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [16] | “stroke” + “Actovegin” | 2020 | 66 | 413 | 10 |
| [17] | “stroke” + “Actovegin” | 2021 | 30 | 165 | 10 |
| [18] | “stroke” + “Actovegin” | 2021 | 30 | 46 | 10 |
| [19] | “stroke” + “Actovegin” | 2020 | 17 | 69 | 9 |
| [20] | “stroke” + “Actovegin” | 2021 | 12 | 22 | 6 |
| [21] | “stroke” + “Actovegin” | 2021 | 10 | 34 | 5 |
| [22] | “stroke” + “Actovegin” | 2020 | 10 | 42 | 5 |
| [2] | “stroke” + “Actovegin” | 2020 | 8 | 75 | 4 |
| [23] | “stroke” + “Actovegin” | 2020 | 7 | 48 | 4 |
| [24] | “stroke” + “Actovegin” | 2020 | 3 | 36 | 2 |
| [25] | “stroke” + “Actovegin” | 2022 | 3 | 146 | 2 |
| [10] | “stroke” + “Actovegin” | 2021 | 2 | 38 | 1 |
| [9] | “stroke” + “Actovegin” | 2020 | 2 | 75 | 1 |
| [26] | “stroke” + “Actovegin” | 2021 | 2 | 37 | 1 |
| [27] | “stroke” + “Actovegin” | 2022 | 0 | 31 | 0 |
| [28] | “stroke” + “Actovegin” | 2022 | 0 | 26 | 0 |
| Ref. | Study Name/ID | Publication Year | Population | Actovegin Treatment | Placebo | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [8] | ARTEMIDA Unique identifier: NCT01582854. | 2017 | 503 | 248 | 255 | Actovegin had a beneficial effect on cognitive outcomes in patients with post-stroke cognitive impairment. The safety experience was consistent with the known safety and tolerability profile of the drug. These results warrant confirmation in additional robustly designed studies. |
| [39] | (APOLLO) NCT03469349 | 2020 | 366 | 184 | 182 | The results of this 12-week course of Actovegin demonstrated its superiority over a placebo in the increase in ICD and ACD at weeks 2, 12, and 24 from the start of treatment. Actovegin has an acceptable safety and tolerability profile. |
| [20] | European Stroke Organisation and European Academy of Neurology joint guidelines on post-stroke cognitive impairment | 2021 | Includes data only from ARTEMIDA | A beneficial effect of Actovegin compared to a placebo was reported, but the effect size described may be less than the minimal clinically significant difference. | ||
| [27] | Actovegin in the management of patients after ischemic stroke: A systematic review | 2022 | Includes data only from ARTEMIDA and other heterogeneous data | The benefits of Actovegin are uncertain, and there is a potential risk of harm in patients with stroke. | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anghelescu, A.; Firan, F.C.; Onose, G.; Munteanu, C.; Trandafir, A.-I.; Ciobanu, I.; Gheorghița, Ș.; Ciobanu, V. PRISMA Systematic Literature Review, including with Meta-Analysis vs. Chatbot/GPT (AI) regarding Current Scientific Data on the Main Effects of the Calf Blood Deproteinized Hemoderivative Medicine (Actovegin) in Ischemic Stroke. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1623. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11061623
Anghelescu A, Firan FC, Onose G, Munteanu C, Trandafir A-I, Ciobanu I, Gheorghița Ș, Ciobanu V. PRISMA Systematic Literature Review, including with Meta-Analysis vs. Chatbot/GPT (AI) regarding Current Scientific Data on the Main Effects of the Calf Blood Deproteinized Hemoderivative Medicine (Actovegin) in Ischemic Stroke. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(6):1623. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11061623
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnghelescu, Aurelian, Florentina Carmen Firan, Gelu Onose, Constantin Munteanu, Andreea-Iulia Trandafir, Ilinca Ciobanu, Ștefan Gheorghița, and Vlad Ciobanu. 2023. "PRISMA Systematic Literature Review, including with Meta-Analysis vs. Chatbot/GPT (AI) regarding Current Scientific Data on the Main Effects of the Calf Blood Deproteinized Hemoderivative Medicine (Actovegin) in Ischemic Stroke" Biomedicines 11, no. 6: 1623. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11061623
APA StyleAnghelescu, A., Firan, F. C., Onose, G., Munteanu, C., Trandafir, A.-I., Ciobanu, I., Gheorghița, Ș., & Ciobanu, V. (2023). PRISMA Systematic Literature Review, including with Meta-Analysis vs. Chatbot/GPT (AI) regarding Current Scientific Data on the Main Effects of the Calf Blood Deproteinized Hemoderivative Medicine (Actovegin) in Ischemic Stroke. Biomedicines, 11(6), 1623. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11061623







