Direct Detection of Lyme Borrelia: Recent Advancement and Use of Aptamer Technology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
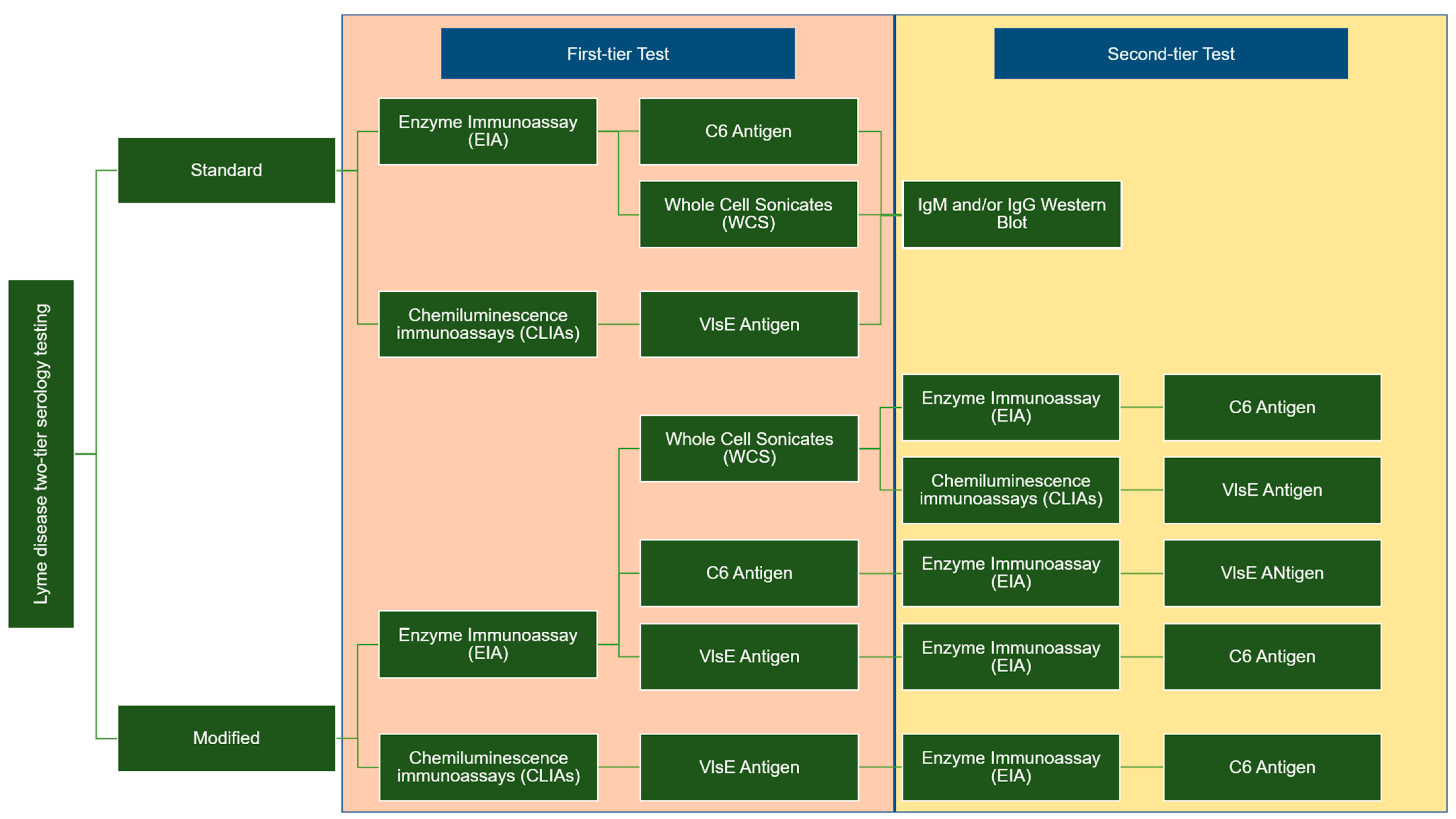
2. Current Guidelines for LD Diagnostic Test
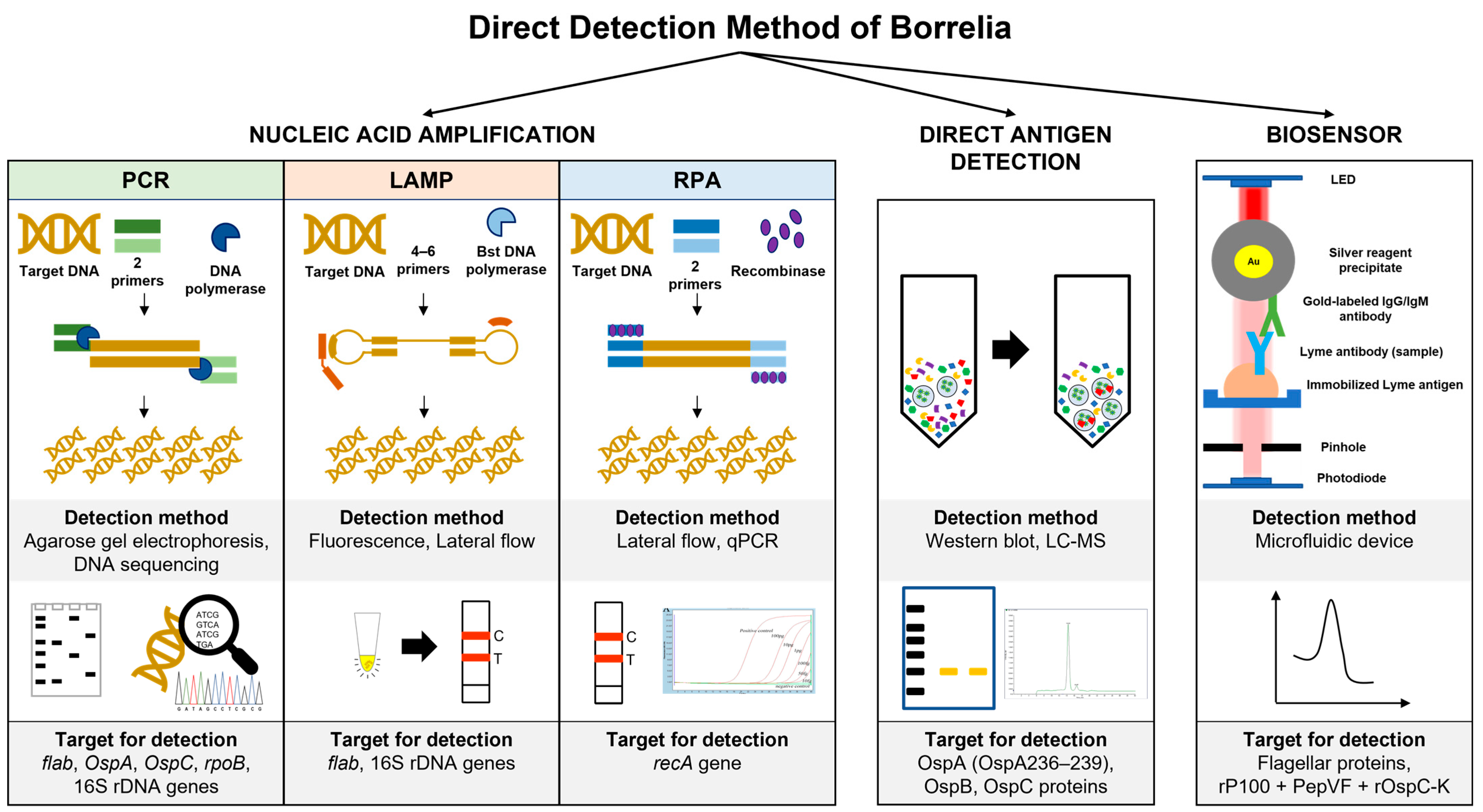
3. Direct Detection Method of Borrelia
3.1. Nucleic Acid Amplification
3.2. Direct Antigen Detection
3.3. Biosensor
4. Aptamer for Borrelia Antigen Detection
5. Current Aptamer Development for Borrelia Antigen Detection
6. Future Direction of the Use of LD Aptasensor
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Steere, A.C.; Strle, F.; Wormser, G.P.; Hu, L.T.; Branda, J.A.; Hovius, J.W.; Li, X.; Mead, P.S. Lyme borreliosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2016, 2, 16090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanova, L.; Christova, I.; Neves, V.; Aroso, M.; Meirelles, L.; Brisson, D.; Gomes-Solecki, M. Comprehensive seroprofiling of sixteen B. burgdorferi OspC: Implications for Lyme disease diagnostics design. Clin. Immunol. 2009, 132, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranton, G.; Seinost, G.; Theodore, G.; Postic, D.; Dykhuizen, D. Distinct levels of genetic diversity of Borrelia burgdorferi are associated with different aspects of pathogenicity. Res. Microbiol. 2001, 152, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanek, G.; Strle, F. Lyme borreliosis–from tick bite to diagnosis and treatment. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 42, 233–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, E.D.; Gerber, M.A. Lyme Disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2000, 31, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, A.R.; Strle, F.; Wormser, G.P. Comparison of Lyme Disease in the United States and Europe. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 2017–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritt, B.S.; Mead, P.S.; Johnson, D.K.H.; Neitzel, D.F.; Respicio-Kingry, L.B.; Davis, J.P.; Schiffman, E.; Sloan, L.M.; Schriefer, E.M.; Replogle, A.J.; et al. Identification of a novel pathogenic Borrelia species causing Lyme borreliosis with unusually high spirochaetaemia: A descriptive study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parola, P.; Paddock, C.D. Travel and tick-borne diseases: Lyme disease and beyond. Travel. Med. Infect. Dis. 2018, 26, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge, L.M.A.; De Janeiro, B.P.G.D.R.; Lupi, O.; Hozannah, A.R.; Filho, F.B.; Usp, B. Lyme disease in a Brazilian traveler who returned from Germany. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2017, 92, 148–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soloria, H.; Adams, D. Lyme Arthritis in a Military Dependent Child transferred from Japan. Mil. Med. 2020, 185, e301–e302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, M.; Watanabe, Y.; Kawabata, H. A case of Lyme disease in a Japanese woman. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 11, 625–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vien, V.P.; Bassi, R.; Maxim, T.; Bogoch, I.I. Lyme disease vs Baggio–Yoshinari syndrome in a returned traveller from Brazil. J. Travel Med. 2017, 24, tax055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subedi, S.; Dickeson, D.J.; Branley, J.M. First report of Lyme neuroborreliosis in a returned Australian traveller. Med. J. Aust. 2015, 203, 39–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, J.A.; Marrotte, R.R.; Desrosiers, N.; Fiset, J.; Gaitan, J.; Gonzalez, A.; Koffi, J.K.; Lapointe, F.-J.; Leighton, P.A.; Lindsay, L.R.; et al. Climate change and habitat fragmentation drive the occurrence of Borrelia burgdorferi, the agent of Lyme disease, at the northeastern limit of its distribution. Evol. Appl. 2014, 7, 750–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelder, M.; Wijayasri, S.; Russell, C.; Johnson, K.; Marchand-Austin, A.; Cronin, K.; Johnson, S.; Badiani, T.; Patel, S.; Sider, D. The continued rise of Lyme disease in Ontario, Canada: 2017. Can. Commun. Dis. Rep. 2018, 44, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogden, N.H.; Lindsay, L.R.; Morshed, M.; Sockett, P.N.; Artsob, H. The emergence of Lyme disease in Canada. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2009, 180, 1221–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, B.L.; Tourand, Y.; Brissette, C.A.; Hermance, M.E.; Thangamani, S.; Knox, K.K.; Thomm, A.M.; Harrington, Y.A.; Ketter, E.; Patitucci, J.M.; et al. Brave New Worlds: The Expanding Universe of Lyme Disease. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2017, 17, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.-Q.; Liu, K.; Li, X.-L.; Liang, S.; Yang, Y.; Yao, H.-W.; Sun, R.-X.; Sun, Y.; Chen, W.-J.; Zuo, S.-Q.; et al. Emerging tick-borne infections in mainland China: An increasing public health threat. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 1467–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariana, A.; Zuraidawati, Z.; Ho, T.M.; Kulaimi, B.M.; Saleh, I.; Shukor, M.N.; Shahrul-Anuar, M.S. Ticks (Ixodidae) and other ectoparasites in Ulu Muda Forest Reserve, Kedah, Malaysia. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2008, 39, 496–506. [Google Scholar]
- Mariana, A.; Zuraidawati, Z.; Ho, T.M.; Mohd Kulaimi, B.; Saleh, I.; Shukor, M.N.; Shahrul-Anuar, M.S. A survey of ectoparasites in Gunung Stong Forest Reserve, Kelantan, Malaysia. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2005, 36, 1125–1131. [Google Scholar]
- Khoo, J.J.; Ishak, S.N.; Lim, F.S.; Mohd-Taib, F.S.; Khor, C.S.; Loong, S.K.; AbuBakar, S. Detection of a Borrelia sp. From Ixodes granulatus Ticks Collected From Rodents in Malaysia. J. Med. Entomol. 2018, 55, 1642–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paramasvaran, S.; Sani, A.R.; Hassan, L.; Krishnasamy, M.; Jeffery, J.; Oothuman, P.; Salleh, I.; Lim, K.H.; Sumarni, M.G.; Santhana, R.L. Ectoparasite fauna of rodents and shrews from four habitats in Kuala Lumpur and the states of Selangor and Negeri Sembilan, Malaysia and its public health significance. Trop. Biomed. 2009, 26, 303–311. [Google Scholar]
- Madinah, A.; Fatimah, A.; Mariana, A.; Abdullah, M.T. Ectoparasites of small mammals in four localities of wildlife reserves in Peninsular Malaysia. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2011, 42, 803–813. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mariana, A.; Mohd, K.B.; Halimaton, I.; Suhaili, Z.A.; Shahrul-Anuar, M.S.; Nor, Z.M.; Ho, T.M. Acarine ectoparasites of Panti Forest Reserve in Johore, Malaysia. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2011, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, A.C.C.; Qiu, Y.; Moustafa, M.A.M.; Nakao, R.; Shimozuru, M.; Onuma, M.; Mohd-Azlan, J.; Tsubota, T. Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi Sensu Lato and Relapsing Fever Borrelia in Feeding Ixodes Ticks and Rodents in Sarawak, Malaysia: New Geographical Records of Borrelia yangtzensis and Borrelia miyamotoi. Pathogens 2020, 9, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, K.; Ito, T.; Asashima, N.; Ohno, M.; Nagai, R.; Fujita, H.; Koizumi, N.; Takano, A.; Watanabe, H.; Kawabata, H. Case report: Borrelia valaisiana infection in a Japanese man associated with traveling to foreign countries. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2007, 77, 1124–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, X.B.; Jia, N.; Jiang, B.G.; Sun, T.; Zheng, Y.C.; Huo, Q.B.; Liu, K.; Ma, L.; Zhao, Q.-M.; Yang, H.; et al. Lyme borreliosis caused by diverse genospecies of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato in northeastern China. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Off. Publ. Eur. Soc. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chee-Sieng, K.; Habibi, H.; Nurul-Farhana, M.-R.; Josephine Rebecca, C.; Siti-Sarah, N.; Jefree, J.; Loong, S.-K.; Abd-Jamil, J.; Khoo, J.-J.; Lee, H.-Y. Seroprevalence of Borrelia burgdorferi among the indigenous people (Orang Asli) of Peninsular Malaysia. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2019, 13, 449–454. [Google Scholar]
- Branda, J.A.; Linskey, K.; Kim, Y.A.; Steere, A.C.; Ferraro, M.J. Two-tiered antibody testing for Lyme disease with use of 2 enzyme immunoassays, a whole-cell sonicate enzyme immunoassay followed by a VlsE C6 peptide enzyme immunoassay. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2011, 53, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molins, C.R.; Delorey, M.J.; Sexton, C.; Schriefer, M.E. Lyme Borreliosis Serology: Performance of Several Commonly Used Laboratory Diagnostic Tests and a Large Resource Panel of Well-Characterized Patient Samples. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 2726–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipsett, S.C.; Branda, J.A.; McAdam, A.J.; Vernacchio, L.; Gordon, C.D.; Gordon, C.R.; Gordon, C.R.; Nigrovic, L.E. Evaluation of the C6 Lyme Enzyme Immunoassay for the Diagnosis of Lyme Disease in Children and Adolescents. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 63, 922–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pegalajar-Jurado, A.; Schriefer, M.E.; Welch, R.J.; Couturier, M.R.; MacKenzie, T.; Clark, R.J.; Ashton, L.V.; Delorey, M.J.; Molins, C.R. Evaluation of Modified Two-Tiered Testing Algorithms for Lyme Disease Laboratory Diagnosis Using Well-Characterized Serum Samples. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e01943-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatchette, L.; Lindsay, R. Modified two-tiered testing algorithm for Lyme disease serology: The Canadian context. Can. Commun. Dis. Rep. 2020, 46, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waddell, L.A.; Greig, J.; Mascarenhas, M.; Harding, S.; Lindsay, R.; Ogden, N. The Accuracy of Diagnostic Tests for Lyme Disease in Humans, A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of North American Research. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalish, R.A.; McHugh, G.; Granquist, J.; Shea, B.; Ruthazer, R.; Steere, A.C. Persistence of immunoglobulin M or immunoglobulin G antibody responses to Borrelia burgdorferi 10–20 years after active Lyme disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2001, 33, 780–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, S.; Nayak, S.; Williams, T.; Maria, F.S.d.S.; Guedes, M.S.; Chaves, R.C.; Linder, V.; Marques, A.R.; Horn, E.J.; Wong, S.J.; et al. A Multiplexed Serologic Test for Diagnosis of Lyme Disease for Point-of-Care Use. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2019, 57, e01142-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teny, M.J.; Alan, J.T. Appropriate laboratory testing in Lyme disease. Clevel. Clin. J. Med. 2019, 86, 751. [Google Scholar]
- Das, S.; Hammond-McKibben, D.; Guralski, D.; Lobo, S.; Fiedler, P.N. Development of a sensitive molecular diagnostic assay for detecting Borrelia burgdorferi DNA from the blood of Lyme disease patients by digital PCR. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0235372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerar, T.; Korva, M.; Avšič-Županc, T.; Ružić-Sabljić, E. Detection, identification and genotyping of Borrellia spp. in rodents in Slovenia by PCR and culture. BMC Vet. Res. 2015, 11, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerar, T.; Ružić-Sabljić, E.; Glinšek, U.; Zore, A.; Strle, F. Comparison of PCR methods and culture for the detection of Borrelia spp. in patients with erythema migrans. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2008, 14, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguero-Rosenfeld, M.E.; Wang, G.; Schwartz, I.; Wormser, G.P. Diagnosis of lyme borreliosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 18, 484–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mygland, Å.; Ljøstad, U.; Fingerle, V.; Rupprecht, T.; Schmutzhard, E.; Steiner, I. EFNS guidelines on the diagnosis and management of European Lyme neuroborreliosis. Eur. J. Neurol. 2010, 17, 8–16.e1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picha, D.; Moravcova, L.; Zdarsky, E.; Maresova, V.; Hulinsky, V. PCR in lyme neuroborreliosis: A prospective study. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2005, 112, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Guan, G.; Niu, Q.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Ma, M.; Ren, Q.; Liu, A.; Luo, J.; et al. Development and application of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for rapid detection of Borrelia burgdorferi s. l. in ticks. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2013, 60, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.L.; Hou, X.X.; Geng, Z.; Lou, Y.L.; Wan, K.L.; Hao, Q. Combination of Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay and Nested PCR for Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato in Human Serum Samples. Biomed. Environ. Sci. BES 2015, 28, 312–315. [Google Scholar]
- Mori, Y.; Nagamine, K.; Tomita, N.; Notomi, T. Detection of loop-mediated isothermal amplification reaction by turbidity derived from magnesium pyrophosphate formation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 289, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobato, I.M.; O’Sullivan, C.K. Recombinase polymerase amplification: Basics, applications and recent advances. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 98, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, H.-X.; Zhang, L.; Hou, X.-X.; Wan, K.-L.; Hao, Q. A Novel Isothermal Assay of Borrelia burgdorferi by Recombinase Polymerase Amplification with Lateral Flow Detection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; McHugh, G.A.; Damle, N.; Sikand, V.K.; Glickstein, L.; Steere, A.C. Burden and viability of Borrelia burgdorferi in skin and joints of patients with erythema migrans or lyme arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 2238–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dam, A.P. Molecular diagnosis of Borrelia bacteria for the diagnosis of Lyme disease. Expert Opin. Med. Diagn. 2011, 5, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonin, S. Diagnostic Tools for Assessment in Humans. Open Dermatol. J. 2016, 10, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ružić-Sabljić, E.; Cerar, T. Progress in the molecular diagnosis of Lyme disease. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2017, 17, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trevisan, G.; Bonin, S.; Ruscio, M. A Practical Approach to the Diagnosis of Lyme Borreliosis: From Clinical Heterogeneity to Laboratory Methods. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolte, O. Nucleic Acid Amplification Based Diagnostic of Lyme (Neuro-)borreliosis—Lost in the Jungle of Methods, Targets, and Assays? Open Neurol. J. 2012, 6, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorward, D.W.; Schwan, T.G.; Garon, C.F. Immune capture and detection of Borrelia burgdorferi antigens in urine, blood, or tissues from infected ticks, mice, dogs, and humans. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1991, 29, 1162–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klempner, M.S.; Schmid, C.H.; Hu, L.; Steere, A.C.; Johnson, G.; McCloud, B.; Noring, R.; Weinstein, A. Intralaboratory reliability of serologic and urine testing for Lyme disease. Am. J. Med. 2001, 110, 217–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, C.S.F.; Anderson, K.W.; Benitez, K.Y.V.; Soloski, M.J.; Aucott, J.N.; Phinney, K.W.; Turko, I.V. Quantification of Borrelia burgdorferi Membrane Proteins in Human Serum: A New Concept for Detection of Bacterial Infection. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 11383–11388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, T.A.; Tamburro, D.; Fredolini, C.; Espina, B.H.; Lepene, B.S.; Ilag, L.; Espina, V.; Petricoin, E.F.; Liotta, L.A.; Luchini, A. The use of hydrogel microparticles to sequester and concentrate bacterial antigens in a urine test for Lyme disease. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 1157–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magni, R.; Espina, B.H.; Shah, K.; Lepene, B.; Mayuga, C.; Douglas, T.A.; Espina, V.; Rucker, S.; Dunlap, R.; Petricoin, E.F.I.; et al. Application of Nanotrap technology for high sensitivity measurement of urinary outer surface protein A carboxyl-terminus domain in early stage Lyme borreliosis. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earnhart, C.G.; Rhodes, D.V.L.; Smith, A.A.; Yang, X.; Tegels, B.; Carlyon, J.A.; Pal, U.; Marconi, R.T. Assessment of the potential contribution of the highly conserved C-terminal motif (C10) of Borrelia burgdorferi outer surface protein C in transmission and infectivity. Pathog. Dis. 2014, 70, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathiesen, M.J.; Christiansen, M.; Hansen, K.; Holm, A.; Åsbrink, E.; Theisen, M. Peptide-based OspC enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for serodiagnosis of Lyme borreliosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1998, 36, 3474–3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolange, V.; Simon, S.; Morel, N. Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi antigens in tissues and plasma during early infection in a mouse model. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerner, M.B.; Dailey, J.; Goldsmith, B.R.; Brisson, D.; Johnson, A.C. Detecting Lyme disease using antibody-functionalized single-walled carbon nanotube transistors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 45, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.; Sridhara, A.; Melo, R.; Richer, L.; Chee, N.H.; Kim, J.; Linder, V.; Steinmiller, D.; Sia, S.K.; Gomes-Solecki, M. Microfluidics-based point-of-care test for serodiagnosis of Lyme Disease. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruscito, A.; DeRosa, M.C. Small-Molecule Binding Aptamers: Selection Strategies, Characterization, and Applications. Front. Chem. 2016, 4, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eremeeva, E.; Fikatas, A.; Margamuljana, L.; Abramov, M.; Schols, D.; Groaz, E.; Herdewijn, P. Highly stable hexitol based XNA aptamers targeting the vascular endothelial growth factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 4927–4939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, V.B.; Taylor, A.I.; Cozens, C.; Abramov, M.; Renders, M.; Zhang, S.; Chaput, J.C.; Wengel, J.; Peak-Chew, S.-Y.; McLaughlin, S.H.; et al. Synthetic genetic polymers capable of heredity and evolution. Science 2012, 336, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, M.R.; Otto, C.; Fenton, K.E.; Chaput, J.C. Improving Polymerase Activity with Unnatural Substrates by Sampling Mutations in Homologous Protein Architectures. ACS Chem. Biol. 2016, 11, 1210–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.G.; Damha, M.J. Polymerase-directed synthesis of 2′-deoxy-2′-fluoro-beta-D-arabinonucleic acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 5310–5311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wum, Q.; Chen, J.; Ni, X.; Dai, J. A DNA Aptamer Based Method for Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein. Virol. Sin. 2020, 35, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, D.G.; Jeon, I.J.; Kim, J.D.; Song, M.S.; Han, S.R.; Lee, S.W.; Jung, H.; Oh, J.-W. RNA aptamer-based sensitive detection of SARS coronavirus nucleocapsid protein. Analyst 2009, 134, 1896–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondratov, I.G.; Khasnatinov, M.A.; Potapova, U.V.; Potapov, V.V.; Levitskii, S.A.; Leonova, G.N.; Pavlenko, E.V.; Solovarov, I.S.; Denikina, N.N.; Kulakova, N.V.; et al. Obtaining aptamers to a fragment of surface protein E of tick-borne encephalitis virus. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 2013, 448, 19–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, S.; Yao, H.; Wang, L.; Lu, J.; Jiang, F.; Lu, A.; Zhang, G. Chemical Modifications of Nucleic Acid Aptamers for Therapeutic Purposes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odeh, F.; Nsairat, H.; Alshaer, W.; Ismail, M.A.; Esawi, E.; Qaqish, B.; Al Bawab, A.; Ismail, S.I. Aptamers Chemistry: Chemical Modifications and Conjugation Strategies. Molecules 2019, 25, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, S.; Zhuo, Z.; Pan, Y.; Yu, Y.; Li, F.; Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Wu, X.; Li, D.; Wan, Y. Recent Progress in Aptamer Discoveries and Modifications for Therapeutic Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 9500–9519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elskens, J.P.; Elskens, J.M.; Madder, A. Chemical Modification of Aptamers for Increased Binding Affinity in Diagnostic Applications: Current Status and Future Prospects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priem, S.; Burmester, G.R.; Kamradt, T.; Wolbart, K.; Rittig, M.G.; Krause, A. Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi by polymerase chain reaction in synovial membrane, but not in synovial fluid from patients with persisting Lyme arthritis after antibiotic therapy. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1998, 57, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santino, I.; Berlutti, F.; Pantanella, F.; Sessa, R.; Del Piano, M. Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato DNA by PCR in serum of patients with clinical symptoms of Lyme borreliosis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2008, 283, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.J. Laboratory Diagnostic Testing for Borrelia burgdorferi Infection. Lyme Disease: An Evidence-Based Approach; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2011; pp. 73–88. [Google Scholar]
- Flynn, C.D.; Sandomierski, M.; Kim, K.; Lewis, J.; Lloyd, V.; Ignaszak, A. Electrochemical Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi Using a Biomimetic Flow Cell System. ACS Meas. Sci. Au 2023, 3, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dattwyler, R.J.; Gomes-Solecki, M. Peptide Diagnostic Agent for Lyme Disease. U.S. Patent 7887815B2, 15 February 2011. Google Patents. [Google Scholar]
- Tabb, J.S.; Rapoport, E.; Han, I.; Lombardi, J.; Green, O. An antigen-targeting assay for Lyme disease: Combining aptamers and SERS to detect the OspA protein. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2022, 41, 102528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Zhao, X.; Wallace, G.Q.; Brunet, M.-H.; Wilkinson, K.J.; Wu, P.; Cai, C.; Bazuin, C.G.; Masson, J.-F. Multiplexed SERS Detection of Microcystins with Aptamer-Driven Core–Satellite Assemblies. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 6545–6556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Ma, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z. Aptamer based SERS detection of Salmonella Typhimurium using DNA-assembled gold nanodimers. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, C.; Xiao, R.; Tang, L.; Huang, J.; Wu, D.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, S.; et al. Sensitive and specific detection of clinical bacteria via vancomycin-modified Fe3O4@Au nanoparticles and aptamer-functionalized SERS tags. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 3751–3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, Y.; Wan, N.; Shi, L.; Wang, C.; Sun, Z.; Xiao, R.; Wang, S. Dual-recognition surface-enhanced Raman scattering(SERS)biosensor for pathogenic bacteria detection by using vancomycin-SERS tags and aptamer-Fe3O4@Au. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1077, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavyalova, E.; Ambartsumyan, O.; Zhdanov, G.; Gribanyov, D.; Gushchin, V.; Tkachuk, A.; Rudakova, E.; Nikiforova, M.; Kuznetsova, N.; Popova, L. SERS-Based Aptasensor for Rapid Quantitative Detection of SARS-CoV-2. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Xu, X.; Xia, Y.; Wang, Z. SERS Aptasensor for Salmonella Typhimurium Detection based on Spiny Gold Nanoparticles. Food Control. 2017, 84, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukushkin, V.I.; Ivanov, N.M.; Novoseltseva, A.A.; Gambaryan, A.S.; Yaminsky, I.V.; Kopylov, A.M.; Zavyalova, F.G. Highly sensitive detection of influenza virus with SERS aptasensor. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Park, S.-G.; Choi, N.; Moon, J.-I.; Dang, H.; Das, A.; Lee, S.; Kim, D.-G.; Chen, L.; Choo, J. SERS imaging-based aptasensor for ultrasensitive and reproducible detection of influenza virus A. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 167, 112496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, N.; Shen, M.; Wu, S.; Zhao, C.; Ma, X.; Wang, Z. Graphene oxide wrapped Fe3O4@Au nanostructures as substrates for aptamer-based detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 2653–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Wang, Z.-P.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Z.; He, Y. A SERS aptasensor based on porous Au-NC nanoballoons for Staphylococcus aureus detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1190, 339175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, C.; Ignaszak, A. Lyme Disease Biosensors: A Potential Solution to a Diagnostic Dilemma. Biosensors 2020, 10, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B. Sandwich electrochemical thrombin assay using a glassy carbon electrode modified with nitrogen- and sulfur-doped graphene oxide and gold nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.-K.; Kim, H.-R.; Yoon, S.-J.; Lee, K.-B.; Kim, J.; Kim, B.-C. Colorimetric Aptasensor for Detecting Bacillus carboniphilus Using Aptamer Isolated with a Non-SELEX-Based Method. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, J.; Pang, W.; Yan, G. An aptamer-based fluorescence probe for facile detection of lipopolysaccharide in drinks. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 54920–54926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Ma, L.; Ma, K.; Xu, B.; Liu, L.; Tian, W. Label-Free Aptamer-Based Biosensor for Specific Detection of Chloramphenicol Using AIE Probe and Graphene Oxide. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 12886–12892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labib, M.; Zamay, A.S.; Kolovskaya, O.S.; Reshetneva, I.T.; Zamay, G.S.; Kibbee, R.J.; Sattar, S.A.; Zamay, T.N.; Berezovski, M.V. Aptamer-Based Viability Impedimetric Sensor for Bacteria. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 8966–8969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urmann, K.; Arshavsky-Graham, S.; Walter, J.G.; Scheper, T.; Segal, E. Whole-cell detection of live Lactobacillus acidophilus on aptamer-decorated porous silicon biosensors. Analyst 2016, 141, 5432–5440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Detection Methods | Target Molecules | Sensitivity | LOD | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nested PCR | p66, 16S rRNA gene, fla gene, 23S rRNA gene, 5S rRNA-23S rRNA gene spacer, recA gene, OspA gene | 4–100% | ND | [41,42,43] |
| LAMP | 16S rRNA | 32.7% | 0.2 to 0.02 pg | [44] |
| fla gene | 37.5% | 20 copies | [45] | |
| RPA | recA gene | 90% | 50 femtograms | [48] |
| Hydrogel microparticles | B. burgdorferi OspA and OspB | ND | 700 pg/mL | [58] |
| Nanotrap technology | OspA 236–239 | 87.5% | 1.7 pg/mL | [59] |
| SPIE-IA | OspC | ND | 10 ng/mL–17 pg/mL | [62] |
| mChip-Ld | VlsE, PepVF, OspC | 80% to 100% | ND | [36] |
| FETs | p41 | Unavailable | 1 ng/mL | [63] |
| Microfluidics | rP100, PepVF, rOspC-K | 84% | ND | [64] |
| SERS (aptasensor) | OspA | 91–96% | 1 × 104 ng/mL | [83] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nik Kamarudin, N.A.A.; Mawang, C.I.; Ahamad, M. Direct Detection of Lyme Borrelia: Recent Advancement and Use of Aptamer Technology. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2818. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11102818
Nik Kamarudin NAA, Mawang CI, Ahamad M. Direct Detection of Lyme Borrelia: Recent Advancement and Use of Aptamer Technology. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(10):2818. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11102818
Chicago/Turabian StyleNik Kamarudin, Nik Abdul Aziz, Christina Injan Mawang, and Mariana Ahamad. 2023. "Direct Detection of Lyme Borrelia: Recent Advancement and Use of Aptamer Technology" Biomedicines 11, no. 10: 2818. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11102818
APA StyleNik Kamarudin, N. A. A., Mawang, C. I., & Ahamad, M. (2023). Direct Detection of Lyme Borrelia: Recent Advancement and Use of Aptamer Technology. Biomedicines, 11(10), 2818. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11102818





