Capsanthin Inhibits Atherosclerotic Plaque Formation and Vascular Inflammation in ApoE−/− Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Treatments
2.2. Immunoblotting
2.3. Animal Studies
2.4. Hematological Parameter
2.5. Measurement of Lipid Parameters and Plasma Cytokines
2.6. Oil Red O Staining
2.7. Histological Analysis
2.8. Immunohistochemistry
2.9. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Capsanthin Inhibits VCAM-1 Expression and NF-κB p65 (s536) Phosphorylation in TNF-α-Stimulated HUVECs
3.2. Dietary Capsanthin Regulates Plasma Lipid Levels of WD-fed ApoE−/− Mice
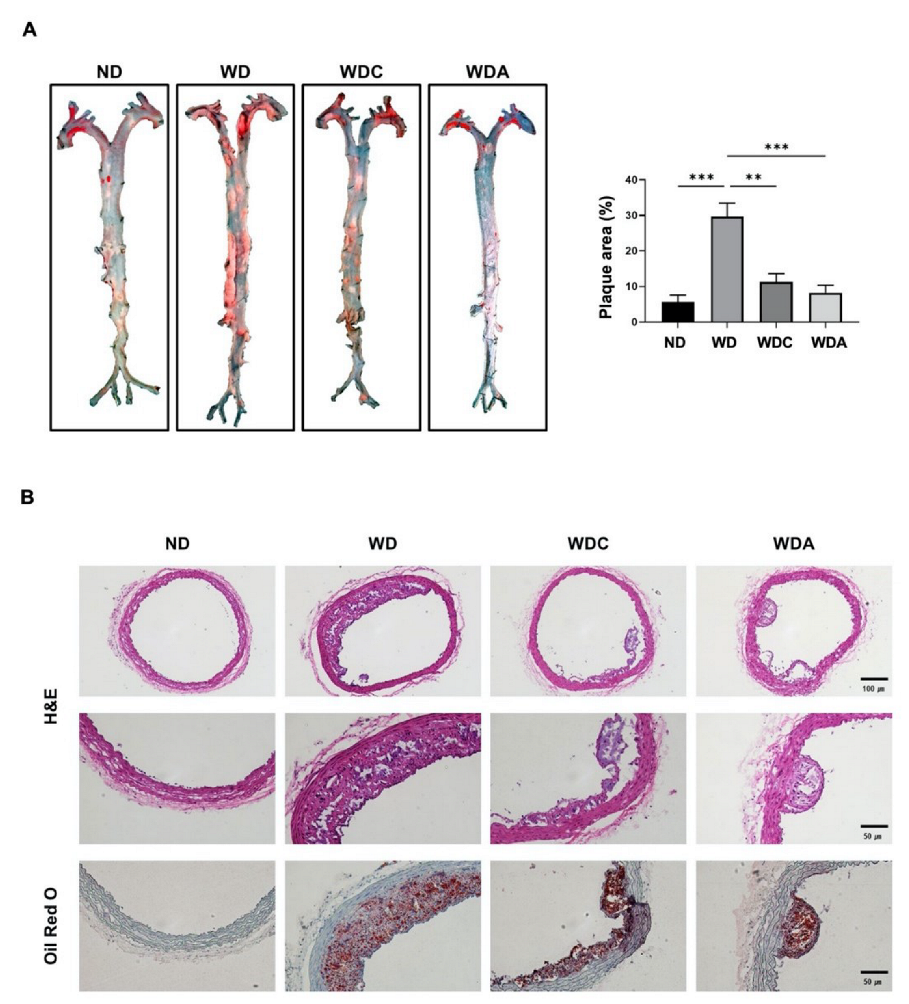
3.3. Capsanthin Reduces WD-Induced Atherosclerotic Plaque Formation
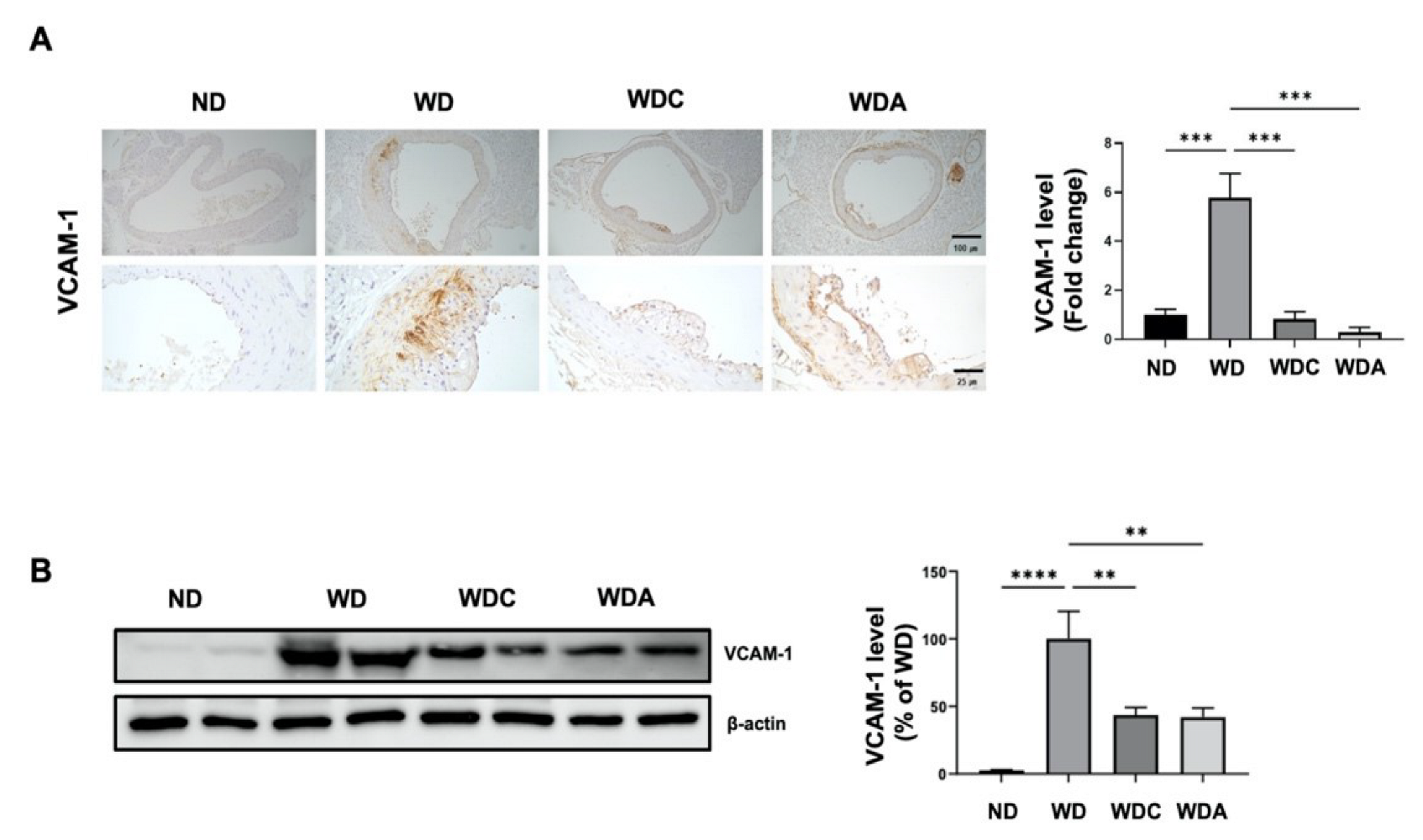
3.4. Capsanthin Inhibits Vascular Inflammation in Atherosclerotic Mice
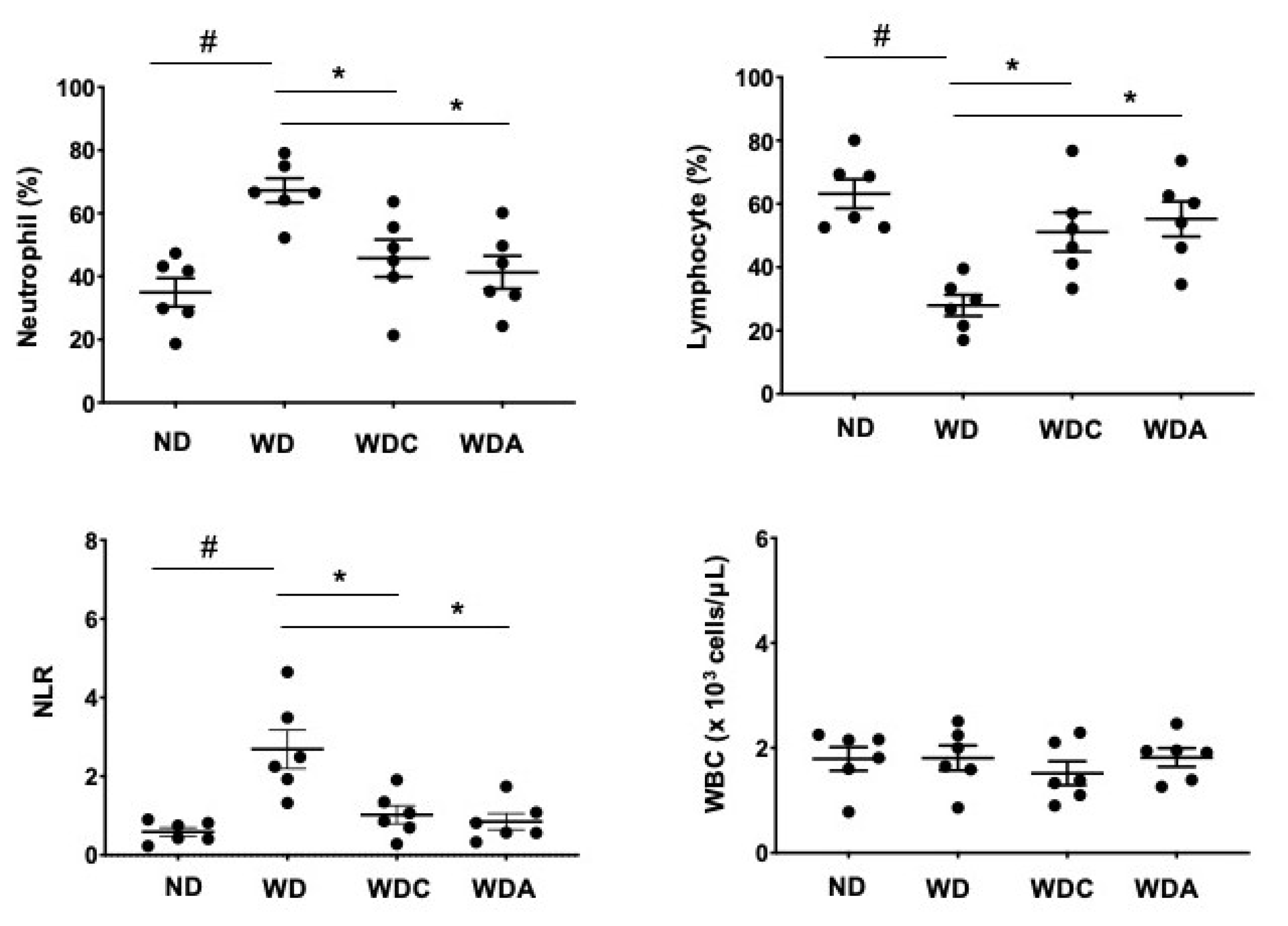
3.5. Capsanthin Attenuates the Neutrophil–Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR), an Inflammatory Marker, in Atherosclerotic Mice
3.6. Capsanthin Inhibits Plasma Inflammatory Cytokines
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frostegard, J. Immunity, atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease. BMC Med. 2013, 11, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, C.; Chimowitz, M.I. Stroke Caused by Atherosclerosis of the Major Intracranial Arteries. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 502–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagnoli, L.G.; Bonanno, E.; Sangiorgi, G.; Mauriello, A. Role of inflammation in atherosclerosis. J. Nucl. Med. 2007, 48, 1800–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libby, P.; Ridker, P.M.; Maseri, A. Inflammation and atherosclerosis. Circulation 2002, 105, 1135–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libby, P. Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Nature 2002, 420, 868–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Back, M.; Hansson, G.K. Anti-inflammatory therapies for atherosclerosis. Nat. Rev. Cardiol 2015, 12, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chistiakov, D.A.; Melnichenko, A.A.; Grechko, A.V.; Myasoedova, V.A.; Orekhov, A.N. Potential of anti-inflammatory agents for treatment of atherosclerosis. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2018, 104, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soehnlein, O.; Libby, P. Targeting inflammation in atherosclerosis—From experimental insights to the clinic. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 589–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theodorou, K.; Boon, R.A. Endothelial Cell Metabolism in Atherosclerosis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 6, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cahill, P.A.; Redmond, E.M. Vascular endothelium—Gatekeeper of vessel health. Atherosclerosis 2016, 248, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudau, M.; Genis, A.; Lochner, A.; Strijdom, H. Endothelial dysfunction: The early predictor of atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc. J. Afr. 2012, 23, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krieglstein, C.F.; Granger, D.N. Adhesion molecules and their role in vascular disease. Am. J. Hypertens 2001, 14, 44S–54S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborn, L.; Hession, C.; Tizard, R.; Vassallo, C.; Luhowskyj, S.; Chi-Rosso, G.; Lobb, R. Direct expression cloning of vascular cell adhesion molecule 1, a cytokine-induced endothelial protein that binds to lymphocytes. Cell 1989, 59, 1203–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobryshev, Y.V. Monocyte recruitment and foam cell formation in atherosclerosis. Micron 2006, 37, 208–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emini Veseli, B.; Perrotta, P.; De Meyer, G.R.A.; Roth, L.; Van der Donckt, C.; Martinet, W.; De Meyer, G.R.Y. Animal models of atherosclerosis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 816, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plump, A.S.; Smith, J.D.; Hayek, T.; Aalto-Setala, K.; Walsh, A.; Verstuyft, J.G.; Rubin, E.M.; Breslow, J.L. Severe hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice created by homologous recombination in ES cells. Cell 1992, 71, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieger, M.; Herz, J. Structures and functions of multiligand lipoprotein receptors: Macrophage scavenger receptors and LDL receptor-related protein (LRP). Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1994, 63, 601–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.R.; Joo, H.K.; Lee, E.O.; Park, M.S.; Cho, H.S.; Kim, S.; Jin, H.; Jeong, J.O.; Kim, C.S.; Jeon, B.H. Plasma APE1/Ref-1 Correlates with Atherosclerotic Inflammation in ApoE−/− Mice. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maoka, T. Carotenoids as natural functional pigments. J. Nat. Med. 2020, 74, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Concepcion, M.; Avalos, J.; Bonet, M.L.; Boronat, A.; Gomez-Gomez, L.; Hornero-Mendez, D.; Limon, M.C.; Melendez-Martinez, A.J.; Olmedilla-Alonso, B.; Palou, A.; et al. A global perspective on carotenoids: Metabolism, biotechnology, and benefits for nutrition and health. Prog. Lipid Res. 2018, 70, 62–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, A.A.; Perez-Galvez, A. Carotenoids as a Source of Antioxidants in the Diet. Subcell. Biochem. 2016, 79, 359–375. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, L.E.; Abraham, A.; Kulkarni, G.; Shettigar, N.; Dave, T.; Kulkarni, M. Capsanthin, a Plant-Derived Xanthophyll: A Review of Pharmacology and Delivery Strategies. AAPS PharmSciTech 2021, 22, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Rodriguez, E.; Sanchez-Prieto, M.; Olmedilla-Alonso, B. Assessment of carotenoid concentrations in red peppers (Capsicum annuum) under domestic refrigeration for three weeks as determined by HPLC-DAD. Food Chem. X 2020, 6, 100092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arimboor, R.; Natarajan, R.B.; Menon, K.R.; Chandrasekhar, L.P.; Moorkoth, V. Red pepper (Capsicum annuum) carotenoids as a source of natural food colors: Analysis and stability—A review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 1258–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moukarzel, A.A.; Bejjani, R.A.; Fares, F.N. Xanthophylls and eye health of infants and adults. J. Med. Liban 2009, 57, 261–267. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, V.C.; Rosen, R.B.; Farah, M. Macular pigment in retinal health and disease. Int. J. Retina Vitreous 2016, 2, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanmugham, V.; Subban, R. Extraction of capsanthin from Capsicum annum L. fruits and its effect on carbomer-induced intraocular pressure in Albino Wistar rats. J. Food Biochem. 2021, 45, e13776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Galvez, A.; Minguez-Mosquera, M.I. Structure-reactivity relationship in the oxidation of carotenoid pigments of the pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 4864–4869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maoka, T.; Mochida, K.; Kozuka, M.; Ito, Y.; Fujiwara, Y.; Hashimoto, K.; Enjo, F.; Ogata, M.; Nobukuni, Y.; Tokuda, H.; et al. Cancer chemopreventive activity of carotenoids in the fruits of red paprika Capsicum annuum L. Cancer Lett. 2001, 172, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Garcia, E.; Carvajal-Lerida, I.; Perez-Galvez, A. Carotenoids exclusively synthesized in red pepper (capsanthin and capsorubin) protect human dermal fibroblasts against UVB induced DNA damage. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2016, 15, 1204–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, H.; Saito, S.; Nakamura, N.; Maoka, T. Paprika Pigments Attenuate Obesity-Induced Inflammation in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. ISRN Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 763758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joo, H.K.; Lee, Y.R.; Lee, E.O.; Kim, S.; Jin, H.; Kim, S.; Lim, Y.P.; An, C.G.; Jeon, B.H. Protective Role of Dietary Capsanthin in a Mouse Model of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Med. Food 2021, 24, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Z.; Wang, M.; Xing, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, H. Myricetin ameliorates atherosclerosis in the low-density-lipoprotein receptor knockout mice by suppression of cholesterol accumulation in macrophage foam cells. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 16, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanta, S.; Yin, C.; Weber, C.; Hu, D.; Habenicht, A.J. Aorta Atherosclerosis Lesion Analysis in Hyperlipidemic Mice. Biol. Protocol. 2016, 6, e1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kempe, S.; Kestler, H.; Lasar, A.; Wirth, T. NF-kappaB controls the global pro-inflammatory response in endothelial cells: Evidence for the regulation of a pro-atherogenic program. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 5308–5319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ley, K.; Huo, Y. VCAM-1 is critical in atherosclerosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 107, 1209–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, L.B.; Yu, Z.M.; Guo, P.; Wang, Q.Q.; Qi, R.M.; Shan, M.J.; Lv, J.; Gong, T. Neutrophils and neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio: Inflammatory markers associated with intimal-media thickness of atherosclerosis. Thromb. Res. 2018, 170, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corriere, T.; Di Marca, S.; Cataudella, E.; Pulvirenti, A.; Alaimo, S.; Stancanelli, B.; Malatino, L. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio is a strong predictor of atherosclerotic carotid plaques in older adults. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2018, 28, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramji, D.P.; Davies, T.S. Cytokines in atherosclerosis: Key players in all stages of disease and promising therapeutic targets. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015, 26, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabi, F.; Arain, M.A.; Rajput, N.; Alagawany, M.; Soomro, J.; Umer, M.; Soomro, F.; Wang, Z.; Ye, R.; Liu, J. Health benefits of carotenoids and potential application in poultry industry: A review. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2020, 104, 1809–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, E.J. The role of carotenoids in human health. Nutr. Clin. Care 2002, 5, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabir, M.T.; Rahman, M.H.; Shah, M.; Jamiruddin, M.R.; Basak, D.; Al-Harrasi, A.; Bhatia, S.; Ashraf, G.M.; Najda, A.; El-Kott, A.F.; et al. Therapeutic promise of carotenoids as antioxidants and anti-inflammatory agents in neurodegenerative disorders. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 146, 112610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oshima, S.; Sakamoto, H.; Ishiguro, Y.; Terao, J. Accumulation and clearance of capsanthin in blood plasma after the ingestion of paprika juice in men. J. Nutr. 1997, 127, 1475–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aizawa, K.; Inakuma, T. Dietary capsanthin, the main carotenoid in paprika (Capsicum annuum), alters plasma high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol levels and hepatic gene expression in rats. Br. J. Nutr. 2009, 102, 1760–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joo, H.K.; Choi, S.; Lee, Y.R.; Lee, E.O.; Park, M.S.; Park, K.B.; Kim, C.S.; Lim, Y.P.; Park, J.T.; Jeon, B.H. Anthocyanin-Rich Extract from Red Chinese Cabbage Alleviates Vascular Inflammation in Endothelial Cells and Apo E−/− Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefer, D.J. Statins as potent antiinflammatory drugs. Circulation 2002, 106, 2041–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortese, F.; Gesualdo, M.; Cortese, A.; Carbonara, S.; Devito, F.; Zito, A.; Ricci, G.; Scicchitano, P.; Ciccone, M.M. Rosuvastatin: Beyond the cholesterol-lowering effect. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 107, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, A.B.; Jacob, S. A simple practice guide for dose conversion between animals and human. J. Basic Clin. Pharm. 2016, 7, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Plasma Lipids | ND | WD | WDC | WDA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TC (mg/dL) | 447.5 ± 31.6 | 1470.0 ± 77.2 ## | 764.8 ± 119.7 *** | 958.3 ± 53.7 *** |
| LDL-C (mg/dL) | 187.3 ± 20.3 | 823.3 ± 47.0 ## | 374.6 ± 60.8 *** | 540.9 ± 31.4 *** |
| HDL-C (mg/dL) | 62.9 ± 7.7 | 99.3 ± 10.2 ## | 63.9 ± 3.8 ** | 80.9 ± 3.3 |
| TG (mg/dL) | 97.0 ± 15.2 | 184.5 ± 24.7 ## | 117.5 ± 14.1 * | 116.0 ± 12.5 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.; Lee, Y.-R.; Lee, E.-O.; Jin, H.; Choi, Y.-H.; Joo, H.-K.; Jeon, B.-H. Capsanthin Inhibits Atherosclerotic Plaque Formation and Vascular Inflammation in ApoE−/− Mice. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1780. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10081780
Kim S, Lee Y-R, Lee E-O, Jin H, Choi Y-H, Joo H-K, Jeon B-H. Capsanthin Inhibits Atherosclerotic Plaque Formation and Vascular Inflammation in ApoE−/− Mice. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(8):1780. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10081780
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Sungmin, Yu-Ran Lee, Eun-Ok Lee, Hao Jin, Yeon-Hee Choi, Hee-Kyoung Joo, and Byeong-Hwa Jeon. 2022. "Capsanthin Inhibits Atherosclerotic Plaque Formation and Vascular Inflammation in ApoE−/− Mice" Biomedicines 10, no. 8: 1780. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10081780
APA StyleKim, S., Lee, Y.-R., Lee, E.-O., Jin, H., Choi, Y.-H., Joo, H.-K., & Jeon, B.-H. (2022). Capsanthin Inhibits Atherosclerotic Plaque Formation and Vascular Inflammation in ApoE−/− Mice. Biomedicines, 10(8), 1780. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10081780








