Allergic Rhinitis: Pathophysiology and Treatment Focusing on Mast Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mast Cells’ Role in Allergic Inflammation
3. MCs’ Link to the Adaptive Immune Response
4. MCs’ Role in AR Initiation, Progression, and Modulation
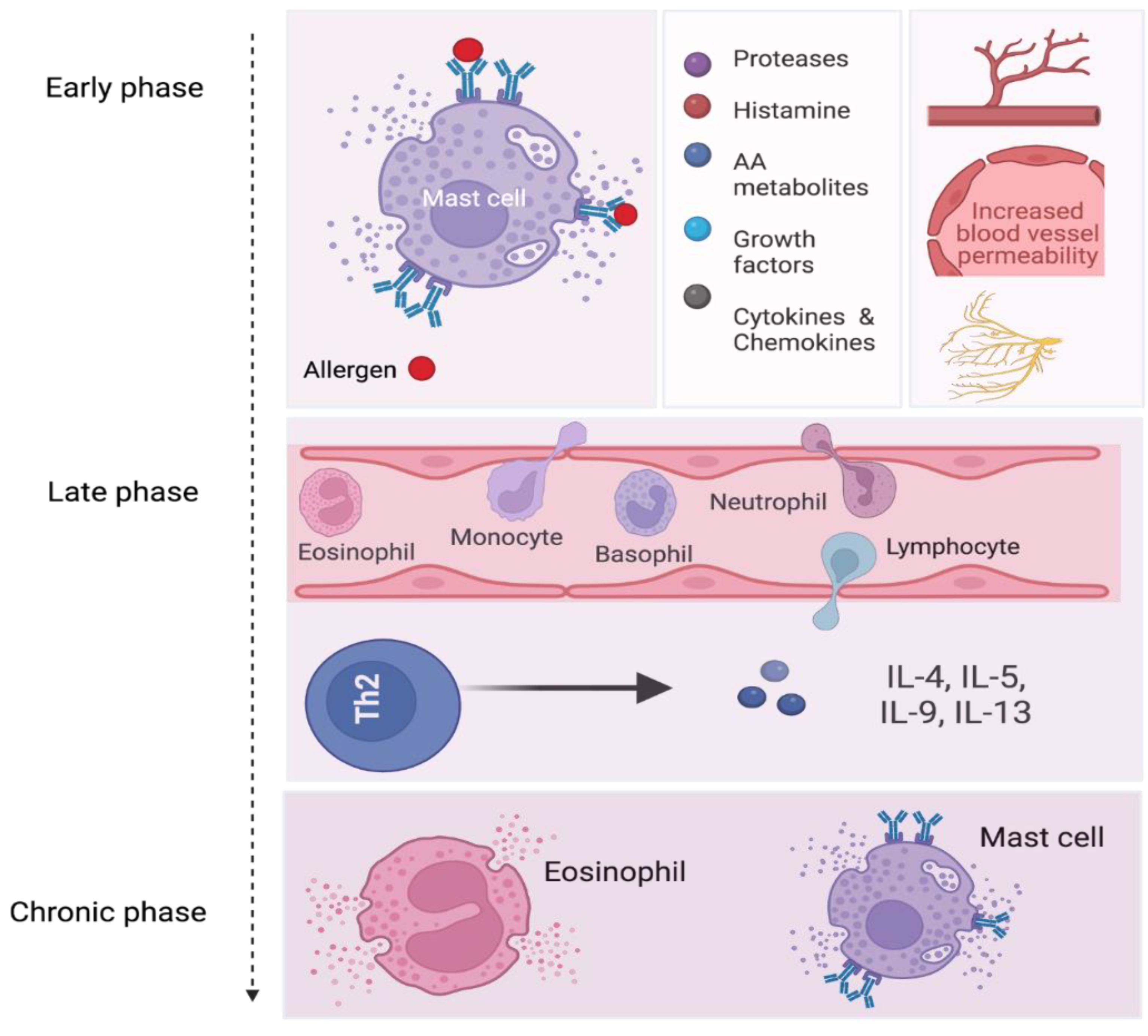
5. Phases of Allergic Inflammation
6. CD48 in AR and CRSwNP
7. Differential Gene Expression Profiles in AR Patients
8. Overview of AR Treatment
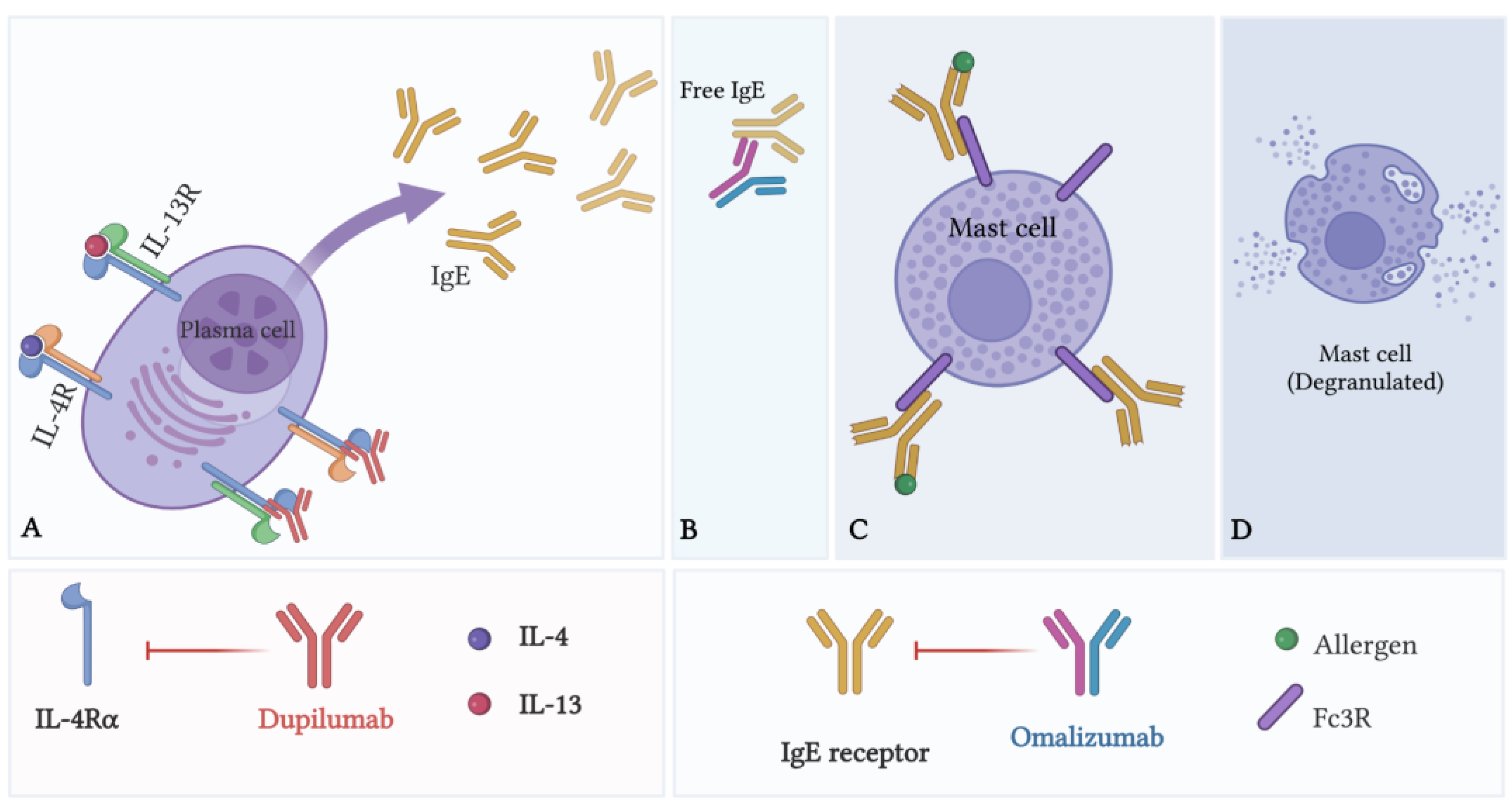
9. AR Pharmacotherapy Specifically Targeting MCs and Their Pathways (Table 1)
| Agent | Mechanism of Action | Effect on MCs and Immune Cells |
|---|---|---|
| Antihistamines | Histamine receptor blockade | Inhibiting histamine’s effect |
| GCSs | Modifications of gene transcription leading to reduction in inflammatory mediators synthesis (i.e., IL1-8, TNFα, IFN-γ, and GM-CSF) and controlling preonset activation of MCs and eosinophils | Attenuated recruitment and activation of MCs, eosinophils, and other immune cells |
| LTRAs | Blockade of leukotriene receptors | Attenuating immune cell activation by leukotrienes |
| CS | MC stabilization | Limiting inflammatory mediator release from MCs; attenuating the allergic inflammation |
| Omalizumab | Blockade of IgE antibodies | Limiting MC activation and degranulation |
| Dupilumab | Blockade of IL-4Rα subunit of IL-4 and IL-13 receptors | Limiting MC activation and degranulation |
| Allergen immunotherapy | Early desensitization of MCs, generation of regulatory lymphocytes responses, and regulation of IgE production | Reduction in MC and eosinophil activity |
10. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hox, V.; Lourijsen, E.; Jordens, A.; Aasbjerg, K.; Agache, I.; Alobid, I.; Bachert, C.; Boussery, K.; Campo, P.; Fokkens, W.; et al. Benefits and harm of systemic steroids for short- and long-term use in rhinitis and rhinosinusitis: An EAACI position paper. Clin. Transl. Allergy 2020, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Justiz Vaillant, A.A.; Vashisht, R.; Zito, P.M. Immediate Hypersensitivity Reactions. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK513315/ (accessed on 24 September 2022).
- Wise, S.K.; Lin, S.Y.; Toskala, E.; Orlandi, R.R.; Akdis, C.A.; Alt, J.A.; Azar, A.; Baroody, F.M.; Bachert, C.; Canonica, G.W.; et al. International Consensus Statement on Allergy and Rhinology: Allergic Rhinitis: ICAR: Allergic Rhinitis. Int. Forum. Allergy Rhinol. 2018, 8, 108–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhouri, S.; House, S.A. Allergic Rhinitis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538186/ (accessed on 7 November 2021).
- Di Lorenzo, G.; Mansueto, P.; Melluso, M.; Candore, G.; Colombo, A.; Pellitteri, M.E.; Drago, A.; Potestio, M.; Caruso, C. Allergic rhinitis to grass pollen: Measurement of inflammatory mediators of mast cell and eosinophils in native nasal fluid lavage and in serum out of and during pollen season. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1997, 100, 832–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, P.; Keith, P.K.; Kim, H. Allergic rhinitis. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2018, 14, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puzzovio, P.G.; Levi-Schaffer, F. Latest Progresses in Allergic Diseases Biomarkers: Asthma and Atopic Dermatitis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 747364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangwar, R.S.; Pahima, H.; Puzzovio, P.G.; Levi-Schaffer, F. Update on Eosinophil Interaction with Mast Cells: The Allergic Effector Unit. In Eosinophils; Walsh, G.M., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 221–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, C.J.; Uddin, M.J.; Saha, S.K.; Darmstadt, G.L. Prevalence of atopic dermatitis, asthma and rhinitis from infancy through adulthood in rural Bangladesh: A population-based, cross-sectional survey. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e042380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokkens, W.J.; Lund, V.J.; Hopkins, C.; Hellings, P.W.; Kern, R.; Reitsma, S.; Toppila-Salmi, S.; Bernal-Sprekelsen, M.; Mullol, J.; Alobid, I.; et al. European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps 2020. Rhinol. Off. Organ Int. Rhinol. Soc. 2020, 58 (Suppl. S29), 1–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelardi, M.; Giancaspro, R.; Cassano, M.; Ribatti, D. The Underestimated Role of Mast Cells in the Pathogenesis of Rhinopathies. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2022, 183, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helman, S.N.; Barrow, E.; Edwards, T.; DelGaudio, J.M.; Levy, J.M.; Wise, S.K. The Role of Allergic Rhinitis in Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Immunol. Allergy Clin. North Am. 2020, 40, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuruvilla, M.E.; Vanijcharoenkarn, K.; Levy, J.M. The Role of Mast Cells in Aspirin-Exacerbated Respiratory Disease (AERD) Pathogenesis: Implications for Future Therapeutics. J. Asthma Allergy 2020, 13, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krystel-Whittemore, M.; Dileepan, K.N.; Wood, J.G. Mast Cell: A Multi-Functional Master Cell. Front. Immunol. 2016, 6, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Je, I.G.; Song, J.; Fei, X.; Lee, S.; Yang, H.; Kang, W.; Jang, Y.H.; Seo, S.Y.; Kim, S.H. SG-SP1 Suppresses Mast Cell-Mediated Allergic Inflammation via Inhibition of FcεRI Signaling. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsoulis-Dimitriou, K.; Kotrba, J.; Voss, M.; Dudeck, J.; Dudeck, A. Mast Cell Functions Linking Innate Sensing to Adaptive Immunity. Cells 2020, 9, 2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalfe, D.D.; Pawankar, R.; Ackerman, S.J.; Akin, C.; Clayton, F.; Falcone, F.H.; Gleich, G.J.; Irani, A.-M.; Johansson, M.W.; Klion, A.D.; et al. Biomarkers of the involvement of mast cells, basophils and eosinophils in asthma and allergic diseases. World Allergy Organ. J. 2016, 9, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, A.M.; Cripps, A.W.; West, N.P.; Cox, A.J. Modulation of Allergic Inflammation in the Nasal Mucosa of Allergic Rhinitis Sufferers With Topical Pharmaceutical Agents. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoabi, Y.; Rahimli Alekberli, F.; Minai-Fleminger, Y.; Eliashar, R.; Levi-Schaffer, F. CD48 Expression on Eosinophils in Nasal Polyps of Chronic Rhinosinusitis Patients. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2021, 182, 962–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patente, T.A.; Pinho, M.P.; Oliveira, A.A.; Evangelista, G.C.M.; Bergami-Santos, P.C.; Barbuto, J.A.M. Human Dendritic Cells: Their Heterogeneity and Clinical Application Potential in Cancer Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2019, 9, 3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.; Tikoo, S.; Weninger, W. Mast cell granules: Modulating adaptive immune response remotely. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 1731–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyte, F.C.L.; Nelson, H.S. Recent advances in allergic rhinitis. F1000Research 2018, 7, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sy, C.B.; Siracusa, M.C. The Therapeutic Potential of Targeting Cytokine Alarmins to Treat Allergic Airway Inflammation. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whetstone, C.E.; Ranjbar, M.; Omer, H.; Cusack, R.P.; Gauvreau, G.M. The Role of Airway Epithelial Cell Alarmins in Asthma. Cells 2022, 11, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puzzovio, P.G.; Levi-Schaffer, F. The allergic effector unit: From basic science to drug-targetable mast cell–eosinophil interactions in patients. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 3845–3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roufosse, F. Targeting the Interleukin-5 Pathway for Treatment of Eosinophilic Conditions Other than Asthma. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puzzovio, P.G.; Eliashar, R.; Levi-Schaffer, F. Tezepelumab administration in moderate-to-severe uncontrolled asthma: Is it all about eosinophils? J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 149, 1582–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, N.; Terawaki, S.; Shimizu, K.; Oikawa, D.; Sakamoto, H.; Sunami, K.; Tokunaga, F. Th2 cells and macrophages cooperatively induce allergic inflammation through histamine signaling. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatarkiewicz, J.; Rzodkiewicz, P.; Żochowska, M.; Staniszewska, A.; Bujalska-Zadrożny, M. New antihistamines—Perspectives in the treatment of some allergic and inflammatory disorders. Arch. Med. Sci. 2019, 15, 537–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangam, E.B.; Jemima, E.A.; Singh, H.; Baig, M.S.; Khan, M.; Mathias, C.B.; Church, M.K.; Saluja, R. The Role of Histamine and Histamine Receptors in Mast Cell-Mediated Allergy and Inflammation: The Hunt for New Therapeutic Targets. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Hong, H.; Zuo, K.; Han, M.; Li, J.; Wen, W.; Xu, G.; Miao, B.; Li, H. Expression of leukotriene and its receptors in eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps: Expression of LT and its receptors in ECRS. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2016, 6, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuzzo, B.; Lappin, S.L. Physiology, Leukotrienes. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526114/ (accessed on 24 September 2022).
- Lee, K.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, T.H. The Biology of Prostaglandins and Their Role as a Target for Allergic Airway Disease Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branicka, O.; Jura-Szołtys, E.; Rogala, B.; Glück, J. Elevated Serum Level of CD48 in Patients with Intermittent Allergic Rhinitis. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2021, 182, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, A.M.; West, N.P.; Smith, P.K.; Cripps, A.W.; Cox, A.J. Adult allergic rhinitis sufferers have unique nasal mucosal and peripheral blood immune gene expression profiles: A case–control study. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2022, 10, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossenbaccus, L.; Linton, S.; Garvey, S.; Ellis, A.K. Towards definitive management of allergic rhinitis: Best use of new and established therapies. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2020, 16, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heffler, E.; Brussino, L.; Del Giacco, S.; Paoletti, G.; Minciullo, P.L.; Varricchi, G.; Scadding, G.; Malvezzi, L.; De Virgilio, A.; Spriano, G.; et al. New drugs in early-stage clinical trials for allergic rhinitis. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2019, 28, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, N.P.; Vickery, J.; Blaiss, M.S. Management of Rhinitis: Allergic and Non-Allergic. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2011, 3, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipworth, B.; Newton, J.; Ram, B.; Small, I.; Schwarze, J. An algorithm recommendation for the pharmacological management of allergic rhinitis in the UK: A consensus statement from an expert panel. NPJ Prim. Care Respir. Med. 2017, 27, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jo-Watanabe, A.; Okuno, T.; Yokomizo, T. The Role of Leukotrienes as Potential Therapeutic Targets in Allergic Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamada, T.; Ichinose, M. Leukotriene Receptor Antagonists and Antiallergy Drugs. In Pharmacology and Therapeutics of Asthma and COPD; Page, C.P., Barnes, P.J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 153–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minutello, K.; Gupta, V. Cromolyn Sodium. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557473/ (accessed on 24 September 2022).
- Puzzovio, P.G.; Brüggemann, T.R.; Pahima, H.; Mankuta, D.; Levy, B.D.; Levi-Schaffer, F. Cromolyn Sodium differentially regulates human mast cell and mouse leukocyte responses to control allergic inflammation. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 178, 106172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsabouri, S.; Ntritsos, G.; Koskeridis, F.; Evangelou, E.; Olsson, P.; Kostikas, K. Omalizumab for the treatment of allergic rhinitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Rhinology 2021, 59, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaliere, C.; Begvarfaj, E.; Incorvaia, C.; Sposato, B.; Brunori, M.; Ciofalo, A.; Greco, A.; de Vincentiis, M.; Masieri, S. Long-term omalizumab efficacy in allergic rhinitis. Immunol. Lett. 2020, 227, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevaert, P.; Omachi, T.A.; Corren, J.; Mullol, J.; Han, J.; Lee, S.E.; Kaufman, D.; Ligueros-Saylan, M.; Howard, M.; Zhu, R.; et al. Efficacy and safety of omalizumab in nasal polyposis: 2 randomized phase 3 trials. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 146, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masieri, S.; Cavaliere, C.; Begvarfaj, E.; Rosati, D.; Minni, A. Effects of omalizumab therapy on allergic rhinitis: A pilot study. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 20, 5249–5255. [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein, S.F.; Katial, R.; Jayawardena, S.; Pirozzi, G.; Staudinger, H.; Eckert, L.; Joish, V.N.; Amin, N.; Maroni, J.; Rowe, P.; et al. Efficacy and safety of dupilumab in perennial allergic rhinitis and comorbid asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 142, 171–177.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachert, C.; Han, J.K.; Desrosiers, M.; Hellings, P.W.; Amin, N.; Lee, S.E.; Mullol, J.; Greos, L.S.; Bosso, J.V.; Laidlaw, T.M.; et al. Efficacy and safety of dupilumab in patients with severe chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (LIBERTY NP SINUS-24 and LIBERTY NP SINUS-52): Results from two multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group phase 3 trials. Lancet 2019, 394, 1638–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, A.T.; Han, J.K.; Hellings, P.; Heffler, E.; Gevaert, P.; Bachert, C.; Xu, Y.; Chuang, C.C.; Neupane, B.; Msihid, J.; et al. Indirect Treatment Comparison of Biologics in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 2461–2471.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakli, H.A.; Riley, T.D. Allergic Rhinitis. Prim. Care Clin. Off. Pract. 2016, 43, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drazdauskaitė, G.; Layhadi, J.A.; Shamji, M.H. Mechanisms of Allergen Immunotherapy in Allergic Rhinitis. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2021, 21, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akdis, M.; Akdis, C.A. Mechanisms of allergen-specific immunotherapy: Multiple suppressor factors at work in immune tolerance to allergens. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zoabi, Y.; Levi-Schaffer, F.; Eliashar, R. Allergic Rhinitis: Pathophysiology and Treatment Focusing on Mast Cells. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2486. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102486
Zoabi Y, Levi-Schaffer F, Eliashar R. Allergic Rhinitis: Pathophysiology and Treatment Focusing on Mast Cells. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(10):2486. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102486
Chicago/Turabian StyleZoabi, Yara, Francesca Levi-Schaffer, and Ron Eliashar. 2022. "Allergic Rhinitis: Pathophysiology and Treatment Focusing on Mast Cells" Biomedicines 10, no. 10: 2486. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102486
APA StyleZoabi, Y., Levi-Schaffer, F., & Eliashar, R. (2022). Allergic Rhinitis: Pathophysiology and Treatment Focusing on Mast Cells. Biomedicines, 10(10), 2486. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102486






