Interplay between Partial EMT and Cisplatin Resistance as the Drivers for Recurrence in HNSCC
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Patients’ Profile
2.2. Enzyme Immunohistochemistry and TissueFAXS Acquisition
2.3. Ki-67 Level Quantification by StrataQuest in Primary Tumor and Recurrence Tumor Slides
2.4. Cell Culture, Cell Transfection and Generation of an EMT/MET Model by Ectopic KLF4-Overexpression and TGF-Beta1 Treatment
2.5. Western Blot Analysis to Detect the Different Protein Levels of EMT/MET Markers in SCC-25 Cells
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
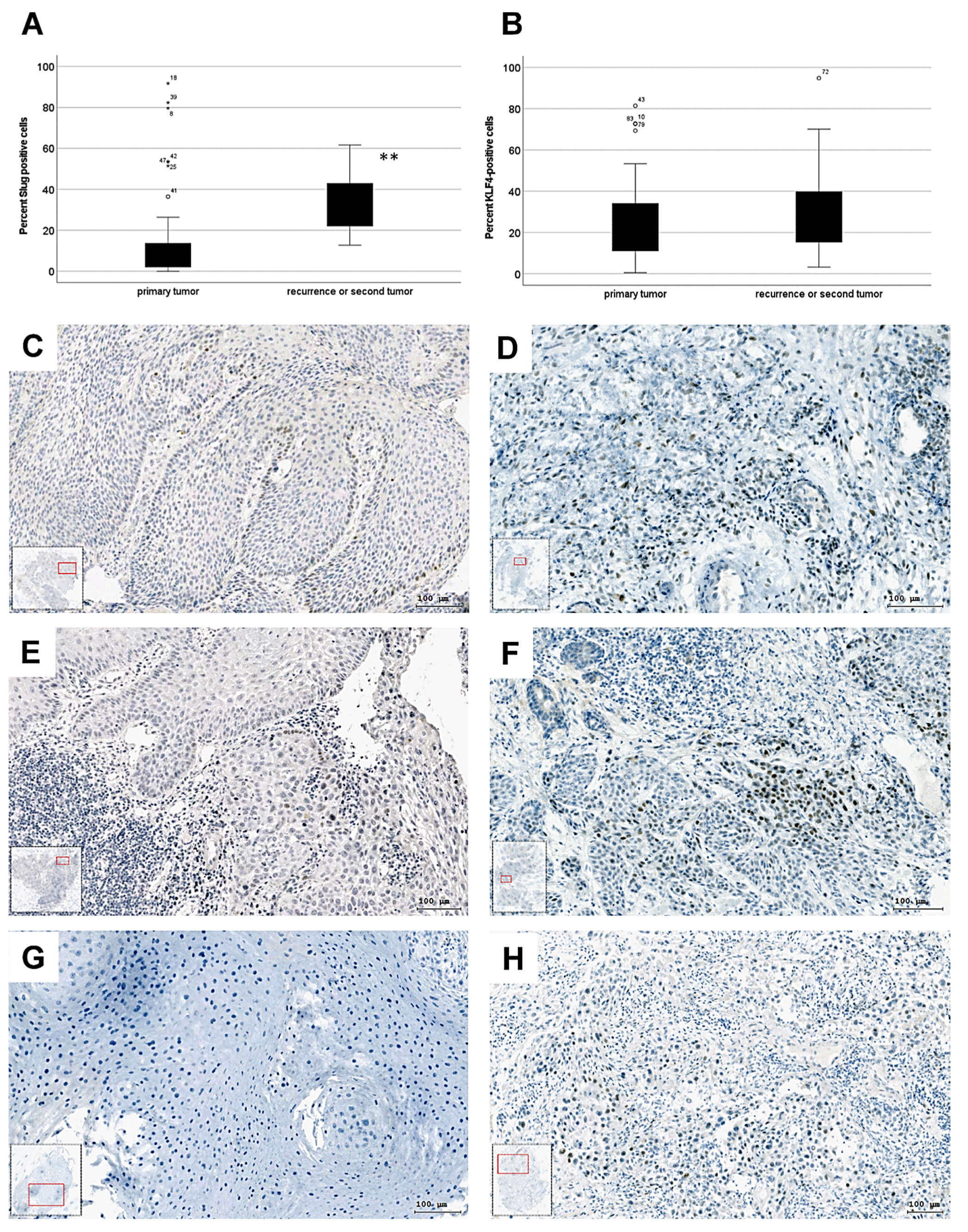
3.1. Slug-Positive Cells Expand after Therapy in HNSCC
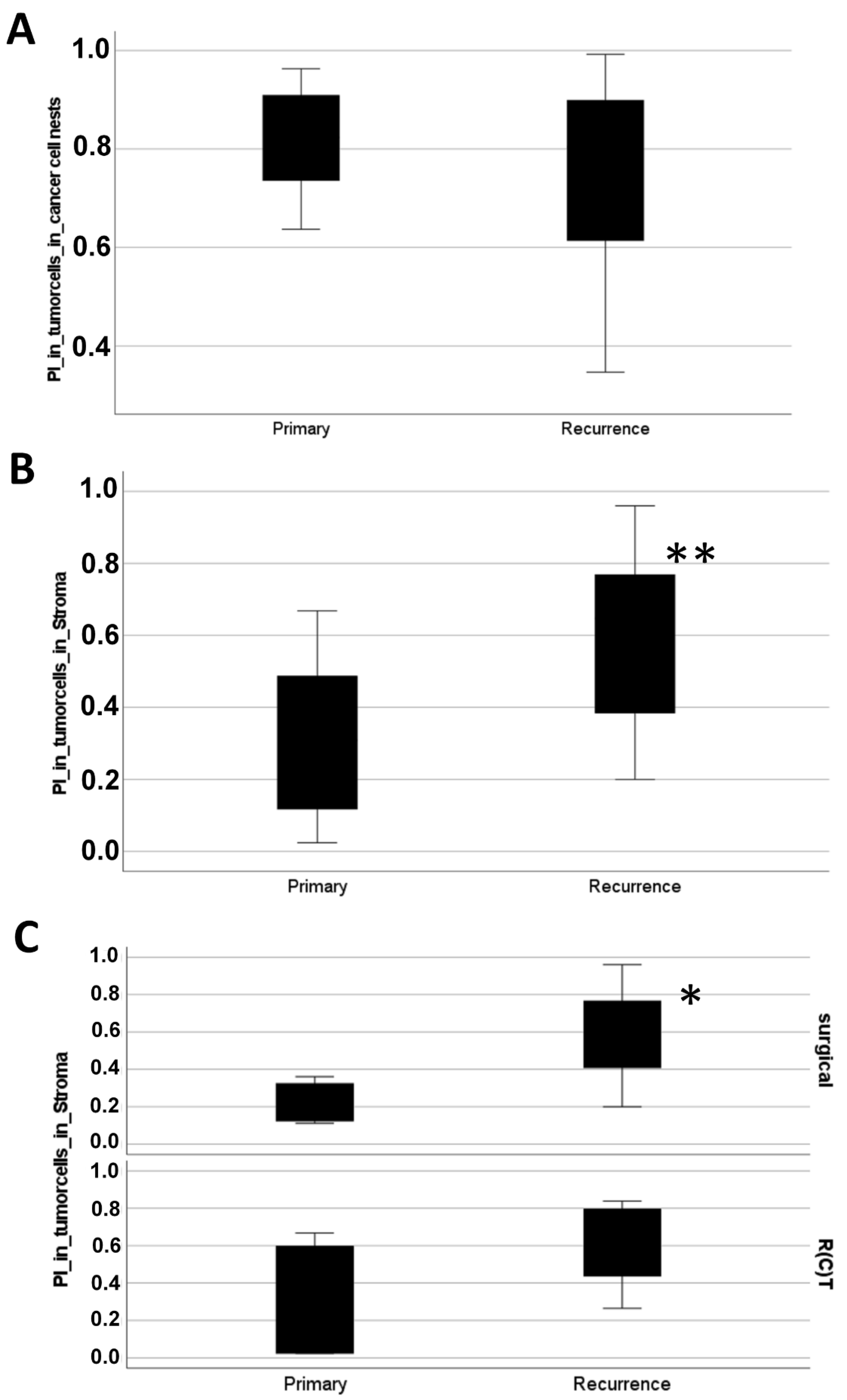
3.2. Disseminating Proliferating Cells Spread after Therapy in HNSCC
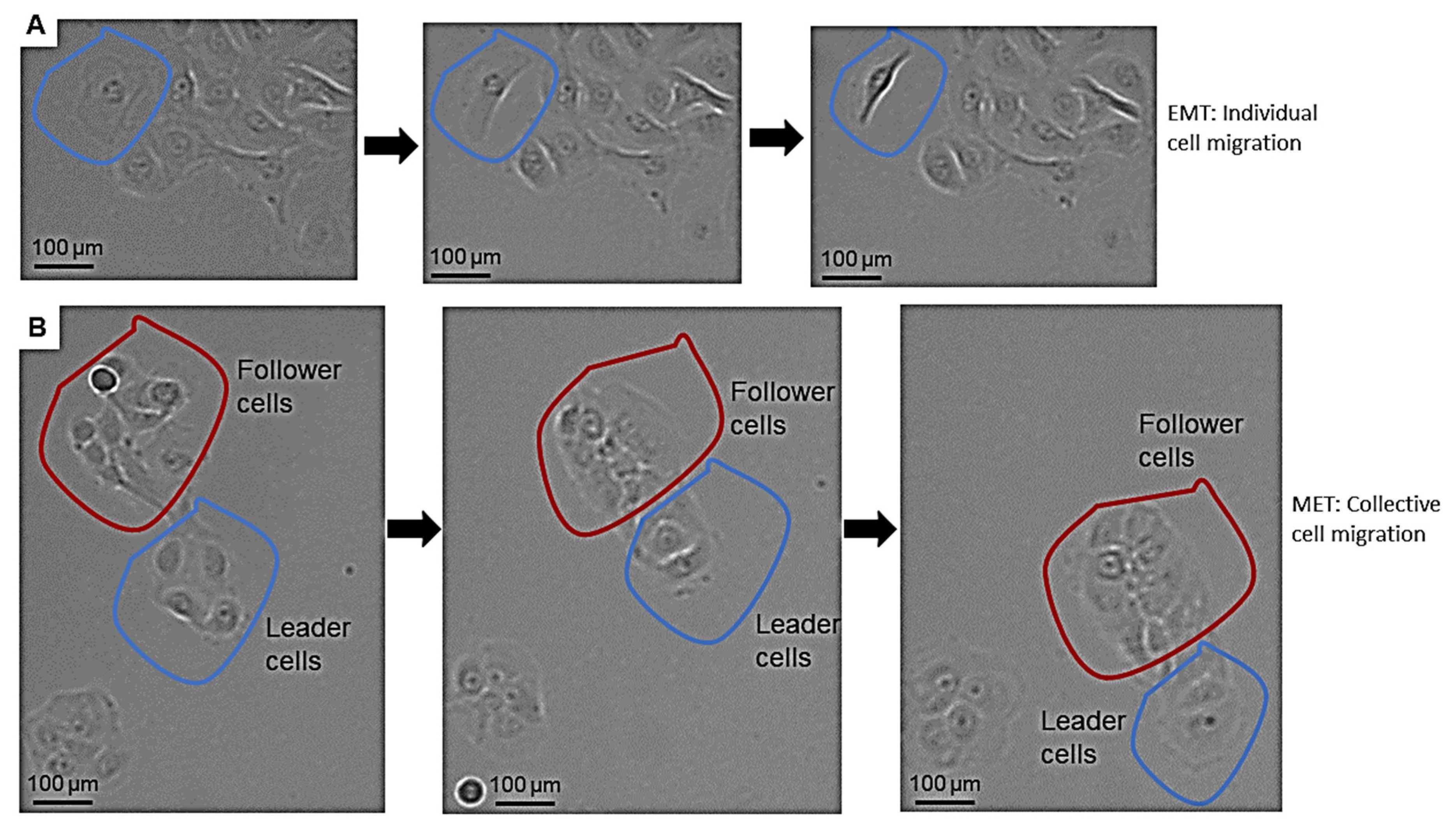
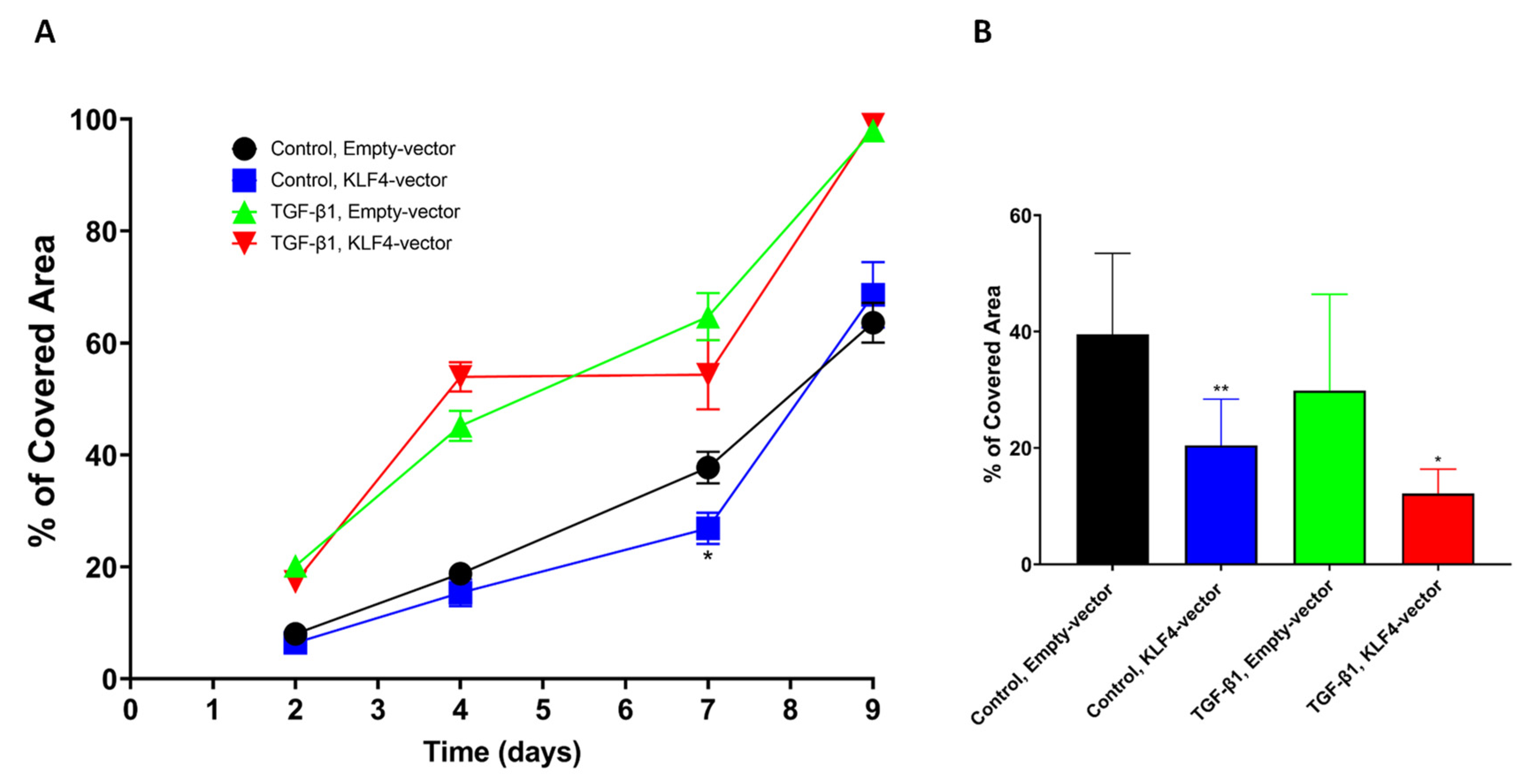
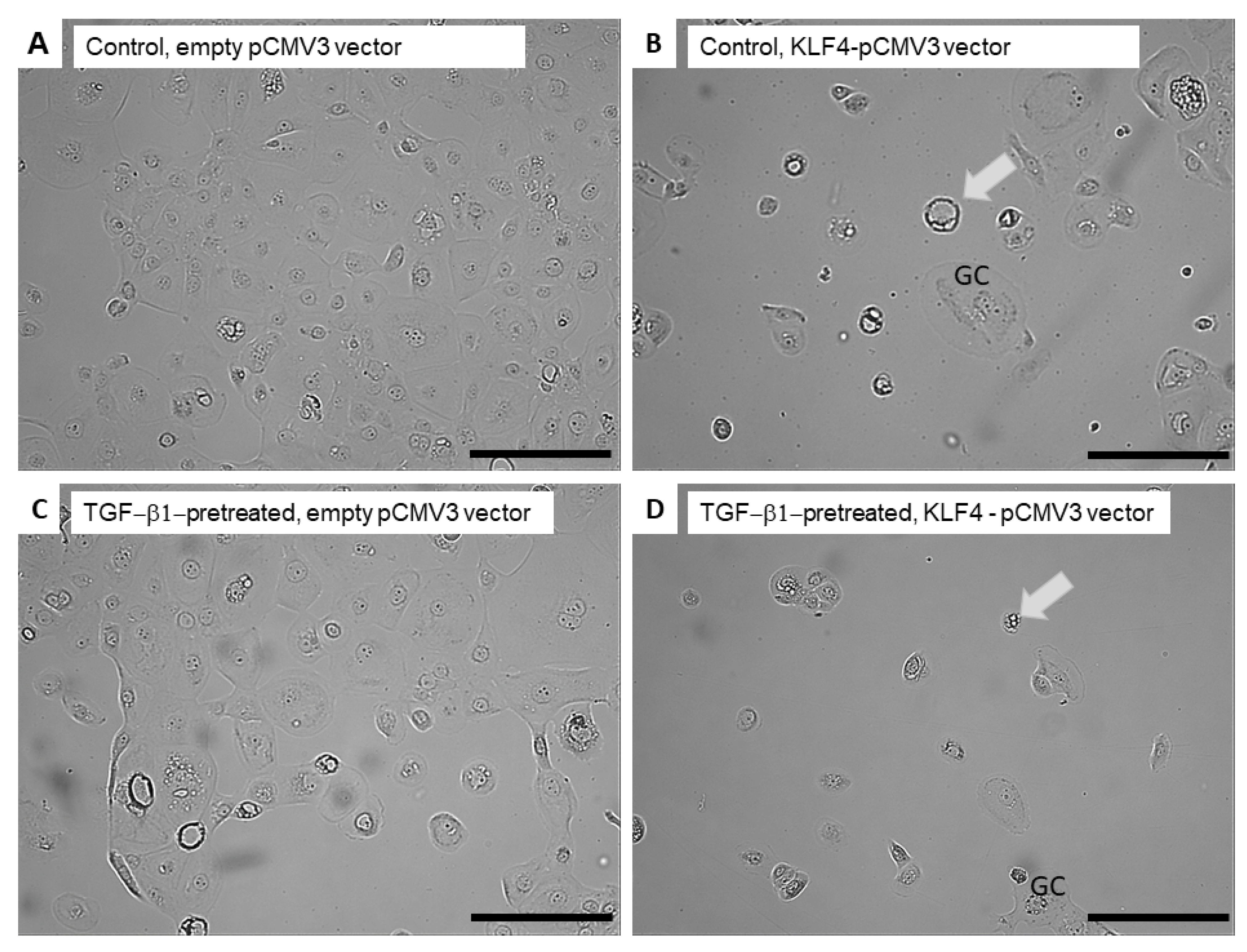
3.3. pEMT Enables the Expansion of Therapy-Resistant Cells in HNSCC via Single and Collective Cell Migration
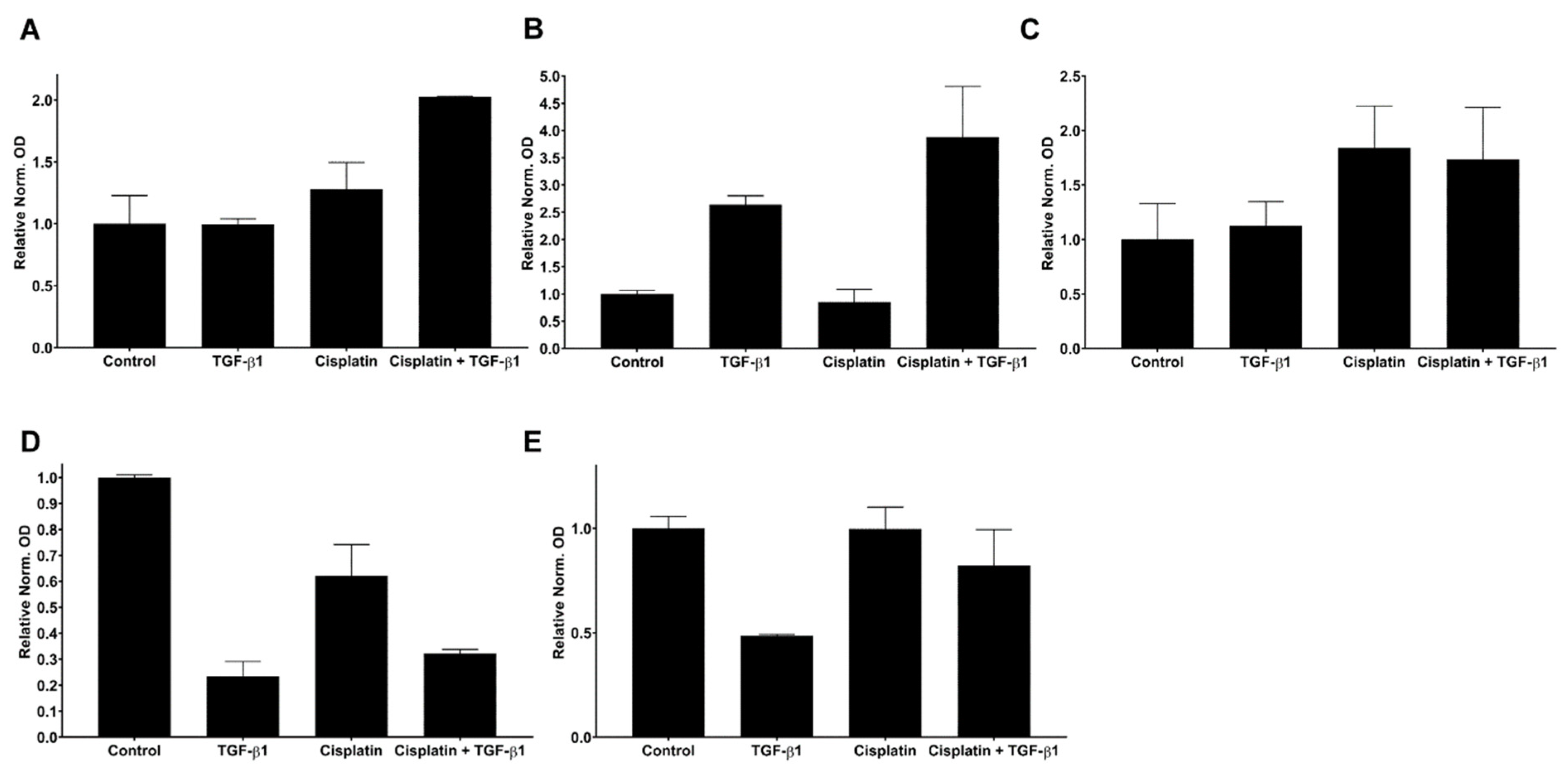
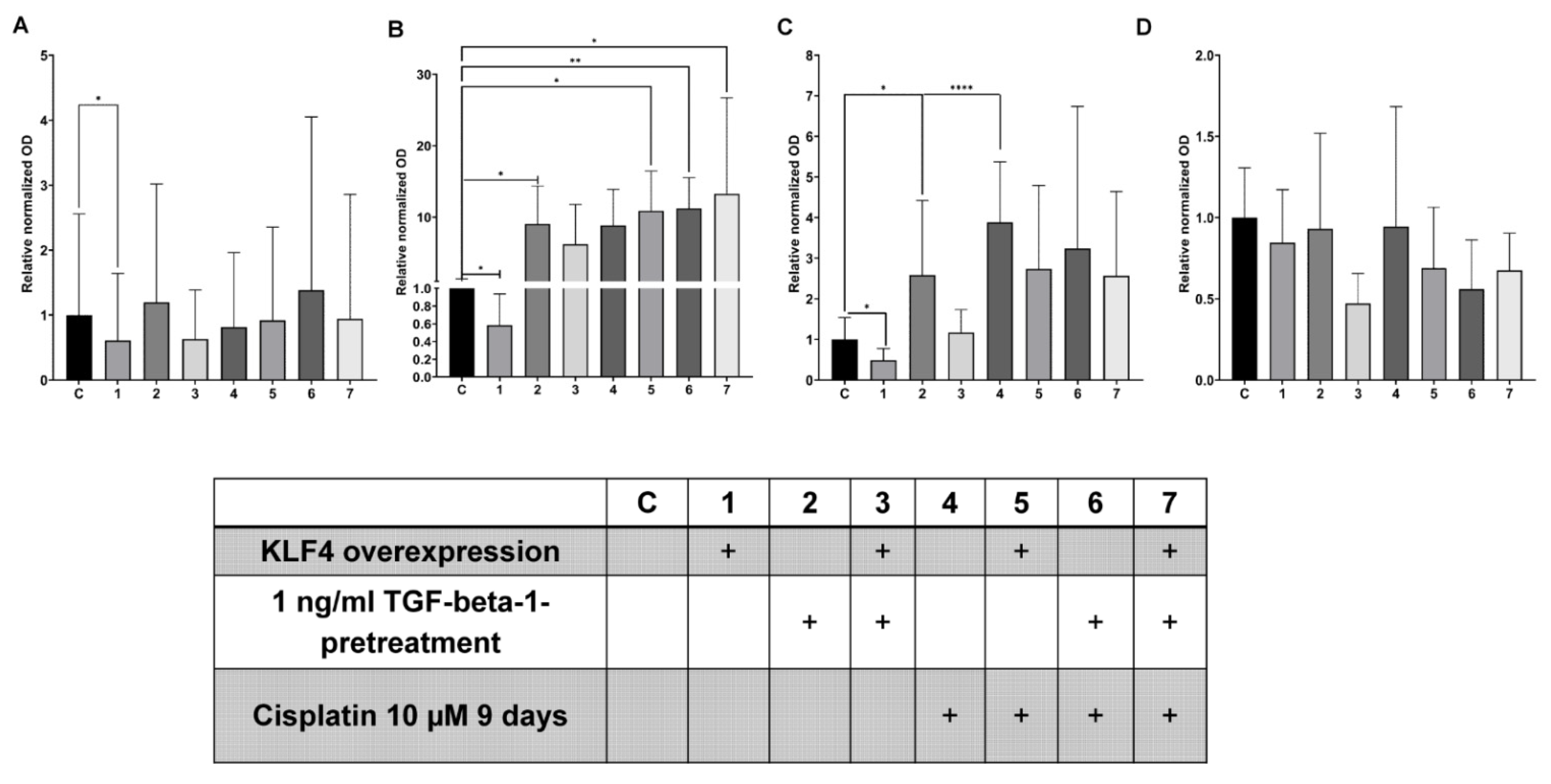
3.4. Interplay between TGF-Beta1-Induced EMT and Cisplatin in Simultaneous Treatment System
3.5. KLF4-Overexpression Downregulates Slug, Vimentin and p-p38 after TGF-Beta1-Induced EMT
3.6. Transient KLF4-Overexpression Sensitizes SCC-25 Cells to Cisplatin
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CAFs | cancer-associated fibroblasts |
| GAPDH | Glycerin aldehyde dehydrogenase |
| HNSCC | Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma |
| HPV | Human papilloma virus |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| KLF4 | Krüppel-like-factor-4 |
| MET | mesenchymal to epithelial transition |
| MAPK | mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| p-EMT | partial epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition |
| TGF-β1 | Transforming-growth-factor-beta-1 |
| TF | Transcription Factor |
| R(C)T | Radiochemotherapy |
| SLUG | Transcription Factor Slug |
References
- Steinbichler, T.B.; Dudas, J.; Skvortsov, S.; Ganswindt, U.; Riechelmann, H.; Skvortsova, I.-I. Therapy resistance mediated by cancer stem cells. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2018, 53, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinbichler, T.B.; Alshaimaa, A.; Maria, M.V.; Daniel, D.; Herbert, R.; Jozsef, D.; Ira-Ida, S. Epithelial-mesenchymal crosstalk induces radioresistance in HNSCC cells. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 3641–3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dudás, J.; Ladányi, A.; Ingruber, J.; Steinbichler, T.B.; Riechelmann, H. Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition: A Mechanism that Fuels Cancer Radio/Chemoresistance. Cells 2020, 9, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ingruber, J.; Savic, D.; Steinbichler, T.; Sprung, S.; Fleischer, F.; Glueckert, R.; Schweigl, G.; Skvortsova, I.-I.; Riechelmann, H.; Dudás, J. KLF4, Slug and EMT in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cells 2021, 10, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, C.D.; Parvani, J.G.; Schiemann, W.P. The relevance of the TGF-β Paradox to EMT-MET programs. Cancer Lett. 2013, 341, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brabletz, T.; Kalluri, R.; Nieto, M.A.; Weinberg, R.A. EMT in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinbichler, T.B.; Dudas, J.; Ingruber, J.; Glueckert, R.; Sprung, S.; Fleischer, F.; Cidlinsky, N.; Dejaco, D.; Kofler, B.; Giotakis, A.I.; et al. Slug Is A Surrogate Marker of Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) in Head and Neck Cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riechelmann, H.; Steinbichler, T.B.; Sprung, S.; Santer, M.; Runge, A.; Ganswindt, U.; Gamerith, G.; Dudas, J. The Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transcription Factor Slug Predicts Survival Benefit of Up-Front Surgery in Head and Neck Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingruber, J.; Dudás, J.; Savic, D.; Schweigl, G.; Steinbichler, T.B.; Greier, M.D.C.; Santer, M.; Carollo, S.; Trajanoski, Z.; Riechelmann, H. EMT-related transcription factors and protein stabilization mechanisms involvement in cadherin switch of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Exp. Cell Res. 2022, 414, 113084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brabletz, T.; Jung, A.; Reu, S.; Porzner, M.; Hlubek, F.; Kunz-Schughart, L.; Knuechel, R.; Kirchner, T. Variable -catenin expression in colorectal cancers indicates tumor progression driven by the tumor environment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 10356–10361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brabletz, T. To differentiate or not—Routes towards metastasis. Nat. Cancer 2012, 12, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hay, E.D.; Zuk, A. Transformations between epithelium and mesenchyme: Normal, pathological, and experimentally induced. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1995, 26, 678–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, E.D. Organization and fine structure of epithelium and mesenchyme in the developing chick embryo. In Epithelial-Mesenchymal Interactions; Fleischmajer, R., Billingham, R.E., Eds.; Williams & Wilkins Co: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1968; pp. 31–55. [Google Scholar]
- Bakir, B.; Chiarella, A.M.; Pitarresi, J.R.; Rustgi, A.K. EMT, MET, Plasticity, and Tumor Metastasis. Trends Cell Biol. 2020, 30, 764–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, D.; Saha, P.; Samanta, A.; Bishayee, A. Emerging Concepts of Hybrid Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Cancer Progression. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puram, S.V.; Tirosh, I.; Parikh, A.S.; Patel, A.P.; Yizhak, K.; Gillespie, S.; Rodman, C.; Luo, C.L.; Mroz, E.A.; Emerick, K.S.; et al. Single-Cell Transcriptomic Analysis of Primary and Metastatic Tumor Ecosystems in Head and Neck Cancer. Cell 2017, 171, 1611–1624.e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steinbichler, T.B.; Metzler, V.; Pritz, C.; Riechelmann, H.; Dudas, J. Tumor-associated fibroblast-conditioned medium induces CDDP resistance in HNSCC cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 2508–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, D.; Dai, C.; Peng, S. Mechanism of the Mesenchymal–Epithelial Transition and Its Relationship with Metastatic Tumor Formation. Mol. Cancer Res. 2011, 9, 1608–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaffer, C.L.; Thompson, E.W.; Williams, E.D. Mesenchymal to Epithelial Transition in Development and Disease. Cells Tissues Organs 2007, 185, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbalakshmi, A.R.; Sahoo, S.; McMullen, I.; Saxena, A.N.; Venugopal, S.K.; Somarelli, J.A.; Jolly, M.K. KLF4 Induces Mesenchymal–Epithelial Transition (MET) by Suppressing Multiple EMT-Inducing Transcription Factors. Cancers 2021, 13, 5135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, S.-K.; Yang, M.-H.; Chang, S.-Y.; Chang, Y.-C.; Li, W.-Y.; Tsai, T.-L.; Wang, Y.-F.; Chu, P.-Y.; Hsieh, S.-L. Persistent Krüppel-like factor 4 expression predicts progression and poor prognosis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2011, 102, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, M.; Eustace, A.J.; Busschots, S.; Breen, L.; Crown, J.; Clynes, M.; O’Donovan, N.; Stordal, B.; O’Donovan, N. In vitro Development of Chemotherapy and Targeted Therapy Drug-Resistant Cancer Cell Lines: A Practical Guide with Case Studies. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, M.; Chen, G.; Li, Y.-P. TGF-β and BMP signaling in osteoblast, skeletal development, and bone formation, homeostasis and disease. Bone Res. 2016, 4, 16009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dejaco, D.; Steinbichler, T.; Schartinger, V.H.; Fischer, N.; Anegg, M.; Dudas, J.; Posch, A.; Widmann, G.; Riechelmann, H. Specific growth rates calculated from CTs in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A retrospective study performed in Austria. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e025359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dudás, J.; Dietl, W.; Romani, A.; Reinold, S.; Glueckert, R.; Schrott-Fischer, A.; Dejaco, D.; Chacko, L.J.; Tuertscher, R.; Schartinger, V.H.; et al. Nerve Growth Factor (NGF)—Receptor Survival Axis in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dudás, J.; Bitsche, M.; Schartinger, V.; Falkeis, C.; Sprinzl, G.M.; Riechelmann, H. Fibroblasts produce brain-derived neurotrophic factor and induce mesenchymal transition of oral tumor cells. Oral Oncol. 2011, 47, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Zheng, H.; Zhan, Y.; Fan, S. An emerging tumor invasion mechanism about the collective cell migration. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 5301–5312. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.-S.; Jiang, J.; Chen, B.-J.; Wang, K.; Tang, Y.-L.; Liang, X.-H. Plasticity of cancer cell invasion: Patterns and mechanisms. Transl. Oncol. 2020, 14, 100899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Yang, D.; Yi, W.; Cao, H.; Xiao, G. Roles of leader and follower cells in collective cell migration. Mol. Biol. Cell 2021, 32, 1267–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendleton, K.P.; Grandis, J.R. Cisplatin-Based Chemotherapy Options for Recurrent and/or Metastatic Squamous Cell Cancer of the Head and Neck. Clin. Med. Insights: Ther. 2013, 5, CMT-S10409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Griso, A.B.; Acero-Riaguas, L.; Castelo, B.; Cebrián-Carretero, J.L.; Sastre-Perona, A. Mechanisms of Cisplatin Resistance in HPV Negative Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Cells 2022, 11, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galluzzi, L.; Senovilla, L.; Vitale, I.; Michels, J.; Martins, I.; Kepp, O.; Castedo, M.; Kroemer, G. Molecular mechanisms of cisplatin resistance. Oncogene 2011, 31, 1869–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siemer, S.; Fauth, T.; Scholz, P.; Al-Zamel, Y.; Khamis, A.; Gül, D.; Freudelsperger, L.; Wollenberg, B.; Becker, S.; Stauber, R.H.; et al. Profiling Cisplatin Resistance in Head and Neck Cancer: A Critical Role of the VRAC Ion Channel for Chemoresistance. Cancers 2021, 13, 4831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, D.-W.; Pouliot, L.M.; Hall, M.D.; Gottesman, M.M. Cisplatin Resistance: A Cellular Self-Defense Mechanism Resulting from Multiple Epigenetic and Genetic Changes. Pharmacol. Rev. 2012, 64, 706–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haslehurst, A.M.; Koti, M.; Dharsee, M.; Nuin, P.; Evans, K.; Geraci, J.; Childs, T.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; Weberpals, J.; et al. EMT transcription factors snail and slug directly contribute to cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moyret-Lalle, C.; Prodhomme, M.K.; Burlet, D.; Kashiwagi, A.; Petrilli, V.; Puisieux, A.; Seimiya, H.; Tissier, A. Role of EMT in the DNA damage response, double-strand break repair pathway choice and its implications in cancer treatment. Cancer Sci. 2022, 113, 2214–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magan, M.; Wiechec, E.; Roberg, K. CAFs affect the proliferation and treatment response of head and neck cancer spheroids during co-culturing in a unique in vitro model. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekharan, V.K.; Li, Y.; Andrade, J.; Laimins, L.A. Post-Transcriptional Regulation of KLF4 by High-Risk Human Papillomaviruses Is Necessary for the Differentiation-Dependent Viral Life Cycle. PLOS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.-N.; Abou-Kheir, W.; Yin, J.J.; Fang, L.; Hynes, P.; Casey, O.; Hu, D.; Wan, Y.; Seng, V.; Sheppard-Tillman, H.; et al. Critical and Reciprocal Regulation of KLF4 and SLUG in Transforming Growth Factor β-Initiated Prostate Cancer Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2012, 32, 941–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vitali, R.; Mancini, C.; Cesi, V.; Tanno, B.; Mancuso, M.; Bossi, G.; Zhang, Y.; Martinez, R.V.; Calabretta, B.; Dominici, C.; et al. Slug (SNAI2) Down-Regulation by RNA Interference Facilitates Apoptosis and Inhibits Invasive Growth in Neuroblastoma Preclinical Models. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 4622–4630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tania, M.; Khan, M.A.; Fu, J. Epithelial to mesenchymal transition inducing transcription factors and metastatic cancer. Tumour Biol. 2014, 35, 7335–7342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.; Wang, M.; Guo, W.; Zhao, X.; Tu, X.; Huang, S.; Zou, X.; Peng, X. Wild-type p53 suppresses the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and stemness in PC-3 prostate cancer cells by modulating miR-145. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 42, 1473–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fujimoto, S.; Hayashi, R.; Hara, S.; Sasamoto, Y.; Harrington, J.; Tsujikawa, M.; Nishida, K. KLF4 prevents epithelial to mesenchymal transition in human corneal epithelial cells via endogenous TGF-β2 suppression. Regen. Ther. 2019, 11, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolós, V.; Peinado, H.; Perez-Moreno, M.A.; Fraga, M.F.; Esteller, M.; Cano, A. The transcription factor Slug represses E-cadherin expression and induces epithelial to mesenchymal transitions: A comparison with Snail and E47 repressors. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cappellesso, R.; Marioni, G.; Crescenzi, M.; Giacomelli, L.; Guzzardo, V.; Mussato, A.; Staffieri, A.; Martini, A.; Blandamura, S.; Fassina, A. The prognostic role of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers E-cadherin and Slug in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Histopathology 2015, 67, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Chao, Y.; He, R.; Liu, J.; Yuan, Y.; Zhao, W.; Han, C.; Song, X. KLF4, a miR-32-5p targeted gene, promotes cisplatin-induced apoptosis by upregulating BIK expression in prostate cancer. Cell Commun. Signal. 2018, 16, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yadav, S.S.; Kumar, M.; Varshney, A.; Yadava, P.K. KLF4 sensitizes the colon cancer cell HCT-15 to cisplatin by altering the expression of HMGB1 and hTERT. Life Sci. 2019, 220, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Yu, Z. Krüppel-Like Factor 4 Enhances Sensitivity of Cisplatin to Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma (ESCC) Cells. Med. Sci. Monit. 2017, 23, 3353–3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez-Limón, A.; Joaquin, M.; Caballero, M.; Posas, F.; de Nadal, E. The p38 Pathway: From Biology to Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wagner, E.F.; Nebreda, Á.R. Signal integration by JNK and p38 MAPK pathways in cancer development. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 537–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Roy, S.; Kar, M.; Padhi, S.; Saha, A.; Anuja, K.; Banerjee, B. Role of p38 MAPK in disease relapse and therapeutic resistance by maintenance of cancer stem cells in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2018, 47, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Roy, S.; Anuja, K.; Thakur, S.; Akhter, Y.; Padhi, S.; Banerjee, B. p38 Mitogen-activated protein kinase modulates cisplatin resistance in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma cells. Arch. Oral Biol. 2020, 122, 104981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaczynski, J.; Cook, T.; Urrutia, R. Sp1- and Kruppel-like transcription factors. Genome Biol. 2003, 4, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ingruber, J.; Dudas, J.; Sprung, S.; Lungu, B.; Mungenast, F. Interplay between Partial EMT and Cisplatin Resistance as the Drivers for Recurrence in HNSCC. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2482. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102482
Ingruber J, Dudas J, Sprung S, Lungu B, Mungenast F. Interplay between Partial EMT and Cisplatin Resistance as the Drivers for Recurrence in HNSCC. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(10):2482. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102482
Chicago/Turabian StyleIngruber, Julia, Jozsef Dudas, Susanne Sprung, Bianca Lungu, and Felicitas Mungenast. 2022. "Interplay between Partial EMT and Cisplatin Resistance as the Drivers for Recurrence in HNSCC" Biomedicines 10, no. 10: 2482. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102482
APA StyleIngruber, J., Dudas, J., Sprung, S., Lungu, B., & Mungenast, F. (2022). Interplay between Partial EMT and Cisplatin Resistance as the Drivers for Recurrence in HNSCC. Biomedicines, 10(10), 2482. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102482






