High Quality Performance of Novel Immunoassays for the Sensitive Quantification of Soluble PD-1, PD-L1 and PD-L2 in Blood
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Assay Development and Optimization
2.2. Quality Control
2.3. Imprecision
2.4. Dilution Linearity
2.5. Assay Measuring Range
2.6. Selectivity
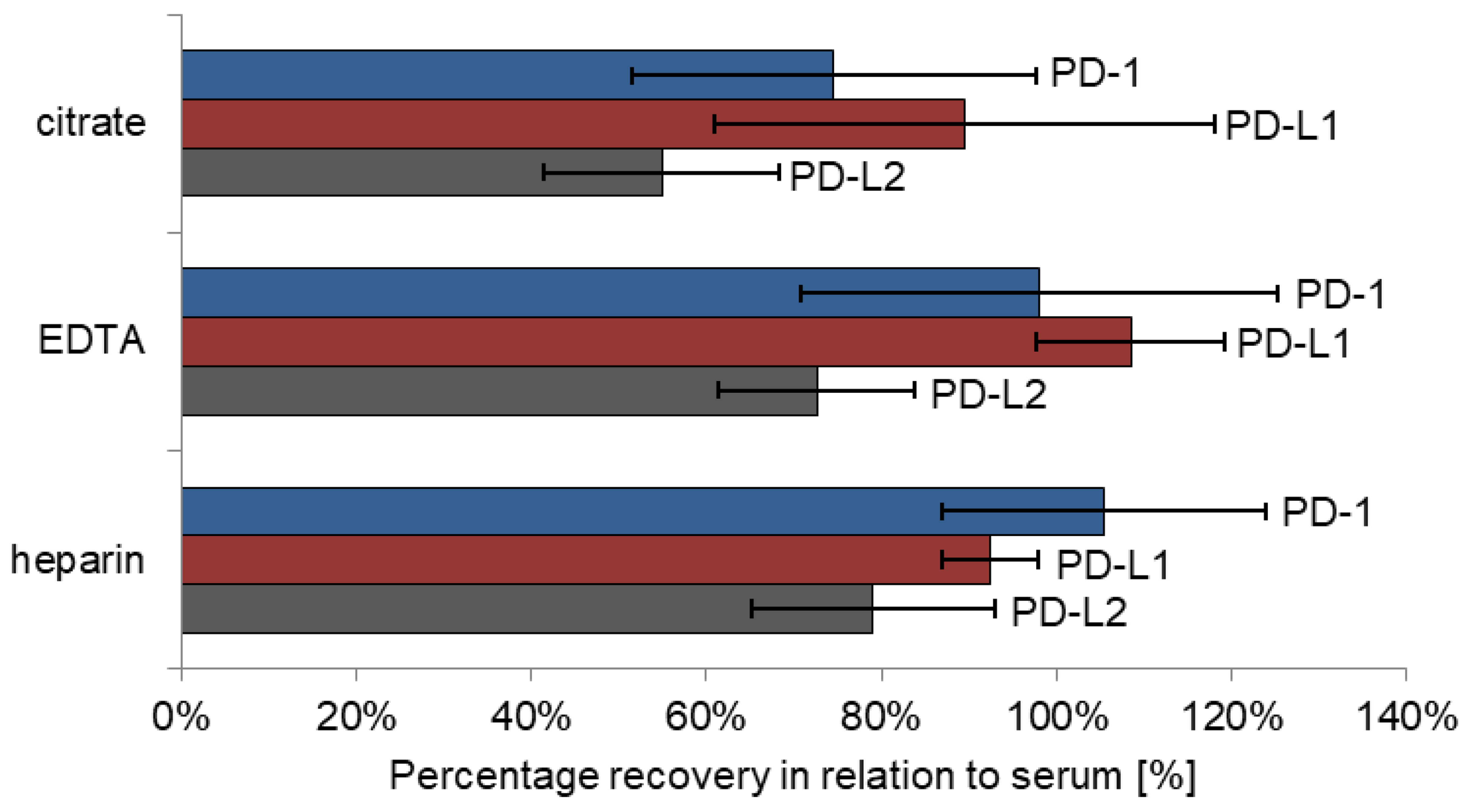
2.7. Matrix Effects
2.8. Healthy Subjects
2.9. Blood Sample Preparation
2.10. Statistics and Data Interpretation
3. Results
3.1. Assay Development and Optimization
3.2. Imprecision
3.3. Dilution Linearity
3.4. Assay Measurement Range
3.5. Selectivity
3.6. Matrix Effects
3.7. Healthy Subjects
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Keir, M.E.; Butte, M.J.; Freeman, G.J.; Sharpe, A.H. PD-1 and Its Ligands in Tolerance and Immunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 26, 677–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Li, C.W.; Chung, E.M.; Yang, R.; Kim, Y.S.; Park, A.H.; Lai, Y.J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.H.; Liu, J.; et al. Targeting Glycosylated PD-1 Induces Potent Antitumor Immunity. Tumor Biol. Immunol. 2020, 80, 2298–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, G.J.; Long, A.J.; Iwai, Y.; Bourque, K.; Chernova, T.; Nishimura, H.; Fitz, L.J.; Malenkovich, N.; Okazaki, T.; Byrne, M.C.; et al. Engagement of the PD-1 immunoinhibitory receptor by a novel B7 family member leads to negative regulation of lymphocyte activation. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 192, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blank, C.; Gajewski, T.F.; Mackensen, A. Interaction of PD-L1 on tumor cells with PD-1 on tumor-specific T cells as a mechanism of immune evasion: Implications for tumor immunotherapy. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2005, 54, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, Y.; Agata, Y.; Shibahara, K.; Honjo, T. Induced expression of PD-1, a novel member of the immunoglobulin gene superfamily, upon programmed cell death. EMBO J. 1992, 11, 3887–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schildberg, F.A.; Klein, S.R.; Freeman, G.J.; Sharpe, A.H. Coinhibitory Pathways in the B7-CD28 Ligand-Receptor Family. Immunity 2016, 44, 955–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzec, M.; Zhang, Q.; Goradia, A.; Raghunath, P.N.; Liu, X.; Paessler, M.; Paessler, M.; Wang, H.Y.; Wysocka, M.; Cheng, M.; et al. Oncogenic kinase NPM/ALK induces through STAT3 expression of immunosuppressive protein CD274 (PD-L1, B7-H1). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 20852–20857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, L.M.; Sage, P.T.; Sharpe, A.H. The PD-1 Pathway in Tolerance and Autoimmunity. Immunol. Rev. 2010, 236, 219–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patsoukis, N.; Brown, J.; Petkova, V.; Liu, F.; Li, L.; Boussiotis, V.A. Selective effects of PD-1 on Akt and Ras pathways regulate molecular components of the cell cycle and inhibit T cell proliferation. Sci. Signal. 2012, 5, ra46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.A.; Dorfman, D.M.; Ma, F.-R.; Sullivan, E.L.; Munoz, O.; Wood, C.R.; Greenfield, E.A.; Freeman, G.J. Blockade of Programmed Death-1 Ligands on Dendritic Cells Enhances T Cell Activation and Cytokine Production. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 1257–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, H.; Strome, S.E.; Salomao, D.R.; Tamura, H.; Hirano, F.; Flies, D.B.; Roche, P.C.; Lu, J.; Zhu, G.; Tamada, K.; et al. Tumor-associated B7-H1 promotes T-cell apoptosis: A potential mechanism of immune evasion. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samstein, R.M.; Lee, C.H.; Shoushtari, A.N.; Hellmann, M.D.; Shen, R.; Janjigian, Y.Y.; DBarron, A.; Zehir, A.; Jordan, E.J.; Omuro, A.; et al. Tumor mutational load predicts survival after immunotherapy across multiple cancer types. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schadendorf, D.; Hodi, F.S.; Robert, C.; Weber, J.S.; Margolin, K.; Hamid, O.; Patt, D.; Chen, T.T.; Berman, D.M.; Wolchok, J.D. Pooled analysis of long-term survival data from phase II and phase III trials of ipilimumab in unresectable or metastatic melanoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 1889–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brahmer, J.; Reckamp, K.L.; Baas, P.; Crinò, L.; Eberhardt, W.E.; Poddubskaya, E.; Antonia, S.; Pluzanski, A.; Vokes, E.E.; Holgado, E.; et al. Nivolumab versus Docetaxel in Advanced Squamous-Cell Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Hu-Lieskovan, S.; Wargo, J.A.; Ribas, A. Primary, Adaptive, and Acquired Resistance to Cancer Immunotherapy. Cell 2017, 168, 707–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquez-Rodas, I.; Cerezuela, P.; Soria, A.; Berrocal, A.; Riso, A.; Gonzalez-Cao, M.; Martin-Algarra, S. Immune checkpoint inhibitors: Therapeutic advances in melanoma. Ann. Transl. Med. 2015, 3, 267. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Yang, J.; Hua, W.; Li, Z.; Xu, Z.; Qian, Q. Monitoring checkpoint inhibitors: Predictive biomarkers in immunotherapy. Front. Med. 2019, 13, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, M.K.; Postow, M.A.; Wolchok, J.D. Targeting T Cell Co-receptors for Cancer Therapy. Immunity 2016, 44, 1069–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempke, W.C.M.; Fenchel, K.; Dale, S.P. Programmed cell death ligand-1 (PD-L1) as a biomarker for non- small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treatment—Are we barking up the wrong tree? Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2018, 7, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, C.; Yin, L.; Zhou, X.; Lei, C.; Tong, R.; Huang, M.; Gong, Y.; Ding, Z.; Xue, J.; Zhu, J.; et al. Assessment of programmed cell death ligand-1 expression with multiple immunohistochemistry antibody clones in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, 816–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.P.; Kurzrock, R. PD-L1 expression as a Predictive Biomarker in Cancer Immunotherapy. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Andreasson, U.; Perret-Liaudet, A.; van Waalwijk van Doorn, L.J.; Blennow, K.; Chiasserini, D.; Engelborghs, S.; Fladby, T.; Genc, S.; Kruse, N.; Kuiperij, H.B.; et al. A practical guide to immunoassay method validation. Front. Neurol. 2015, 6, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use. Guideline on Bioanalytical Method Validation; Volume EMEA/CHMP; Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Meso Scale Discovery. Proinflammatory Panel 1 (Human) Kits; Meso Scale Discovery: Rockville, MD, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.W.; Devanarayan, V.; Barrett, Y.C.; Weiner, R.; Allinson, J.; Fountain, S.; Keller, S.; Weinryb, I.; Green, M.; Duan, L.; et al. Fit-for-purpose method development and validation for successful biomarker measurement. Pharm. Res. 2006, 23, 312–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahoney, K.M.; Ross-Macdonald, P.; Yuan, L.; Song, L.; Veras, E.; Wind-Rotolo, M.; McDermott, D.F.; Stephen Hodi, F.; Choueiri, T.K.; Freeman, G.J. Soluble PD-L1 as an early marker of progressive disease on nivolumab. J. Immunother Cancer. 2022, 10, e003527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duchemann, B.; Remon, J.; Naigeon, M.; Mezquita, L.; Ferrara, R.; Cassard, L.; Jouniaux, J.M.; Boselli, L.; Grivel, J.; Auclin, E.; et al. Integrating Circulating Biomarkers in the Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Treatment in Lung Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, M.; Chamoto, K.; Higuchi, K.; Yamashita, S.; Noda, K.; Iino, T.; Miura, M.; Yamasaki, T.; Ogawa, O.; Sonobe, M.; et al. Analytical performance of a new automated chemiluminescent magnetic immunoassays for soluble PD-1, PD-L1, and CTLA-4 in human plasma. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Assay | Sample | N | Mean Conc. (ng/mL) | CV (%) | Range (ng/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PD-1 | Sample I | 11 | 0.58 | 7.8 | 0.52–0.67 |
| Sample II | 12 | 0.29 | 6.5 | 0.23–0.31 | |
| Sample III | 15 | 0.06 | 6.4 | 0.05–0.07 | |
| PD-L1 | Sample IV | 12 | 0.43 | 3.8 | 0.40–0.45 |
| Sample V | 12 | 0.03 | 4.2 | 0.02–0.03 | |
| Sample VI | 12 | 0.0038 | 7.1 | 0.0028–0.0048 | |
| PD-L2 | Sample VII | 11 | 7.60 | 4.5 | 7.46–8.43 |
| Sample VIII | 12 | 1.21 | 10.0 | 1.00–1.51 | |
| Sample IX | 13 | 0.09 | 9.9 | 0.07–0.11 |
| Assay | Sample | N | Mean Conc. (ng/mL) | CV (%) | Range (ng/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PD-1 | Sample X | 12 | 0.17 | 12.7 | 0.13–0.22 |
| Sample XI | 14 | 0.06 | 13.3 | 0.05–0.09 | |
| PD-L1 | Sample XII | 14 | 19.53 | 15.5 | 15.41–24.97 |
| Sample XIII | 14 | 1.27 | 12.5 | 1.00–1.61 | |
| PD-L2 | Sample XIV | 12 | 3.40 | 13.2 | 2.50–3.94 |
| Sample XV | 10 | 0.44 | 23.4 | 0.31–0.59 |
| Marker | LOD | LLOQ | ULOQ | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Signal | N | Conc. | CV (%) | N | Conc. | CV (%) | |
| PD-1 | 23 | 218 | 15 | 0.0073 | 9.1 | 16 | 30.0 | 17.5 |
| PD-L1 | 30 | 226 | 5 | 0.0073 | 5.1 | 5 | 30.0 | 2.6 |
| PD-L2 | 27 | 146 | 15 | 0.0073 | 16.1 | 16 | 30.0 | 6.0 |
| PD-1 * | PD-L1 * | PD-L2 * | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum | 0.042 | 0.0073 | 0.064 |
| 1st Quartile | 0.13 | 0.0073 | 0.18 |
| Median | 0.23 | 0.0073 | 0.30 |
| Mean | 1.34 | 0.012 | 0.96 |
| 3rd Quartile | 0.55 | 0.0095 | 0.57 |
| Maximum | 30.00 | 0.14 | 29.011 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Krueger, K.; Mayer, Z.; Gerckens, M.; Boeck, S.; Luppa, P.; Holdenrieder, S. High Quality Performance of Novel Immunoassays for the Sensitive Quantification of Soluble PD-1, PD-L1 and PD-L2 in Blood. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2405. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102405
Krueger K, Mayer Z, Gerckens M, Boeck S, Luppa P, Holdenrieder S. High Quality Performance of Novel Immunoassays for the Sensitive Quantification of Soluble PD-1, PD-L1 and PD-L2 in Blood. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(10):2405. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102405
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrueger, Kimberly, Zsuzsanna Mayer, Miriam Gerckens, Stefan Boeck, Peter Luppa, and Stefan Holdenrieder. 2022. "High Quality Performance of Novel Immunoassays for the Sensitive Quantification of Soluble PD-1, PD-L1 and PD-L2 in Blood" Biomedicines 10, no. 10: 2405. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102405
APA StyleKrueger, K., Mayer, Z., Gerckens, M., Boeck, S., Luppa, P., & Holdenrieder, S. (2022). High Quality Performance of Novel Immunoassays for the Sensitive Quantification of Soluble PD-1, PD-L1 and PD-L2 in Blood. Biomedicines, 10(10), 2405. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102405






