Resistin Modulates the Functional Activity of Colostral Macrophages from Mothers with Obesity and Diabetes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Subjects
2.3. Colostrum Sampling and Separation of Colostral Cells
2.4. Resistin Levels Determination
2.5. Resistin Treatment of Cells
2.6. Cell Subsets
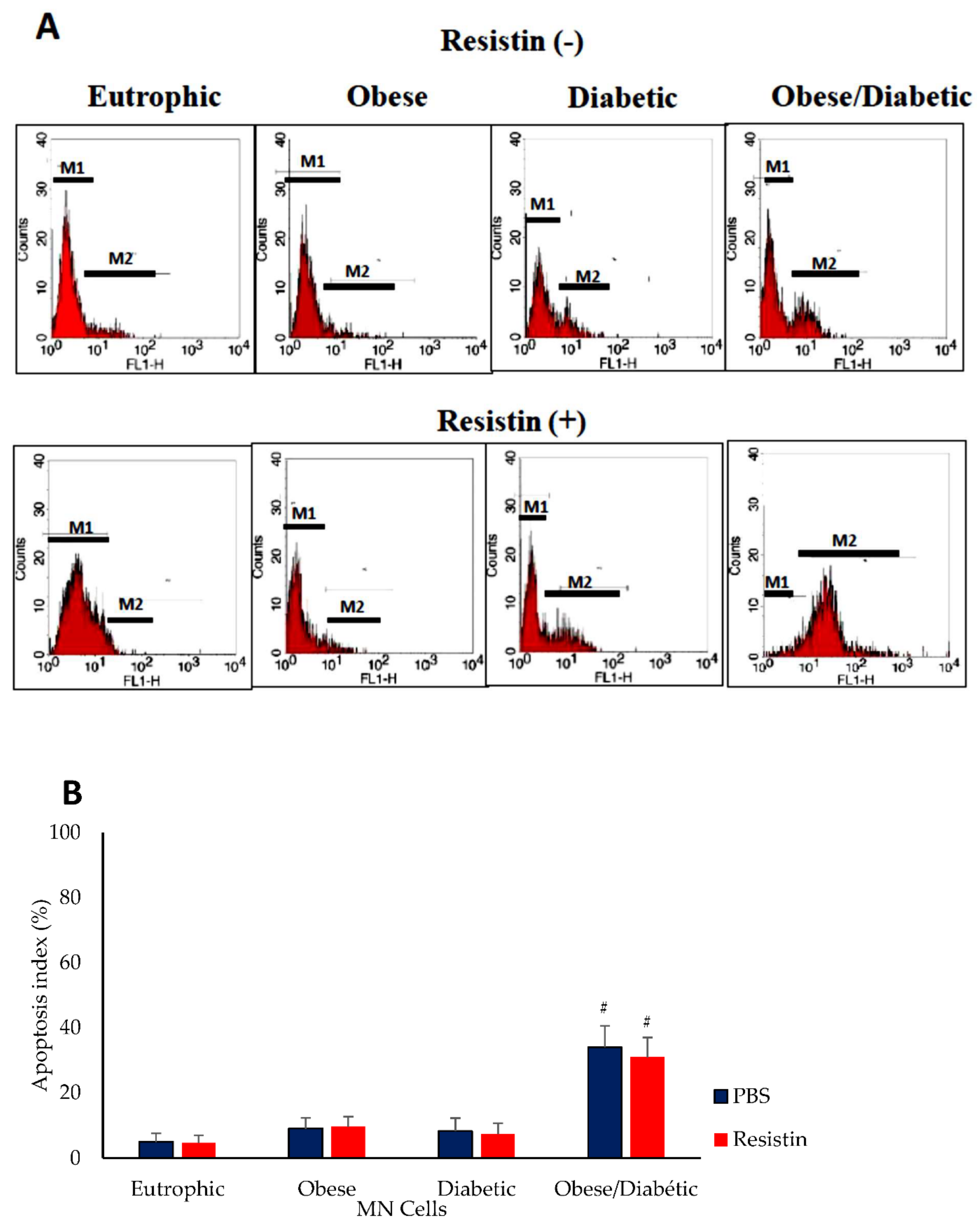
2.7. Apoptosis Assay
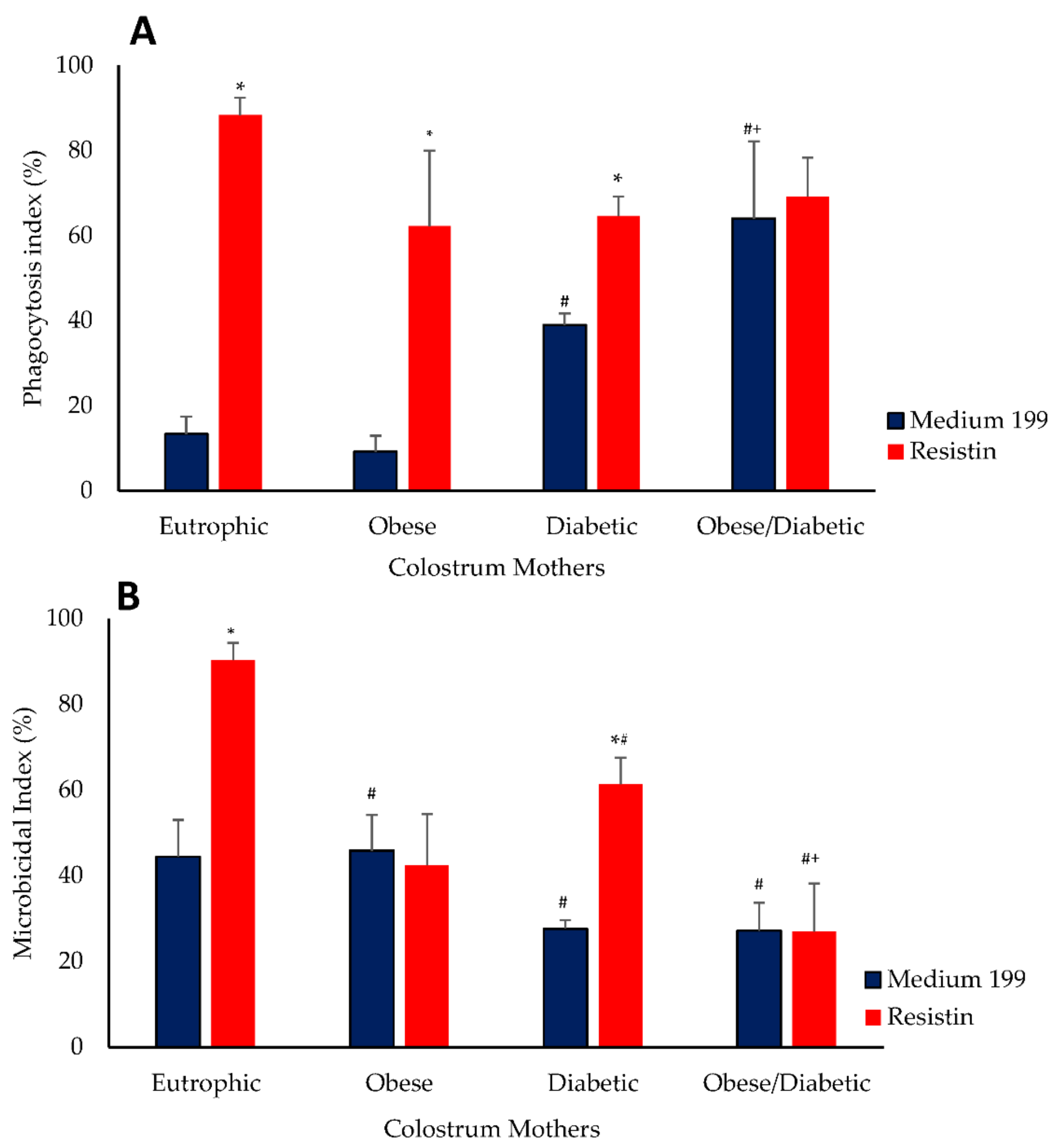
2.8. Bactericidal Assay
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
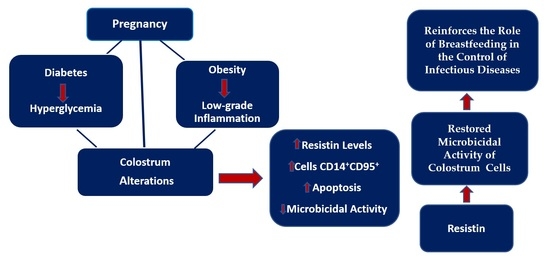
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interests
Abbreviations
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| CD14+ | Cluster of differentiation 14 |
| CD95+ | Cluster of differentiation 95—Fas receptor |
| DAMPs | Damage-associated molecular patterns |
| DM2 | Type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| dUTP | Deoxyuridine triphosphates |
| EPEC | Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli |
| FITC | Fluorescein-5-isothiocyanate |
| GDM | Gestational diabetes mellitus |
| MN cells | Mononuclear cells |
| OGTT | Oral glucose tolerance test |
| PE | Phycoerythrin |
| RELMs | Resistin-like molecules |
| sCD14 | Soluble cluster of differentiation 14 |
References
- American Diabetes Association (ADA). Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, S81–S90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werlang, I.C.R.; Bernardi, J.R.; Nunes, M.; Marcelino, T.B.; Bosa, V.L.; Michalowski, M.B.; Silva, C.H.; Goldani, M.Z. Impact of perinatal different intrauterine environments on child growth and development: Planning and baseline data for a cohort study. JMIR Res. Protoc. 2019, 8, e12970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkie, G.; Leftwich, H.K. Do optimizing care preconception for women with diabetes and obesity. Clin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2021, 64, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coustan, D.R.; Laptook, A.R. Medical Management of Pregnancy Complicated by Diabetes, 5th, ed.; American Diabetes Association: Arlington County, VA, USA, 2013; 188p. [Google Scholar]
- Atawia, R.T.; Bunch, K.L.; Toque, H.A.; Caldwell, R.B.; Caldwell, R.W. Mechanisms of obesity-induced metabolic and vascular dysfunctions. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 2019, 24, 890–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escoté, X.; Gómez-Zorita, S.; López-Yoldi, M.; Milton-Laskibar, I.; Fernández-Quintela, A.; Martínez, J.A.; Moreno-Aliaga, M.J.; Portillo, M.P. Role of omentin, vaspin, cardiotrophin-1, TWEAK and NOV/CCN3 in obesity and diabetes development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yogev, Y.; Catalano, P.M. Pregnancy and obesity. Obstet. Gynecol. Clin. N. Am. 2009, 36, 285–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kratzsch, K.J.; Kiess, W. Adipocytokines: Leptin—The classical, resistin—The controversical, adiponectin—The promising, and more to come. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 19, 525–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, D.; Kant, S.; Pandey, S.; Ehtesham, N.Z. Resistin in metabolism, inflammation, and disease. FEBS J. 2020, 287, 3141–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.D.; Rajala, M.W.; Rossetti, L.; Scherer, P.E.; Shapiro, L. Disulfide-dependent multimeric assembly of resistin family hormones. Science 2004, 304, 1154–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holcomb, I.N.; Kabakoff, R.C.; Chan, B.; Baker, T.W.; Gurney, A.; Henzel, W.; Nelson, C.; Lowman, H.B.; Wright, B.D.; Skelton, N.J.; et al. FIZZ1, a novel cysteine-rich secreted protein associated with pulmonary inflammation, defines a new gene family. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 4046–4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acquarone, E.; Monacelli, F.; Borghi, R.; Nencioni, A.; Odetti, P. Resistin: A reappraisal. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2019, 178, 46–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filková, M.; Haluzik, M.; Gay, S.; Senolt, L. The role of resistin as a regulator of inflammation: Implications for various human pathologies. Clin. Immunol. 2009, 133, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.K.; Kwak, M.K.; Kim, H.J.; Ahima, R.S. Linking resistin, inflammation, and cardiometabolic diseases. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2017, 32, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.-W.; Gao, Y.-H.; Song, W.-X.; Liu, B.; Ding, L.; Dong, N.; Qi, X. An update on the emerging role of resistin on the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2019, 28, 1532164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eliana, U.D.; Fly, A.D. The function and alteration of immunological properties in human milk of obese mothers. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gila-Diaz, A.; Arribas, S.M.; Algara, A.; Martín-Cabrejas, M.A.; De Pablo, Á.L.L.; De Pipaón, M.S.; Ramiro-Cortijo, D. A review of bioactive factors in human breastmilk: A focus on prematurity. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimori, M.; França, E.L.; Fiorin, V.; Morais, T.C.; Honorio-França, A.C.; Abreu, L.C. Changes in the biochemical and immunological components of serum and colostrum of overweight and obese mothers. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2015, 15, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- França, E.L.; Silva, V.A.; Volpato, R.M.J.; Silva, P.A.; Brune, M.F.S.S.; Honorio-França, A.C. Maternal anemia induces changes in immunological and nutritional components of breast milk. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal. Med. 2013, 26, 1223–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute of Medicine (US); National Research Council (US); Committee to Reexamine IOM Pregnancy Weight Guidelines. Weight Gain during Pregnancy: Reexamining the Guidelines; Rasmussen, K.M., Yaktine, A.L., Eds.; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudge, M.V.C.; Calderon, I.M.P.; Ramos, M.D.; Abbade, J.F.; Rujolo, L.M. Perinatal outcome of pregnancies complicated by diabetes and by maternal daily hyperglycemia not related to diabetes A retrospective 10-year analysis. Gynecol. Obstet. Investig. 2000, 50, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Zheng, Q.; Ford, S.P.; Nathanielsz, P.W.; Ren, J. Maternal obesity, lipotoxicity and cardiovascular diseases in offspring. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2013, 55, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savino, F.; Sorrenti, M.; Benetti, S.; Lupica, M.M.; Liguori, A.S.; Oggero, R. Resistin and leptina in breast milk and infants in earlu life. Early Hum. Dev. 2012, 10, 779–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Zhao, J.; Meng, H.; Zhang, X. Adipose tissue-resident immune cells in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lumeng, C.N.; Bodzin, J.L.; Saltiel, A.R. Obesity induces a phenotypic switch in adipose tissue macrophage polarization. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haziot, A.; Chen, S.; Ferrero, E.; Low, M.G.; Silber, R.; Goyert, S.M. The monocyte differentiation antigen, CD14, is anchored to the cell membrane by a phosphatidylinositol linkage. J. Immunol. 1988, 141, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Simmons, D.L.; Tan, S.; Tenen, D.G.; Nicholson-Weller, A.; Seed, B. Monocyte antigen CD14 is a phospholipid anchored membrane protein. Blood 1989, 73, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler-Heitbrock, L.; Ancuta, P.; Crowe, S.; Dalod, M.; Grau, V.; Hart, D.N.; Leenen, P.J.M.; Liu, Y.J.; MacPherson, G.; Randolph, G.J.; et al. Nomenclature of monocytes and dendritic cells in blood. Blood 2010, 116, e74–e80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shive, C.L.; Jiang, W.; Anthony, D.D.; Lederman, M.M. Soluble CD14 is a nonspecific marker of monocyte activation. AIDS 2015, 29, 1263–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaegashi, Y.; Shirakawa, K.; Sato, N.; Suzuki, Y.; Kojika, M.; Imai, S.; Takahashi, G.; Miyata, M.; Furusako, S.; Endo, S. Evaluation of a newly identified soluble CD14 subtype as a marker for sepsis. J. Infect. Chemother. 2005, 11, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luche, E.; Cousin, B.; Garidou, L.; Serino, M.; Waget, A.; Barreau, C.; André, M.; Valet, P.; Courtney, M.; Casteilla, L.; et al. Metabolic endotoxemia directly increases the proliferation of adipocyte precursors at the onset of metabolic diseases through a CD14-dependent mechanism. Mol. Metab. 2013, 2, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoccal, K.F.; Bitencourt, C.S.; Paula-Silva, F.W.G.; Sorgi, C.A.; Bordon, K.C.F.; Arantes, E.C.; Faccioli, L.H. TLR2, TLR4 and CD14 recognize venom-associated molecular patterns from Tityus serrulatus to induce macrophage-derived inflammatory mediators. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoccal, K.F.; Gardinassi, L.G.; Sorgi, C.A.; Meirelles, A.F.G.; Bordon, K.C.F.; Glezer, I.; Cupo, P.; Matsuno, A.K.; Bollela, V.R.; Arantes, E.C.; et al. CD36 shunts eicosanoid metabolism to repress CD14 licensed interleukin-1β release and inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donath, M.Y.; Størling, J.; Maedler, K.; Mandrup-Poulsen, T. Inflammatory mediators and islet β-cell failure: A link between type 1 and type 2 diabetes. J. Mol. Med. 2003, 81, 455–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurma, K.; Boizard-Moracchini, A.; Galli, G.; Jean, M.; Vacher, P.; Blanco, P.; Legembre, P. Soluble CD95L in cancers and chronic inflammatory disorders, a new therapeutic target? Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2021, 1876, e188596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guegan, J.P.; Ginestier, C.; Charafe-Jauffret, E.; Ducret, T.; Quignard, J.F.; Vacher, P.; Legembre, P. CD95/Fas and metastatic disease: What does not kill you makes you stronger. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2019, 60, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galli, G.; Vacher, P.; Ryffel, B.; Blanco, P.; Legembre, P. Fas/CD95 signaling pathway in damage-associated molecular pattern (DAMP)-sensing receptors. Cells. 2022, 11, 1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonner-Weir, S. Islet growth and development in the adult. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2000, 24, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, T. Apoptosis in pancreatic β-islet cells in type 2 diabetes. Bosn. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2016, 16, 162–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blüher, M.; Klöting, N.; Wueest, S.; Schoenle, E.J.; Schön, M.R.; Dietrich, A.; Fasshauer, M.; Stumvoll, M.; Konrad, D. Fas and FasL expression in human adipose tissue is related to obesity, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, E36–E44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendeloski, K.P.T.; Ono, E.; Torloni, M.R.; Mattar, R.; Daher, S. Maternal obesity and inflammatory mediators: A controversial association. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2017, 77, e12674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagundes, D.L.G.; França, E.L.; Fernandes, R.T.S.; Hara, C.C.; Morceli, G.; Honorio-França, A.C.; Calderon, I.M. Changes in T-cell phenotype and cytokines profile in maternal blood, cord blood and colostrum of diabetic mothers. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2016, 29, 998–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, T.C.; de Abreu, L.C.; de Quental, O.B.; Pessoa, R.S.; Fujimori, M.; Daboin, B.E.G.; França, E.L.; Honorio-França, A.C. Obesity as an inflammatory agent can cause cellular changes in human milk due to the actions of the adipokines leptin and adiponectin. Cells 2019, 8(6), 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morais, T.C.; Honorio-França, A.C.; Fujimori, M.; de Quental, O.B.; Pessoa, R.S.; França, E.L.; de Abreu, L.C. Melatonin action on the activity of phagocytes from the colostrum of obese women. Medicina 2019, 55(10), 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, K.-Z.; Li, Y.-R.; Zhang, D.; Yuan, J.-H.; Zhang, C.-S.; Liu, Y.; Song, L.-M.; Lin, Q.; Li, M.-W.; Dong, J. Relation of circulating resistin to insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes and obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savino, F.; Liguori, S.A.; Fissore, M.F.; Oggero, R. Breast milk hormones and their protective effect on obesity. Int. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2009, 2009, 327505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameters | Normal Weight Non-Diabetic (N = 28) | Obese Non-Diabetic (N = 27) | Normal Weight Diabetic (N = 20) | Obese Diabetic (N = 20) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 28.3 ± 4.1 | 27.4 ± 3.9 | 32.3 ± 6.2 | 31.5 ± 4.3 |
| Gestational age (weeks) | 38.9 ± 2.5 | 37.2 ± 3.5 | 37.5 ± 1.4 | 36.8 ± 4.5 |
| BMI-1 | 23.7 ± 2.1 | 32.8 ± 4.6 | 24.2 ± 1.6 | 34.8 ± 5.2 |
| BMI-2 | 33.6 ± 4.2 | 39.2 ± 4.9 | 36.4 ± 4.8 | 41.1 ± 4.5 |
| Hypertension (%) | 0 | 10 | 15 | 25 |
| Physical exercise (%) | 38 | 35 | 65 | 75 |
| Blood glucose level (mg/dL) | 85.5 ± 4.6 | 92 ± 5.7 | 114.7 ± 7.5 * | 119.8 ± 6.8 * |
| Colostrum glucose level (mg/dL) | 76,8 ± 5.5 | 81.2 ± 0.44 | 101.4 ± 4.1 * | 112.4 ± 3.9 * |
| Resistin (ng/mL) | 141.1 ± 63.9 | 153.2 ± 69.7 | 181.7 ± 20.2 | 375.3 ± 120.2 * |
| (%) Cells Expressing | Resistin | Normal Weight Non-Diabetic | Obese Non-Diabetic | Normal Weight Diabetic | Obese Diabetic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | 29.1 ± 14.5 | 37.1± 10.3 | 34.6 ± 10.9 | 43.8 ± 19.2 * | |
| CD14+ | Yes | 28.6 ± 12.2 | 29.5 ± 11.8 | 30.5 ± 7.5 | 41.8 ± 19.1 * |
| No | 21.8 ± 14.5 | 31.4± 10.3 | 27.0.6 ± 10.9 | 38.4 ± 19.2 * | |
| CD95+ | Yes | 23.6 ± 5.2 | 25.6 ± 10.4 | 27.2 ± 8.3 | 35.6 ± 9.1 * |
| No | 21.3 ± 12.2 | 30.0± 12.1 | 25.9 ± 9.4 | 45.8 ± 16.5 * | |
| CD14 + CD95+ | Yes | 22.7 ± 4.1 | 24.4 ± 10.2 | 24.1 ± 7.2 | 36.4 ± 9.2 *# |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dalcin, L.D.L.; Fagundes-Triches, D.L.G.; de Queiroz, A.A.; Torres, A.H.F.; França, D.C.H.; Soares, T.A.; Ramos, L.C.d.S.; Antônio, C.R.S.S.; Fujimori, M.; França, E.L.; et al. Resistin Modulates the Functional Activity of Colostral Macrophages from Mothers with Obesity and Diabetes. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2332. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102332
Dalcin LDL, Fagundes-Triches DLG, de Queiroz AA, Torres AHF, França DCH, Soares TA, Ramos LCdS, Antônio CRSS, Fujimori M, França EL, et al. Resistin Modulates the Functional Activity of Colostral Macrophages from Mothers with Obesity and Diabetes. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(10):2332. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102332
Chicago/Turabian StyleDalcin, Letícia Damas Leão, Danny Laura Gomes Fagundes-Triches, Adriele Ataides de Queiroz, André Henrique Furtado Torres, Danielle Cristina Honorio França, Tatiane Araújo Soares, Luana Cristina da Silva Ramos, Carla Roberta Silva Souza Antônio, Mahmi Fujimori, Eduardo Luzia França, and et al. 2022. "Resistin Modulates the Functional Activity of Colostral Macrophages from Mothers with Obesity and Diabetes" Biomedicines 10, no. 10: 2332. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102332
APA StyleDalcin, L. D. L., Fagundes-Triches, D. L. G., de Queiroz, A. A., Torres, A. H. F., França, D. C. H., Soares, T. A., Ramos, L. C. d. S., Antônio, C. R. S. S., Fujimori, M., França, E. L., & Honorio-França, A. C. (2022). Resistin Modulates the Functional Activity of Colostral Macrophages from Mothers with Obesity and Diabetes. Biomedicines, 10(10), 2332. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102332