Abstract
Botulinum neurotoxins (BoNT) are the most potent toxins, which are produced by Clostridium bacteria and cause the life-threatening disease of botulism in all vertebrates. Specifically, animal botulism represents a serious environmental and economic concern in animal production due to the high mortality rates observed during outbreaks. Despite the availability of vaccines against BoNT, there are still many outbreaks of botulism worldwide. Alternative assays capable of replacing the conventional in vivo assay in terms of rapid and sensitive quantification, and the applicability for on-site analysis, have long been perused. Herein, we present a simple, highly sensitive and label-free optical biosensor for real-time detection of BoNT serotype C using a porous silicon Fabry–Pérot interferometer. A competitive immunoassay coupled to a biochemical cascade reaction was adapted for optical signal amplification. The resulting insoluble precipitates accumulated within the nanostructure changed the reflectivity spectra by alternating the averaged refractive index. The augmented optical performance allowed for a linear response within the range of 10 to 10,000 pg mL−1 while presenting a detection limit of 4.8 pg mL−1. The practical aspect of the developed assay was verified using field BoNT holotoxins to exemplify the potential use of the developed optical approach for rapid bio-diagnosis of BoNT. The specificity and selectivity of the assay were successfully validated using an adjacent holotoxin relevant for farm animals (BoNT serotype D). Overall, this work sets the foundation for implementing a miniaturized interferometer for routine on-site botulism diagnosis, thus significantly reducing the need for animal experimentation and shortening analysis turnaround for early evidence-based therapy.
1. Introduction
Botulinum neurotoxins (BoNT) are the strongest toxins known in nature, causing the severe neurological disease of botulism [1,2]. BoNT is produced by spore-forming anaerobic bacterial strains of Clostridium botulinum (C. botulinum) and several other clostridial species [3]. These neurotoxins are immunologically classified into seven classical serotypes (named A–G) based on their antigenic properties, and their specific typing is important for epidemiological reasons [4,5]. BoNT-C and BoNT-D (including their mosaic variants) are accounted for botulism in farm animals, while BoNT-A, B, E and F induce botulism primarily in humans [1]. The active toxins mode of action is characterized by the blockage of neurotransmitter release (i.e., acetylcholine) at neuromuscular junctions, which leads to flaccid paralysis and respiratory failure in both humans and animals [6]. BoNT holotoxin is a single polypeptide chain of 150 kDa that, upon proteolytic cleavage, is translated to two subunits [7]. The zinc-dependent light chain (50 kDa) characterized by endopeptidase activity is linked via a single disulfide bond to the heavy chain (100 kDa) that consists of a C-terminal receptor-binding domain and N-terminal trans locational domain [8]. BoNT present high binding affinity and specificity to neuronal receptors that results in the proteolysis of vesicle-associated membrane protein (VAMP) and N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor (SNARE) complexes, thereby preventing neurotransmitter release [9]. In spite of the availability of vaccines against BoNT, there are still many outbreaks of botulism worldwide [7,10]. In the US alone, C. botulinum spores inhabit ~35% of examined soil samples, exemplifying its high environmental prevalence [11]. Moreover, botulism outbreaks cause significant economic losses due to animals’ death, production loss, and rejection of contaminated animal feed and animal products [12]. To date, to the best of our knowledge, there are no economic evaluations of animal BoNT outbreaks. While surveillance data are available for humans, animal botulism is not listed among the 117 notifiable diseases monitored by the World Organization for Animal Health [13]. In most European countries, animal botulism is not a notifiable disease, leading to a lack of animal botulism data regarding case numbers and outbreaks [14]. However, a possible rise in the frequency of reported outbreaks in France, Italy, and some other European countries can change the overview of the monitoring importance [10,12,15,16].
Currently, the accepted method of botulism detection and serotype identification is the mouse lethality assay (MLA) [11,17]. The gold-standard approach is highly reliable, sensitive, and can be applied to complex matrices diagnosis, i.e., different foods, environmental, and clinical samples [2]. Although being a standard procedure, the in vivo approach suffers from significant disadvantages [5]. The MLA is an expensive, complex, low-throughput approach, includes animal experimentations, and is time-consuming. The latter parameter (overall turnaround) is exceptionally long for a life-threatening disease (2–4 days), making real-time assessment impractical [1,7]. Alternatively, the endopep-mass spectrometry assay allows for high confidence and enhanced sensitivity detection of all known serotypes by typing their proteolytic activity products [5,18]. This technique is limited to explicit laboratories due to the high level of expertise and complex instrumentation needed for the analysis [19]. Other advanced rapid techniques, such as ELISA, cell- or DNA-based assays, show significantly less sensitivity than the MLA and cannot be utilized for practical diagnosis [4,20]. Thus, alternative assays capable of replacing the MLA, in terms of rapid and sensitive quantification, and the applicability for on-site analysis, have long been perused.
Sensor or biosensor technology offers an opportunity to fulfill this niche, as it offers significant advantages in comparison to conventional assays, such as amplified sensitivity and selectivity, continuous measurements, rapid end-to-end analysis, miniaturization, and reproducibility [21,22,23,24,25]. Specifically, porous silicon (PSi) thin films continue to attract immense interest for the development of label-free optical transducers [26,27,28,29,30,31]. The porous nanostructure owes several beneficial features for the design and development of a sophisticated sensing platform. This includes a rapid and tunable fabrication process resulting in high surface area, various photonic structures, enhanced sensitivity, and label-free practical detection of any biorecognition event occurring within the porous void [32,33]. The reflectivity spectra of the porous scaffold are monitored in real-time by interferogram average over wavelength (IAW) or reflective interferometric Fourier transform spectroscopy (RIFTS), two highly sensitive approaches influenced by refractive index alterations [28].
This study presents a simple, rapid, and highly sensitive optical biosensor for real-time detection of BoNT-C available in complex media by immunorecognition response. The overall label-free sensing concept is schematically illustrated in Figure 1. The PSi based Fabry–Pérot interferometer was designed to quantify minute BoNT-C concentrations by monitoring the reflectivity spectra using miniaturized equipment (Figure 1a). A competitive immunoassay included highly specific monovalent antibodies against the target analyte, followed by sequential immunorecognition of horseradish peroxidase (HRP) preadsorbed secondary antibodies to amplify the optical response (Figure 1b). The amplification reaction included the oxidation of the enzymatic substrate, 4-chloro-1-naphthol (4CN), into insoluble products [34,35]. The resulting precipitates accumulated within the pores and changed the reflectivity spectra (Figure 1c) by alternating the averaged refractive index (Figure 1d). The inherent sensitivity, specificity, and selectivity were thoroughly assessed using the porous nanostructure. The practical aspect of the developed assay was verified using field BoNT samples under optimized conditions to exemplify the potential use of the developed optical approach for rapid bio-diagnosis of BoNT.
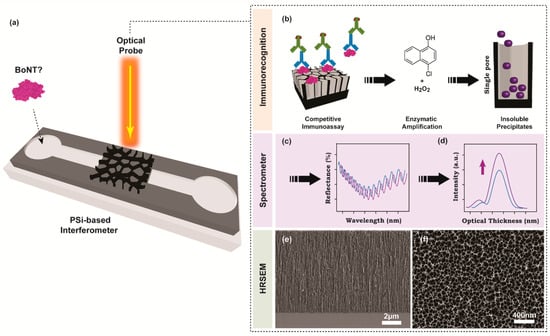
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of nanostructured PSi-based interferometer for the detection of botulinum toxins. (a) The PSi nanostructure is illuminated with white light perpendicular to the sample surface, while the reflected light is captured and detected by a miniaturized spectrometer. (b) Competitive immunoassay employs highly purified primary antibodies against target analyte (BoNT-C) that are attached to the porous support. Next, secondary antibodies modified with HRP are applied to amplify the optical signal. The amplification reaction includes the oxidation of 4CN substrate in the presence of hydrogen peroxide to produce insoluble products that precipitate and accumulate within the pores. (c) The catalytic reaction is monitored in real-time by the RIFTS approach. (d) The obtained reflectance spectrum is Fourier transformed into an indicative peak with characteristic effective optical thickness and amplitude (intensity), which correlate with enzymatic reaction product infiltration into the pores. HRSEM micrographs of a typical oxidized PSi thin film. (e) Cross-section and (f) top views.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Boron-doped p-type silicon wafers with 1.0 mΩ.cm were supplied by Siltronix Silicon Technologies (France). Aqueous 48% hydrofluoric acid (HF) and absolute ethanol (EtOH) were purchased from Merck Millipore (Israel). Gelatin (fish skin), glutaraldehyde (GluAld) solution (Grade II, 25% in H2O), sodium hydroxide, sodium hypochlorite, 4CN, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), and HEPES buffer were obtained from Sigma–Aldrich Chemicals (Israel). C. botulinum toxoid complex C (BoNT-C), D (BoNT-D), and polyclonal monovalent antibodies (IgG, from Rabbit serum) were obtained from Metabiologics (Madison, WI, USA). A goat anti-rabbit (IgG) HRP preadsorbed antibody was supplied by Zotal Ltd. (Israel). Deionized water from the ultrapure water system (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) was used throughout the experiments.
2.2. Porous Silicon Fabrication
PSi thin films were fabricated by two sequential electrochemical anodization steps, as previously described [26,27]. The first anodization step was performed under a constant current density of 375 mA cm−2 for 30 s in 3:1 v/v ratio of 48% HF and EtOH, respectively. Caution: HF is highly toxic and physical contact should be avoided. The resulting layer was chemically detached by alkaline dissolution in 0.1 M sodium hydroxide, and mild post-polishing treatment (1:3:1 v/v ratio of ultrapure water, EtOH and 48% HF, respectively) applied for 90 s each. The second anodization step included a constant current density of 525 mA cm−2 applied for 30 s. The freshly etched PSi thin films were thermally oxidized at 800 °C for 1 h in a tubular furnace (Lindberg/Blue M, Thermo Scientific) under ambient conditions producing oxidized nanostructures (PSiO2). Morphological characteristics were obtained using a high-resolution scanning electron microscopy (HRSEM, Carl Zeiss Ultra Plus, Jena, Germany).
2.3. Interferometer Biofunctionalization
The porous nanostructures were physically adsorbed with 50 µL of gelatin solution (10 mg mL−1) applied for 30 min, followed by a HEPES buffer (pH 7.4) vigorous wash to remove loosely bound molecules. The resulting thin films were cross-linked using GluAld solution (2.5% v/v), following a previous report [27]. Immediately, 20 µL of BoNT-C toxoid (1 µg mL−1) was applied on the GluAld modified surface for 30 min at room temperature and allowed to incubate overnight at 4 °C. Later, the PSi films were thoroughly rinsed with HEPES buffer (pH 7.4) to remove loosely bound molecules.
2.4. Optical Studies
A detailed description of the optical system and data analysis can be found in our previous work [27]. Briefly, reflectance spectra were acquired within the VIS-NIR range and analyzed by applying fast Fourier transformation (FFT). The resulting single peak position along the χ-axis is characterized by indicative effective optical thickness (EOT) and the y-axis by the amplitude (intensity) [36]. The EOT refers to the nanostructure average refractive index (n) of the porous layer and the total depth (L) governed by the Fabry–Pérot equation [32,37]. The FFT amplitude correlates with the refractive index contrast of neighboring interfaces that define the relevant layer [36].
2.4.1. Surface Functionalization Characterization
Surface functionalization steps were optically characterized by measuring the relative EOT changes performed in dry conditions and defined as:
where is the 2nL value after each functionalization step (gelatin, GluAld, BoNT-C, antibodies) and is the 2nL value of unmodified PSiO2 film [35]. Additionally, the spectroscopic liquid infiltration method (SLIM) was used to assess the optical porosity after each modification step [27,36].
2.4.2. BoNT-C Detection Using Immunorecognition
Various concentrations (0–10,000 pg mL−1) of the target analyte were pre-incubated in HEPES buffer (460 µL) with 40 µL of 0.5 µg mL−1 primary antibodies (pAb, produced in rabbit) for 15 min to achieve an antigen-antibody complex formation. The pre-incubated solutions were applied on BoNT-C functionalized PSiO2 thin films for 30 min and rinsed three times with HEPES buffer (5 min, each) to remove unbound moieties. Then, 40 µL of HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies (sAb) (50 µg mL−1, anti-rabbit produced in goat, IgG) were added and allowed to incubate for 30 min, followed by a post-treatment washing procedure with HEPES buffer. The treated PSiO2 surfaces were impregnated inside a flow cell configuration and equilibrated by dosing 0.84 mM 4CN for 5 min. After a stable baseline, the biochemical response of HRP molecules was activated by the addition of H2O2 (5 µL, 30% v/v) to the cycled solution. The biochemical responses of HRP-conjugated sAb are presented as the relative intensity of the observed FFT peak:
where is the obtained optical intensity response following HRP residues activation by the administration of H2O2 onto 4CN substrate with respect to (intensity values recorded during initial optical experiment baseline prior biochemical response activation in 4CN only). The optical experiments were completed once stable relative intensity values were obtained (~20 min), assuming surface saturation with the precipitation of the insoluble products. The relative responses of the aforementioned experiments are presented as the relative activity and defined as:
where represents the relative intensity of different BoNT concentrations interactions with the porous nanostructure and is the maximal relative intensity without the addition of BoNT onto the optical platform.
2.5. Detection of BoNT-C in Field Samples
Field samples were obtained from samples received for routine diagnosis of animal botulism at the National Reference Laboratory for Botulism at the Department of Bacteriology in the Kimron Veterinary Institute. Anaerobic culturing and the following MLA were performed as described before [38]. MLA was performed in accordance with the KVI Institutional Animal Care Committee for handling laboratory animals and under ethical approval n. 020_b15963_24. BoNT-C and BoNT-D positive samples following the neutralization assay were chosen for the current study. The field BoNT holotoxins were diluted to 1:100 and stored in the freezer (−20 °C) for further use. Note: both toxins were handled according to the biosafety measures within a dedicated cabinet enclosure and neutralized immediately after the experiment termination using sodium hypochlorite for 10 min.
3. Results
3.1. Interferometer Design and Characterization
The nanostructured PSi based Fabry–Pérot interferometer for label-free detection of BoNT-C relies on measuring the refractive index alteration upon biochemical reaction products’ precipitation inside the porous matrix. The latter reaction is utilized as a signal amplification process to augment the specific immunorecognition events occurring on the solid support. Therefore, the physical dimensions of the nanostructure were designed to accommodate sufficient enzymatic reaction products within the pores that will induce pronounced optical sensitivity. The electrochemical anodization of boron-doped silicon wafers included a constant current density of 525 mA cm−2, which was applied for 30 s to produce a homogeneous single optical layer. Immediately after, the freshly prepared PSi thin films were thermally oxidized to yield PSiO2 nanostructures. The oxidation process is a crucial passivation step of a highly porous scaffold, offering means to minimize the surface-related aging effect in aqueous media and thus preserve its optical properties [34]. The structural features of the resulting porous nanostructures were characterized by HRSEM imaging. Figure 1e,f shows a cross-section and top views of a typical PSiO2 thin film, respectively, revealing a porous layer of ~8.5 µm deep and cylindrical-shaped pores of 70 ± 20 nm in diameter. Next, the PSiO2 nanostructure was passivated with gelatin, a conventional blocking agent in immunoblot research, to minimize the non-specific adsorption of complex media constituents with the porous support. The physically adsorbed gelatin moieties were utilized as anchoring points for grafting functional biomaterials through a cross-linking agent. Herein, GluAld solution was used to immobilize BoNT-C toxoid on the gelatin-modified porous-thin-film for the competitive immunoassay approach. The inherent biofunctionalization steps upon interferometer’s bottom-up surface modifications were confirmed by RIFTS, which offers a direct and real-time spectral evaluation of the molecular level interactions occurring within and on top of the porous scaffold [26]. It is expected that the addition or binding of molecular moieties onto the pore walls will modulate a red-shift in the FFT peak, which corresponds with the average refractive index increase [32,37]. Figure 2a,b depicts the reflectivity spectra (Fabry–Pérot fringe pattern) and the corresponding FFT, respectively, following different biofunctionalization steps (including gelatin, GluAld, BoNT, pAb). Indeed, the EOT response is increased with each of the described modification steps. Moreover, the averaged relative responses of the applied modification steps are summarized in Table 1, and a similar trend is presented. Note: The EOT values are normalized with the 2nL value of unmodified PSiO2 film. To further complement the attained characterization steps, the accessible porous volume was assessed using SLIM. Table 1 depicts a gradual decrease in the open porosity values upon the different layers’ addition and relatively fixed total depth. Overall, these results indicate successful surface functionalization with strategic bioreceptors for the competitive immunoassay.
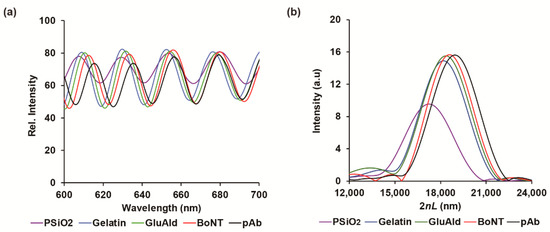
Figure 2.
Biofunctionalization characterization using RIFTS. (a) Reflectivity spectra and (b) the corresponding FFT following different biofunctionalization steps (i.e., gelatin, GluAld, BoNT, pAb).

Table 1.
BoNT-C toxoid biofunctionalization characterization using RIFTS and SLIM.
3.2. BoNT-C Detection Using Immunorecognition
The developed biosensing approach for rapid BoNT-C detection was accomplished by utilizing high-affinity antibodies in the competitive immunoassay. The resulting complexes (antigen-antibody) anchored on the porous scaffold were amplified using sAb modified with HRP. The biochemical signal amplification was evaluated in real-time using the RIFTS technique by optical data assortment upon enzymatic reaction products’ precipitation into the pores. Figure 3a depicts the sensorgrams of the entire BoNT-C dynamic range (0, 10, 100, 1000, and 10,000 pg mL−1). All interferometers similarly interacted with HRP-conjugated sAb and the oxidation substrate. The biosensing experiments include the acquisition of a stable baseline using 4CN in HEPES buffer for 5 min, followed by the addition of H2O2 to the reaction solution to activate the enzymatic response. The optical experiments were completed once stable relative intensity values were obtained (~20 min), assuming porous surface saturation with the insoluble products. The maximal optical response is attained for conditions omitting BoNT-C from the assay (0 pg mL−1), in which pronounced insoluble products were entrapped within the PSiO2. The significant relative intensity value of 2.88 at 20 min is ascribed to the absence of competing or interfering molecules in the immunoassay, resulting in evident interactions with the BoNT-C modified nanostructure. The relative optical responses are proportionally decreased upon augmented toxoid concentrations evaluated by the optical platform. The results represent a decrease in insoluble products’ entrapment within the nanostructure, thus minimizing the average refractive index of the entire porous scaffold. The specificity of the assay’s counterparts was evaluated by eliminating pAb from the reaction solution, thus evaluating the systems’ background noise. Figure 3a shows an insignificant relative response (value of 0.98), thus eliminating biochemical reaction products’ entrapment within the pores. The presented control conditions cross-validate that the attributed optical signals are assigned to the specific target analyte recognition followed by a biochemical cascade reaction. Figure 3b depicts the calibration curve of the net relative activity after subtracting the background noise from the different conditions. The linear trend of the relative activity is steadily decreased and governed by the regression equation of relative activity = −6.96 × Ln (CBoNT-C) + 107.21 (R2 = 0.98). The resulting fit indicates sufficient optical linearity within the entire studied dynamic range of 0 to 10,000 pg mL−1. The theoretical detection limit is calculated as 4.8 pg mL−1 using 3 Sa/m, where Sa is the standard deviation of the y-axis (3.65%) and m is the slope of the fitting line [39]. The analytical performance of the developed sensing interferometer was compared with other advanced rapid in vitro assays, including the conventional MLA approach, see Table 2. The presented sensitivity threshold, assay duration, and portability for on-site analysis are sufficiently adequate for the detection of BoNT [1,3,7].
Figure 3.
Biosensing system optical response toward BoNT-C toxoid different concentrations. (a) Representative relative intensity changes vs. time of the HRP catalytic response for the different target analyte concentrations (0−10,000 pg mL−1). Negative control omitting the addition of pAb to the protocol assay. Note: all sensorgrams present optical baselines with 0.8 mM 4CN in HEPES buffer (a1) followed by the addition of H2O2 to the cycled solution (a2). The biosensor is fixed in a custom-made flow cell, and the reflectivity spectra are recorded every 30 s. (b) The corresponding calibration curve of the relative activity for the different toxoid concentrations. Data are reported as mean ± SD (n = 4).

Table 2.
State-of-the-art BoNT detection techniques.
3.3. Field Samples BoNT-C Detection
The practical aspect of the developed assay was verified using real BoNT samples under optimized conditions. BoNT-C and BoNT-D were diluted 100-fold prior to interaction with BoNT-C modified PSiO2 to determine the actual serotype in the analyzed sample. All samples were subjected to similar pre-treatment procedures and were later evaluated by the optical setup using RIFTS. Figure 4 depicts the relative activity values acquired by the BoNT-C solid-state competitive immunoassay. The presented activity values are 54 ± 7% and 85 ± 2% for BoNT-C and BoNT-D (p < 0.01), respectively. The attained lower values for BoNT-C suggest higher toxin content in the analyzed samples, resulting in decreased catalytic activities of the HRP moieties. It should be noted that the resulting optical indication for BoNT-D samples is within the sensitivity threshold of the optical setup. These results suggest that the developed assay toward BoNT-C analysis in real samples is highly specific. To further clarify the obtained results, the relative activity values were used to estimate the toxins’ concentrations in the unknown samples using the regression equation. Indeed, the estimated values are 2896 ± 2515 and 25 ± 7 pg mL−1 for BoNT-C and BoNT-D, respectively. Additionally, the selectivity of the biosensing system was evaluated by interacting both toxins at equivalent volumes of 50-fold dilution (receiving equivalent final concentrations). The obtained relative activity values are 48 ± 3% (p > 0.25 with respect to BoNT-C), indicating a highly selective analytical approach for real toxins analysis. The corresponding BoNT-C concentration in the presence of interfering toxin is calculated as 5599 ± 2783 pg mL−1. The augmented results are ascribed to the heteroscedasticity of the semi-logarithmic scale, especially within the wide dynamic range of target BoNT-C concentrations. Overall, the attained results correlate between the acquired optical signals and the specific target concentration while applying the highly specific pAb. The developed porous interferometer provides key advantages over the conventionally used in vivo assay. First, the presented concept is not based on animal experimentation, thus omitting welfare and ethical issues related to the MLA approach. Second, the analysis is performed in a simple and rapid format, offering near real-time detection and quantification of hazardous toxins. Third, the optical platform presents high sensitivity that can be potentially applied for selective identification of any target BoNT in complex media as animals’ rumen or intestine, human feces, animal feed, or suspected foodstuff without hindering its spectral resolution. Additionally, the reflective-based approach can be easily adapted for on-site analysis, thus eliminating the need for complex laboratory-based facilities and instrumentations. Further research should focus on simultaneous detection and discrimination of BoNT serotypes in a high-throughput manner. Such array format will significantly promote field studies focused on botulism outbreaks in animals and allow the acquisition of epidemiological data in real-time scenarios.
Figure 4.
Reflective-based response of the immunological recognition assay for evaluating real BoNT samples. They averaged relative activity values of the different toxins, including selectivity evaluation. Data are reported as mean ± SD (N = 3).
4. Conclusions
In summary, we have successfully demonstrated a simple, rapid, and label-free optical biosensing approach for highly specific diagnosis of BoNT-C, relevant for veterinary botulism. The biochemical cascade reaction was utilized for signal amplification and toxins’ internal content differentiation using the RIFTS approach. As a proof-of-concept, the sensing performance of the developed interferometer was sufficiently applied for selective analysis of real BoNT holotoxins. The resulting sensing approach can be further fine-tuned and adapted for systematic on-site diagnosis of all seven BoNT serotypes derived from animal feed, food, and the environment using simple and portable equipment. Overall, the surveillance data will positively affect animals’ health by rapid elucidation of the occurring disease, thus potentially minimizing the economic and animal welfare impacts.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.E., S.E.B., and G.S.; methodology, Z.B. and D.N.K.; validation, Z.B. and D.N.K.; formal analysis, D.N.K. and G.S.; investigation, Z.B. and D.N.K.; resources, S.E.B. and G.S.; writing—original draft preparation, D.N.K. and G.S.; writing—review and editing, D.E., S.E.B., and G.S.; visualization, D.N.K. and G.S.; supervision, S.E.B. and G.S.; project administration, S.E.B. and G.S.; funding acquisition, D.E., S.E.B., and G.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Israeli Ministry of Agriculture, grant number 20-07-0021.
Institutional Review Board Statement
MLA was performed in accordance with the KVI Institutional Animal Care Committee for handling laboratory animals and under ethical approval n. 020_b15963_24.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
D.N.K. is grateful for the ARO outstanding postdoctoral award.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Von Berg, L.; Stern, D.; Pauly, D.; Mahrhold, S.; Weisemann, J.; Jentsch, L.; Hansbauer, E.-M.; Müller, C.; Avondet, M.A.; Rummel, A. Functional detection of botulinum neurotoxin serotypes A to F by monoclonal neoepitope-specific antibodies and suspension array technology. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Schill, K.M.; Fry, H.C.; Duncan, T.V. A Quantum Dot Nanobiosensor for Rapid Detection of Botulinum Neurotoxin Serotype E. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 2118–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čapek, P.; Dickerson, T. Sensing the Deadliest Toxin: Technologies for Botulinum Neurotoxin Detection. Toxins 2010, 2, 24–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, H.-P.; Chuang, H.-S. Rapid and Sensitive Nano-Immunosensors for Botulinum. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åberg, A.T.; Karlsson, I.; Hedeland, M. Modification and validation of the Endopep-mass spectrometry method for botulinum neurotoxin detection in liver samples with application to samples collected during animal botulism outbreaks. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, J.M.; Blumental, J.R.; Merson, M.H.; Lombaed, G.L.; Dowell, V.R., Jr.; Gangarosa, E.J. Clinical features of types A and B food-borne botulism. Ann. Intern. Med. 1981, 95, 442–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, R.J.; Thomas, C.A.; Halliwell, J.; Gwenin, C.D. Rapid Detection of Botulinum Neurotoxins-A Review. Toxins 2019, 11, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rossetto, O.; Megighian, A.; Scorzeto, M.; Montecucco, C. Botulinum neurotoxins. Toxicon 2013, 67, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliwell, J.; Gwenin, C. A label free colorimetric assay for the detection of active botulinum neurotoxin type A by SNAP-25 conjugated colloidal gold. Toxins 2013, 5, 1381–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rasetti-Escargueil, C.; Lemichez, E.; Popoff, M.R. Human Botulism in France, 1875–2016. Toxins 2020, 12, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, E.A. Clostridium botulinum and the most poisonous poison. In Foodborne Pathogens; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 553–601. [Google Scholar]
- Hansbauer, E.-M.; Skiba, M.; Endermann, T.; Weisemann, J.; Stern, D.; Dorner, M.B.; Finkenwirth, F.; Wolf, J.; Luginbühl, W.; Messelhäußer, U.; et al. Detection, differentiation, and identification of botulinum neurotoxin serotypes C, CD, D, and DC by highly specific immunoassays and mass spectrometry. Analyst 2016, 141, 5281–5297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harris, A. Clostridium botulinum. In Encyclopedia of Food and Health; Caballero, B., Finglas, P.M., Toldrá, F., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2016; pp. 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Maréchal, C.; Anniballi, F.; Bano, L.; Tevell, A.; Seyboldt, C.; Koene, M.; Bilei, S.; Derman, Y.; Chemaly, M. Workshop on the risks associated with animal botulism and ANIBOTNET final meeting. Euroreference 2020, 4, 33–41. [Google Scholar]
- Karsen, H.; Ceylan, M.R.; Bayındır, H.; Akdeniz, H. Foodborne botulism in Turkey, 1983 to 2017. Infect. Dis. 2019, 51, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anniballi, F.; Auricchio, B.; Fiore, A.; Lonati, D.; Locatelli, C.A.; Lista, F.; Fillo, S.; Mandarino, G.; De Medici, D. Botulism in Italy, 1986 to 2015. Eurosurveillance 2017, 22, 30550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rasetti-Escargueil, C.; Lemichez, E.; Popoff, M.R. Public health risk associated with botulism as foodborne zoonoses. Toxins 2020, 12, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moura, H.; Terilli, R.R.; Woolfitt, A.R.; Gallegos-Candela, M.; McWilliams, L.G.; Solano, M.I.; Pirkle, J.L.; Barr, J.R. Studies on botulinum neurotoxins type/C1 and mosaic/DC using Endopep-MS and proteomics. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 61, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björnstad, K.; Tevell Åberg, A.; Kalb, S.R.; Wang, D.; Barr, J.R.; Bondesson, U.; Hedeland, M. Validation of the Endopep-MS method for qualitative detection of active botulinum neurotoxins in human and chicken serum. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 7149–7161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eivazzadeh-Keihan, R.; Pashazadeh-Panahi, P.; Baradaran, B.; Guardia, M.d.l.; Hejazi, M.; Sohrabi, H.; Mokhtarzadeh, A.; Maleki, A. Recent progress in optical and electrochemical biosensors for sensing of Clostridium botulinum neurotoxin. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 103, 184–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Qin, W. Recent advances in potentiometric biosensors. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 124, 115803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Wu, W. Nanomaterial-based Optical Biosensors for the Detection of Foodborne Bacteria. Food Rev. Int. 2020, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Campbell, A.S.; de Ávila, B.E.-F.; Wang, J. Wearable biosensors for healthcare monitoring. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 389–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Yang, Z.; Wilkinson, J.S.; Zhou, X. Optical biosensors based on refractometric sensing schemes: A review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 144, 111693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arshavsky-Graham, S.; Massad-Ivanir, N.; Segal, E.; Weiss, S. Porous Silicon-Based Photonic Biosensors: Current Status and Emerging Applications. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 441–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshavsky-Graham, S.; Urmann, K.; Salama, R.; Massad-Ivanir, N.; Walter, J.-G.; Scheper, T.; Segal, E. Aptamers vs. antibodies as capture probes in optical porous silicon biosensors. Analyst 2020, 145, 4991–5003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.N.; Pinker, N.; Shtenberg, G. Porous Silicon Fabry–Pérot Interferometer for N-Acetyl-β-D-Glucosaminidase Biomarker Monitoring. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 1969–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, S.; Paghi, A.; La Mattina, A.A.; Debrassi, A.; Dähne, L.; Barillaro, G. Decoration of Porous Silicon with Gold Nanoparticles via Layer-by-Layer Nanoassembly for Interferometric and Hybrid Photonic/Plasmonic (Bio) sensing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 43731–43740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reta, N.; Michelmore, A.; Saint, C.P.; Prieto-Simon, B.; Voelcker, N.H. Label-free bacterial toxin detection in water supplies using porous silicon nanochannel sensors. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 1515–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.; Zhao, Y.; Nattoo, C.A.; Layouni, R.; Weiss, S.M. A smartphone biosensor based on analysing structural colour of porous silicon. Analyst 2019, 144, 3942–3948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumeria, T.; McInnes, S.J.P.; Maher, S.; Santos, A. Porous silicon for drug delivery applications and theranostics: Recent advances, critical review and perspectives. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2017, 14, 1407–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sailor, M.J. Porous Silicon in Practice: Preparation, Characterization and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Weinheim, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Sailor, M.J.; Chang, B.-Y. Fabrication of a Lateral Gradient Rugate in Porous Silicon for a Miniature Spectrometer Application. ChemElectroChem 2019, 6, 5967–5972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtenberg, G.; Massad-Ivanir, N.; Fruk, L.; Segal, E. Nanostructured Porous Si Optical Biosensors: Effect of Thermal Oxidation on Their Performance and Properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 16049–16055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtenberg, G.; Massad-Ivanir, N.; Segal, E. Detection of trace heavy metal ions in water by nanostructured porous Si biosensors. Analyst 2015, 140, 4507–4514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massad-Ivanir, N.; Shtenberg, G.; Zeidman, T.; Segal, E. Construction and characterization of porous SiO2/hydrogel hybrids as optical biosensors for rapid detection of bacteria. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 2269–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massad-Ivanir, N.; Shtenberg, G.; Tzur, A.; Krepker, M.A.; Segal, E. Engineering Nanostructured Porous SiO2 Surfaces for Bacteria Detection via “Direct Cell Capture”. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 3282–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elad, D.; Yas-Natan, E.; Aroch, I.; Shamir, M.; Kleinbart, S.; Hadash, D.; Chaffer, M.; Greenberg, K.; Shlosberg, A. Natural Clostridium botulinum type C toxicosis in a group of cats. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 5406–5408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaur, S.; Law, C.S.; Williamson, N.H.; Kempson, I.; Popat, A.; Kumeria, T.; Santos, A. Environmental Copper Sensor Based on Polyethylenimine-Functionalized Nanoporous Anodic Alumina Interferometers. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 5011–5020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, H.-Y.; Wang, Y.-C.; Tang, S.-S.; Liu, H.-W. A highly sensitive immuno-polymerase chain reaction assay for Clostridium botulinum neurotoxin type A. Toxicon 2004, 43, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.; Halevi, S.; Melman, P.; Schwartz, J.; Cai, S.; Singh, B.R. A Novel Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensor for the Rapid Detection of Botulinum Neurotoxins. Biosensors 2017, 7, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Savage, A.C.; Buckley, N.; Halliwell, J.; Gwenin, C. Botulinum neurotoxin serotypes detected by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Toxins 2015, 7, 1544–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).