On the Radiolytic Stability of Potentiometric Sensors with Plasticized Polymeric Membranes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Potentiometric Sensors
2.2. Sensor Irradiation
2.3. Potentiometric Measurements
2.4. Electrochemical Impedance Measurements
2.5. NMR Spectroscopic Measurements
3. Results and Discussions
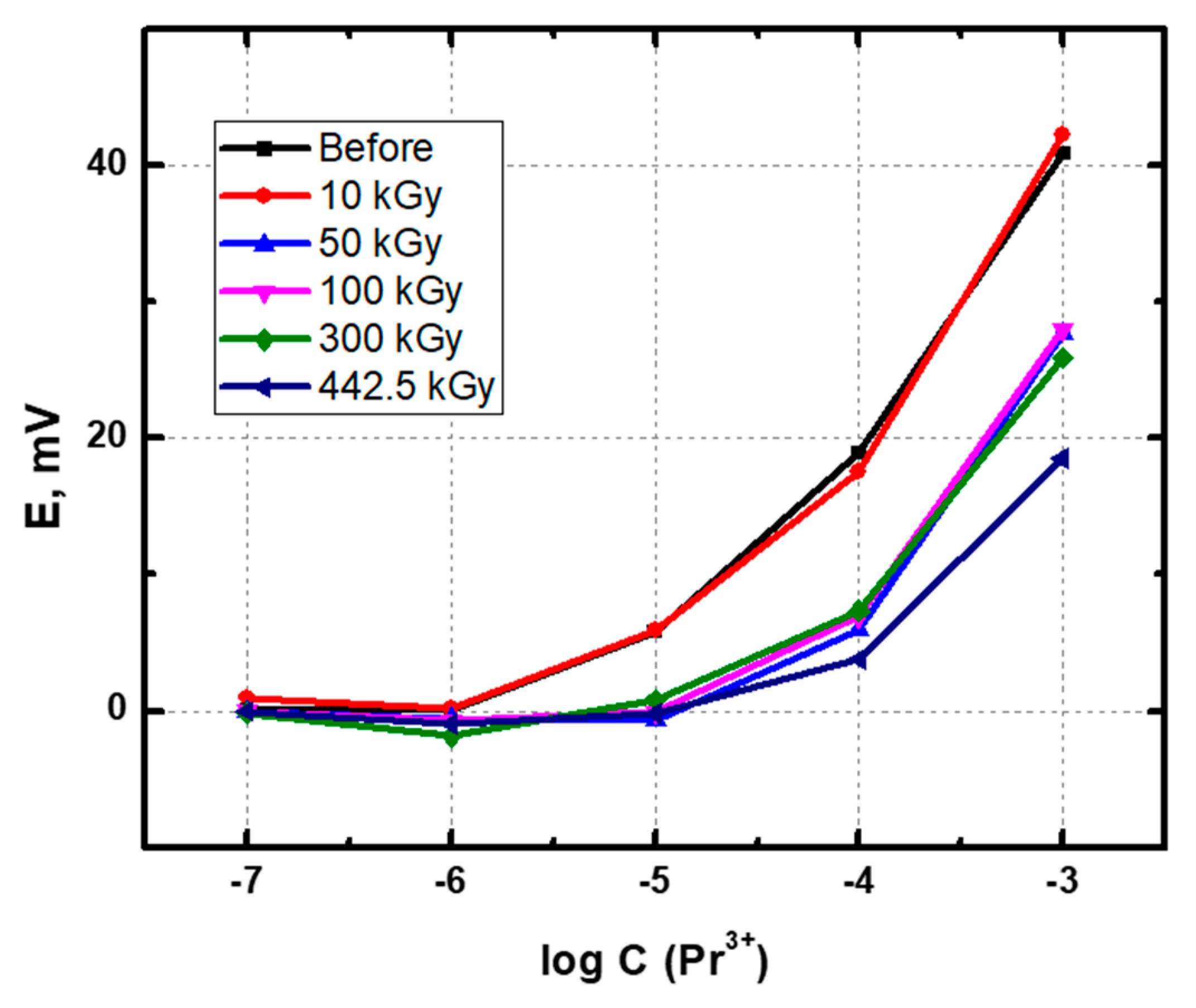
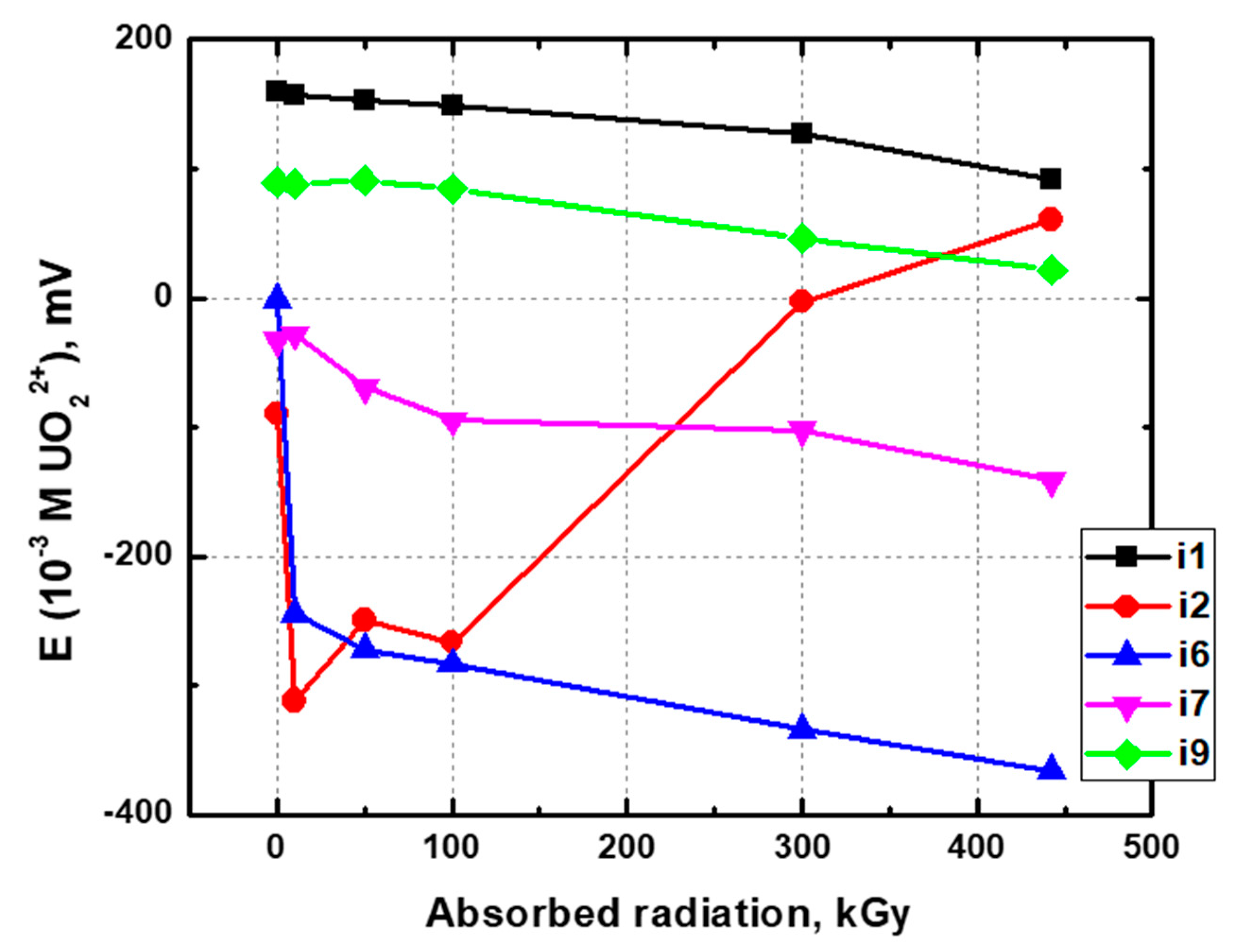
3.1. Potentiometric Measurements
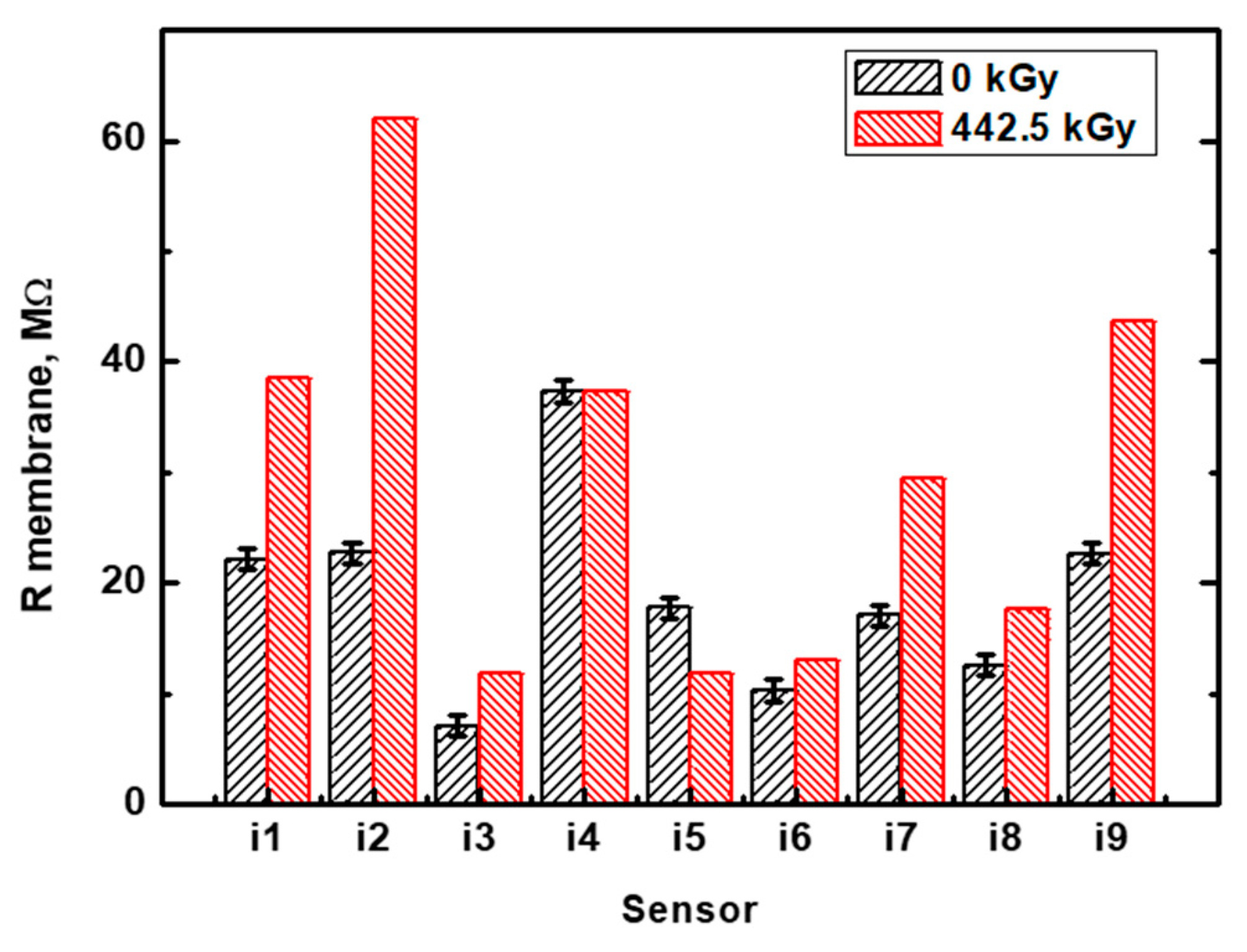
3.2. Electrochemical Impedance Measurements
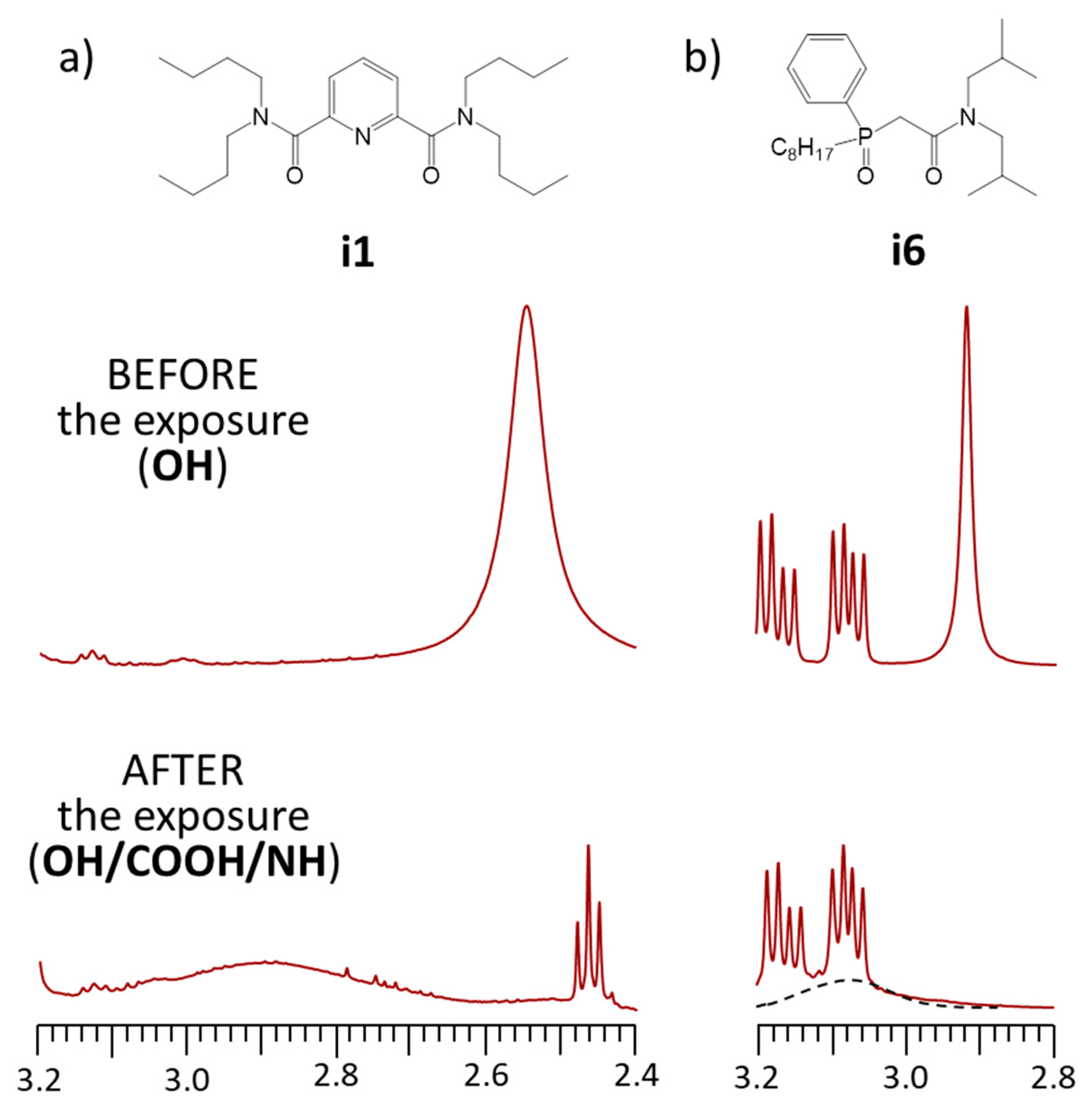
3.3. NMR Spectroscopic Measurements
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crespo, G.A. Recent advances in ion-selective membrane electrodes for in situ environmental water analysis. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 245, 1023–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrilla, M.; Cuartero, M.; Crespo, G.A. Wearable potentiometric ion sensors. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 110, 303–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özbek, O.; Berkel, C.; Isildak, Ö. Applications of potentiometric sensors for the determination of drug molecules in biological samples. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2020, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bratov, A.; Abramova, N.; Ipatov, A. Recent trends in potentiometric sensor arrays—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 678, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oleneva, E.; Savosina, J.; Agafonova-Moroz, M.; Lumpov, A.; Babain, V.; Jahatspanian, I.; Legin, A.; Kirsanov, D. Potentiometric multisensor system for tetra- and hexavalent actinide quantification in complex rare earth metal mixtures related to spent nuclear fuel reprocessing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 288, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savosina, J.; Agafonova-Moroz, M.; Yaroshenko, I.; Ashina, J.; Babain, V.; Lumpov, A.; Legin, A.; Kirsanov, D. Plutonium (IV) quantification in technologically relevant media using potentiometric sensor array. Sensors 2020, 20, 1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Agafonova-Moroz, M.; Savosina, J.; Voroshilov, Y.; Lukin, S.; Lumpov, A.; Babain, V.; Oleneva, E.; Legin, A.; Kirsanov, D. Quantification of thorium and uranium in real process streams of mayak radiochemical plant using potentiometric multisensor array. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2020, 323, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumova, Y.A.; Sapozhnikova, N.V.; Egorova, O.N.; Lumpov, A.A. Determination of concentrations of fission products by ICP–AES in solutions from spent nuclear fuel reprocessing. Radiochemistry 2017, 59, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, S.A.; Levitskaia, T.G.; Johnsen, A.M.; Orton, C.R.; Peterson, J.M. Spectroscopic monitoring of spent nuclear fuel reprocessing streams: An evaluation of spent fuel solutions via Raman, visible, and near-infrared spectroscopy. Radiochim. Acta 2011, 99, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirsanov, D.; Babain, V.; Agafonova-Moroz, M.; Lumpov, A.; Legin, A. Combination of optical spectroscopy and chemometric techniques—A possible way for on-line monitoring of Spent Nuclear Fuel (SNF) reprocessing. Radiochim. Acta 2012, 100, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilski, H. The radiation induced degradation of polymers. Int. J. Radiat. Appl. Instrum. Part. C Radiat. Phys. Chem. 1987, 29, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torikai, A.; Geetha, R.; Nagaya, S.; Fueki, K. Radiation-induced degradation of polyethylene: Polymer structure and stability. J. Polym. Sci. Part. A Polym. Chem. 1990, 28, 3639–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, H. In-field behavior of and cumulative effects on certain electrodes in a gamma field. Anal. Chem. 1970, 42, 1593–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulens, J.; West, S.J.; Ross, J.W. Influence of high gamma radiation fields on response of ion-selective electrodes. Anal. Chem. 1984, 56, 2367–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarzana, C.A.; Groenewold, G.S.; Mincher, B.J.; Mezyk, S.P.; Wilden, A.; Schmidt, H.; Modolo, G.; Wishart, J.F.; Cook, A.R. A comparison of the γ -radiolysis of TODGA and T(EH)DGA using UHPLC-ESI-MS analysis. Solvent Extr. Ion. Exch. 2015, 33, 431–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, R.K.; Becker, E.D.; Cabral de Menezes, S.M.; Goodfellow, R.; Granger, P. NMR Nomenclature. Nuclear spin properties and conventions for chemical shifts (IUPAC recommendations 2001). Pure Appl. Chem. 2001, 73, 1795–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

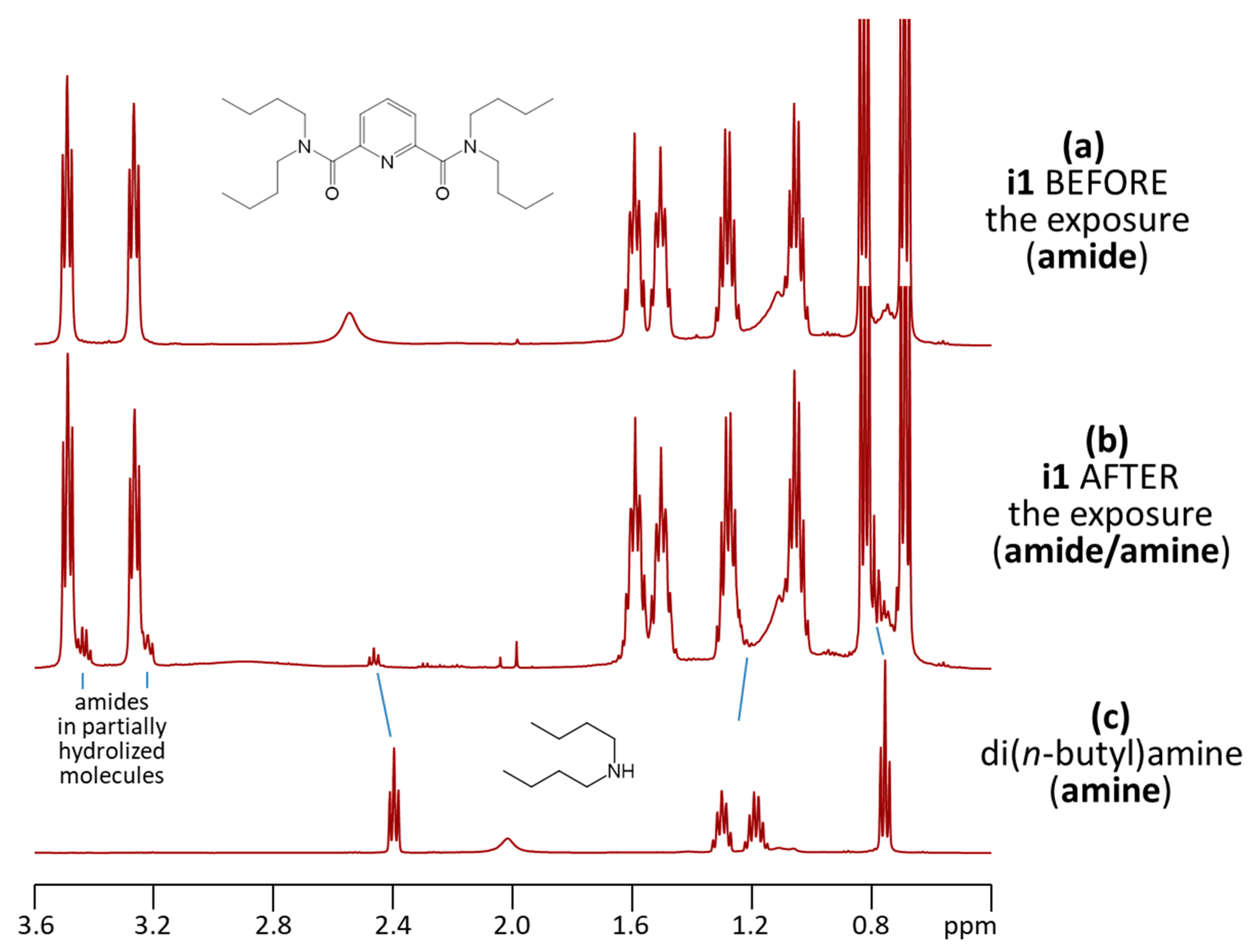
| Sensor | Ionophore | Chemical Structure | Cation Exchanger |
|---|---|---|---|
| i1 | 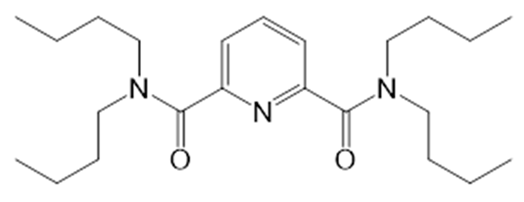 | N,N’,N,N′-Tetrabutyldiamide of dipicolinic acid | TFPB |
| i2 |  | Tetraphenylmethylene diphosphine dioxide | TFPB |
| i3 | 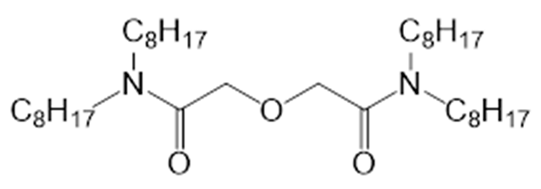 | N,N,N′,N′-Tetraoctyldiamide of diglycolic acid | CCD |
| i4 |  | 1,9-Bis-(diphenylphosphynyl)-3,6-dibenzo-2,8-dioxa-5-methyl-phosphineoxanonane | TFPB |
| i5 |  | 5,11,17,23-Tetra(diethylcarbamoyl-ethoxymethylcarboxamido)-25,26,27,28-tetrapropoxycalix[4]aren | CCD |
| i6 |  | Phenyloctyl-N,N-di-iso-butylcarbamoyl-methylen phosphine oxide | CCD |
| i7 | 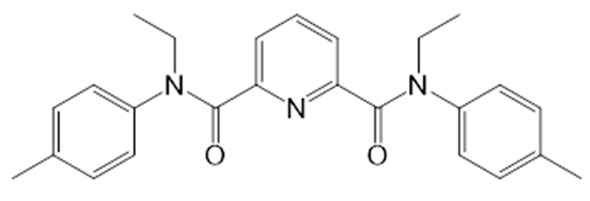 | N,N′-Diethyl-N,N′-di-p-tolyldiamide of dipicolinic acid | TFPB |
| i8 | 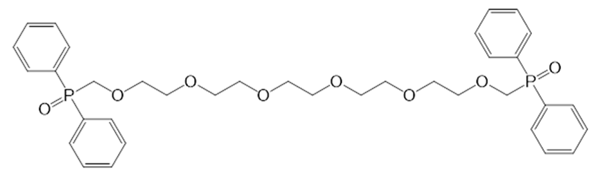 | 1,18-Bis-(diphenylphosphynyl)-2,5,8,11,14,17-hexaoxaoctadecane | CCD |
| i9 | 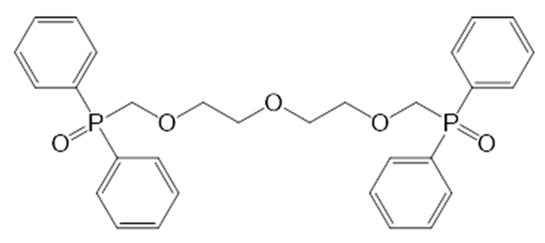 | 1,9-Bis-(diphenylphosphynyl)-2,5,8-trioxanonane | CCD |
| Pr3+ | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Absorbed Radiation, kGy | i1 | i2 | i3 | i4 | i5 | i6 | i7 | i8 | i9 |
| 0 | 15 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 17 | 18 | 15 | 11 | 7 |
| 10 | 18 | 5 | 7 | 5 | 18 | 18 | 15 | 10 | 11 |
| 50 | 12 | 5 | 7 | 6 | 17 | 19 | 9 | 11 | 10 |
| 100 | 13 | 2 | 6 | 5 | 19 | 18 | 8 | 13 | 9 |
| 300 | 8 | 5 | 7 | 7 | 18 | 19 | 2 | 5 | 9 |
| 442.5 | 4 | 3 | 8 | 4 | 18 | 19 | 1 | −7 | 6 |
| Gd3+ | |||||||||
| 0 | 16 | 12 | 15 | 9 | 15 | 17 | 19 | 13 | 10 |
| 10 | 15 | −2 | 10 | 2 | 12 | 15 | 19 | 9 | 9 |
| 50 | 12 | −5 | 12 | 1 | 11 | 13 | 13 | 12 | 9 |
| 100 | 12 | −3 | 10 | 3 | 8 | 10 | 11 | 11 | 7 |
| 300 | 5 | −2 | 11 | 1 | 4 | 7 | 2 | 1 | 4 |
| 442.5 | 6 | −2 | 13 | 4 | 0 | 7 | 3 | 0 | 3 |
| UO22+ | |||||||||
| 0 | 18 | 23 | −2 | 21 | 12 | 64 | 20 | 9 | 21 |
| 10 | 20 | 23 | −1 | 22 | 6 | 59 | 29 | 11 | 19 |
| 50 | 16 | 18 | −2 | 19 | 7 | 50 | 19 | 13 | 21 |
| 100 | 14 | 18 | 0 | 18 | 5 | 46 | 18 | 10 | 16 |
| 300 | 9 | 8 | −1 | 16 | 2 | 39 | 8 | 10 | 13 |
| 442.5 | 8 | 12 | 1 | 14 | −1 | 37 | 9 | 2 | 10 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Savosina, J.; Agafonova-Moroz, M.; Khaydukova, M.; Legin, A.; Babain, V.; Tolstoy, P.; Kirsanov, D. On the Radiolytic Stability of Potentiometric Sensors with Plasticized Polymeric Membranes. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9080214
Savosina J, Agafonova-Moroz M, Khaydukova M, Legin A, Babain V, Tolstoy P, Kirsanov D. On the Radiolytic Stability of Potentiometric Sensors with Plasticized Polymeric Membranes. Chemosensors. 2021; 9(8):214. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9080214
Chicago/Turabian StyleSavosina, Julia, Marina Agafonova-Moroz, Maria Khaydukova, Andrey Legin, Vasiliy Babain, Peter Tolstoy, and Dmitry Kirsanov. 2021. "On the Radiolytic Stability of Potentiometric Sensors with Plasticized Polymeric Membranes" Chemosensors 9, no. 8: 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9080214
APA StyleSavosina, J., Agafonova-Moroz, M., Khaydukova, M., Legin, A., Babain, V., Tolstoy, P., & Kirsanov, D. (2021). On the Radiolytic Stability of Potentiometric Sensors with Plasticized Polymeric Membranes. Chemosensors, 9(8), 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9080214






