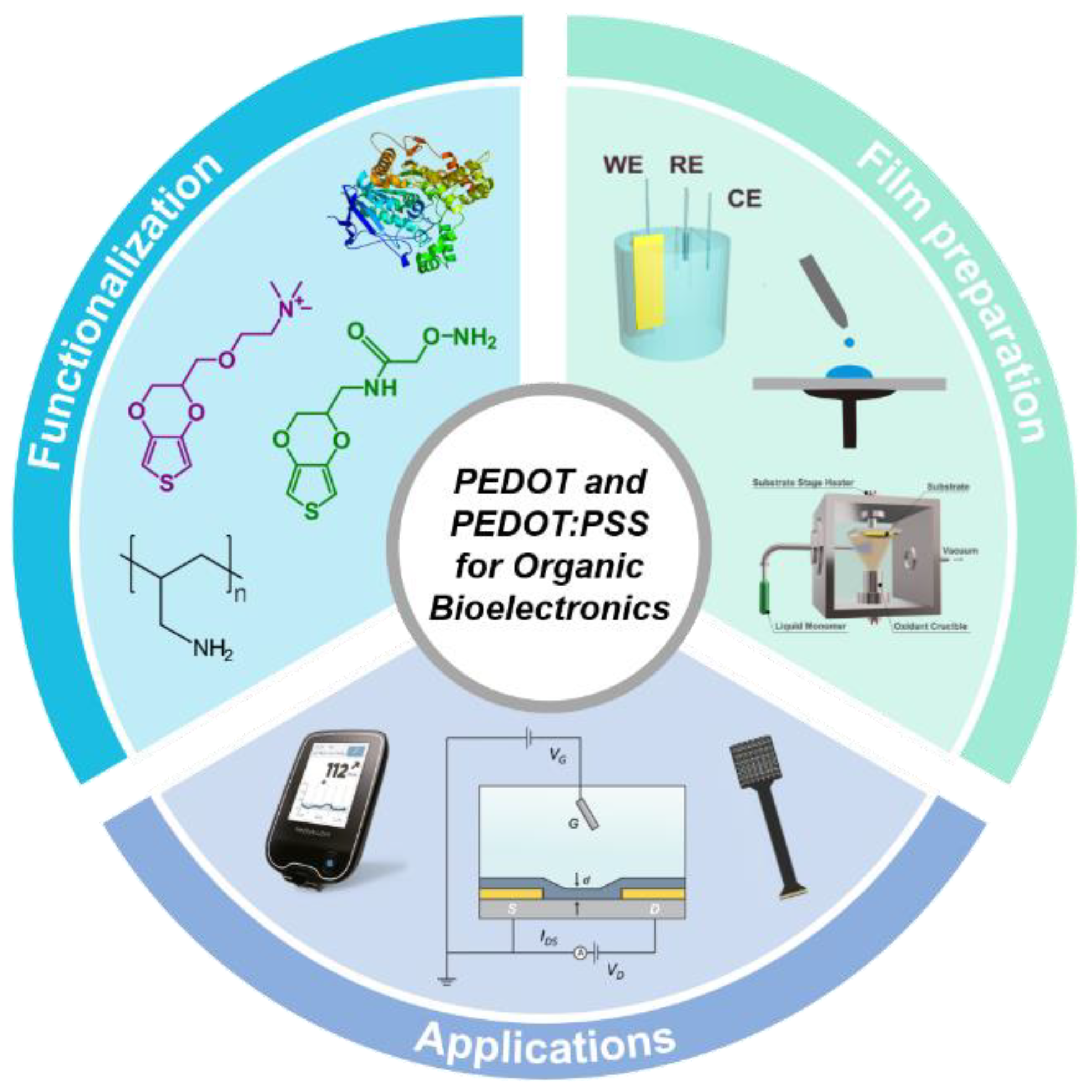
Functionalization Strategies of PEDOT and PEDOT:PSS Films for Organic Bioelectronics Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Preparation of PEDOT and PEDOT:PSS Films
2.1. Polymerization-Based Film Preparation
2.1.1. Solution–Cast Polymerization
2.1.2. Electrochemical Polymerization
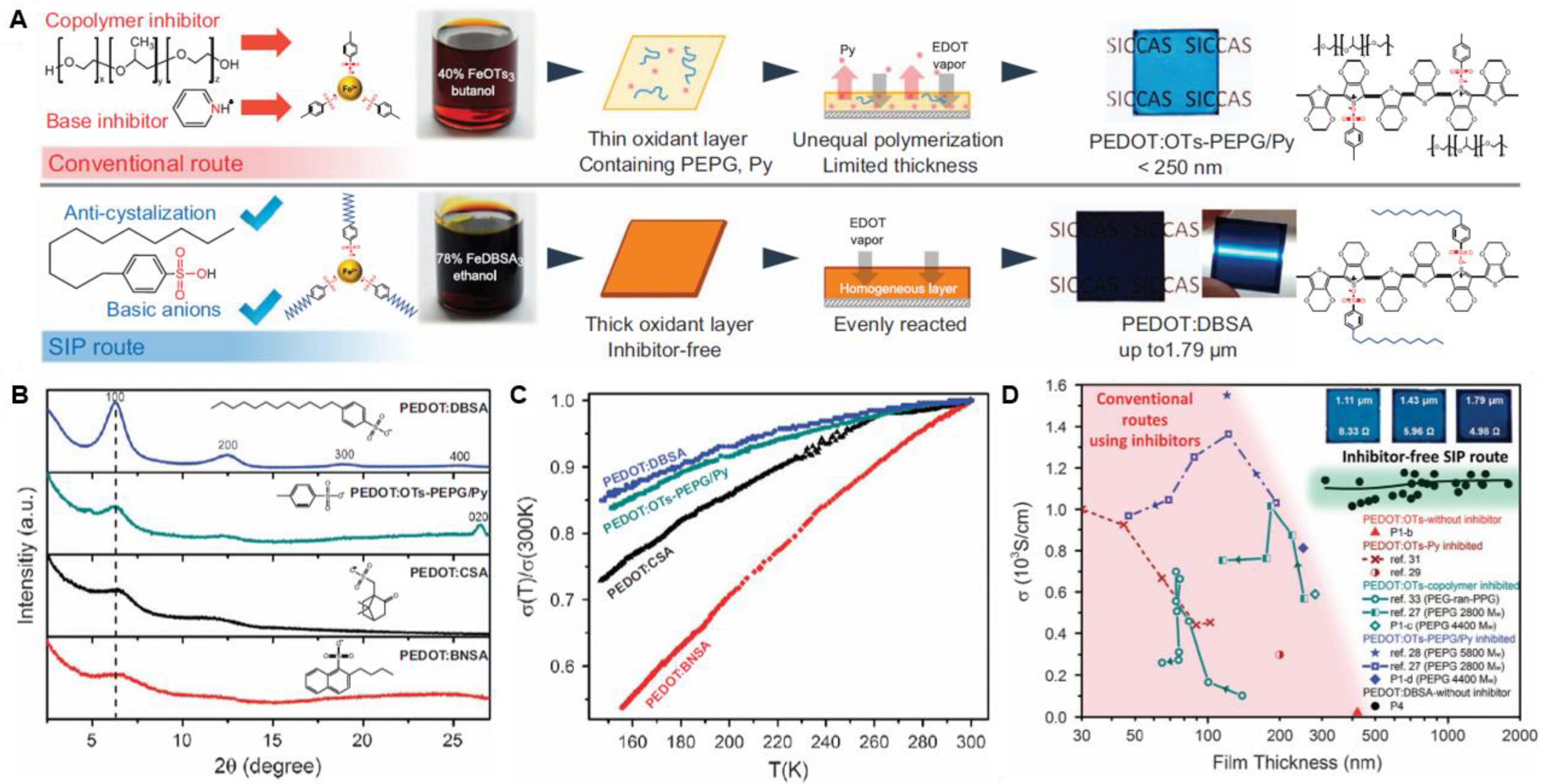
2.1.3. Vapor-Phase Polymerization and Chemical Vapor Deposition
2.2. PEDOT:PSS Films
2.3. Summary
3. Functionalization Strategies for PEDOT and PEDOT:PSS Films
3.1. Derivatization of the EDOT Monomer
3.2. Addition of Molecules to the Polymerization Solution
3.3. Functionalization of PEDOT:PSS Films
3.3.1. Blending Methods
3.3.2. Post-Functionalization of PEDOT:PSS Films
3.4. Summary
4. Bioelectronics Applications Based on PEDOT and PEDOT:PSS Films
4.1. Organic Electrochemical Transistors
4.2. Biosensing
4.3. Electrophysiological Recording
4.4. Cell Interfacing and Tissue Engineering
4.5. Overview
5. Summary and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simon, D.T.; Gabrielsson, E.O.; Tybrandt, K.; Berggren, M. Organic Bioelectronics: Bridging the Signaling Gap between Biology and Technology. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 13009–13041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zeglio, E.; Rutz, A.L.; Winkler, T.E.; Malliaras, G.G.; Herland, A. Conjugated Polymers for Assessing and Controlling Biological Functions. Adv. Mater. 2019, 1806712, 1806712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smela, E. Conjugated polymer actuators for biomedical applications. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 481–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Promsuwan, K.; Meng, L.; Suklim, P.; Limbut, W.; Thavarungkul, P.; Kanatharana, P.; Mak, W.C. Bio-PEDOT: Modulating Carboxyl Moieties in Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) for Enzyme-Coupled Bioelectronic Interfaces. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 39841–39849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, K.A.; Langhals, N.B.; Joseph, M.D.; Richardson-Burns, S.M.; Hendricks, J.L.; Kipke, D.R. Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) polymer coatings facilitate smaller neural recording electrodes. J. Neural Eng. 2011, 8, 014001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivnay, J.; Inal, S.; Salleo, A.; Owens, R.M.; Berggren, M.; Malliaras, G.G. Organic electrochemical transistors. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2018, 3, 17086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macchia, E.; Manoli, K.; Di Franco, C.; Picca, R.A.; Österbacka, R.; Palazzo, G.; Torricelli, F.; Scamarcio, G.; Torsi, L. Organic Field-Effect Transistor Platform for Label-Free, Single-Molecule Detection of Genomic Biomarkers. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 1822–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strakosas, X.; Bongo, M.; Owens, R.M. The organic electrochemical transistor for biological applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berggren, M.; Richter-Dahlfors, A. Organic bioelectronics. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 3201–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeglio, E.; Inganäs, O. Active Materials for Organic Electrochemical Transistors. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenoy, G.E.; Van der Schueren, B.; Scotto, J.; Boulmedais, F.; Ceolín, M.R.; Bégin-Colin, S.; Bégin, D.; Marmisollé, W.A.; Azzaroni, O. Layer-by-layer assembly of iron oxide-decorated few-layer graphene/PANI:PSS composite films for high performance supercapacitors operating in neutral aqueous electrolytes. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 283, 1178–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berggren, M.; Crispin, X.; Fabiano, S.; Jonsson, M.P.; Simon, D.T.; Stavrinidou, E.; Tybrandt, K.; Zozoulenko, I. Ion Electron–Coupled Functionality in Materials and Devices Based on Conjugated Polymers. Adv. Mater. 2019, 1805813, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keene, S.T.; van der Pol, T.P.A.; Zakhidov, D.; Weijtens, C.H.L.; Janssen, R.A.J.; Salleo, A.; van de Burgt, Y. Enhancement-Mode PEDOT:PSS Organic Electrochemical Transistors Using Molecular De-Doping. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fenoy, G.E.; Scotto, J.; Azcárate, J.; Rafti, M.; Marmisollé, W.A.; Azzaroni, O. Powering Up the Oxygen Reduction Reaction through the Integration of O2-Adsorbing Metal–Organic Frameworks on Nanocomposite Electrodes. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2018, 1, 5428–5436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenoy, G.E.; Giussi, J.M.; von Bilderling, C.; Maza, E.M.; Pietrasanta, L.I.; Knoll, W.; Marmisollé, W.A.; Azzaroni, O. Reversible modulation of the redox activity in conducting polymer nanofilms induced by hydrophobic collapse of a surface-grafted polyelectrolyte. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 518, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gueye, M.N.; Carella, A.; Faure-Vincent, J.; Demadrille, R.; Simonato, J.-P. Progress in understanding structure and transport properties of PEDOT-based materials: A critical review. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2020, 108, 100616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Liu, T.; Zhou, Y. Recent Advances of Synthesis, Properties, Film Fabrication Methods, Modifications of Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene), and Applications in Solution-Processed Photovoltaics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 2006213, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Mitta, G.; Marmisollé, W.A.; Trautmann, C.; Toimil-Molares, M.E.; Azzaroni, O. An All-Plastic Field-Effect Nanofluidic Diode Gated by a Conducting Polymer Layer. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1700972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohayon, D.; Inal, S. Organic Bioelectronics: From Functional Materials to Next-Generation Devices and Power Sources. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groenendaal, L.; Zotti, G.; Aubert, P.H.; Waybright, S.M.; Reynolds, J.R. Electrochemistry of poly(3,4-alkylenedioxythiophene) derivatives. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 855–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strakosas, X.; Wei, B.; Martin, D.C.; Owens, R.M. Biofunctionalization of polydioxythiophene derivatives for biomedical applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 4952–4968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Minudri, D.; Mantione, D.; Dominguez-Alfaro, A.; Moya, S.; Maza, E.; Bellacanzone, C.; Antognazza, M.R.; Mecerreyes, D. Water Soluble Cationic Poly(3,4-Ethylenedioxythiophene) PEDOT-N as a Versatile Conducting Polymer for Bioelectronics. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2020, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermanson, G.T. Bioconjugate Techniques; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; ISBN 9780123822390. [Google Scholar]
- Petsagkourakis, I.; Kim, N.; Tybrandt, K.; Zozoulenko, I.; Crispin, X. Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene): Chemical Synthesis, Transport Properties, and Thermoelectric Devices. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2019, 5, 1800918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winther-Jensen, B.; Breiby, D.W.; West, K. Base inhibited oxidative polymerization of 3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene with iron(III)tosylate. Synth. Met. 2005, 152, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchmeyer, S.; Reuter, K. Scientific importance, properties and growing applications of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene). J. Mater. Chem. 2005, 15, 2077–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Zozoulenko, I. Why Is Pristine PEDOT Oxidized to 33%? A Density Functional Theory Study of Oxidative Polymerization Mechanism. J. Phys. Chem. B 2019, 123, 5160–5167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, Y.H.; Nikolov, N.; Pollack, S.K.; Mastrangelo, J.; Martin, B.D.; Shashidhar, R. Towards a transparent, highly conductive poly (3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene). Adv. Funct. Mater. 2004, 14, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elschner, A.; Kirchmeyer, S.; Lövenich, W.; Merker, U.; Reuter, K. PEDOT: Principles and Applications of an Intrinsically Conductive Polymer; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; ISBN 9781420069129. [Google Scholar]
- Gueye, M.N.; Carella, A.; Massonnet, N.; Yvenou, E.; Brenet, S.; Faure-Vincent, J.; Pouget, S.; Rieutord, F.; Okuno, H.; Benayad, A.; et al. Structure and Dopant Engineering in PEDOT Thin Films: Practical Tools for a Dramatic Conductivity Enhancement. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 3462–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.U.; Bubnova, O.; Jafari, M.J.; Brooke, R.; Liu, X.; Gabrielsson, R.; Ederth, T.; Evans, D.R.; Andreasen, J.W.; Fahlman, M.; et al. Acido-basic control of the thermoelectric properties of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)tosylate (PEDOT-Tos) thin films. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 10616–10623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, W.; Yao, Q.; Qu, S.; Chen, H.; Zhang, T.; Chen, L. Micron-thick highly conductive PEDOT films synthesized via self-inhibited polymerization: Roles of anions. NPG Asia Mater. 2017, 9, e405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.S.; Jang, W.; Wang, D.H. The investigation of the seebeck effect of the poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)-tosylate with the various concentrations of an oxidant. Polymers 2018, 11, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cosnier, S.; Karyakin, A.; Cosnier, S. Electropolymerization; Cosnier, S., Karyakin, A., Eds.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2010; ISBN 9783527630592. [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson, L.A.A.; Carlsson, F.; Inganäs, O.; Arwin, H. Spectroscopic ellipsometry studies of the optical properties of doped poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene): An anisotropic metal. Thin Solid Films 1998, 313–314, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zotti, G.; Zecchin, S.; Schiavon, G.; Louwet, F.; Groenendaal, L.; Crispin, X.; Osikowicz, W.; Salaneck, W.; Fahlman, M. Electrochemical and XPS Studies toward the Role of Monomeric and Polymeric Sulfonate Counterions in the Synthesis, Composition, and Properties of Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene). Macromolecules 2003, 36, 3337–3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoudjit, A.; Bader, M.M.; Wan Salim, W.W.A. Study of electropolymerized PEDOT:PSS transducers for application as electrochemical sensors in aqueous media. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2018, 17, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melato, A.I.; Mendonça, M.H.; Abrantes, L.M. Effect of the electropolymerisation conditions on the electrochemical, morphological and structural properties of PEDOTh films. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2009, 13, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poverenov, E.; Li, M.; Bitler, A.; Bendikov, M. Major effect of electropolymerization solvent on morphology and electrochromic properties of PEDOT films. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 4019–4025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cysewska, K.; Karczewski, J.; Jasiński, P. Influence of electropolymerization conditions on the morphological and electrical properties of PEDOT film. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 176, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Wang, Z. Effects of polymerization potential on the properties of electrosynthesized PEDOT films. Electrochim. Acta 2003, 48, 1713–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castagnola, V.; Descamps, E.; Lecestre, A.; Dahan, L.; Remaud, J.; Nowak, L.G.; Bergaud, C. Parylene-based flexible neural probes with PEDOT coated surface for brain stimulation and recording. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 67, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubert, P.H.; Groenendaal, L.; Louwet, F.; Lutsen, L.; Vanderzande, D.; Zotti, G. In situ conductivity measurements on polyethylenedioxythiophene derivatives with different counter ions. Synth. Met. 2002, 126, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castagnola, V.; Bayon, C.; Descamps, E.; Bergaud, C. Morphology and conductivity of PEDOT layers produced by different electrochemical routes. Synth. Met. 2014, 189, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval-Rojas, A.P.; Cortés, M.T.; Hurtado, J. Electrochemical synthesis of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) doped with a new bis(pyrazolyl)methane disulfonate and its behavior towards dopamine detection. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 837, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, E.; Won, Y.; Lee, H.; Suh, K. The preparation and characteristics of conductive poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) thin film by vapor-phase polymerization. Synth. Met. 2003, 139, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winther-Jensen, B.; West, K. Vapor-phase polymerization of 3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene: A route to highly conducting polymer surface layers. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 4538–4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, M.; Fabretto, M.; Evans, D.; Hojati-Talemi, P.; Gruber, C.; Murphy, P. Vacuum vapour phase polymerization of high conductivity PEDOT: Role of PEG-PPG-PEG, the origin of water, and choice of oxidant. Polymer 2012, 53, 2146–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawal, A.T.; Wallace, G.G. Vapour phase polymerisation of conducting and non-conducting polymers: A review. Talanta 2014, 119, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chelawat, H.; Vaddiraju, S.; Gleason, K. Conformal, conducting poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) thin films deposited using bromine as the oxidant in a completely dry oxidative chemical vapor deposition process. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 2864–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhu, C.; Jiang, F.; Liu, G.; Liu, C.; Jiang, Q.; Xu, J.; An, J.; Liu, P. Regulating monomer assembly to enhance PEDOT capacitance performance via different oxidants. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 601, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuber, K.; Fabretto, M.; Hall, C.; Murphy, P. Improved PEDOT conductivity via suppression of crystallite formation in Fe(III) tosylate during vapor phase polymerization. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2008, 29, 1503–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xu, D.; Huang, A.; Yuan, H.; Xie, J.; Chen, X.; He, Y.; Zhang, T.; Shen, H. Controllable vapor phase polymerization of PEDOT films using imidazole as an inhibitor and their electrical and electrochromic properties. Synth. Met. 2020, 269, 116523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Paine, D.C.; Gleason, K.K. Heavily doped poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) thin films with high carrier mobility deposited using oxidative CVD: Conductivity stability and carrier transport. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 7187–7196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drewelow, G.; Wook Song, H.; Jiang, Z.T.; Lee, S. Factors controlling conductivity of PEDOT deposited using oxidative chemical vapor deposition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 501, 114105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirabedin, M.; Vergnes, H.; Caussé, N.; Vahlas, C.; Caussat, B. Liquid antimony pentachloride as oxidant for robust oxidative chemical vapor deposition of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 554, 149501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanasov, S.E.; Losego, M.D.; Gong, B.; Sachet, E.; Maria, J.P.; Williams, P.S.; Parsons, G.N. Highly conductive and conformal poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) thin films via oxidative molecular layer deposition. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 3471–3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moni, P.; Lau, J.; Mohr, A.C.; Lin, T.C.; Tolbert, S.H.; Dunn, B.; Gleason, K.K. Growth Temperature and Electrochemical Performance in Vapor-Deposited Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) Thin Films for High-Rate Electrochemical Energy Storage. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2018, 1, 7093–7105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirabedin, M.; Vergnes, H.; Caussé, N.; Vahlas, C.; Caussat, B. An out of the box vision over oxidative chemical vapor deposition of PEDOT involving sublimed iron trichloride. Synth. Met. 2020, 266, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Xu, J. Scientific Importance of Water-Processable PEDOT–PSS and Preparation, Challenge and New Application in Sensors of Its Film Electrode: A Review. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2017, 55, 1121–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perinka, N.; Kim, C.H.; Kaplanova, M.; Bonnassieux, Y. Preparation and Characterization of Thin Conductive Polymer Films on the base of PEDOT:PSS by Ink-Jet Printing. Phys. Procedia 2013, 44, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuk, H.; Lu, B.; Lin, S.; Qu, K.; Xu, J.; Luo, J.; Zhao, X. 3D printing of conducting polymers. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horii, T.; Hikawa, H.; Katsunuma, M.; Okuzaki, H. Synthesis of highly conductive PEDOT:PSS and correlation with hierarchical structure. Polymer 2018, 140, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Yu, J.; Tian, Q.; Shi, J.; Zhang, M.; Chen, S.; Zang, L. Application of pedot:Pss and its composites in electrochemical and electronic chemosensors. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Liu, C.; Jiang, Q.; Xu, J. Effective Approaches to Improve the Electrical Conductivity of PEDOT:PSS: A Review. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2015, 1, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, A.I.; Katsigiannopoulos, D.; Mumtaz, M.; Petsagkourakis, I.; Pecastaings, G.; Fleury, G.; Schatz, C.; Pavlopoulou, E.; Brochon, C.; Hadziioannou, G.; et al. How to Choose Polyelectrolytes for Aqueous Dispersions of Conducting PEDOT Complexes. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 1959–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantione, D.; del Agua, I.; Sanchez-Sanchez, A.; Mecerreyes, D. Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) derivatives: Innovative conductive polymers for bioelectronics. Polymers 2017, 9, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donahue, M.J.; Sanchez-Sanchez, A.; Inal, S.; Qu, J.; Owens, R.M.; Mecerreyes, D.; Malliaras, G.G.; Martin, D.C. Tailoring PEDOT properties for applications in bioelectronics. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2020, 140, 100546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casalini, S.; Dumitru, A.C.; Leonardi, F.; Bortolotti, C.A.; Herruzo, E.T.; Campana, A.; De Oliveira, R.F.; Cramer, T.; Garcia, R.; Biscarini, F. Multiscale sensing of antibody-antigen interactions by organic transistors and single-molecule force spectroscopy. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 5051–5062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sassolas, A.; Blum, L.J.; Leca-Bouvier, B.D. Immobilization strategies to develop enzymatic biosensors. Biotechnol. Adv. 2012, 30, 489–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenoy, G.E.; Marmisollé, W.A.; Azzaroni, O.; Knoll, W. Acetylcholine biosensor based on the electrochemical functionalization of graphene field-effect transistors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 148, 111796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hackett, A.J.; Malmström, J.; Travas-Sejdic, J. Functionalization of conducting polymers for biointerface applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2017, 70, 18–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Ouyang, J. Significant Different Conductivities of the Two Grades of Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):Poly(styrenesulfonate), Clevios P and Clevios PH1000, Arising from Different Molecular Weights. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 4131–4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galán, T.; Prieto-Simón, B.; Alvira, M.; Eritja, R.; Götz, G.; Bäuerle, P.; Samitier, J. Label-free electrochemical DNA sensor using “click”-functionalized PEDOT electrodes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bazaco, R.B.; Gómez, R.; Seoane, C.; Bäuerle, P.; Segura, J.L. Specific recognition of a nucleobase-functionalized poly(3,4-ethylenedioxithiophene) (PEDOT) in aqueous media. Tetrahedron Lett. 2009, 50, 4154–4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Lu, B.; Duan, X.; Xu, J.; Hu, D.; Zhang, K.; Zhu, X.; Sun, H.; Ming, S.; Wang, Z.; et al. Novel chiral PEDOTs for selective recognition of 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine enantiomers: Synthesis and characterization. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2015, 53, 2238–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagwat, N.; Kiick, K.L.; Martin, D.C. Electrochemical deposition and characterization of carboxylic acid functionalized PEDOT copolymers. J. Mater. Res. 2014, 29, 2835–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagwat, N.; Murray, R.E.; Shah, S.I.; Kiick, K.L.; Martin, D.C. Biofunctionalization of PEDOT films with laminin-derived peptides. Acta Biomater. 2016, 41, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Povlich, L.K.; Cho, J.C.; Leach, M.K.; Corey, J.M.; Kim, J.; Martin, D.C. Synthesis, copolymerization and peptide-modification of carboxylic acid-functionalized 3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene (EDOTacid) for neural electrode interfaces. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gen. Subj. 2013, 1830, 4288–4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, L.; Kuo, C.C.; Farrell, B.; Pathak, S.; Wei, B.; Qu, J.; Martin, D.C. Poly[3,4-ethylene dioxythiophene (EDOT)-co-1,3,5-tri[2-(3,4-ethylene dioxythienyl)]-benzene (EPh)] copolymers (PEDOT-co-EPh): Optical, electrochemical and mechanical properties. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 5010–5020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantione, D.; Stavrinidou, E.; Pavlopoulou, E.; Istif, E.; Dufil, G.; Vallan, L.; Parker, D.; Brochon, C.; Cloutet, E.; Hadziioannou, G.; et al. Thiophene-based trimers for in vivo electronic functionalization of tissues. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2020, 2, 4065–4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Ouyang, L.; Liu, J.; Martin, D.C. Post-polymerization functionalization of poly(3,4-propylenedioxythiophene) (PProDOT) via thiol-ene “click” chemistry. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 5028–5034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hai, W.; Goda, T.; Takeuchi, H.; Yamaoka, S.; Horiguchi, Y.; Matsumoto, A.; Miyahara, Y. Specific Recognition of Human Influenza Virus with PEDOT Bearing Sialic Acid-Terminated Trisaccharides. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 14162–14170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daprà, J.; Lauridsen, L.H.; Nielsen, A.T.; Rozlosnik, N. Comparative study on aptamers as recognition elements for antibiotics in a label-free all-polymer biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 43, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
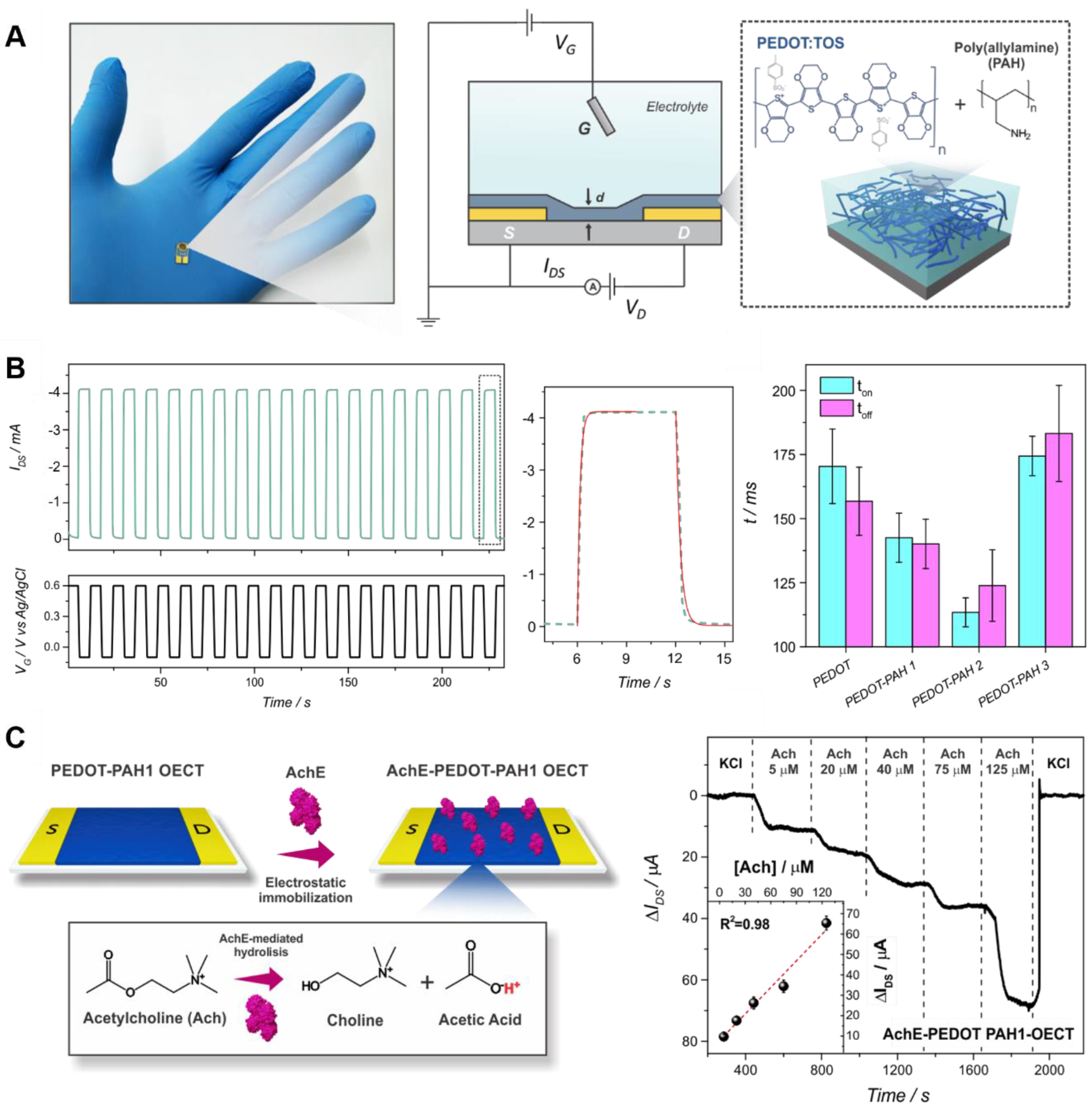
- Jimison, L.H.; Hama, A.; Strakosas, X.; Armel, V.; Khodagholy, D.; Ismailova, E.; Malliaras, G.G.; Winther-Jensen, B.; Owens, R.M. PEDOT:TOS with PEG: A biofunctional surface with improved electronic characteristics. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 19498–19505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabretto, M.; Jariego-Moncunill, C.; Autere, J.P.; Michelmore, A.; Short, R.D.; Murphy, P. High conductivity PEDOT resulting from glycol/oxidant complex and glycol/polymer intercalation during vacuum vapour phase polymerisation. Polymer 2011, 52, 1725–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, A.; D’Ilario, L.; Francolini, I.; Piozzi, A.; Pizzi, E. Partially sulfonated ethylene-vinyl alcohol copolymer as new substrate for 3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene vapor phase polymerization. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2014, 52, 1203–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongo, M.; Winther-Jensen, O.; Himmelberger, S.; Strakosas, X.; Ramuz, M.; Hama, A.; Stavrinidou, E.; Malliaras, G.G.; Salleo, A.; Winther-Jensen, B.; et al. PEDOT:gelatin composites mediate brain endothelial cell adhesion. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 3860–3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sappia, L.D.; Piccinini, E.; Marmisollé, W.; Santilli, N.; Maza, E.; Moya, S.; Battaglini, F.; Madrid, R.E.; Azzaroni, O. Integration of Biorecognition Elements on PEDOT Platforms through Supramolecular Interactions. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sappia, L.D.; Piccinini, E.; von Binderling, C.; Knoll, W.; Marmisollé, W.; Azzaroni, O. PEDOT-polyamine composite films for bioelectrochemical platforms-flexible and easy to derivatize. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 109, 110575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenoy, G.E.; Bilderling, C.; Knoll, W.; Azzaroni, O.; Marmisollé, W.A. PEDOT:Tosylate-Polyamine-Based Organic Electrochemical Transistors for High-Performance Bioelectronics. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2021, 7, 2100059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora-Sequeira, R.; Ardao, I.; Starbird, R.; García-González, C.A. Conductive nanostructured materials based on poly-(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) and starch/κ-carrageenan for biomedical applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 189, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harman, D.G.; Gorkin, R.; Stevens, L.; Thompson, B.; Wagner, K.; Weng, B.; Chung, J.H.Y.; In Het Panhuis, M.; Wallace, G.G. Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):dextran sulfate (PEDOT:DS)—A highly processable conductive organic biopolymer. Acta Biomater. 2015, 14, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, Y.; Li, C.M.; Wang, S.; Shi, J.; Ooi, C.P. Incorporation of collagen in poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) for a bifunctional film with high bio- and electrochemical activity. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2010, 92, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vara, H.; Collazos-Castro, J.E. Biofunctionalized Conducting Polymer/Carbon Microfiber Electrodes for Ultrasensitive Neural Recordings. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 27016–27026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polino, G.; Lubrano, C.; Scognamiglio, P.; Mollo, V.; De Martino, S.; Ciccone, G.; Matino, L.; Langella, A.; Netti, P.; Di Carlo, A.; et al. Synthesis and characterization of PEDOT-PEGDA blends for bioelectronic applications: Surface properties and effects on cell morphology. Flex. Print. Electron. 2020, 5, 014012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedi, A.; Hasanzadeh, M.; Tayebi, L. Conductive nanofibrous Chitosan/PEDOT:PSS tissue engineering scaffolds. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Rai, P.; Sharma, J.G.; Sharma, A.; Malhotra, B.D. PEDOT:PSS/PVA-Nanofibers-Decorated Conducting Paper for Cancer Diagnostics. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2016, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strakosas, X.; Sessolo, M.; Hama, A.; Rivnay, J.; Stavrinidou, E.; Malliaras, G.G.; Owens, R.M. A facile biofunctionalisation route for solution processable conducting polymer devices. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 2537–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, R.X.; Zhang, M.; Tan, F.; Leung, P.H.M.; Zhao, X.Z.; Chan, H.L.W.; Yang, M.; Yan, F. Detection of bacteria with organic electrochemical transistors. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 22072–22076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlauto, L.; D’Angelo, A.N.; Vagni, P.; Leccardi, M.J.I.A.; Mor, F.M.; Cuttaz, E.A.; Heuschkel, M.O.; Stoppini, L.; Ghezzi, D. Development and characterization of PEDOT:PSS/alginate soft microelectrodes for application in neuroprosthetics. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collazos-Castro, J.E.; Polo, J.L.; Hernández-Labrado, G.R.; Padial-Cañete, V.; García-Rama, C. Bioelectrochemical control of neural cell development on conducting polymers. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 9244–9255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenoy, G.E.; Maza, E.; Zelaya, E.; Marmisollé, W.A.; Azzaroni, O. Layer-by-layer assemblies of highly connected polyelectrolyte capped-Pt nanoparticles for electrocatalysis of hydrogen evolution reaction. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 416, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decher, G.; Hong, J.D.; Schmitt, J. Buildup of ultrathin multilayer films by a self-assembly process: III. Consecutively alternating adsorption of anionic and cationic polyelectrolytes on charged surfaces. Thin Solid Films 1992, 831–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iler, R.K. Multilayers of colloidal particles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1966, 21, 569–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, J.J.; Cui, J.; Björnmalm, M.; Braunger, J.A.; Ejima, H.; Caruso, F. Innovation in Layer-by-Layer Assembly. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 14828–14867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rydzek, G.; Ji, Q.; Li, M.; Schaaf, P.; Hill, J.P.; Boulmedais, F.; Ariga, K. Electrochemical nanoarchitectonics and layer-by-layer assembly: From basics to future. Nano Today 2015, 10, 138–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pappa, A.M.; Inal, S.; Roy, K.; Zhang, Y.; Pitsalidis, C.; Hama, A.; Pas, J.; Malliaras, G.G.; Owens, R.M. Polyelectrolyte Layer-by-Layer Assembly on Organic Electrochemical Transistors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 10427–10434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, J.G.; Li, H.; Chow, J.K.; Geissler, S.A.; Mcelroy, A.B.; Nguy, L.; Hernandez, D.S.; Schmidt, C.E. Conducting polymer-based multilayer films for instructive biomaterial coatings Dip coating direction Weakly aligned broblasts on multilayer lms: Glass-conducting polymer-chitosan-gelatin Passage of a DC current through the lm enhances cell alignment DC cu. Futur. Sci. OA 2015, 1, 79. [Google Scholar]
- David, M.; Barsan, M.M.; Brett, C.M.A.; Florescu, M. Improved glucose label-free biosensor with layer-by-layer architecture and conducting polymer poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene). Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 255, 3227–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daikuzono, C.M.; Dantas, C.A.R.; Volpati, D.; Constantino, C.J.L.; Piazzetta, M.H.O.; Gobbi, A.L.; Taylor, D.M.; Oliveira, O.N.; Riul, A. Microfluidic electronic tongue. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 207, 1129–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodagholy, D.; Rivnay, J.; Sessolo, M.; Gurfinkel, M.; Leleux, P.; Jimison, L.H.; Stavrinidou, E.; Herve, T.; Sanaur, S.; Owens, R.M.; et al. High transconductance organic electrochemical transistors. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Si, H.; Zhang, X.; Lin, S. Functional sensing interfaces of PEDOT:PSS organic electrochemical transistors for chemical and biological sensors: A mini review. Sensors 2019, 19, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hempel, F.; Law, J.K.Y.; Nguyen, T.C.; Lanche, R.; Susloparova, A.; Vu, X.T.; Ingebrandt, S. PEDOT:PSS organic electrochemical transistors for electrical cell-substrate impedance sensing down to single cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 180, 113101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivnay, J.; Leleux, P.; Ferro, M.; Sessolo, M.; Williamson, A.; Koutsouras, D.A.; Khodagholy, D.; Ramuz, M.; Strakosas, X.; Owens, R.M.; et al. High-performance transistors for bioelectronics through tuning of channel thickness. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1400251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liang, Y.; Ernst, M.; Brings, F.; Kireev, D.; Maybeck, V.; Offenhäusser, A.; Mayer, D. High Performance Flexible Organic Electrochemical Transistors for Monitoring Cardiac Action Potential. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, 1800304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inal, S.; Malliaras, G.G.; Rivnay, J. Benchmarking organic mixed conductors for transistors. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cea, C.; Spyropoulos, G.D.; Jastrzebska-Perfect, P.; Ferrero, J.J.; Gelinas, J.N.; Khodagholy, D. Enhancement-mode ion-based transistor as a comprehensive interface and real-time processing unit for in vivo electrophysiology. Nat. Mater. 2020, 19, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, W.; Goda, T.; Takeuchi, H.; Yamaoka, S.; Horiguchi, Y.; Matsumoto, A.; Miyahara, Y. Human influenza virus detection using sialyllactose-functionalized organic electrochemical transistors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 260, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, M.H.; Low, C.T.J.; Brandon, N.P.; Yufit, V.; Hashim, M.A.; Irfan, M.F.; Akhtar, J.; Ruiz-Trejo, E.; Hussain, M.A. Progress in the electrochemical modification of graphene-based materials and their applications. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 107, 425–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buth, F.; Donner, A.; Sachsenhauser, M.; Stutzmann, M.; Garrido, J.A. Biofunctional electrolyte-gated organic field-effect transistors. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 4511–4517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wustoni, S.; Hidalgo, T.C.; Hama, A.; Ohayon, D.; Savva, A.; Wei, N.; Wehbe, N.; Inal, S. In Situ Electrochemical Synthesis of a Conducting Polymer Composite for Multimetabolite Sensing. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2020, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carli, S.; Di Lauro, M.; Bianchi, M.; Murgia, M.; De Salvo, A.; Prato, M.; Fadiga, L.; Biscarini, F. Water-Based PEDOT:Nafion Dispersion for Organic Bioelectronics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 29807–29817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronkainen, N.J.; Halsall, H.B.; Heineman, W.R. Electrochemical biosensors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iost, R.M.; Crespilho, F.N. Layer-by-layer self-assembly and electrochemistry: Applications in biosensing and bioelectronics. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 31, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhand, C.; Das, M.; Datta, M.; Malhotra, B.D. Recent advances in polyaniline based biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 2811–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfart, F.; Hryniewicz, B.M.; Góes, M.S.; Corrêa, C.M.; Torresi, R.; Minadeo, M.A.O.S.; Córdoba de Torresi, S.I.; Oliveira, R.D.; Marchesi, L.F.; Vidotti, M. Conducting polymers revisited: Applications in energy, electrochromism and molecular recognition. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2017, 21, 2489–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scouten, W.H.; Luong, J.H.T.; Stephen Brown, R. Enzyme or protein immobilization techniques for applications in biosensor design. Trends Biotechnol. 1995, 13, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Turner, A.P.F.; Mak, W.C. Tunable 3D nanofibrous and bio-functionalised PEDOT network explored as a conducting polymer-based biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 159, 112181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayathilaka, W.A.D.M.; Qi, K.; Qin, Y.; Chinnappan, A.; Serrano-García, W.; Baskar, C.; Wang, H.; He, J.; Cui, S.; Thomas, S.W.; et al. Significance of Nanomaterials in Wearables: A Review on Wearable Actuators and Sensors. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Gao, W. Wearable and flexible electronics for continuous molecular monitoring. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 1465–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scotto, J.; Piccinini, E.; von Bilderling, C.; Coria-Oriundo, L.L.; Battaglini, F.; Knoll, W.; Marmisolle, W.A.; Azzaroni, O. Flexible conducting platforms based on PEDOT and graphite nanosheets for electrochemical biosensing applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 525, 146440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, J.; Chung, S.; Pei, M.; Cho, K.; Yang, H.; Hong, Y. One-Step Interface Engineering for All-Inkjet-Printed, All-Organic Components in Transparent, Flexible Transistors and Inverters: Polymer Binding. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 8819–8829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Nyein, H.Y.Y.; Gao, W.; Javey, A. Flexible Electrochemical Bioelectronics: The Rise of In Situ Bioanalysis. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Yadavalli, V.K. Flexible Biosensors for the Impedimetric Detection of Protein Targets Using Silk-Conductive Polymer Biocomposites. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 1040–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, R.K.; Farghaly, A.A.; Wang, C.; Collinson, M.M.; Kundu, S.C.; Yadavalli, V.K. Conducting polymer-silk biocomposites for flexible and biodegradable electrochemical sensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 81, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Agua, I.; Mantione, D.; Ismailov, U.; Sanchez-Sanchez, A.; Aramburu, N.; Malliaras, G.G.; Mecerreyes, D.; Ismailova, E. DVS-Crosslinked PEDOT:PSS Free-Standing and Textile Electrodes toward Wearable Health Monitoring. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2018, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covey, E.; Carter, M. Basic Electrophysiological Methods; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2015; ISBN 9780199939862. [Google Scholar]
- Walz, W. Electrophysiological Recording Techniques; Neuromethods; Vertes, R.P., Stackman, R.W., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2011; Volume 54, ISBN 978-1-60327-201-8. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; Offenhäusser, A.; Ingebrandt, S.; Mayer, D. PEDOT:PSS-Based Bioelectronic Devices for Recording and Modulation of Electrophysiological and Biochemical Cell Signals. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijk, G.; Rutz, A.L.; Malliaras, G.G. Stability of PEDOT:PSS-Coated Gold Electrodes in Cell Culture Conditions. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, P.D.; Moskalyuk, A.; Barthold, C.; Gutöhrlein, K.; Heusel, G.; Schröppel, B.; Samba, R.; Giugliano, M. Low-Impedance 3D PEDOT:PSS Ultramicroelectrodes. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taccola, S.; Poliziani, A.; Santonocito, D.; Mondini, A.; Denk, C.; Ide, A.N.; Oberparleiter, M.; Greco, F.; Mattoli, V. Toward the use of temporary tattoo electrodes for impedancemetric respiration monitoring and other electrophysiological recordings on skin. Sensors 2021, 21, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, L.M.; Sudha, S.; Tarantino, S.; Esposti, R.; Bolzoni, F.; Cavallari, P.; Cipriani, C.; Mattoli, V.; Greco, F. Ultraconformable Temporary Tattoo Electrodes for Electrophysiology. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Velasco-Bosom, S.; Karam, N.; Carnicer-Lombarte, A.; Gurke, J.; Casado, N.; Tomé, L.C.; Mecerreyes, D.; Malliaras, G.G. Conducting Polymer-Ionic Liquid Electrode Arrays for High-Density Surface Electromyography. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 2100374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carli, S.; Bianchi, M.; Zucchini, E.; Di Lauro, M.; Prato, M.; Murgia, M.; Fadiga, L.; Biscarini, F. Electrodeposited PEDOT:Nafion Composite for Neural Recording and Stimulation. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vreeland, R.F.; Atcherley, C.W.; Russell, W.S.; Xie, J.Y.; Lu, D.; Laude, N.D.; Porreca, F.; Heien, M.L. Biocompatible PEDOT:Nafion composite electrode coatings for selective detection of neurotransmitters in vivo. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 2600–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paulsen, B.D.; Tybrandt, K.; Stavrinidou, E.; Rivnay, J. Organic mixed ionic–electronic conductors. Nat. Mater. 2020, 19, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahlman, M.; Fabiano, S.; Gueskine, V.; Simon, D.; Berggren, M.; Crispin, X. Interfaces in organic electronics. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2019, 4, 627–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzocchi, M.; Gualandi, I.; Calienni, M.; Zironi, I.; Scavetta, E.; Castellani, G.; Fraboni, B. Physical and Electrochemical Properties of PEDOT:PSS as a Tool for Controlling Cell Growth. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 17993–18003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, J.G.; Lee, J.Y.; Schmidt, C.E. Biomimetic conducting polymer-based tissue scaffolds. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2013, 24, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Svennersten, K.; Bolin, M.H.; Jager, E.W.H.; Berggren, M.; Richter-Dahlfors, A. Electrochemical modulation of epithelia formation using conducting polymers. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 6257–6264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maione, S.; Gil, A.M.; Fabregat, G.; Del Valle, L.J.; Triguero, J.; Laurent, A.; Jacquemin, D.; Estrany, F.; Jiménez, A.I.; Zanuy, D.; et al. Electroactive polymer-peptide conjugates for adhesive biointerfaces. Biomater. Sci. 2015, 3, 1395–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sekine, J.; Luo, S.C.; Wang, S.; Zhu, B.; Tseng, H.R.; Yu, H.H. Functionalized conducting polymer nanodots for enhanced cell capturing: The synergistic effect of capture agents and nanostructures. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 4788–4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Someya, T.; Bao, Z.; Malliaras, G.G. The rise of plastic bioelectronics. Nature 2016, 540, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Yang, X.; Deng, L.; Ying, D.; Lu, A.; Zhang, L.; Yu, A.; Duan, B. Biocompatible Chitin Hydrogel Incorporated with PEDOT Nanoparticles for Peripheral Nerve Repair. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yang, X.; Thomas, A.K.; Patsis, P.A.; Kurth, T.; Kräter, M.; Eckert, K.; Bornhäuser, M.; Zhang, Y. Noncovalently Assembled Electroconductive Hydrogel. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 14418–14425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spencer, A.R.; Primbetova, A.; Koppes, A.N.; Koppes, R.A.; Fenniri, H.; Annabi, N. Electroconductive Gelatin Methacryloyl-PEDOT:PSS Composite Hydrogels: Design, Synthesis, and Properties. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 4, 1558–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]














| Approach | Advantages | Issues |
|---|---|---|
| Solution–cast polymerization | Simple procedure Production of large-area films Low cost | Thickness may be difficult to control Adhesion of the film can be a problem |
| Electropolymerization | Excellent connection between the substrate and the film Easy control of morphology and thickness Simple copolymerization | Conductive substrates are required Potentiostat needed Usually performed in organic solvents |
| VPP and CVD | Endows the modification of all-kind of substrates Production of very high-quality films | More complex equipment required Difficult to control the process conditions |
| PEDOT:PSS dispersion | Commercially available Water dispersible Wide variety of substrates can be modified Different deposition techniques Easy to scale-up | Low conductivity PSS hampers functionalization Further treatment steps to improve properties |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fenoy, G.E.; Azzaroni, O.; Knoll, W.; Marmisollé, W.A. Functionalization Strategies of PEDOT and PEDOT:PSS Films for Organic Bioelectronics Applications. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9080212
Fenoy GE, Azzaroni O, Knoll W, Marmisollé WA. Functionalization Strategies of PEDOT and PEDOT:PSS Films for Organic Bioelectronics Applications. Chemosensors. 2021; 9(8):212. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9080212
Chicago/Turabian StyleFenoy, Gonzalo E., Omar Azzaroni, Wolfgang Knoll, and Waldemar A. Marmisollé. 2021. "Functionalization Strategies of PEDOT and PEDOT:PSS Films for Organic Bioelectronics Applications" Chemosensors 9, no. 8: 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9080212
APA StyleFenoy, G. E., Azzaroni, O., Knoll, W., & Marmisollé, W. A. (2021). Functionalization Strategies of PEDOT and PEDOT:PSS Films for Organic Bioelectronics Applications. Chemosensors, 9(8), 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9080212