Silver Nanoparticles Grown on Cross-Linked Poly (Methacrylic Acid) Microspheres: Synthesis, Characterization, and Antifungal Activity Evaluation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Characterization Methods
2.2. Synthesis of P(MAA-co-MBA) Microspheres
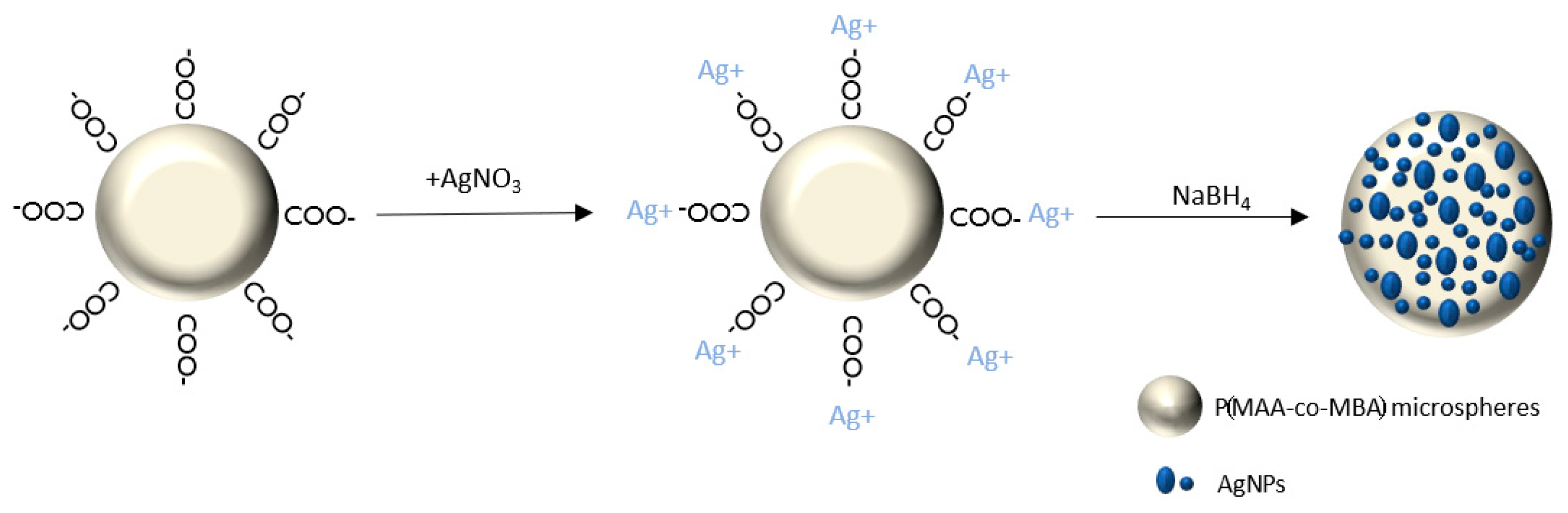
2.3. Silver Nanoparticles’ Growth on P(MAA-co-MBA) Microspheres (PMAA@Ag)
2.4. Evaluation of Antifungal Activity Using the Dilution Method
3. Results and Discussion
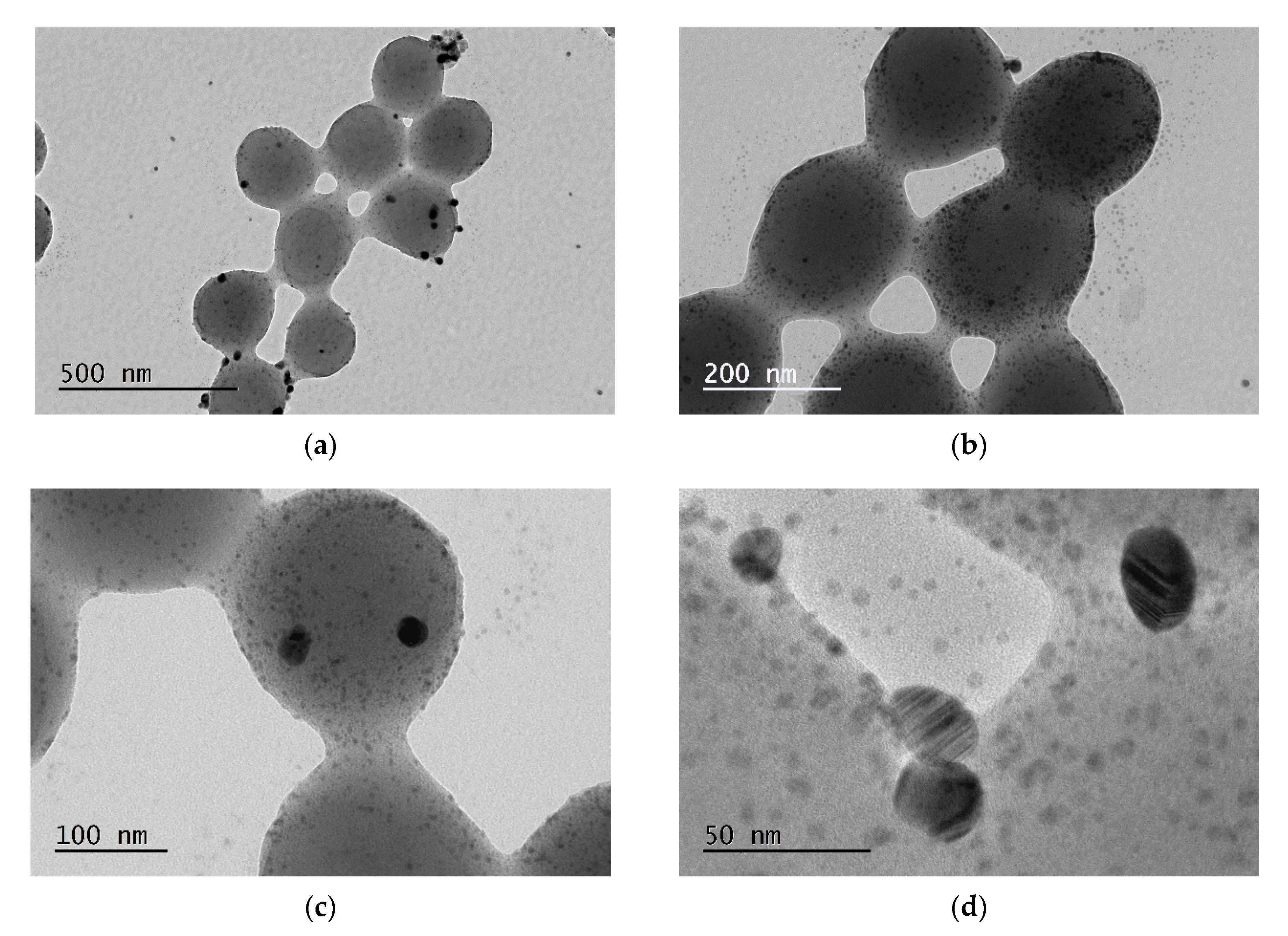
3.1. Synthesis of PMAA-co-MBA Microspheres
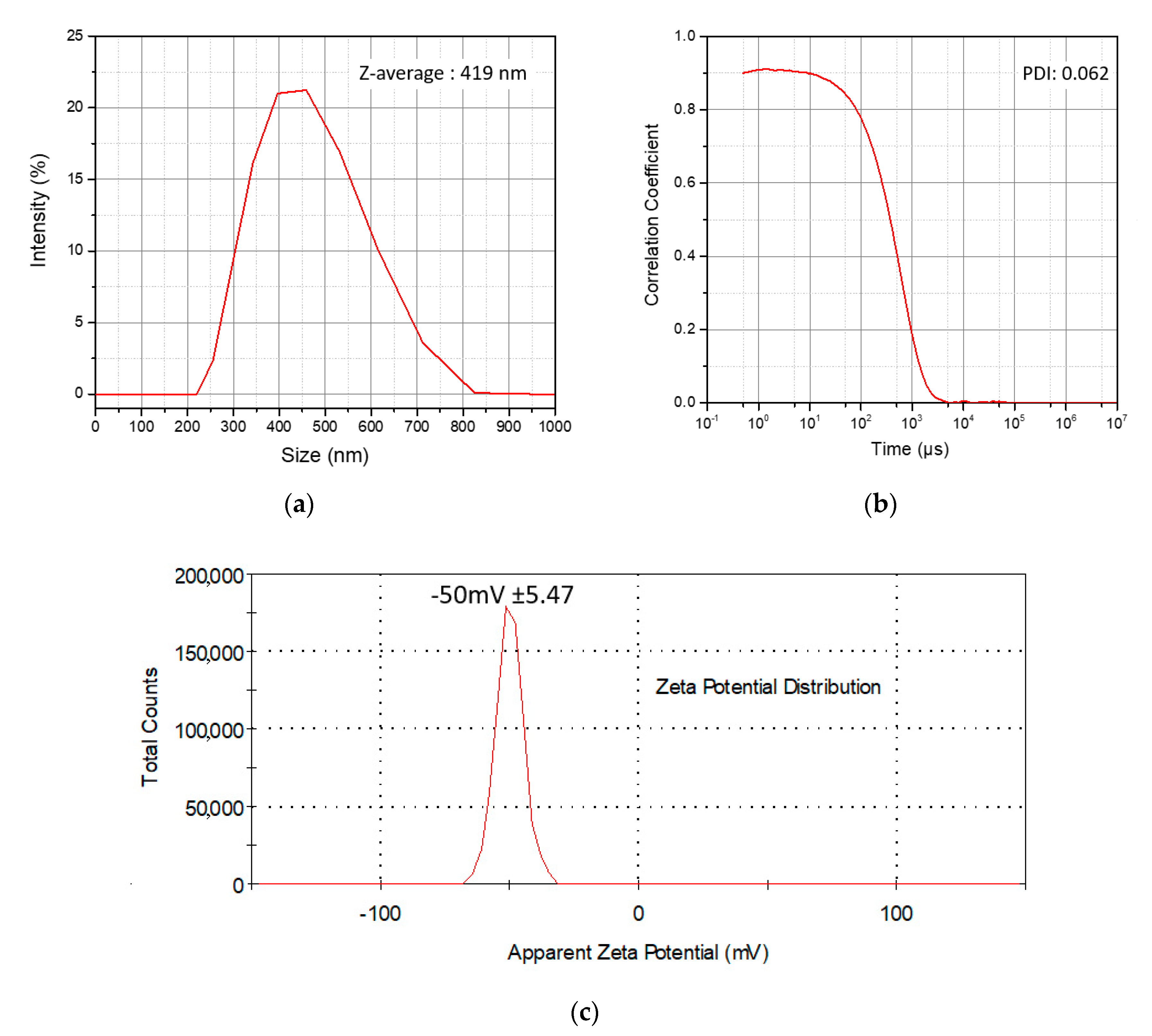
3.2. Size Distribution and Surface Charge of the P(MAA-co-MBA) Microspheres
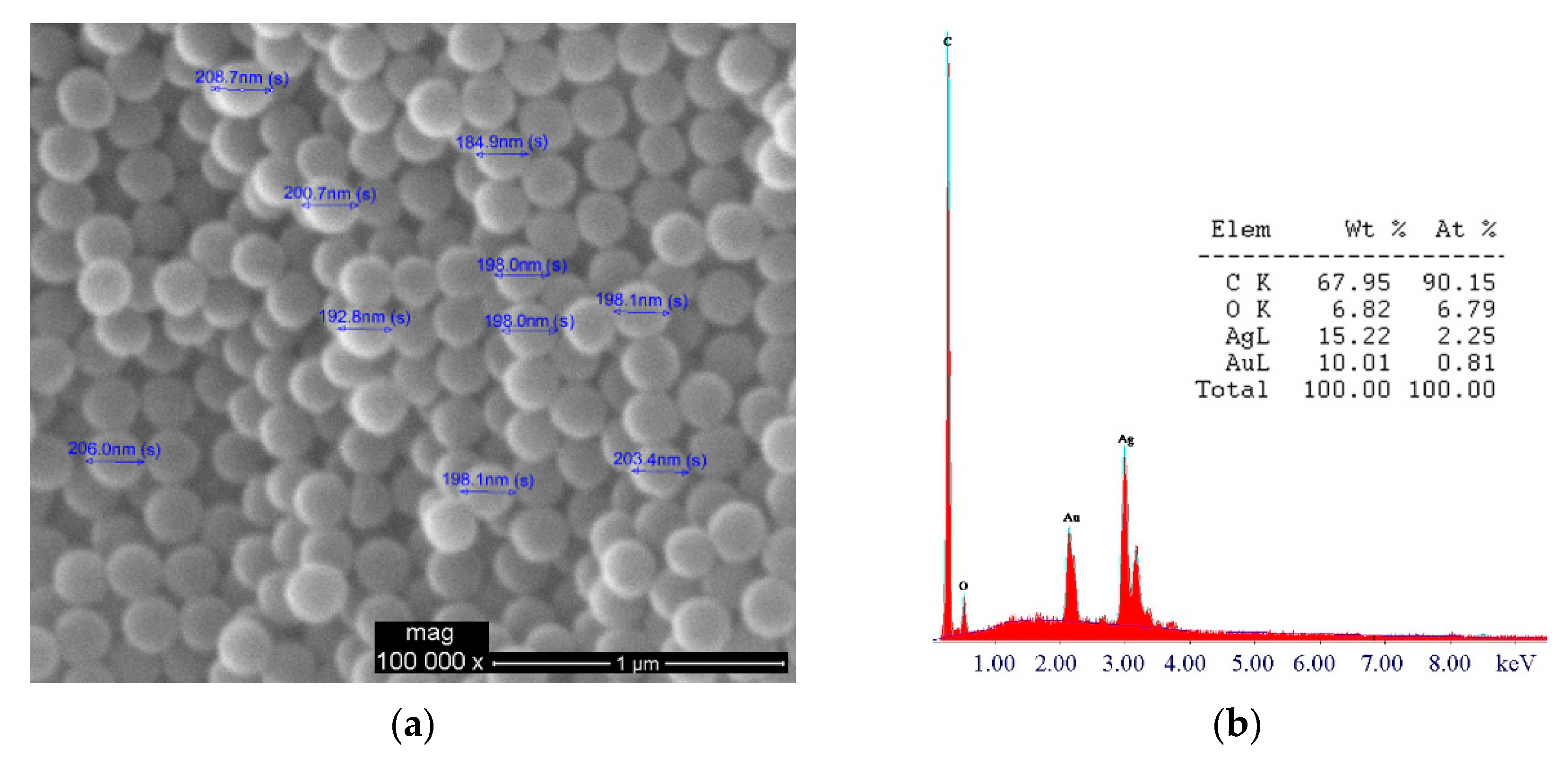
3.3. Growth of AgNPs
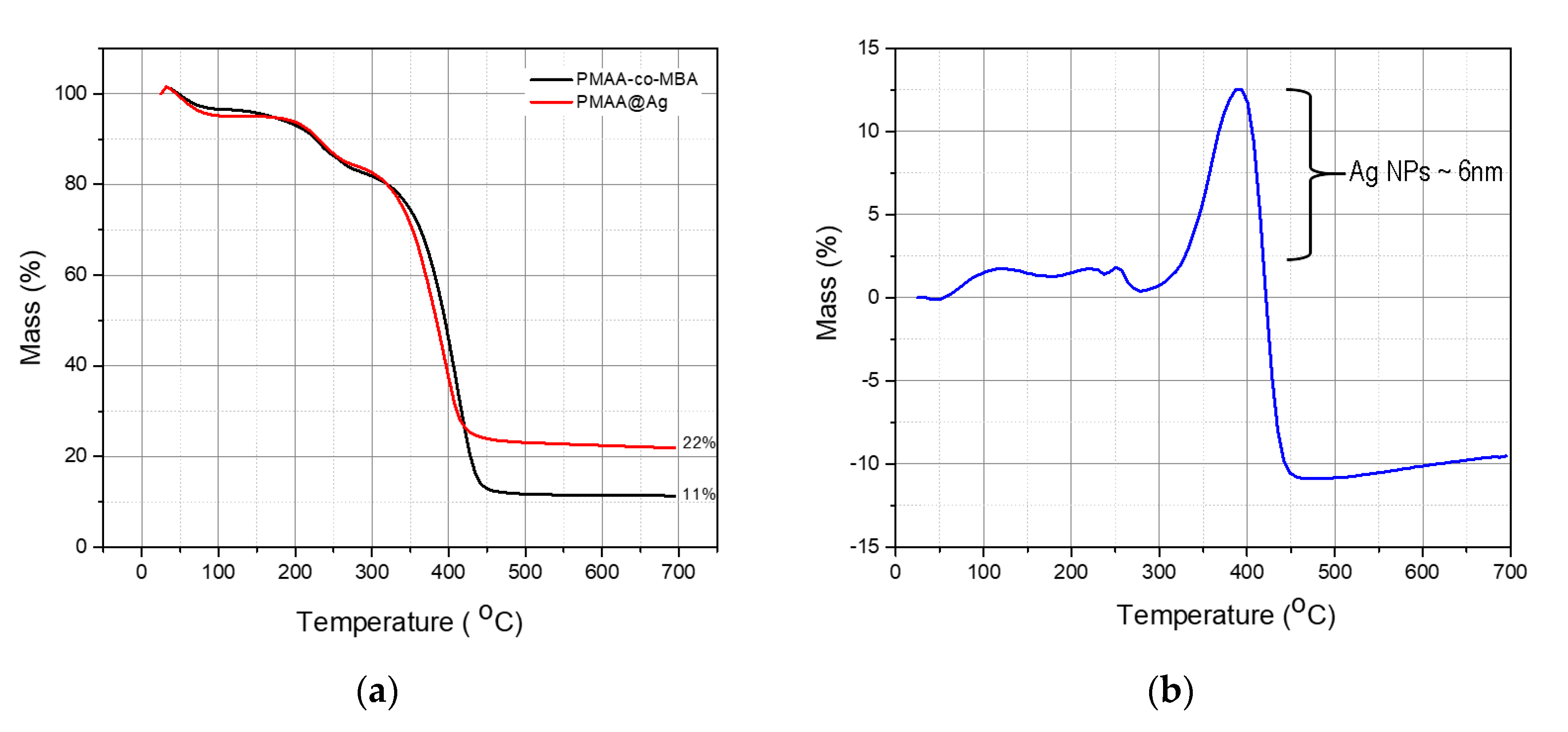
3.4. Quantification of AgNPs
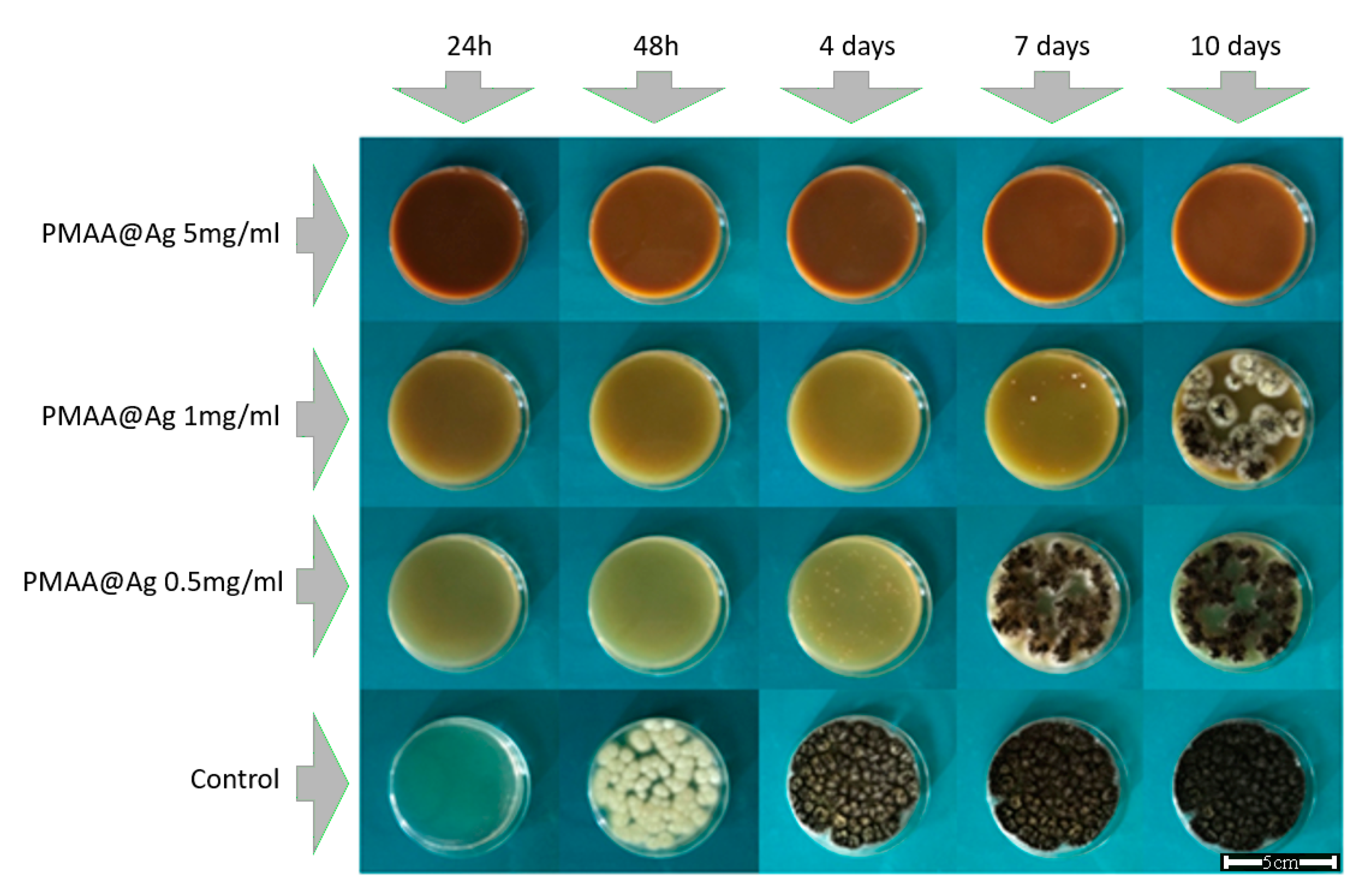
3.5. Antifungal Activity Assessment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Braga, L.R.; Rangel, E.T.; Suarez, P.A.Z.; Machado, F. Simple synthesis of active films based on PVC incorporated with silver nanoparticles: Evaluation of the thermal, structural and antimicrobial properties. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2018, 15, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Basumatary, I.B.; Sudhani, H.P.K.; Bajpai, V.K.; Chen, L.; Shukla, S.; Mukherjee, A. Plant extract mediated silver nanoparticles and their applications as antimicrobials and in sustainable food packaging: A state-of-the-art review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 112, 651–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, K.; Ai, C.; Yan, L.; Jiang, C.; Shi, J. Improvement of antifungal and antibacterial activities of food packages using silver nanoparticles synthesized by iturin A. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2021, 28, 100669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.; Rosado, T.; Gonzalez-Pérez, M.; Gobbo, D.; Teixeira, D.; Candeias, A.; Caldeira, A.T. Production of Antagonistic Compounds by Bacillus sp. with Antifungal Activity against Heritage Contaminating Fungi. Coatings 2018, 8, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goffredo, G.B.; Citterio, B.; Biavasco, F.; Stazi, F.; Barcelli, S.; Munafò, P. Nanotechnology on wood: The effect of photocatalytic nanocoatings against Aspergillus niger. J. Cult. Herit. 2017, 27, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, I.F.; Guillén, E.G.; Jesús, M.; Silva, F.; Mitchell, S.G. Preventing fungal growth on heritage paper with antifungal and cellulase inhibiting magnesium oxide nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 6412–6419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treseder, K.K.; Lennon, J.T. Fungal Traits That Drive Ecosystem Dynamics on Land. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2015, 79, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McNamara, C.J.; Mitchell, R. Microbial deterioration of historic stone. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2005, 3, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, H.C. Alternative and conventional anti-fouling strategies. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2005, 56, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabir Mahr, M.; Hübert, T.; Stephan, I.; Militz, H. Decay protection of wood against brown-rot fungi by titanium alkoxide impregnations. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2013, 77, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, A. Decontamination and “deconsolidation” of historical wood preservatives and wood consolidants in cultural heritage. J. Cult. Herit. 2012, 13, S196–S202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Khisroon, M.; Khan, A.; Gulfam, N.; Siraj, M.; Zaidi, F.; Ahmadullah; Abidullah; Fatima, S.H.; Noreen, S.; et al. Bioaccumulation of Heavy Metals in Water, Sediments, and Tissues and Their Histopathological Effects on Anodonta cygnea (Linea, 1876) in Kabul River, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. BioMed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 1910274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pryshchepa, O.; Pomastowski, P.; Buszewski, B. Silver nanoparticles: Synthesis, investigation techniques, and properties. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 284, 102246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takamiya, A.S.; Monteiro, D.R.; Gorup, L.F.; Silva, E.A.; de Camargo, E.R.; Gomes-Filho, J.E.; de Oliveira, S.H.P.; Barbosa, D.B. Biocompatible silver nanoparticles incorporated in acrylic resin for dental application inhibit Candida albicans biofilm. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 118, 111341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craciunescu, O.; Seciu, A.-M.; Zarnescu, O. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of a biomimetic scaffold embedding silver nanoparticles for improved treatment of oral lesions. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 123, 112015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Wang, Y.Y.; Huang, J.; Chen, C.Y.; Wang, Z.X.; Xie, H. Silver nanoparticles: Synthesis, medical applications and biosafety. Theranostics 2020, 10, 8996–9031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dibrov, P.; Dzioba, J.; Gosink, K.K.; Häse, C.C. Chemiosmotic Mechanism of Antimicrobial Activity of Ag+ in Vibrio cholerae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, H.-J.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.-H.; Hahn, J.-S.; Gu, M.B.; Yoon, J. Silver-ion-mediated reactive oxygen species generation affecting bactericidal activity. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1027–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, O.; Vig Slenters, T.; Brunetto, P.S.; Villaruz, A.E.; Sturdevant, D.E.; Otto, M.; Landmann, R.; Fromm, K.M. Silver Coordination Polymers for Prevention of Implant Infection: Thiol Interaction, Impact on Respiratory Chain Enzymes, and Hydroxyl Radical Induction. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beer, C.; Foldbjerg, R.; Hayashi, Y.; Sutherland, D.S.; Autrup, H. Toxicity of silver nanoparticles—Nanoparticle or silver ion? Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 208, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Kim, K.S.; Lamsal, K.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, S.B.; Jung, M.; Sim, S.J.; Kim, H.S.; Chang, S.J.; Kim, J.K.; et al. An in vitro study of the antifungal effect of silver nanoparticles on oak wilt pathogen Raffaelea sp. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 19, 760–764. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Radhakrishnan, V.S.; Mudiam, M.K.R.; Kumar, M.; Dwivedi, S.P.; Singh, S.P.; Prasad, T. Silver nanoparticles induced alterations in multiple cellular targets, which are critical for drug susceptibilities and pathogenicity in fungal pathogen (Candida albicans). Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 2647–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ivask, A.; Kurvet, I.; Kasemets, K.; Blinova, I.; Aruoja, V.; Suppi, S.; Vija, H.; Käkinen, A.; Titma, T.; Heinlaan, M.; et al. Size-Dependent Toxicity of Silver Nanoparticles to Bacteria, Yeast, Algae, Crustaceans and Mammalian Cells In Vitro. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kittler, S.; Greulich, C.; Diendorf, J.; Köller, M.; Epple, M. Toxicity of Silver Nanoparticles Increases during Storage Because of Slow Dissolution under Release of Silver Ions. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 4548–4554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorobantu, L.S.; Fallone, C.; Noble, A.J.; Veinot, J.; Ma, G.; Goss, G.G.; Burrell, R.E. Toxicity of silver nanoparticles against bacteria, yeast, and algae. J. Nanopart. Res. 2015, 17, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, M.; Sikder, M.T.; Rahman, M.M.; Ullah, A.K.M.A.; Hossain, K.F.B.; Banik, S.; Hosokawa, T.; Saito, T.; Kurasaki, M. A systematic review on silver nanoparticles-induced cytotoxicity: Physicochemical properties and perspectives. J. Adv. Res. 2018, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.C.; Seligy, V.L.; Massarsky, A.; Moon, T.W.; Rippstein, P.; Tan, J.; Tayabali, A.F. Comparison of toxicity of uncoated and coated silver nanoparticles. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2013, 429, 012025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Ji, Z.; Chang, C.H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, M.; Liao, Y.-P.; Lin, S.; Meng, H.; Li, R.; Sun, B.; et al. Use of Coated Silver Nanoparticles to Understand the Relationship of Particle Dissolution and Bioavailability to Cell and Lung Toxicological Potential. Small 2014, 10, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamouda, H.I.; Abdel-Ghafar, H.M.; Mahmoud, M.H.H. Multi-walled carbon nanotubes decorated with silver nanoparticles for antimicrobial applications. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoc Dung, T.T.; Phan Thi, L.-A.; Nam, V.N.; Nhan, T.T.; Quang, D.V. Preparation of silver nanoparticle-containing ceramic filter by in-situ reduction and application for water disinfection. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Barnes, L.-M.; Maslakov, K.I.; Howell, C.A.; Illsley, M.J.; Dyer, P.; Savina, I.N. In situ synthesis of silver or selenium nanoparticles on cationized cellulose fabrics for antimicrobial application. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 121, 111859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorcroft, S.C.T.; Jayne, D.G.; Evans, S.D.; Ong, Z.Y. Stimuli-Responsive Release of Antimicrobials Using Hybrid Inorganic Nanoparticle-Associated Drug-Delivery Systems. Macromol. Biosci. 2018, 18, e1800207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh, N.T.K.; Maclean, N.; Mahiddine, S. Mechanisms of Nucleation and Growth of Nanoparticles in Solution. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 7610–7630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlberg, B.; Ye, L.-L.; Liu, J. Surface-Confined Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticle Composite Coating on Electrospun Polyimide Nanofibers. Small 2011, 7, 3057–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, S.; Jiang, C.; Guo, J.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, Y. Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Loaded onto Polymer-Inorganic Composite Materials and Their Regulated Catalytic Activity. Polymers 2019, 11, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanisch, M.; Mačković, M.; Taccardi, N.; Spiecker, E.; Klupp Taylor, R.N. Synthesis of silver nanoparticle necklaces without explicit addition of reducing or templating agents. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 4287–4289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levard, C.; Hotze, E.M.; Lowry, G.V.; Brown, G.E., Jr. Environmental transformations of silver nanoparticles: Impact on stability and toxicity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 6900–6914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, K.; Jindal, R.; Saini, D. Synthesis, optimization and characterization of PVA-co-poly(methacrylic acid) green adsorbents and applications in environmental remediation. Polym. Bull. 2020, 77, 3079–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Yang, X.; Wu, Q. Antifungal capability of TiO2 coated film on moist wood. Build. Environ. 2009, 44, 1088–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzipavlidis, A.; Bilalis, P.; Tziveleka, L.A.; Boukos, N.; Charitidis, C.A.; Kordas, G. Nanostructuring the surface of dual responsive hollow polymer microspheres for versatile utilization in nanomedicine-related applications. Langmuir 2013, 29, 9562–9572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kneipp, K.; Moskovits, M.; Kneipp, H. Surface-Enhanced Rama Scattering—Physics and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; ISBN 978-3-540-33567-2. [Google Scholar]
- Du, J.; Jing, C. Preparation of Fe3O4@Ag SERS substrate and its application in environmental Cr(VI) analysis. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 358, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, Q.; Zhang, P.; Li, J.M.; Ma, W.F.; Guo, J.; Hu, J.; Wang, C.C. Silver-coated magnetite-carbon core-shell microspheres as substrate-enhanced SERS probes for detection of trace persistent organic pollutants. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 5210–5216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, F.; Huang, B.; Yang, X.; Huang, W. Synthesis of monodisperse poly(methacrylic acid) microspheres by distillation–precipitation polymerization. Eur. Polym. J. 2007, 43, 3923–3932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilalis, P.; Boukos, N.; Kordas, G.C. Novel PEGylated pH-sensitive polymeric hollow microspheres. Mater. Lett. 2012, 67, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.B.; Rahman, M.M.; Marwani, H.M.; Asiri, A.M.; Alamry, K.A. Exploration of silver oxide nanoparticles as a pointer of lanthanum for environmental applications. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2014, 45, 2770–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, X.; Tang, K. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using soluble soybean polysaccharide and their application in antibacterial coatings. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 166, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, H.; Santhosh, C.; Sinha, R.K. Seed mediated synthesis of highly stable CTAB capped triangular silver nanoplates for LSPR sensing. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 105075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Xu, X.-H.N. Synthesis and characterization of tunable rainbow colored colloidal silver nanoparticles using single-nanoparticle plasmonic microscopy and spectroscopy. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 9867–9876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcia, M.A. Surface plasmons in metallic nanoparticles: Fundamentals and applications. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2011, 44, 283001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-T.; Wang, C.-Y.; Hong, Y.-J.; Kang, Y.-T.; Lai, S.-E.; Chang, P.; Yew, T.-R. Electron beam manipulation of gold nanoparticles external to the beam. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 31652–31656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárdenas, G.; Muñoz, C.; Carbacho, H. Thermal properties and TGA–FTIR studies of polyacrylic and polymethacrylic acid doped with metal clusters. Eur. Polym. J. 2000, 36, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausner, S.; Weis, S.; Wielage, B.; Wagner, G. Low temperature joining of copper by Ag nanopaste: Correlation of mechanical properties and process parameters. Weld. World 2016, 60, 1277–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kunc, F.; Balhara, V.; Sun, Y.; Daroszewska, M.; Jakubek, Z.J.; Hill, M.; Brinkmann, A.; Johnston, L.J. Quantification of surface functional groups on silica nanoparticles: Comparison of thermogravimetric analysis and quantitative NMR. Analyst 2019, 144, 5589–5599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marambio-Jones, C.; Hoek, E.M.V. A review of the antibacterial effects of silver nanomaterials and potential implications for human health and the environment. J. Nanopart. Res. 2010, 12, 1531–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-J.; Sung, W.S.; Suh, B.K.; Moon, S.-K.; Choi, J.-S.; Kim, J.G.; Lee, D.G. Antifungal activity and mode of action of silver nano-particles on Candida albicans. BioMetals 2009, 22, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lara, H.H.; Garza-Treviño, E.N.; Ixtepan-Turrent, L.; Singh, D.K. Silver nanoparticles are broad-spectrum bactericidal and virucidal compounds. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2011, 9, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morones, J.R.; Elechiguerra, J.L.; Camacho, A.; Holt, K.; Kouri, J.B.; Ramírez, J.T.; Yacaman, M.J. The bactericidal effect of silver nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 2346–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ansari, M.A.; Asiri, S.M.M.; Alzohairy, M.A.; Alomary, M.N.; Almatroudi, A.; Khan, F.A. Biofabricated Fatty Acids-Capped Silver Nanoparticles as Potential Antibacterial, Antifungal, Antibiofilm and Anticancer Agents. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatoon, U.T.; Rao, G.V.S.N.; Mohan, M.K.; Ramanaviciene, A.; Ramanavicius, A. Comparative study of antifungal activity of silver and gold nanoparticles synthesized by facile chemical approach. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 5837–5844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

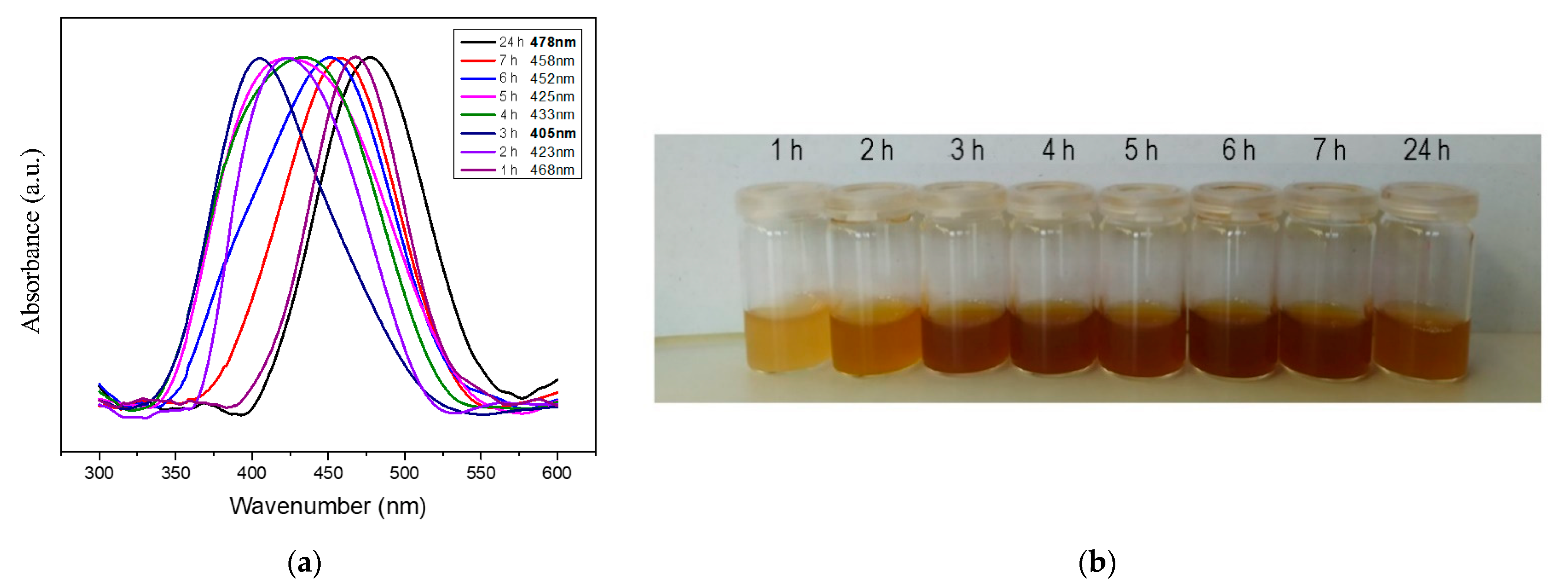
| Time of Stirring in AgNO3 (h) | Absorption Band Maximum (nm) | Band FWHM | Band Area |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 468 | 68.53 | 10.52 |
| 2 | 423 | 84.97 | 13.14 |
| 3 | 405 | 88.98 | 13.53 |
| 4 | 433 | 110.38 | 18.73 |
| 5 | 425 | 116.13 | 19.75 |
| 6 | 452 | 103.90 | 16.24 |
| 7 | 458 | 84.89 | 13.15 |
| 24 | 478 | 78.19 | 12.23 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kainourgios, P.; Tziveleka, L.-A.; Kartsonakis, I.A.; Ioannou, E.; Roussis, V.; Charitidis, C.A. Silver Nanoparticles Grown on Cross-Linked Poly (Methacrylic Acid) Microspheres: Synthesis, Characterization, and Antifungal Activity Evaluation. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9070152
Kainourgios P, Tziveleka L-A, Kartsonakis IA, Ioannou E, Roussis V, Charitidis CA. Silver Nanoparticles Grown on Cross-Linked Poly (Methacrylic Acid) Microspheres: Synthesis, Characterization, and Antifungal Activity Evaluation. Chemosensors. 2021; 9(7):152. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9070152
Chicago/Turabian StyleKainourgios, Panagiotis, Leto-Aikaterini Tziveleka, Ioannis A. Kartsonakis, Efstathia Ioannou, Vassilios Roussis, and Costas A. Charitidis. 2021. "Silver Nanoparticles Grown on Cross-Linked Poly (Methacrylic Acid) Microspheres: Synthesis, Characterization, and Antifungal Activity Evaluation" Chemosensors 9, no. 7: 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9070152
APA StyleKainourgios, P., Tziveleka, L.-A., Kartsonakis, I. A., Ioannou, E., Roussis, V., & Charitidis, C. A. (2021). Silver Nanoparticles Grown on Cross-Linked Poly (Methacrylic Acid) Microspheres: Synthesis, Characterization, and Antifungal Activity Evaluation. Chemosensors, 9(7), 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9070152











