“Out of Pocket” Protein Binding—A Dilemma of Epitope Imprinted Polymers Revealed for Human Hemoglobin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Electrochemical Measurements
2.3. MIP-Electrosynthesis, Template Removal, and Rebinding
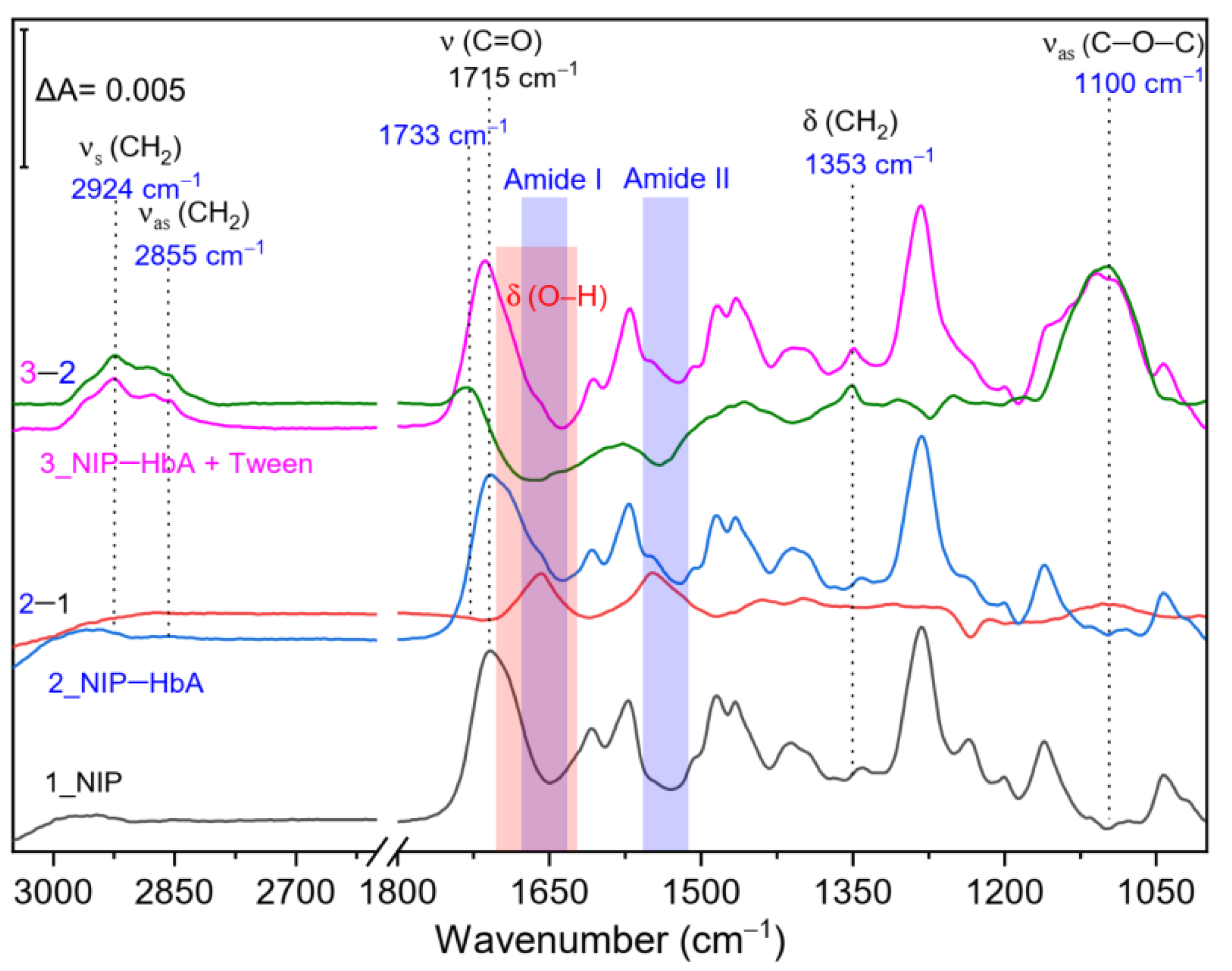
2.4. SEIRA Spectroscopic Measurements
2.5. Atomic Force Microscopy Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
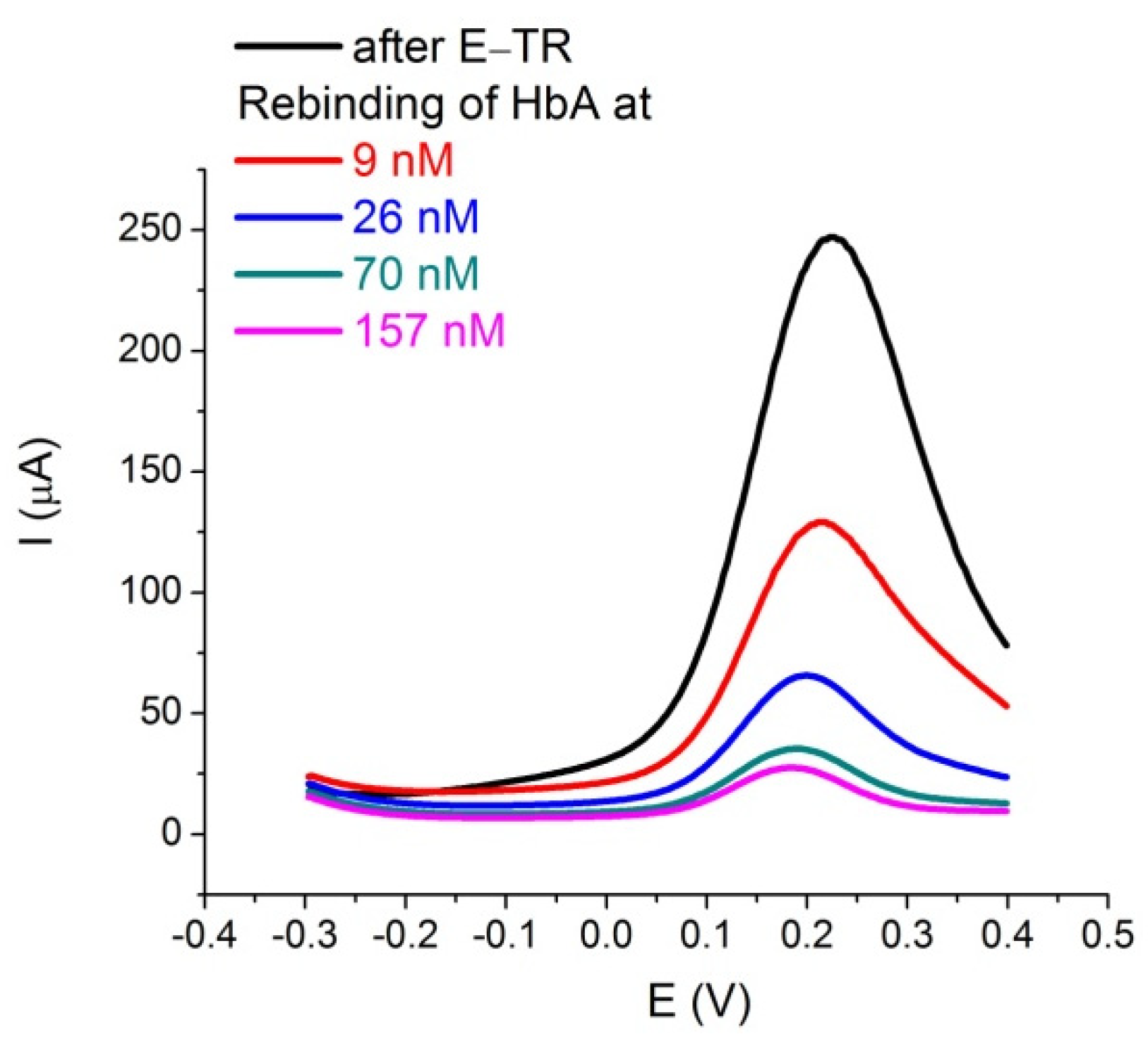
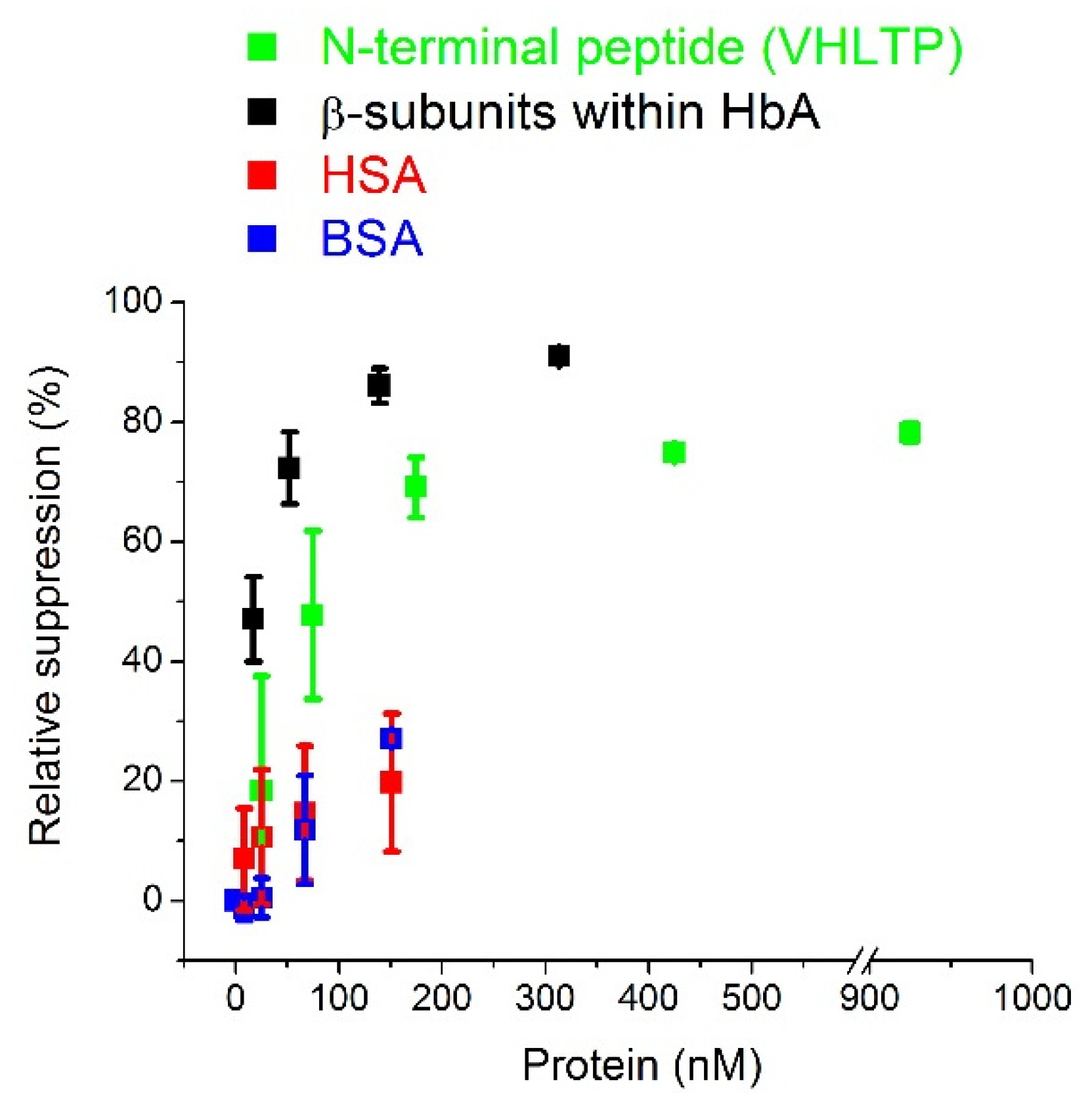
3.1. Electrochemical Characterization of HbA Binding to the MIPs and Cross-Reactivity Studies
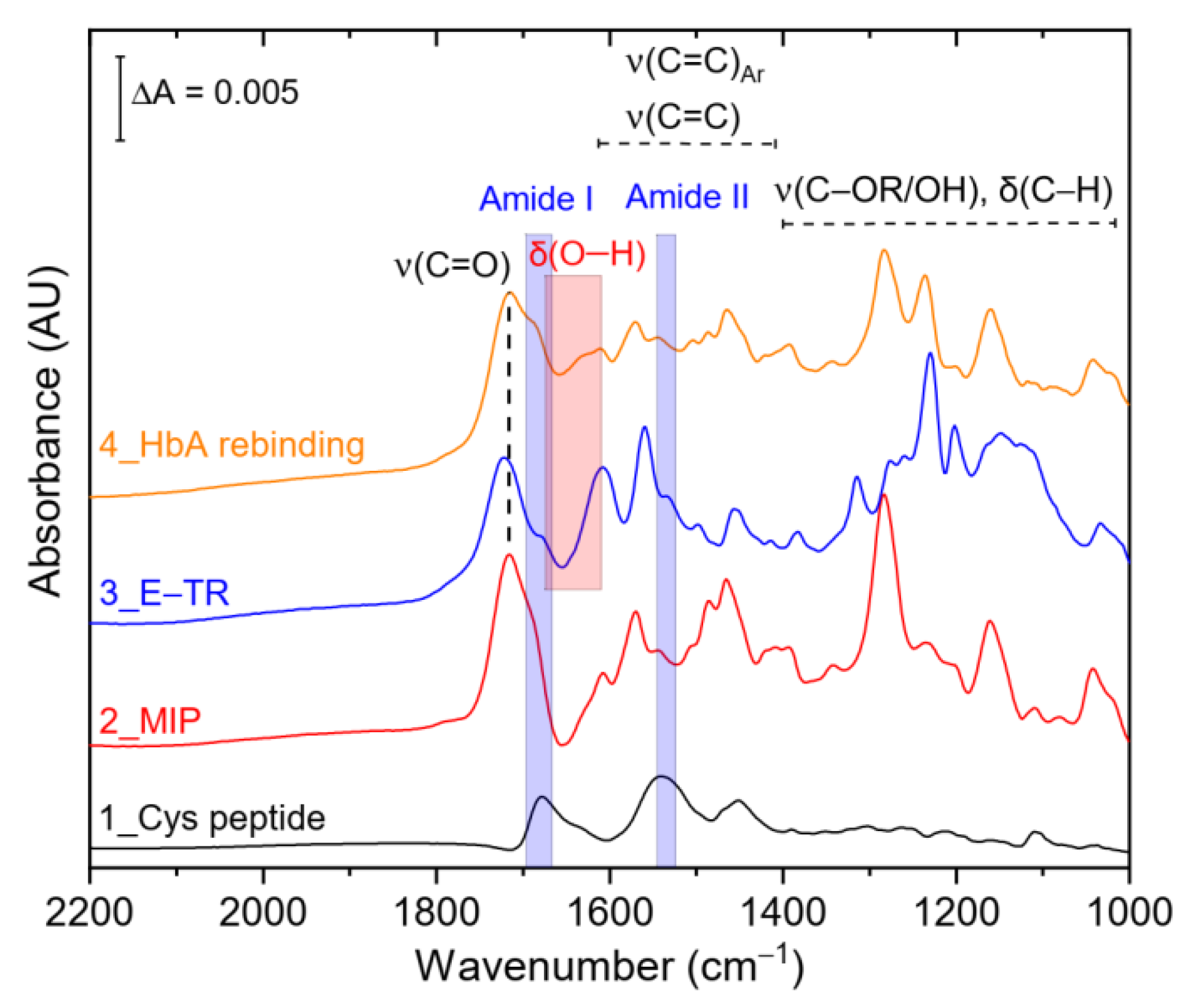
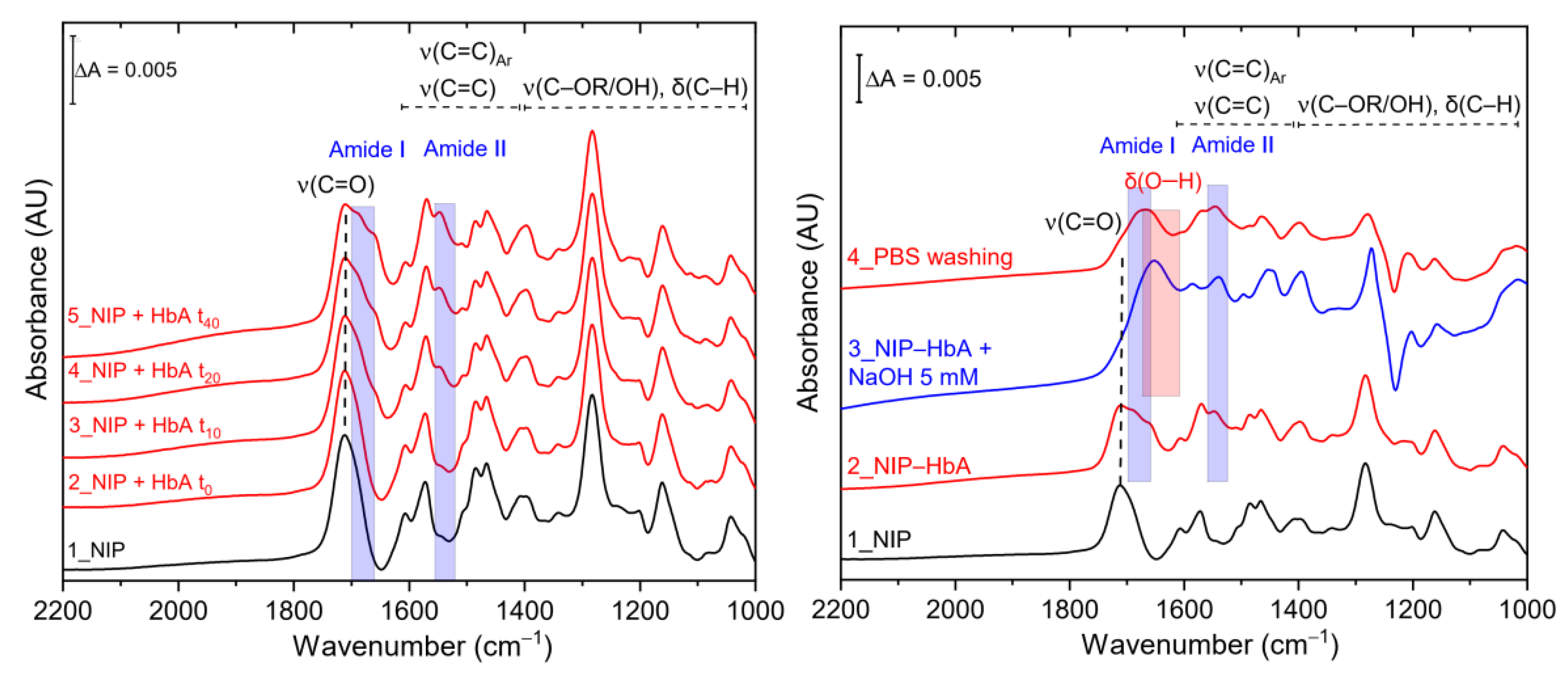
3.2. SEIRA and AFM Characterization of HbA Binding to the NIP and Hierarchical MIP
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thom, C.S.; Dickson, C.F.; Gell, D.; Weiss, M.J. Hemoglobin Variants: Biochemical Properties and Clinical Correlates. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2013, 3, a011858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Tam, M.F.; Simplaceanu, V.; Ho, C. New Look at Hemoglobin Allostery. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 1702–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billett, H.H. Chapter 151. Hemoglobin and Hematocrit, 3rd ed.; Walker, H.K., Hall, W.D., Hurst, J.W., Eds.; Butterworths: Boston, MA, USA, 1990; ISBN 040990077X. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Haemoglobin Concentrations for the Diagnosis of Anaemia and Assessment of Severity; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Janz, T.; Lu, K.; Povlow, M.R.; Urso, B. A Review of Colorectal Cancer Detection Modalities, Stool DNA, and Fecal Immunochemistry Testing in Adults Over the Age of 50. Cureus 2016, 8, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, T.J.; Basu, A. Biomarkers in diabetes: Hemoglobin A1c, vascular and tissue markers. Transl. Res. 2012, 159, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jetzschmann, K.J.; Zhang, X.; Yarman, A.; Wollenberger, U.; Scheller, F.W. Label-Free MIP Sensors for Protein Biomarkers. In Label-Free Biosensing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 291–321. [Google Scholar]
- Raziq, A.; Kidakova, A.; Boroznjak, R.; Reut, J.; Öpik, A.; Syritski, V. Development of a portable MIP-based electrochemical sensor for detection of SARS-CoV-2 antigen. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 178, 113029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Giulio, T.; Mazzotta, E.; Malitesta, C. Molecularly Imprinted Polyscopoletin for the Electrochemical Detection of the Chronic Disease Marker Lysozyme. Biosensors 2020, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-H.; Thomas, J.L.; Su, Z.-L.; Yeh, W.-K.; Monzel, A.S.; Bolognin, S.; Schwamborn, J.C.; Yang, C.-H.; Lin, H.-Y. Epitope imprinting of alpha-synuclein for sensing in Parkinson’s brain organoid culture medium. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 175, 112852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ma, Y.; Wang, L. High selectivity sensing of bovine serum albumin: The combination of glass nanopore and molecularly imprinted technology. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 178, 113056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, L.M. Electropolymerized molecularly imprinted polymers: Perceptions based on recent literature for soon-to-be world-class scientists. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2021, 25, 100640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheubong, C.; Takano, E.; Kitayama, Y.; Sunayama, H.; Minamoto, K.; Takeuchi, R.; Furutani, S.; Takeuchi, T. Molecularly imprinted polymer nanogel-based fluorescence sensing of pork contamination in halal meat extracts. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 172, 112775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalecki, J.; Iskierko, Z.; Cieplak, M.; Sharma, P.S. Oriented Immobilization of Protein Templates: A New Trend in Surface Imprinting. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 3710–3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanavicius, S.; Jagminas, A.; Ramanavicius, A. Advances in Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Based Affinity Sensors (Review). Polymers 2021, 13, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khumsap, T.; Corpuz, A.; Nguyen, L.T. Epitope-imprinted polymers: Applications in protein recognition and separation. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 11403–11414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, O.; Lieberzeit, P.A.; Blaas, D.; Dickert, F.L. Artificial Antibodies for Bioanalyte Detection—Sensing Viruses and Proteins. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2006, 16, 1269–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirhagl, R.; Podlipna, D.; Lieberzeit, P.A.; Dickert, F.L. Comparing biomimetic and biological receptors for insulin sensing. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 3128–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chunta, S.; Suedee, R.; Boonsriwong, W.; Lieberzeit, P.A. Biomimetic sensors targeting oxidized-low-density lipoprotein with molecularly imprinted polymers. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1116, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haupt, K.; Rangel, P.X.M.; Bui, B.T.S. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers: Antibody Mimics for Bioimaging and Therapy. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 9554–9582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, A.G.; Haq, I.; Cowen, T.; Di Masi, S.; Trivedi, S.; Alanazi, K.; Piletska, E.; Mujahid, A.; Piletsky, S.A. Design and fabrication of a smart sensor using in silico epitope mapping and electro-responsive imprinted polymer nanoparticles for determination of insulin levels in human plasma. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 169, 112536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, F.T.; Ferreira, M.J.M.; Puga, J.R.; Sales, M.G.F. Screen-printed electrode produced by printed-circuit board technology. Application to cancer biomarker detection by means of plastic antibody as sensing material. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 223, 927–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ertürk, G.; Uzun, L.; Tümer, M.A.; Say, R.; Denizli, A. Fab fragments imprinted SPR biosensor for real-time human immunoglobulin G detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 28, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fresco-Cala, B.; Mizaikoff, B. Surrogate Imprinting Strategies: Molecular Imprints via Fragments and Dummies. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 2, 3714–3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, S.L.; Fajardo, L.M.; Cunha, L.D.A.; Sotomayor, M.D.P.T.; Machado, F.B.C.; Ferrão, L.F.A.; Pividori, M.I. Theoretical and experimental study for the biomimetic recognition of levothyroxine hormone on magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 107, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.S.; Iskierko, Z.; Noworyta, K.; Cieplak, M.; Borowicz, P.; Lisowski, W.; D’Souza, F.; Kutner, W. Synthesis and application of a “plastic antibody” in electrochemical microfluidic platform for oxytocin determination. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 100, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Zhang, K.; Kamra, T.; Bülow, L.; Ye, L. Preparation of protein imprinted polymer beads by Pickering emulsion polymerization. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 3, 1254–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagán, H.; Zhou, T.; Eriksson, N.L.; Bülow, L.; Ye, L. Synthesis and characterization of epitope-imprinted polymers for purification of human hemoglobin. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 41705–41712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhou, T.; Kettisen, K.; Ye, L.; Bülow, L. Chromatographic separation of hemoglobin variants using robust molecularly imprinted polymers. Talanta 2019, 199, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachkov, A.; Minoura, N. Towards molecularly imprinted polymers selective to peptides and proteins. The epitope approach. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Protein Struct. Mol. Enzym. 2001, 1544, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachkov, A.; Minoura, N. Recognition of oxytocin and oxytocin-related peptides in aqueous media using a molecularly imprinted polymer synthesized by the epitope approach. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 889, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimatsu, K.; Yamazaki, T.; Hoshino, Y.; Rose, P.E.; Epstein, L.F.; Miranda, L.P.; Tagari, P.; Beierle, J.M.; Yonamine, Y.; Shea, K.J. Epitope Discovery for a Synthetic Polymer Nanoparticle: A New Strategy for Developing a Peptide Tag. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 1194–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechtrirat, D.; Jetzschmann, K.J.; Stöcklein, W.F.M.; Scheller, F.W.; Gajovic-Eichelmann, N. Protein Rebinding to a Surface-Confined Imprint. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 5231–5237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Li, S.; Liu, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, W.; Pei, J.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y. Epitope Imprinting Technology: Progress, Applications, and Perspectives toward Artificial Antibodies. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, e1902048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishino, H.; Huang, C.-S.; Shea, K.J. Selective Protein Capture by Epitope Imprinting. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 2392–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Gupta, N.; Raghuwanshi, R. Epitope Imprinting Approach to Monitor Diseases. J. Mol. Genet. Med. 2017, 11, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Iskierko, Z.; Sharma, P.S.; Noworyta, K.R.; Borowicz, P.; Cieplak, M.; Kutner, W.; Bossi, A.M. Selective PQQPFPQQ Gluten Epitope Chemical Sensor with a Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Recognition Unit and an Extended-Gate Field-Effect Transistor Transduction Unit. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 4537–4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.-Q.; Guo, T.-Y.; Song, M.-D.; Zhang, B.-H.; Zhang, B.-L. Hemoglobin Recognition by Imprinting in Semi-Interpenetrating Polymer Network Hydrogel Based on Polyacrylamide and Chitosan. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 2601–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, Q.; Liu, Q.; Li, W.; He, X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y. Preparation of bovine hemoglobin-imprinted polymer beads via the photografting surface-modified method. Front. Chem. China 2008, 3, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, X.; Zhao, Q.; Shao, D.; Geng, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, J.-J. Preparation and Recognition Properties of Bovine Hemoglobin Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 3999–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.-Y.; He, X.-W.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-K. Novel Hybrid Structure Silica/CdTe/Molecularly Imprinted Polymer: Synthesis, Specific Recognition, and Quantitative Fluorescence Detection of Bovine Hemoglobin. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 12609–12616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Ashley, J.; Feng, X.; Sun, Y. Detection of hemoglobin using hybrid molecularly imprinted polymers/carbon quantum dots-based nanobiosensor prepared from surfactant-free Pickering emulsion. Talanta 2018, 190, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Tan, W.; Xu, H. Protein molecularly imprinted polyacrylamide membrane: For hemoglobin sensing. Analyst 2010, 135, 2523–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, X.; Xing, Z.; Zhu, A.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, G.; Li, C.; Zhou, H. Molecularly imprinted polymers based electrochemical sensor for bovine hemoglobin recognition. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 168, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yang, L.; Xing, Z.; Lu, X.; Kan, X. Surface molecularly imprinted polymers-based electrochemical sensor for bovine hemoglobin recognition. Analyst 2013, 138, 6962–6968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, F.; Xia, J.; Xia, L.; Zhang, F.; Bi, S.; Shi, G.; Xia, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; et al. An ionic liquid-modified graphene based molecular imprinting electrochemical sensor for sensitive detection of bovine hemoglobin. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 61, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Hong, M.; Bin, Q.; Lin, Z.; Lin, Z.; Cai, Z.; Chen, G. Highly sensitive protein molecularly imprinted electro-chemical sensor based on gold microdendrites electrode and prussian blue mediatedamplification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 42, 612–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, S.M.; Sette, G.; Phan, Q. Electrochemical probing of selective haemoglobin binding in hydrogel-based molecularly imprinted polymers. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 9203–9208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossi, A.; Piletsky, S.A.; Piletska, E.V.; Righetti, P.G.; Turner, A.P.F. Surface-Grafted Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Protein Recognition. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 5281–5286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caserta, G.; Zhang, X.; Yarman, A.; Supala, E.; Wollenberger, U.; Gyurcsányi, R.E.; Zebger, I.; Scheller, F.W. Insights in electrosynthesis, target binding, and stability of peptide-imprinted polymer nanofilms. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 381, 138236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osawa, M. Surface-Enhanced Infrared Absorption. In Near-Field Optics and Surface Plasmon Polaritons; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; pp. 163–187. [Google Scholar]
- Miyake, H.; Ye, S.; Osawa, M. Electroless deposition of gold thin films on silicon for surface-enhanced infrared spectroelectrochemistry. Electrochem. Commun. 2002, 4, 973–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waffo, A.; Yesildag, C.; Caserta, G.; Katz, S.; Zebger, I.; Lensen, M.; Wollenberger, U.; Scheller, F.; Altintas, Z. Fully electrochemical MIP sensor for artemisinin. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 275, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yarman, A.; Erdossy, J.; Katz, S.; Zebger, I.; Jetzschmann, K.J.; Altintas, Z.; Wollenberger, U.; Gyurcsányi, R.E.; Scheller, F.W. Electrosynthesized MIPs for transferrin: Plastibodies or nano-filters? Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 105, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altintas, Z.; Takiden, A.; Utesch, T.; Mroginski, M.A.; Schmid, B.; Scheller, F.W.; Süssmuth, R.D. Integrated Approaches Toward High-Affinity Artificial Protein Binders Obtained via Computationally Simulated Epitopes for Protein Recognition. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1807332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warring, S.L.; Krasowska, M.; Beattie, D.A.; McQuillan, A.J. Adsorption of a Polyethoxylated Surfactant from Aqueous Solution to Silica Nanoparticle Films Studied with in Situ Attenuated Total Reflection Infrared Spectroscopy and Colloid Probe Atomic Force Microscopy. Langmuir 2018, 34, 13481–13490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Ma, X.; Li, J. An Insulin Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensor Based on Epitope Imprinting. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2017, 45, 1360–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.-Y.; Zhang, X.-M.; Yan, Y.-J.; He, X.-W.; Li, W.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-K. Thermo-sensitive imprinted polymer embedded carbon dots using epitope approach. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 79, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Liu, J.; Li, S.; Li, Q.; Wu, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Deng, N.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, L.; et al. Epitope imprinted polyethersulfone beads by self-assembly for target protein capture from the plasma proteome. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 9521–9524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Li, S.; Liu, J.; Liu, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y. Multiepitope Templates Imprinted Particles for the Simultaneous Capture of Various Target Proteins. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 5621–5625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.-P.; Jia, C.; He, X.-W.; Li, W.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-K. Thermosensitive Metal Chelation Dual-Template Epitope Imprinting Polymer Using Distillation–Precipitation Polymerization for Simultaneous Recognition of Human Serum Albumin and Transferrin. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 9060–9068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moczko, E.; Guerreiro, A.; Cáceres, C.; Piletska, E.; Sellergren, B.; Piletsky, S.A. Epitope approach in molecular imprinting of antibodies. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2019, 1124, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.T.; He, X.W.; Li, W.Y.; Zhang, Y.K. Oriented surface epitope imprinted polymer-based quartz crystal microbalance sensor for cytochrome c. Talanta 2019, 191, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, R.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wen, Y.; Liu, Z. Specific recognition of proteins and peptides via controllable oriented surface imprinting of boronate affinity-anchored epitopes. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 1831–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Yang, K.; Liu, J.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y. Surface-Imprinted Nanoparticles Prepared with a His-Tag-Anchored Epitope as the Template. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 4617–4620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Yang, K.; Deng, N.; Min, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y. Thermoresponsive Epitope Surface-Imprinted Nanoparticles for Specific Capture and Release of Target Protein from Human Plasma. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 5747–5751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Yang, K.; Zhao, B.; Li, X.; Liu, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y. Epitope imprinting enhanced IMAC (EI-IMAC) for highly selective purification of His-tagged protein. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 1960–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Li, M.; Tong, P.; Zhao, C.; Li, J.; Xu, G. A strategy for construction of highly sensitive glycosyl imprinted electrochemical sensor based on sandwich-like multiple signal enhancement and determination of neural cell adhesion molecule. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 156, 112150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ma, X.; Li, M.; Zhang, Y. Does polysaccharide is an idea template selection for glycosyl imprinting? Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 99, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| MIP | Target | Kd |
|---|---|---|
| Hierarchical MIP (VHLTP template) | VHLTP | 64.6 ± 12.9 nM [50] |
| HbA | 9.06 ± 0.8 nM | |
| Random-MIP (VHLTP template) | VHLTP | 1.4 ± 0.3 μM [50] |
| HbA | 20.4 ± 0.3 nM |
| Sample | Thickness (nm) |
|---|---|
| After electropolymerization | 9.3 ± 0.8 |
| After anodic polarization | 9.6 ± 0.1 |
| After adsorption of 1 μM HbA | 11.1 ± 0.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Caserta, G.; Yarman, A.; Supala, E.; Waffo, A.F.T.; Wollenberger, U.; Gyurcsányi, R.E.; Zebger, I.; Scheller, F.W. “Out of Pocket” Protein Binding—A Dilemma of Epitope Imprinted Polymers Revealed for Human Hemoglobin. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9060128
Zhang X, Caserta G, Yarman A, Supala E, Waffo AFT, Wollenberger U, Gyurcsányi RE, Zebger I, Scheller FW. “Out of Pocket” Protein Binding—A Dilemma of Epitope Imprinted Polymers Revealed for Human Hemoglobin. Chemosensors. 2021; 9(6):128. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9060128
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiaorong, Giorgio Caserta, Aysu Yarman, Eszter Supala, Armel F. Tadjoung Waffo, Ulla Wollenberger, Róbert E. Gyurcsányi, Ingo Zebger, and Frieder W. Scheller. 2021. "“Out of Pocket” Protein Binding—A Dilemma of Epitope Imprinted Polymers Revealed for Human Hemoglobin" Chemosensors 9, no. 6: 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9060128
APA StyleZhang, X., Caserta, G., Yarman, A., Supala, E., Waffo, A. F. T., Wollenberger, U., Gyurcsányi, R. E., Zebger, I., & Scheller, F. W. (2021). “Out of Pocket” Protein Binding—A Dilemma of Epitope Imprinted Polymers Revealed for Human Hemoglobin. Chemosensors, 9(6), 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9060128









