Development of Gold Nanoparticles Decorated Molecularly Imprinted–Based Plasmonic Sensor for the Detection of Aflatoxin M1 in Milk Samples
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Apparatus
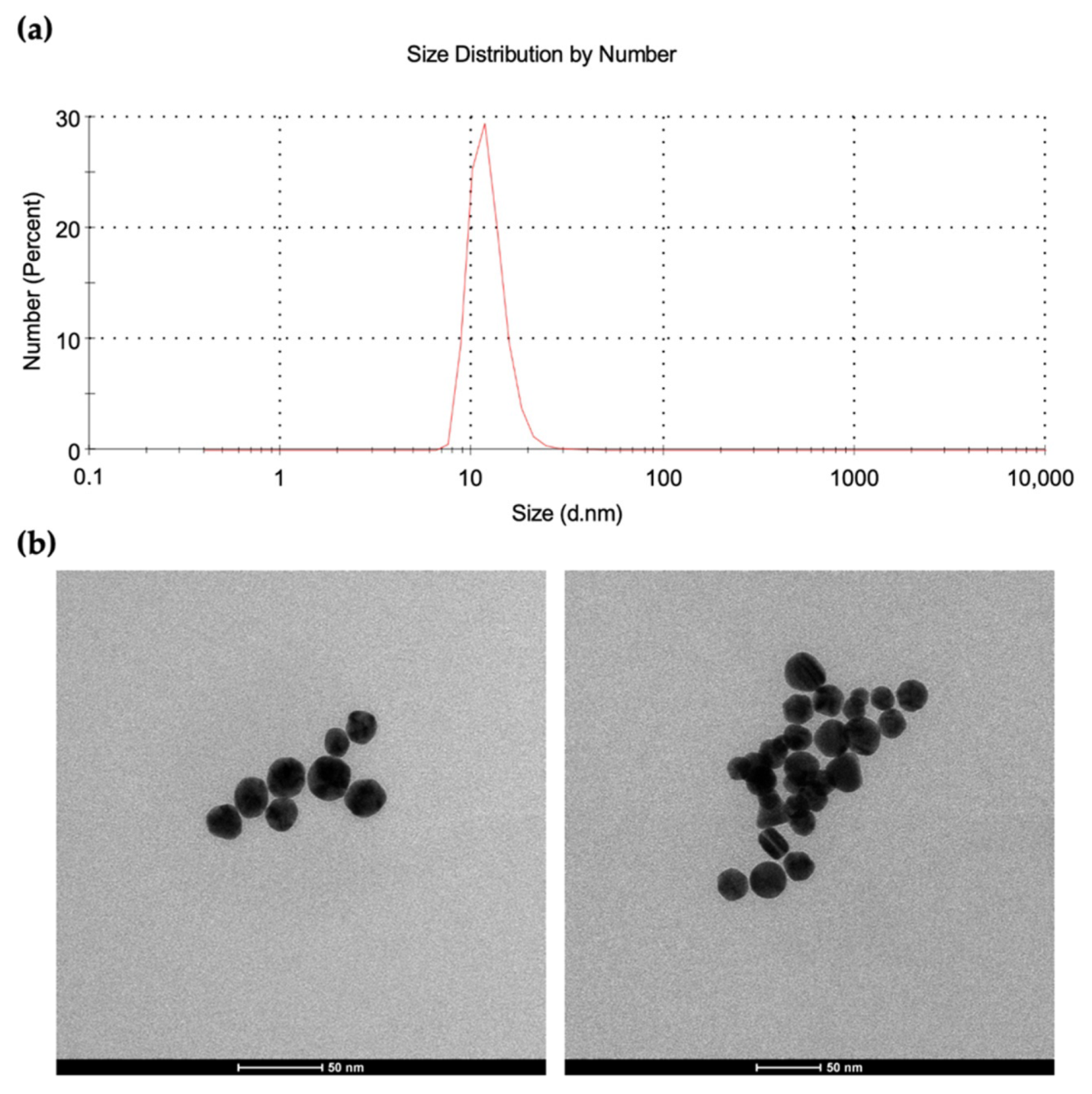
2.2. Preparation of Gold Nanoparticles
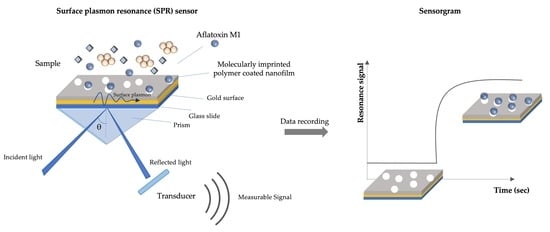
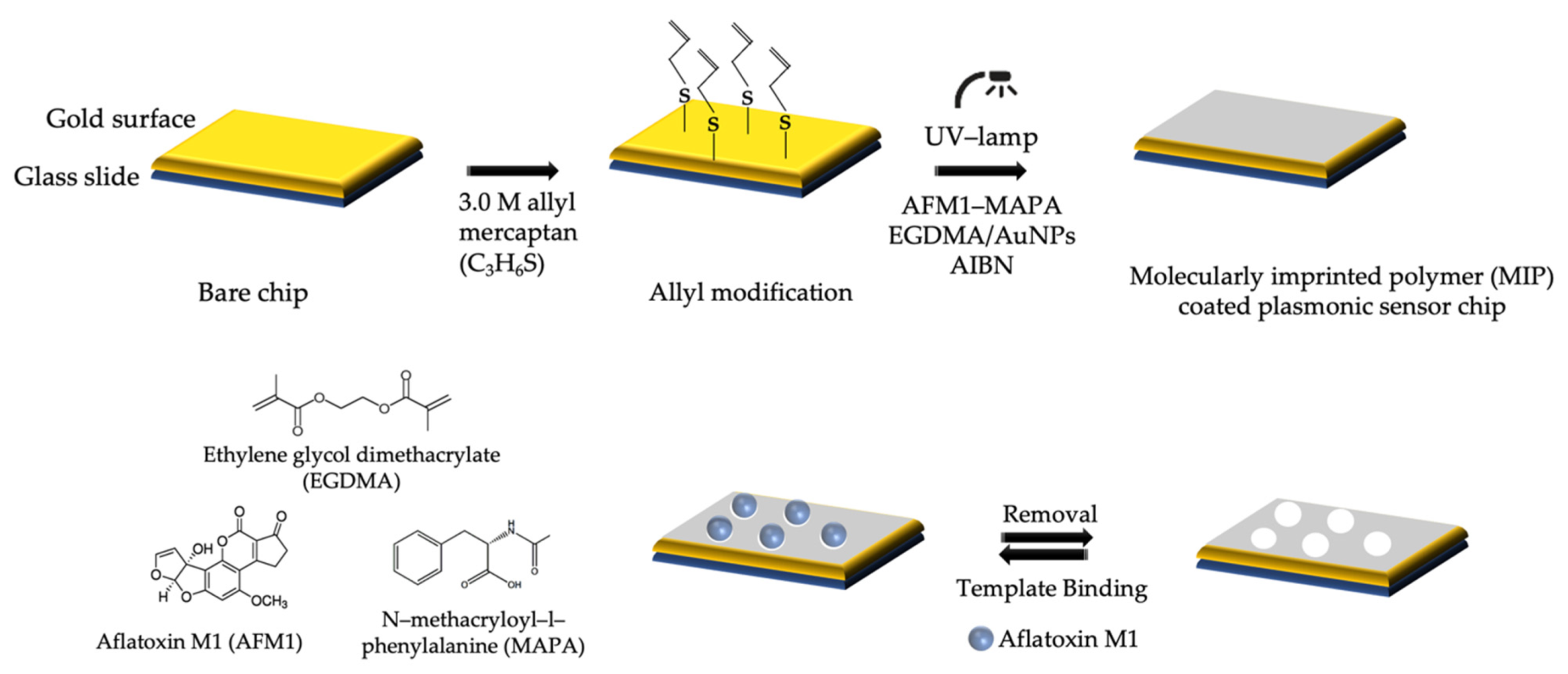
2.3. Development of Molecularly Imprinted–Based Plasmonic Sensor
2.3.1. SPR Sensor Chip Modification
2.3.2. The Removal of Template Molecule
2.3.3. Characterization of SPR Sensor
2.4. Detection of AFM1
2.5. Selectivity, Reusability, and Stability Studies
2.6. Detection of AFM1 in Milk Samples
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of AuNPs
3.2. Characterization Results of SPR Sensor Chips
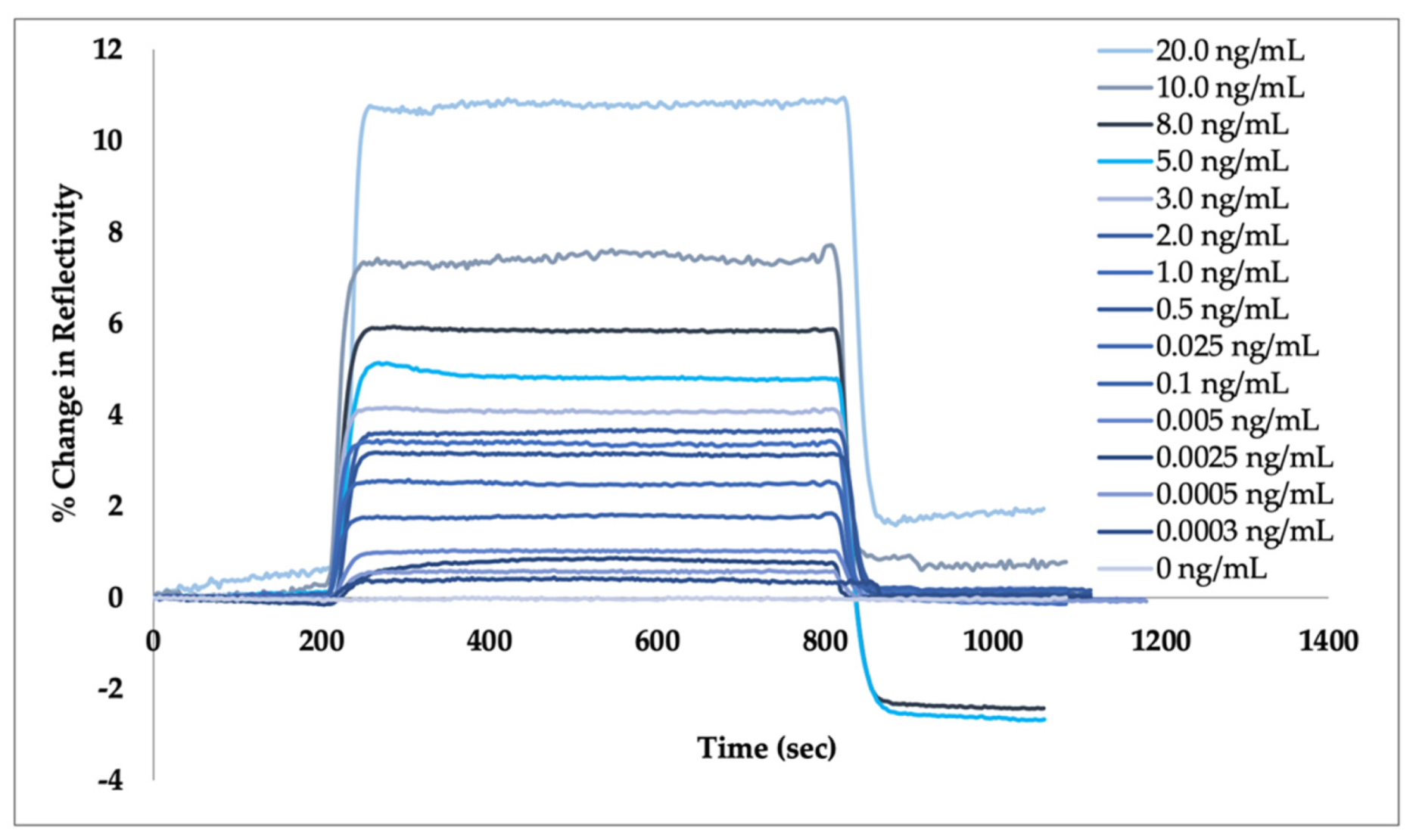
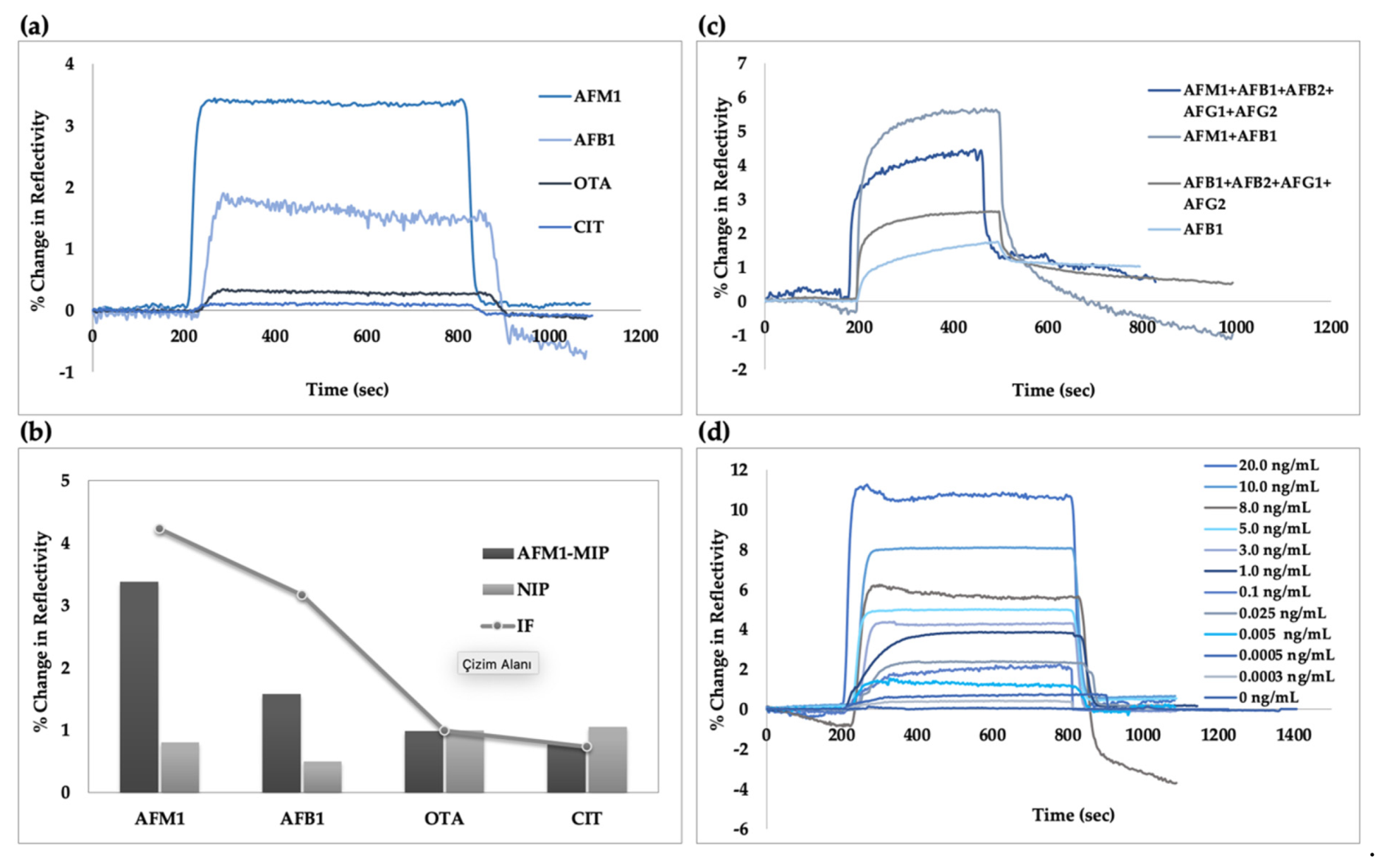
3.3. Plasmonic Sensor for Aflatoxin M1 Detection
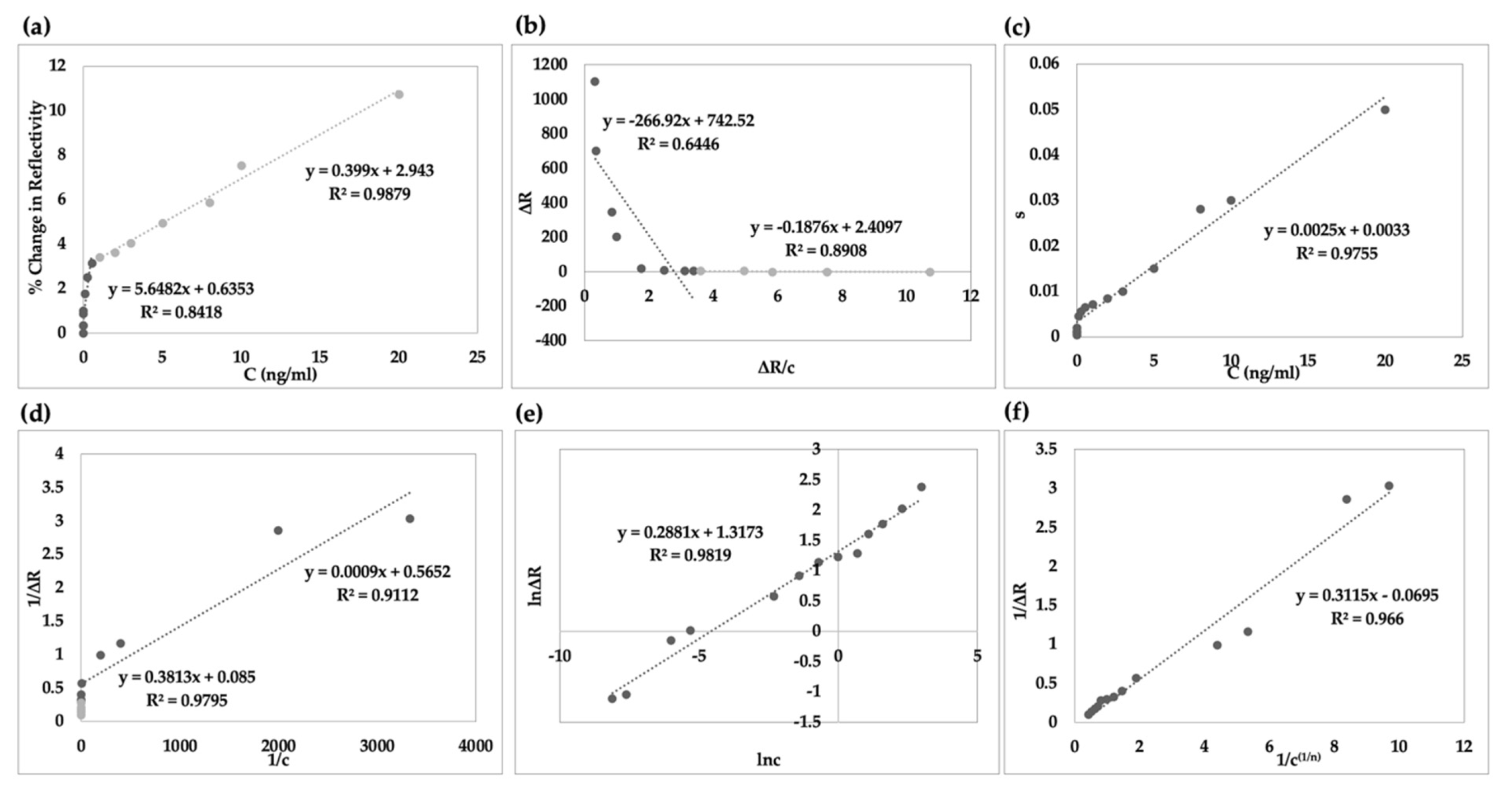
3.4. Kinetic Analysis and Adsorption Isotherm
3.5. Selectivity
3.6. Milk Sample
3.7. Reusability and Stability
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ketney, O.; Santini, A.; Oancea, S. Recent Aflatoxin Survey Data in Milk and Milk Products: A Review. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2017, 70, 320–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abera, B.D.; Falco, A.; Ibba, P.; Cantarella, G.; Petti, L.; Lugli, P. Development of Flexible Dispense−Printed Electrochemical Immunosensor for Aflatoxin M1 Detection in Milk. Sensors 2019, 19, 3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beitollahi, H.; Tajik, S.; Dourandish, Z.; Zhang, K.; Van Le, Q.; Jang, H.W.; Kim, S.Y.; Shokouhimehr, M. Recent Advances in the Aptamer–Based Electrochemical Biosensors for Detecting Aflatoxin B1 and Its Pertinent Metabolite Aflatoxin M1. Sensors 2020, 20, 3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskola, M.; Kos, G.; Elliott, C.T.; Hajšlová, J.; Mayar, S.; Eskola, M.; Kos, G.; Elliott, C.T.; Hajšlová, J.; Mayar, S.; et al. Worldwide Contamination of Food-Crops with Mycotoxins: Validity of the Widely Cited ‘ FAO Estimate ’ of 25%. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 2773–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danesh, N.M.; Bostan, H.B.; Abnous, K.; Ramezani, M.; Youssefi, K.; Taghdisi, S.M.; Karimi, G. Ultrasensitive Detection of Aflatoxin B1 and Its Major Metabolite Aflatoxin M1 Using Aptasensors: A Review. Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 99, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karapetis, S.; Nikolelis, D.; Hianik, T. Label-Free and Redox Markers−Based Electrochemical Aptasensors for Aflatoxin M1 Detection. Sensors 2018, 18, 4218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ong, J.Y.; Pike, A.; Tan, L.L. Recent Advances in Conventional Methods and Electrochemical Aptasensors for Mycotoxin Detection. Foods 2021, 10, 1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchese, S.; Polo, A.; Ariano, A.; Velotto, S.; Costantini, S.; Severino, L. Aflatoxin B1 and M1: Biological Properties and Their Involvement in Cancer Development. Toxins 2018, 10, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nidhina, N.; Bhavya, M.L.; Bhaskar, N.; Muthukumar, S.P.; Murthy, P.S. Aflatoxin Production by Aspergillus Flavus in Rumen Liquor and Its Implications. Food Control 2017, 71, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovanni, S.D.; Zambrini, V.; Varriale, A.; Auria, S.D. Sweet Sensor for the Detection of Aflatoxin M1 in Whole Milk. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 12803–12807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaz, A.; Silva, A.C.C.; Rodrigues, P.; Venâncio, A. Detection Methods for Aflatoxin M1 in Dairy Products. Microorganisms 2020, 1, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiong, J.; Xiong, L.; Zhou, H.; Liu, Y.; Wu, L. Occurrence of Aflatoxin B1 in Dairy Cow Feedstuff and Aflatoxin M1 in UHT and Pasteurized Milk in Central China. Food Control 2018, 92, 386–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, X.; Pan, M.; Hu, N.; Wang, J.; Wang, S. Quartz Crystal Microbalance Sensor Based on Covalent Organic Framework Composite and Molecularly Imprinted Polymer of Poly(o-Aminothiophenol) with Gold Nanoparticles for the Determination of Aflatoxin B1. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 291, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Wang, Y.M.; Nennich, Y.L.; Liu, J. Transfer of Dietary Aflatoxin B1 to Milk Aflatoxin M1 and Effect of Inclusion of Adsorbent in the Diet of Dairy Cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 2545–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC. Some Naturally Occurring Substances: Food Items and Constituents, Heterocyclic Aromatic Amines and Mycotoxins. In IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; IARC: Lyon, France, 1993; Volume 56. [Google Scholar]
- IARC. Some Traditional Herbal Medicines, Some Mycotoxins, Naphthalene and Styrene. In IARC Monograph on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risk to Humans; IARC: Lyon, France, 2002; Volume 82. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. CPG Sec 527.400 Whole Milk, Lowfat Milk, Skim Milk−AGatoxin M1. FDA Compliance Policy Guides; FDA: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Gurban, A.M.; Epure, P.; Oancea, F.; Doni, M. Achievements and Prospects in Electrochemical−Based Biosensing Platforms for Aflatoxin M1 Detection in Milk and Dairy Products. Sensors 2017, 17, 2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bervis, N.; Lor, S.; Juan, T.; Carraminana, J.J.; Herrera, A.; Arina, A.; Herrera, M. Field Monitoring of Aflatoxins in Feed and Milk of High-Yielding Dairy Cows under Two Feeding Systems. Toxins 2021, 13, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodadadi, M.; Malekpour, A.; Mehrgardi, M.A. Aptamer Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles for Effective Extraction of Ultratrace Amounts of Aflatoxin M1 Prior Its Determination by HPLC. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1564, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shundo, L.; Sabino, M. Aflatoxin M1 in Milk by Immunoaffinity Column Cleanup with TLC/HPLC Determination. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2006, 37, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodríguez−Carrasco, Y.; Izzo, L.; Gaspari, A.; Graziani, G.; Mañes, J.; Ritieni, A. Simultaneous Determination of AFB1 and AFM1 in Milk Samples by Ultra High Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Quadrupole Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry. Beverages 2018, 4, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vdovenko, M.M.; Lu, C.C.; Yu, F.Y.; Sakharov, I.Y. Development of Ultrasensitive Direct Chemiluminescent Enzyme Immunoassay for Determination of Aflatoxin M1 in Milk. Food Chem. 2014, 158, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radoi, A.; Targa, M.; Prieto-Simon, B.; Marty, J. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) Based on Superparamagnetic Nanoparticles for Aflatoxin M1 Detection. Talanta 2008, 77, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istamboulié, G.; Paniel, N.; Zara, L.; Reguillo Granados, L.; Barthelmebs, L.; Noguer, T. Development of an Impedimetric Aptasensor for the Determination of Aflaatoxin M1 in Milk. Talanta 2016, 146, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, S.; Kumari, V.; Sharma, V.; Ahmad, F. Gold Nanoparticle-Based Sensors in Food Safety Applications. Food Anal. Methods 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezani, M.; Esmaelpourfarkhani, M.; Taghdisi, S.M.; Abnous, K.; Alibolandi, M. Application of nanosensors for food safety. In Nanosensors for Smart Cities; Han, B., Nguyen, T.A., Singh, P.K., Tomer, V.K., Farmani, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 369–386. ISBN 9780128198704. [Google Scholar]
- Homola, J. Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensors for Detection of Chemical and Biological Species. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 462–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dostálek, J.; Knoll, W. Long Range Surface Plasmon-Enhanced Fluorescence Spectroscopy for the Detection of Aflatoxin M1 in Milk. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 2264–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szunerits, S.; Spadavecchia, J.; Boukherroub, R. Surface Plasmon Resonance: Signal Amplification Using Colloidal Gold Nanoparticles for Enhanced Sensitivity. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2014, 33, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, X.; Hall, E.A.H. Contribution of Gold Nanoparticles to the Signal Amplification in Surface Plasmon Resonance. Analyst 2012, 137, 4712–4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, J.; Akamatsu, K.; Hara, N.; Miyoshi, D.; Nawafune, H.; Tamaki, K.; Sugimoto, N. SPR Sensor Chip for Detection of Small Molecules Using Molecularly Imprinted Polymer with Embedded Gold Nanoparticles. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 4282–4285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostafiz, B.; Arjomand, S.; Banan, K.; Afsharara, H.; Hatamabadi, D.; Mousavi, P.; Mustansar, C.; Keçili, R.; Ghorbani-Bidkorbeh, F. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Carbon Paste Electrode (MIP−CPE)-Based Sensors for the Sensitive Detection of Organic and Inorganic Environmental Pollutants: A Review. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 32, e00144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Yuan, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y. Novel Molecularly Imprinted Polymer (MIP) Multiple Sensors for Endogenous Redox Couples Determination and Their Applications in Lung Cancer Diagnosis. Talanta 2019, 199, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseri, M.; Mohammadniaei, M.; Sun, Y.; Ashley, J. The Use of Aptamers and Molecularly Imprinted Polymers in Biosensors for Environmental Monitoring: A Tale of Two Receptors. Chemosensors 2020, 8, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhoundian, M.; Rüter, A.; Shinde, S. Ultratrace Detection of Histamine Using a Molecularly-Imprinted Polymer-Based Voltammetric Sensor. Sensors 2017, 17, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holthoff, E.L.; Stratis-cullum, D.N.; Hankus, M.E. A Nanosensor for TNT Detection Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymers and Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering. Sensors 2011, 11, 2700–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paruli, E.I.I.I.; Soppera, O.; Haupt, K.; Gonzato, C. Photopolymerization and Photostructuring of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 4769–4790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akgönüllü, S.; Bakhshpour, M.; Denizli, A. Molecularly imprinted bionanomaterials and their biomedical applications. In Bionanomaterials Fundamentals and Biomedical Applications; Singh, R.P., Singh, K.R., Eds.; IOP Science: London, UK, 2021; pp. 9–27. ISBN 9780750337670. [Google Scholar]
- Battal, D.; Akgönüllü, S.; Yalcin, M.S.; Yavuz, H.; Denizli, A. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Based Quartz Crystal Microbalance Sensor System for Sensitive and Label-Free Detection of Synthetic Cannabinoids in Urine. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 111, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akgönüllü, S.; Battal, D.; Yalcin, M.S.; Yavuz, H.; Denizli, A. Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Synthetic Cannabinoids JWH-018, JWH-073 and Their Metabolites Using Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Coated QCM Nanosensor in Artificial Saliva. Microchem. J. 2020, 153, 104454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saylan, Y.; Akgönüllü, S.; Yavuz, H.; Ünal, S.; Denizli, A. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Based Sensors for Medical Applications. Sensors 2019, 19, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin-Esteban, A. Recent Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Sample Preparation Techniques in Environmental Analysis. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2016, 9, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türkmen, D.; Özkaya Türkmen, M..; Akgönüllü, S.; Denizli, A. Development of Ion Imprinted Based Magnetic Nanoparticles for Selective Removal of Arsenic (III) and Arsenic (V) from Wastewater. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2021, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caserta, G.; Zhang, X.; Yarman, A.; Supala, E.; Wollenberger, U.; Gyurcsányi, R.E.; Zebger, I.; Scheller, F.W. Insights in Electrosynthesis, Target Binding, and Stability of Peptide-Imprinted Polymer Nanofilms. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 381, 138236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saylan, Y.; Denizli, A. Molecular Fingerprints of Hemoglobin on a Nanofilm Chip. Sensors 2018, 18, 3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, C.H.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, S.F.; Fang, Z.B.; Yang, H.H.; Chen, X.; Chen, G.N. Sensing HIV Related Protein Using Epitope Imprinted Hydrophilic Polymer Coated Quartz Crystal Microbalance. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 31, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, X.; Yamauchi, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Shiigi, H.; Nagaoka, T. A Rapid and Specific Bacterial Detection Method Based on Cell-Imprinted Microplates. Analyst 2018, 143, 1505–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Detections, S.; Capoferri, D.; Ruslan, A.-D.; Del Carlo, M.; Compagnone, D.; Merkoci, A. Electrochromic Molecular Imprinting Sensor for Visual and Smartphone-Based Detections. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 5850–5856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Appell, M.; Mueller, A. Mycotoxin Analysis Using Imprinted Materials Technology: Recent Developments. J. AOAC Int. 2016, 99, 861–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonsriwong, W.; Chunta, S.; Thepsimanon, N.; Singsanan, S.; Lieberzeit, P.A. Thin Film Plastic Antibody-Based Microplate Assay for Human Serum Albumin Determination. Polymers 2021, 13, 1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surapong, N.; Burakham, R. Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymer for the Selective Enrichment of Glyphosate, Glufosinate, and Aminomethylphosphonic Acid Prior to High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 27007–27016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akgönüllü, S.; Yavuz, H.; Denizli, A. SPR Nanosensor Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Film with Gold Nanoparticles for Sensitive Detection of Aflatoxin B1. Talanta 2020, 219, 121219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enustun, B.V.; Turkevich, J. Coagulation of Colloidal Gold. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1963, 85, 3317–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodbodak, S.; Hesari, J.; Peighambardoust, S.H.; Mahkam, M. Selective Decontamination of Aflatoxin M1 in Milk by Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Coated on the Surface of Stainless Steel Plate. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2018, 71, 868–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horemans, F.; Alenus, J.; Bongaers, E.; Weustenraed, A.; Thoelen, R.; Duchateau, J.; Lutsen, L.; Vanderzande, D.; Wagner, P.; Cleij, T.J. MIP−Based Sensor Platforms for the Detection of Histamine in the Nano- and Micromolar Range in Aqueous Media. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 148, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yang, D.; Li, P.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Ding, X.; Mao, J.; Wu, J. Palladium Nanoparticles-Based Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer Aptasensor for Highly Sensitive Detection of Aflatoxin M1 in Milk. Toxins 2017, 9, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, N.; Sun, P.; Wang, J.Q.; Zhen, Y.P.; Han, R.W.; Xu, X.M. Occurrence of Aflatoxin M1 in UHT Milk and Pasteurized Milk in China Market. Food Control 2013, 29, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, B.; Xu, S.; Huang, Y.; Su, F.; Huang, Z.; Fang, H.; Peng, J. Gold Nanorods Etching-Based Plasmonic Immunoassay for Qualitative and Quantitative Detection of Aflatoxin M1 in Milk. Food Chem. 2020, 329, 127160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasoju, A.; Shahdeo, D.; Khan, A.A.; Shrikrishna, N.S. Fabrication of Microfluidic Device for Aflatoxin M1 Detection in Milk Samples with Specific Aptamers. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jalalian, S.H.; Ramezani, M.; Danesh, N.M.; Alibolandi, M.; Abnous, K.; Taghdisi, S.M. A Novel Electrochemical Aptasensor for Detection of Aflatoxin M1 Based on Target-Induced Immobilization of Gold Nanoparticles on the Surface of Electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 117, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacher, G.; Pal, S.; Kanungo, L.; Bhand, S. A Label-Free Silver Wire Based Impedimetric Immunosensor for Detection of Aflatoxin M1 in Milk. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 168, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Catanante, G.; Hayat, A.; Istamboulie, G.; Ben, I.; Bhand, S.; Marty, J.L.; Louis, J. Development of Structure Switching Aptamer Assay for Detection of Aflatoxin M1 in Milk Sample. Talanta 2016, 158, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karczmarczyk, A.; Dubiak-Szepietowska, M.; Vorobii, M.; Rodriguez-Emmenegger, C.; Dostálek, J.; Feller, K.H. Sensitive and Rapid Detection of Aflatoxin M1 in Milk Utilizing Enhanced SPR and p(HEMA) Brushes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 81, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emir Diltemiz, S.; Ecevit, K. High-Performance Formaldehyde Adsorption on CuO/ZnO Composite Nanofiber Coated QCM Sensors. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 783, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayyun, T.S.; Mseer, A.H. Comparison of the Experimental Results with the Langmuir and Freundlich Models for Copper Removal on Limestone Adsorbent. Appl. Water Sci. 2019, 9, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Langmuir, I. The Adsorption of Gases on Plane Surfaces of Glass, Mica and Platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stromer, B.S.; Woodbury, B.; Williams, C.F. Tylosin Sorption to Diatomaceous Earth Described by Langmuir Isotherm and Freundlich Isotherm Models. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 912–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latour, R.A. The Langmuir Isotherm: A Commonly Applied but Misleading Approach for the Analysis of Protein Adsorption Behavior. J. Biomed. Mater. Res.-Part A 2014, 103, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Sensor Type | Method | Linear Range | LOD | Sample | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmonic | Gold-nanorod-etching-based plasmonic immunoassay | 0.25–10 ng/mL | 0.11 ng/mL | Milk (supermarket) | [59] |
| Colorimetric | Microfluidic paper-based analytical device | 328.27 ng/mL–0.33 pg/mL | 0.98 pg/mL–3.28 pg/mL | Standard buffer and spiked buffalo milk | [60] |
| Electrochemical | Target-induced immobilization of AuNP-based electrochemical aptasensor | 0.002–0.6 ng/mL | 0.9 pg/mL | Milk and serum sample | [61] |
| Impedimetric | Label-free silver-wire-based impedimetric immunosensor | 0.25–100 pg/mL | 1.0 pg/mL | Milk | [62] |
| Fluorescence | Switching aptasensing platform | 0.001–2 ng/mL | 0.005 ng/mL | Milk (local market) | [63] |
| Plasmonic | Poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) p(HEMA) brush | 0.1–1000 ng/mL | 18.0 pg/mL | Milk | [64] |
| Plasmonic (SPR sensor) | Molecularly imprinted polymer nanofilm with embedded gold nanoparticles | 0.0003–20 ng/mL | 0.4 pg/mL | Buffer solution and spiked raw milk | This work |
| Association Binding Kinetic | Equilibrium Analysis (Scatchard) | Langmuir | Freundlich | Langmuir–Freundlich | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ka (ng.mL−1)−1.s−1 | 0.0025 | ΔRmax | 13.64 | ΔRmax | 12.5 | ΔRmax | 3.42 | ΔRmax | 16.66 |
| kd (s−1) | 0.0033 | KA (ng.mL−1)−1 | 0.14 | KD (ng.mL−1) | 4.75 | n | 1.28 | 1/n | 0.28 |
| KA (ng.mL−1)−1 | 0.75 | KD ng.mL−1 | 1.91 | KA (ng.mL−1)−1 | 0.38 | R2 | 0.9819 | KD (ng.mL−1) | 5.16 |
| KD ng.mL−1 | 1.32 | R2 | 0.8908 | R2 | 0.9795 | KA (ng.mL−1)−1 | 0.19 | ||
| R2 | 0.9755 | R2 | 0.9819 | ||||||
| Mycotoxin | MIP | NIP | IF (MIP/NIP) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔR | k | ΔR | k | k’ | ||
| AFM1 | 3.38 | – | 0.8 | – | – | 4.22 |
| AFB1 | 1.62 | 1.87 | 0.5 | 1.6 | 1.33 | 3.16 |
| OTA | 0.98 | 3.44 | 0.99 | 0.80 | 4.26 | 0.98 |
| CIT | 0.77 | 4.38 | 1.05 | 0.76 | 5.76 | 0.73 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akgönüllü, S.; Yavuz, H.; Denizli, A. Development of Gold Nanoparticles Decorated Molecularly Imprinted–Based Plasmonic Sensor for the Detection of Aflatoxin M1 in Milk Samples. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 363. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9120363
Akgönüllü S, Yavuz H, Denizli A. Development of Gold Nanoparticles Decorated Molecularly Imprinted–Based Plasmonic Sensor for the Detection of Aflatoxin M1 in Milk Samples. Chemosensors. 2021; 9(12):363. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9120363
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkgönüllü, Semra, Handan Yavuz, and Adil Denizli. 2021. "Development of Gold Nanoparticles Decorated Molecularly Imprinted–Based Plasmonic Sensor for the Detection of Aflatoxin M1 in Milk Samples" Chemosensors 9, no. 12: 363. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9120363
APA StyleAkgönüllü, S., Yavuz, H., & Denizli, A. (2021). Development of Gold Nanoparticles Decorated Molecularly Imprinted–Based Plasmonic Sensor for the Detection of Aflatoxin M1 in Milk Samples. Chemosensors, 9(12), 363. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9120363